Coupling Coordination and Spatiotemporal Analysis of Urban Compactness and Land-Use Efficiency in Resource-Based Areas: A Case Study of Shanxi Province, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Evaluation Index System Data Sources
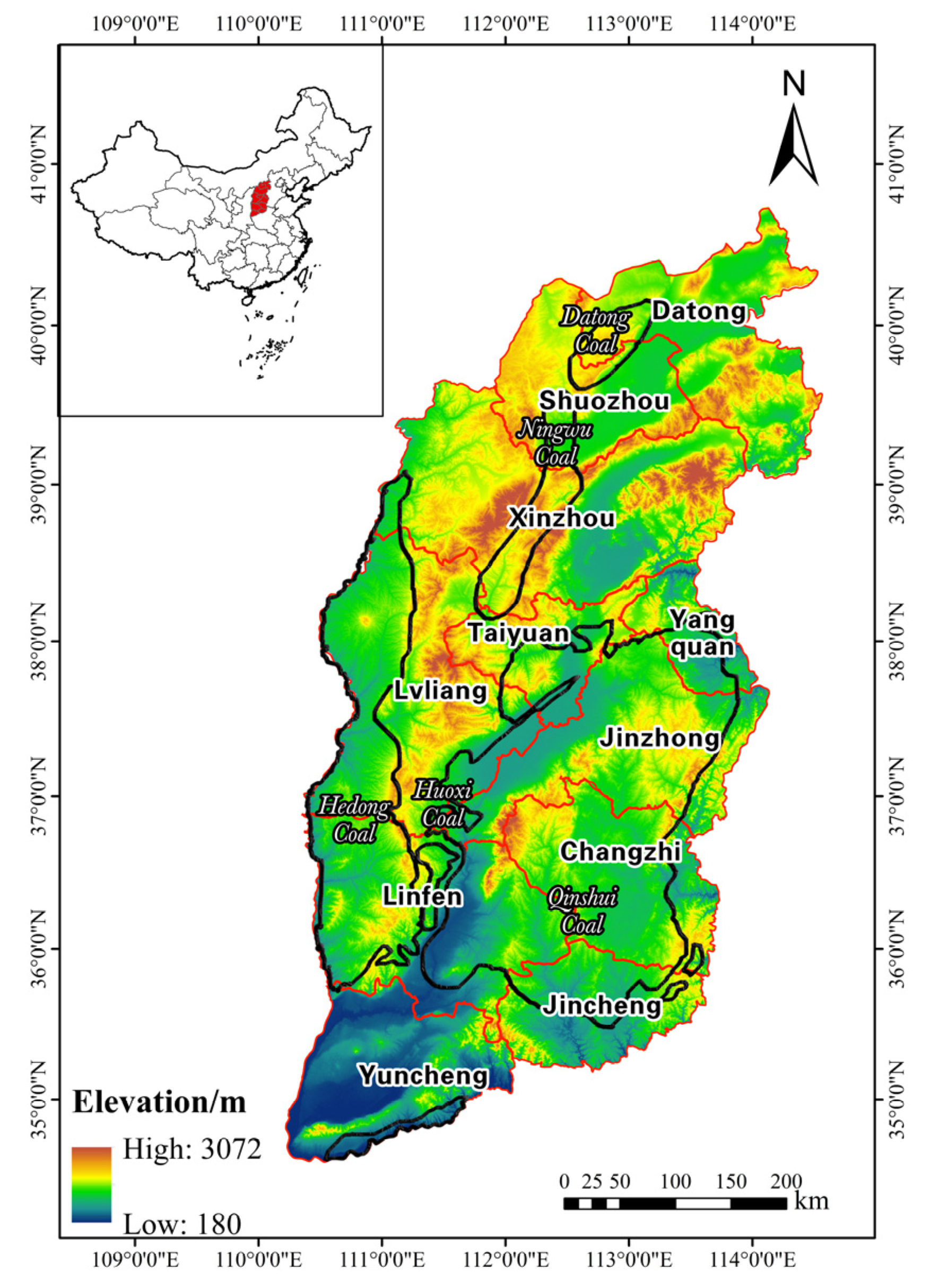
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Evaluation Index System
2.3.1. Urban Compactness Index System
2.3.2. Land-Use Efficiency Index System
3. Methods
3.1. Compactness Measurement Method
3.2. The Two-Stage Network Super-EBM Model Considering Undesirable Outputs
3.3. Coupling-Coordination Degree Model (CCDM)
3.4. Hot-Spot Analysis
3.5. The Spatial-Divergence Characterization Method
4. Results
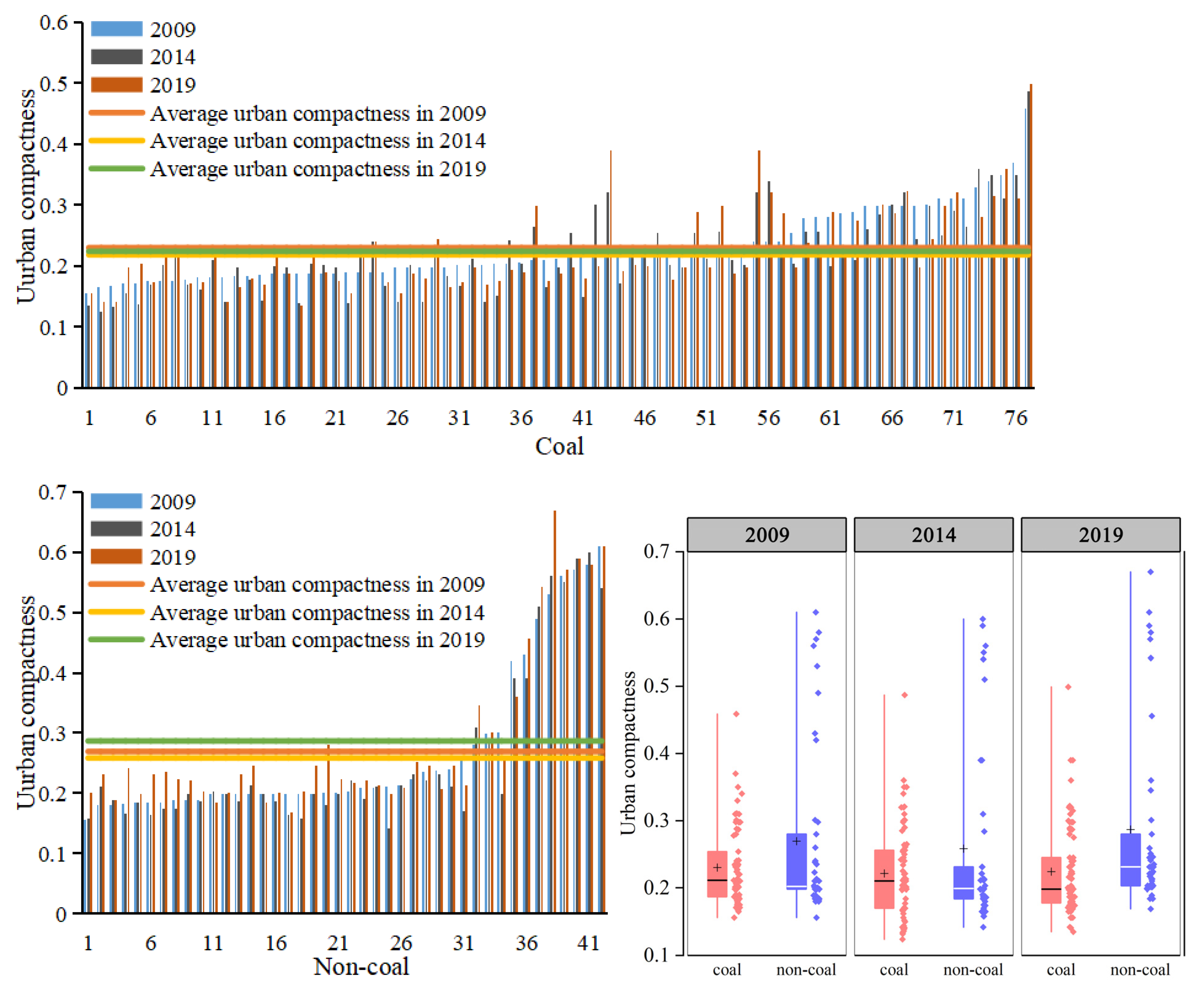
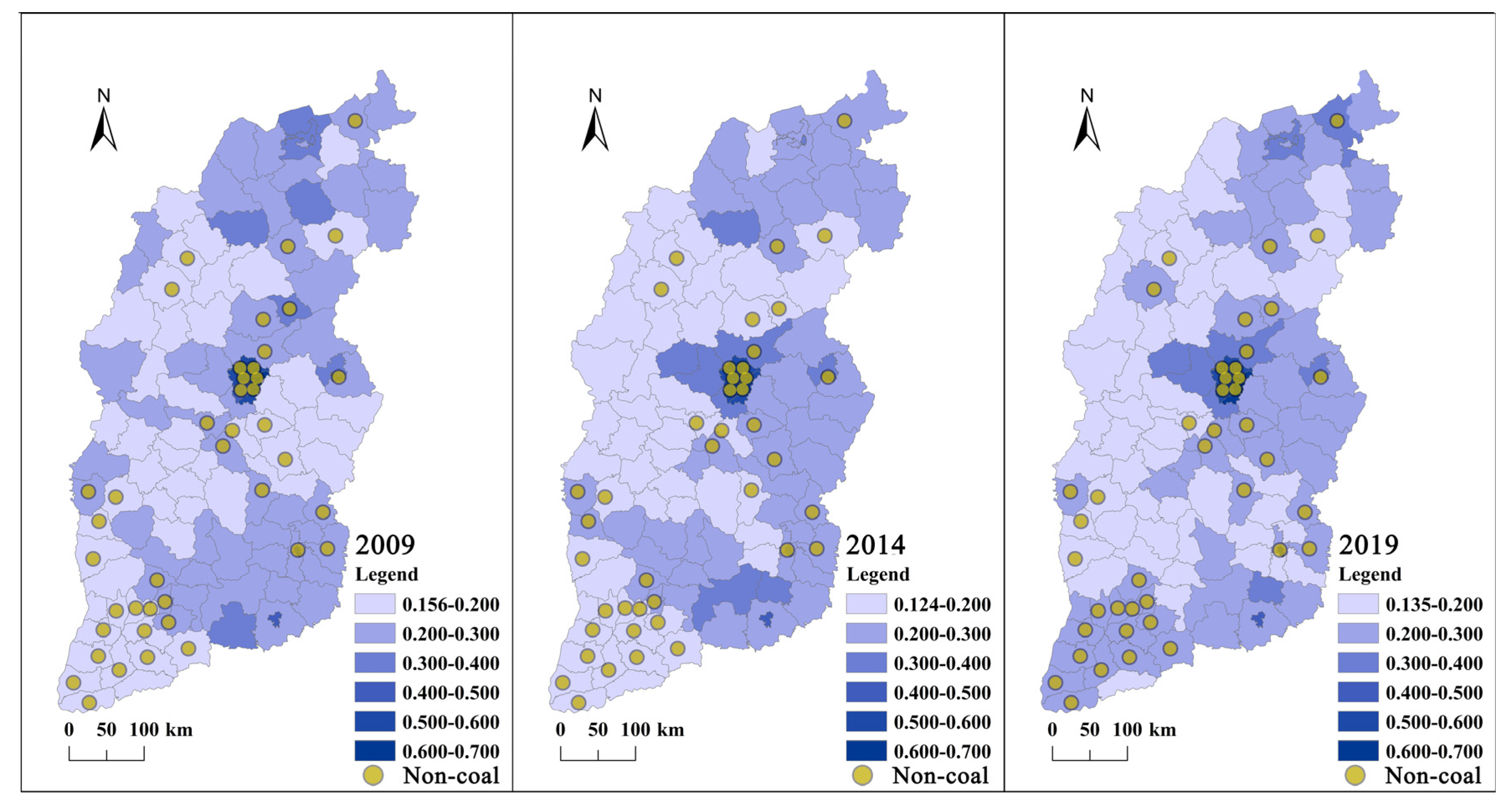
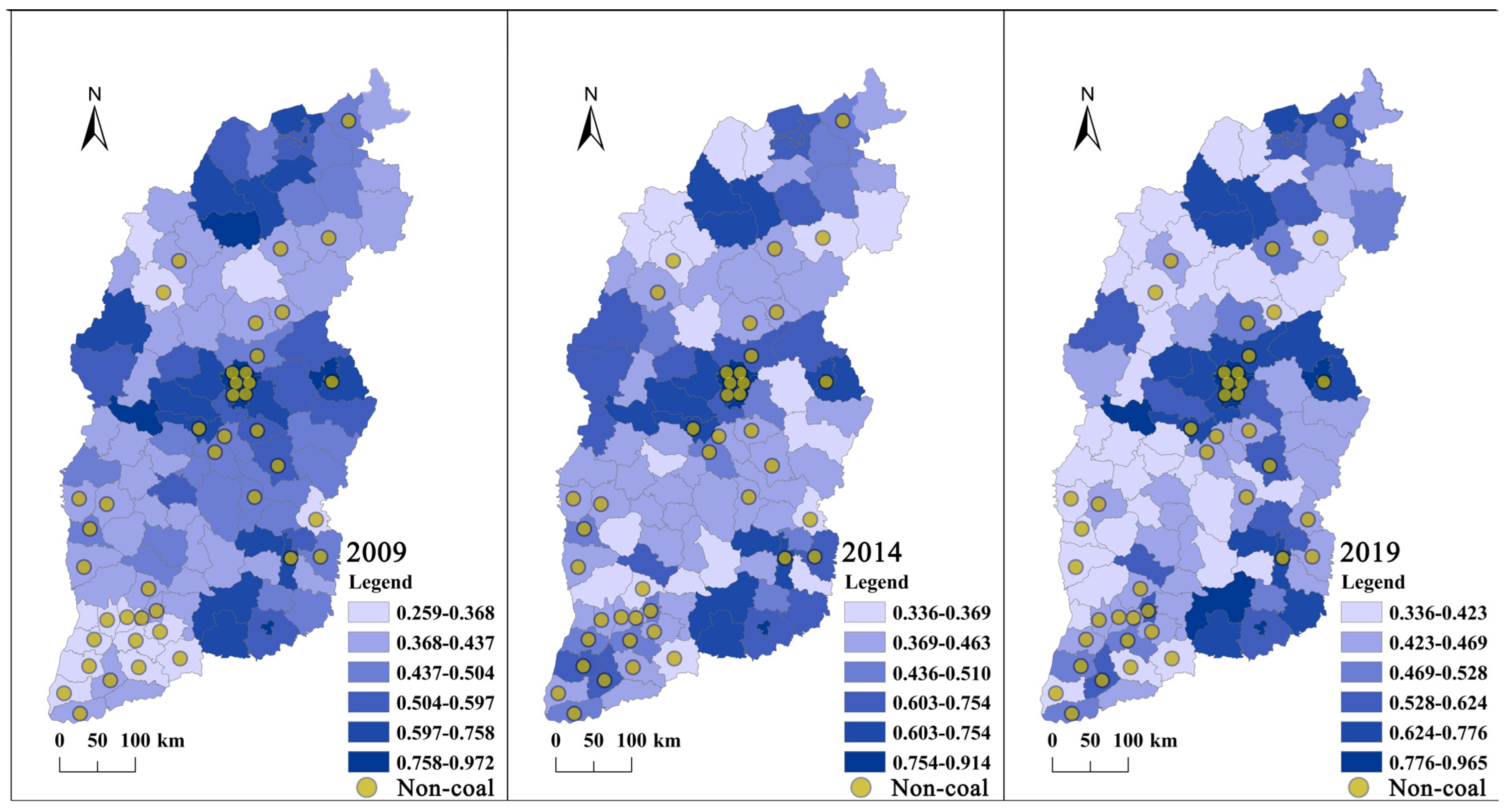
4.1. Analysis of Spatial–Temporal Changes of Urban Compactness
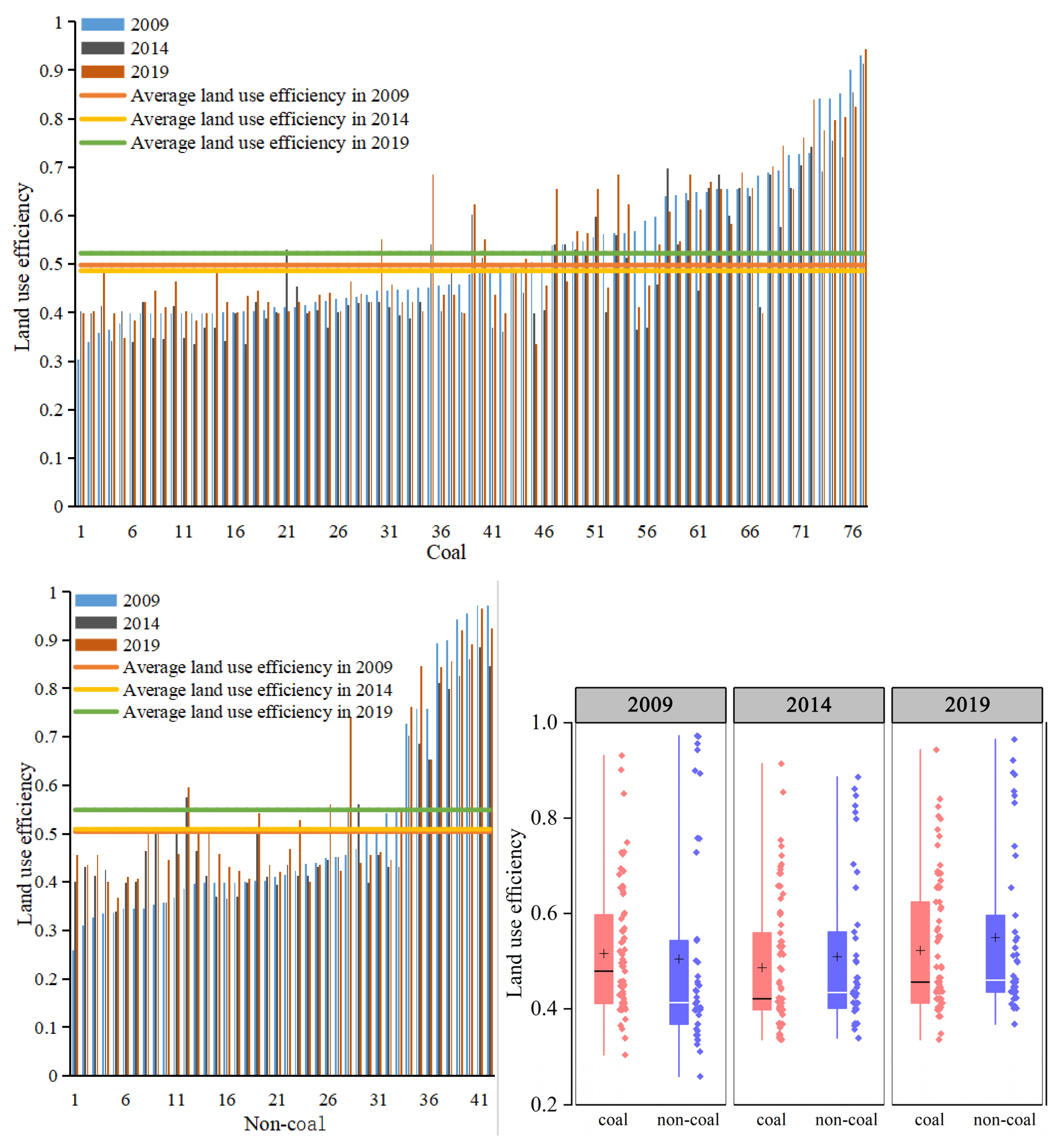
4.2. Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Changes of Land-Use Efficiency
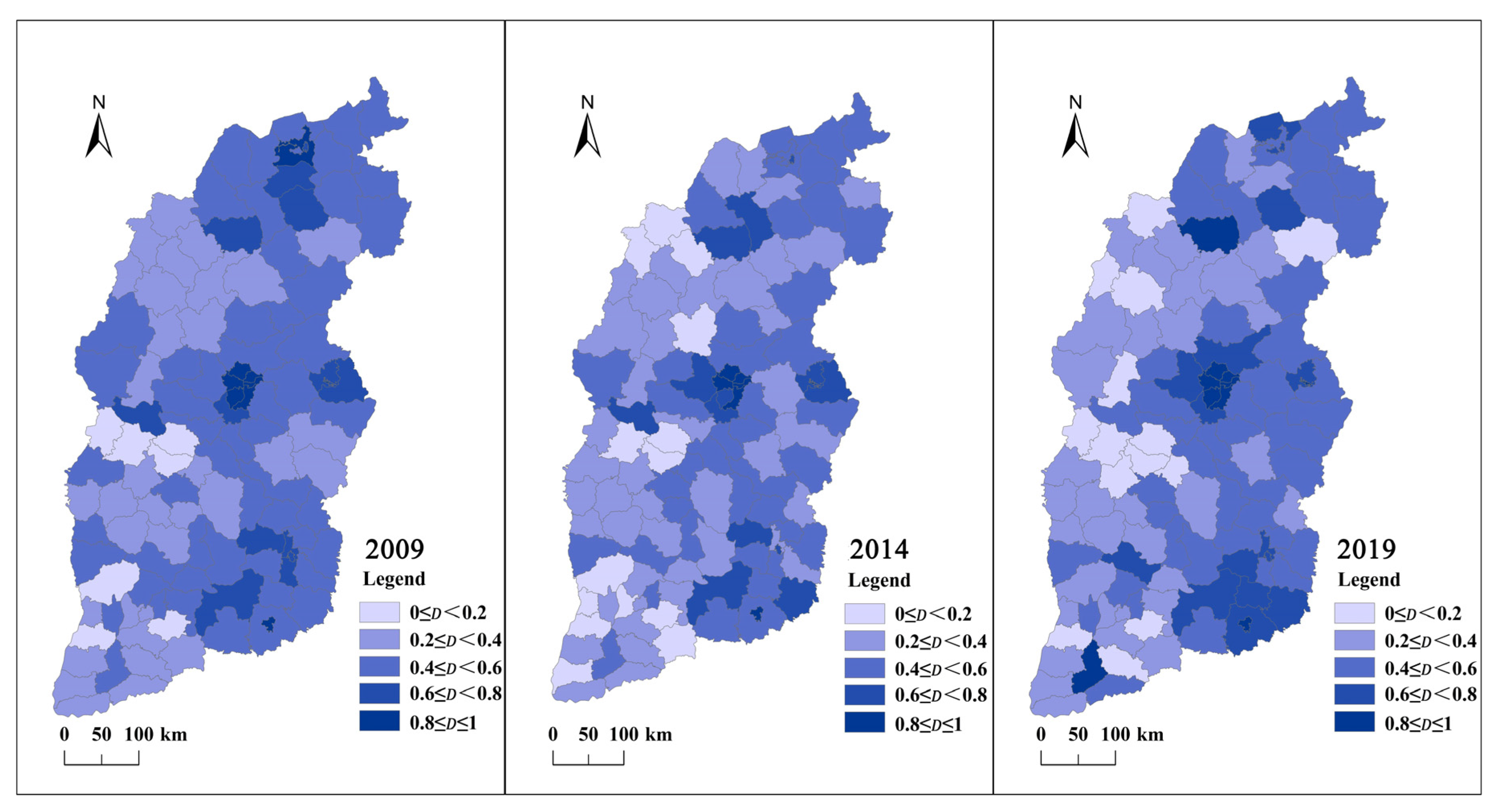
4.3. Analysis of Coupling-Coordination Degree
4.3.1. Coupling-Coordination Degree of Urban Compactness and Land-Use Efficiency
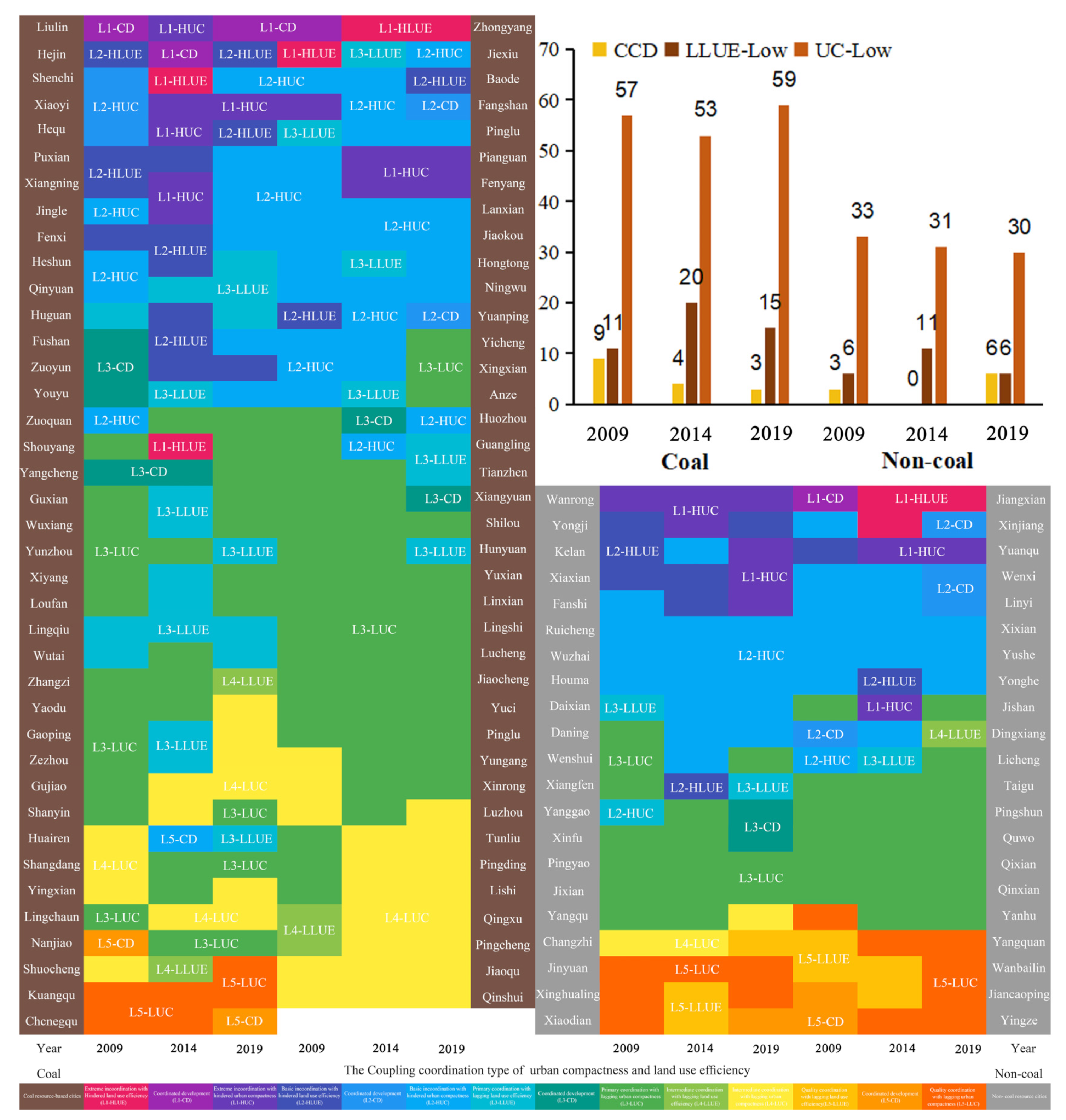
4.3.2. Coupling-Coordination Types of Urban Compactness and Land-Use Efficiency
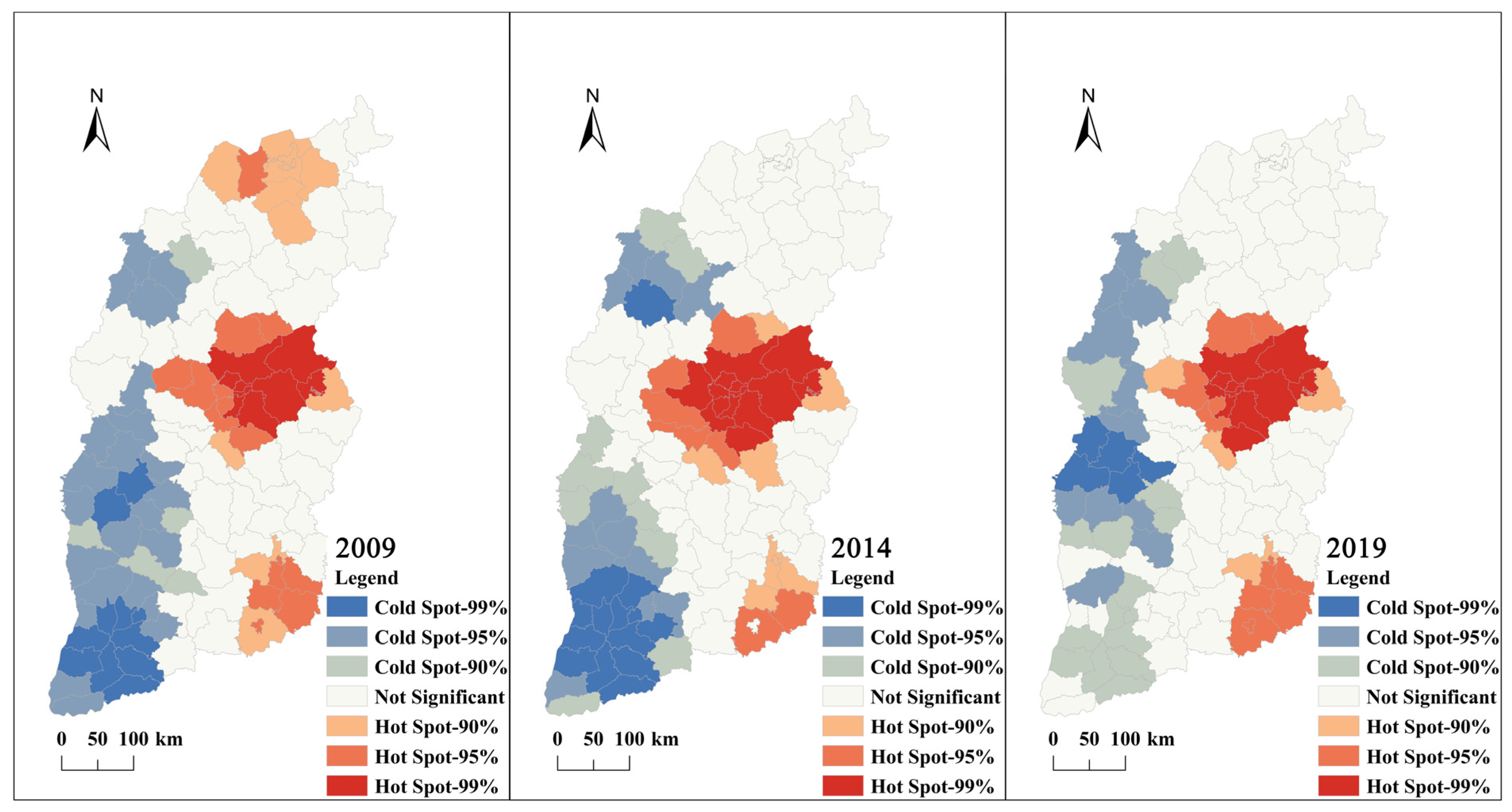
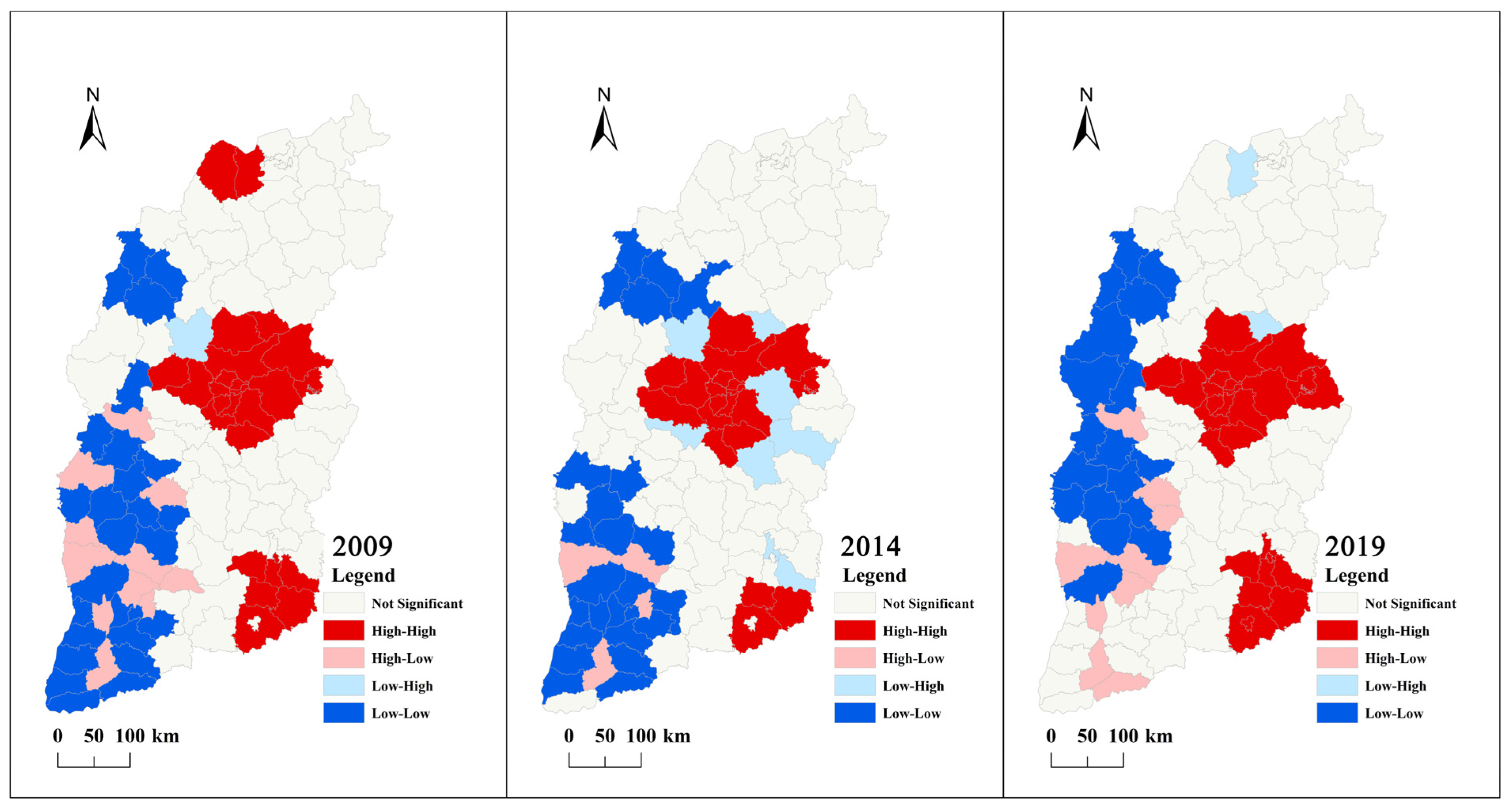
4.4. Hot-Spot Analysis
4.5. Spatial Divergence Characterization Analysis
5. Discussion
5.1. Changes in Urban Compactness
5.2. Changes in Land-Use Efficiency
5.3. Changes in Coupling-Coordination Degree
5.4. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giles-Corti, B.; Vernez-Moudon, A.; Reis, R.; Turrell, G.; Dannenberg, A.L.; Badland, H.; Foster, S.; Lowe, M.; Sallis, J.F.; Stevenson, M.; et al. City planning and population health: A global challenge. Lancet 2016, 388, 2912–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haaland, C.; van den Bosch, C.K. Challenges and strategies for urban green-space planning in cities undergoing densification: A review. Urban For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Fragkias, M.; Gueneralp, B.; Reilly, M.K. A Meta-Analysis of Global Urban Land Expansion. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, M.; Thompson, J.; de Sa, T.H.; Ewing, R.; Mohan, D.; McClure, R.; Roberts, I.; Tiwari, G.; Giles-Corti, B.; Sun, X.; et al. Land use, transport, and population health: Estimating the health benefits of compact cities. Lancet 2016, 388, 2925–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Chang, J.; Luo, P.; Kang, Y.; Li, S. Landscape dynamics and human disturbance processes in wetlands in a mining city: A case study in Huaibei, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chang, J.; Feng, S.-S. Effects of urban growth boundaries on urban spatial structural and ecological functional optimization in the Jining Metropolitan Area, China. Land Use Policy 2022, 117, 106113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Zhai, L.; Feng, S.; Walz, U. Restoration priority assessment of coal mining brownfields from the perspective of enhancing the connectivity of green infrastructure networks. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, W.; Li, B.; Duan, L.; Zhang, T.; Jia, Q. Construction Land Expansion of Resource-Based Cities in China: Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Driving Factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, M. Planning, Transformation and Development of Resource Based Industrial Cities. Open House Int. 2017, 42, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, F.; Yan, L.; Wang, D. The complexity for the resource-based cities in China on creating sustainable development. Cities 2020, 97, 102571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Hu, X.; Hassink, R.; Ni, J. Industrial structure or agency: What affects regional economic resilience? Evidence from resource-based cities in China. Cities 2020, 106, 102906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Development characteristics, influencing mechanism and coping strategies of resource-based cities in developing countries: A case study of urban agglomeration in Northeast China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 25336–25348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Jiang, X. Evaluating Sustainable Urbanization of Resource-Based Cities Based on the McKinsey Matrix: Case Study in China. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2018, 144, 05017020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouratidis, K. Built environment and social well-being: How does urban form affect social life and personal relationships? Cities 2018, 74, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouratidis, K. Compact city, urban sprawl, and subjective well-being. Cities 2019, 92, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anabtawi, S. Towards a Better Understanding of Compact Cities. J. Plan. Lit. 2023, 27, 130–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, J.D.; Debrunner, G. Planning with power. Implementing urban densification policies in Zurich, Switzerland. Land Use Policy 2022, 123, 106400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Lau, S.-K.; Chau, C.K. Potential mutual efforts of landscape factors to improve residential soundscapes in compact urban cities. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 227, 104534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, H.; Emberger, G.; Ishida, H.; Fukuda, A.; Kobayakawa, S. Dynamic simulations of compact city development to counter future population decline. Cities 2022, 127, 103753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibri, S.E.; Krogstie, J.; Karrholm, M. Compact city planning and development: Emerging practices and strategies for achieving the goals of sustainability. Dev. Built Environ. 2020, 4, 100021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.; Fuller, D. Urban form in Canada at a small-area level: Quantifying “compactness” and “sprawl” with bayesian multivariate spatial factor analysis. Environ. Plan. B-Urban Anal. City Sci. 2022, 49, 1300–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herburger, J. It’s not about compact cities. Dialogues Hum. Geogr. 2023, 13, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarlane, C. Density and the compact city. Dialogues Hum. Geogr. 2023, 13, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haarstad, H.; Kjaeras, K.; Roe, P.G.; Tveiten, K. Diversifying the compact city: A renewed agenda for geographical research. Dialogues Hum. Geogr. 2022, 13, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, E.; LeeJongyeol; Hee-Yeon, L. Measurement of Urban Form in Urban Growth Management: Urban Sprawl versus Compactness. Korea Spat. Plan. Rev. 2006, 51, 223–247. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Tang, L.; Qiu, Q.; Wu, G. The compactness of spatial structure in Chinese cities: Measurement, clustering patterns and influencing factors. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2020, 6, 1743763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.; Oh, S.E.S.; Choi, S.; Kim, B.H.S. Viability of compact cities in the post-COVID-19 era: Subway ridership variations in Seoul Korea. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2022, 71, 175–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, S.; Pradhan, B.; Mojaddadi, H. City Compactness: Assessing the Influence of the Growth of Residential Land Use. J. Urban Technol. 2018, 25, 21–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, N. Urban form revisited-Selecting indicators for characterising European cities. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 96, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.G.; Xu, G.L.; Tian, Z.Q. Built-up land efficiency in urban China: Insights from the General Land Use Plan (2006–2020). Habitat Int. 2016, 51, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Kong, Y.; Ren, X.H.; Shi, Y.K.; Chiang, S.W. The determinants of urban sustainability in Chinese resource-based cities: A panel quantile regression approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.H.; Ke, S.G. Evaluating the effectiveness of sustainable urban land use in China from the perspective of sustainable urbanization. Habitat Int. 2018, 77, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.W.; Yu, S.; Li, G.D.; Zhang, J.F. Exploring the influence of urban form on land-use efficiency from a spatiotemporal heterogeneity perspective: Evidence from 336 Chinese cities. Land Use Policy 2020, 95, 104576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Fang, B.; Xu, H.Z.Y.; He, S.S.; Li, X. Study on the coordinated relationship between Urban Land use efficiency and ecosystem health in China. Land Use Policy 2021, 102, 105235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.Q.; Zhou, K.L.; Yang, S.L. Land use efficiency and influencing factors of urban agglomerations in China. Land Use Policy 2019, 88, 104143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Fang, C.L.; Shu, T.H.; Ren, Y.T. Spatiotemporal impacts of urban structure upon urban land-use efficiency: Evidence from 280 cities in China. Habitat Int. 2023, 131, 102727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.S.; Chen, X.Y.; Wu, Y.C.; Li, S.W.; Wei, J.J.; Zhou, Q. National Modern Agricultural Industrial Parks: Development Characteristics, Regional Differences, and Experience Inspiration-Case Study of 200 NMAIPs in China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yeung, G.; Zhu, D.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L. Efficiency of urban land use in China’s resource-based cities, 2000–2018. Land Use Policy 2022, 115, 106009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhong, J.-L.; Zhang, Q.-F.; Xiang, X.; Huang, H. Exploring the coupling coordination and key factors between urbanization and land use efficiency in ecologically sensitive areas: A case study of the Loess Plateau, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 86, 104148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chen, W.J.; Ning, S.Y.; Liu, E.N.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.A.; Zhao, M.J. Exploring the industrial land use efficiency of China’s resource-based cities. Cities 2019, 93, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Yue, L.; Ahmad, F.; Draz, M.U.; Chandio, A.A.; Ahmad, M.; Amin, W. Empirical investigation of urban land use efficiency and influencing factors of the Yellow River basin Chinese cities. Land Use Policy 2022, 117, 106117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhou, G.L.; Ma, Z.P.; Sun, H.R.; Fu, H. Coordinated Relationship between Compactness and Land-Use Efficiency in Shrinking Cities: A Case Study of Northeast China. Land 2022, 11, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J.; Gu, C.; Chen, Y.J. Analysis of Coupling Relation between Urban Spatial Compactness and Degree of Land Use Mix Based on Compact City Theory: The Case of Downtown Shenyang, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.F.; Bian, Z.F.; Yan, Q.W.; Pan, Y.Q. Spatio-Temporal Distributions of the Land Use Efficiency Coupling Coordination Degree in Mining Cities of Western China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, S.; Pradhan, B.; Mansor, S.; Shariff, A.R.M. GIS-based modeling for the spatial measurement and evaluation of mixed land use development for a compact city. GIScience Remote Sens. 2015, 52, 18–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhan, J.Y.; Wang, C.; Twumasi-Ankrah, M.J. Coupling coordination analysis and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between sustainable development and ecosystem services in Shanxi Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.J.; Liu, X.X. Urban Land Use Efficiency under Resource-Based Economic Transformation—A Case Study of Shanxi Province. Land 2021, 10, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.H.; Wang, J.Q.; Du, Z.Q.; Wu, Z.T.; Zhang, H.; Ma, K.M. Spatiotemporal evolution of ecosystem services and its potential drivers in coalfields of Shanxi Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Bai, Z.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, X. Analyses of traits and driving forces on urban land expansion in a typical coal-resource-based city in a loess area. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Bai, Z.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, X. Characteristic analysis and pattern evolution on landscape types in typical compound area of mine agriculture urban in Shanxi Province, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, H. Industrial Structure, Environmental Pressure and Ecological Resilience of Resource-Based Cities-Based on Panel Data of 24 Prefecture-Level Cities in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 885976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, G.; Guo, X. Long-Term and Short-Term Effects of Carbon Emissions on Regional Healthy Development in Shanxi Province, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Bai, Z.; Sun, Q.; Zhou, W. Rural settlement changes in compound land use areas: Characteristics and reasons of changes in a mixed mining-rural-settlement area in Shanxi Province, China. Habitat Int. 2017, 61, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, S.; Parent, J.; Civco, D.L. Ten compactness properties of circles: Measuring shape in geography. Can. Geogr.-Geogr. Can. 2010, 54, 441–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curiel, R.P.; Patino, J.E.; Anderson, B. A scaling model for measuring the morphology of African cities: Implications for future energy needs. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.03003. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, M.S.; Sarkar, S. Prediction of urban expansion by using land cover change detection approach. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Tang, L.; Xu, M.; Yang, X. Landscape pattern indices for evaluating urban spatial morphology—A case study of Chinese cities. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 99, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.Y.; Chang, T.H.; Chiu, Y.H.; Yang, C.Y.; Lin, T.Y. Considering climate change and regional differences: An efficiency assessment of coal mine use and land restoration. Nat. Resour. Forum 2023, 47, 578–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.Y.; Wang, X.J. Land-Use Efficiency in Shandong (China): Empirical Analysis Based on a Super-SBM Model. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.H.; Lin, M.Y.; Qiu, Y. Regional differences and dynamic evolution of urban land green use efficiency within the Yangtze river economic belt, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 10, 1098924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.W.; Shao, Z.F.; Fang, S.H.; Huang, X. Quantifying Dynamic Coupling Coordination Degree of Human-Environmental Interactions during Urban-Rural Land Transitions of China. Land 2022, 11, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.Y.; Lee, J.; Zhou, T.; Wu, D. Shrinking cities and resource-based economy: The economic restructuring in China’s mining cities. Cities 2017, 60, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, A.; Sun, Z. How regional economic integration influence on urban land use efficiency? A case study of Wuhan metropolitan area, China. Land Use Policy 2020, 90, 104329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masini, E.; Tomao, A.; Barbati, A.; Corona, P.; Serra, P.; Salvati, L. Urban Growth, Land-use Efficiency and Local Socioeconomic Context: A Comparative Analysis of 417 Metropolitan Regions in Europe. Environ. Manag. 2019, 63, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitti, M.; Ferrara, C.; Perini, L.; Carlucci, M.; Salvati, L. Long-Term Urban Growth and Land Use Efficiency in Southern Europe: Implications for Sustainable Land Management. Sustainability 2015, 7, 3359–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, K.; Iida, A.; Watanabe, S.; Osawa, K. Efficiency and sustainability of land-resource use on a small island. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 054004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Nes, A. Spatial Configurations and Walkability Potentials. Measuring Urban Compactness with Space Syntax. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.L.; Jin, J.F.; Chen, Q.H.; Fang, X. On Physical Urban Boundaries, Urban Sprawl, and Compactness Measurement: A Case Study of the Wen-Tai Region, China. Land 2022, 11, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.C. Prioritizing compactness for a better quality of life: The case of US cities. Cities 2022, 123, 103566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Elements | Primary Indicator | Indicators | Entropy | CRITIC | Comprehensive Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population compactness | Residential population density | Urban population/Residential land area | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.07 |
| Employment population density | Number of employees in the city/Urban land area | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.07 | |
| Population growth elasticity | Urban population growth rate/Urban construction land growth rate | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.06 | |
| Economic compactness | The proportion of output value of secondary and tertiary industries | The output value of secondary and tertiary industries/Urban land area | 0.08 | 0.0.7 | 0.06 |
| Fixed investment intensity | Urban fixed asset investment/ Urban land area | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.08 | |
| Economic growth elasticity | Urban GDP growth rate/Urban construction land growth rate | 0.06 | 0.1 | 0.06 | |
| Infrastructure compactness | Number of secondary and primary schools per 10,000 people | Number of schools/Resident population | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.08 |
| Number of health institutions in 10,000 persons | Number of hospitals, clinics/Resident population | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | |
| Drainage efficiency | Urban land area/Length of drainage pipes in a built-up area | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.06 | |
| Road traffic compactness | Number of buses owned per 10,000 persons | Buses run per 10,000 people | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| Public transport efficiency | Total number of bus passengers/There are buses operating at the end of the year | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | |
| Per capita road area | Road area/Urban population | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.05 | |
| Land-use compactness | Urban development and utilization intensity | Built-up area/Urban land area | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.06 |
| Urban land consolidation degree | Urban land area/Number of urban land patches | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.05 | |
| Urban land center aggregation degree | The proportion of the largest urban land patch area | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.05 | |
| Ecological environment compactness | Per capita public green space | Urban public green area/Urban population | 0.03 | 0.4 | 0.04 |
| Sewage treatment rate | The volume of treated effluent/Total effluent discharge | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | |
| Comprehensive utilization rate of industrial solid waste | General Industrial Solid Waste Utilization/(General industrial solid Waste production + Storage capacity for comprehensive utilization in previous years) | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.04 |
| Stage | Type | Variable Name | Attribute |
|---|---|---|---|
| The first stage | Land input | Urban construction land area (ha) | − |
| Capital input | Total fixed asset investment (10 thousand tons) | − | |
| Labor input | Urban employed population (10 thousand people) | − | |
| Desirable output | The added value of the city’s secondary and tertiary industries (CNY, 10 thousand) | + | |
| Intermediate variable | Undesirable output | Cumulative occupation of damaged land by mining (ha) | − |
| Industrial solid waste production (10 thousand tons) | − | ||
| The second stage | Environmental governance input | Mine rehabilitation investment (CNY, 10 thousand) | − |
| Desirable output | Comprehensive utilization of industrial solid waste (10 thousand tons) | + | |
| Mine rehabilitation area (ha) | + |
| Range of D Value | Level of CCD | f (Uc) and f (Ul) Relationship | Type of CCD |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 ≤ D < 0.2 | Extreme coordination | f(Uc) − f(Ul) > 0.1 | Extreme coordination with hindered land-use efficiency |
| 0 ≤ |f(Uc) − f(Ul)| ≤ 0.1 | Coordinated development | ||
| f(Ul) − f(Uc) > 0.1 | Extreme coordination with hindered urban compactness | ||
| 0.2 ≤ D < 0.4 | Basic coordination | f(Uc) − f(Ul) > 0.1 | Basic l coordination with hindered land-use efficiency |
| 0 ≤ |f(Uc) − f(Ul)| ≤ 0.1 | Coordinated development | ||
| f(Ul) − f(Uc) > 0.1 | Basic coordination with hindered urban compactness | ||
| 0.4 ≤ D < 0.6 | Primary coordination | f(Uc) − f(Ul) > 0.1 | Primary coordination with lagging land-use efficiency |
| Coordinated development | |||
| Primary coordination with lagging urban compactness | |||
| 0 ≤ |f(Uc) − f(Ul)| ≤ 0.1 | |||
| f(Ul) − f(Uc) > 0.1 | |||
| 0.6 ≤ D < 0.8 | Intermediate coordination | f(Uc) − f(Ul) > 0.1 | Intermediate coordination with lagging land-use efficiency |
| 0 ≤ |f(Uc) − f(Ul)| ≤ 0.1 | Coordinated development | ||
| f(Ul) − f(Uc) > 0.1 | Intermediate coordination with lagging urban compactness | ||
| 0.8 ≤ D ≤ 1 | Quality coordination | f(Uc) − f(Ul) > 0.1 | Quality coordination with lagging land-use efficiency |
| 0 ≤ |f(Uc) − f(Ul)| ≤ 0.1 | Coordinated development | ||
| f(Ul) − f(Uc) > 0.1 | Quality coordination with lagging urban compactness |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Chang, J.; Li, Z.; Ming, L.; Li, C.; Li, C. Coupling Coordination and Spatiotemporal Analysis of Urban Compactness and Land-Use Efficiency in Resource-Based Areas: A Case Study of Shanxi Province, China. Land 2023, 12, 1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091658
Chen Y, Chang J, Li Z, Ming L, Li C, Li C. Coupling Coordination and Spatiotemporal Analysis of Urban Compactness and Land-Use Efficiency in Resource-Based Areas: A Case Study of Shanxi Province, China. Land. 2023; 12(9):1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091658
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yedong, Jiang Chang, Zixuan Li, Li Ming, Cankun Li, and Cheng Li. 2023. "Coupling Coordination and Spatiotemporal Analysis of Urban Compactness and Land-Use Efficiency in Resource-Based Areas: A Case Study of Shanxi Province, China" Land 12, no. 9: 1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091658
APA StyleChen, Y., Chang, J., Li, Z., Ming, L., Li, C., & Li, C. (2023). Coupling Coordination and Spatiotemporal Analysis of Urban Compactness and Land-Use Efficiency in Resource-Based Areas: A Case Study of Shanxi Province, China. Land, 12(9), 1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091658







