Analysis of Spatiotemporal Interaction Characteristics and Decoupling Effects of Urban Expansion in the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
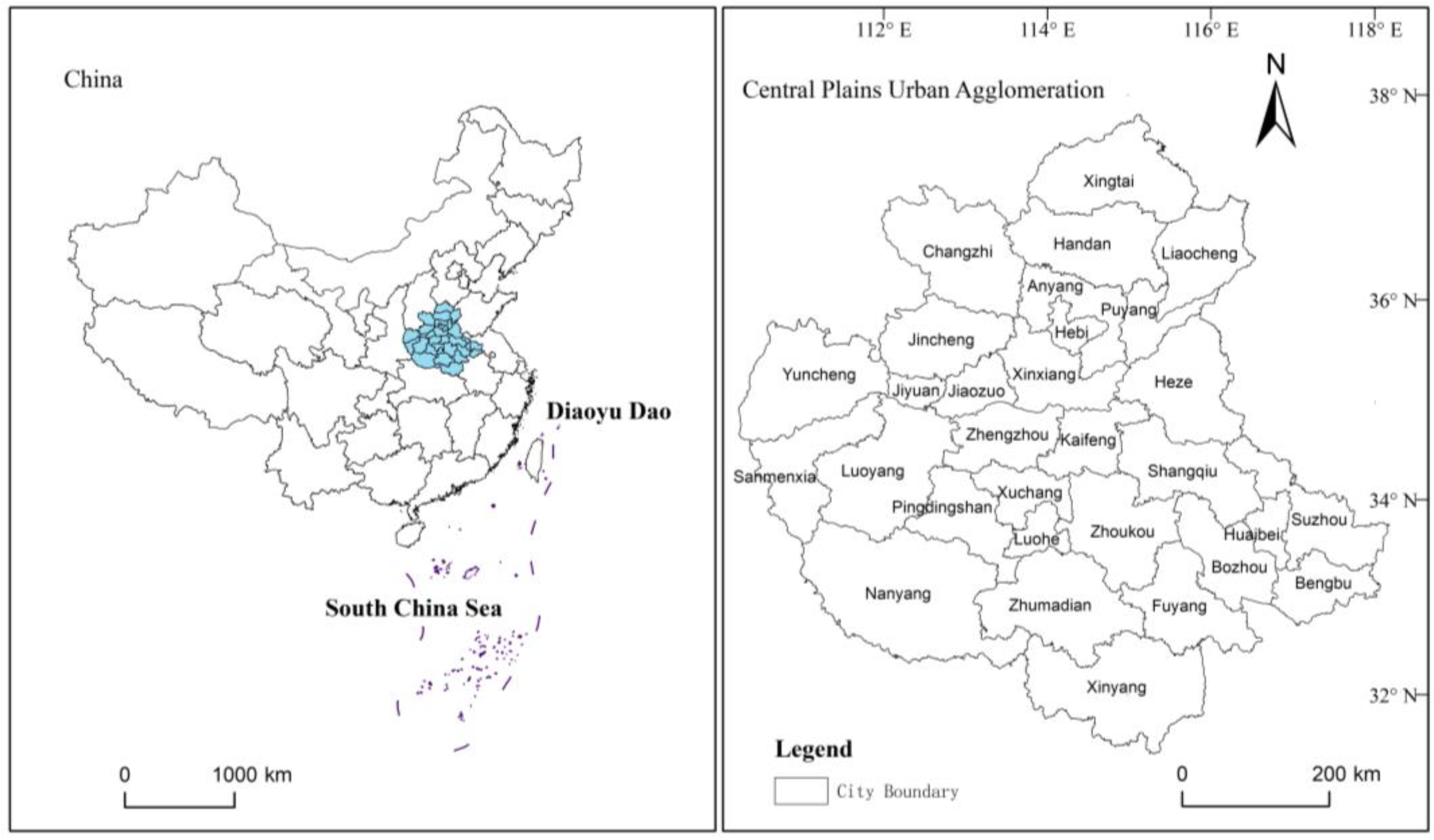
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Expansion Intensity Index
2.3.2. Exploratory Spatiotemporal Data Analysis
2.3.3. Standard Deviation Ellipse
2.3.4. Decoupling Model
3. Results
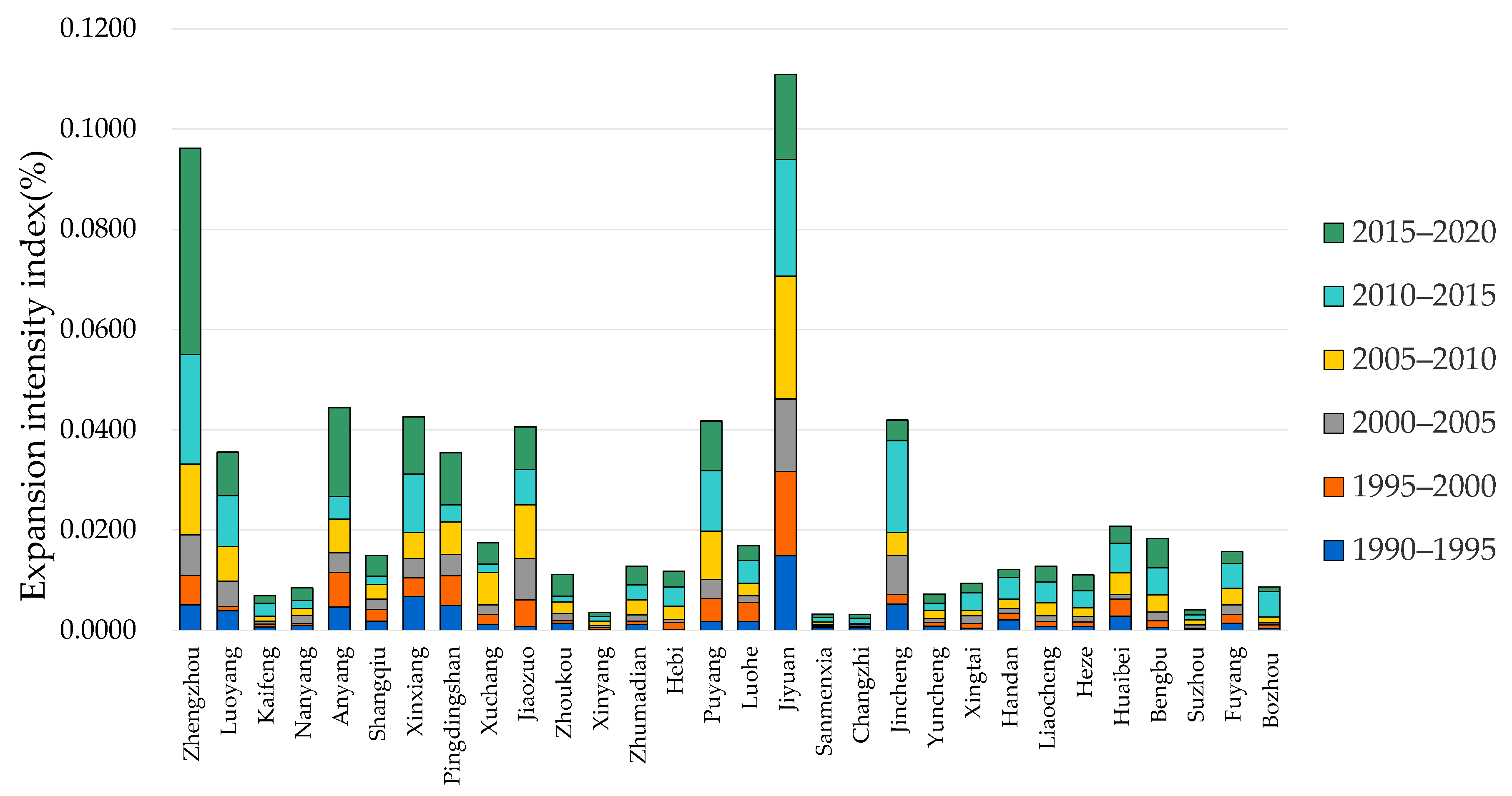
3.1. Analysis of Urbanization Scale Change Characteristics
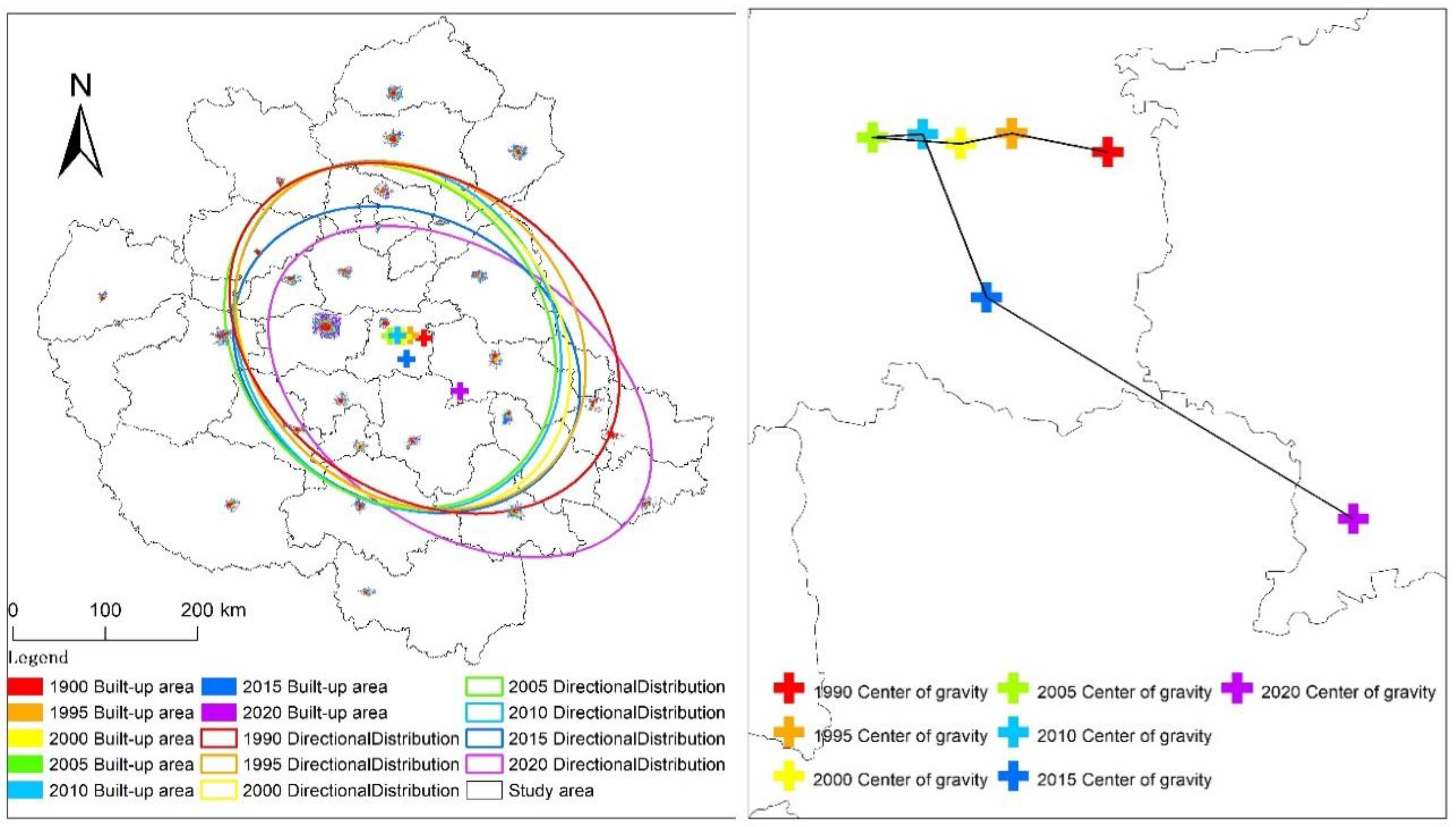
3.2. Analysis on the Evolution Characteristics of Urbanization Direction
3.3. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Interaction Characteristics of Urbanization
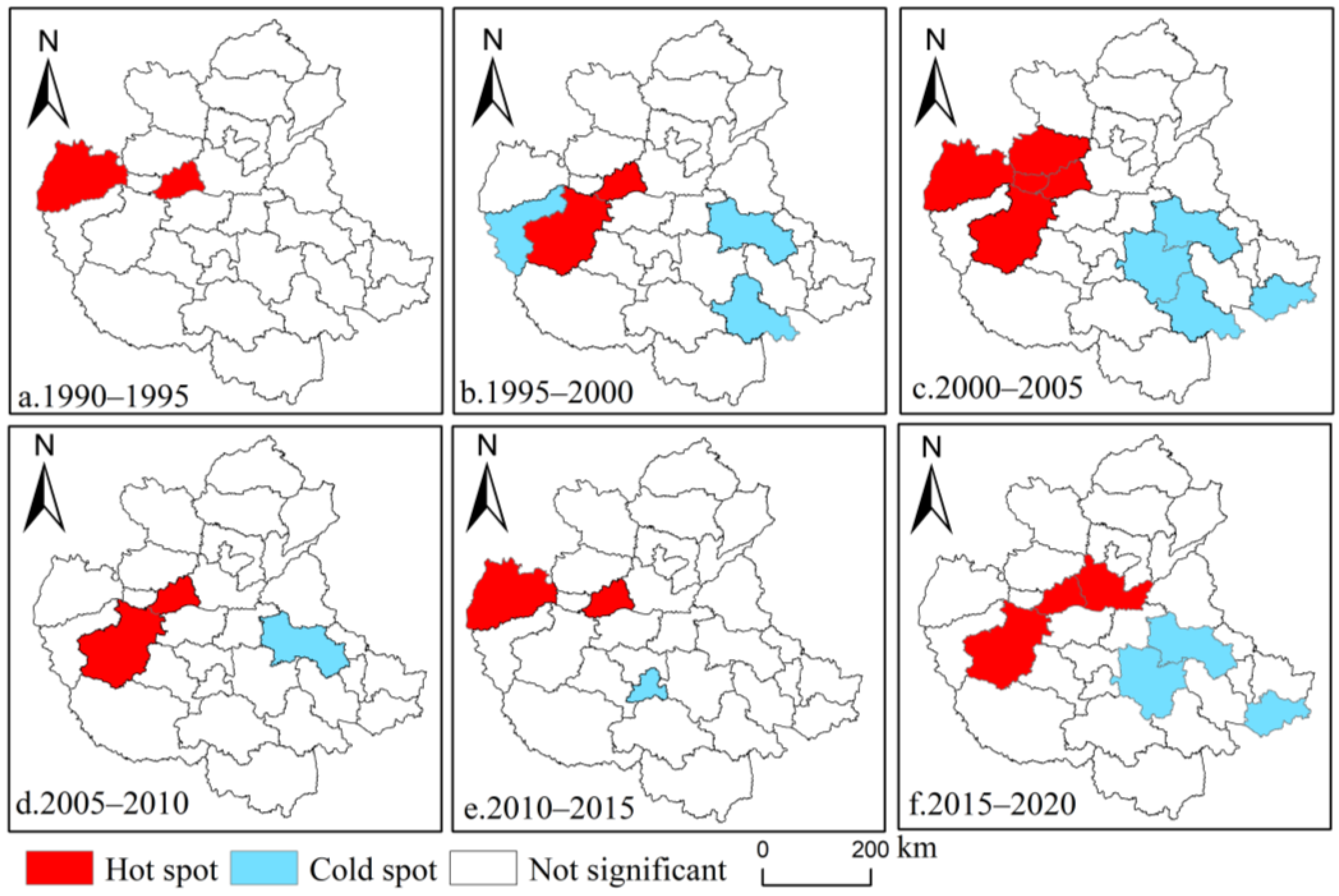
3.3.1. Analysis of Spatial Agglomeration Characteristics
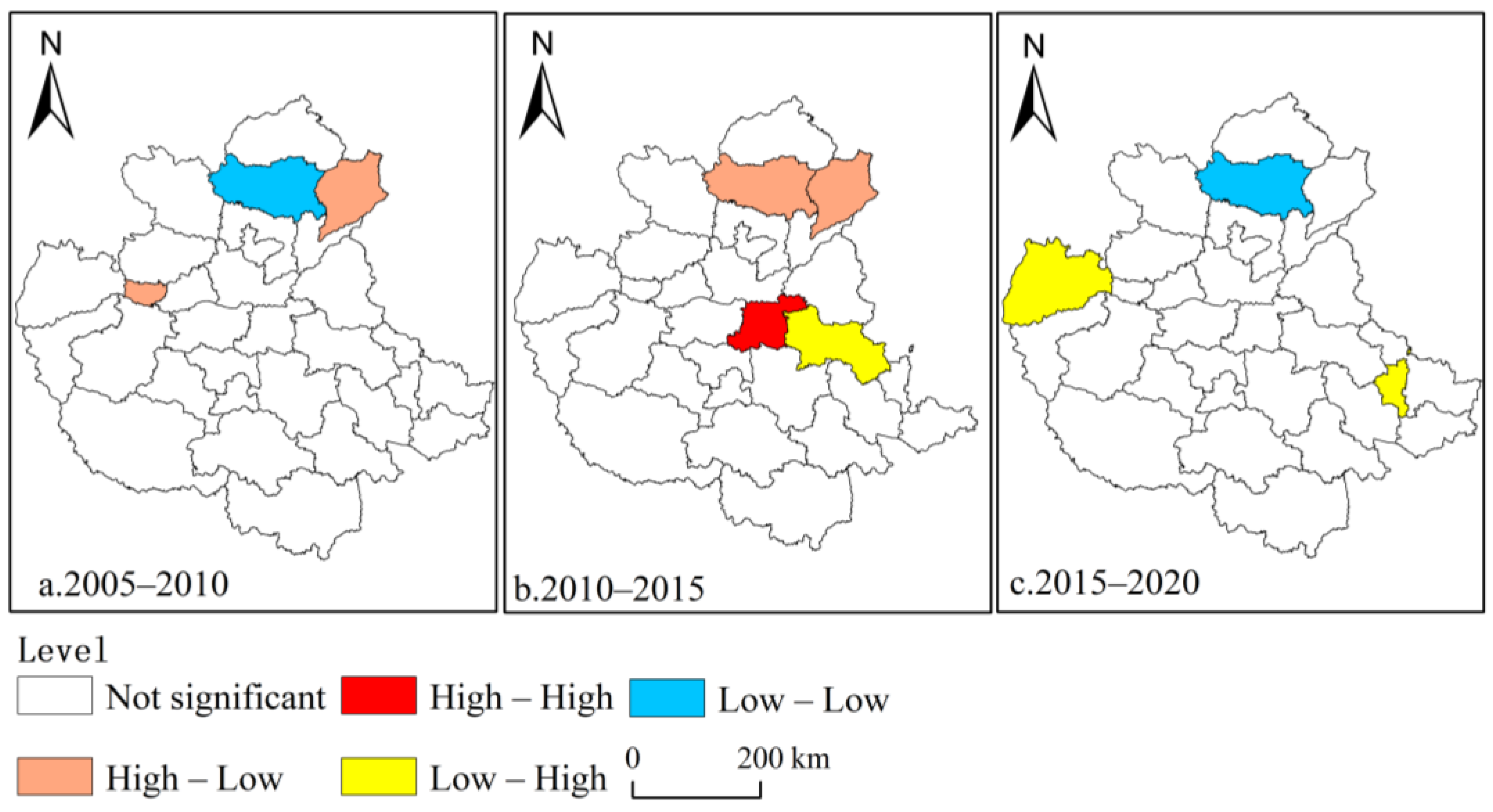
3.3.2. Spatiotemporal Interaction Feature Analysis
3.4. Analysis of the Correlation between Urban Spatial Expansion and Economic Development
3.4.1. Analysis of the Correlation between Urban Expansion and Peripheral Economic Development
3.4.2. Analysis of Decoupling between Urban Expansion and Its Own Economic Development
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saliminezhad, A.; Bahramian, P. The causal relationship between urbanization and economic growth in US: Fresh evidence from the Toda–Yamamoto approach. J. Contemp. Urban Aff. 2019, 3, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- UN-Habitat, United Nations Human Settlements Programme. World Cities Report 2020: The Value of Sustainable Urbanization; UN Habitat: Nairobi, Kenya, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Sun, S.; Fang, C. The varying driving forces of urban expansion in China: Insights from a spatial-temporal analysis. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 174, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhou, K.; Yang, S. Land use efficiency and influencing factors of urban agglomerations in China. Land Use Policy 2019, 88, 104143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, B.; Dong, Q. The Limit of Urban Land Expansion Based on Population Growth and Economic Development: A Case Study of Shandong Province in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louafi, O. The phenomenon of mobility, a development challenge for the city of Algiers. J. Contemp. Urban Aff. 2019, 3, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akande, O.K. Urbanization, housing quality and health: Towards a redirection for housing provision in Nigeria. J. Contemp. Urban Aff. 2021, 5, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Du, G. Quantifying spatio-temporal patterns of urban expansion in Beijing during 1985–2013 with rural-urban development transformation. Land Use Policy 2018, 74, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, C.; Jiang, J. A comparative study of urban expansion in Beijing, Tianjin and Shijiazhuang over the past three decades. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 134, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L. Urban land density function: A new method to characterize urban expansion. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 139, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Liu, Y.; Fan, P. Measuring urban sprawl and its drivers in large Chinese cities: The case of Hangzhou. Land Use Policy 2013, 31, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, G.; Liu, D.; Yu, H.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, J. The interaction of population, industry and land in process of urbanization in China: A case study in Jilin Province. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Wei, Y.D.; Korinek, K. Modelling urban expansion in the transitional Greater Mekong Region. Urban Stud. 2018, 55, 1729–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Ge, B.; Li, Y. Impacts of state-led and bottom-up urbanization on land use change in the peri-urban areas of Shanghai: Planned growth or uncontrolled sprawl? Cities 2017, 60, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liang, X.; Leng, J.; Xu, X.; Liao, W.; Qiu, Y.A.; Wu, Q.; et al. Global projections of future urban land expansion under shared socioeconomic pathways. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Dang, X.; Sun, Q.; Wang, S. Multi-scenario simulation of urban land change in Shanghai by random forest and CA-Markov model. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 55, 102045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ma, L.; Li, X.; Ai, B.; Li, S.; He, Z. Simulating urban growth by integrating landscape expansion index (LEI) and cellular automata. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, S.; Ewing, R. A longitudinal study of changes in urban sprawl between 2000 and 2010 in the United States. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 128, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Güneralp, B.; Hutyra, L.R. Global forecasts of urban expansion to 2030 and direct impacts on biodiversity and carbon pools. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16083–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duvernoy, I.; Zambon, I.; Sateriano, A.; Salvati, L. Pictures from the other side of the fringe: Urban growth and peri-urban agriculture in a post-industrial city (Toulouse, France). J. Rural Stud. 2018, 57, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Huang, Q.; He, C.; Ma, Q. Dynamics of urbanization levels in China from 1992 to 2012: Perspective from DMSP/OLS nighttime light data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 721–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Li, F. Urban sprawl in China: Differences and socioeconomic drivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, P.; Ouyang, Z.; Nguyen, D.D.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; Park, H.; Chen, J. Urbanization, economic development, environmental and social changes in transitional economies: Vietnam after Doimoi. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 187, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xie, H. Interactive relationship among urban expansion, economic development, and population growth since the reform and opening up in China: An analysis based on a vector error correction model. Land 2019, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, G.; Yin, X.; Wu, G.; Gao, N. Rethinking the Contribution of Land Element to Urban Economic Growth: Evidence from 30 Provinces in China. Land 2022, 11, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Guo, R.; Yan, Y. Heterogeneous Effects of Urban Sprawl on Economic Development: Empirical Evidence from China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.D.; Li, H.; Yue, W. Urban land expansion and regional inequality in transitional China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 163, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.; Li, C.; Boe-Gibson, G. Economic growth and expansion of China’s urban land area: Evidence from administrative data and night lights, 1993–2012. Sustainability 2014, 6, 7850–7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Miao, C.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X. Spatiotemporal patterns of urban sprawl and its relationship with economic development in China during 1990–2010. Habitat Int. 2018, 79, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, B.; Liu, G.; Zhai, Q. Does the expansion of urban construction land promote regional economic growth in China? Evidence from 108 cities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, K.; Chen, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X. How Do Urban Land Expansion, Land Finance, and Economic Growth Interact? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, Z. Coupling and coordination level of the population, land, economy, ecology and society in the process of urbanization: Measurement and spatial differentiation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Fan, P.; Wei, Y.D.; Qi, J. Economic development, urban expansion, and sustainable development in Shanghai. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2014, 28, 783–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Qi, W.; Fu, B.; Wang, K. Geographical transformations of urban sprawl: Exploring the spatial heterogeneity across cities in China 1992–2015. Cities 2020, 105, 102415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, C.; Xiu, C.; Liu, D. A new approach to measurement of regional inequality in particular directions. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brueckner, J.K.; Mills, E.; Kremer, M. Urban sprawl: Lessons from urban economics [with comments]. Brook.-Whart. Pap. Urban Aff. 2001, 65–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Luan, W.; Zhang, Z.; Su, M. Relationship between urban construction land expansion and population/economic growth in Liaoning Province, China. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Sun, Z.; Guo, H.; Xing, Q.; Du, W.; Cai, G. A standardized dataset of built-up areas of China’s cities with populations over 300,000 for the period 1990–2015. Big Earth Data 2021, 6, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Sun, J.; Guo, H.; Jiang, H.; Gao, J.; Wang, J. A Dataset of Built-Up Areas of Chinese Cities in 2020; Science Data Bank; Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, S.; Lu, H. Quantitative influence of land-use changes and urban expansion intensity on landscape pattern in Qingdao, China: Implications for urban sustainability. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, W.; Yin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, L.; Yi, X. Spatial-temporal evolution characteristics and drivers of carbon emission intensity of resource-based cities in China. Resour. Effic. Environ. Impact Assess. 2023, 67, 16648714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakidis, P.C.; Journel, A.G. Geostatistical space–time models: A review. Math. Geol. 1999, 31, 651–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ord, J.K.; Getis, A. Local spatial autocorrelation statistics: Distributional issues and an application. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L.; Syabri, I.; Smirnov, O. Visualizing multivariate spatial correlation with dynamically linked windows. In Proceedings of the CSISS Workshop on New Tools for Spatial Data Analysis, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 10 May 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, A.T.; Liu, Y.; Rey, S.J.; Anselin, L. Exploring movement object patterns. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2012, 49, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefever, D.W. Measuring geographic concentration by means of the standard deviational ellipse. Am. J. Sociol. 1926, 32, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Chen, B.; Yu, L.; Xin, Q.; Gong, P.; Xu, B. How does urban expansion interact with cropland loss? A comparison of 14 Chinese cities from 1980 to 2015. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhou, L.; Sun, D.; Hu, F. Impacts of urban expansion on the loss and fragmentation of cropland in the major grain production areas of China. Land 2022, 11, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Pu, L.; Jiang, C.; Gong, G.; Tan, H.; Wang, X.; He, G. Unveiling the spatial-temporal variation of urban land use efficiency of Yangtze River Economic Belt in China under carbon emission constraints. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 10, 2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapio, P. Towards a theory of decoupling: Degrees of decoupling in the EU and the case of road traffic in Finland between 1970 and 2001. Transp. Policy 2005, 12, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, X.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y. Is urban sprawl decoupled from the quality of economic growth? Evidence from Chinese cities. Sustainability 2019, 12, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ran, H.; Zhang, F.; Chan, N.W.; Tan, M.L.; Kung, H.T.; Shi, J. New Composite Nighttime Light Index (NCNTL): A New Index for Urbanization Evaluation Research. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Xiao, X.; Li, J.; Zhao, B.; Fu, B. Multi-source data-driven identification of urban functional areas: A case of Shenyang, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xu, X.; Zheng, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of the Relationship between Economic Development and Water Resources–Ecological Management Capacity in China Based on Nighttime Lighting Data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Hu, X. The effects of urbanization and urban sprawl on CO2 emissions in China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 1792–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Wang, S. Research on Urban Expansion and Population Density Change of an Urban Agglomeration in the Central-Southern Region of Liaoning Province, China. Complexity 2022, 2022, 5327023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Su, S. Determinants of urban expansion and their relative importance: A comparative analysis of 30 major metropolitans in China. Habitat Int. 2016, 58, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Decoupling Type | ΔA | ΔGDP | Decoupling Elasticity (e) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative decoupling | Growth negative decoupling | >0 | >0 | e > 1.2 |
| Strong negative decoupling | >0 | <0 | e < 0 | |
| Weak negative decoupling | <0 | <0 | 0 < e < 0.8 | |
| Decoupling | Weak decoupling | >0 | >0 | 0 < e < 0.8 |
| Strong decoupling | <0 | >0 | e < 0 | |
| Recession decoupling | <0 | <0 | e > 1.2 | |
| Connections | Growth Links | >0 | >0 | 0.8 < e < 1.2 |
| Recession Link | <0 | <0 | 0.8 < e < 1.2 | |
| Index | 1990–1995 | 1995–2000 | 2000–2005 | 2005–2010 | 2010–2015 | 2015–2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area growth (km2) | 268.63 | 303.72 | 344.24 | 572.29 | 816.45 | 853.73 |
| Average annual expansion (km2/year) | 53.726 | 60.744 | 68.848 | 114.458 | 163.29 | 170.746 |
| Year | 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (km2) | 1.23 | 1.12 | 1.06 | 1.05 | 1.06 | 0.98 | 1.10 |
| Elliptical azimuth | 125.3° | 136° | 141.30 | 143.31 | 148.93 | 119.96 | 125.50 |
| Elliptical oblateness | 0.25 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.20 | 0.35 |
| Stage | Growth Negative Decoupling | Weak Decoupling | Growth Connection |
|---|---|---|---|
| First (2005–2010) | 1/3.3% | 26/86.7% | 3/10% |
| Second (2010–2015) | 4/13.3% | 23/76.67% | 3/10% |
| Third (2015–2020) | 4/13.3% | 20/66.67% | 6/20% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhao, B.; Pei, Q. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Interaction Characteristics and Decoupling Effects of Urban Expansion in the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration. Land 2023, 12, 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12040772
Wang Z, Wang L, Zhao B, Pei Q. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Interaction Characteristics and Decoupling Effects of Urban Expansion in the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration. Land. 2023; 12(4):772. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12040772
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhaolan, Li Wang, Biao Zhao, and Qian Pei. 2023. "Analysis of Spatiotemporal Interaction Characteristics and Decoupling Effects of Urban Expansion in the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration" Land 12, no. 4: 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12040772
APA StyleWang, Z., Wang, L., Zhao, B., & Pei, Q. (2023). Analysis of Spatiotemporal Interaction Characteristics and Decoupling Effects of Urban Expansion in the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration. Land, 12(4), 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12040772







