Energy and the Macrodynamics of Agrarian Societies
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Energy Paradigm, Structural Change, and Social Organization
1.2. Energy and the Ecodynamics of Civilizations
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Energy and Socio-Ecological Complexity
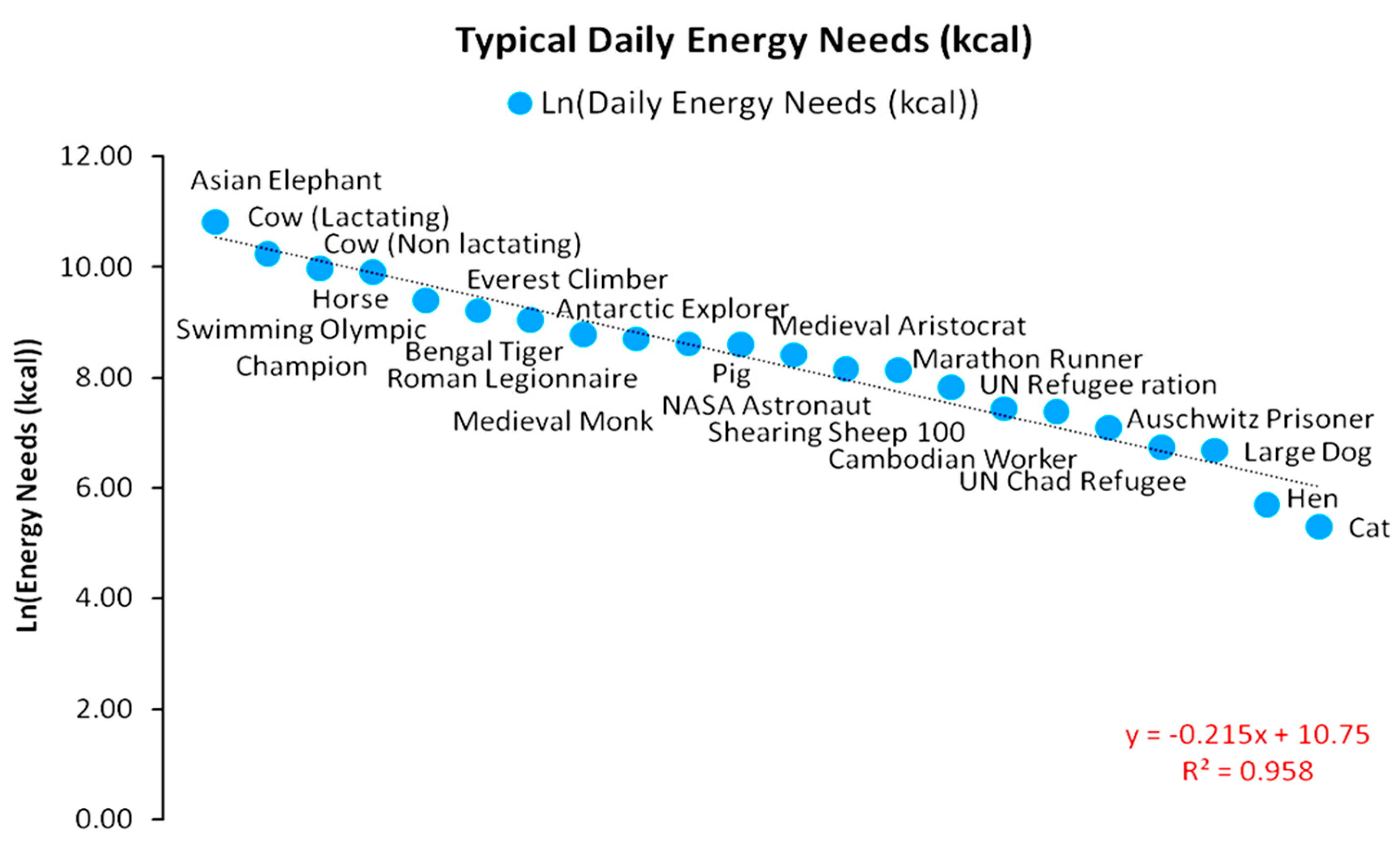
2.2. Energy and Growth in Agrarian Societies
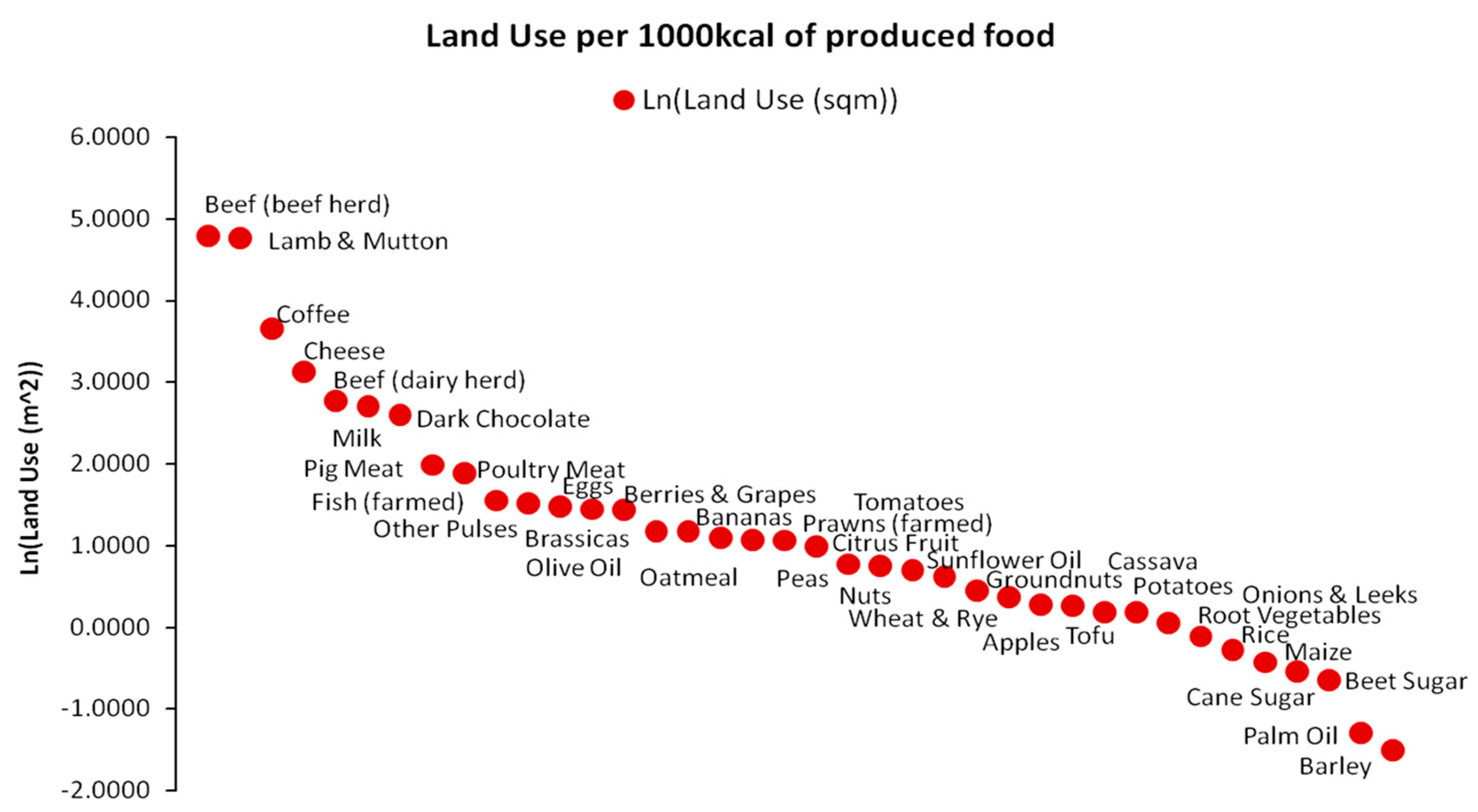
2.3. Agrarian Energy Paradigm Structure and Resource Distribution
2.4. Energy Use Growth Macrodynamic Modeling
3. Results
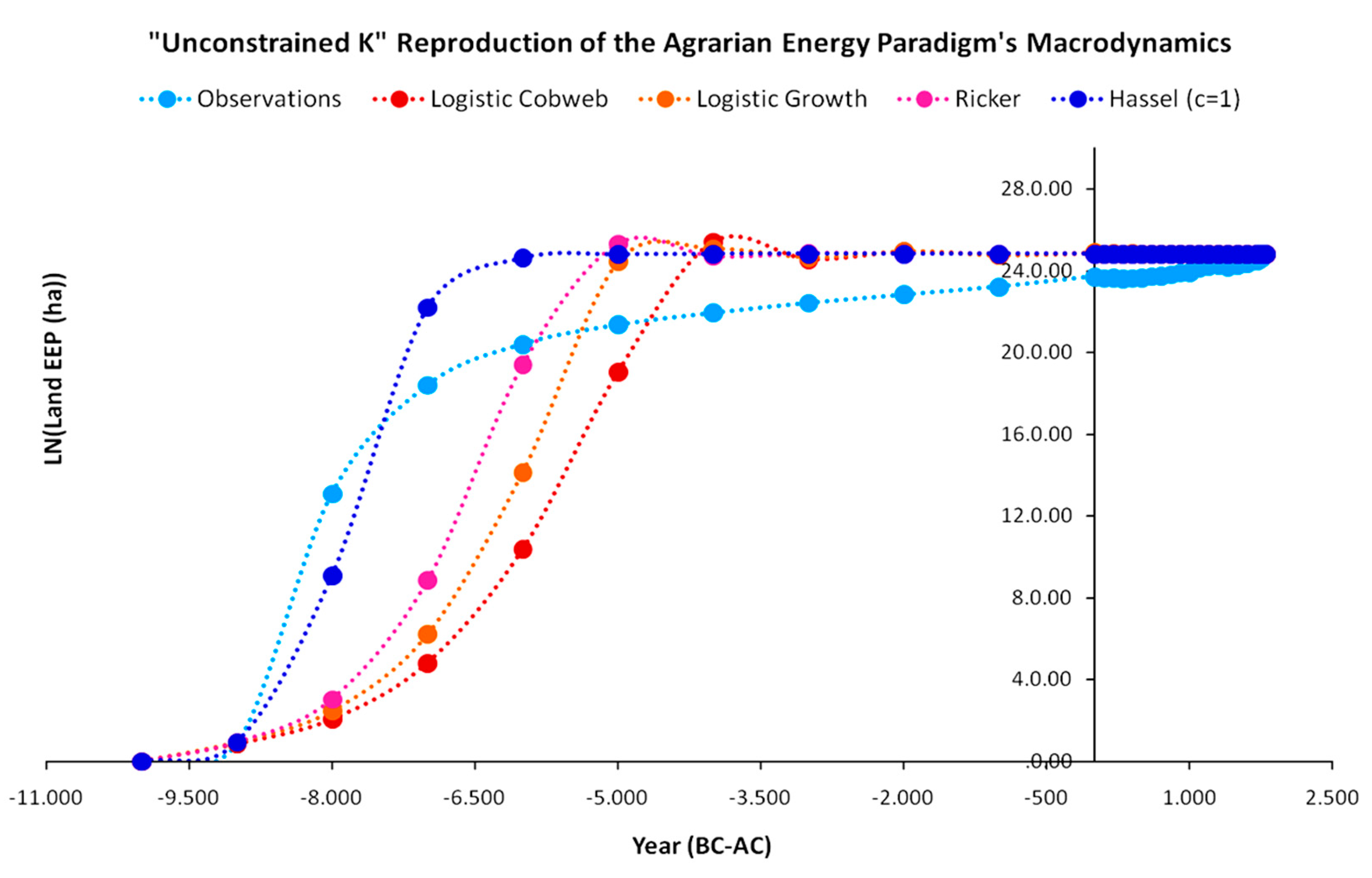
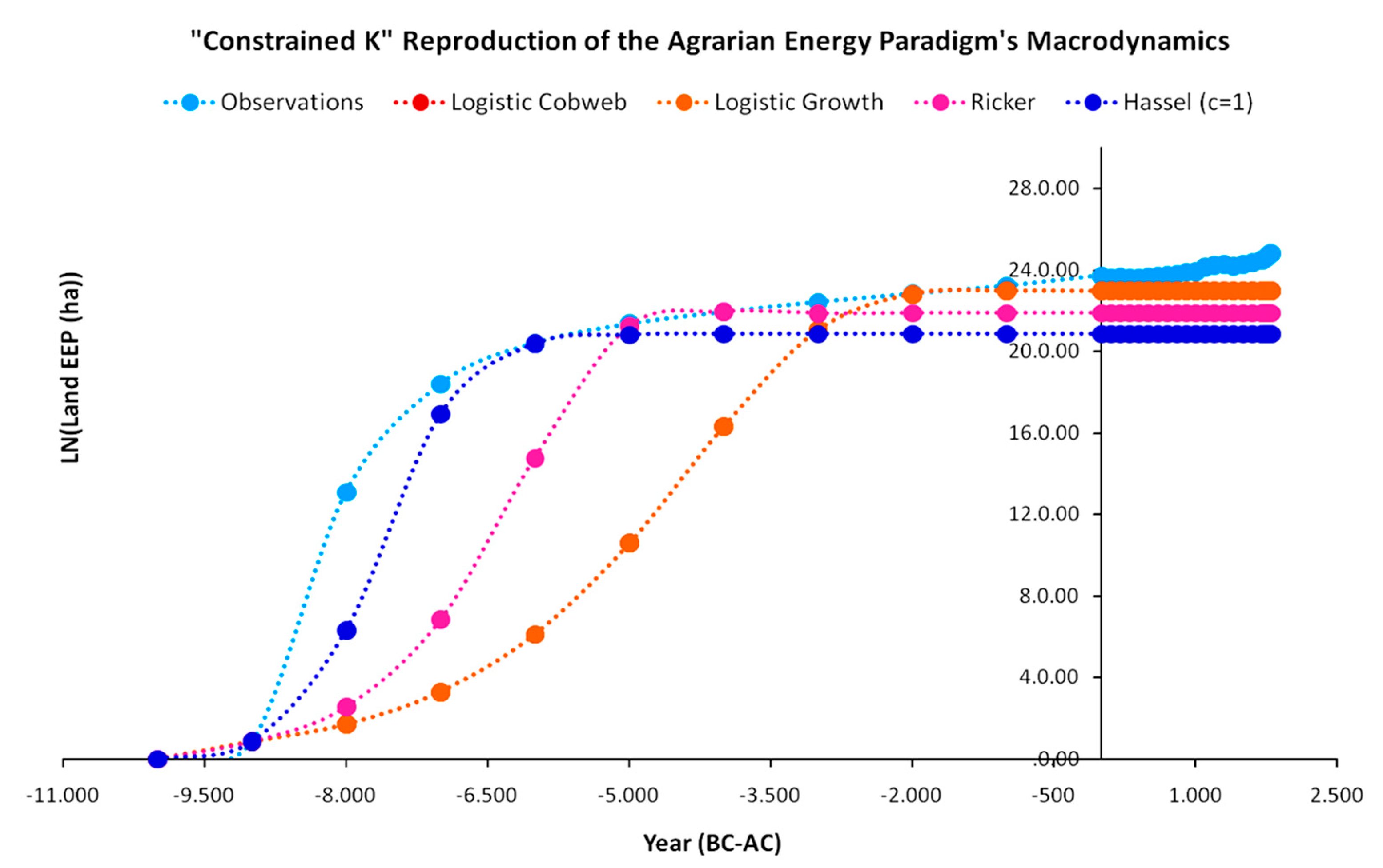
3.1. Energy Equivalent Population Growth Model Fits
3.2. Carrying Capacity Mechanics: The Limiting Factor
4. Discussion
4.1. Energy Paradigm Scale
4.2. Competition and Stability
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Energy Equivalent Population Maps
Appendix A.1. The Logistic Cobweb Map

Appendix A.2. The Logistic Growth Map
Appendix A.3. The Beverton–Holt Map (Hassel Map (c = 1))

Appendix A.4. The Ricker Map

Appendix B. Energy, Intrinsic Growth Rate and Carrying Capacity

| Population Map | OSMP Formula | OSMP Parameter a | TSMP/OSMP Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic Cobweb | (a − 1)/2b | a = 2 | [(1 − a)/(−b)]/(a/2b) |
| Logistic Growth | (a + 1)/2b | a = 1 | [(a/b)]/[(a + 1)/2b] |
| Beverton–Holt | (a − 1)/b | a ∝ Et | [(a−1)/b]/[a/(1 + b∙Et−1)2] |
| Ricker | 1/b | a = e~2.71 | ln(a) |
References
- White, L. The Evolution of Culture: The Development of Civilization to the Fall of Rome; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1959; ISBN 0-07-069682-9. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, H.L. Ancient Society; KP Bagghi & Company: New Delhi, India, 1877. [Google Scholar]
- White, K.D. The Efficiency of Roman Farming under the Empire. Agric. Hist. 1956, 30, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Tainter, J. The Collapse of Complex Societies; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1988; ISBN 978-0521386739. [Google Scholar]
- Karakatsanis, G. Exergy and the economic process. Energy Procedia 2016, 97, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kümmel, R. The Second Law of Economics: Energy, Entropy and the Origins of Wealth; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-1441993649. [Google Scholar]
- Chaisson, E.J. Complexity: An Energetics Agenda. Complexity 2004, 9, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigogine, I. Time, Structure and Fluctuations. Science 1978, 201, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgescu-Roegen, N. The Entropy Law and the Economic Process; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1971; ISBN 9780674281653. [Google Scholar]
- Karakatsanis, G. Energy and the Capital of Nations; European Geosciences Union (EGU) General Assembly: Vienna, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, E.C. Land Use and Ecological Change: A 12,000-Year History. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2021, 46, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, H.J.; Robinson, E.; Kelly, R.L. Agriculture, population growth, and statistical analysis of the radiocarbon record. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, E.C.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Goldewijk, K.K. Anthropogenic Biomes: 10,000 BCE to 2015 CE. Land 2020, 9, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopfenberg, R. An expansion of the demographic transition model: The dynamic link between agricultural productivity and population. Biodiversity 2015, 15, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krausmann, F. Milk, Manure, and Muscle Power. Livestock and the Transformation of Preindustrial Agriculture in Central Europe. Hum. Ecol. 2004, 32, 735–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, E.; Gunilla, A. Agro-Ecosystems from Neolithic Time to the Present. Ecol. Bull. 1991, 41, 293–314. [Google Scholar]
- Haswell, M. Energy for Subsistence, 2nd ed.; Palgrave Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 1985; ISBN 978-0333384275. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, E. Environment, Subsistence and System: The Ecology of Small-Scale Social Formations; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1982; ISBN 978-0521287036. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, P. From Subsistence to Exchange; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2000; ISBN 978-0691117829. [Google Scholar]
- Clarck, C. The Economics of Subsistence Agriculture, 4th ed.; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 1970; ISBN 978-0333116586. [Google Scholar]
- Bowles, S.; Choi, J.K. Coevolution of farming and private property during the early Holocene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 22, 8830–8835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sargentis, F.G.; Iliopoulou, T.; Dimitriadis, P.; Mamassis, N.; Koutsoyiannis, D. Stratification: An Entropic View of Society’s Structure. World 2021, 2, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.A.; Rising, J. Tipping point dynamics in global land use. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 125012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kümmel, R.; Ayres, R.U.; Lindenberger, D. Thermodynamic Laws, Economic Methods and the Productive Power of Energy. J. Non-Equilib. Thermodyn. 2010, 35, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odum, H.T. Environment, Power & Society for the 21st Century: The Hierarchy of Energy; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0231128872. [Google Scholar]
- Odum, H.T. Environmental Accounting: Emergy and Environmental Decision Making; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1996; ISBN 0-471-11442-1. [Google Scholar]
- Odum, H.T. Environment, Power & Society; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1971; ISBN 0-471-65270-9. [Google Scholar]
- Our World in Data (OWiD). Global Primary Energy Consumption by Source. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/global-energy-substitution (accessed on 5 August 2023).
- Our World in Data (OWiD). Land use over the long-term, 10,000BCE to 2016. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/land-use-over-the-long-term?time=earliest..latest (accessed on 5 August 2023).
- Goldewijk, K.K.; Beusen, A.; Doelman, J.; Stehfest, E. Anthropogenic land use estimates for the Holocene-HYDE 3.2. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2017, 9, 927–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Our World in Data (OWiD). Land Use of Foods per 1000 Kilocalories. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/land-use-kcal-poore (accessed on 5 August 2023).
- Poore, J.; Nemecek, T. Reducing food’s environmental impacts through producers and consumers. Science 2018, 360, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smil, V. Energy in World History; Westview Press: Boulder, CO, USA, 1994; ISBN 0-8133-1901-3. [Google Scholar]
- Smil, V. Energy and Civilization: A History; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; ISBN 9780262035774. [Google Scholar]
- Smil, V. Energy Transitions; Greenwood Publishing Group: Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-313-38178-2. [Google Scholar]
- Chaisson, E.J. Long-Term Global Heating from Energy Usage. Eos Trans AGU 2011, 89, 253–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadows, D.H.; Meadows, L.D.; Randers, J.; Behrens, W.W., III. The Limits to Growth: A Report for the Club of Rome’s Project on the Predicament of Mankind; Universe Books: New York, NY, USA, 1972; ISBN 0-87663-165-0. [Google Scholar]
- Crutzen, P.J. Geology of mankind. Nature 2002, 415, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, J.; Williams, A.; Hughes, J.K.; Black, M.; Murphy, R. Energy and the food system. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2010, 365, 2991–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, D.; Hurd, L.E.; Bellotti, A.C.; Forster, M.J.; Oka, I.N.; Whitman, R.J. Food Production and the Energy Crisis. Science 1973, 182, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Molina, M.G.; Toledo, M.; Toledo, V.M. The Social Metabolism: A Socio-Ecological Theory of Historical Change; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-3-319-06358-4. [Google Scholar]
- Lindeman, R.L. The Trophic-Dynamic Aspect of Ecology. Ecology 1942, 23, 399–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, D.; Pimentel, M.H. Food, Energy and Society, 3rd ed.; CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-1-4200-4667-0. [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport, R.A. The Flow of Energy in an Agricultural Society. Sci. Am. 1971, 225, 116–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Pig Site. Back to the Basics of Feeding Pigs. Available online: https://www.thepigsite.com/articles/back-to-the-basics-of-feeding-pigs (accessed on 5 August 2023).
- Baez, J.C. Renyi Entropy and Free Energy (v4). Quantum Physics (quant-ph). arXiv 2011, arXiv:1102.2098v4. [Google Scholar]
- Michael Gizicki-Neundlinger, Simone Gingrich, Dino Güldner, Fridolin Krausmann & Enric Tello. Land, food and labour in pre-industrial agro-ecosystems: A socio-ecological perspective on early 19th century seigneurial systems. Hist. Agrar. 2017, 71, 37–78.
- Apostolides, A.; Cambell, B.; Broadberry, S.; Overton, M.; van Leeuwen, B. English Agricultural Output and Labour Productivity, 1250-1850: Some Preliminary Estimates. Reconstructing the National Income of Britain and Holland, c. 1270/1500 to 1850; Reference Number F/00215AR. 2008. Available online: https://www.basvanleeuwen.net/bestanden/agriclongrun1250to1850.pdf26November2008 (accessed on 23 June 2023).
- Our World in Data. (OWiD). Population, 10,000BCE to 2021. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/population (accessed on 5 August 2023).
- Fisher, J.C.; Pry, R.H. A Simple Substitution Model of Technological Change. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 1971, 3, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprinkle, J.E. Matching forage Resources with cow herd Supplementation. Arizona Cooperative Extension; The University of Arizona, College of Agriculture and Life Sciences. Available online: https://extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az9523-2015_0.pdf (accessed on 5 August 2023).
- Extension. Nutrition for Backyard Chicken Flocks. Alabama A&M & Auburn Universities. Available online: https://www.aces.edu/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/ANR-1317_NutritionforBackyardChickenFlocks_071222aL.pdf (accessed on 5 August 2023).
- Tuomisto, H.L.; de Mattos, M.J.T. Environmental Impacts of Cultured Meat Production. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 6117–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakatsanis, G. Energy and the Agroeconomic Complexity of Ehiopia; European Geosciences Union (EGU) General Assembly: Vienna, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, G.; van Buren, A. Energy in the Transition from Rural Subsistence. Dev. Policy Rev. 1982, A15, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotka, A.J. Contribution to the Energetics of Evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 8, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontarakis, E.; Karakatsanis, G.; Dimitriadis, P.; Iliopoulou, T.; Koutsoyiannis, D. Hydroclimate and Agricultural Output in Developing Countries; European Geosciences Union (EGU) General Assembly: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotayev, A.; Malkov, A.; Khaltourina, D. Introduction to Social Macrodynamics: Secular Cycles and Millennial Trends. Editorial URSS: Moscow, Russian Federation. 2006. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/233821695_Introduction_to_social_macrodynamics_Secular_cycles_and_millennial_trends (accessed on 5 August 2023).
- Anazawa, M. Inequality in resource allocation and population dynamics models. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 182178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebig, J. Organic Chemistry in its Applications to Agriculture and Physiology; Taylor & Walton: London, UK, 1840. [Google Scholar]
- Our World in Data (OWiD). Freshwater Withdrawals of Foods per 1000 kilocalories. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/freshwater-withdrawals-per-1000kcal (accessed on 5 August 2023).
- Our World in Data (OWiD). Eutrophying Emissions per 1000 Kilocalories. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/eutrophying-emissions-kcal (accessed on 5 August 2023).
- Halter, A.N.; Carter, H.O.; Hocking, J.G. A Note on the Transcendental Production Function. J. Farm Econ. 1957, 39, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debertin, D.L. Agricultural Production Economics, 2nd ed.; Macmillan Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 0-02-328060-3. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, M.; Gaëlle, N.; Cinardi, G.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Vanwambeke, S.O.; Wint, G.R.W.; Robinson, T.P. Global distribution data for cattle, buffaloes, horses, sheep, goats, pigs, chickens and ducks in 2010. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakatsanis, G.; Mamassis, N. Energy, trophic dynamics and ecosystem services. Land 2023. submitted, under review. [Google Scholar]
- Işik, C.; Kasimati, E.; Ongan, S. Analyzing the causalities between economic growth, financial development, international trade, tourism expenditure and/on the CO2 emissions in Greece. Energy Sources Part B Econ. Plan. Policy 2017, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, C.W.J.; Newbold, P. Spurious Regressions in Econometrics. J. Econom. 1974, 2, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, R. Simple Mathematical Models With Very Complicated Dynamics. Nature 1976, 261, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassel, M.P. Density-Dependence in Single-Species Populations. J. Anim. Ecol. 1975, 44, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricker, W.E. Stock and Recruitment. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1954, 11, 559–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackey, M.C. Time’s Arrow: The Origins of Thermodynamic Behavior; Dover Publications Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1992; 2003 reprint; ISBN 0-486-43243-2. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J.L.; Newman, C.M. When will a large complex system be stable? J. Theor. Biol. 1985, 113, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisstein, E.W.; Lambert W-Function. From MathWorld-A Wolfram Web Resource. Available online: https://mathworld.wolfram.com/LambertW-Function.html (accessed on 5 August 2023).
- Hardin, G. The Tragedy of the Commons. Science 1968, 162, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
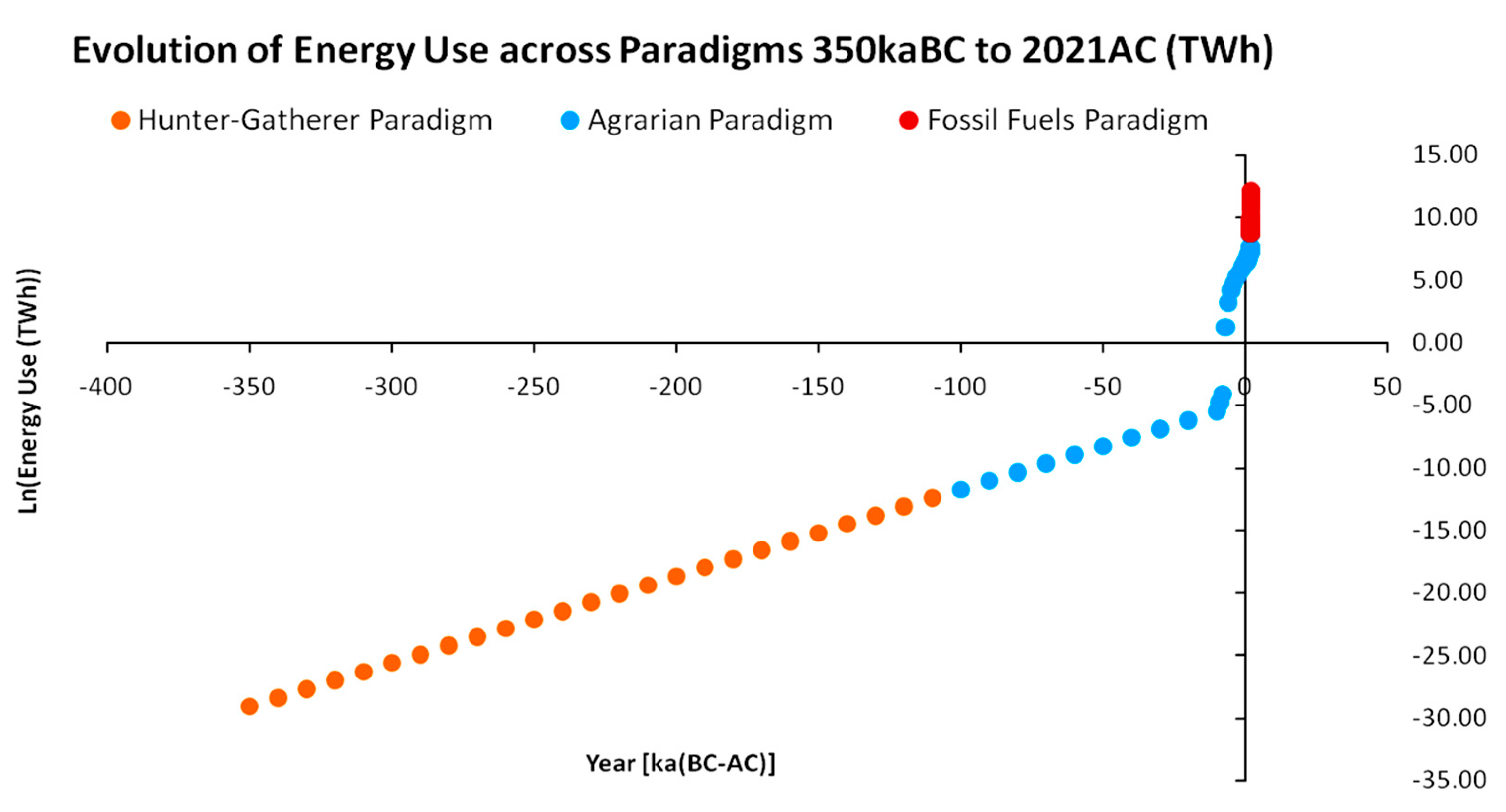
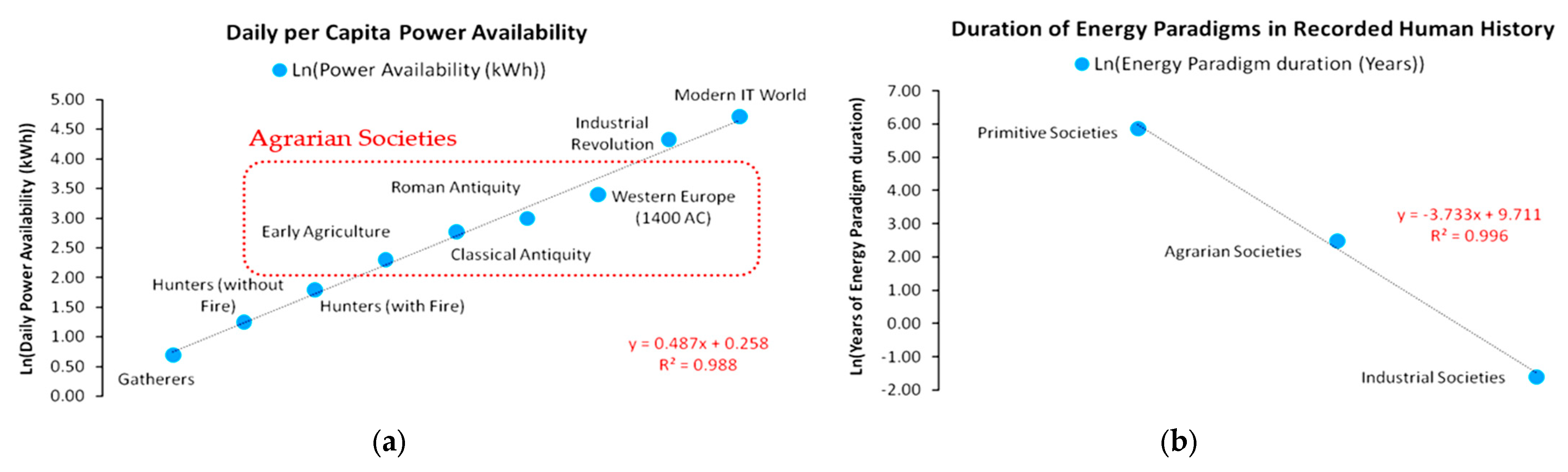
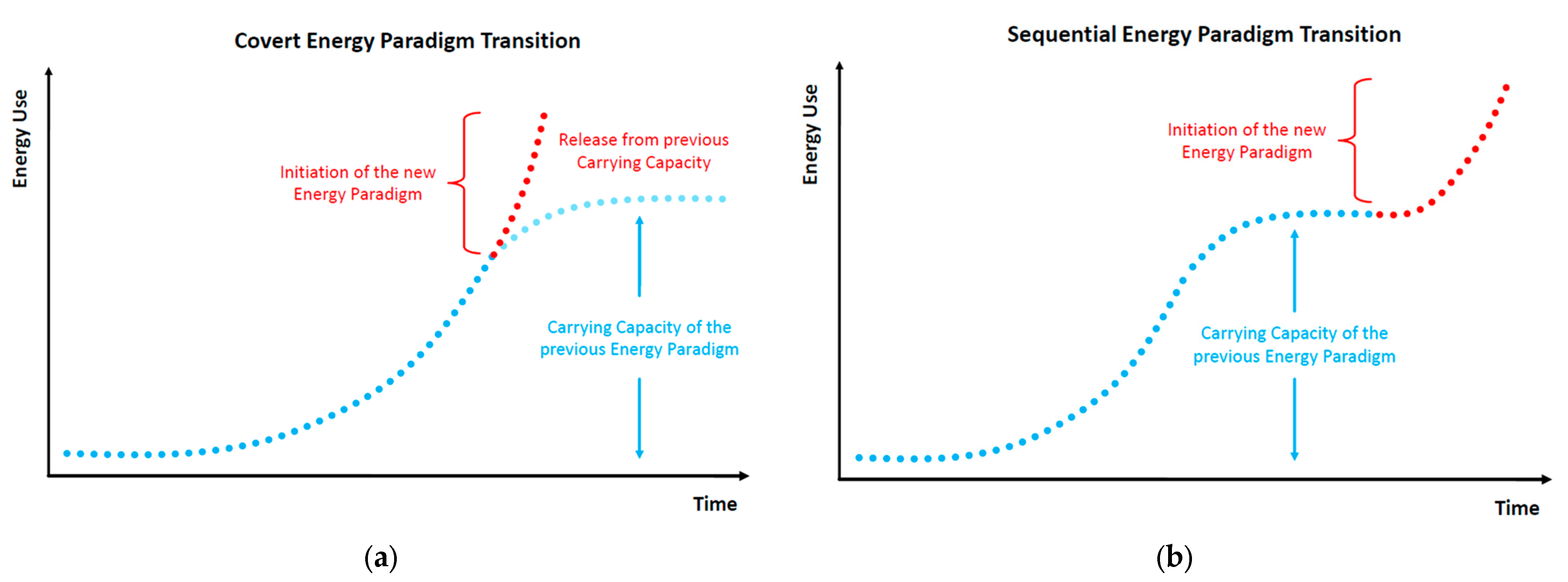
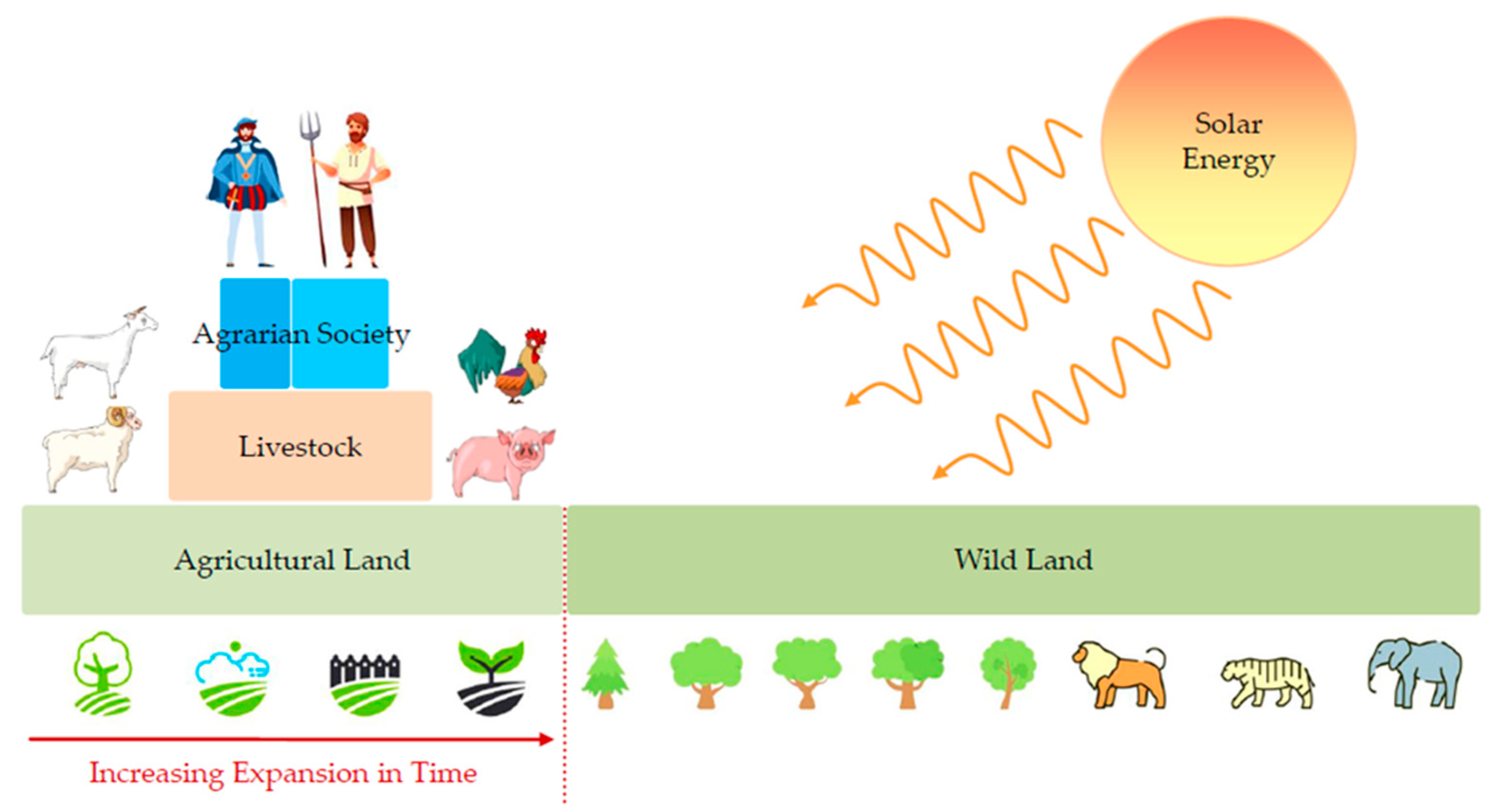
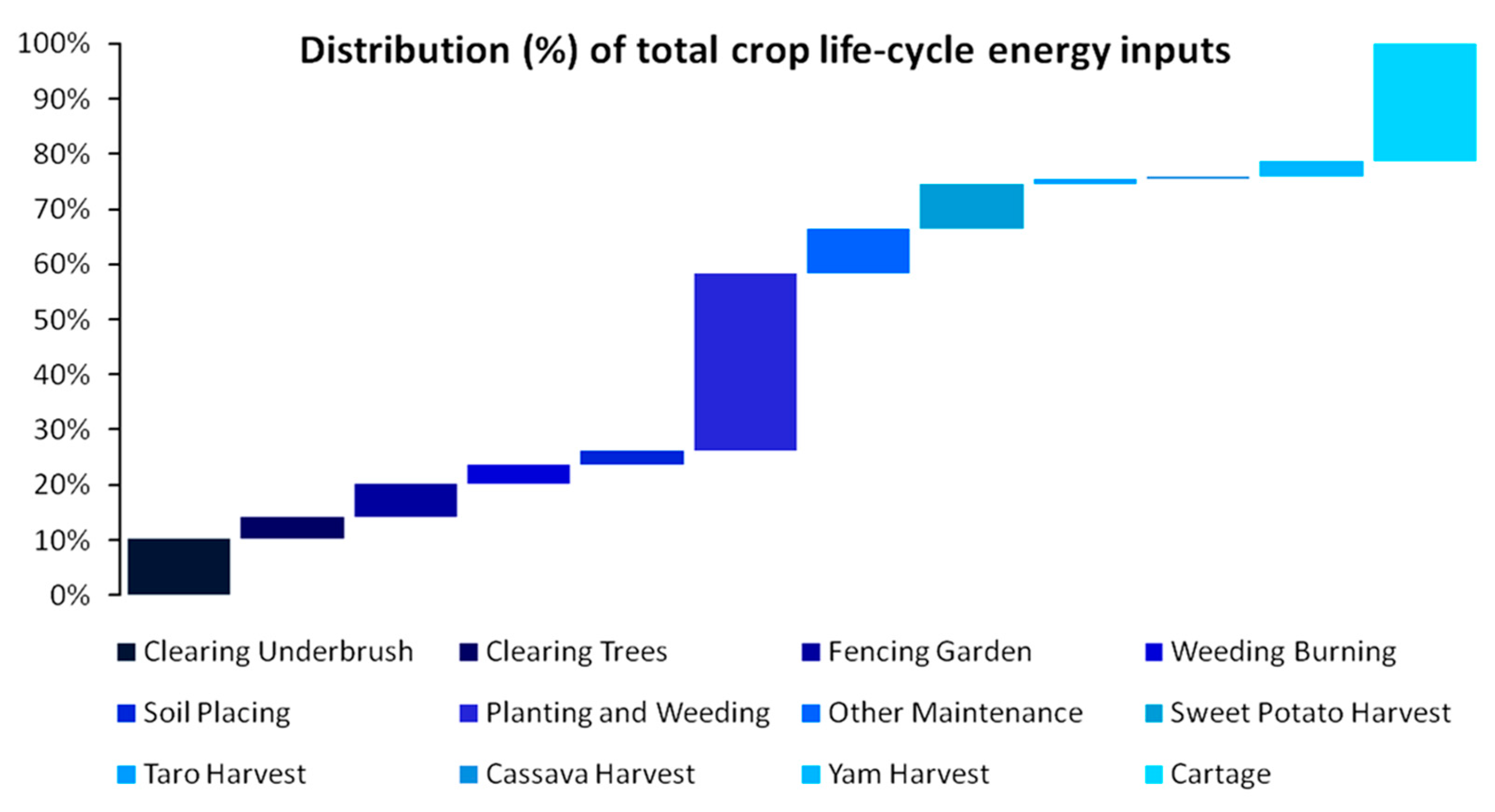
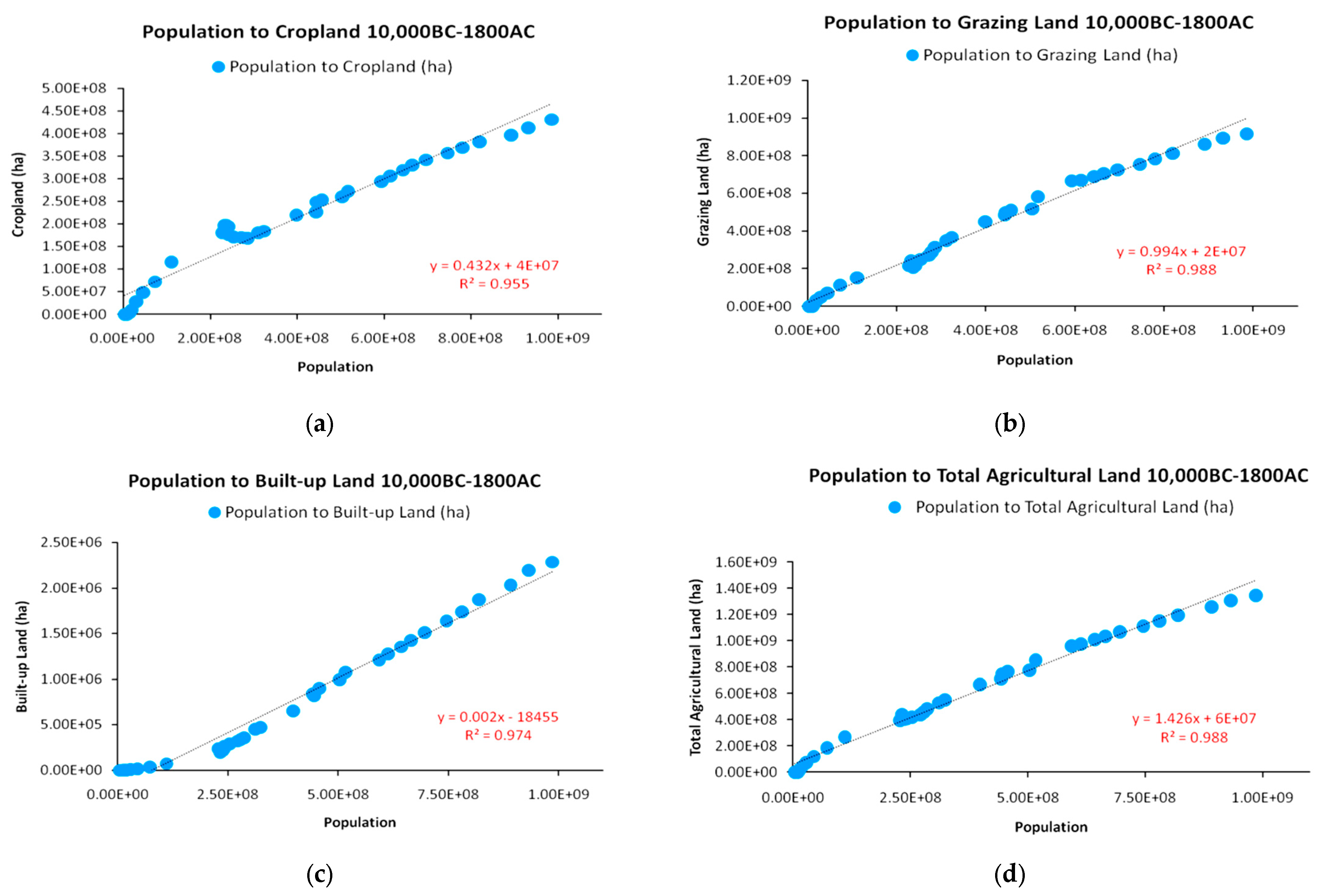
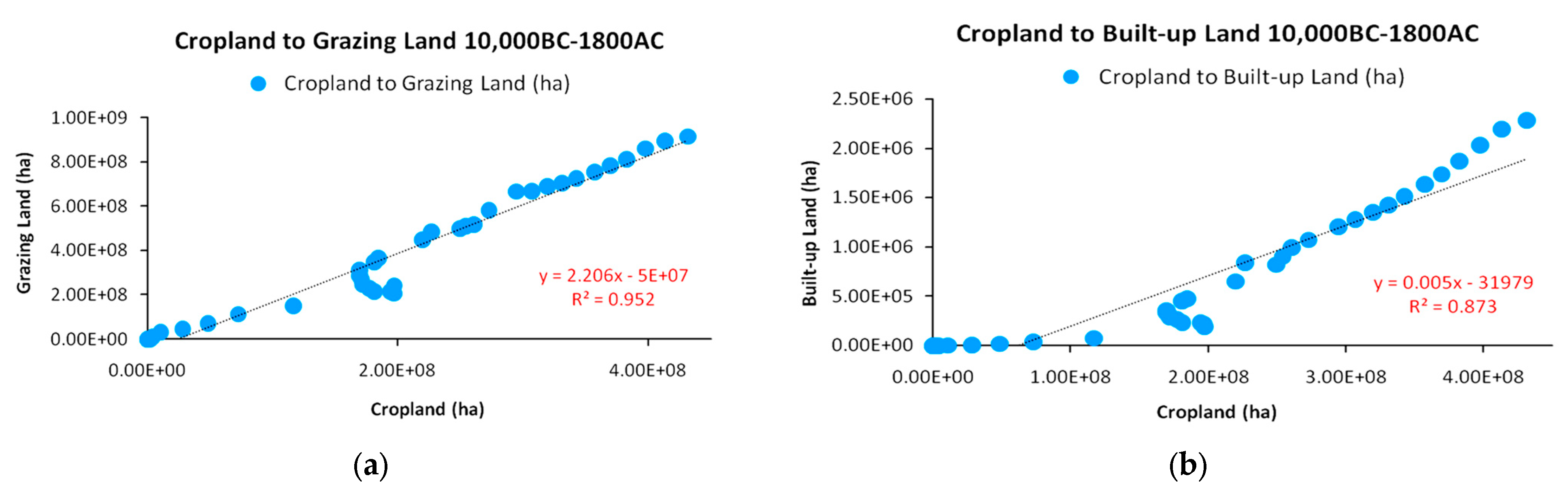
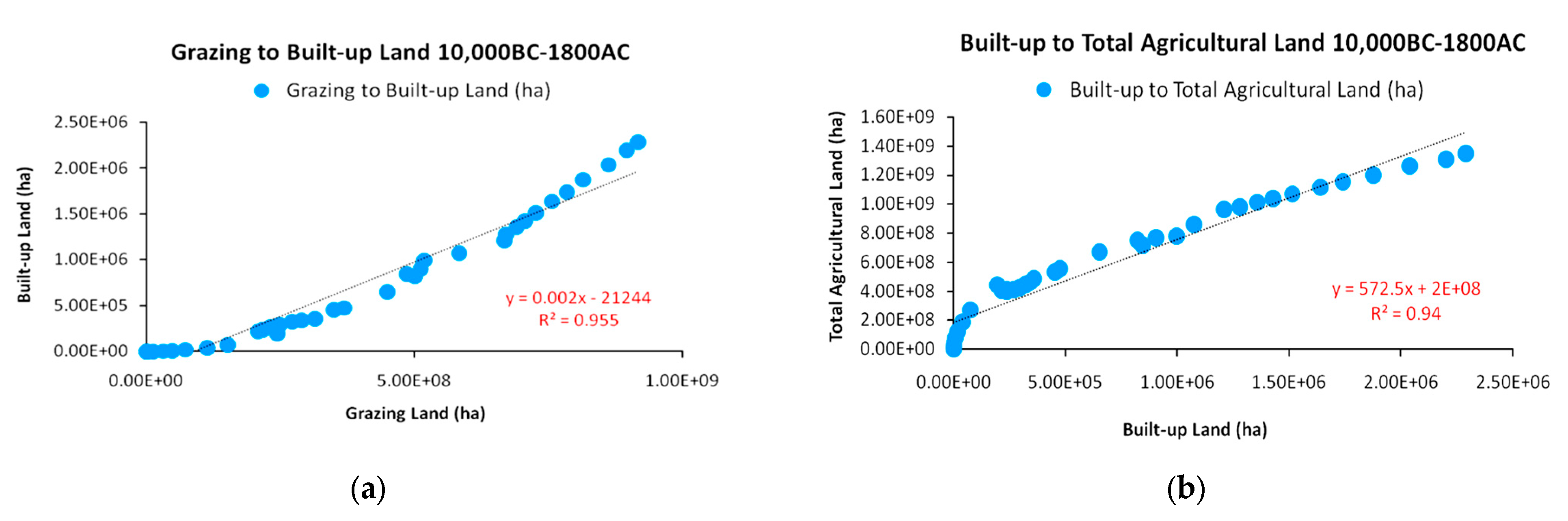


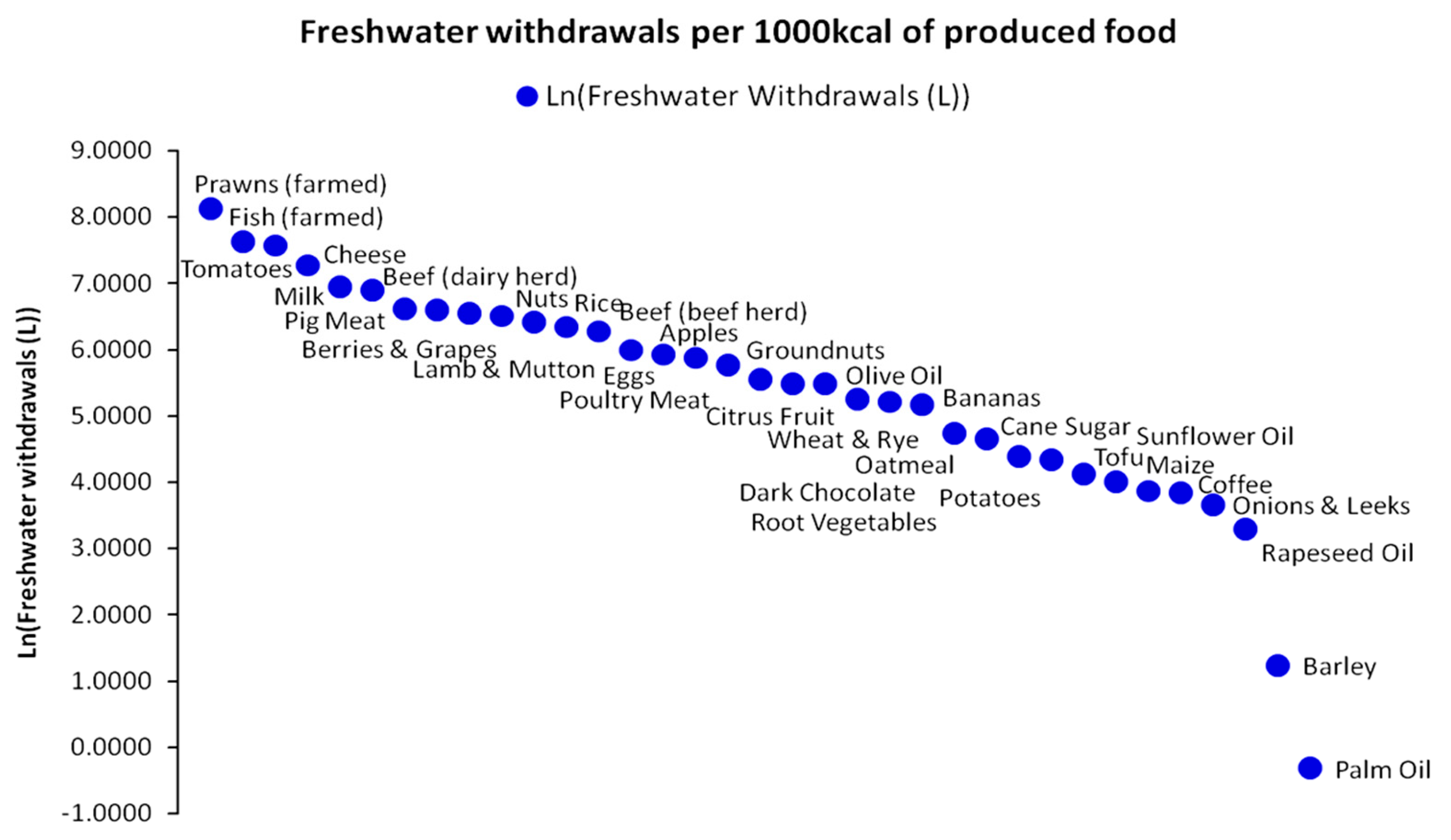
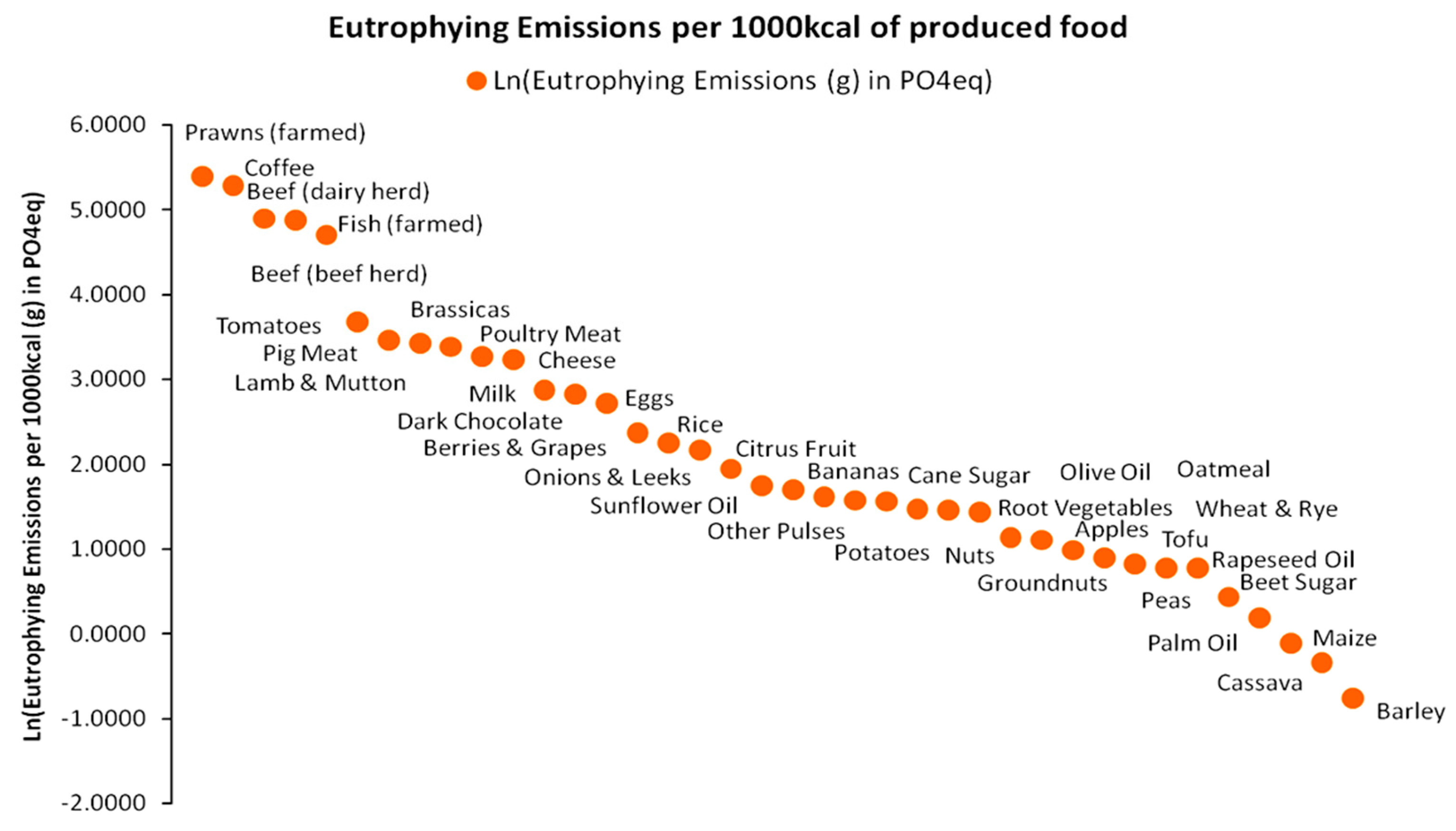
| Population Map | Parameter a | Parameter b | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic Cobweb | 2.4354 | 0.0578 | 0.8924 |
| Logistic Growth | 1.6931 | 0.0681 | 0.9115 |
| Beverton–Holt (Hassel c = 1) | 14.6546 | 0.5499 | 0.9752 |
| Ricker | 3.3850 | 0.0491 | 0.9338 |
| Population Map | Parameter a | Parameter b | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic Cobweb | 2.0000 | 0.0435 | 0.8559 |
| Logistic Growth | 1.0000 | 0.0435 | 0.8559 |
| Beverton–Holt (Hassel c = 1) | 9.9311 | 0.4281 | 0.9741 |
| Ricker | 3.0599 | 0.0511 | 0.9271 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karakatsanis, G.; Mamassis, N. Energy and the Macrodynamics of Agrarian Societies. Land 2023, 12, 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12081603
Karakatsanis G, Mamassis N. Energy and the Macrodynamics of Agrarian Societies. Land. 2023; 12(8):1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12081603
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarakatsanis, Georgios, and Nikos Mamassis. 2023. "Energy and the Macrodynamics of Agrarian Societies" Land 12, no. 8: 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12081603
APA StyleKarakatsanis, G., & Mamassis, N. (2023). Energy and the Macrodynamics of Agrarian Societies. Land, 12(8), 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12081603







