Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of the Coupling Coordination of Urban Ecological Resilience and New Quality Productivity at the Provincial Scale in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Research Status
2.2. Mechanism Analysis
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Data Source
3.3. Index System
3.4. Research Methods
3.4.1. Entropy Weight-CRITIC Method
3.4.2. TOPSIS
3.4.3. Coupling Coordination Degree Model
3.4.4. Global Spatial Autocorrelation
3.4.5. GTWR Model
4. Results
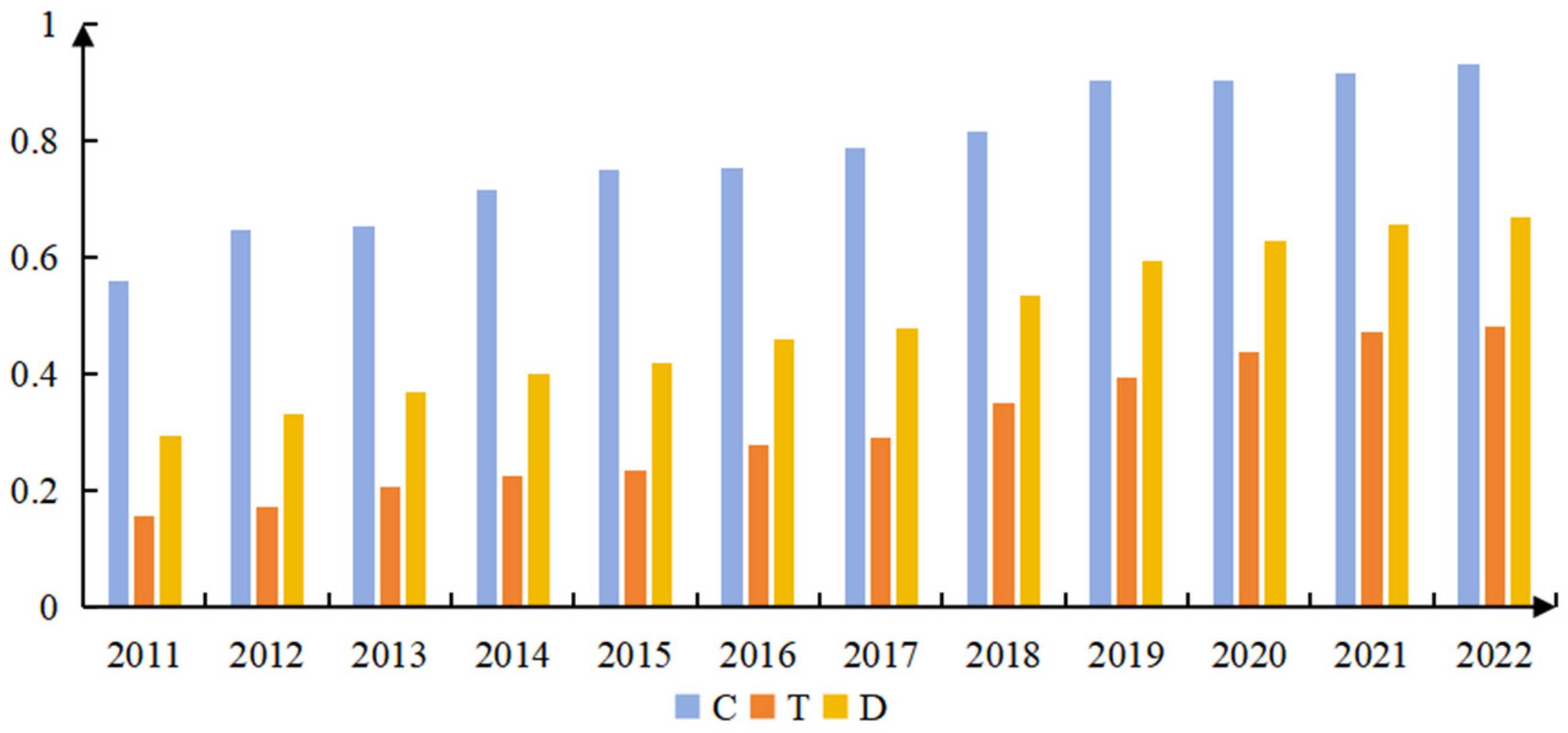
4.1. Development Level of UER and NQP
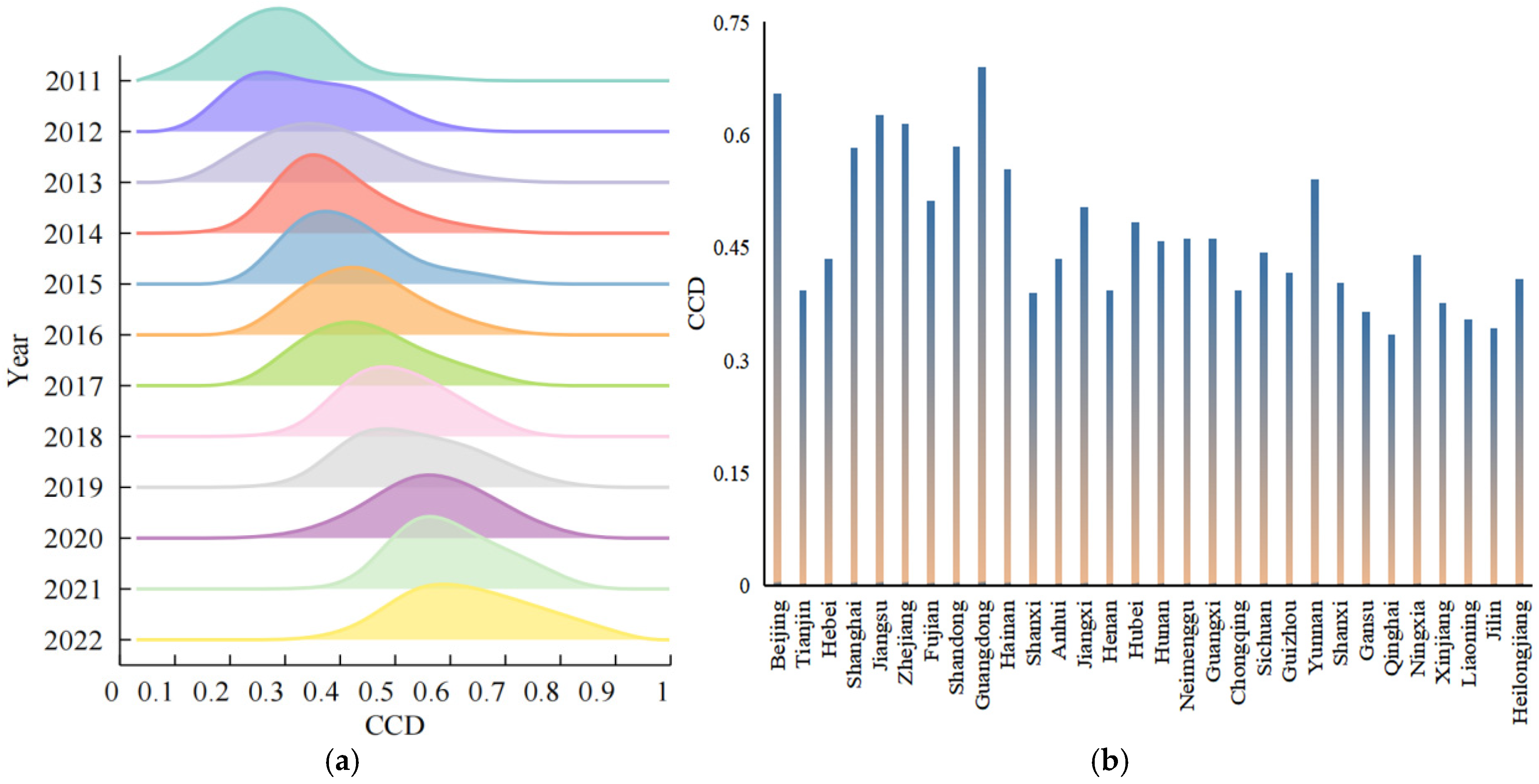
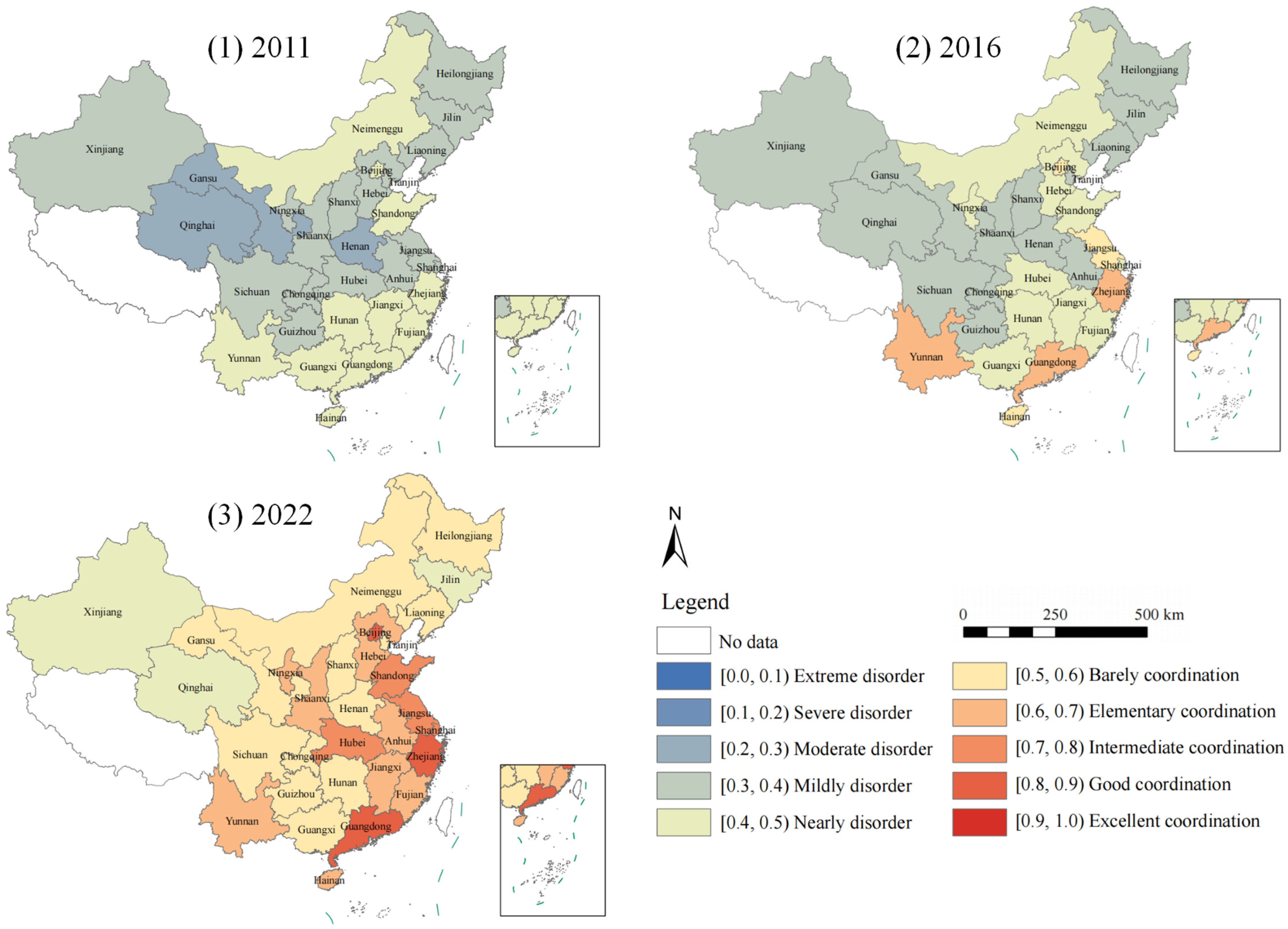
4.2. CCD Level
4.3. Influencing Factors
4.3.1. Spatial Correlation
4.3.2. GTWR Model Test
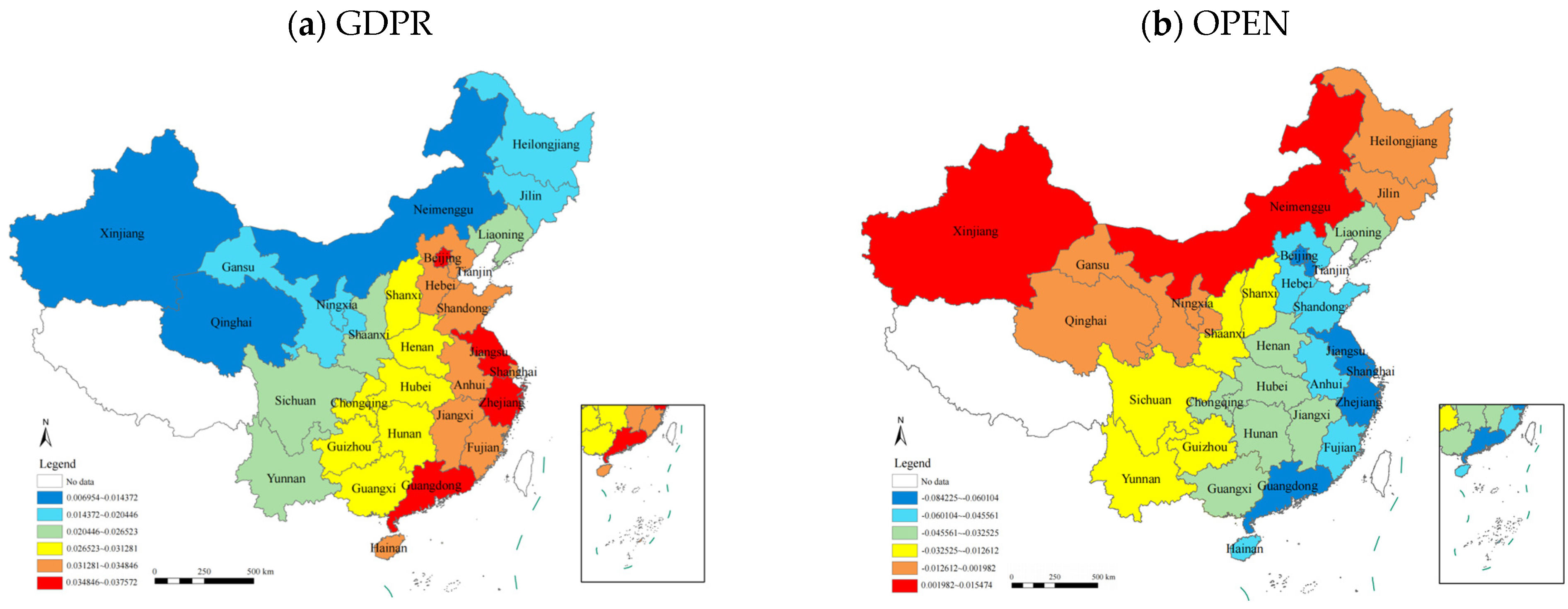
4.3.3. Temporal Changes in Influencing Factors
4.3.4. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Influencing Factors
5. Discussion
5.1. Analysis of UER and NQP Levels
5.2. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of CCD
5.3. Analysis of Influencing Factors
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, Y.; Tong, L.; Mei, L. The effect of industrial agglomeration on green development efficiency in Northeast China since the revitalization. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Lei, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, L. Opportunities for low-carbon socioeconomic transition during the revitalization of Northeast China: Insights from Heilongjiang province. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 683, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y. The Coupling Coordination Degree of Economic, Social and Ecological Resilience of Urban Agglomerations in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Su, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S. Constructing ecological security patterns based on ecosystem services trade-offs and ecological sensitivity: A case study of Shenzhen metropolitan area, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L. Driving rural industry revitalization in the digital economy era: Exploring strategies and pathways in China. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0292241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J. Green transformation of circular economy from the perspective of ecological environment protection. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2020, 21, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Su, Z.; Fu, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y. Research on the Ecological Innovation Efficiency of the Zhongyuan Urban Agglomeration: Measurement, Evaluation and Optimization. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Noorliza, K.; Zhang, X. Enhancing Environmental, Social, and Governance Performance through New Quality Productivity and Green Innovation. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, Z. Synergistic industrial agglomeration, new quality productive forces and high-quality development of the manufacturing industry. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 94, 103373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, L. New Quality Productivity and Chinese Modernization: Analysis based on the Perspective of Scientific and Technological Innovation. Int. J. Soc. Sci. Public Adm. 2024, 2, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folke, C.; Carpenter, S.; Elmqvist, T.; Gunderson, L.; Holling, C.S.; Walker, B. Resilience and sustainable development: Building adaptive capacity in a world of transformations. Ambio 2002, 31, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yodo, N.; Wang, P. Engineering Resilience Quantification and System Design Implications: A Literature Survey. J. Mech. Des. 2016, 138, 111408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holling, C.S. Resilience and Stability of Ecological Systems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1973, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.R.; Holling, C.S. Novelty, Adaptive Capacity, and Resilience. Ecol. Soc. 2010, 15, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, P.; Folke, C.; Berkes, F. Adaptive comanagement for building resilience in social-ecological systems. Environ. Manag. 2004, 34, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabisch, N.; Frantzeskaki, N.; Pauleit, S.; Naumann, S.; Davis, M.; Artmann, M.; Haase, D.; Knapp, S.; Korn, H.; Stadler, J.; et al. Nature-based solutions to climate change mitigation and adaptation in urban areas: Perspectives on indicators, knowledge gaps, barriers, and opportunities for action. Ecol. Soc. 2016, 21, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhai, G.; Zhou, S.; Shi, Y. Risk reduction through urban spatial resilience: A theoretical framework. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2021, 27, 921–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Sharma, B.; Kumar, N.; Kumar, A. Establishing Conceptual Components for Urban Resilience: Taking Clues from Urbanization through a Planner’s Lens. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2023, 24, 04022040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Shu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, F. Temporal and spatial changes in industrial structure and resource and environmental carrying capacity of the Three Gorges ecological economic corridor of the Yangtze River, China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W. Optimisation of ecological security patterns in ecologically transition areas under the perspective of ecological resilience—A case of Taohe River. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112315. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Jiao, S.; Hu, J.; Guo, Q.; Yang, Y. An Ecological Resilience Assessment of a Resource-Based City Based on Morphological Spatial Pattern Analysis. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Tang, Y.; Bi, M.; Xiao, Z.; Zhong, Y. Analysis of Urban Resilience in Water Network Cities Based on Scale-Density-Morphology-Function (SDMF) Framework: A Case Study of Nanchang City, China. Land 2022, 11, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xiu, C.; Song, W. Landscape-Based Assessment of Urban Resilience and Its Evolution: A Case Study of the Central City of Shenyang. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhou, G.; Sun, H.; Fu, H.; Wu, H.; Liu, Y. Regrowth or smart decline? A policy response to shrinking cities based on a resilience perspective. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 108, 105431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salizzoni, E.; Perez-Campana, R.; Alcalde-Rodriguez, F.; Talavera-Garcia, R. Local Planning Practice towards Resilience: Insights from the Adaptive Co-Management and Design of a Mediterranean Wetland. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z. Assessment of temporal and spatial progress of urban resilience in Guangzhou under rainstorm scenarios. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 66, 102578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.U.; Ahmed, A.; Gilja, G.; Valyrakis, M.; Ghumman, A.R.; Pasha, G.A.; Farooq, R.J.W. A Laboratory Study of the Role of Nature-Based Solutions in Improving Flash Flooding Resilience in Hilly Terrains. Water 2023, 16, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhen, F.; Xie, Z. Urban resilience assessment based on contradiction between supply and demand of the daily activity-environment system: A case study on Nanjing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 144567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Kou, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H. System dynamics modelling for improving urban resilience in Beijing, China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 161, 104954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Xiang, P. Deciphering the spatial and temporal evolution of urban anthropogenic resilience within the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 88, 104274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, H. Environmental management and labor productivity: The moderating role of quality management. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 255, 109795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, L. Spatiotemporal effects of renewable energy technology innovation on industrial cleaner production: A geographically temporally weighted analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima Junior, P.; Deconto, D.C.S.; Andrella Neto, R.; Cavalcanti, C.J.d.H.; Ostermann, F. Marx como referencial para análise de relações entre ciência, tecnologia e sociedade. Ciência Educ. 2014, 20, 175–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lin, L.; Gu, T.; Shi, Y. The Influence of New Quality Productive Forces on High-Quality Agricultural Development in China: Mechanisms and Empirical Testing. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.; Chen, S.; Feng, Z.; Li, J. Industrial robots and firm productivity. Struct. Chang. Econ. Dyn. 2023, 67, 388–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Said, R.; Ismail, N.W.; Hamzah, H.Z. Impact of industrial robot on labour productivity: Empirical study based on industry panel data. Innov. Green Dev. 2024, 3, 100148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharin, R.; Syah Aji, R.H.; Yussof, I.; Mohd Saukani, N. Impact of human resource investment on labor productivity in Indonesia. Interdiscip. J. Manag. Stud. 2020, 13, 139–164. [Google Scholar]
- Poláková, M.; Suleimanová, J.H.; Madzík, P.; Copuš, L.; Molnárová, I.; Polednová, J. Soft skills and their importance in the labour market under the conditions of Industry 5.0. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Li, J.; Jin, Z. Can Digital Economy Drive Income Level Growth in the Context of Sustainable Development? Fresh Evidence from “Broadband China”. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Hao, Y. Path to sustainable development: Does digital economy matter in manufacturing green total factor productivity? Sustain. Dev. 2023, 31, 360–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Liang, C.; Yeung, A.C.; Zhou, H. The impact of intelligent manufacturing on labor productivity: An empirical analysis of Chinese listed manufacturing companies. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2024, 267, 109070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Song, M.; Cui, L. Driving force for China’s economic development under Industry 4.0 and circular economy: Technological innovation or structural change? J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 271, 122680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ma, X.; Chen, B.; Shang, Y.; Song, M. Challenges toward carbon neutrality in China: Strategies and countermeasures. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 176, 105959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Cheng, Y.; Yao, X. Environmental regulation, green technology innovation, and industrial structure upgrading: The road to the green transformation of Chinese cities. Energy Econ. 2021, 98, 105247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Peng, Y.-L.; Ma, C.-Q.; Shen, B. Can environmental innovation facilitate carbon emissions reduction? Evidence from China. Energy Policy 2017, 100, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Li, G. The drivers of eco-innovation and its impact on performance: Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 176, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Hu, W.-Q. A research on coordination between economy, society and environment in China: A case study of Jiangsu. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Shahzad, S.J.H.; Ahmad, N.; Alam, S. Financial development and environmental quality: The way forward. Energy Policy 2016, 98, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.-h.; Yuan, Y.-j.; Huang, J.-j. Different types of environmental regulations and heterogeneous influence on “green” productivity: Evidence from China. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 132, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asara, V.; Otero, I.; Demaria, F.; Corbera, E. Socially sustainable degrowth as a social–ecological transformation: Repoliticizing sustainability. Sustain. Sci. 2015, 10, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Li, J. Towards a green world: How do green technology innovations affect total-factor carbon productivity. Energy Policy 2019, 131, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerberg, J. Technological progress, structural change and productivity growth: A comparative study. In Innovation, Economic Development and Policy; Edward Elgar Publishing: Camberley, UK, 2018; pp. 214–232. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Lin, B. Economic growth model, structural transformation, and green productivity in China. Appl. Energy 2017, 187, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Tang, D.; Kong, H.; Boamah, V. Impact of industrial structure upgrading on green total factor productivity in the Yangtze river economic belt. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, C.; Shao, C.; Lee, C.-C. Green technology innovation and financial development: Do environmental regulation and innovation output matter? Energy Econ. 2021, 98, 105237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhan, J.; Zhao, F.; Yan, H.; Zhang, F.; Wei, X. Impacts of urbanization-induced land-use changes on ecosystem services: A case study of the Pearl River Delta Metropolitan Region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y. Assessing urban resilience in China from the perspective of socioeconomic and ecological sustainability. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 102, 107163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colding, J.; Marcus, L.; Barthel, S. Promoting Partnership between Urban Design and Urban Ecology Through Social-Ecological Resilience Building; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Zhu, X.; Wu, H.; Li, Z. Assessment of urban ecological resilience and its influencing factors: A case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration of China. Land 2022, 11, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Xiu, C.; Bai, L.; Zhong, Y.; Wei, Y.J.C. Comprehensive evaluation of urban resilience based on the perspective of landscape pattern: A case study of Shenyang city. Cities 2020, 104, 102722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Tian, J.; Li, X. Enhancing urban ecological resilience through integrated green technology progress: Evidence from Chinese cities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 36349–36366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Fang, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L. The evaluation and obstacle analysis of urban resilience from the multidimensional perspective in Chinese cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 86, 104160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Fang, C.; Liu, H.; Liu, X. Evaluating urban ecosystem resilience using the DPSIR framework and the ENA model: A case study of 35 cities in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 72, 102997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Jia, S.; Cui, X. From efficiency to resilience: Unraveling the dynamic coupling of land use economic efficiency and urban ecological resilience in Yellow River Basin. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Geng, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, K.; Liu, S. Increasing green infrastructure-based ecological resilience in urban systems: A perspective from locating ecological and disturbance sources in a resource-based city. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 61, 102354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Z. A review of social-ecological system resilience: Mechanism, assessment and management. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 723, 138113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Yu, Y.; Yang, S.; Lv, Y.; Sarker, M.N.I. Urban resilience for urban sustainability: Concepts, dimensions, and perspectives. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cui, Z.; Lin, J.; Xie, J.; Su, K. The coupling relationship between urbanization and ecological resilience in the Pearl River Delta. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 44–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y. How to scientifically understand “new quality productivity”. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2024, 39, 797–803. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Jiang, K.-Z. Coupling Mechanism, Factor Deconstruction and Symbiotic Path Between Dual Carbon Strategy and New Quality Productivity. J. Univ. Electron. Sci. Technol. China 2024, 26, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.; Bai, G.; Shen, Z.; Xia, L. Digital economy and its spatial effect on green productivity gains in manufacturing: Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 378, 134539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. Economics. The Influence Mechanism of Data Asset Management Regulation and New Quality Productivity on Innovation. J. Stat. Econ. 2024, 1, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Ding, Y.; Shi, Z.; He, Y. The impact of digital economy on total factor carbon productivity: The threshold effect of technology accumulation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 55691–55706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Shi, Y.; Wojewodzki, M.; Wei, Y.; Guo, M. The Impact of New-Type Urbanization Policy on Urban Green Total Factor Productivity: New Evidence from China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Q.; Bento, V.A.; Meng, X.; Li, X. Vegetation drought risk assessment based on the multi-weight methods in Northwest China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vavrek, R.; Chovancová. Assessment of economic and environmental energy performance of EU countries using CV-TOPSIS technique. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 106, 105519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Yang, F.; Yu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Huang, J.; Wei, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C. Quantization of the coupling mechanism between eco-environmental quality and urbanization from multisource remote sensing data. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimian, H.; Zou, W.; Chen, Y.; Xia, J.; Wang, Z. Landscape ecological risk assessment and driving factor analysis in Dongjiang river watershed. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Zhu, J.; Lou, K.; Yang, L. Coupling coordination and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between urbanization and ecological environment in Shaanxi Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wu, B.; Barry, M. Geographically and temporally weighted regression for modeling spatio-temporal variation in house prices. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Qing, W.; Li, C.; Yang, Y. Differential Evaluation of Ecological Resilience in 45 Cities along the Yangtze River in China: A New Multidimensional Analysis Framework. Land 2024, 13, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariken, M.; Zhang, F.; weng Chan, N.; Kung, H.-T. Coupling coordination analysis and spatio-temporal heterogeneity between urbanization and eco-environment along the Silk Road Economic Belt in China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Yang, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Q. Coupling coordination degree measurement and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between economic development and ecological environment—Empirical evidence from tropical and subtropical regions of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Jabeen, G. Relating economic openness and export diversification to eco-efficiency: Is green innovation critical? Int. J. Financ. Econ. 2024, 29, 3203–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Crespo, R.; Yao, J. Geographical and temporal weighted regression (GTWR). Geogr. Anal. 2015, 47, 431–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhu, X. A social-ecological resilience assessment and governance guide for urbanization processes in East China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Xie, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, P. An integrated approach for evaluating dynamics of urban eco-resilience in urban agglomerations of China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z.; Yuan, C.; Zhuolu, L.; Weiling, J. Ecological Resilience Assessment of an Emerging Urban Agglomeration: A Case Study of Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Circle, China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 31, 2381–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xu, C. Increasing urban ecological resilience based on ecological security pattern: A case study in a resource-based city. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 175, 106486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, Q. City size and urban labor productivity in China: New evidence from spatial city-level panel data analysis. Econ. Syst. 2017, 41, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Dong, X. Understanding regional talent attraction and its influencing factors in China: From the perspective of spatiotemporal pattern evolution. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Guo, J.; Guo, Z.; Lee, J.C.; Liu, G.; Wang, N. Urban ecological transition: The practice of ecological civilization construction in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, M.; Wang, X.; Qi, C. Spatiotemporal evolution and influencing factors of ecological civilization construction in China. Complexity 2020, 2020, 8829144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, P.; Chen, L. A quantitative framework to evaluate urban ecological resilience: Broadening understanding through multi-attribute perspectives. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1144244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, X. Conservation; Recycling. Industrial agglomeration, technological innovation and carbon productivity: Evidence from China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 166, 105330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Subsystem | Index | Attribute | Weight | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UER | Nature | Urban green coverage rate (%) [59] | + | 0.0423 |
| NDVI [59,60] | + | 0.0317 | ||
| Industrial “three wastes” emissions (t) [61] | − | 0.1364 | ||
| Sewage treatment rate (%) [61] | + | 0.1023 | ||
| Soil erosion degree (t km−2 a−1) [62] | − | 0.0714 | ||
| Economy | GDP per capita (yuan) growth rate (%) [61,63] | + | 0.1306 | |
| Output of the tertiary sector as a percentage of GDP (%) [64] | + | 0.1492 | ||
| Completed investment in industrial pollution control (billion yuan) [65] | − | 0.0667 | ||
| Energy consumption per unit of GDP (t standard coal/10,000 yuan) [66] | − | 0.0104 | ||
| Society | Degree of population urbanization (persons/km2) [66] | + | 0.0135 | |
| Comprehensive utilization rate of industrial solid waste (%) [67] | + | 0.0949 | ||
| Natural population growth rate (%) [68] | + | 0.0107 | ||
| Investment in infrastructure construction (100 million yuan) [65] | + | 0.1079 | ||
| Urban sewage treatment rate (%) [66] | + | 0.0320 | ||
| NQP | New quality laborers | Regional investment in science (100 million yuan) [69] | + | 0.0549 |
| Regional investment in education (100 million yuan) [34] | + | 0.0494 | ||
| Number of persons enrolled in university (people) [70] | + | 0.1099 | ||
| Number of R&D personnel (people) [71] | + | 0.1386 | ||
| New quality labor materials | Number of Internet users per 100 people (units) [72] | + | 0.0675 | |
| Telecom business volume per capita (units) [70] | + | 0.1028 | ||
| Digital inclusive finance index [69] | + | 0.0704 | ||
| Total number of digital patents (units) [72] | + | 0.0649 | ||
| Digital economy index [73] | + | 0.0361 | ||
| New quality labor objects | Ratio of the sum of emerging industry income to GDP (%) [69] | + | 0.0382 | |
| Total renewable energy electricity consumption (billion kWh) [69] | + | 0.0794 | ||
| Robot installation density (units/square meter) [71] | + | 0.0363 | ||
| Ratio of R&D investment to GDP (%) [74] | + | 0.0844 | ||
| Ratio of green patent applications to total patents (%) [8] | + | 0.0673 |
| Year | Moran’s I | Year | Moran’s I |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 0.197 *** | 2017 | 0.196 *** |
| 2012 | 0.203 *** | 2018 | 0.217 *** |
| 2013 | 0.211 *** | 2019 | 0.223 *** |
| 2014 | 0.170 ** | 2020 | 0.228 *** |
| 2015 | 0.168 ** | 2021 | 0.230 *** |
| 2016 | 0.189 *** | 2022 | 0.235 *** |
| Variable | Meaning | Description of the Variable |
|---|---|---|
| GDPR | Economic development | GDP per capita (10,000 yuan) |
| OPEN | Foreign investment | Annual foreign investment (100 million yuan) |
| UBR | Urbanization rate | Proportion of urban resident population to total population (%) |
| IS | Industrial structure | Secondary industry output value as a percentage of GDP (%) |
| TI | Technological innovation | R&D expenditure (100 million yuan) |
| ER | Environmental regulation | Environmental protection investment as a percentage of GDP (%) |
| Variable | GDPR | OPEN | UBR | IS | TI | ER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIF | 5.065 | 3.385 | 1.950 | 2.011 | 1.374 | 0.844 |
| Model | GTWR | GWR | OLS |
|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.9977 | 0.9962 | 0.9433 |
| AICc | −671.599 | −587.069 | 13.1508 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Sun, K. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of the Coupling Coordination of Urban Ecological Resilience and New Quality Productivity at the Provincial Scale in China. Land 2024, 13, 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13121998
Yang L, Xu Y, Zhu J, Sun K. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of the Coupling Coordination of Urban Ecological Resilience and New Quality Productivity at the Provincial Scale in China. Land. 2024; 13(12):1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13121998
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Li, Yue Xu, Junqi Zhu, and Keyu Sun. 2024. "Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of the Coupling Coordination of Urban Ecological Resilience and New Quality Productivity at the Provincial Scale in China" Land 13, no. 12: 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13121998
APA StyleYang, L., Xu, Y., Zhu, J., & Sun, K. (2024). Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of the Coupling Coordination of Urban Ecological Resilience and New Quality Productivity at the Provincial Scale in China. Land, 13(12), 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13121998









