Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Habitat Quality Analysis in the Temperate Desert Sub-Region of Ordos Plateau, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
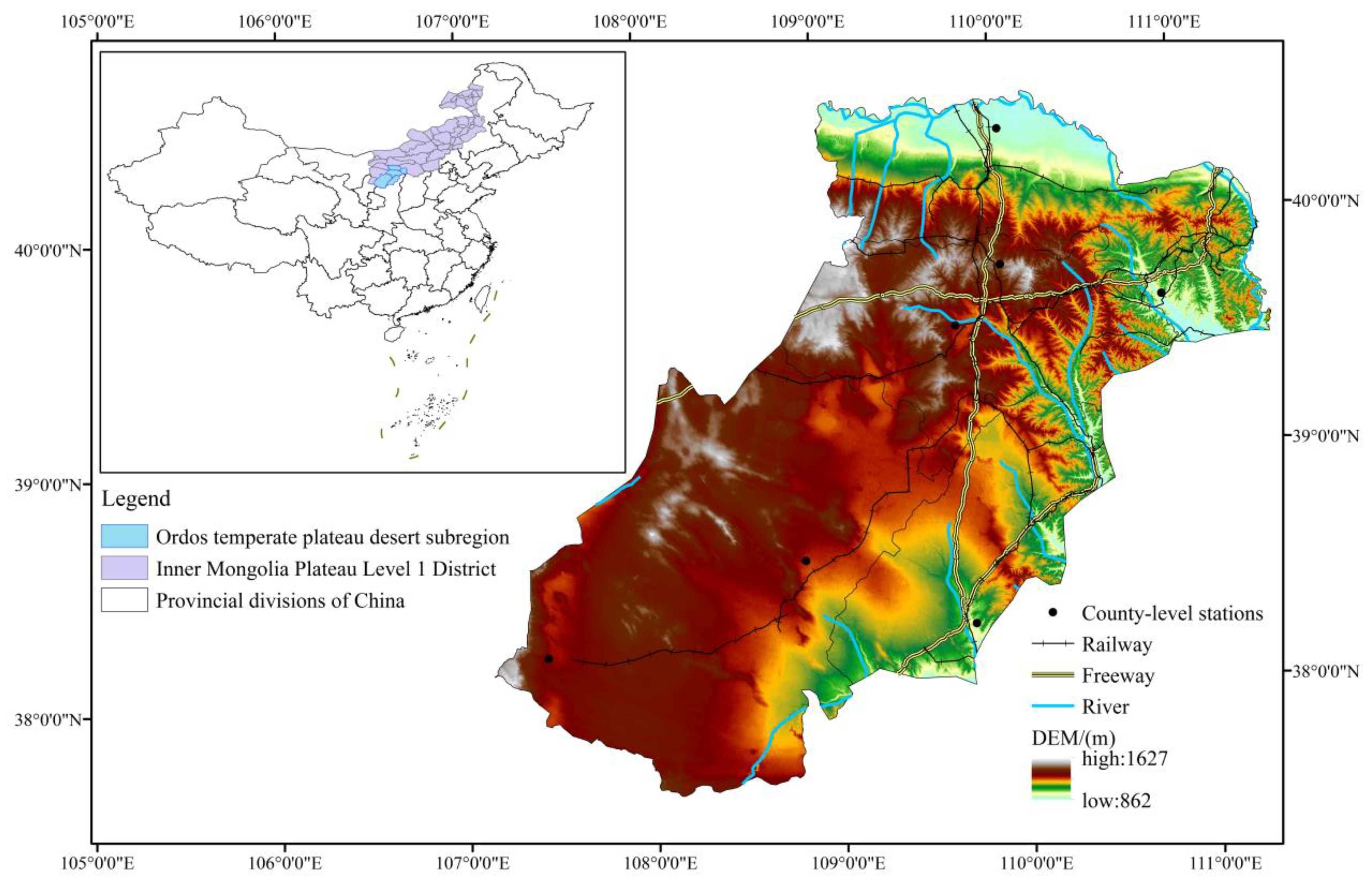
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Research Data
2.3. Research Methodology
2.3.1. PLUS Model
2.3.2. InVEST Model
2.3.3. Multi-Scene Simulation
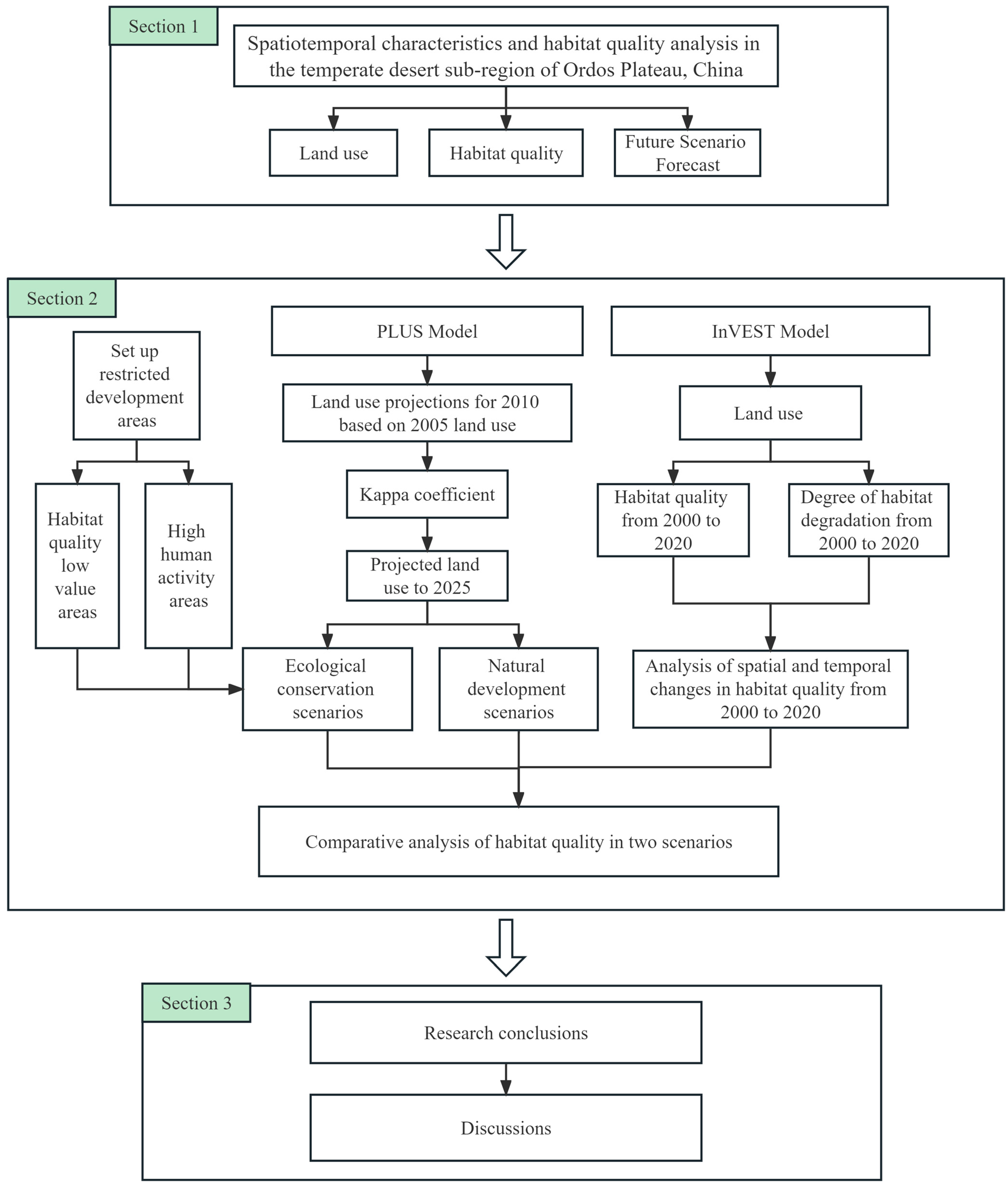
2.3.4. Research Flow Chart
3. Results
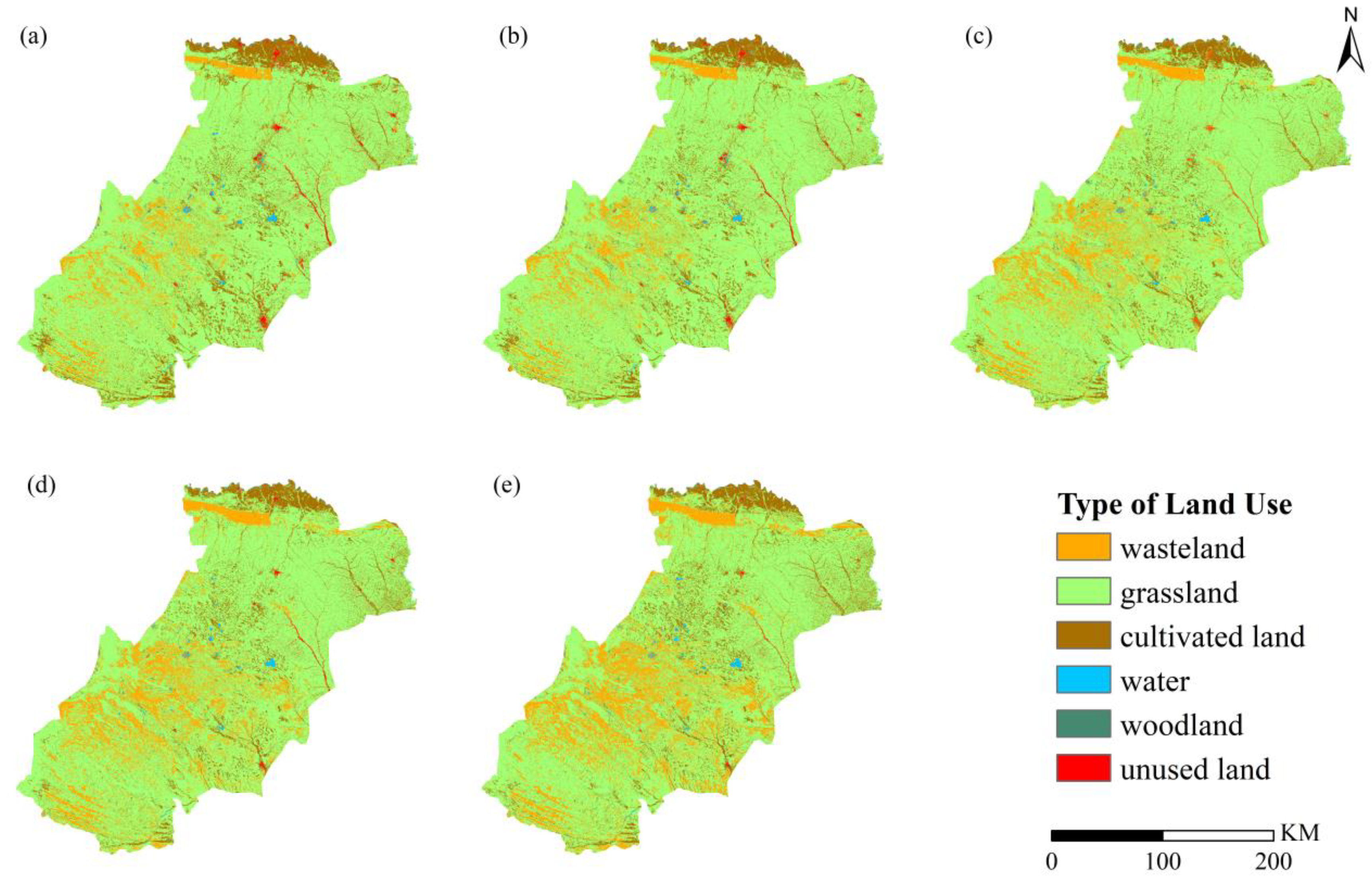
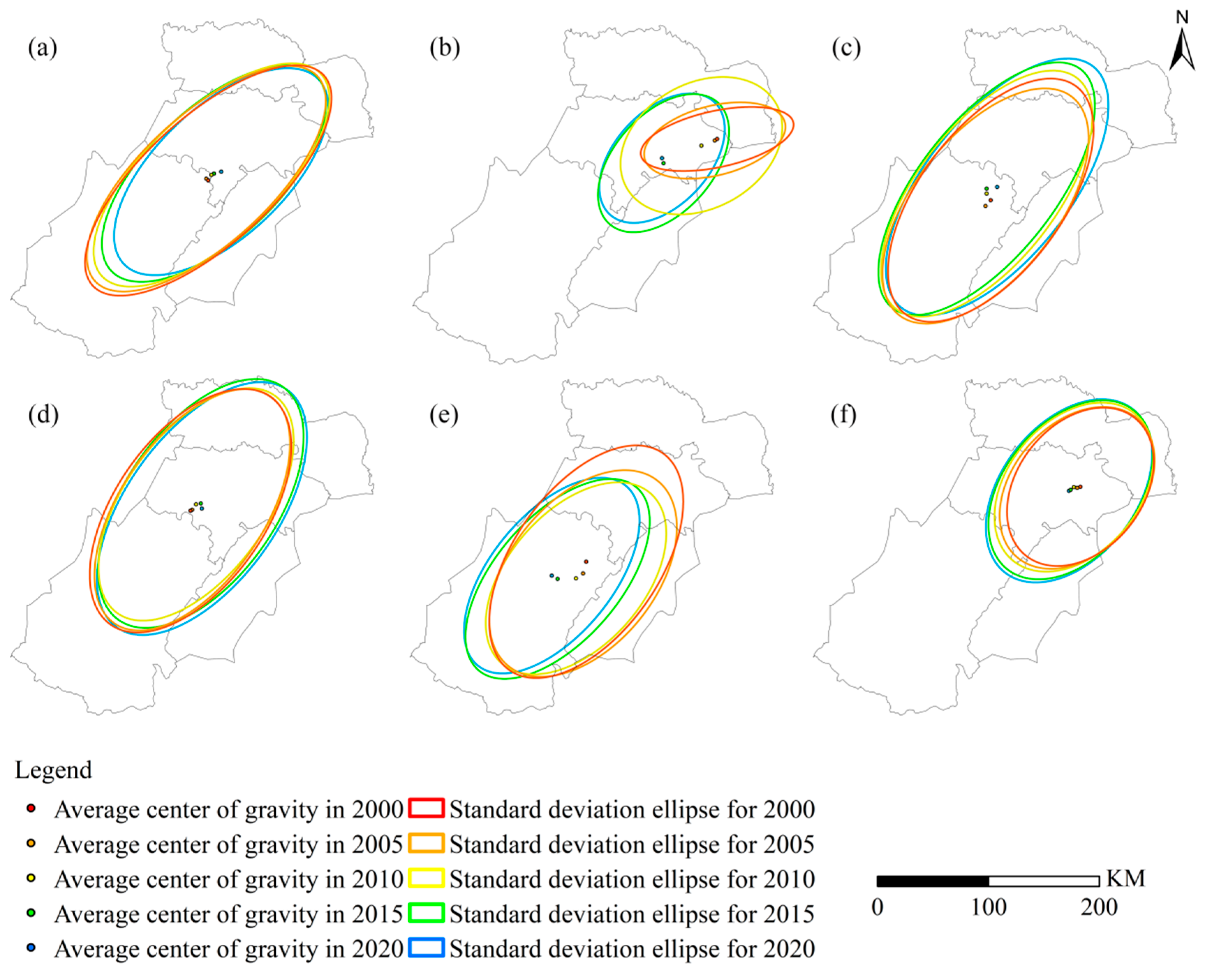
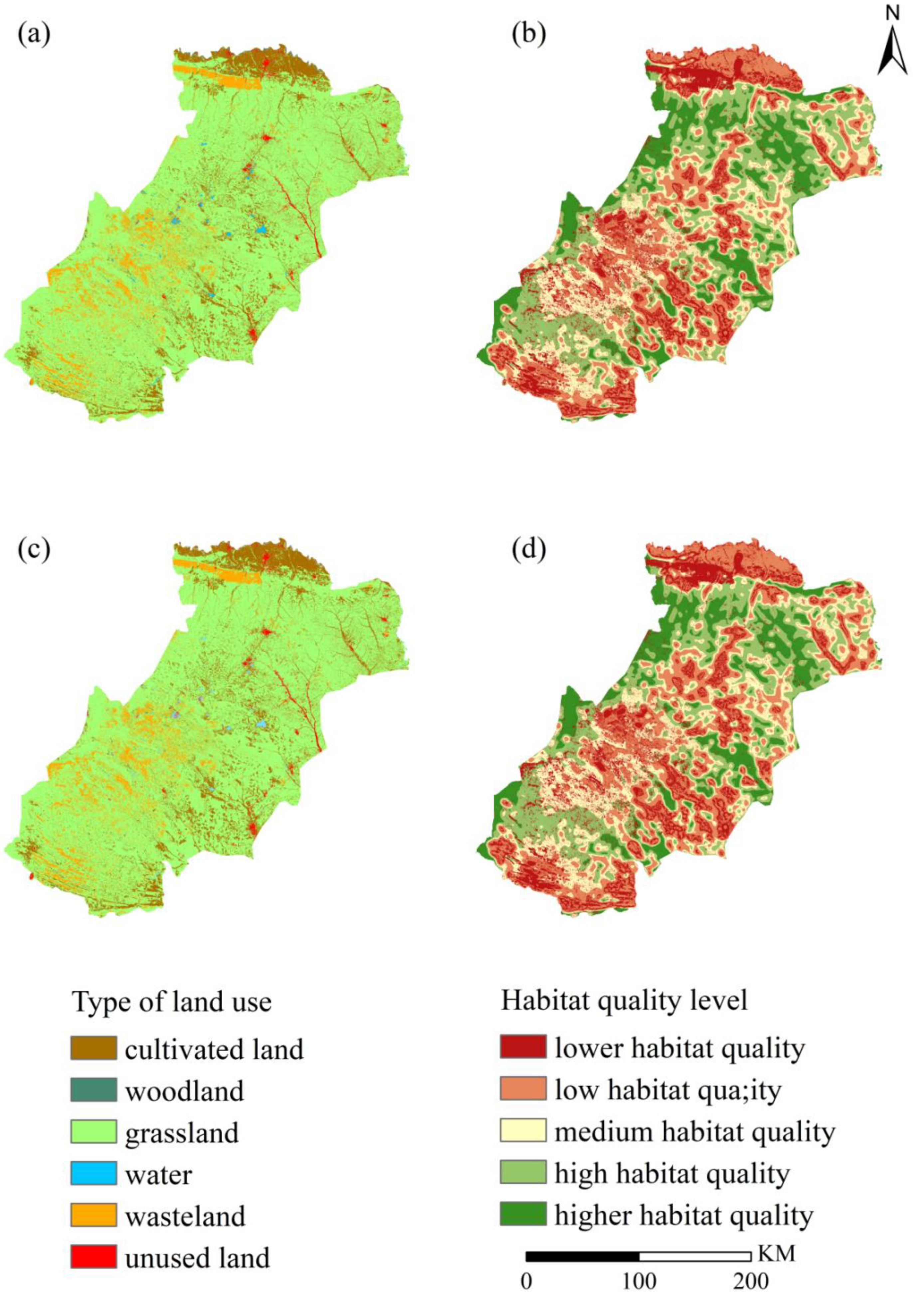
3.1. Land Use Change from 2000 to 2020
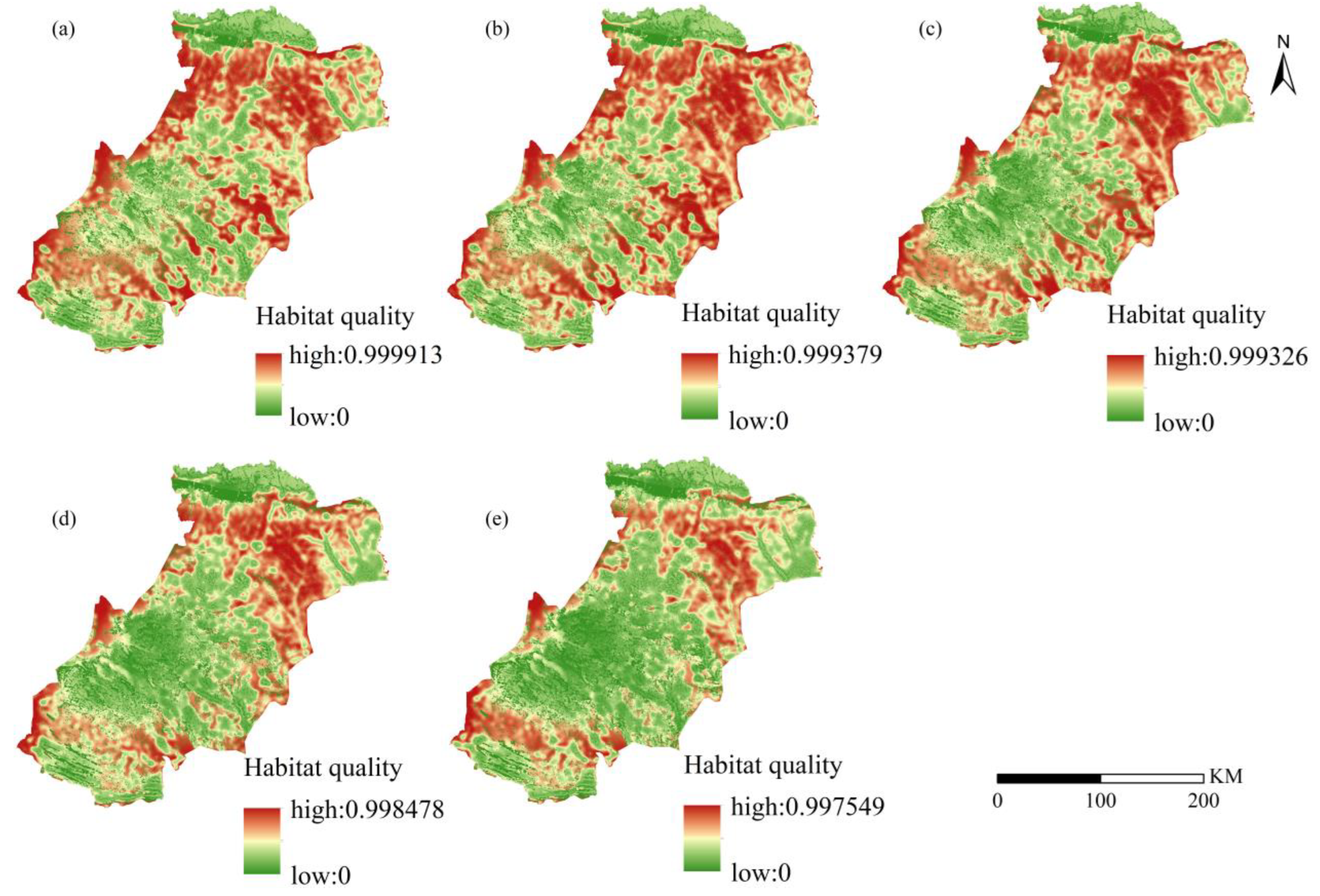
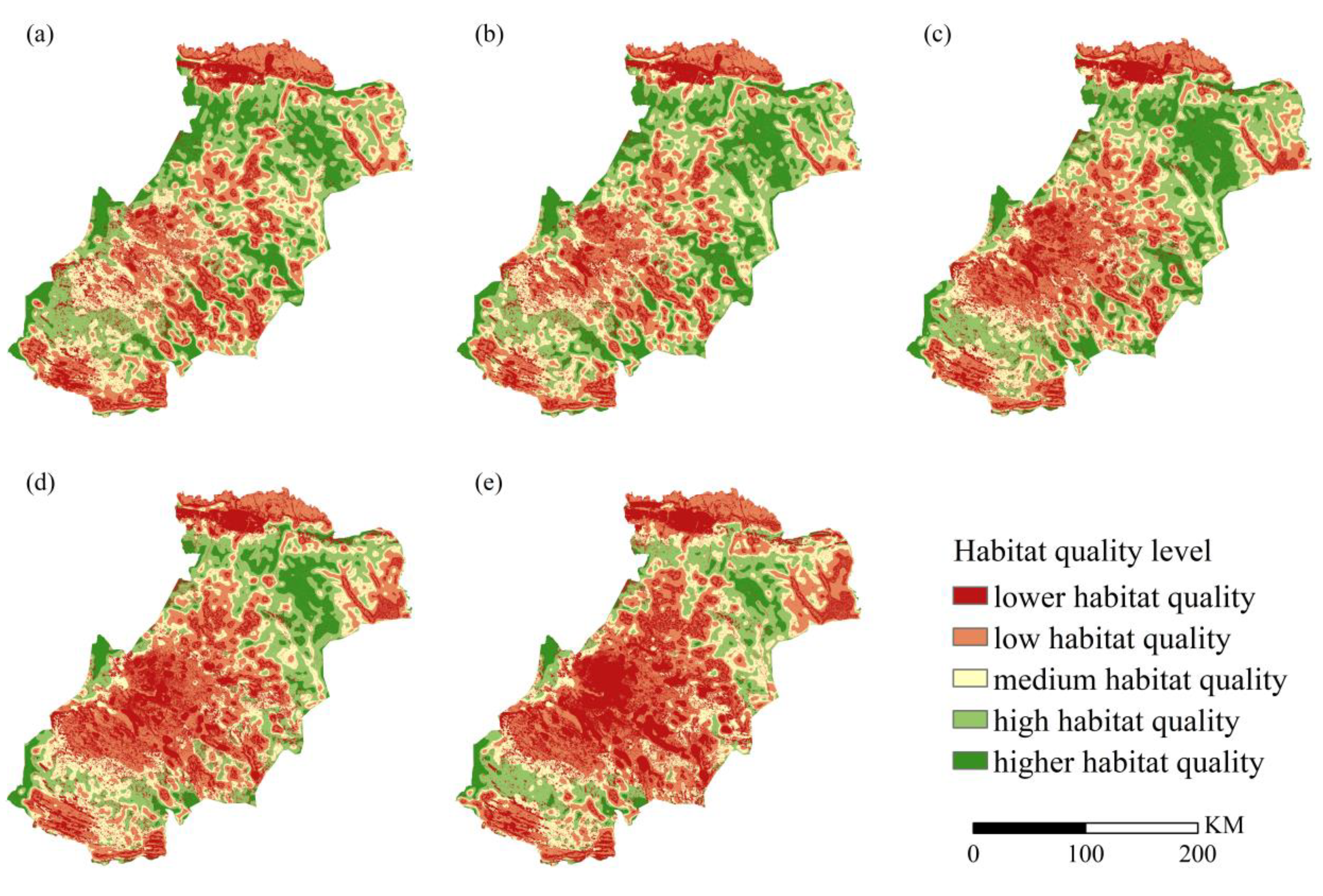
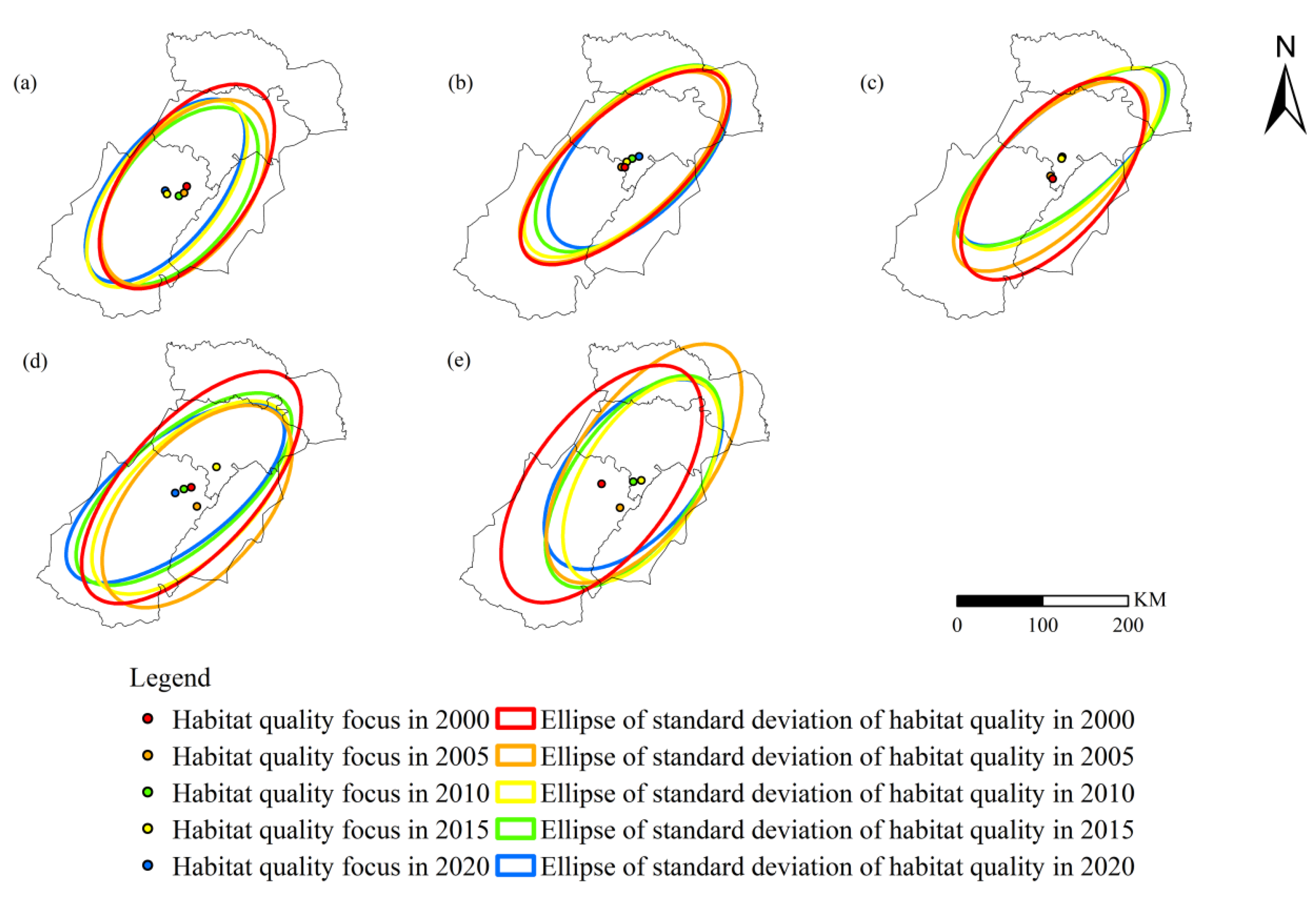
3.2. Habitat Quality Changes from 2000 to 2020
Change in Habitat Quality Class
3.3. Habitat Quality in Relation to Land Use
3.4. Land Use Projections to 2025
4. Discussion
4.1. Reasons for Land Use Change
4.2. Reasons for Changes in Habitat Quality
4.3. Innovations and Highlights
4.4. Suggestions and Outlook
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Winkler, K.; Fuchs, R.; Rounsevell, M.; Herold, M. Global land use changes are four times greater than previously estimated Nature Communications. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.B.; Wu, F.E.; Zhang, Y.N.; Han, S.; Liu, Y.Q. Spatial and temporal changes of habitat quality in Jiangsu Yancheng Wetland National Nature Reserve-Rare birds of China. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 4807–4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.R.; Chen, Y.Q.; Li, L.M.; Chen, Z.Z.; Chen, X.H.; Wu, T.T.; Li, Y.L. Spatiotemporal change of habitat quality in Hainan Island of China based on changes in land use. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, E.; Inácio, M.; Bogdzevič, K.; Kalinauskas, M.; Karnauskaitė, D.; Pereira, P. Future scenarios impact on land use change and habitat quality in Lithuania. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedler, B.; Lang, S. A spatially explicit patch model of habitat quality, integrating spatio-structural indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.L.; Sun, C.G.; Fan, F.L. Estimating the characteristic spatiotemporal variation in habitat quality using the invest model—A case study from Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.N.; Tao, F.; Liu, R.R.; Wang, Z.L.; Leng, H.J.; Zhou, T. Multi-scenario simulation and ecological risk analysis of land use based on the PLUS model: A case study of Nanjing. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 85, 104055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.C.; Wang, P.; Xiong, P.S.; Li, C.H.; Quan, B. Spatial Pattern Simulation of Land Use Based on FLUS Model under Ecological Protection: A Case Study of Hengyang City. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.P.; Liang, X.; Li, X.; Xu, X.C.; Ou, J.P.; Chen, Y.M.; Yi, L.S.; Wang, S.J.; Pei, F.S. A future land use simulation model (FLUS) for simulating multiple land use scenarios by coupling human and natural effects. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 168, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.Q.; Abudureheman, M.; Halike, A.; Yao, K.X.; Yao, L.; Tang, H.; Tuheti, B. Temporal and spatial variation analysis of habitat quality on the PLUS-InVEST model for Ebinur Lake Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhao, D.Y.; Deng, L. Landscape pattern simulation for ecosystem service value regulation of Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 95, 106798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Li, X.; Mao, Y.T.; Li, L.; Wang, X.R.; Lin, Q. Dynamic simulation of land use change and assessment of carbon storage based on climate change scenarios at the city level: A case study of Bortala, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 134, 108499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.Z.; Huang, Y.P. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Ecosystem Service Value in Wuhan Metropolitan Area Based on PLUS-GMOP Model. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Zhu, K.W.; Liu, J.P. Evolution and prediction of land cover and biodiversity function in Chongqing section of Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 258–267. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.L.; Wang, F. Simulation and analysis of land use scenarios in Guangzhou based on PLUS model and taking into account traffic planning. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2022, 12, 120. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.L.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, L.Y.; Niu, L.D.; Pan, M. Land use simulation and ecosystem service value assessment in Nujiang Prefecture—A multi-scenario analysis based on PLUS model. China’s Agric. Resour. Zoning 2023, 44, 140–149. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.J.; Yu, D.D.; Nv, N. Biodiversity and ecosystem services assessment index system in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Yohannes, H.; Soromessa, T.; Argaw, M.; Dewan, A. Spatio-temporal changes in habitat quality and linkage with landscape characteristics in the Beressa watershed, Blue Nile basin of Ethiopian highlands. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 281, 111885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Zhang, L. Land-use change and ecosystem services: Concepts, methods and progress. Prog. Geogr. 2014, 33, 441–446. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.X.; Li, S.J.; Liu, Z.S. Multi-Scenario Simulation and Prediction of Regional Habitat Quality Based on a System Dynamic and Patch-Generating Land-Use Simulation Coupling Model—A Case Study of Jilin Province. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.J.; Ma, Y.W.; Cai, S.Q.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.M. Application of SolVES model in social value assessment of ecosystem service functions. J. World For. Res. 2023, 36, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L.M.; Feng, X.H.; Sun, R.F.; Gao, H. Spatial and temporal responses of habitat quality to urbanization: A case study of Changchun City, Jilin Province, China. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2020, 31, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.M.; Wang, Y. Habitat quality assessment of Dianchi watershed based on InVEST model. Three Gorges Ecol. Environ. Monit. 2022, 7, 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, T.Q.; Wang, X.R. Spatial-temporal evolution analysis of habitat quality in Changzhutan urban agglomeration based on InVEST model. For. Resour. Manag. 2022, 5, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Xie, B.; Zhang, D. Spatial-temporal evolution of habitat quality in the Yellow River Basin and its influencing factors. J. Desert Res. 2021, 41, 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Fu, B.H.; Shi, P.L.; Cudahy, T.; Zhang, J.; Xu, H. Satellite monitoring the spatial-temporal dynamics of desertification in response to climate change and human activities across the Ordos Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, J.; Xu, D.Y.; Ren, H.Y. Identification of desertification dynamics and the impact of climate change and human activities in Ordos from 2000 to 2010. Glacial Permafr. 2013, 35, 48–56. [Google Scholar]
- He, N.; Guo, W.X.; Wang, H.W.; Yu, L.; Cheng, S.Y.; Huang, L.T.; Jiao, X.Y.; Chen, W.X.; Zhou, H.T. Temporal and Spatial Variations in Landscape Habitat Quality under Multiple Land-Use/Land-Cover Scenarios Based on the PLUS-InVEST Model in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Land 2023, 12, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Fan, J.W.; Huang, L.; Tang, Y.L.; Yue, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.H. Theoretical research and technical scheme of comprehensive zoning of natural resources in China. Resour. Sci. 2020, 42, 1870–1882. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.M.; Long, Y.P.; Jia, X.P.; Wang, H.B.; Li, Y.S. Vegetation response to climatic variation and human activities on the Ordos Plateau from 2000 to 2016. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Liu, H.X.; Zhang, A.B.; Cui, X.M.; Zhao, A.Z. Spatiotemporal variations and its influencing factors of grassland net primary productivity in Inner Mongolia, China during the period 2000–2014. J. Arid Environ. 2019, 165, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.M.; Zhou, Q.L.; Ma, Q.; Kuang, W.N.; Daryanto, S.; Wang, L.X.; Wu, J.; Liu, B.; Zhu, J.L.; Cao, C.Y. Scale effect of climate factors on soil organic carbon stock in natural grasslands of northern China. Ecol. Indi. 2023, 146, 109757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Wu, H.C.; Hinnov, L.A.; Wang, X.L.; Yang, T.S.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, S.H. A record of astronomically forced climate change in a late Ordovician (Sandbian) deep marine sequence, Ordos Basin, North China. Sediment. Geol. 2016, 341, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, C.; Qi, X.; Zheng, Z.S.; Jia, K. PLUS-model based multi-scenario land space simulation of the Lower Yellow River Region and its ecological effects. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biau, G. Analysis of a random forests model. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2012, 13, 1063–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Shiferaw, H.; Bewket, W.; Alamirew, T.; Zeleke, G.; Teketay, D.; Bekele, K.; Schaffner, U.; Eckert, S. Implications of land use/land cover dynamics and Prosopis invasion on ecosystem service values in Afar Region, Ethiopia. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 675, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Liu, G.X.; Xiang, A.C.; Xiao, S.M.; Lin, D.R.; Lin, Y.B.; Lu, Y. Terrain gradient response of landscape ecological environment to land use and land cover change in the hilly watershed in South China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, P.N.; Tian, Y.; Huang, H.; Xiao, L. Evolution of Habitat Quality and Its Topographic Gradient Effect in Northwest Hubei Province from 2000 to 2020 Based on the InVEST Model. Land 2021, 10, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, M.; Fonseca, C.; Vergílio, M.; Calado, H.; Gil, A. Spatial assessment of habitat conservation status in a Macaronesian island based on the InVEST model: A case study of Pico Island (Azores, Portugal). Land Use Policy 2018, 78, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.F.; Cao, A.H.; Wang, F.Y. Response and multi-scenario prediction of carbon storage and habitat quality to land use in liaoning Province, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneseyee, A.B.; Noszczyk, T.; Soromessa, T.; Elias, E. The InVEST habitat quality model associated with land use/cover changes: A qualitative case study of the Winike Watershed in the Omo-Gibe Basin, Southwest Ethiopia. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, L.; Sun, T.C.; Wang, T.W.; Li, Z.X.; Cai, C.F. Evolution and prediction of landscape pattern and habitat quality based on CA-Markov and InVEST model in Hubei section of Three Gorges Reservoir Area (TGRA). Sustainability 2018, 10, 3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.F.; Wu, Q.R.; Wei, P.P.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, X.W.; Pang, C.K. Explore the mitigation mechanism of urban thermal environment by integrating geographic detector and standard deviation ellipse (SDE). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, J.J.; Yang, C.X.; Wei, C.F. Implementation Process of General Land-Use Planning and Its Adjustment—A Case Study of Rongchang District in Chongqing, China. Environ. Res. Pubilic Health 2021, 18, 5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.W.; Hu, X.J.; Wang, Y.Z.; Chen, C.Y. Simulation and Prediction of Territorial Spatial Layout at the Lake-Type Basin Scale: A Case Study of the Dongting Lake Basin in China from 2000 to 2050. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zhou, L.; Sun, D.Q.; Yuan, B.; Hu, F.M. Evaluating the impact of urban expansion on the habitat quality and constructing ecological security patterns: A case study of Jiziwan in the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Luo, S.Q.; Liu, X.; Luo, T.Y.; Liu, X.J. Research on the Dynamic Evolution of the Landscape Pattern in the Urban Fringe Area of Wuhan from 2000 to 2020. Geo-Information 2022, 11, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Lü, Y.; Fu, B.; Lü, D.; Wu, X.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Y. A modified habitat quality model to incorporate the effects of ecological restoration. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 104029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.J.; Shi, X.Y.; He, J.; Yuan, Y.; Qu, L.L. Identification and optimization strategy of county ecological security pattern: A case study in the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.S.; Yu, W.Y.; Meng, P.; Zhang, J.S.; Zhang, J.X. InVEST model analysis of the impacts of land use change on landscape pattern and habitat quality in the Xiaolangdi Reservoir area of the Yellow River basin. China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 2870–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Luo, X. Study on Spatiotemporal Evolution Features and Affecting Factors of Collaborative Governance of Pollution Reduction and Carbon Abatement in Urban Agglomerations of the Yellow River Basin. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.B.; Wu, Y.L.; Gou, A.P. Habitat quality evolution characteristics and multi-scenario prediction in Shenzhen based on PLUS and InVEST models. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1146347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Q.; Yu, Y.H.; Wang, J.J.; Liu, W.D. Analysis of the spatiotemporal variation in habitat quality based on the invest model—A case study of Shangri-la city, northwest Yunnan, China. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. IOP Publ. 2021, 1961, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.X.; Cheng, W.M. Effects of land use/cover on regional habitat quality under different geomorphic types based on InVEST model. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Data Type | Secondary Data Type | Data Source |
|---|---|---|
| Land use data | Land use data for 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020 | The 30 m annual land cover datasets and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2021 (https://zenodo.org/record/5816591/export/hx/ (accessed on 20 October 2022)) |
| Soil data | Soil texture data | The HWSD World Soil Database published by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (https://www.fao.org/home/ (accessed on 20 October 2022)) |
| Terrain data | DEM | The “ASTER GDEM 30M Resolution Digital Elevation Model” published by the Geospatial Data Cloud Platform of the Computer Network Information Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| Slope | ||
| Climate data | Annual average rainfall data | The National Geoscience Data Center (http://www.geodata.cn/ (accessed on 20 November 2022)) |
| Annual average temperature data | ||
| Road accessibility data | Distance from river | The remote sensing monitoring data of land use in China released by the Resource Environment Science and Data Center (https://www.resdc.cn/ (accessed on 20 October 2022)) |
| Distance from county seat | ||
| Distance from highway | ||
| Distance from railroad | ||
| Distance from primary roads | ||
| Socio-economic data | Luminous data | |
| GDP | ||
| Population | The spatial distribution of population in 2000, China (https://hub.worldpop.org/ (accessed on 20 October 2022)). |
| Threat Feeds | Maximum Coercive Distance (km) | Weight | Spatial Attenuation Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivated land | 4 | 0.6 | Linear |
| Wasteland | 8 | 0.4 | Exponential |
| Unused land | 6 | 0.5 | Linear |
| Type of Land Use | Habitat Suitability | Cultivated Land | Wasteland | Unused Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivated land | 0.3 | 0 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
| Woodland | 1 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
| Grassland | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Water | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| Wasteland | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 |
| Unused land | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0 |
| Now Future | Cultivated Land | Woodland | Grassland | Water | Wasteland | Unused Land | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenery | NDS | ECS | NDS | ECS | NDS | ECS | NDS | ECS | NDS | ECS | NDS | ECS |
| Cultivated land | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Woodland | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Grassland | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Water | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Wasteland | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Unused land | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pei, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhao, X.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Luo, X.; Xing, L.; Wang, C.; et al. Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Habitat Quality Analysis in the Temperate Desert Sub-Region of Ordos Plateau, China. Land 2023, 12, 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12071470
Pei M, Liu X, Wang J, Liu J, Zhao X, Li H, Wang R, Luo X, Xing L, Wang C, et al. Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Habitat Quality Analysis in the Temperate Desert Sub-Region of Ordos Plateau, China. Land. 2023; 12(7):1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12071470
Chicago/Turabian StylePei, Min, Xiaohuang Liu, Jinjie Wang, Jiufen Liu, Xiaofeng Zhao, Hongyu Li, Ran Wang, Xinping Luo, Liyuan Xing, Chao Wang, and et al. 2023. "Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Habitat Quality Analysis in the Temperate Desert Sub-Region of Ordos Plateau, China" Land 12, no. 7: 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12071470
APA StylePei, M., Liu, X., Wang, J., Liu, J., Zhao, X., Li, H., Wang, R., Luo, X., Xing, L., Wang, C., & Zhao, H. (2023). Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Habitat Quality Analysis in the Temperate Desert Sub-Region of Ordos Plateau, China. Land, 12(7), 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12071470






