Salinity Effects on Soil Structure and Hydraulic Properties: Implications for Pedotransfer Functions in Coastal Areas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
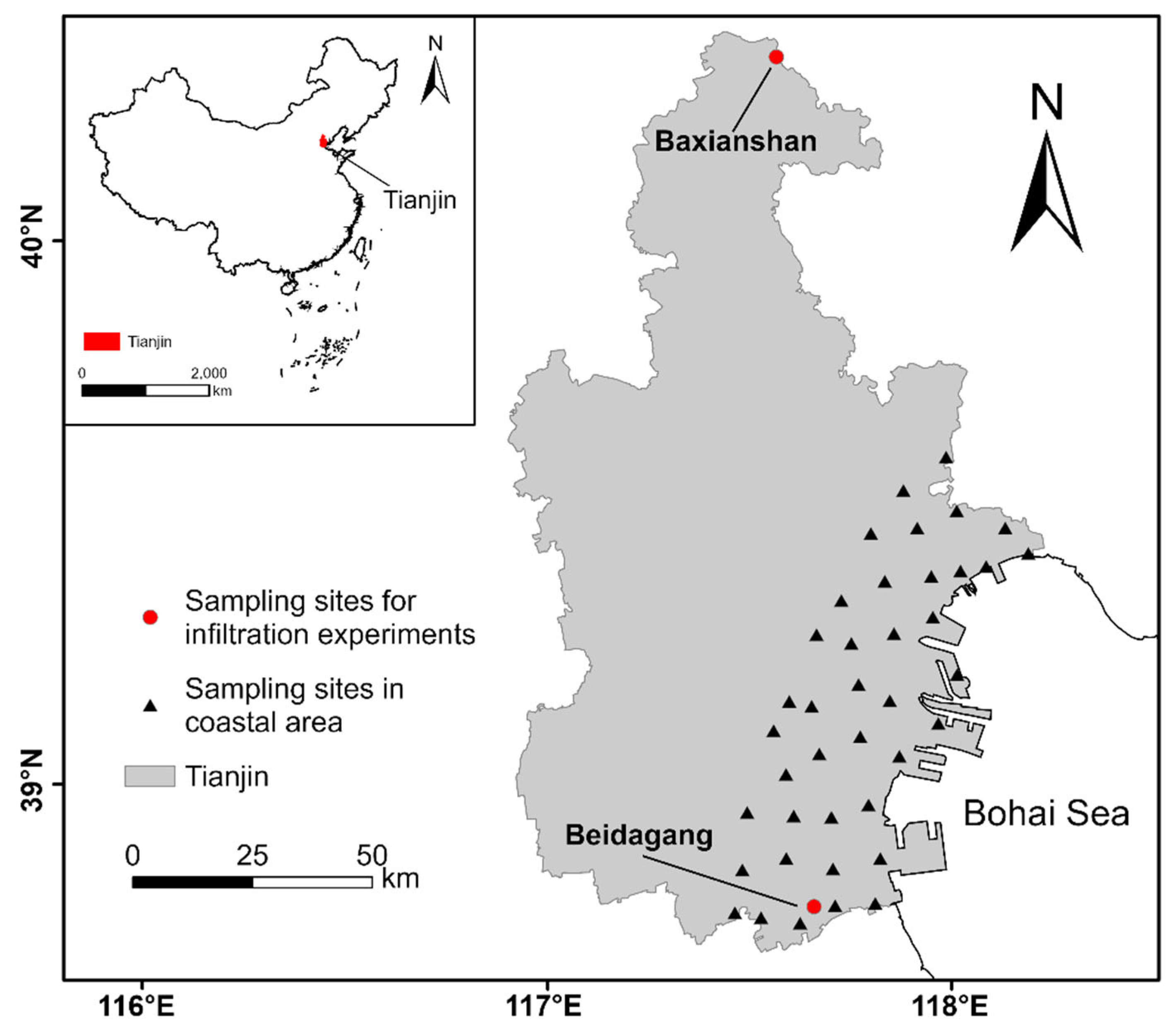
2.1. Study Area and Field Campaign
2.2. Lab Experiments
2.2.1. Measurements of Soil Properties
2.2.2. Soil Column Infiltration Experiments
2.2.3. Determination of Soil Water-Retention Curves
2.2.4. Construction of Salinity-Based PTFs
3. Results and Discussion
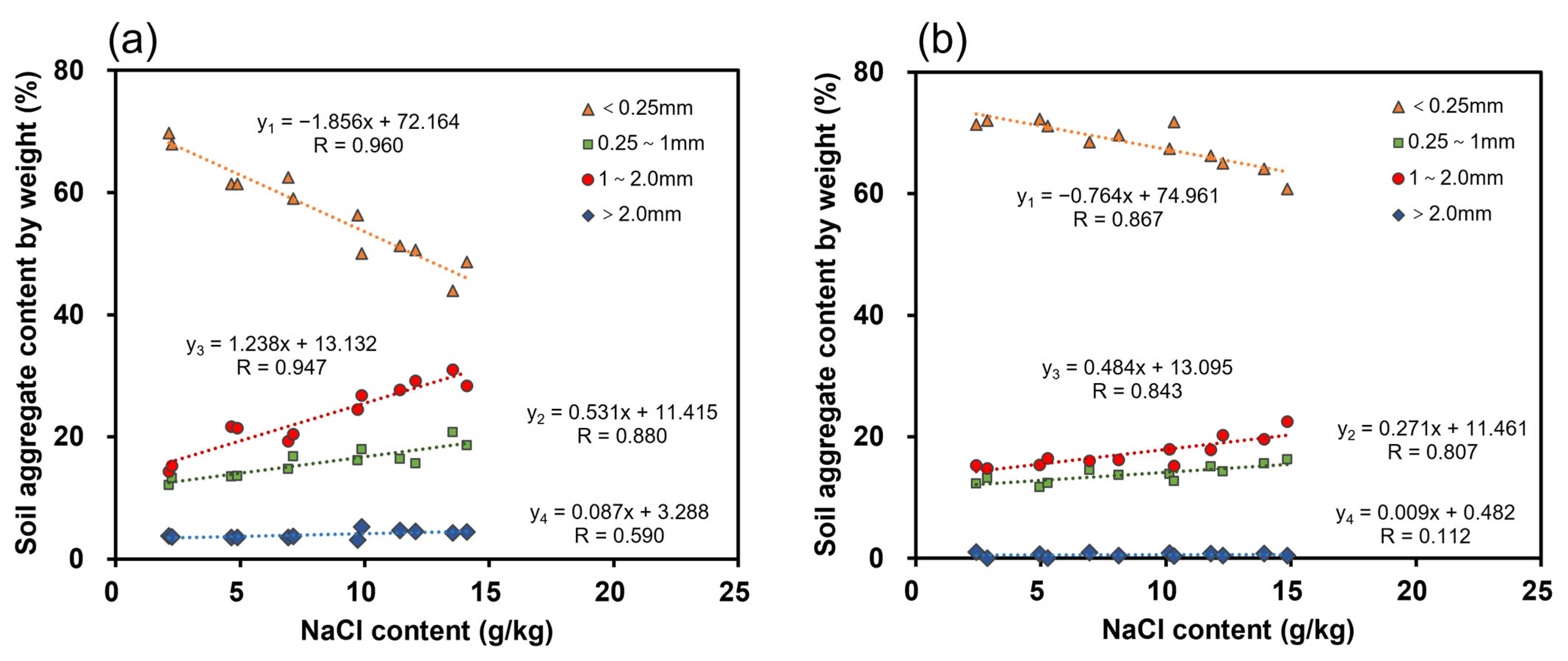
3.1. Impacts of Salinity on Soil Aggregates
3.2. Impacts of Salinity on Soil Hydraulic Properties
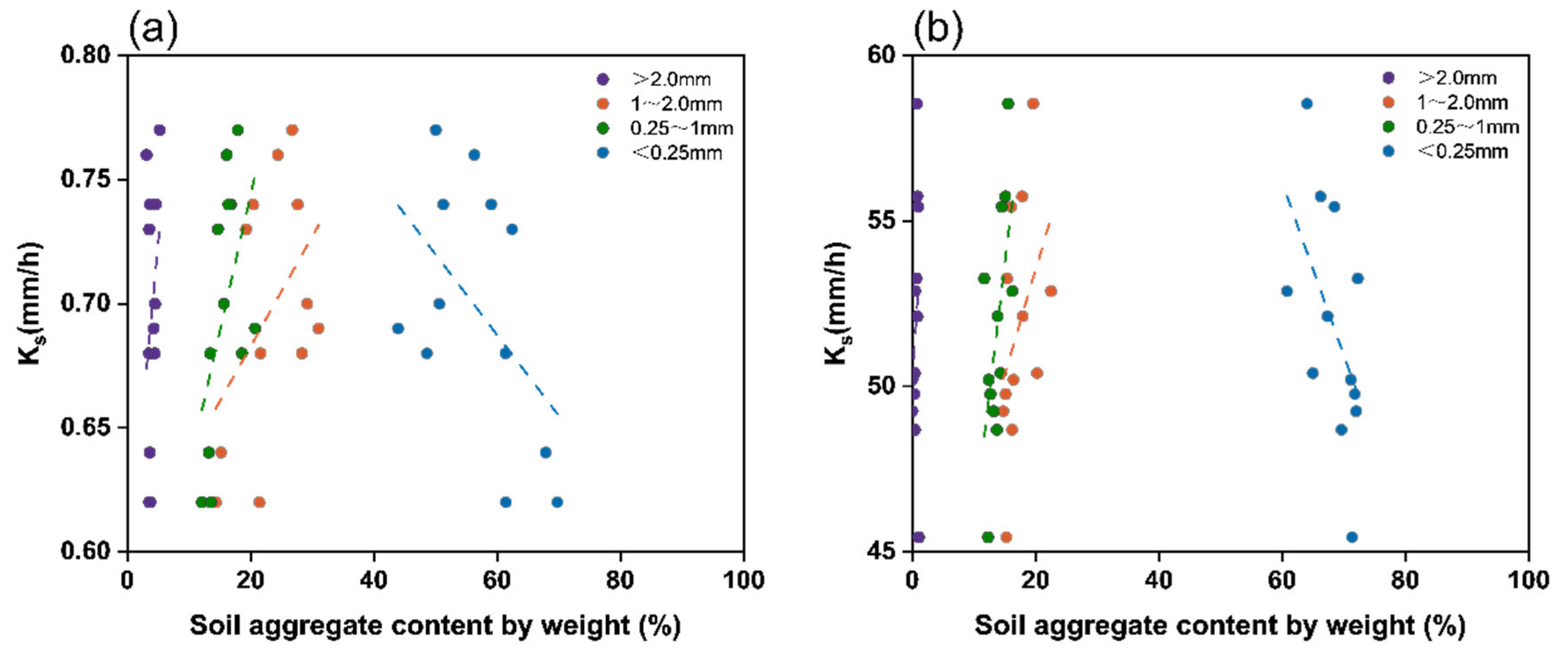
3.2.1. Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity
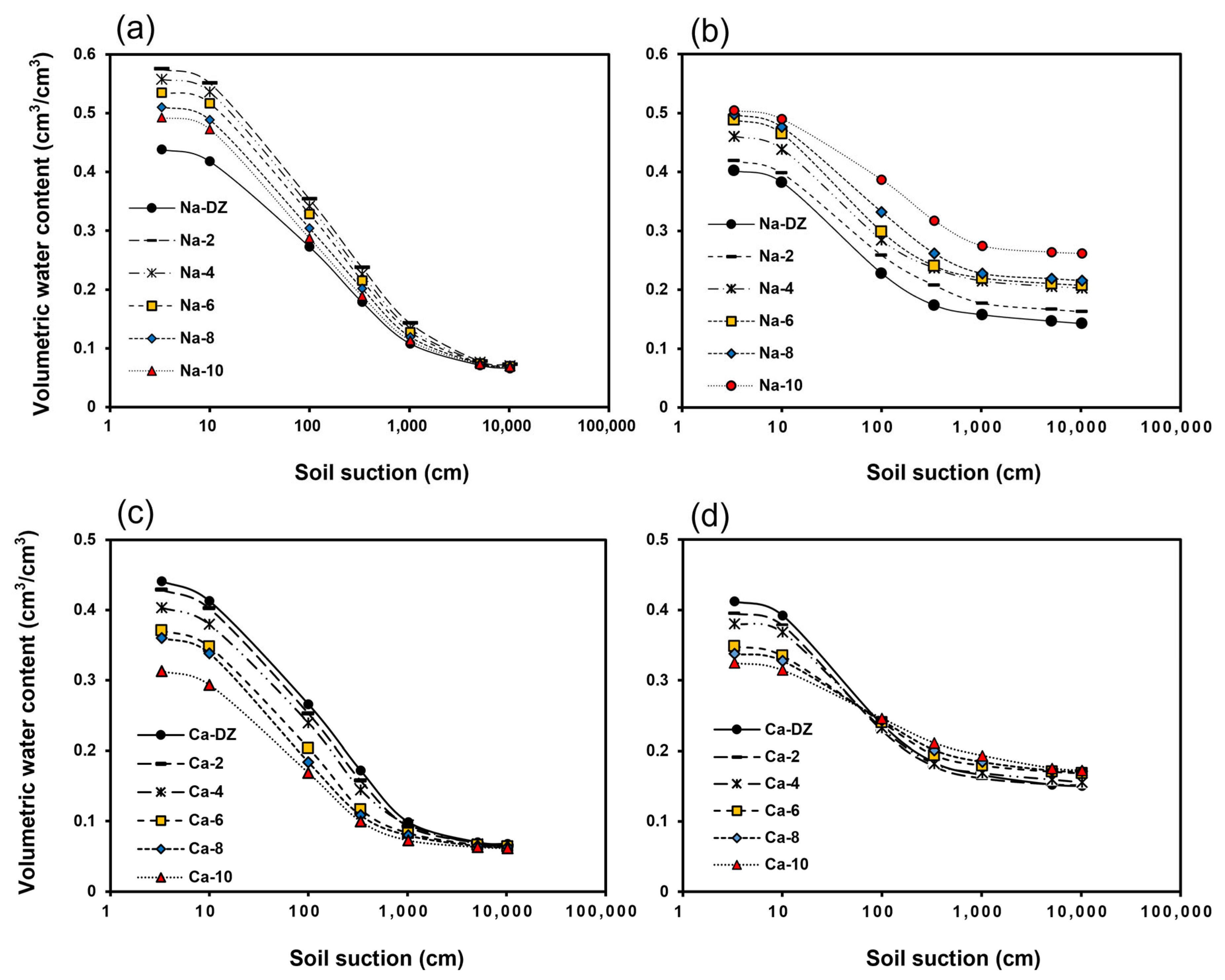
3.2.2. Soil Water-Retention Curves
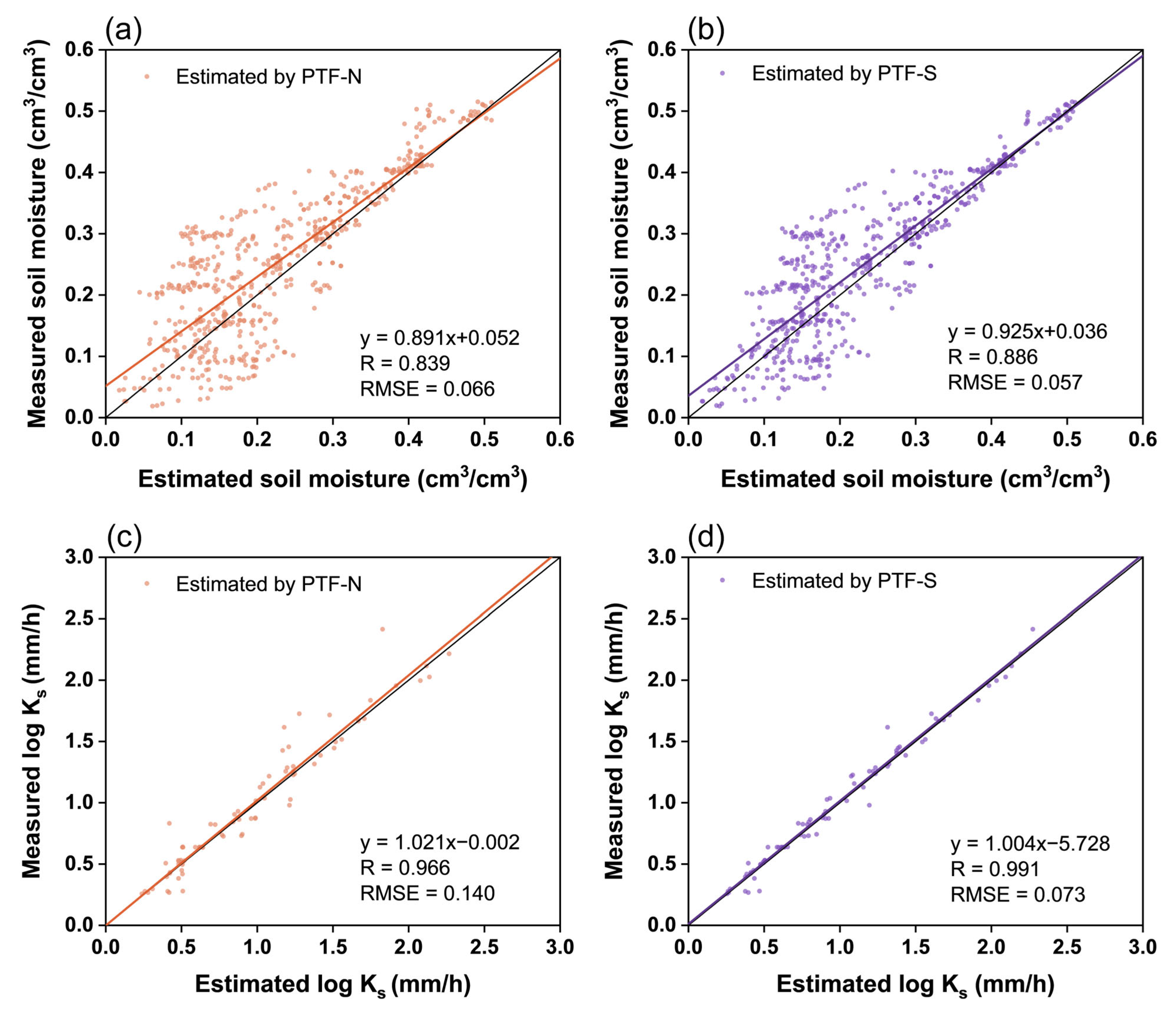
3.3. Peodotransfer Functions for Saline Soils
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, J.; Kang, Y.; Wan, S.; Hu, W.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, T. Soil Salinity Management with Drip Irrigation and Its Effects on Soil Hydraulic Properties in North China Coastal Saline Soils. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 115, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, N.A.L.; Bonell, M.; Coles, N.; MacDonald, A.M.; Auton, C.A.; Stevenson, R. Soil Characteristics and Landcover Relationships on Soil Hydraulic Conductivity at a Hillslope Scale: A View towards Local Flood Management. J. Hydrol. 2013, 497, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feki, M.; Ravazzani, G.; Ceppi, A.; Mancini, M. Influence of Soil Hydraulic Variability on Soil Moisture Simulations and Irrigation Scheduling in a Maize Field. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 202, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zlotnik, V.A.; Wedin, D.; Wally, K.D. Spatial Trends in Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity of Vegetated Dunes in the Nebraska Sand Hills: Effects of Depth and Topography. J. Hydrol. 2008, 349, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Hur, M.; Yolcu, G.; Uysal, H.; Lado, M.; Paz, A. Soil Structure Changes: Aggregate Size and Soil Texture Effects on Hydraulic Conductivity under Different Saline and Sodic Conditions. Soil Res. 2009, 47, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Werner, A.D.; Li, Y.; Jiang, S.; Tan, Z. Root-Induced Changes of Soil Hydraulic Properties—A Review. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.A.; Nemes, A.; Reinsch, S.; Radbourne, A.; Bentley, L.; Keith, A.M. Global Meta-Analysis of Soil Hydraulic Properties on the Same Soils with Differing Land Use. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wedin, D.; Zlotnik, V.A. Field Evidence of a Negative Correlation between Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity and Soil Carbon in a Sandy Soil. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, N.; Koestel, J.; Messing, I.; Moeys, J.; Lindahl, A. Influence of Soil, Land Use and Climatic Factors on the Hydraulic Conductivity of Soil. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 5185–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, P.L.; Billings, S.A.; Hirmas, D.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Ziegler, S.; Murenbeeld, K.; Ajami, H.; Guthrie, A.; Singha, K.; et al. Embracing the Dynamic Nature of Soil Structure: A Paradigm Illuminating the Role of Life in Critical Zones of the Anthropocene. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 225, 103873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Shao, M.; Wang, Q.; Fan, J.; Horton, R. Temporal Changes of Soil Hydraulic Properties under Different Land Uses. Geoderma 2009, 149, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranian Kabir, E.; Bashari, H.; Bassiri, M.; Mosaddeghi, M.R. Effects of Land-Use/Cover Change on Soil Hydraulic Properties and Pore Characteristics in a Semi-Arid Region of Central Iran. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 197, 104478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; She, D.; Wang, H. Effect of Salinity on Soil Structure and Soil Hydraulic Characteristics. Can. J. Soil. Sci. 2021, 101, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopmans, J.W.; Qureshi, A.S.; Kisekka, I.; Munns, R.; Grattan, S.R.; Rengasamy, P.; Ben-Gal, A.; Assouline, S.; Javaux, M.; Minhas, P.S.; et al. Chapter One—Critical Knowledge Gaps and Research Priorities in Global Soil Salinity. In Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Volume 169, pp. 1–191. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, P.; Bogunovic, I.; Muñoz-Rojas, M.; Brevik, E.C. Soil Ecosystem Services, Sustainability, Valuation and Management. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 5, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, J.; Daliakopoulos, I.N.; del Moral, F.; Hueso, J.J.; Tsanis, I.K. A Review of Soil-Improving Cropping Systems for Soil Salinization. Agronomy 2019, 9, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazihizina, N.; Barrett-Lennard, E.G.; Colmer, T.D. Plant Growth and Physiology under Heterogeneous Salinity. Plant Soil 2012, 354, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheeseman, J.M. The Evolution of Halophytes, Glycophytes and Crops, and Its Implications for Food Security under Saline Conditions. New Phytol. 2015, 206, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, T.B.; Šimůnek, J.; Gonçalves, M.C.; Martins, J.C.; Prazeres, A.; Castanheira, N.L.; Pereira, L.S. Field Evaluation of a Multicomponent Solute Transport Model in Soils Irrigated with Saline Waters. J. Hydrol. 2011, 407, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekakis, E.H.; Antonopoulos, V.Z. Modeling the Effects of Different Irrigation Water Salinity on Soil Water Movement, Uptake and Multicomponent Solute Transport. J. Hydrol. 2015, 530, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, J.; Ye, M.; Yang, J. Modelling the Salt Accumulation and Leaching Processes in Arid Agricultural Areas with a New Mass Balance Model. J. Hydrol. 2020, 591, 125329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescimanno, G.; Iovino, M.; Provenzano, G. Influence of Salinity and Sodicity on Soil Structural and Hydraulic Characteristics. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1995, 59, 1701–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemo, T.; Kramer, I.; Levy, G.J.; Mau, Y. Salinity and Sodicity Can Cause Hysteresis in Soil Hydraulic Conductivity. Geoderma 2022, 413, 115765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeh, I.O.A.; Onus, A. Spatial Analysis of Soil Salinity and Soil Structural Stability in a Semiarid Region of New South Wales, Australia. Environ. Manag. 2008, 42, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Sharma, S.; Nisar, S.; Choudhary, O.P. Structural Stability and Organic Matter Stabilization in Soils: Differential Impacts of Soil Salinity and Sodicity. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 1751–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaslou, H.; Hadifard, H.; Ghanizadeh, A.R. Effect of Cations and Anions on Flocculation of Dispersive Clayey Soils. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihlap, E.; Steffens, M.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Initial Soil Aggregate Formation and Stabilisation in Soils Developed from Calcareous Loess. Geoderma 2021, 385, 114854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Kang, D.; Ma, X. Differences in Loam Water Retention and Shrinkage Behavior: Effects of Various Types and Concentrations of Salt Ions. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 167, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Shahbazi, K.; Shahidi, R.; Davatgar, N.; Bazargan, K.; Rezaei, H.; Saadat, S.; Seuntjens, P.; Cornelis, W. How to Relevantly Characterize Hydraulic Properties of Saline and Sodic Soils for Water and Solute Transport Simulations. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 125777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olorunfemi, I.; Fasinmirin, J.; Ojo, A. Modeling Cation Exchange Capacity and Soil Water Holding Capacity from Basic Soil Properties. EJSS 2016, 5, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.; Gutierrez, M.; Diplas, P.; Petrie, J.; Wayllace, A.; Lu, N.; Muñoz, J.J. Comparison of Testing Techniques and Models for Establishing the SWCC of Riverbank Soils. Eng. Geol. 2010, 110, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assouline, S. What Can We Learn From the Water Retention Characteristic of a Soil Regarding Its Hydrological and Agricultural Functions? Review and Analysis of Actual Knowledge. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2021WR031026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereecken, H.; Weynants, M.; Javaux, M.; Pachepsky, Y.; Schaap, M.G.; van Genuchten, M.T. Using Pedotransfer Functions to Estimate the van Genuchten–Mualem Soil Hydraulic Properties: A Review. Vadose Zone J. 2010, 9, 795–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, N.G.; Singh, S.K. Pedotransfer Functions for Estimating Soil Hydraulic Properties: A Review. Pedosphere 2016, 26, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezlit, Y.D.; Bennett, J.M.; Raine, S.R.; Smith, R.J. Modification of the McNeal Clay Swelling Model Improves Prediction of Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity as a Function of Applied Water Quality. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 2149–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khataar, M.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Amiri Chayjan, R.; Mahboubi, A.A. Prediction of Water Quality Effect on Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity of Soil by Artificial Neural Networks. Paddy Water Env. 2018, 16, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopp, H.; Arriaga, F.; Daigh, A.; Bleam, W. Analysis of Pedotransfer Functions to Predict the Effects of Salinity and Sodicity on Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity of Soils. Geoderma 2020, 362, 114078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Gu, B.; Chen, D.; Tang, J.; Xu, X.; Qiao, Z.; Wang, J. Physicochemical Properties and Salinization Characteristics of Soils in Coastal Land Reclamation Areas: A Case Study of China-Singapore Tianjin Eco-City. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Gao, M.; Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Bi, M. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Soil Salinization and Its Impact on Cultivated Land Productivity in the BOHAI Rim Region. Water 2023, 15, 2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callesen, I.; Palviainen, M.; Armolaitis, K.; Rasmussen, C.; Kjønaas, O.J. Soil Texture Analysis by Laser Diffraction and Sedimentation and Sieving–Method and Instrument Comparison with a Focus on Nordic and Baltic Forest Soils. Front. For. Glob. Change 2023, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, R. Applications of Ion Chromatography for the Determination of Inorganic Cations. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2009, 39, 230–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ8892017; Soil Quality-Determination of Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC)-Hexamminecobalt Trichloride Solution-Spectrophotometric Method. Ministry of Environmental Protection of China: Suzhou, China, 2017.
- HJ6152011; Soil–Determination of Organic Carbon–Potassium Dichromate Oxidation Spectrophotometric Method. Ministry of Environmental Protection of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Jury, W.A.; Horton, R. Soil Physics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-0-471-05965-3. [Google Scholar]
- Yoder, R.E. A Direct Method of Aggregate Analysis of Soils and a Study of the Physical Nature of Erosion Losses. Agron. J. 1936, 28, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, H.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H. Influence of Slaking on the Size Distributions of Water-Stable Aggregates. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2022, 86, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeal, B.L. Prediction of the Effect of Mixed-Salt Solutions on Soil Hydraulic Conductivity. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1968, 32, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, R.; Smucker, A. Structure Formation and Its Consequences for Gas and Water Transport in Unsaturated Arable and Forest Soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 82, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, A. Mechanics of Heterogeneous Fluids in Porous Media; Water Resources Publications: Littleton, CO, USA, 1977; ISBN 978-0-918334-17-6. [Google Scholar]
- Bittelli, M.; Flury, M. Errors in Water Retention Curves Determined with Pressure Plates. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Zuo, C.; Liu, D.; Li, L.; Chen, J. Soil-Water Characteristics of Unsaturated Residual Soil and Estimation of Matric Suction. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2016, 33, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Genuchten, M.T. A Closed-Form Equation for Predicting the Hydraulic Conductivity of Unsaturated Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genuchten, M.V.; Leij, F.; Yates, S. The RETC Code for Quantifying the Hydraulic Functions of Unsaturated Soils; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1991; EPA/600/2-91/065 (NTIS 92-119668); Available online: https://www.pc-progress.com/Documents/programs/retc.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2024).
- Schaap, M.G.; Leij, F.J. Improved Prediction of Unsaturated Hydraulic Conductivity with the Mualem-van Genuchten Model. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streiner, D.L. Regression in the Service of the Superego: The Do’s and Don’ts of Stepwise Multiple Regression. Can. J. Psychiatry 1994, 39, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillaci, C.; Perego, A.; Valkama, E.; Märker, M.; Saia, S.; Veronesi, F.; Lipani, A.; Lombardo, L.; Tadiello, T.; Gamper, H.A.; et al. New Pedotransfer Approaches to Predict Soil Bulk Density Using WoSIS Soil Data and Environmental Covariates in Mediterranean Agro-Ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.-J.; Yang, J.-S.; Wu, D.-H.; Li, F.-R.; Gao, P.; Wang, X.-P. Evaluation of Pedotransfer Functions for Estimating Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity in Coastal Salt-Affected Mud Farmland. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 902–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, G.W.; Fetene, M. Assessment of Soil Erosion Hazard in Kilie Catchment, East Shoa, Ethiopia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2012, 23, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Bossuyt, H.; Degryze, S.; Denef, K. A History of Research on the Link between (Micro)Aggregates, Soil Biota, and Soil Organic Matter Dynamics. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 79, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartzia-Bengoetxea, N.; González-Arias, A.; Merino, A.; Martínez de Arano, I. Soil Organic Matter in Soil Physical Fractions in Adjacent Semi-Natural and Cultivated Stands in Temperate Atlantic Forests. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1674–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, H.M.S.K.; Camps-Arbestain, M.; Hedley, M. Effect of Biochar on Soil Physical Properties in Two Contrasting Soils: An Alfisol and an Andisol. Geoderma 2013, 209–210, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillel, D. Introduction to Environmental Soil Physics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; ISBN 978-0-08-049577-4. [Google Scholar]
- Deb, S.K.; Shukla, M.K. Variability of Hydraulic Conductivity Due to Multiple Factors. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 8, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiphoori, A.; Ma, X.; Arratia, P.E.; Jerolmack, D.J. Formation of Stable Aggregates by Fluid-Assembled Solid Bridges. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3375–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, F.G.; Maud, R.R. Dispersive Soils: A Review from a South African Perspective. Q. J. Eng. Geol. 1994, 27, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopp, H.W.; Daigh, A.L.M. Measured Saline and Sodic Solutions Effects on Soil Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity, Electrical Conductivity and Sodium Adsorption Ratio. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2020, 34, 264–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamie, R.; De Smedt, F. Experimental and Statistical Study of Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity and Relations with Other Soil Properties of a Desert Soil. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Wang, T.; Han, Q.; Kong, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Lang, Y. Impacts of Vegetation and Tidal Conditions on Porewater and Salt Transport in Coastal Wetlands: Numerical Simulations and Field Evidence. J. Hydrol. 2024, 636, 131251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behbahani, A.; Ryan, R.J.; McKenzie, E.R. Impacts of Salinity on the Dynamics of Fine Particles and Their Associated Metals during Stormwater Management. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, J.; Zheng, J. Correlation between Soil Water Retention Capability and Soil Salt Content. Pedosphere 2000, 10, 275–280. [Google Scholar]
- Tuli, A.; Kosugi, K.; Hopmans, J.W. Simultaneous Scaling of Soil Water Retention and Unsaturated Hydraulic Conductivity Functions Assuming Lognormal Pore-Size Distribution. Adv. Water Resour. 2001, 24, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.L.; Ratcliffe, I.; Greenwell, H.C.; Williams, P.A.; Cliffe, S.; Coveney, P.V. Clay Swelling—A Challenge in the Oilfield. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2010, 98, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Xiao-Feng, T.; Yu, Z.; Tao, G. Swelling of K+, Na+ and Ca2+-Montmorillonites and Hydration of Interlayer Cations: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Chin. Phys. B 2010, 19, 109101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Edraki, M.; Berry, L. Investigating the Settling Behaviour of Saline Tailing Suspensions Using Kaolinite, Bentonite, and Illite Clay Minerals. Powder Technol. 2018, 326, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, G.; Tewolde, H.; Zhang, F.; Yan, C.; Yang, M. Soil Aggregation and Water Holding Capacity of Soil Amended with Agro-Industrial Byproducts and Poultry Litter. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, E.; Gens, A.; Lloret, A. Suction Effects on a Compacted Clay under Non-Isothermal Conditions. Géotechnique 2003, 53, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Ni, W.; Lü, X.; Tuo, W. Exploring the Mechanical Behavior and Microstructure of Compacted Loess Subjected to Dry-Wet Cycles and Chemical Contamination. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2024, 16, 3673–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obi, J.C.; Ogban, P.I.; Ituen, U.J.; Udoh, B.T. Development of Pedotransfer Functions for Coastal Plain Soils Using Terrain Attributes. CATENA 2014, 123, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Site | Soil Taxonomy | Soil Texture | EC (dS/m) | pH | Bulk Density (g/cm3) | Ks (cm/h) | Sand (%) | Silt (%) | Clay (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDG | Typic Salorthids | Silt clay | 7.6 | 8.46 | 1.45 | 0.38 | 3.17 | 56.30 | 40.53 |
| BXS | Typic Hapludalfs | Sandy loam | 6.9 | 7.69 | 1.40 | 1.20 | 67.42 | 22.18 | 10.40 |
| Texture | NaCl | CaCl2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (g/kg) | Ks (mm/h) | Content (g/kg) | Ks (mm/h) | |
| Silt clay | 2.21 | 0.62 | 1.98 | 0.63 |
| 2.37 | 0.64 | 2.26 | 0.61 | |
| 4.45 | 0.68 | 4.45 | 0.76 | |
| 4.98 | 0.62 | 4.98 | 0.72 | |
| 6.44 | 0.73 | 6.44 | 0.83 | |
| 7.26 | 0.74 | 7.76 | 0.84 | |
| 9.54 | 0.78 | 9.85 | 0.91 | |
| 9.84 | 0.73 | 10.49 | 0.87 | |
| 11.62 | 0.72 | 11.70 | 0.97 | |
| 12.13 | 0.76 | 12.23 | 0.89 | |
| 13.44 | 0.66 | 13.38 | 0.79 | |
| 14.08 | 0.68 | 14.42 | 0.86 | |
| Sandy loam | 2.34 | 45.44 | 1.74 | 45.27 |
| 2.92 | 49.25 | 2.52 | 49.64 | |
| 4.85 | 54.26 | 4.78 | 62.37 | |
| 5.30 | 50.2 | 5.20 | 61.4 | |
| 6.72 | 55.43 | 6.63 | 65.43 | |
| 8.15 | 48.69 | 8.21 | 68.69 | |
| 10.42 | 52.12 | 10.20 | 62.06 | |
| 11.26 | 49.77 | 11.36 | 72.77 | |
| 12.05 | 55.74 | 12.25 | 69.72 | |
| 12.48 | 50.4 | 12.68 | 76.98 | |
| 13.87 | 58.55 | 13.79 | 68.75 | |
| 14.64 | 52.88 | 14.25 | 78.49 | |
| Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training set RMSE (cm3/cm3) | 0.058 | 0.059 | 0.061 | 0.056 | 0.066 | 0.061 | 0.062 | 0.056 | 0.055 | 0.062 |
| Validation set RMSE (cm3/cm3) | 0.063 | 0.061 | 0.079 | 0.084 | 0.069 | 0.090 | 0.072 | 0.077 | 0.067 | 0.070 |
| Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training set RMSE (mm/h) | 0.153 | 0.152 | 0.148 | 0.159 | 0.154 | 0.161 | 0.155 | 0.155 | 0.147 | 0.158 |
| Validation set RMSE (mm/h) | 0.167 | 0.178 | 0.185 | 0.153 | 0.17 | 0.142 | 0.18 | 0.174 | 0.168 | 0.172 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, T.; Han, Q. Salinity Effects on Soil Structure and Hydraulic Properties: Implications for Pedotransfer Functions in Coastal Areas. Land 2024, 13, 2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13122077
Zhang X, Zuo Y, Wang T, Han Q. Salinity Effects on Soil Structure and Hydraulic Properties: Implications for Pedotransfer Functions in Coastal Areas. Land. 2024; 13(12):2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13122077
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiao, Yutao Zuo, Tiejun Wang, and Qiong Han. 2024. "Salinity Effects on Soil Structure and Hydraulic Properties: Implications for Pedotransfer Functions in Coastal Areas" Land 13, no. 12: 2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13122077
APA StyleZhang, X., Zuo, Y., Wang, T., & Han, Q. (2024). Salinity Effects on Soil Structure and Hydraulic Properties: Implications for Pedotransfer Functions in Coastal Areas. Land, 13(12), 2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13122077






