Simulated Runoff and Erosion on Soils from Wheat Agroecosystems with Different Water Management Systems, Iran
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
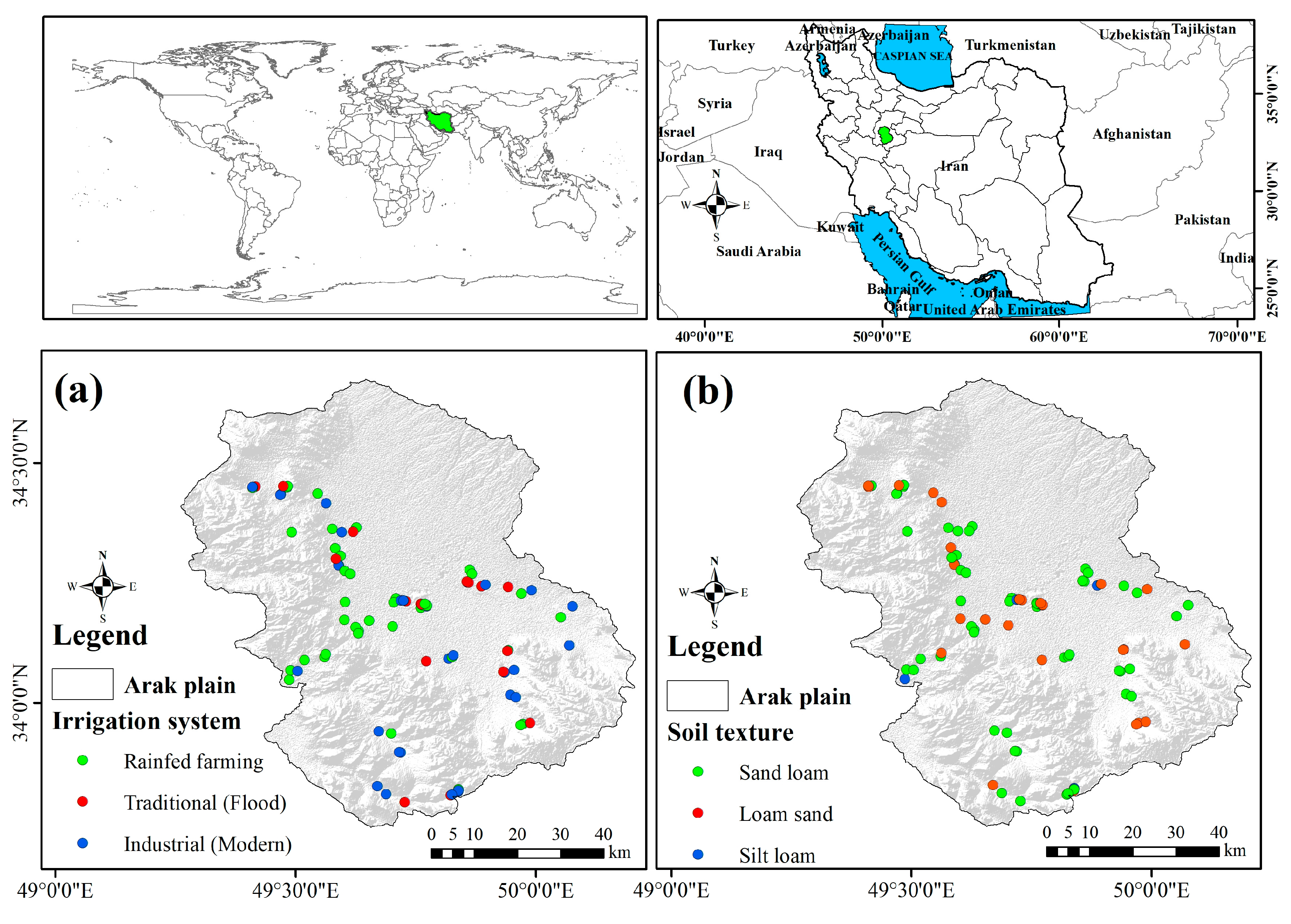
2.1. Study Area and Soil Analysis
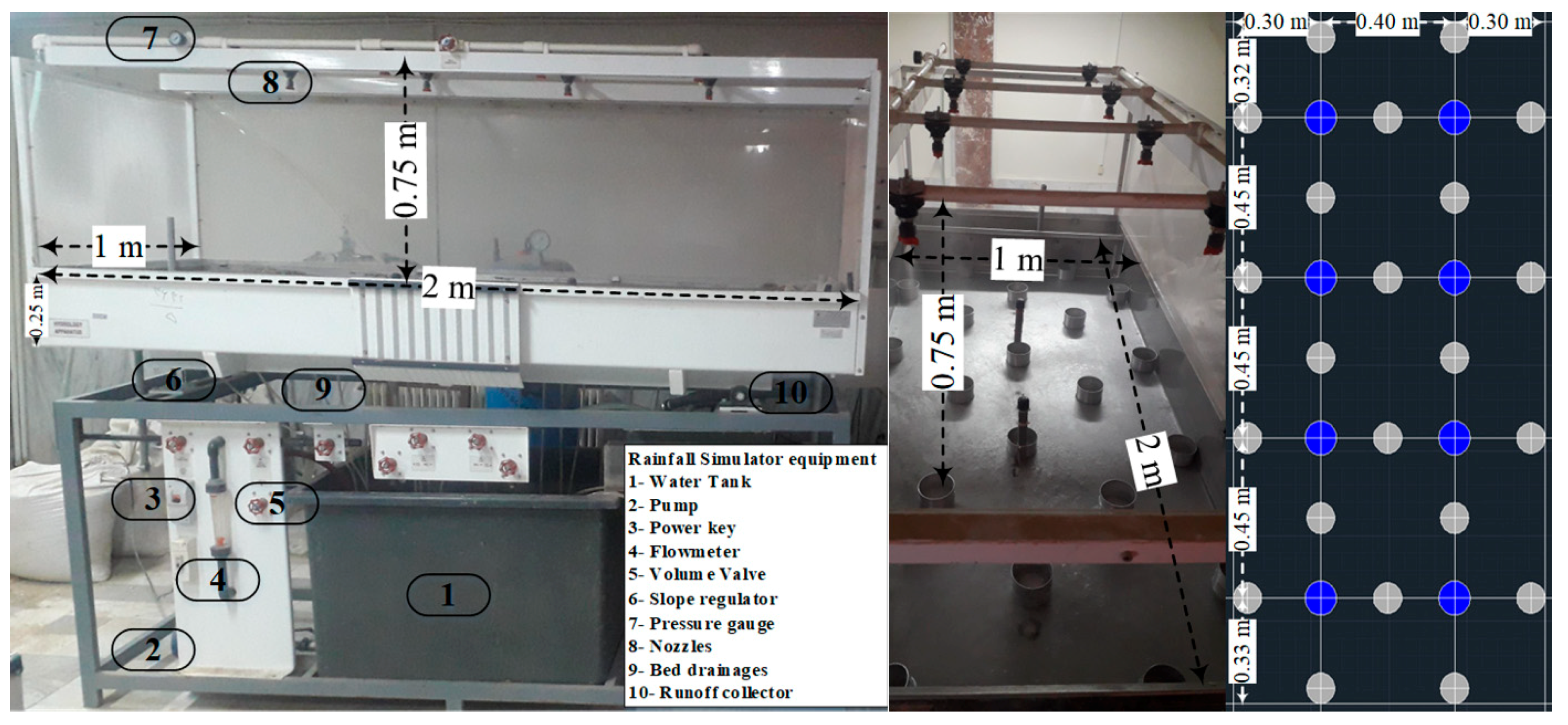
2.2. Rainfall Simulator
2.3. Experiment Method
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
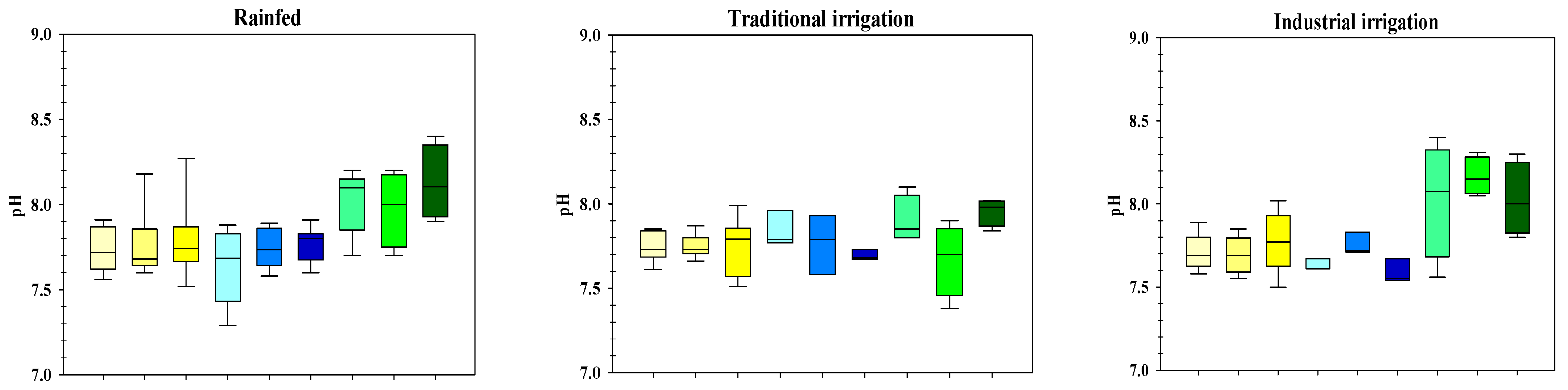
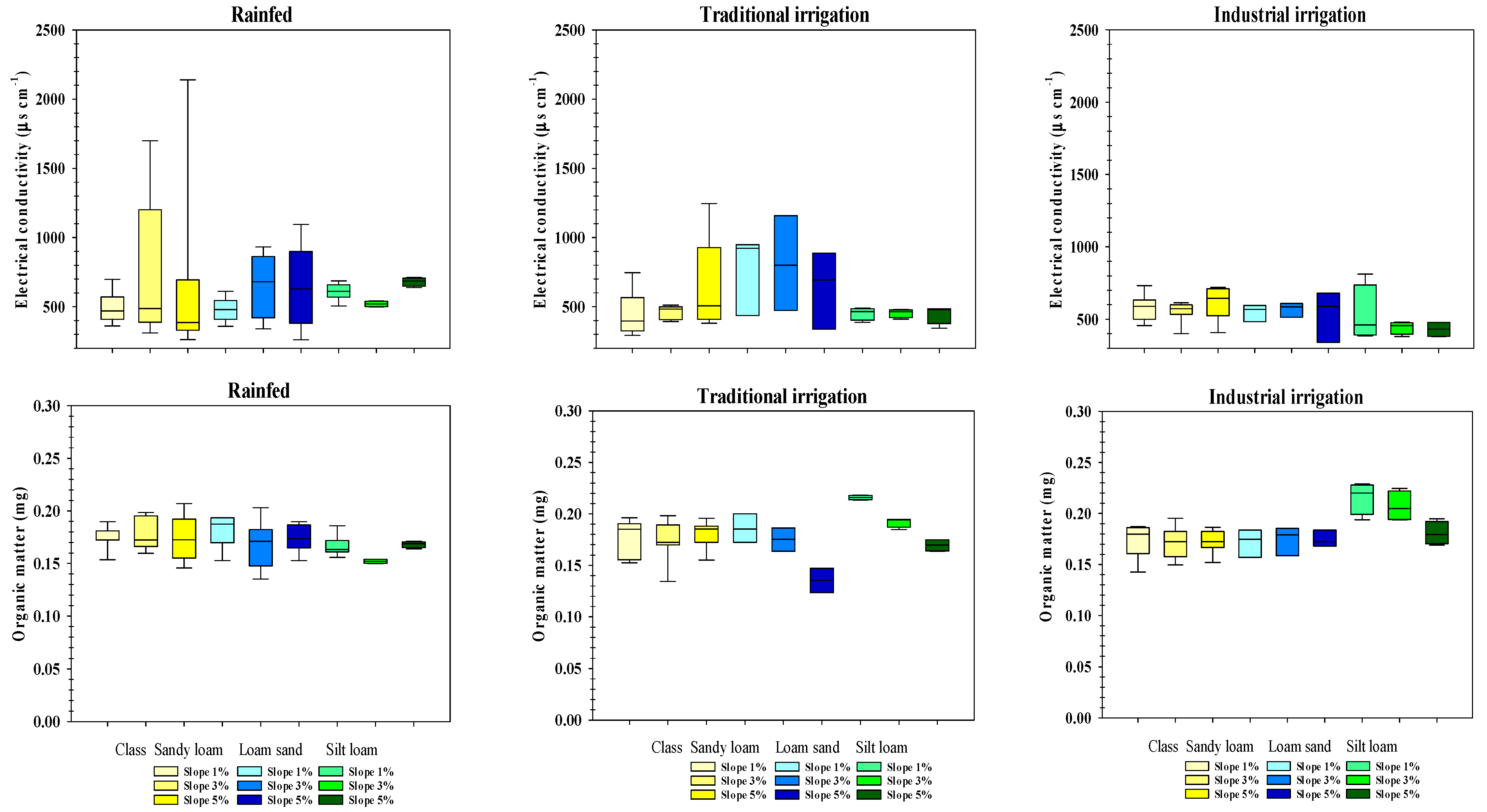
3.1. Soil Characteristics
3.2. Combined Analysis of Simulated Variables
3.3. Correlation Analysis of Simulated Variables
Multilinear Regression
3.4. Runoff Volume
3.5. Runoff Coefficient
3.6. Sediment Concentration
3.7. Soil Erosion
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Oliveira, S.P.; de Lacerda, N.B.; Blum, S.C.; Escobar, M.E.O.; de Oliveira, T.S. Organic carbon and nitrogen stocks in soils of northeastern Brazil converted to irrigated agriculture. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colazo, J.C.; Buschiazzo, D. The impact of agriculture on soil texture due to wind erosion. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlamini, P.; Orchard, C.; Jewitt, G.; Lorentz, S.; Titshall, L.; Chaplot, V. Controlling factors of sheet erosion under degraded grasslands in the sloping lands of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 1711–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, S.B.; Abreu, M.M.; Magalhães, M.R.; Cortez, N. Water erosion aspects of land degradation neutrality to landscape planning tools at national scale. Geoderma 2020, 363, 114093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, M.; Keesstra, S.D.; Baartman, J.E.; Ritsema, C.J.; Melesse, A.M. Evaluating sediment storage dams: Structural off-site sediment trapping measures in northwest Ethiopia. Cuad. Investig. Geográfica 2015, 41, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasanta, T.; Nadal-Romero, E.; Errea, P.; Arnáez, J. The effect of landscape conservation measures in changing landscape patterns: A case study in Mediterranean mountains. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A. Parent material and vegetation affect soil erosion in eastern Spain. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hou, R.; Wu, F.; Keesstra, S. Effect of soil surface roughness on infiltration water, ponding and runoff on tilled soils under rainfall simulation experiments. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 179, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragovich, D.; Morris, R. Fire intensity, slope wash and bio-transfer of sediment in eucalypt forest, Australia. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2002, 27, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhaske, S.N.; Pathak, K.; Basak, A. A comprehensive design of rainfall simulator for the assessment of soil erosion in the laboratory. Catena 2019, 172, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewket, W.; Teferi, E. Assessment of soil erosion hazard and prioritization for treatment at the watershed level: Case study in the Chemoga watershed, Blue Nile basin Ethiopia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2009, 20, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Jazouli, A.; Barakat, A.; Chafiri, A.; El Moutaki, S.; Ettaqy, A. Soil erosion modeled with USLE, GIS, and remote sensing: Case study of Ikkour watershed in Middle Atles (Morocco). Geosci. Lett. 2017, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mati, B.W.; Veihe, A. Application of the USLE in a Savannah environment: Comparative experiences from east and west Africa. Singap. J. Trop. Geogr. 2001, 22, 138–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanjani Jam, M. Evaluation of soil erosion using USLE model in GIS (Case study: Zanjanrood watershed). Rep. Geomat. 2006, 140–146. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Kinnell, P.I.A. Why the universal soil loss equation and the revised version of it do not predict event erosion well? Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinen, B.; Robinson, D.T. Agricultural erosion modelling: Evaluating USLE and WEPP field-scale erosion estimates using UAV time-series data. Environ. Model. Softw. 2021, 137, 104962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudi, I.; Carmi, G.; Berliner, P. Rainfall simulator for field runoff studies. J. Hydrol. 2012, 454, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, H.; Unal, N.E.; Cokgor, S.; Gedikli, A.; Yoon, J.; Koca, K.; Inci, S.B.; Eris, E. A rainfall simulator for laboratory-scale assessment of rainfall-runoff-sediment transport processes over a two-dimensional flume. Catena 2012, 98, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.D.; Harmon, W.C. Multiple-intensity rainfall simulator for erosion research on row sideslopes. Trans. ASAE 1979, 22, 0100–0103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, J.A.; Nearing, M.A. Runoff and sediment losses from rough and smooth soil surfaces in a laboratory experiment. Catena 2005, 59, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasanta, T.; Garcıa-Ruiz, J.M.; Pérez-Rontomé, C.; Sancho-Marcén, C. Runoff and sediment yield in a semi-arid environment: The effect of land management after farmland abandonment. Catena 2000, 38, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bissonnais, Y.; Cerdan, O.; Lecomte, V.; Benkhadra, H.; Souchère, V.; Martin, P. Variability of soil surface characteristics influencing runoff and interrill erosion. Catena 2005, 62, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loch, R.J. Effects of vegetation cover on runoff and erosion under simulated rain and overland flow on a rehabilitated site on the Meandu Mine, Tarong, Queensland. Soil Res. 2000, 38, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiettecatte, W.; Ouessar, M.; Gabriels, D.; Tanghe, S.; Heirman, S.; Abdelli, F. Impact of water harvesting techniques on soil and water conservation: A case study on a micro catchment in southeastern Tunisia. J. Arid Environ. 2005, 61, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assouline, S.; Ben-Hur, M. Effects of rainfall intensity and slope gradient on the dynamics of interrill erosion during soil surface sealing. Catena 2006, 66, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, K.M.; Najafinejad, A.; Noura, N.; Kavian, A. Effects of slope and soil properties on runoff and soil loss using rainfall simulator, Chehel-chai watershed, Golestan province. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 19, 165–178. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Salem, H.M.; Meselhy, A.A. A portable rainfall simulator to evaluate the factors affecting soil erosion in the northwestern coastal zone of Egypt. Nat. Hazards 2021, 105, 2937–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzi, P.; Azarakhshi, M.; Rasoulzadeh, A.; Bashiri, M. The Effects of Geological Units’ Characteristics and Slope Gradient on Runoff and Sediment Yield Using Rainfall Simulator (Case study: Senobar Watershed, Torbat-e-Heydarieh). J. Range Watershed Manag. 2016, 69, 437–447, (In Persian with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Parvisi, Y.; Bayat, R.; Arabkhedri, M.; Fatehi, S. Determination of Main Agents Affecting Soil Erosion in Rainfed Land of Kermanshah Province Using Rainfall Simulator. Iran. J. Watershed Sci. 2020, 14, 70–82, (In Persian with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F.S.; Huang, Y.H.; Wang, M.K.; Lin, J.S.; Zhao, G.; Ge, H.L. Effects of rainfall intensity and slope gradient on steep colluvial deposit erosion in southeast China. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 1741–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Jiang, F.; Wang, M.K.; Ge, H. Flow-driven soil erosion processes and the size selectivity of eroded sediment on steep slopes using colluvial deposits in a permanent gully. Catena 2017, 157, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tang, C.; Zhang, D. Simulated runoff processes on colluvial deposits of Liantanggang Benggang and their water distributions. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 179–185. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Q.; Cai, Q.; Ma, W. Comparative study on rain splash erosion of representative soils in China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayerhofer, C.; Meißl, G.; Klebinder, K.; Kohl, B.; Markart, G. Comparison of the results of a small-plot and a large-plot rainfall simulator–Effects of land use and land cover on surface runoff in Alpine catchments. Catena 2017, 156, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafi, S.; Ghaleni, M.M. Spatial assessment of drought features over different climates and seasons across Iran. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, D.M.; Kalantari, Z.; Ghajarnia, N.; Seifollahi-Aghmiuni, S.; Destouni, G. Variability and change in the hydro-climate and water resources of Iran over a recent 30-year period. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sahandi, M.R.; Soheili, M. Geological Map of Iran: Scale 1:1,000,000; Geological Survey & Mineral Explorations of Iran (GSI): Tehran, Iran, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Guzha, A.C. Effects of tillage on soil microrelief, surface depression storage and soil water storage. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 76, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, W.D.; Carter, M.R.; Gregorich, E.G. Saturated hydraulic properties: Well permeameter. In Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 1025–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Sparks, D.L.; Fendorf, S.E.; Toner, C.V., IV; Carski, T.H. Kinetic methods and measurements. Methods Soil Anal. Part 3 Chem. Methods 1996, 5, 1275–1307. [Google Scholar]
- Jagadamma, S.; Lal, R. Distribution of organic carbon in physical fractions of soils as affected by agricultural management. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2010, 46, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadamma, S.; Lal, R.; Hoeft, R.G.; Nafziger, E.D.; Adee, E.A. Nitrogen fertilization and cropping system impacts on soil properties and their relationship to crop yield in the central Corn Belt, USA. Soil Tillage Res. 2008, 98, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronick, C.J.; Lal, R. Manuring and rotation effects on soil organic carbon concentration for different aggregate size fractions on two soils in northeastern Ohio, USA. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 81, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavi, M.S.; Marschner, P. Drying and wetting in saline and saline-sodic soils—Effects on microbial activity, biomass and dissolved organic carbon. Plant Soil 2012, 355, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soil Survey Staff. Soil survey laboratory methods manual. In Soil Survey Investigations Rep. 42; Version 5; NRCS: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- WMO (World Meteorological Organization). Guide to Instruments and Methods of Observation; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; p. 548. [Google Scholar]
- Avanzato, R.; Beritelli, F. An Innovative Acoustic Rain Gauge Based on Convolutional Neural Networks. Information 2020, 11, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeger, M. Uncertainty of factors determining runoff and erosion processes as quantified by rainfall simulations. Catena 2007, 71, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissen, V.; Sánchez-Hernández, R.; Kampichler, C.; Ramos-Reyes, R.; Sepulveda-Lozada, A.; Ochoa-Goana, S.; de Jong, B.H.J.; Huerta-Lwanga, E.; Hernández-Daumas, S. Effects of land-use change on some properties of tropical soils—An example from Southeast Mexico. Geoderma 2009, 151, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, H.M.; Meselhy, A.; Elhagarey, M.; Ali, A.M.; Wu, W. Soil erosion control and wheat productivity are improved by a developed ridge-furrow and reservoir tillage systems. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2022, 68, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaez, J.; Lasanta, T.; Ruiz-Flaño, P.; Ortigosa, L. Factors affecting runoff and erosion under simulated rainfall in Mediterranean vineyards. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 93, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defersha, M.B.; Melesse, A.M. Effect of rainfall intensity, slope and antecedent moisture content on sediment concentration and sediment enrichment ratio. Catena 2012, 90, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarasa-Belmonte, A.M.; Soriano, J. Empirical study of extreme rainfall intensity in a semi-arid environment at different time scales. J. Arid. Environ. 2014, 100–101, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Han, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q. Assessment of erosion characteristics in purple and yellow soils using simulated rainfall experiments. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawan, M.L.; Bol, R.; Amelung, W.; Brahim, N. Soil organic matter amendments in date palm groves of the Middle Eastern and North African region: A mini-review. J. Arid Land 2016, 8, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.; Lavado, R.S. Climate, organic matter and clay content relationships in the Pampa and Chaco soils, Argentina. Geoderma 1998, 83, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, H.M.; Valero, C.; Muñoz, M.Á.; Gil-Rodríguez, M.; Barreiro, P. Effect of reservoir tillage on rainwater harvesting and soil erosion control under a developed rainfall simulator. Catena 2014, 113, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

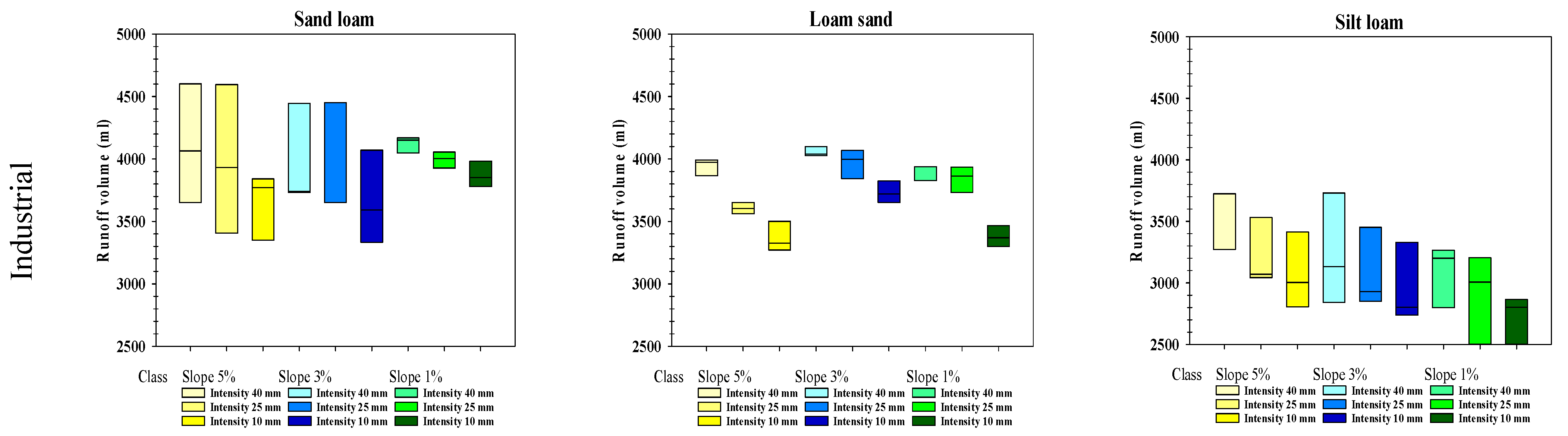

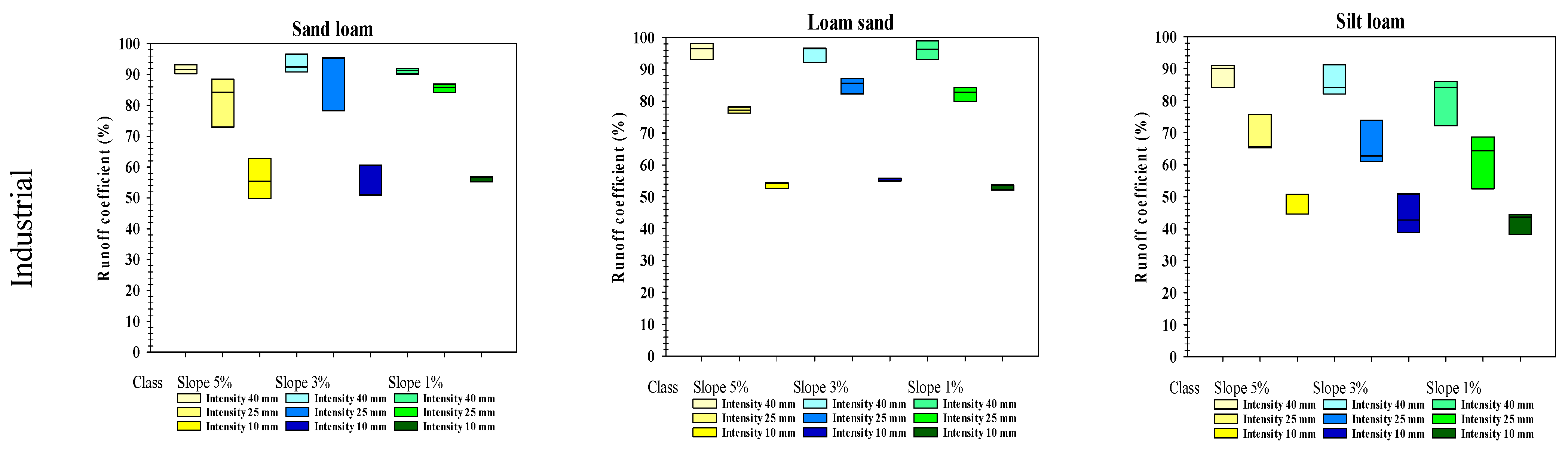
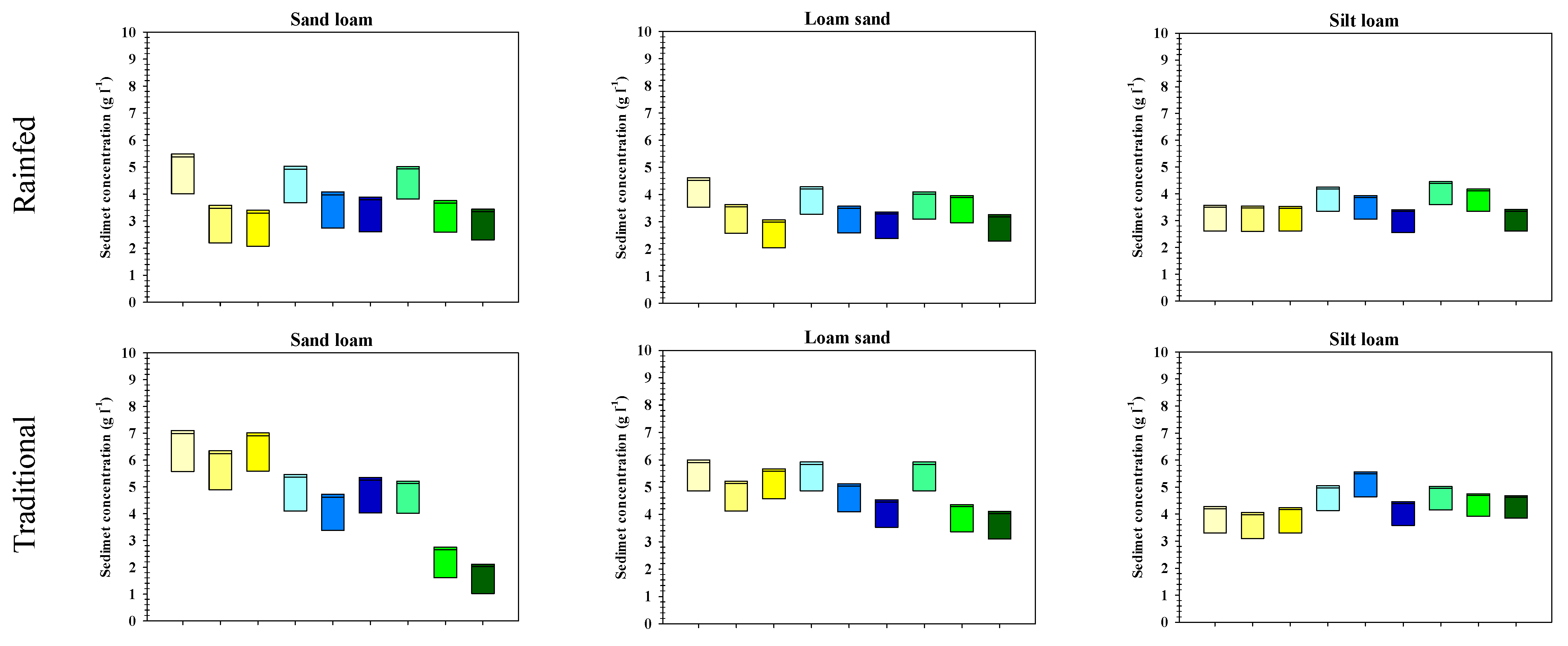

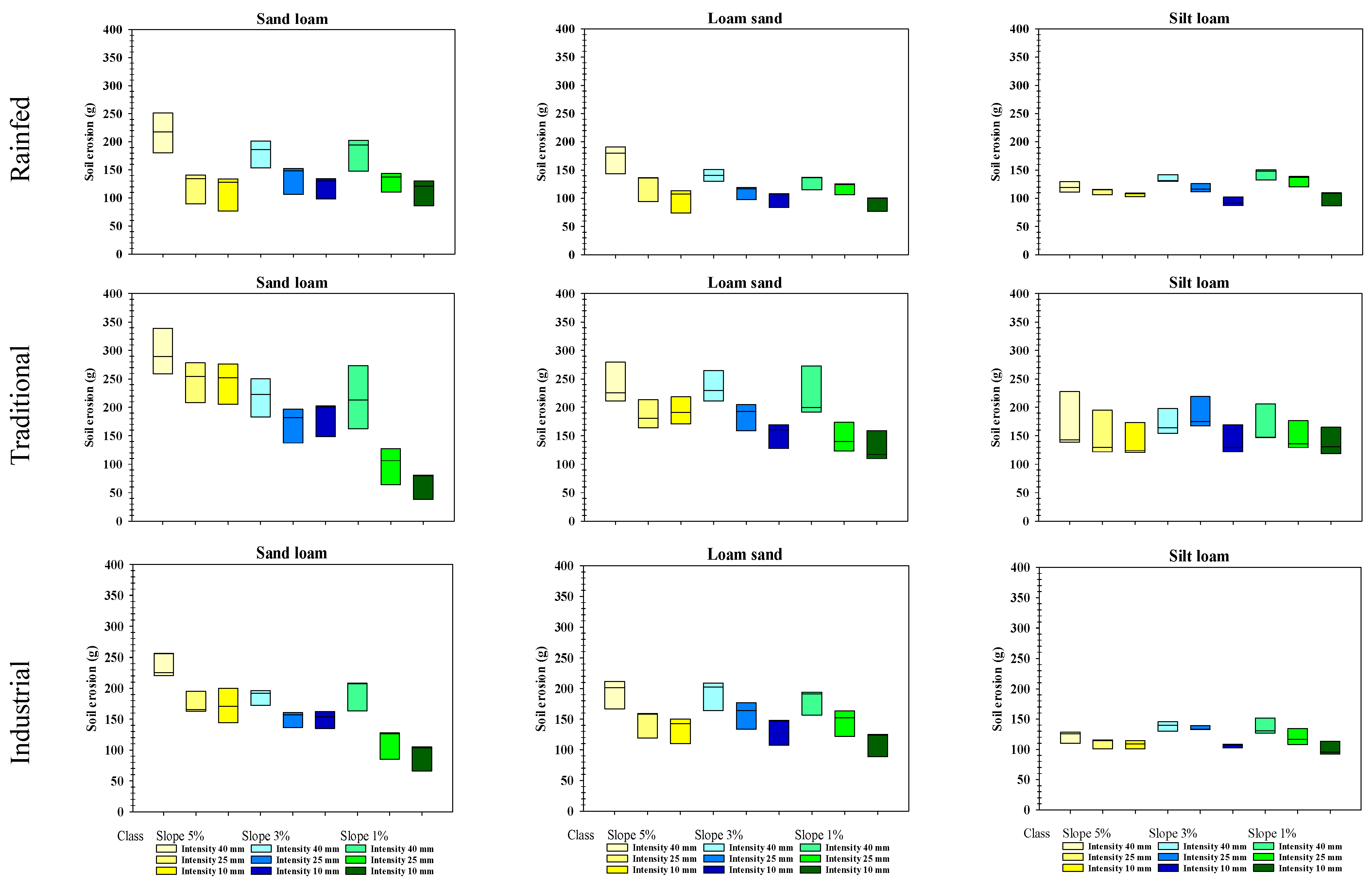
| Water Management System | Farms (No.) | Mean Slope (% of Farms *) | Sandy Loam (% of Farms) | Loamy Sand (% of Farms) | Silty Loam (% of Farms) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1% | 3% | 5% | |||||
| Rainfed (no irrigation) | 31 | 23 | 32 | 45 | 36 | 26 | 39 |
| Traditional Irrigation | 53 | 42 | 45 | 13 | 53 | 32 | 15 |
| Industrial Irrigation | 74 | 16 | 47 | 37 | 58 | 28 | 14 |
| % of all farms | (n = 158) | 26 | 44 | 30 | 52 | 29 | 19 |
| Sum of Variance (S.O.V) | Runoff Volume | Runoff Coefficient | Sediment Concentration | Soil Erosion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Irrigation (I) | 2,006,833.94 ** | 434.79 ** | 23.41 ** | 54,613.47 ** |
| Soil texture (ST) | 7,872,654.2 ** | 1605.9 ** | 1.47 ** | 27,068.34 ** |
| I × ST | 586,709.89 ** | 236.64 ** | 0.67 ** | 2226.49 ** |
| Slope (S) | 996,508.83 ** | 184.53 ** | 5.41 ** | 16,842.31 ** |
| I × S | 226,703.1 ** | 26.05 * | 3.04 ** | 5566.74 ** |
| ST × S | 333,094.34 ** | 68.42 ** | 8.92 ** | 9504.48 ** |
| I × ST × S | 124,345.45 * | 15.3 * | 1.91 ** | 2322.13 ** |
| Rainfall intensity (R) | 3,912,014.44 ** | 32,397.82 ** | 20.93 ** | 65,478.26 ** |
| I × R | 105,755.67 * | 28.82 * | 0.17 ** | 290.22 * |
| ST × R | 26,295.02 * | 201.5 ** | 2.84 ** | 5843.24 ** |
| S × R | 55,072.47 * | 26.83 * | 1.39 ** | 1513.77 ** |
| I × ST × R | 24,576.94 ** | 11.85 * | 0.08 ** | 223.41 * |
| ST × S × R | 6252.62 * | 3.2 * | 0.56 ** | 776.49 ** |
| I × ST × S × R | 13,945.35 * | 8.3 * | 0.35 ** | 575.1 ** |
| Code | Property | RV | RC | SC | SE | pH | EC | OM | CL | SI | SA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RV | 1 | |||||||||
| 2 | RC | 0.78 ** | 1 | ||||||||
| 3 | SC | −0.89 ** | 0.33 * | 1 | |||||||
| 4 | SE | 0.47 ** | 0.22 n.s | 0.96 ** | 1 | ||||||
| 5 | pH | −0.40 ** | −0.31 * | 0.21 n.s | 0.22 n.s | 1 | |||||
| 6 | EC | 0.12 n.s | 0.16 n.s | 0.04 n.s | 0.05 n.s | 0.10 n.s | 1 | ||||
| 7 | OM | −0.55 ** | 0.21 n.s | 0.28 * | 0.24 n.s | 0.25 n.s | 0.39 * | 1 | |||
| 8 | CL | 0.32 * | −0.44 ** | −0.42 ** | −0.37 * | −0.35 * | 0.39 * | 0.48 ** | 1 | ||
| 9 | SI | 0.62 ** | 0.31 * | 0.43 ** | 0.60 ** | 0.12 n.s | −0.38 * | 0.70 ** | 0.69 ** | 1 | |
| 10 | SA | 0.36 * | −0.25 n.s | −0.48 * | −0.35 * | −0.26 * | 0.17 n.s | −0.53 ** | −0.71 ** | −0.96 ** | 1 |
| Farm Type | Soil Texture | Equation (Soil Erosion) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rainfed | Sandy loam | Erosion = 74.35 + 2.23 S + 2.58 RI | 0.75 ** |
| Loamy sand | Erosion = 65.81 + 4.24 S + 1.67 RI | 0.82 ** | |
| Silty loam | Erosion = 100.96 − 3.19 S + 1.06 RI | 0.77 ** | |
| Traditional | Sandy loam | Erosion = 26.64 + 33.80 S + 2.62 RI | 0.81 ** |
| Loamy sand | Erosion = 95.42 + 10.23 S + 2.45 RI | 0.80 ** | |
| Silty loam | Erosion = 129.95 + 0.47 S + 1.00 RI | 0.40 n.s | |
| Industrial | Sandy loam | Erosion = 61.77 + 15.20 S + 2.22 RI | 0.78 ** |
| Loamy sand | Erosion = 95.49 + 2.81 S + 2.05 RI | 0.91 ** | |
| Silty loam | Erosion = 101.15 − 1.39 S + 0.90 RI | 0.60 n.s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharafi, S.; Mohammadi Ghaleni, M.; Dragovich, D. Simulated Runoff and Erosion on Soils from Wheat Agroecosystems with Different Water Management Systems, Iran. Land 2023, 12, 1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091790
Sharafi S, Mohammadi Ghaleni M, Dragovich D. Simulated Runoff and Erosion on Soils from Wheat Agroecosystems with Different Water Management Systems, Iran. Land. 2023; 12(9):1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091790
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharafi, Saeed, Mehdi Mohammadi Ghaleni, and Deirdre Dragovich. 2023. "Simulated Runoff and Erosion on Soils from Wheat Agroecosystems with Different Water Management Systems, Iran" Land 12, no. 9: 1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091790
APA StyleSharafi, S., Mohammadi Ghaleni, M., & Dragovich, D. (2023). Simulated Runoff and Erosion on Soils from Wheat Agroecosystems with Different Water Management Systems, Iran. Land, 12(9), 1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091790





