Chemical Weathering Rates of Soils Developed on Eocene Marls and Sandstones in a Mediterranean Catchment (Istria, Croatia)
Abstract
1. Introduction
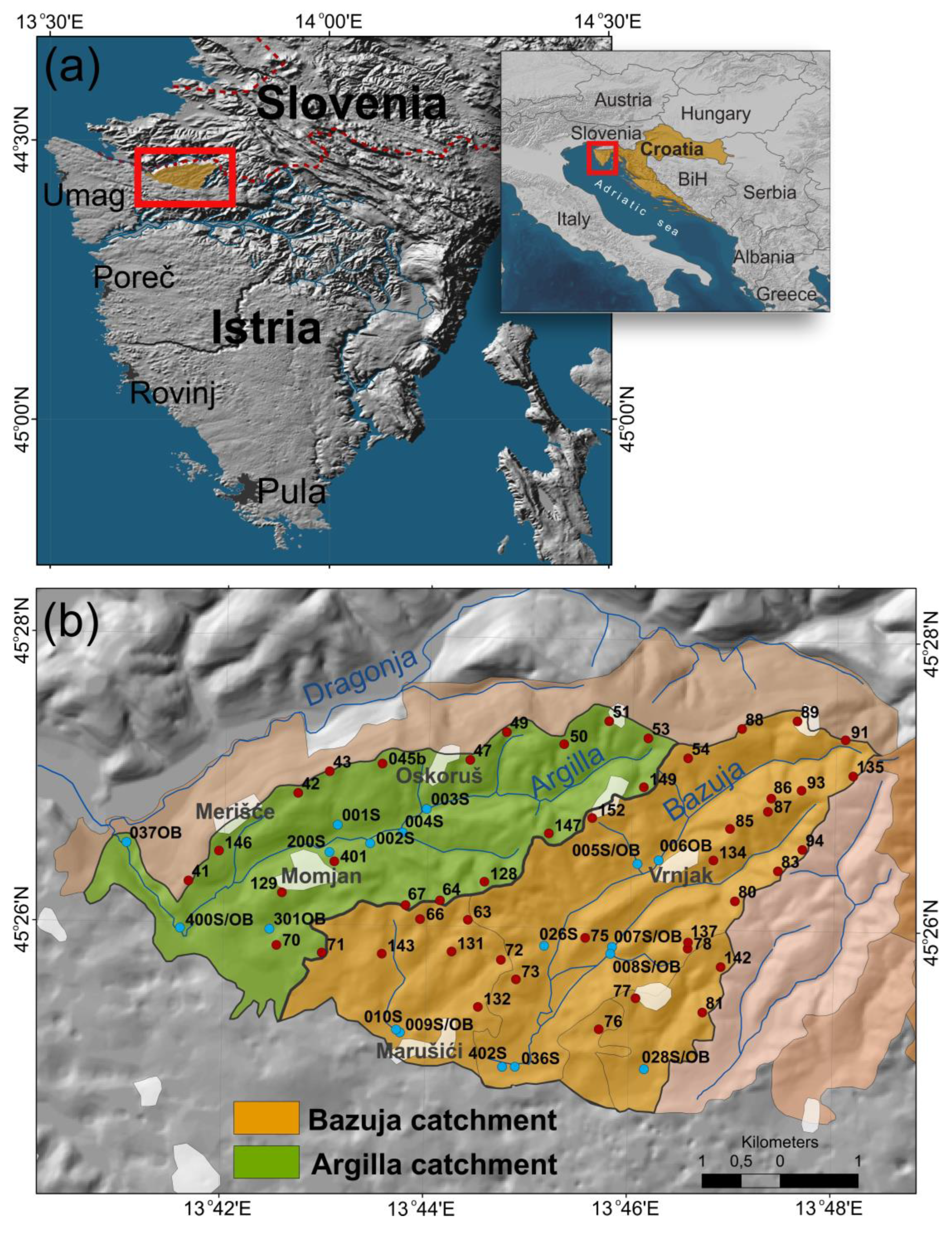
2. Investigation Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sampling Strategy
3.2. Soil Geochemistry
3.3. Theoretical Background
3.4. Construction of Graphs and Maps
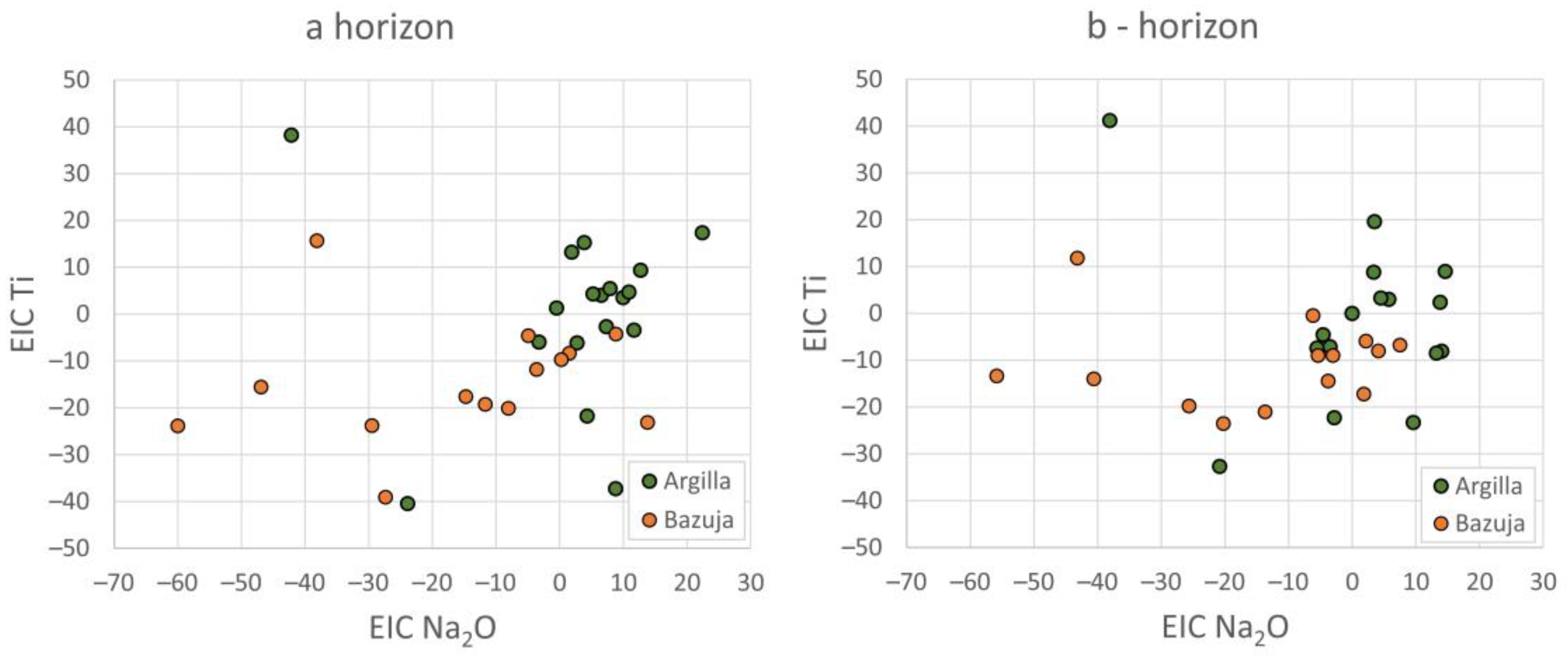
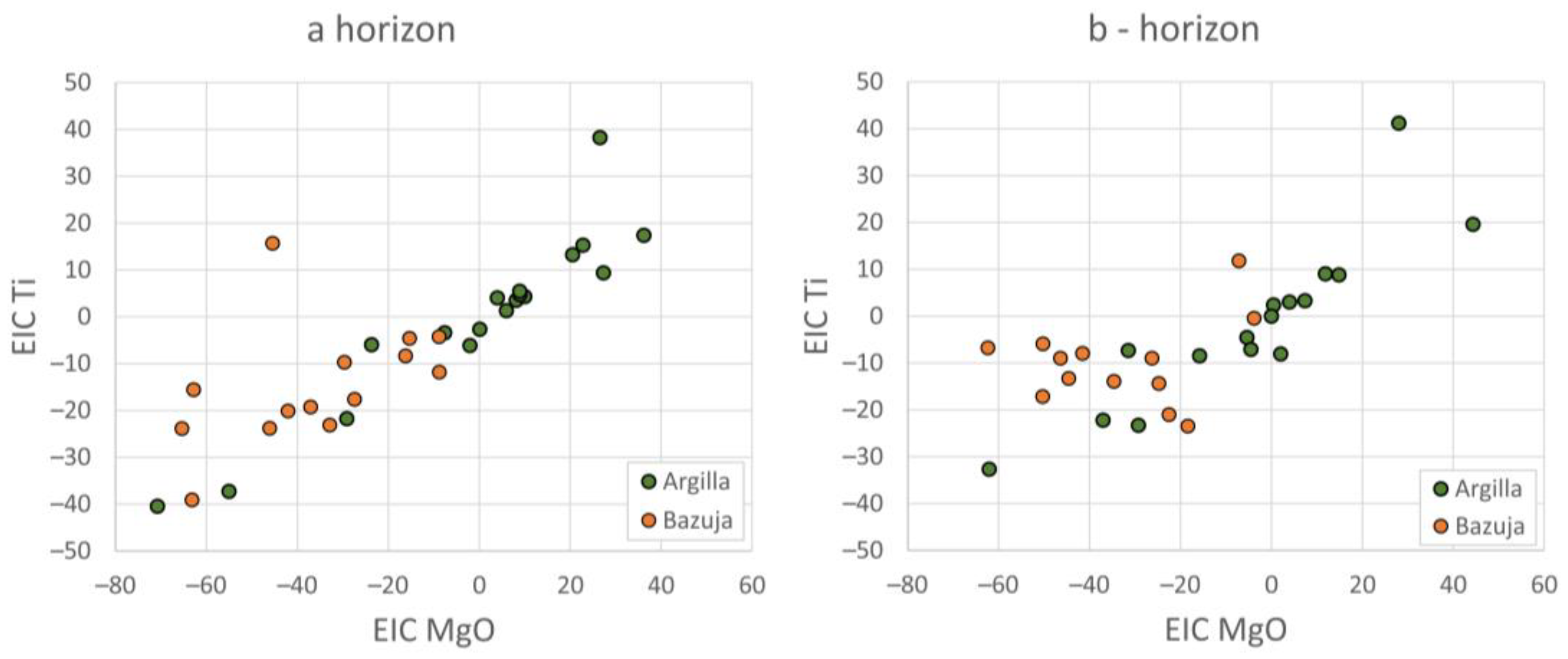
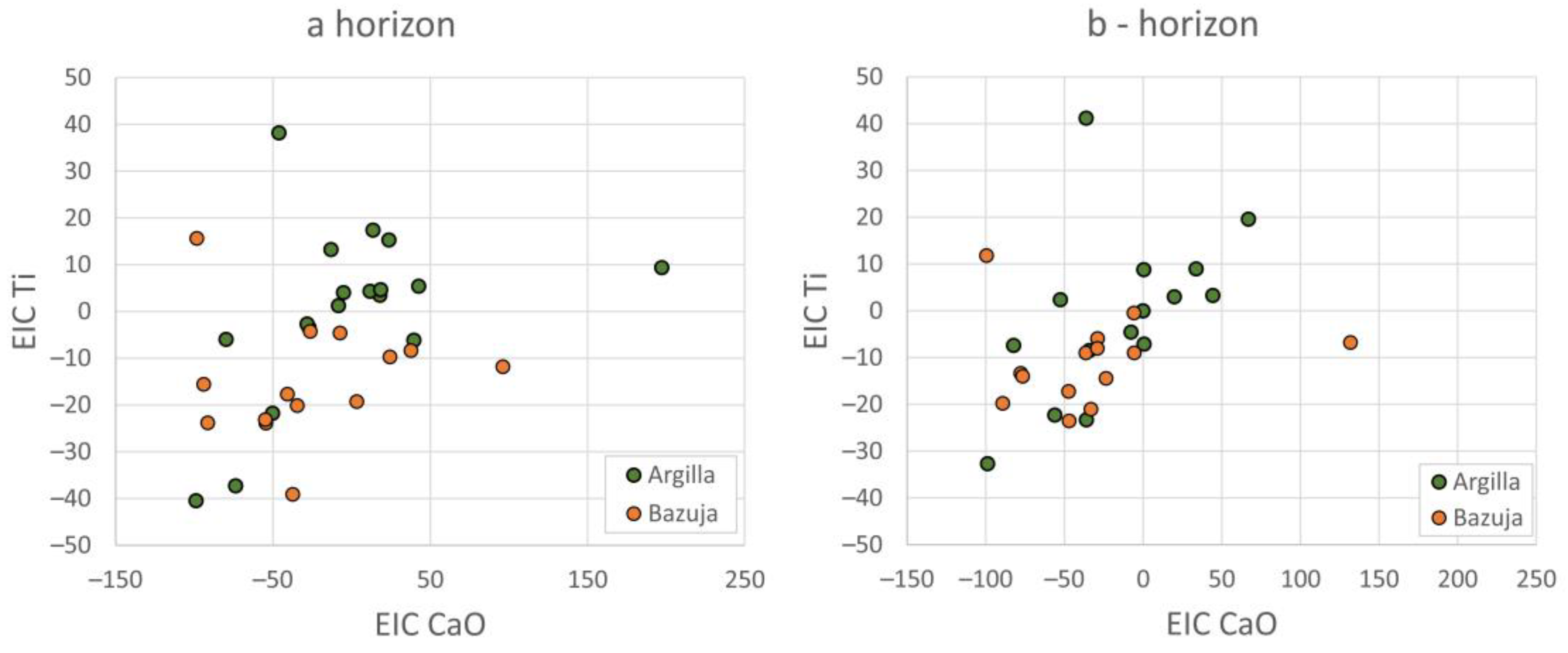
4. Results
4.1. Chemical Soil Composition of the Catchments and Their Comparison
4.2. Chemical Composition of Stream Sediments in the Catchment and Their Comparison
4.3. Analysis of the Overbank Sediment Profiles in the River Bazuja Swallow Hole
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keesstra, S.D.; van Huissteden, J.; Vandenberghe, J.; Van Dam, O.; de Gier, J.; Pleizier, I.D. Evolution of the Morphology of the River Dragonja (SW Slovenia) Due to Land-Use Changes. Geomorphology 2005, 69, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesstra, S.D.; van Dam, O.; Verstraeten, G.; van Huissteden, J. Changing Sediment Dynamics Due to Natural Reforestation in the Dragonja Catchment, SW Slovenia. Catena 2009, 78, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prus, T.; Zupančič, N.; Grčman, H. Soil of the Lower Valley of the Dragonja River (Slovenia). Acta Agric. Slov. 2015, 105, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poesen, J.W.A.; Hooke, J.M. Erosion, Flooding and Channel Management in Mediterranean Environments of Southern Europe. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 1997, 21, 157–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, D.W.; Nater, E.A. Source Apportionment of Lake Bed Sediments to Watersheds in an Upper Mississippi Basin Using a Chemical Mass Balance Method. Catena 2000, 41, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaikie, P.M.; Brookfield, H.C. (Eds.) Land Degradation and Society; Methuen, Milton Park: Abingdon, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, E.C.; Kaplan, J.O.; Fuller, D.Q.; Vavrus, S.; Goldewijk, K.K.; Verburg, P.H. Used Planet: A Global History. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7978–7985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchett William, L. Properties and Management of Forest Soils; Wiley and Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, D.; Coe, M.; Walker, W.; Verchot, L.; Vandecar, K. The Unseen Effects of Deforestation: Biophysical Effects on Climate. Front. For. Glob. Chang. 2022, 5, 756115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir Ahmad, N.S.B.; Mustafa, F.B.; Muhammad Yusoff, S.Y.; Didams, G. A Systematic Review of Soil Erosion Control Practices on the Agricultural Land in Asia. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2020, 8, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poesen, J. Soil Erosion in the Anthropocene: Research Needs. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 64–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Han, J.C.; Ijaz, M.W.; Siyal, A.A.; Ahmad, M.; Yousaf, M. Impact of Sediment Deposition on Flood Carrying Capacity of an Alluvial Channel: A Case Study of the Lower Indus Basin. Water 2022, 14, 3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFA Eurostat’s Annual Data Collection European Forest Accounts (EFA). Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Forests,_forestry_and_logging#Forests_in_the_EU (accessed on 16 April 2023).
- Hu, X.; Næss, J.S.; Iordan, C.M.; Huang, B.; Zhao, W.; Cherubini, F. Recent Global Land Cover Dynamics and Implications for Soil Erosion and Carbon Losses from Deforestation. Anthropocene 2021, 34, 100291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouma, J.; Varallyay, G.; Batjes, N.H. Principal Land Use Changes Anticipated in Europe. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1998, 67, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, J.O.; Krumhardt, K.M.; Zimmermann, N. The Prehistoric and Preindustrial Deforestation of Europe. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2009, 28, 3016–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotterweich, M. The History of Human-Induced Soil Erosion: Geomorphic Legacies, Early Descriptions and Research, and the Development of Soil Conservation-A Global Synopsis. Geomorphology 2013, 201, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Fleischer, L.R.; Lugato, E.; Ballabio, C.; Alewell, C.; Meusburger, K.; Modugno, S.; Schütt, B.; Ferro, V.; et al. An Assessment of the Global Impact of 21st Century Land Use Change on Soil Erosion. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, K.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Yan, W.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, J. Effects of Vegetation Change on Soil Erosion by Water in Major Basins, Central Asia. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckman, K.; Rasmussen, C. Lithologic Controls on Regolith Weathering and Mass Flux in Forested Ecosystems of the Southwestern USA. Geoderma 2011, 164, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.B.; Velbel, M.A. Geochemical Mass Balances and Weathering Rates in Forested Watersheds of the Southern Blue Ridge II. Effects of Botanical Uptake Terms. Geoderma 1991, 51, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulam, V.; Pollak, D.; Podolszki, L. The Analysis of the Flysch Badlands Inventory in Central Istria, Croatia. Geol. Croat. 2014, 67, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulam, V.; Gajski, D.; Podolszki, L. Photogrammetric Measurement Methods of the Gully Rock Wall Retreat in Istrian Badlands. Catena 2018, 160, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovančević, S.D.; Rubinić, J.; Ružić, I.; Radišić, M. Influence of Carbonate-Flysch Contact and Groundwater Dynamics on the Occurrence of Geohazards in Istria, Croatia. Land 2021, 10, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostjančić, I.; Gulam, V.; Frangen, T.; Hećej, N. Relation between Relief and Badland Spatial Distribution in the Paleogene Pazin Basin, Croatia. J. Maps 2023, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesstra, S.D.; Bruijnzeel, L.A.; van Huissteden, J. Meso-Scale Catchment Sediment Budgets: Combining Field Surveys and Modeling in the Dragonja Catchment, Southwest Slovenia. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 1547–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halamić, J.; Miko, S.; Peh, Z.; Galović, L.; Šorša, A. Geochemical Atlas of the Republic of Croatia; Halamić, J., Miko, S., Eds.; Croatian Geological Survey: Zagreb, Croatia, 2009; ISBN 978-953-6907-18-2. [Google Scholar]
- Peh, Z.; Miko, S.; Hasan, O. Geochemical Background in Soils: A Linear Process Domain? An Example from Istria (Croatia). Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 59, 1367–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halamić, J.; Peh, Z.; Miko, S.; Galović, L.; Šorša, A. Geochemical Atlas of Croatia: Environmental Implications and Geodynamical Thread. J. Geochem. Exp. 2012, 115, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, O.; Miko, S.; Ilijanić, N.; Brunović, D.; Dedić, Ž.; Šparica Miko, M.; Peh, Z. Discrimination of Topsoil Environments in a Karst Landscape: An Outcome of a Geochemical Mapping Campaign. Geochem. Trans. 2020, 21, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durn, G.; Ottner, F.; Slovenec, D. Mineralogical and Geochemical Indicators of the Polygenetic Nature of Terra Rossa in Istria, Croatia. Geoderma 1999, 91, 125–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razum, I.; Rubinić, V.; Miko, S.; Ružičić, S.; Durn, G. Coherent Provenance Analysis of Terra Rossa from the Northern Adriatic Based on Heavy Mineral Assemblages Reveals the Emerged Adriatic Shelf as the Main Recurring Source of Siliciclastic Material for Their Formation. CATENA 2023, 226, 107083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durn, G. Terra Rossa in the Mediterranean Region: Parent Materials, Composition and Origin. Geol. Croat. 2003, 56, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miko, S.; Durn, G.; Prohić, E. Evaluation of Terra Rossa Geochemical Baselines from Croatian Karst Regions. J. Geochem. Exp. 1999, 66, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peh, Z.; Miko, S.; Bukovec, D. The Geochemical Background in Istrian Soils. Nat. Croat. 2003, 12, 195–232. [Google Scholar]
- Egli, M.; Mirabella, A.; Sartori, G.; Fitze, P. Weathering Rates as a Function of Climate: Results from a Climosequence of the Val Genova (Trentino, Italian Alps). Geoderma 2003, 111, 99–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.P.; Dietrich, W.E.; Brimhall, G.H. Weathering Profiles, Mass-Balance Analysis, and Rates of Solute Loss: Linkages between Weathering and Erosion in a Small, Steep Catchment. GSA Bull. 2002, 114, 1143–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munroe, J.S.; Farrugia, G.; Ryan, P.C. Parent Material and Chemical Weathering in Alpine Soils on Mt. Mansfield, Vermont, USA. Catena 2007, 70, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Ravella, R.; Ketchum, B.; Bierman, P.R.; Heaney, P.; White, T.; Brantley, S.L. Mineral Weathering and Elemental Transport during Hillslope Evolution at the Susquehanna/Shale Hills Critical Zone Observatory. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 3669–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dengiz, O.; Saǧlam, M.; Özaytekin, H.H.; Başkan, O. Weathering Rates and Some Physico-Chemical Characteristics of Soils Developed on a Calcic Toposequences. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2013, 8, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Tunçay, T.; Dengiz, O.; Bayramin, I.; Kilic, S.; Baskan, O. Chemical Weathering Indices Applied to Soils Developed on Old Lake Sediments in a Semi-Arid Region of Turkey. Eurasian J. Soil Sci. 2019, 8, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Early Proterozoic Climates and Plate Motions Inferred from Major Element Chemistry of Lutites. Nature 1982, 22, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedo, C.M.; Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Unravelling the Effects of Potassium Metasomatism in Sedimentary Rocks and Paleosols, with Implications for Paleoweathering Conditions and Provenance. Geology 1995, 23, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnois, L. The CIW Index: A New Chemical Index of Weathering. Sediment. Geol. 1988, 55, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A. An Index of Weathering for Silicate Rocks. Geol. Mag. 1970, 107, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, J.W.; Logan, J. Eluvial/Illuvial Coefficients of Major Elements and the Corresponding Losses and Gains in Three Soil Profiles. J. Soil Sci. 1982, 33, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkeland, P.W. Soils and Geomorphology; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Merritts, D.J.; Chadwick, O.A.; Hendricks, D.M.; Brimhall, G.H.; Lewis, C.J. The Mass Balance of Soil Evolution on Late Quaternary Marine Terraces, Northern California. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1992, 104, 1456–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.R.; Velbel, M.A. Chemical Weathering Indices Applied to Weathering Profiles Developed on Heterogeneous Felsic Metamorphic Parent Rocks. Chem. Geol. 2003, 202, 397–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, M.; Öhlander, B. Chemical Weathering Rates, Erosion Rates and Mobility of Major and Trace Elements in a Boreal Granitic Till. Aquat. Geochem. 2000, 6, 435–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, P.M.; Davis, A.T. Mineralogical and Geochemical Evidence of Weathering in a Middle to Late Pleistocene Paleosol Sequence in the Driftless Area of Wisconsin. Quat. Res. 2018, 89, 756–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, A.; Raheb, A. Geochemical Indices of Soil Development on Basalt Rocks in Arid to Sub-Humid Climosequence of Central Iran. J. Mt. Sci. 2020, 17, 1652–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, A.; Tikhomirov, D.; Plötze, M.L.; Greinwald, K.; Hartmann, A.; Geitner, C.; Maier, F.; Petibon, F.; Egli, M. Soil Formation and Mass Redistribution during the Holocene Using Meteoric10 Be, Soil Chemistry and Mineralogy. Geosciences 2022, 12, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, P.N.; Walling, D.E.; Leeks, G.J.L. Use of Floodplain Sediment Cores to Investigate Recent Historical Changes in Overbank Sedimentation Rates and Sediment Sources in the Catchment of the River Ouse, Yorkshire, UK. Catena 1999, 36, 21–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egli, M.; Fitze, P. Formulation of pedologic mass balance based on immobile elements: A revision. Soil Sci. 2000, 165, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergant, S.; Tišljar, J.; Šparica, M. Eocene Carbonates and Flysch Deposits of the Pazin Basin. In Field Trip Guidebook: Evolution of Depositional Environments from the Palaeozoic to the Quaternary in the Karst Dinarides and the Pannonian Basin/22nd IAS Meeting of Sedimentology; Vlahović, I., Tišljar, J., Eds.; Institut za Geološka Istraživanja: Zagreb, Croatia, 2003; pp. 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Marinčić, S.; Šparica, M.; Tunis, G.; Uchman, A. The Eocene Flysch Deposits of the Istrian Peninsula in Croatia and Slovenia: Regional, Startigraphic, Sedimentological and Ichtiological Analyses. Annales 1996, 9, 435–460. [Google Scholar]
- Magdalenić, Z. Sedimentologija Flišnih Naslaga Srednje Istre (Sedimentology of Central Istria Flysch Deposits). Acta Geol. 1972, VII, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Makjanić, B.; Volarić, B. Kratki Pregled Klime Istre. In Liburnijske Teme; Katedra Čakavskog Sabora: Opatija, Croatia, 1981; pp. 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Stolbovoy, V.; Montanarella, L.; Filippi, N.; Jones, A.; Gallego, J.; Grassi, G. Soil Sampling Protocol to Certify the Changes of Organic Carbon Stock in Mineral Soils of European Union, Version 2; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2007; Volume 21576, ISBN 9783540892076. [Google Scholar]
- Swennen, R.; Van Der Sluys, J.; Hindel, R.; Brusselmans, A. Geochemistry of Overbank and High-Order Stream Sediments in Belgium and Luxembourg: A Way to Assess Environmental Pollution. J. Geochem. Exp. 1998, 62, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, G.R. Bulk Density. In Mehods of Soil Analysis, Part 4; American Society of Agronomy: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2003; p. 1692. [Google Scholar]
- White, A.F.; Blum, A.E. Effects of Climate on Chemical Weathering in Watersheds. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1729–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melkerud, P.A.; Bain, D.C.; Olsson, M.T. Historical Weathering Based on Chemical Analyses of Two Spodosols in Southern Sweden. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2003, 3, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiles, C.A.; Mora, C.I.; Driese, S.G. Pedogenic Processes and Domain Boundaries in a Vertisol Climosequence: Evidence from Titanium and Zirconium Distribution and Morphology. Geoderma 2003, 116, 279–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimhall, G.H.; Dietrich, W.E. Constitutive Mass Balance Relations between Chemical Composition, Volume, Density, Porosity, and Strain in Metasomatic Hydrochemical Systems: Results on Weathering and Pedogenesis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1987, 51, 567–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimhall, G.H.; Chadwick, O.A.; Lewis, C.J.; Compston, W.; Williams, I.S.; Danti, K.J.; Dietrich, W.E.; Power, M.E.; Hendricks, D.; Bratt, J. Deformational Mass Transport and Invasive Processes in Soil Evolution. Science 1992, 255, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retallack, G. Soils of the Past, an Introduction to Paleopedology; Unwiw Hyman: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; ISBN 9789896540821. [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Markovics, G.; Price, R. Chemical Processes Affecting Alkalis and Alkaline Earths during Continental Weathering. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1980, 44, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.L.; von Blanckenburg, F. Soils as Pacemakers and Limiters of Global Silicate Weathering. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2012, 344, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrier, K.L.; Kirchner, J.W. Effects of Physical Erosion on Chemical Denudation Rates: A Numerical Modeling Study of Soil-Mantled Hillslopes. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 272, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Jin, L.; Brantley, S.L. How Mineralogy and Slope Aspect Affect REE Release and Fractionation during Shale Weathering in the Susquehanna/Shale Hills Critical Zone Observatory. Chem. Geol. 2011, 290, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velbel, M.A.; Price, J.R. Solute Geochemical Mass-Balances and Mineral Weathering Rates in Small Watersheds: Methodology, Recent Advances, and Future Directions. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 1682–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampong, K.; Thilakaranthna, M.S.; Gorim, L.Y. Understanding the Role of Humic Acids on Crop Performance and Soil Health. Front. Agron. 2022, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, Y. The Role of Plants in Controlling Rates and Products of Weathering: Importance of Biological Pumping. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2001, 29, 135–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egli, M.; Dahms, D.; Norton, K. Soil Formation Rates on Silicate Parent Material in Alpine Environments: Different Approaches-Different Results? Geoderma 2014, 213, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miko, S.; Miko Šparica, M.; Hasan, O.; Peh, Z.; Mesić, S.; Bukovec, D. Lead Pollution of the Croatian Mountain Karst Soils Caused by Acid Rain Deposition; Evidence from Geochemical Mapping and Lead Isotopes. In Acid Rain 2005; Conference Abstracts; Huntova, I., Ostatnicka, J., Dostalova, Z., Navratil, T., Eds.; Czech Hydrometeorological Institute: Prague, Czech Republic, 2005; p. 111. [Google Scholar]
- Haeberli, W.; Hoelzle, M.; Paul, F.; Zemp, M. Integrated Monitoring of Mountain Glaciers as Key Indicators of Global Climate Change: The European Alps. Ann. Glaciol. 2007, 46, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanelli, R.; Egli, M.; Mirabella, A.; Giaccai, D.; Abdelmoula, M. Vegetation Effects on Pedogenetic Forms of Fe, Al and Si and on Clay Minerals in Soils in Southern Switzerland and Northern Italy. Geoderma 2007, 141, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porder, S. How Plants Enhance Weathering and How Weathering Is Important to Plants. Elements 2019, 15, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambers, H.; Nascimento, D.L.; Oliveira, R.S.; Shi, J. Do Cluster Roots of Red Alder Play a Role in Nutrient Acquisition from Bedrock? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 11575–11576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velbel, M.A. Geochemical Mass Balances and Weathering Rates in Forested Watersheds of the Southern Blue Ridge. Am. J. Sci. 1985, 285, 904–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


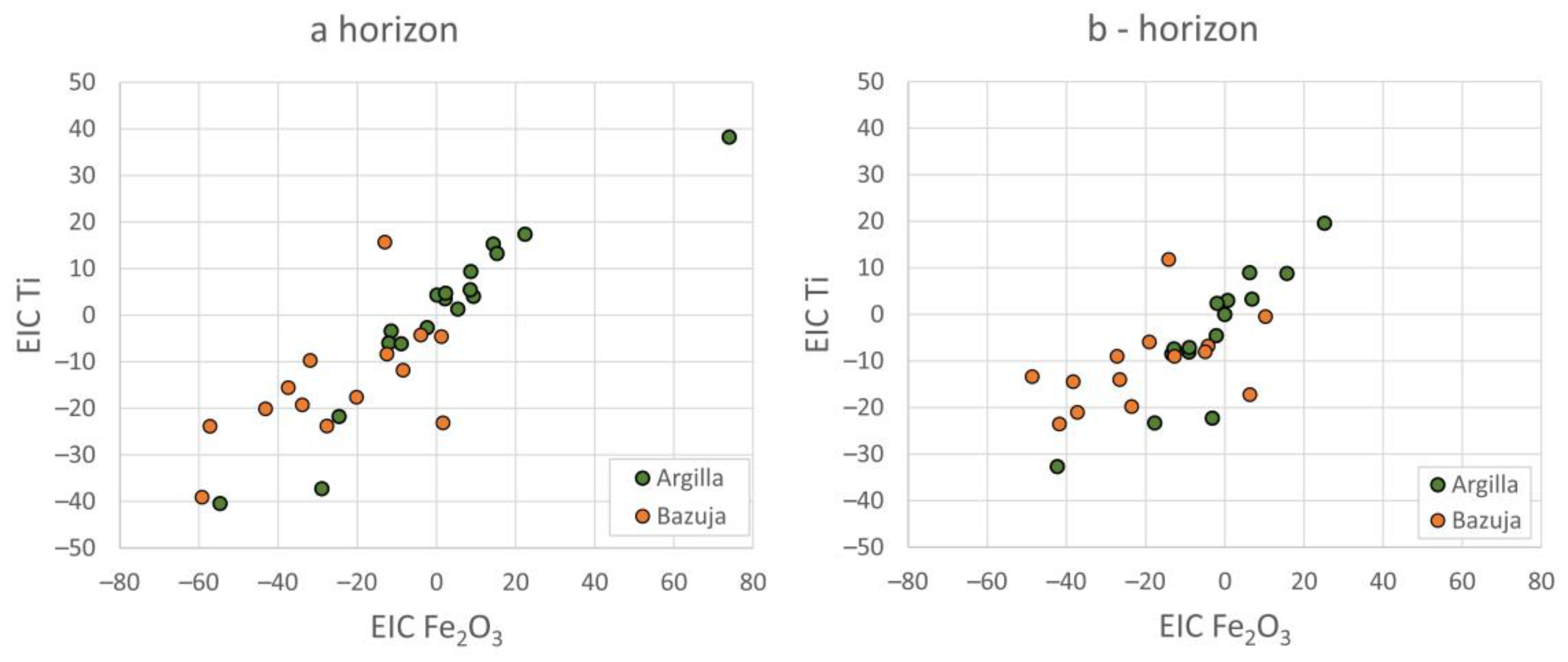
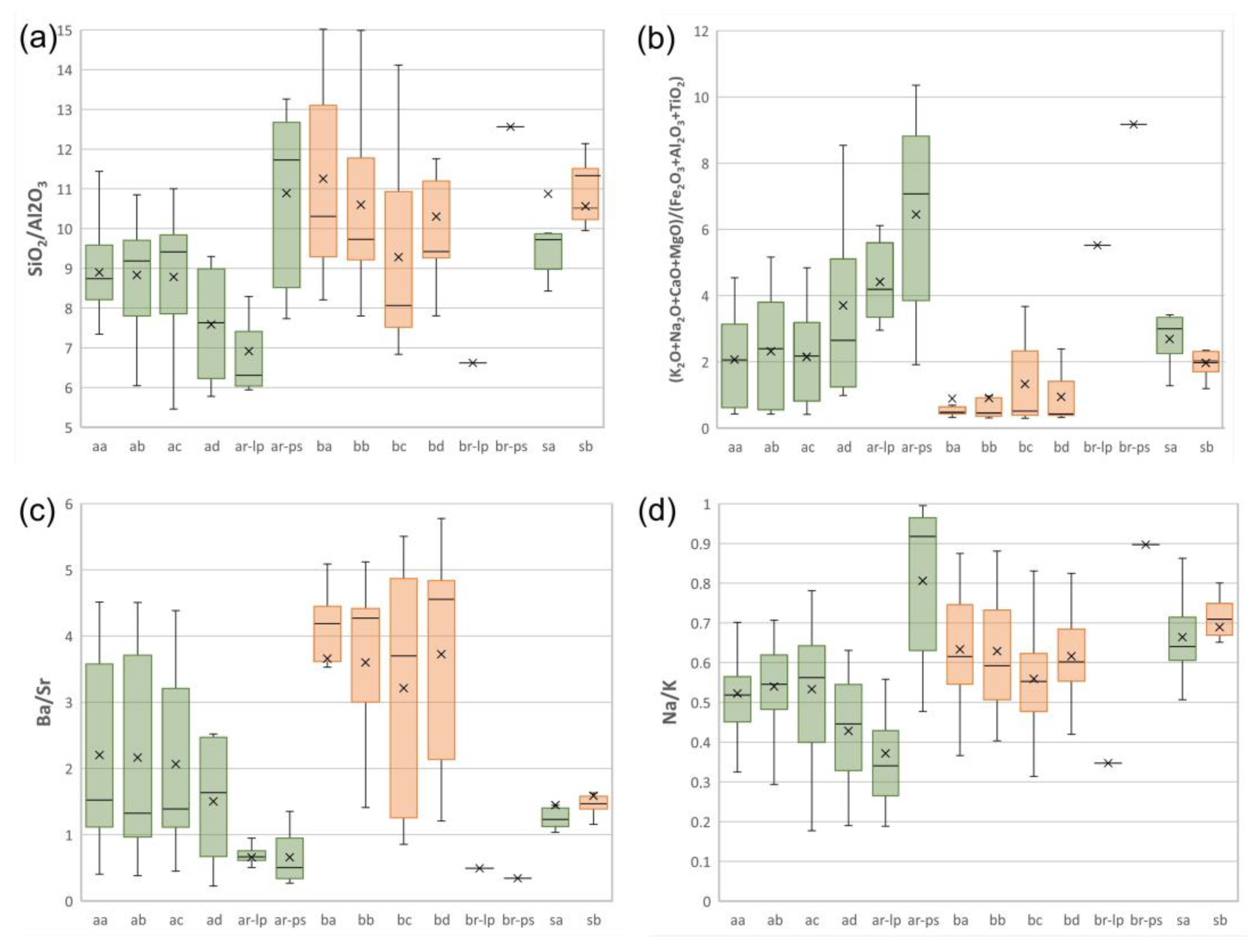
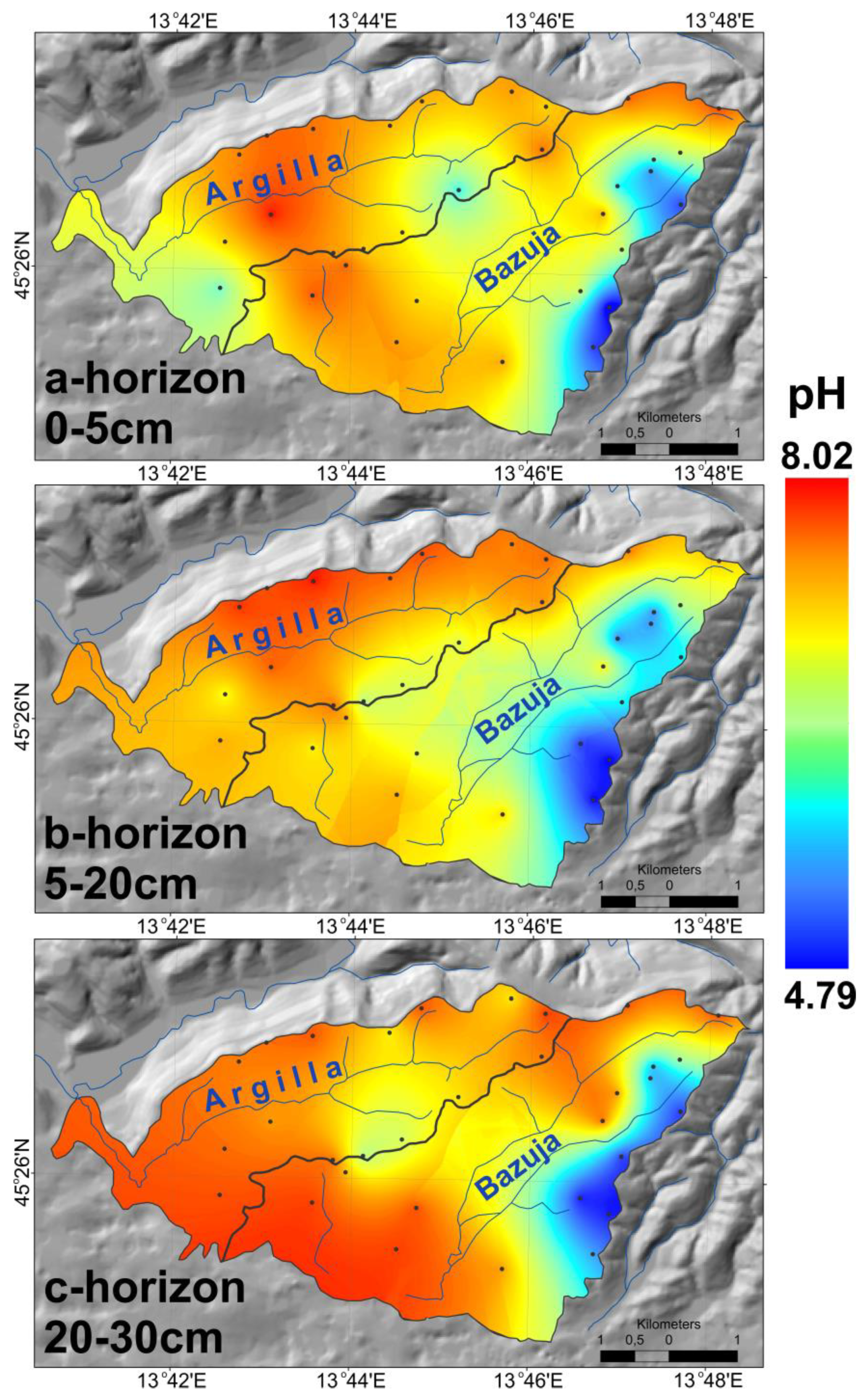
| Argilla Catchment/Horizon | a | b | c | d | sa | ar-ps | ar-lp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2/Al2O3 | 8.90 | 8.90 | 8.78 | 7.58 | 10.87 | 10.89 | 6.91 |
| SiO2/Fe2O3 | 6.93 | 6.91 | 6.80 | 5.96 | 8.44 | 8.46 | 5.59 |
| SiO2/(Fe2O3 + Al2O3 + TiO2) | 6.53 | 6.52 | 6.41 | 5.64 | 7.90 | 8.00 | 5.31 |
| (K2O + Na2O + CaO + MgO)/Al2O3 | 2.80 | 3.03 | 2.94 | 4.88 | 3.69 | 8.80 | 5.75 |
| (K2O + Na2O + CaO + MgO)/(Fe2O3 + Al2O3 + TiO2) | 2.07 | 2.23 | 2.15 | 3.71 | 2.69 | 6.45 | 4.42 |
| Na2O/K2O | 0.52 | 0.54 | 0.53 | 0.43 | 0.66 | 0.81 | 0.37 |
| Ba/Sr | 2.20 | 2.26 | 2.07 | 1.50 | 1.45 | 0.66 | 0.66 |
| Argilla | Bazuja | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EIC Index | a-Horizon | b-Horizon | a-Horizon | b-Horizon |
| SiO2 | 0.66 | 0.16 | −10.76 | −8.90 |
| Al2O3 | −0.19 | −0.48 | −28.31 | −22.99 |
| CaO | −3.73 | 4.71 | −27.05 | −33.40 |
| MgO | −0.46 | −2.84 | −35.79 | −31.91 |
| K2O | 4.72 | −1.06 | −28.25 | −26.67 |
| Na2O | 2.59 | 1.01 | −15.74 | −14.42 |
| Fe2O3 | 1.12 | 2.18 | −24.68 | −20.11 |
| Bazuja/Horizon | a | b | c | d | sb | bs | bm | br-ps | br-lp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2/Al2O3 | 11.70 | 10.96 | 9.33 | 10.57 | 10.56 | 11.61 | 10.31 | 12.56 | 6.62 |
| SiO2/Fe2O3 | 9.10 | 8.54 | 7.26 | 8.29 | 7.99 | 9.05 | 8.13 | 9.37 | 5.47 |
| SiO2/(Fe2O3 + Al2O3 + TiO2) | 8.41 | 7.92 | 6.78 | 7.68 | 7.46 | 8.45 | 7.54 | 8.87 | 5.18 |
| (K2O + Na2O + CaO + MgO)/Al2O3 | 1.18 | 1.10 | 1.45 | 0.52 | 2.65 | 2.52 | 0.90 | 12.99 | 7.06 |
| (K2O + Na2O + CaO + MgO)/ (Fe2O3 + Al2O3 + TiO2) | 0.85 | 0.80 | 1.07 | 0.38 | 1.87 | 1.83 | 0.66 | 9.17 | 5.52 |
| Na2O/K2O | 0.68 | 0.67 | 0.57 | 0.64 | 0.69 | 0.71 | 0.76 | 0.90 | 0.35 |
| Ba/Sr | 3.76 | 3.85 | 3.74 | 4.94 | 1.59 | 1.40 | 3.22 | 0.34 | 0.49 |
| Location | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | TiO2 | P2O5 | MnO | Ba | Ni | Sc | Tot. C | Tot. S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | % | % | |
| 402A | 61.1 | 8.93 | 3.95 | 0.97 | 9.58 | 0.66 | 1.41 | 0.63 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 232.6 | 78.0 | 8.60 | 2.53 | 0.01 |
| 402B | 67.2 | 11.06 | 4.66 | 1.05 | 2.33 | 0.79 | 1.57 | 0.85 | 0.08 | 0.13 | 271.2 | 93.8 | 11.00 | 1.84 | 0.03 |
| 009 | 47.8 | 8.40 | 4.30 | 1.04 | 17.09 | 0.55 | 1.39 | 0.52 | 0.08 | 0.15 | 208.9 | 86.5 | 8.42 | 4.24 | 0.02 |
| a Horizons | b Horizons | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EIC Index | Cultivated | Old Forest | Young Forest | Cultivated | Old Forest | Young Forest |
| SiO2 | 7.95 | −4.98 | −7.93 | 2.69 | −6.10 | −3.03 |
| Al2O3 | 7.50 | −15.20 | −16.25 | 0.21 | −14.48 | −7.66 |
| CaO | 44.18 | −12.40 | −36.90 | 62.64 | −20.11 | −32.58 |
| MgO | 14.39 | −20.96 | −21.56 | 2.70 | −22.19 | −13.56 |
| K2O | 21.50 | −14.53 | −15.24 | 3.47 | −17.92 | −9.78 |
| Na2O | 12.97 | −2.64 | −17.15 | 6.98 | −6.84 | −11.41 |
| Fe2O3 | 6.36 | −14.69 | −10.58 | 0.35 | −13.91 | −1.61 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hasan, O.; Miko, S.; Mesić, S.; Peh, Z. Chemical Weathering Rates of Soils Developed on Eocene Marls and Sandstones in a Mediterranean Catchment (Istria, Croatia). Land 2023, 12, 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12040913
Hasan O, Miko S, Mesić S, Peh Z. Chemical Weathering Rates of Soils Developed on Eocene Marls and Sandstones in a Mediterranean Catchment (Istria, Croatia). Land. 2023; 12(4):913. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12040913
Chicago/Turabian StyleHasan, Ozren, Slobodan Miko, Saša Mesić, and Zoran Peh. 2023. "Chemical Weathering Rates of Soils Developed on Eocene Marls and Sandstones in a Mediterranean Catchment (Istria, Croatia)" Land 12, no. 4: 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12040913
APA StyleHasan, O., Miko, S., Mesić, S., & Peh, Z. (2023). Chemical Weathering Rates of Soils Developed on Eocene Marls and Sandstones in a Mediterranean Catchment (Istria, Croatia). Land, 12(4), 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12040913








