Analysis of Spatiotemporal Changes in the Gravitational Structure of Urban Agglomerations in Northern and Southern Xinjiang Based on a Gravitational Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sources
2.1. Study Area Overview
2.2. Data Source and Processing
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Construction of a Comprehensive Gravity Model
3.2. Urban Attraction Model
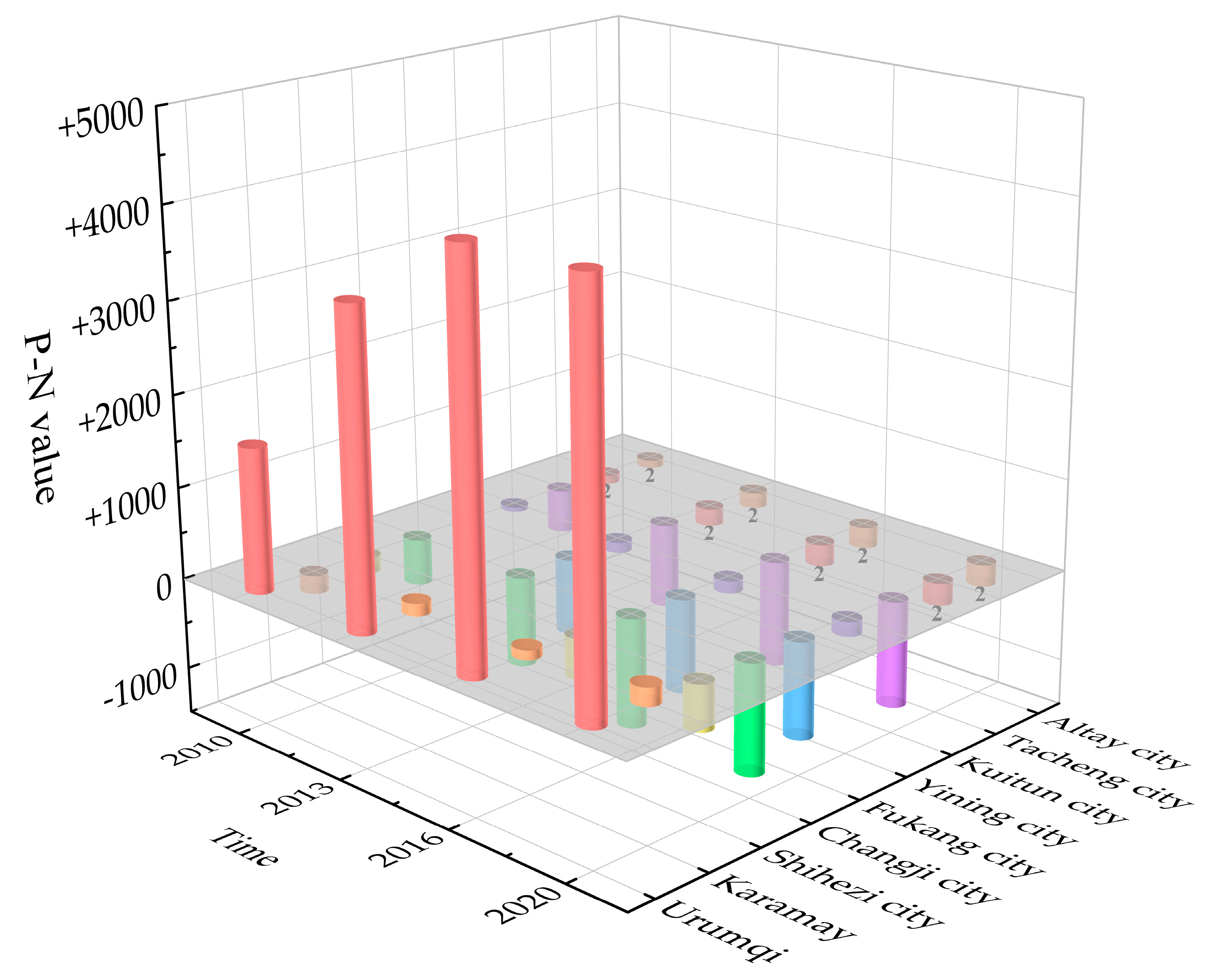
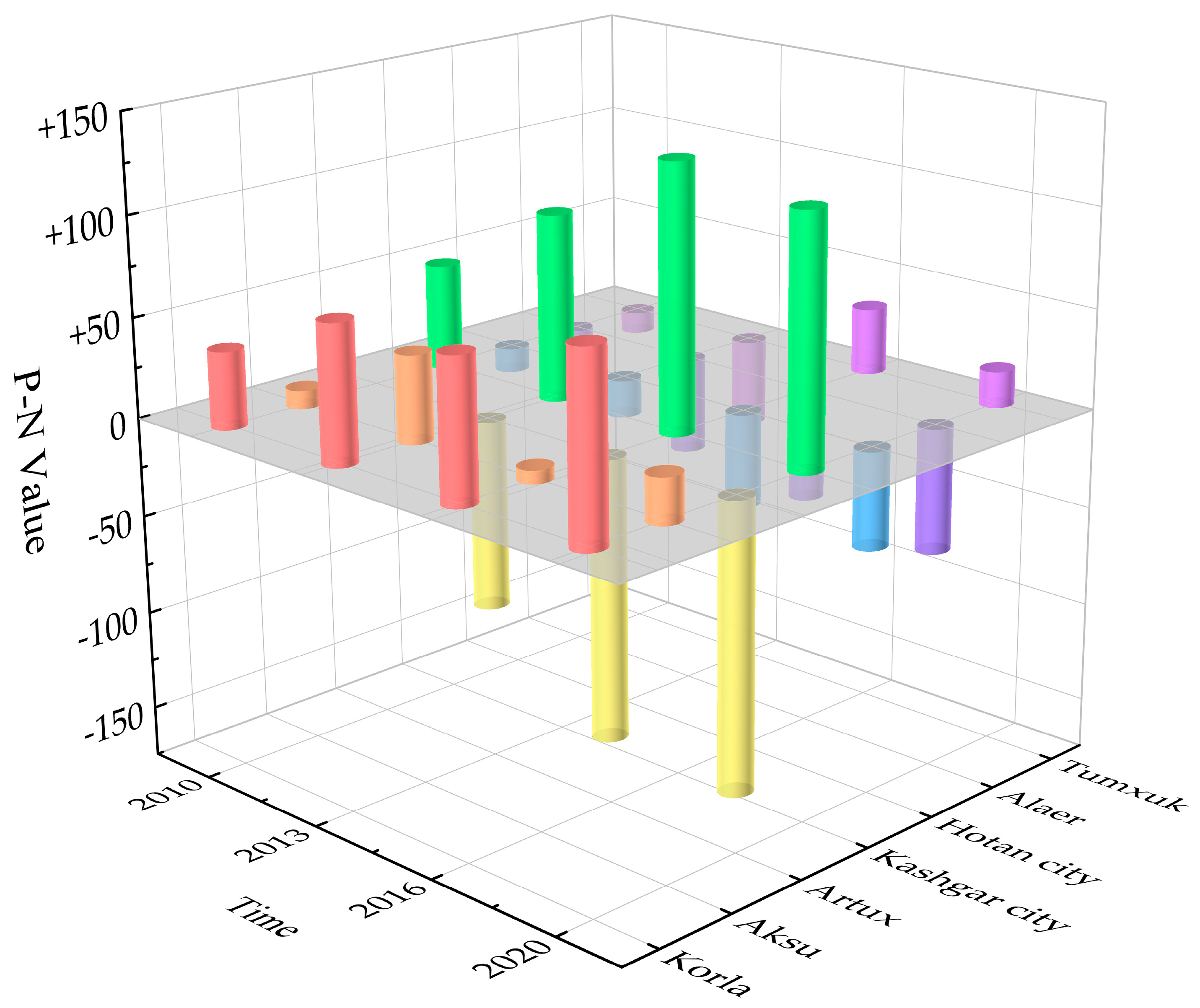
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Spatial and Temporal Characterization of Urban Gravity
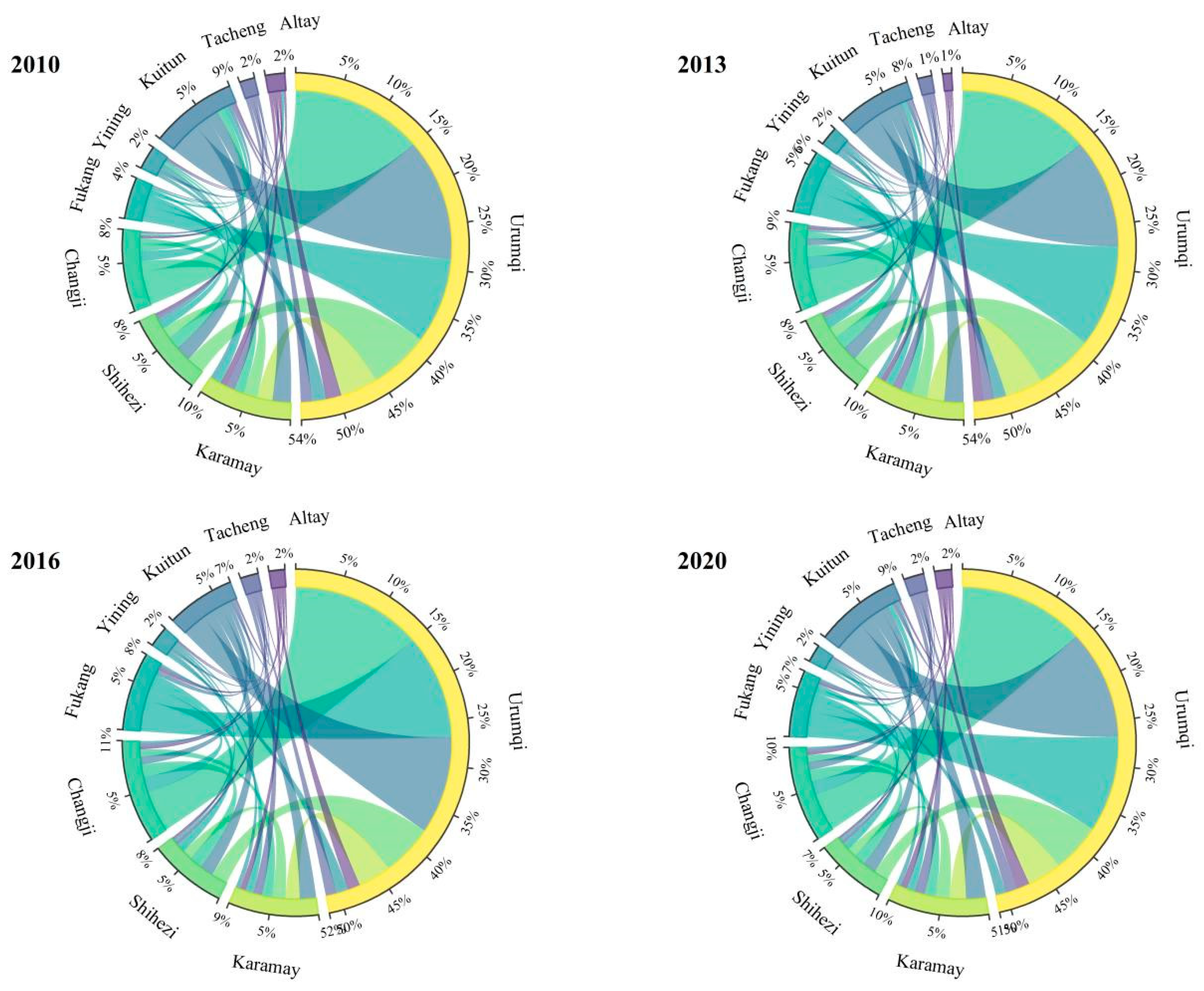
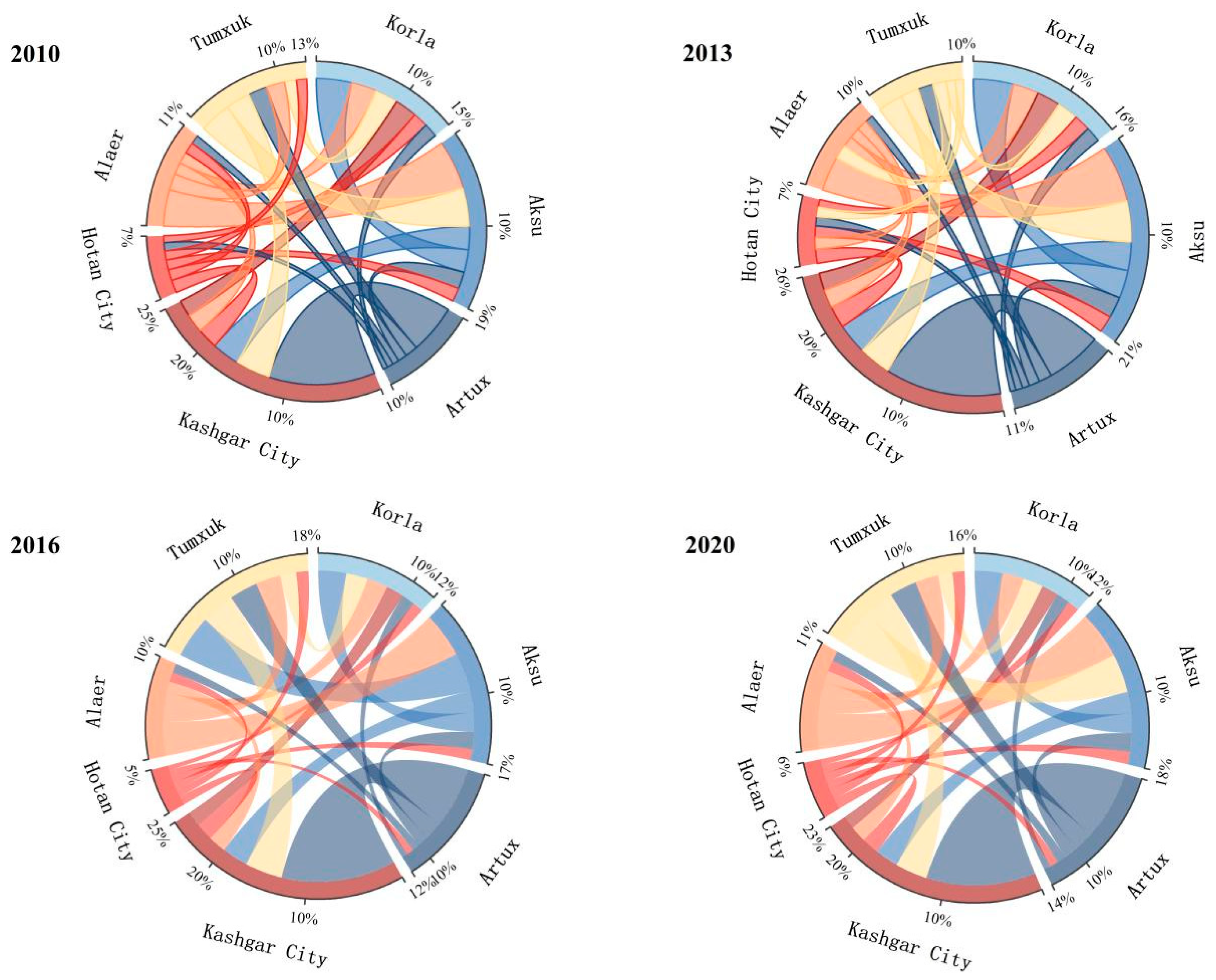
4.2. Characterization of Urban Spatial and Temporal Linkages
4.3. Characterization of the Spatial and Temporal Linkage Structure of Cities
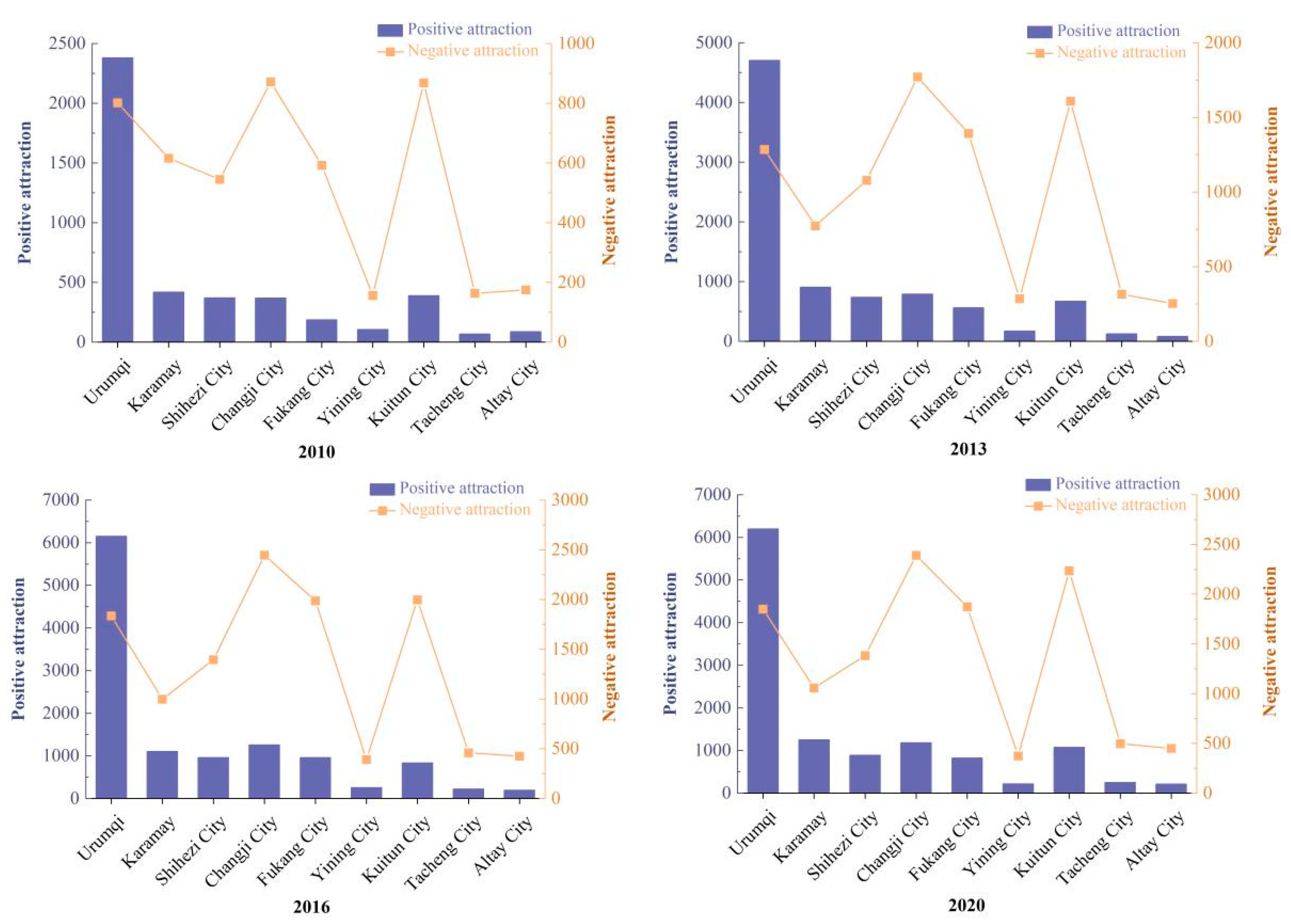
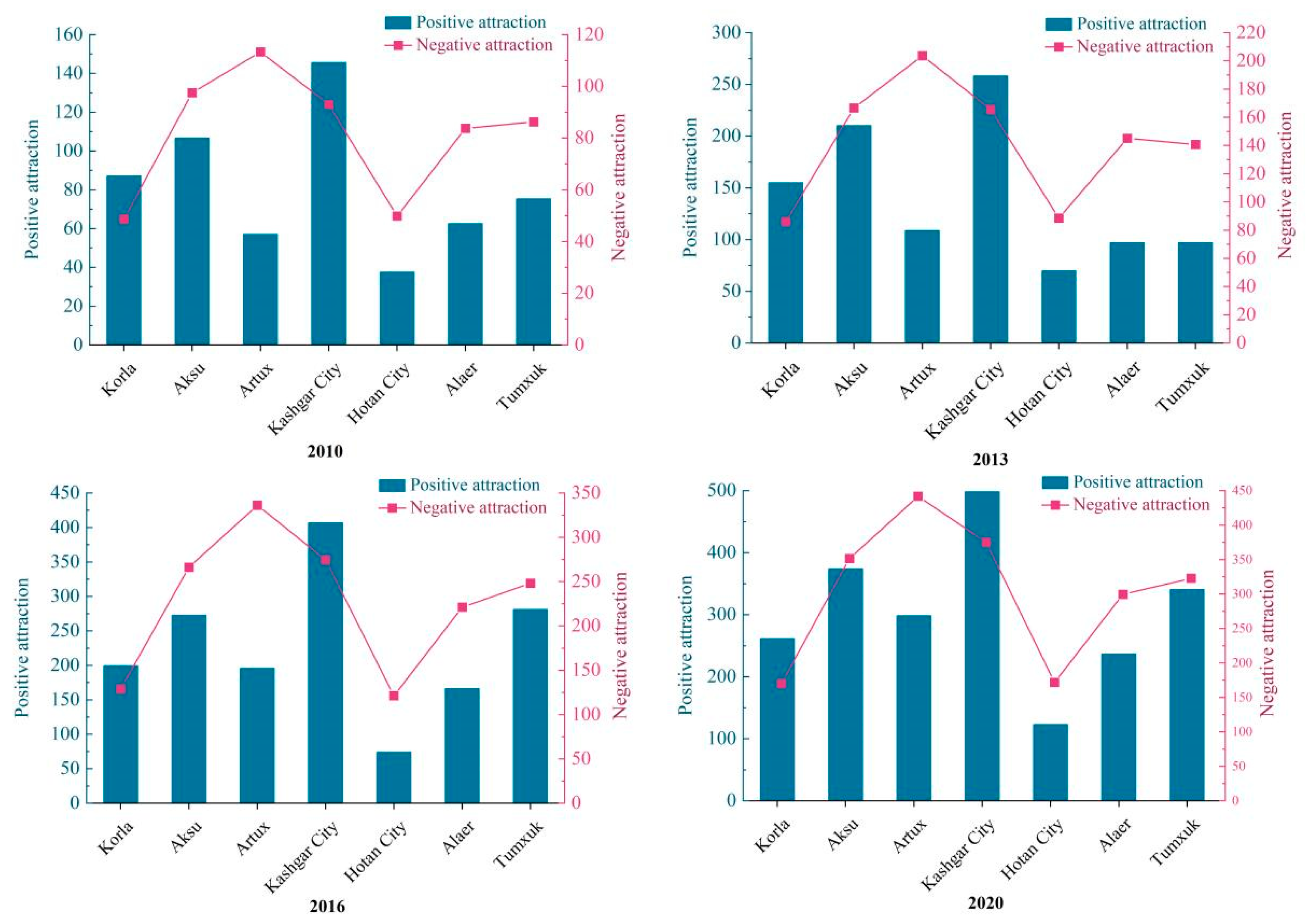
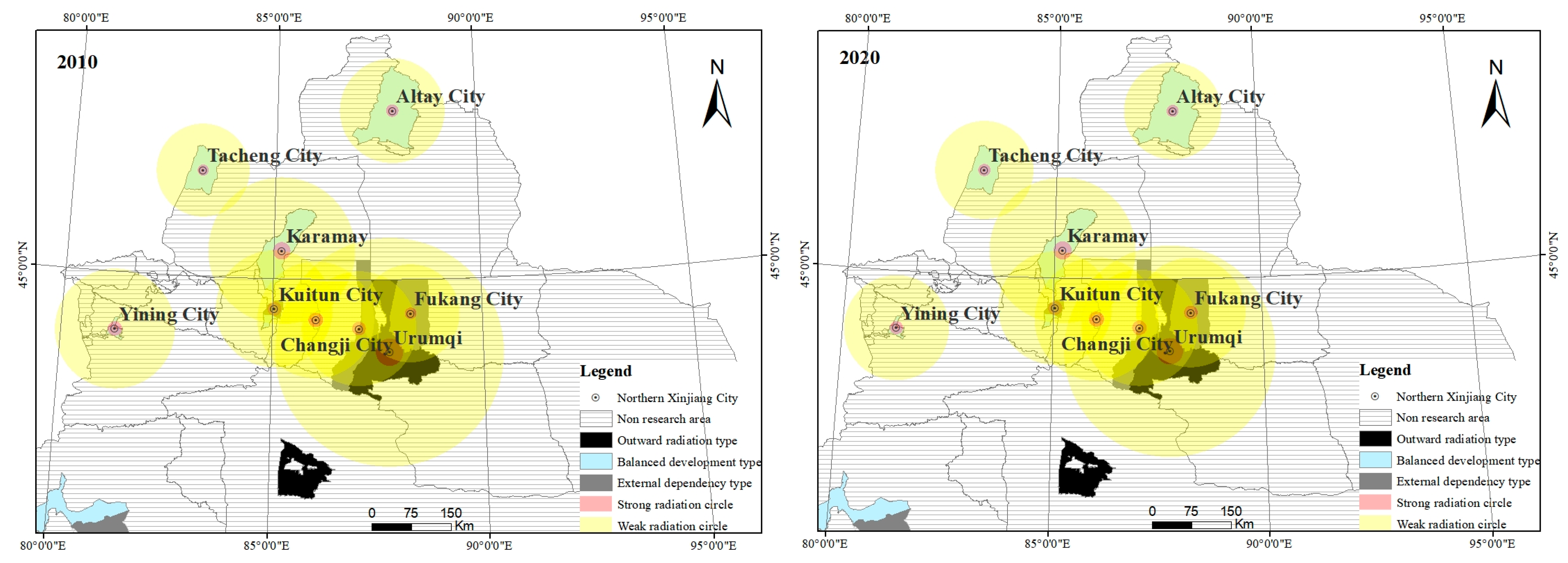
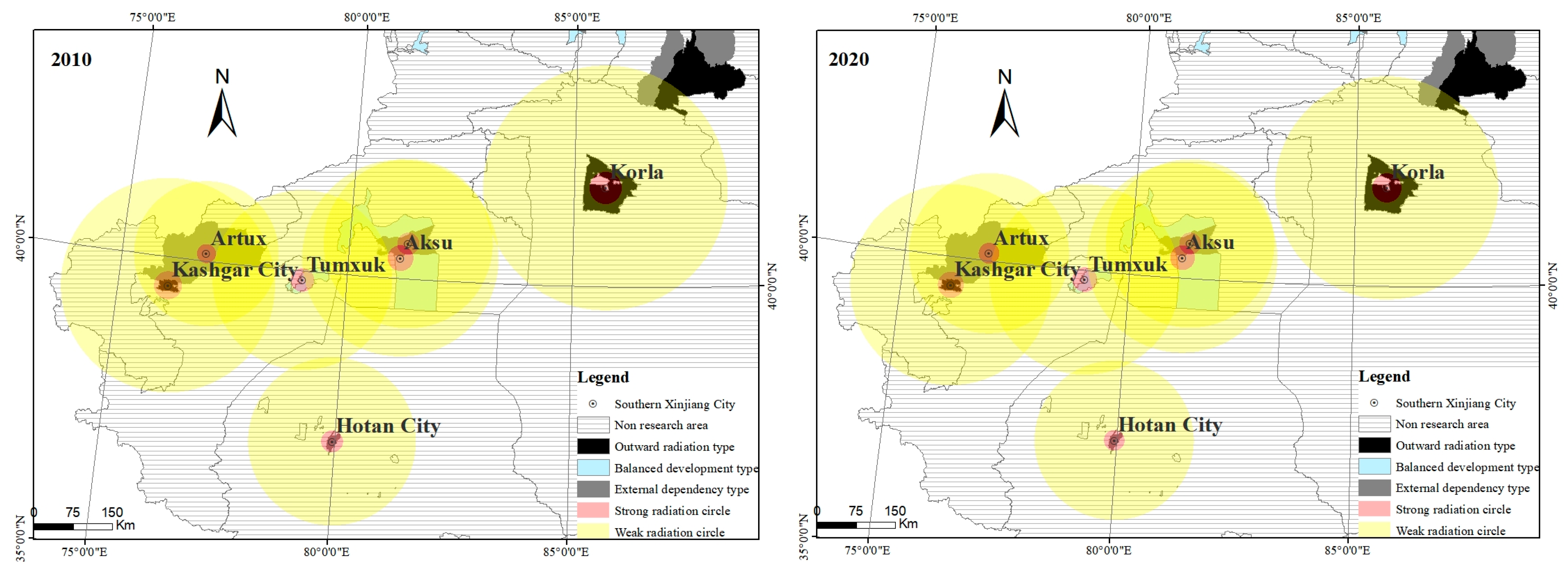
4.4. Scope Analysis of Urban Attractiveness
4.4.1. Analysis of Urban Breakpoints and Field Strengths
4.4.2. Urban Radius
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tao, Z.; Guanghui, J.; Ruijuan, Z.; Qiuyue, Z.; Wenqiu, M.; Qinglei, Z.; Yuling, L. Addressing the rural in situ urbanization (RISU) in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region: Spatio-temporal pattern and driving mechanism. Cities 2018, 75, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rześny Cieplińska, J.; Szmelter Jarosz, A.; Moslem, S. Priority-based stakeholders analysis in the view of sustainable city logistics: Evidence for Tricity, Poland. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 67, 102751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Sherbinin Alex, D.; Shi, G.; Xia, H. The Economic Spatial Structure Evolution of Urban Agglomeration under the Impact of High-Speed Rail Construction: Is There a Difference between Developed and Developing Regions? Land 2022, 11, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, L.; Ren, Y. A spatial effect study on financial agglomeration promoting the green development of urban agglomerations. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 70, 102900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, X.; Ahmed Bhuiyan, M.; Huang, Z. Influence of Economic and Financial Openness in Urban Agglomerations of Major Bay Areas. Emerg. Mark. Financ. Trade 2022, 58, 3689–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derudder, B.; Cao, Z.; Liu, X.; Shen, W.; Dai, L.; Zhang, W.; Caset, F.; Witlox, F.; Taylor, P.J. Changing Connectivities of Chinese Cities in the World City Network, 2010–2016. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 183–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhaowu, Y.; Yawen, Y.; Gaoyuan, Y.; Xiangrong, W.; Henrik, V. Strong contribution of rapid urbanization and urban agglomeration development to regional thermal environment dynamics and evolution. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 446, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boris, A.P. Development similarities in urban clusters: Evidence from a spatial analysis of Israel’s urban system. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2004, 39, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Xue, Y.; Chen, Z.; Miao, Y.; Shi, J. Economic spatial structure of China’s urban agglomerations: Regional differences, distribution dynamics, and convergence. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 87, 104253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengyu, Y.; Bingxuan, H.U. The Impact of City Cluster Development on the Inter-City Disparity: Evidence from China. Chin. J. Urban Environ. Stud. 2022, 10, 2250006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Yaping, Z.; Guofu, Y.; Yinyi, W.; Xiaomeng, C.; Bin, X. Spatial Reconstruction of Traditional Villages towards Synergistic Development in the Fuchun River Basin Based on the Gravity Model. Land 2023, 12, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, Z.; Zhiling, G.; Jingang, L. Analysis of the China’s Interprovincial Innovation Connection Network Based on Modified Gravity Model. Land 2023, 12, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, T.; Tao, L.; Guicai, L.; Lei, Y. Empirical analysis of city contact in Zhujiang (Pearl) River Delta, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao-fang, Y. Structure and restructuring of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei megalopolis in China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2003, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaolin, L.; Xianghui, Z.; Xingyu, P.; Xiuxin, M.; Mingyang, T. The spatial integration and coordinated industrial development of urban agglomerations in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Cities 2020, 104, 102801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BoHua, S. Kepler’s third law of n-body periodic orbits in a Newtonian gravitation field. Sci. China (Phys. Mech. Astron.) 2018, 61, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Yuting, H. Research on the spatial pattern of Hefei metropolitan area based on improved urban gravity model. Acad. J. Bus. Manag. 2020, 2, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Cao, W.; Yang, X. Urban Spatial Linkage characteristics along the lower Yellow River based on an improved gravity model. Areal Res. Dev. 2021, 40, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, S.; Xiu, C. Comparison of the Spatial Expansion Synergy in Five Regional Urban Agglomerations in China Based on the Night Lighting Data. China Land Sci. 2019, 33, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qin, J.; Luo, L.; Feng, Y. Research on the Evaluation of Coordinated Development of Tourism–Economy–Ecological Environment along the Silk Road Economic Belt. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, H. The Structural Features and Centrality Optimization of a Firm Interlocking Network of the Nodal Cities on the South Route of the 21st-Century Maritime Silk Road: The Case of Fujian Province. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhen, H. Detection of spatial and temporal variation characteristics of vegetation cover in the economic zone of the northern slopes of Tianshan Mountains and the influencing factors. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xi, S.; Zhang, M. Provincial division of economic zones based on the improved urban gravity model: A case study of Hunan Province, China. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0261205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanfei, W.; Yansui, L.; Yuheng, L.; Tingting, L. The spatio-temporal patterns of urban–rural development transformation in China since 1990. Habitat Int. 2016, 53, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jin, X. Measurement of Spatial Interaction between Central Towns Based on the Gravity Model. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2016, 36, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wei, Y.D.; Li, H.; Liu, M. Amenity, firm agglomeration, and local creativity of producer services in Shanghai. Cities 2022, 120, 103421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Qi, D. Relationship between Urban Economic Connections and Geoeconomic Relations in Northeast China. Complexity 2020, 2020, 5263048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yue, X.; Li, C.; Wang, M.; Zhang, H.O.; Su, Y. Relationship between Urban Three-Dimensional Spatial Structure and Population Distribution: A Case Study of Kunming’s Main Urban District, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Zhang, A.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B. Modeling urban growth in a metropolitan area based on bidirectional flows, an improved gravitational field model, and partitioned cellular automata. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2019, 33, 877–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhazzani, M.; Alhasoun, F.; Alawwad, Z.; González Marta, C. Urban attractors: Discovering patterns in regions of attraction in cities. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, T.; Marconcini, M.; Marmanis, D.; Zeidler, J.; Elsayed, S.; Metz, A.; Müller, A.; Dech, S. Dimensioning urbanization—An advanced procedure for characterizing human settlement properties and patterns using spatial network analysis. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 55, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yin, G.; Peng, X.; Zhou, X.; Dong, Q. Quantifying the environmental characteristics influencing the attractiveness of commercial agglomerations with big geo-data. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2023, 50, 2470–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, Z. The network structure and driving factors of urban competitiveness based on traffic flow and radiation model: A case study of the urban agglomeration in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2023, 43, 1900–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zhao, F.; Zeng, H.; Lin, M.; Chen, H.; Zuo, X.; He, J.; Hou, Z. Suitability of Underground Space Development in Plateau Cities Based on Geological Environment Analysis: Case Study in Kunming, China. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2021, 147, 05021014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Lin, J.; Cai, A.; Fan, Q. Structure of Polycentric Circles Based on the Urban Radiation Pattern: A Case Study in the Yangtze River Delta Region, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Fan, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, L. Simulating the Spatial Mismatch between Ecosystem Services’ (ESs’) Supply and Demand Based on Their Spatial Transfer in Urban Agglomeration Area, China. Land 2022, 11, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Li, L.I.; Sun, W. Evolution of the Spatial Heterogeneity of Urban Linkages in the urban agglomeration around Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 42, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, M.; Xu, G.; Xiao, R. Distance decay of nighttime lights from urban centers and its application. Prog. Geogr. 2022, 41, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Xu, L.; Yang, L. Structural characteristics and formation mechanism of carbon emission spatial association networks within China. Syst. Eng.-Theory Pract. 2023, 43, 958–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schade, K. Mapping Framework Conditions for Societal Participation of Immigrants—A Cluster Analysis of Medium-Sized Cities in Germany. Erdkunde 2023, 77, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedgenizov, A.; Strizhakov, E. Classification of Urban Focal Points Based on Cluster Analysis. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 667, 012109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Xu, E. Exploration of Urban Network Spatial Structure Based on Traffic Flow, Migration Flow and Information Flow: A Case Study of Shanxi Province, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Li, X.; Liu, X. Evolution of spatial and temporal pattern of regional economic connection network in Xinjiang. Arid Land Geogr. 2022, 45, 1978–1987. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J. A study of the economic growth effects of market integration: An examination of 27 cities in the Yangtze River Delta city cluster. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0287970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Huang, L.; Wang, C.-D.; Yang, H.; Liang, J. AttractRank: District Attraction Ranking Analysis Based on Taxi Big Data. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 17, 1679–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, F.; Chen, M.; Tian, M.; Sun, L.; Su, G.; Liu, R. A Structure Identification Method for Urban Agglomeration Based on Nighttime Light Data and Railway Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral Mateus, H.; Benites-Lazaro Lira, L.; Antonio de Almeida Sinisgalli, P.; Prates da Fonseca Alves, H.; Giatti Leandro, L. Environmental injustices on green and blue infrastructure: Urban nexus in a macrometropolitan territory. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 289, 125829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valls, J.-F.; Sureda, J.; Valls-Tuñon, G. Attractiveness Analysis of European Tourist Cities. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2014, 31, 178–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Luo, X.; Gu, Z. Integration of Xinjiang Production And Construction Corps and Local Government: Exploration on Coordinated Development of Urumqi Metropolitan Area. City Plan. Rev. 2022, 46, 38–43+55. [Google Scholar]

| Level 1 Indicators | Secondary Indicators | Indicator Weights |
|---|---|---|
| Size of economy | Urban population (10,000) | 13.968 |
| GDP per capita (persons/USD) | 7.931 | |
| Share of secondary and tertiary industries (%) | 2.123 | |
| Average wage of employed workers (dollars) | 9.627 | |
| Landholding | Built-up area (Km2) | 21.444 |
| Population density (persons/Km2) | 3.539 | |
| Urban road area per capita (m2) | 5.459 | |
| Level of social development | Total retail sales of social consumer goods (million USD) | 26.499 |
| City gas penetration rate (%) | 1.218 | |
| Eco-Environmental Protection | Public green space per capita (m2) | 6.325 |
| Greening coverage of built-up areas (%) | 1.867 |
| Age | 2010 | 2013 | 2016 | 2020 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | Urban Comprehensive Strength | Urban Comprehensive Gravity | Urban Comprehensive Strength | Urban Comprehensive Gravity | Urban Comprehensive Strength | Urban Comprehensive Gravity | Urban Comprehensive Strength | Urban Comprehensive Gravity |
| Urumqi | 0.5199 | 2380.8623 | 0.7149 | 4706.5183 | 0.7837 | 6149.6849 | 0.7862 | 6197.707 |
| Karamay | 0.214 | 419.2699 | 0.3262 | 908.0753 | 0.3443 | 1101.5086 | 0.3737 | 1253.0383 |
| Shihezi city | 0.159 | 370.8971 | 0.2243 | 737.7493 | 0.2515 | 957.7472 | 0.2376 | 887.7689 |
| Changji city | 0.1308 | 368.5206 | 0.1928 | 791.7402 | 0.2466 | 1257.7024 | 0.2375 | 1183.108 |
| Fukang city | 0.0953 | 186.6684 | 0.1735 | 562.7752 | 0.231 | 957.4028 | 0.2106 | 825.5427 |
| Yining city | 0.143 | 106.2632 | 0.1773 | 171.721 | 0.2172 | 256.3679 | 0.1939 | 216.9976 |
| Kuitun city | 0.1363 | 388.9559 | 0.1764 | 672.3875 | 0.1942 | 836.1194 | 0.227 | 1076.102 |
| Tacheng city | 0.0859 | 68.6727 | 0.1167 | 127.0178 | 0.1571 | 221.2435 | 0.1693 | 251.7137 |
| Altay city | 0.1088 | 87.6592 | 0.0973 | 82.5996 | 0.1568 | 194.593 | 0.1655 | 213.6615 |
| Age | 2010 | 2013 | 2016 | 2020 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | Urban Comprehensive Strength | Urban Comprehensive Gravity | Urban Comprehensive Strength | Urban Comprehensive Gravity | Urban Comprehensive Strength | Urban Comprehensive Gravity | Urban Comprehensive Strength | Urban Comprehensive Gravity |
| Korla | 0.1954 | 87.2826 | 0.2627 | 155.0794 | 0.2821 | 199.5615 | 0.3195 | 261.3781 |
| Aksu | 0.125 | 106.6557 | 0.1839 | 210.3098 | 0.1956 | 272.8875 | 0.2296 | 373.9949 |
| Artux | 0.0671 | 57.0835 | 0.0939 | 108.7569 | 0.1275 | 195.7921 | 0.1616 | 298.635 |
| Kashgar city | 0.1467 | 145.7485 | 0.1949 | 258.3227 | 0.2385 | 406.9163 | 0.2533 | 498.4918 |
| Hotan city | 0.0909 | 37.6211 | 0.1256 | 69.7633 | 0.1212 | 74.1743 | 0.1607 | 123.2423 |
| Alaer | 0.0924 | 62.6546 | 0.1127 | 97.1373 | 0.1503 | 166.4638 | 0.1803 | 236.634 |
| Tumxuk | 0.104 | 75.3698 | 0.1118 | 97.0606 | 0.2135 | 281.3145 | 0.2287 | 340.7354 |
| City Type | City Type Name | City Type Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | Outward-radiation type | Cities exhibit positive attraction as the dominant factor, radiating and driving the surrounding cities. |
| Type 2 | Balanced-development type | Cities exhibit a balance between positive and negative attraction, with a balance between external radiation and absorption. |
| Type 3 | Outward-dependence type | Cities exhibit a dominant negative attraction and are greatly influenced by surrounding cities, mainly relying on the development of central cities. |
| City 1 | City 2 | 2010 | 2020 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific Gravity of Breaking Point | Field Strength | Specific Gravity of Breaking Point | Field Strength | ||
| Urumqi | Karamay | 0.61 | 0.1407 | 0.59 | 0.2253 |
| Urumqi | Shihezi city | 0.64 | 0.5915 | 0.65 | 0.8907 |
| Urumqi | Changji city | 0.67 | 7.7477 | 0.65 | 12.477 |
| Urumqi | Fukang city | 0.7 | 2.8315 | 0.66 | 4.8344 |
| Urumqi | Yining city | 0.66 | 0.0257 | 0.67 | 0.0375 |
| Urumqi | Kuitun city | 0.66 | 0.1987 | 0.65 | 0.3106 |
| Urumqi | Tacheng city | 0.71 | 0.0327 | 0.68 | 0.0537 |
| Urumqi | Altay city | 0.69 | 0.0446 | 0.69 | 0.0676 |
| Karamay city | Shihezi city | 0.54 | 0.1988 | 0.56 | 0.3234 |
| Karamay city | Changji city | 0.56 | 0.0845 | 0.56 | 0.1501 |
| Karamay city | Fukang city | 0.6 | 0.0467 | 0.57 | 0.0898 |
| Karamay city | Yining city | 0.55 | 0.0208 | 0.58 | 0.0325 |
| Karamay city | Kuitun city | 0.56 | 0.3323 | 0.56 | 0.5683 |
| Karamay city | Tacheng city | 0.61 | 0.1002 | 0.6 | 0.1836 |
| Karamay city | Altay city | 0.58 | 0.0371 | 0.6 | 0.0613 |
| Shihenzi city | Changji city | 0.52 | 0.4335 | 0.5 | 0.7123 |
| Shihenzi city | Fukang city | 0.56 | 0.1401 | 0.52 | 0.2507 |
| Shihenzi city | Yining city | 0.51 | 0.0197 | 0.53 | 0.0281 |
| Shihenzi city | Kuitun city | 0.52 | 0.4619 | 0.51 | 0.7276 |
| Shihenzi city | Tacheng city | 0.58 | 0.0246 | 0.54 | 0.0415 |
| Shihenzi city | Altay city | 0.55 | 0.0151 | 0.55 | 0.0228 |
| Changji city | Fukang city | 0.54 | 0.6972 | 0.52 | 1.3887 |
| Changji city | Yining city | 0.49 | 0.0127 | 0.53 | 0.02 |
| Changji city | Kuitun city | 0.49 | 0.1156 | 0.51 | 0.201 |
| Changji city | Tacheng city | 0.55 | 0.0152 | 0.54 | 0.0287 |
| Changji city | Altay city | 0.52 | 0.0211 | 0.55 | 0.0353 |
| Fukang city | Yining city | 0.45 | 0.0089 | 0.51 | 0.0153 |
| Fukang city | Kuitun city | 0.46 | 0.0559 | 0.49 | 0.1064 |
| Fukang city | Tacheng city | 0.51 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 0.0209 |
| Fukang city | Altay city | 0.48 | 0.0181 | 0.53 | 0.0332 |
| Yining city | Kuitun city | 0.51 | 0.028 | 0.48 | 0.0422 |
| Yining city | Tacheng city | 0.56 | 0.0144 | 0.52 | 0.0232 |
| Yining city | Altay city | 0.53 | 0.0051 | 0.52 | 0.0072 |
| Kuitun city | Tacheng city | 0.56 | 0.0312 | 0.54 | 0.0561 |
| Kuitun city | Altay city | 0.53 | 0.0163 | 0.54 | 0.026 |
| Tacheng city | Altay city | 0.47 | 0.0105 | 0.5 | 0.0181 |
| City 1 | City 2 | 2010 | 2020 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific Gravity of Breaking Point | Field Strength | Specific Gravity of Breaking Point | Field Strength | ||
| Korla | Aksu | 0.56 | 0.0209 | 0.54 | 0.036 |
| Korla | Artux | 0.63 | 0.0052 | 0.58 | 0.01 |
| Korla | Kashgar city | 0.54 | 0.0067 | 0.53 | 0.0112 |
| Korla | Hotan city | 0.59 | 0.0061 | 0.59 | 0.0102 |
| Korla | Alaer | 0.59 | 0.0188 | 0.57 | 0.0331 |
| Korla | Tumxuk | 0.58 | 0.0099 | 0.54 | 0.0185 |
| Aksu | Artux | 0.58 | 0.0212 | 0.54 | 0.0438 |
| Aksu | Kashgar city | 0.48 | 0.0255 | 0.49 | 0.0453 |
| Aksu | Hotan city | 0.54 | 0.0138 | 0.54 | 0.0248 |
| Aksu | Alaer | 0.54 | 0.2872 | 0.53 | 0.5425 |
| Aksu | Tumxuk | 0.52 | 0.0945 | 0.5 | 0.1896 |
| Artux | Kashgar city | 0.4 | 2.1001 | 0.44 | 4.1759 |
| Artux | Hotan city | 0.46 | 0.0105 | 0.5 | 0.0215 |
| Artux | Alaer | 0.46 | 0.0112 | 0.49 | 0.0242 |
| Artux | Tumxuk | 0.45 | 0.0399 | 0.46 | 0.0914 |
| Kashgar city | Hotan city | 0.56 | 0.0193 | 0.56 | 0.0337 |
| Kashgar city | Alaer | 0.56 | 0.0145 | 0.54 | 0.0264 |
| Kashgar city | Tumxuk | 0.54 | 0.0455 | 0.51 | 0.088 |
| Hotan | Alaer | 0.5 | 0.0184 | 0.49 | 0.0342 |
| Hotan | Tumxuk | 0.48 | 0.0111 | 0.46 | 0.0221 |
| Alaer | Tumxuk | 0.49 | 0.0622 | 0.47 | 0.1292 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, L.; Chen, H.; Ma, Y. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Changes in the Gravitational Structure of Urban Agglomerations in Northern and Southern Xinjiang Based on a Gravitational Model. Land 2024, 13, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13010029
Liu D, Wang Y, Wang L, Xu L, Chen H, Ma Y. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Changes in the Gravitational Structure of Urban Agglomerations in Northern and Southern Xinjiang Based on a Gravitational Model. Land. 2024; 13(1):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13010029
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Difan, Yuejian Wang, Lei Wang, Liping Xu, Huanhuan Chen, and Yuxiang Ma. 2024. "Analysis of Spatiotemporal Changes in the Gravitational Structure of Urban Agglomerations in Northern and Southern Xinjiang Based on a Gravitational Model" Land 13, no. 1: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13010029
APA StyleLiu, D., Wang, Y., Wang, L., Xu, L., Chen, H., & Ma, Y. (2024). Analysis of Spatiotemporal Changes in the Gravitational Structure of Urban Agglomerations in Northern and Southern Xinjiang Based on a Gravitational Model. Land, 13(1), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13010029






