Delineation of Urban Development Boundary and Carbon Emission Effects in Xuzhou City, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
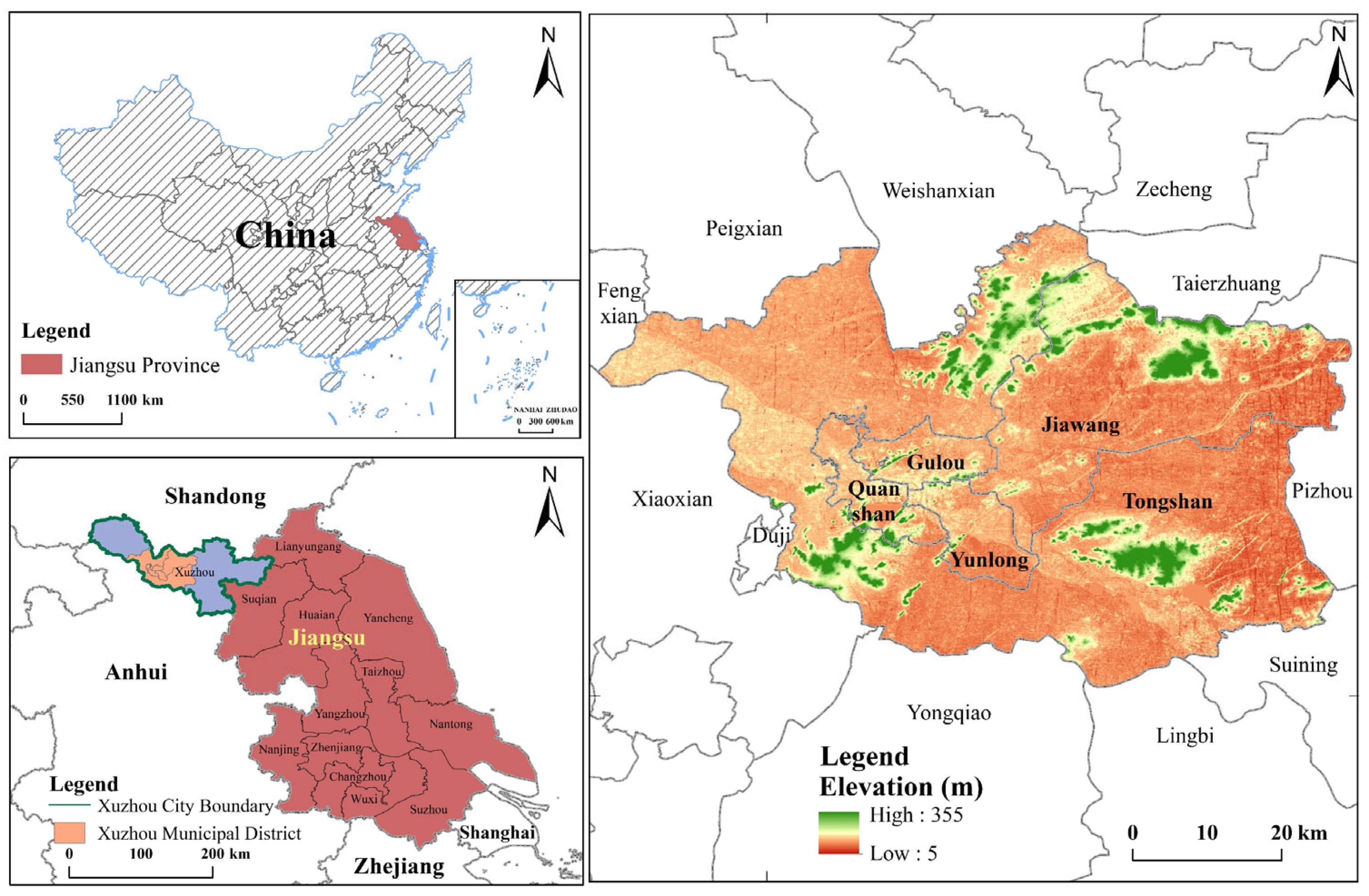
2.1. Study Area
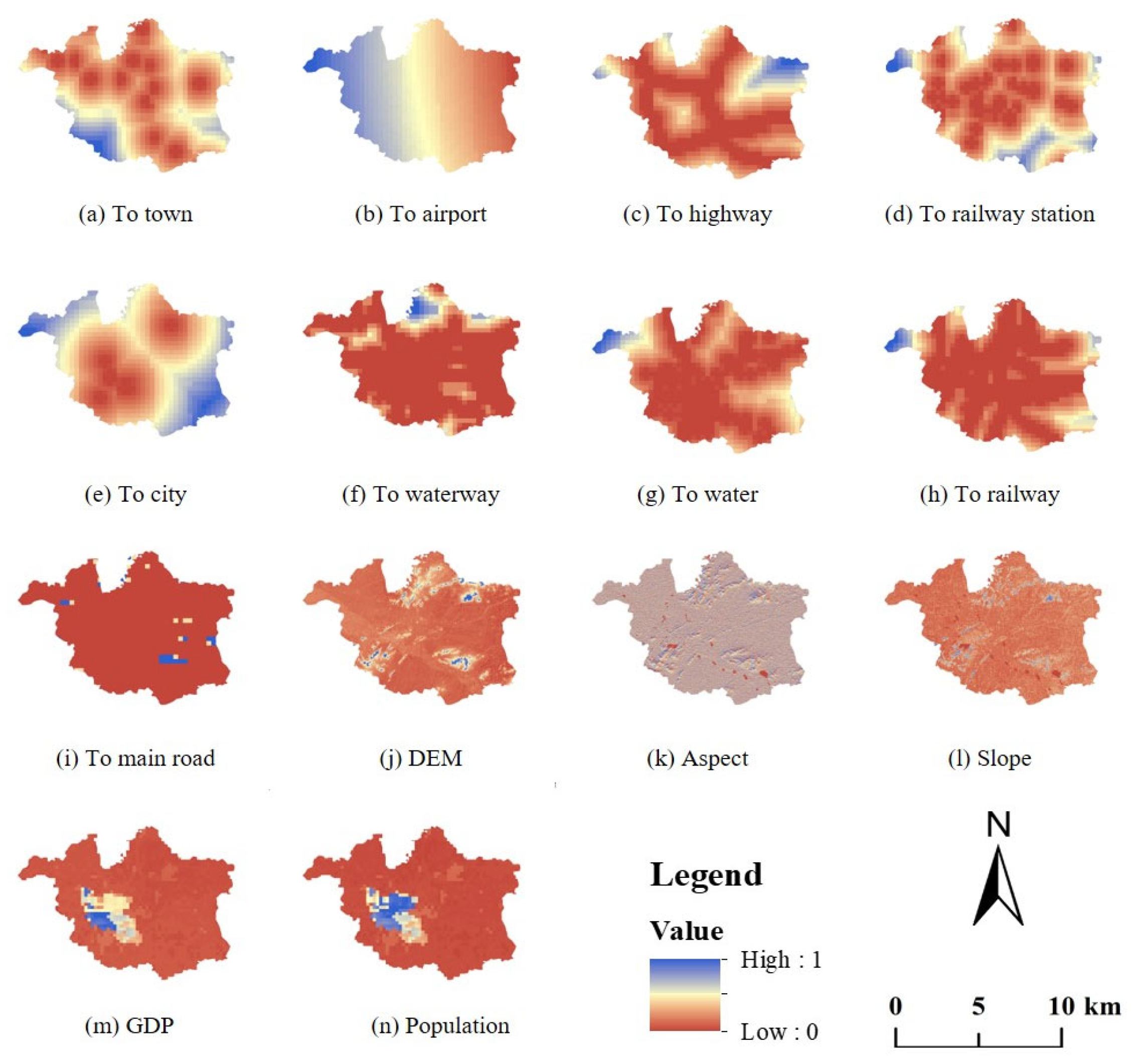
2.2. Data and Preprocessing
2.3. Methodology
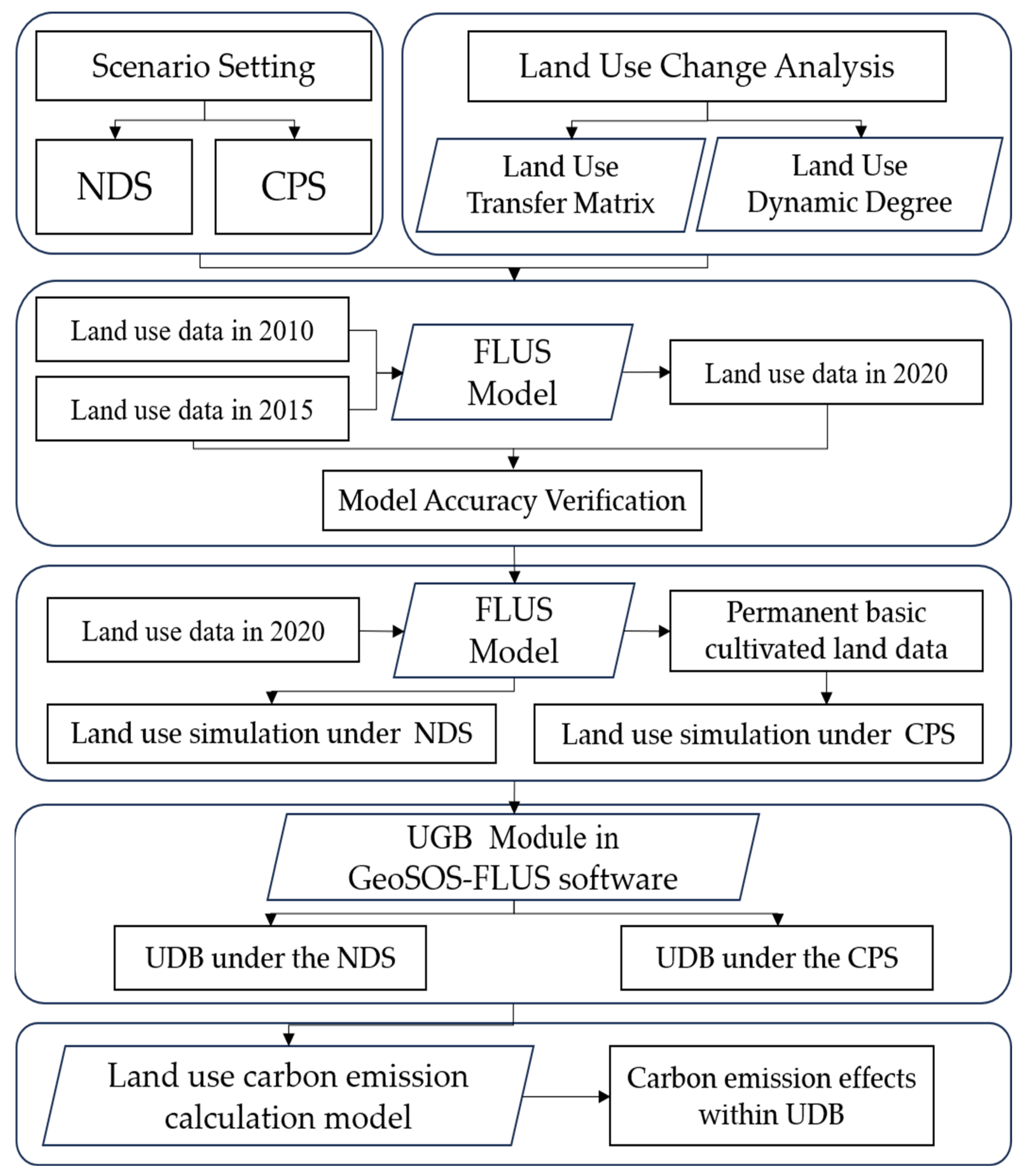
2.3.1. Scenario Setting
2.3.2. Methodology for Land Use Change Analysis
2.3.3. FLUS Model
2.3.4. Calculation of Land Use Carbon Emission
3. Results
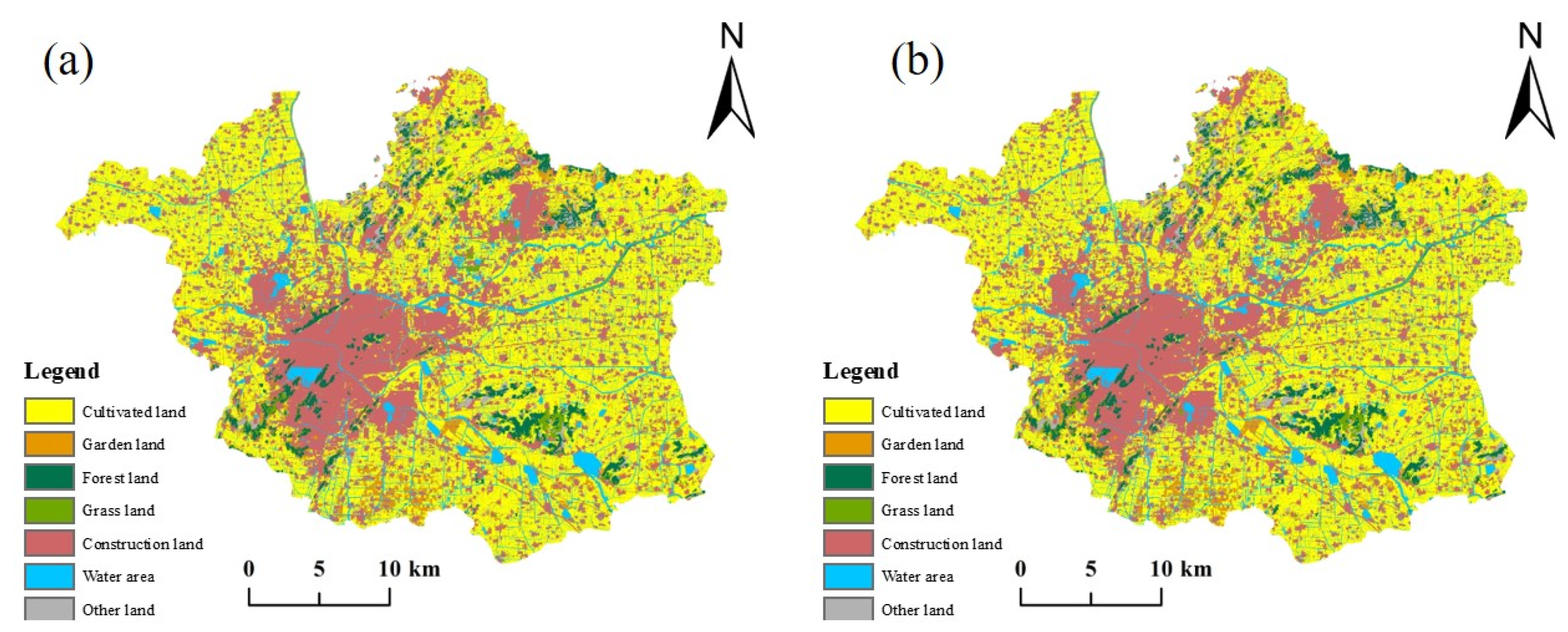
3.1. Analysis of the Status of Land Use Change
3.1.1. Changes in Land Use Area
3.1.2. Changes in Land Use Type Transition
3.1.3. Changes in Land Use Dynamic Degree
3.2. Delineation of UDB in Xuzhou City under Multiple Scenarios
3.2.1. Model Accuracy Verification
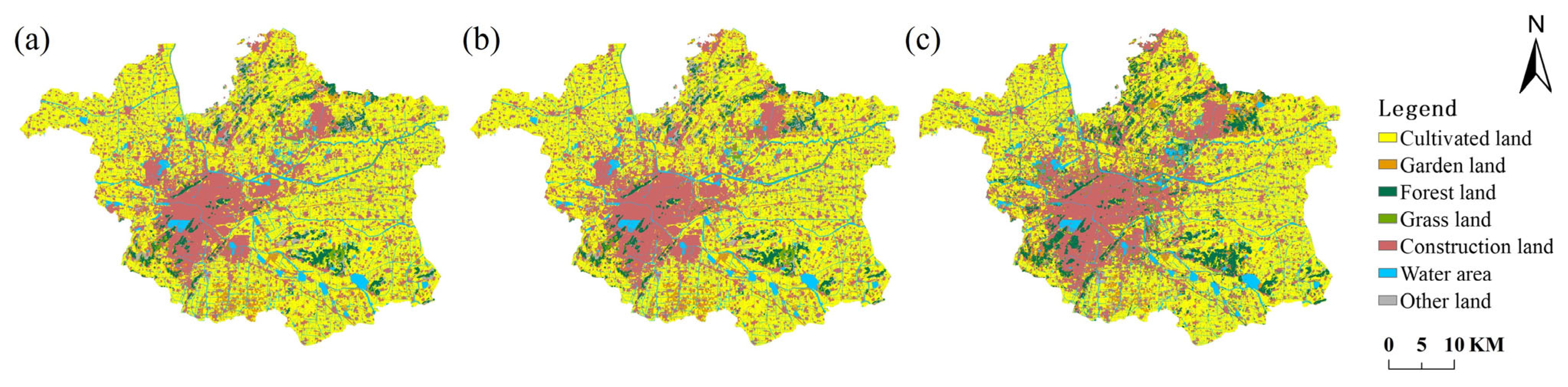
3.2.2. Future Land Use Simulation
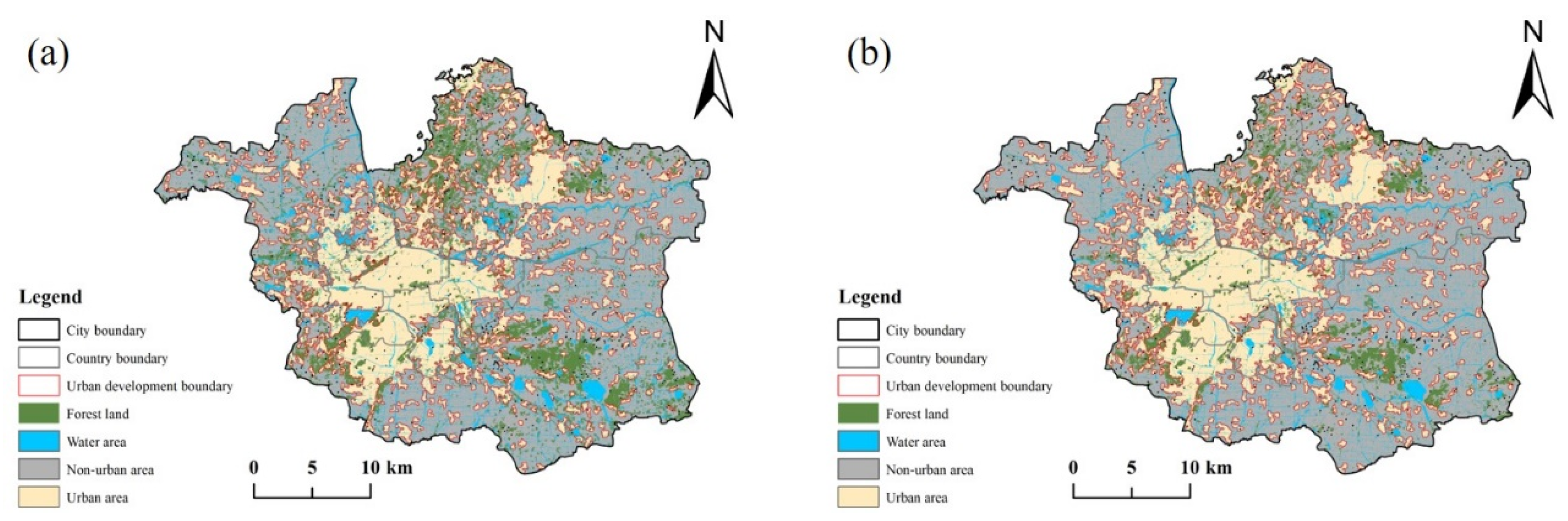
3.2.3. Delineation of Urban Development Boundary (UDB)
3.3. Carbon Emission Effects within UDB under Different Scenarios
3.3.1. Aggregate Analysis of Carbon Emission Effects
3.3.2. Analysis of Regional Differences in Carbon Emission Effects
4. Discussion
4.1. Significance and Innovation
4.2. Policy Proposals for the Future Development of Cities
4.3. Problem Statement and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seto, K.C.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, R.; Fragkias, M. The New Geography of Contemporary Urbanization and the Environment. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2010, 35, 167–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, S. Urban Forms and Future Cities: A Commentary. Urban Plan. 2017, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, L.; Song, C.; Ai, D. Nature-based solutions for urban expansion: Integrating ecosystem services into the delineation of growth boundaries. Habitat Int. 2022, 124, 102575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ou, J.; Li, X.; Ai, B. Combining system dynamics and hybrid particle swarm optimization for land use allocation. Ecol. Model. 2013, 257, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zhao, S.; Dong, J.; Liu, Y.; Meersmans, J.; Li, H.; Wu, J. Applying ant colony algorithm to identify ecological security patterns in megacities. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 117, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; He, C.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Shi, P.; Lu, W. Impacts of global urban expansion on natural habitats undermine the 2050 vision for biodiversity. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 190, 106834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, L.; Du, Z.; Liu, Z.; Qi, Y.; Liu, T.; Gong, P. Toward sustainable land use in China: A perspective on China’s national land surveys. Land Use Policy 2022, 123, 106428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Lau, N.C. Urban Expansion and Drying Climate in an Urban Agglomeration of East China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 6868–6877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Huang, C. How does urbanization affect carbon emission efficiency? Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, X.; Ming, Z.; Nie, R. Urbanization and CO2 emissions in resource-exhausted cities: Evidence from Xuzhou city, China. Nat. Hazards 2019, 99, 807–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Pan, H.; Zhao, M.; Zheng, T.; Nie, J.; Du, M.; Dhakal, S. High-resolution accounting of urban emissions in China. Appl. Energy 2022, 325, 119896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Fang, S.; Zhang, C.; Hu, S.; Nan, D.; Yang, Y. Exploring the impact of urban form on urban land use efficiency under low-carbon emission constraints: A case study in China’s Yellow River Basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 311, 114866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.; Liu, P.; Zhou, K.; He, Q. Evaluating the effectiveness of development-limiting boundary control policy: Spatial difference-in-difference analysis. Land Use Policy 2022, 120, 106229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennaio, M.-P.; Hersperger, A.M.; Bürgi, M. Containing urban sprawl—Evaluating effectiveness of urban growth boundaries set by the Swiss Land Use Plan. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyebi, A.; Perry, P.C.; Tayyebi, A.H. Predicting the expansion of an urban boundary using spatial logistic regression and hybrid raster–vector routines with remote sensing and GIS. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2013, 28, 639–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepinstall-Cymerman, J.; Coe, S.; Hutyra, L.R. Urban growth patterns and growth management boundaries in the Central Puget Sound, Washington, 1986–2007. Urban Ecosyst. 2013, 16, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyebi, A.; Pijanowski, B.C.; Tayyebi, A.H. An urban growth boundary model using neural networks, GIS and radial parameterization: An application to Tehran, Iran. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 100, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Jiao, L.; Zhang, W.; Jia, Q.; Su, F.; Xu, G.; Ma, S. Delineating urban growth boundaries under multi-objective and constraints. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 61, 102279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Hu, K.; Yu, M.; Jia, P.; Zhang, Y. Incorporating Ecological Constraints into the Simulations of Tropical Urban Growth Boundaries: A Case Study of Sanya City on Hainan Island, China. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-N.; Liu, C.-G.; Sun, W. Simulation research of urban development boundary based on ecological constraints: A case study of Nanjing. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 2913–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Wei, X.; Li, Y. Land space optimization of urban-agriculture-ecological functions in the Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan Urban Agglomeration, China. Land Use Policy 2022, 117, 106112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Bai, Y.; Che, L.; Qiao, F.; Xie, L. Incorporating ecological constraints into urban growth boundaries: A case study of ecologically fragile areas in the Upper Yellow River. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 124, 107436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, A.; Esraz-Ul-Zannat, M. Application of urban growth boundary delineation based on a neural network approach and landscape metrics for Khulna City, Bangladesh. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Huang, H.; Ma, S. Simulating urban growth boundaries using a patch-based cellular automaton with economic and ecological constraints. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2018, 33, 55–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Huang, J.; Liu, T. Delimiting urban growth boundaries using the CLUE-S model with village administrative boundaries. Land Use Policy 2019, 82, 422–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhuang, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Gao, Y.; Chen, T.; Huang, Q.; Xu, L.; Chen, D. A new perspective for urban development boundary delineation based on SLEUTH-InVEST model. Habitat Int. 2017, 70, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wei, M.; Li, Z.; Zeng, J. Multi-scenario simulation of urban growth boundaries with an ESP-FLUS model: A case study of the Min Delta region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Song, Y.; Tian, Y. Simulation of land-use pattern evolution in hilly mountainous areas of North China: A case study in Jincheng. Land Use Policy 2022, 112, 105826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, X.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H. The delineation of urban growth boundaries in complex ecological environment areas by using cellular automata and a dual-environmental evaluation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; He, Q. A literature review of urban growth boundary: Theory, modeling, and effectiveness evaluation. Prog. Geogr. 2020, 39, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Ji, X.; Guo, N.; Meng, L. Assessment of urban heat islands for land use based on urban planning: A case study in the main urban area of Xuzhou City, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, B.; Man, W.; Liu, M. Landsat-Based Monitoring of the Heat Effects of Urbanization Directions and Types in Hangzhou City from 2000 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, L.; Cao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhuang, Y.; Liu, X.; Du, Z.; Liu, T.; Yang, B.; et al. Habitat quality dynamics in China’s first group of national parks in recent four decades: Evidence from land use and land cover changes. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Gao, W.; Watari, K.; Fukahori, H. Land use change of Kitakyushu based on landscape ecology and Markov model. J. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, B. How Will Rwandan Land Use/Land Cover Change under High Population Pressure and Changing Climate? Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, S. Analyzing Land Use/Land Cover Changes Using Remote Sensing and GIS in Rize, North-East Turkey. Sensors 2008, 8, 6188–6202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Li, T. Analysis of spatiotemporal changes in cultural heritage protected cities and their influencing factors: Evidence from China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 151, 110327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Huang, X.; Jiang, L.; Jin, C. Empirical study on comparative analysis of dynamic degree differences of land use based on the optimization model. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 9847–9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, R.; Wu, M. Correlation Studies between Land Cover Change and Baidu Index: A Case Study of Hubei Province. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chi, G.; Li, J. The spatial association of ecosystem services with land use and land cover change at the county level in China, 1995–2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklavou, P.; Karatassiou, M.; Parissi, Z.; Galidaki, G.; Ragkos, A.; Sidiropoulou, A. The Role of Transhumance on Land Use/Cover Changes in Mountain Vermio, Northern Greece: A GIS Based Approach. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2017, 45, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yadav, V.; Ghosh, S.K. Assessment and prediction of urban growth for a mega-city using CA-Markov model. Geocarto Int. 2019, 36, 1960–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liang, X.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Ou, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Pei, F. A future land use simulation model (FLUS) for simulating multiple land use scenarios by coupling human and natural effects. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 168, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Tian, H.; Yao, Y. Delineating multi-scenario urban growth boundaries with a CA-based FLUS model and morphological method. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 177, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Liu, X.; Xu, X.; Chen, G.; Liang, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, X. Projections of land use changes under the plant functional type classification in different SSP-RCP scenarios in China. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 1935–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Li, A.; Bian, J.; Nan, X.; Lei, G. Modeling the Impact of Investment and National Planning Policies on Future Land Use Development: A Case Study for Myanmar. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şenik, B.; Kaya, H.S. Landscape sensitivity-based scenario analysis using flus model: A case of Asarsuyu watershed. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 18, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuellar, Y.; Perez, L. Assessing the accuracy of sensitivity analysis: An application for a cellular automata model of Bogota’s urban wetland changes. Geocarto Int. 2023, 38, 2186491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yang, C.-H.; Zhao, Y.-C.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.-P. Spatial Correlations of Land Use Carbon Emissions in Shandong Peninsula Urban Agglomeration: A Perspective from City Level Using Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; He, J.; Hong, X.; Zhang, W.; Qin, C.; Pang, B.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Carbon sources/sinks analysis of land use changes in China based on data envelopment analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 204, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Dinda, S.; Chatterjee, N.D.; Dutta, S.; Bera, D. Spatial-explicit carbon emission-sequestration balance estimation and evaluation of emission susceptible zones in an Eastern Himalayan city using Pressure-Sensitivity-Resilience framework: An approach towards achieving low carbon cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 336, 130417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, T.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, H.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z. Spatial correlation evolution and prediction scenario of land use carbon emissions in China. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 71, 101802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liang, H.; Chang, X.; Cui, Q.; Tao, Y. Land Use Patterns on Carbon Emission and Spatial Association in China. Econ. Geogr. 2015, 35, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Z. Effects of land-use change on carbon emission and its driving factors in Shaanxi Province from 2000 to 2020. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 68313–68326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.-Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, M.-N.; Fang, R.-Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Q.-P.; Wang, Q. Spatial-temporal characteristics of carbon emissions from land use change in Yellow River Delta region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster Olbrich, J.P.; Vich, G.; Miralles-Guasch, C.; Fuentes, L. Urban sprawl containment by the urban growth boundary: The case of the Regulatory Plan of the Metropolitan Region of Santiago of Chile. J. Land Use Sci. 2022, 17, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Hou, B.; Ye, G.; Wang, Z. China’s land-sea coordination practice in territorial spatial planning. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 237, 106545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, D.; Wang, L.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J. Offshore Island Connection Line: A new perspective of coastal urban development boundary simulation and multi-scenario prediction. GIScience Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 801–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, X. Exploring Smart Growth Boundaries of Urban Agglomeration with Land Use Spatial Optimization: A Case Study of Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan City Group, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; He, Q.; Zhu, X. Simulation of Impacts of Urban Agglomeration Land Use Change on Ecosystem Services Value under Multi-Scenarios: Case Study in Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan Urban Agglomeration. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 40, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Chen, C.; Chen, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, F.; Li, S. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Land-Use Change and Delineation of Urban Growth Boundaries in County Area: A Case Study of Xinxing County, Guangdong Province. Land 2022, 11, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, S. Impact of an urban growth boundary across the entire house price spectrum: The two-stage quantile spatial regression approach. Land Use Policy 2019, 80, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, M.; Cigdem, M.; Taylor, E.; Wood, G. Urban growth boundaries and their impact on land prices. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2014, 46, 3010–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, X.; Xiao, Y.; Lin, Z. Spatial and structural characteristics of the ecological network of carbon metabolism of cultivated land based on land use and cover change: A case study of Nanchang, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 30514–30529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Guldmann, J.M.; Gong, J.; Su, H. Urban growth boundaries optimization under low-carbon development: Combining multi-objective programming and patch cellular automata models. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 340, 117934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Qiu, Y.; Yin, L.; Liu, S.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, M. Effects of China’s land-intensive use on carbon emission reduction: A new perspective of industrial structure upgrading. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1073565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Data Attribute | Data Name | Data Source |
|---|---|---|
| Land use data | Land use data of Xuzhou in 2010, 2015, and 2020 | China Land Surveying and Planning Institute |
| Terrain factor data | DEM | Geospatial Data Cloud (https://www.gscloud.cn/, accessed on 18 April 2022) |
| Aspect | ||
| Slope | ||
| Transportation accessibility factor data | To town | Open Street Map (https://www.openstreetmap.org/, accessed on 17 April 2022) |
| To airport | ||
| To highway | ||
| To railway station | ||
| To city | ||
| To waterway | ||
| To water | ||
| To railway | ||
| To main road | ||
| Socio-economic factor data | 1 km × 1 km grid level GDP | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (https://www.resdc.cn/, accessed on 19 April 2022) |
| 1 km × 1 km grid level population |
| Land Use Type | Carbon Emission Coefficient | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| L1 | 42.2 | t C/km2 |
| L2 | −73 | t C/km2 |
| L3 | −57.8 | t C/km2 |
| L4 | −2.1 | t C/km2 |
| L6 | −25.2 | t C/km2 |
| L7 | −0.5 | t C/km2 |
| L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | L5 | L6 | L7 | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 1148.95 | 50.12 | 65.50 | 3.62 | 144.96 | 76.64 | 24.64 | 1514.43 |
| L2 | 40.40 | 27.95 | 10.39 | 0.98 | 13.38 | 7.50 | 2.70 | 103.29 |
| L3 | 6.21 | 1.71 | 89.53 | 2.89 | 8.19 | 1.36 | 2.06 | 111.96 |
| L4 | 12.88 | 2.96 | 18.04 | 8.02 | 7.29 | 2.10 | 1.40 | 52.68 |
| L5 | 77.50 | 10.01 | 30.77 | 17.50 | 609.60 | 36.11 | 5.02 | 786.51 |
| L6 | 79.64 | 6.31 | 11.68 | 3.28 | 44.29 | 161.62 | 3.00 | 309.82 |
| L7 | 15.82 | 3.78 | 26.65 | 5.86 | 12.65 | 1.76 | 13.83 | 80.35 |
| Total | 1381.40 | 102.84 | 252.56 | 42.14 | 840.35 | 287.10 | 52.65 | 2959.03 |
| Period | Single Land Use Dynamic Degree | Comprehensive Land Use Dynamic Degree | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | L5 | L6 | L7 | ||
| 2010–2015 | −0.30 | −0.42 | −0.36 | −0.02 | 0.88 | −0.58 | 0.34 | 0.24 |
| 2015–2020 | −1.48 | 0.30 | 26.30 | −3.88 | 0.38 | −0.89 | −6.74 | 1.09 |
| 2010–2020 | −0.88 | −0.07 | 12.74 | −1.94 | 0.64 | −0.72 | −3.26 | 0.65 |
| Scenario | Carbon Emission of Different Land Use Types within UDB | Net Carbon Emission | Carbon Source | Carbon Sink | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | L5 | L6 | L7 | ||||
| NDS | 4641.80 | −1477.59 | −4708.43 | −35.79 | 10,473,420.62 | −1430.61 | −4.45 | 10,470,405.55 | 10,478,062.42 | −7656.88 |
| CPS | 5702.13 | −1387.19 | −3608.42 | −34.63 | 10,475,773.36 | −1275.73 | −4.04 | 10,475,165.47 | 10,481,475.48 | −6310.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, H.; Li, X.; Geng, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Z. Delineation of Urban Development Boundary and Carbon Emission Effects in Xuzhou City, China. Land 2023, 12, 1819. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091819
Ji H, Li X, Geng Y, Chen X, Wang Y, Cheng J, Chen Z. Delineation of Urban Development Boundary and Carbon Emission Effects in Xuzhou City, China. Land. 2023; 12(9):1819. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091819
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Haitao, Xiaoshun Li, Yiwei Geng, Xin Chen, Yuexiang Wang, Jumei Cheng, and Zhuang Chen. 2023. "Delineation of Urban Development Boundary and Carbon Emission Effects in Xuzhou City, China" Land 12, no. 9: 1819. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091819
APA StyleJi, H., Li, X., Geng, Y., Chen, X., Wang, Y., Cheng, J., & Chen, Z. (2023). Delineation of Urban Development Boundary and Carbon Emission Effects in Xuzhou City, China. Land, 12(9), 1819. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091819







