The Impact of Household Dynamics on Land-Use Change in China: Past Experiences and Future Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Materials and Methods
2.3.1. Statistical Analysis of Data
2.3.2. Detection of Trends and Change-Rates in Household Dynamics
2.3.3. Analysis of Land-Use Data
3. Results
3.1. Household Dynamics in China
3.1.1. Changing Household Numbers
3.1.2. Changing of Household Sizes
3.1.3. Household Size Variation among Provinces of China
3.1.4. Demographic Drivers for Household Structure in China
3.2. Changes in Housing Demand and Land Use during the Past 40 Years in China
3.2.1. Changes in Per-Capita-Housing Area in Urban and Rural Areas
3.2.2. Changes in Construction Area and Completion Area in China
3.2.3. Changes in Land-Use Transitions in China during the Past 40 Years
4. Discussion
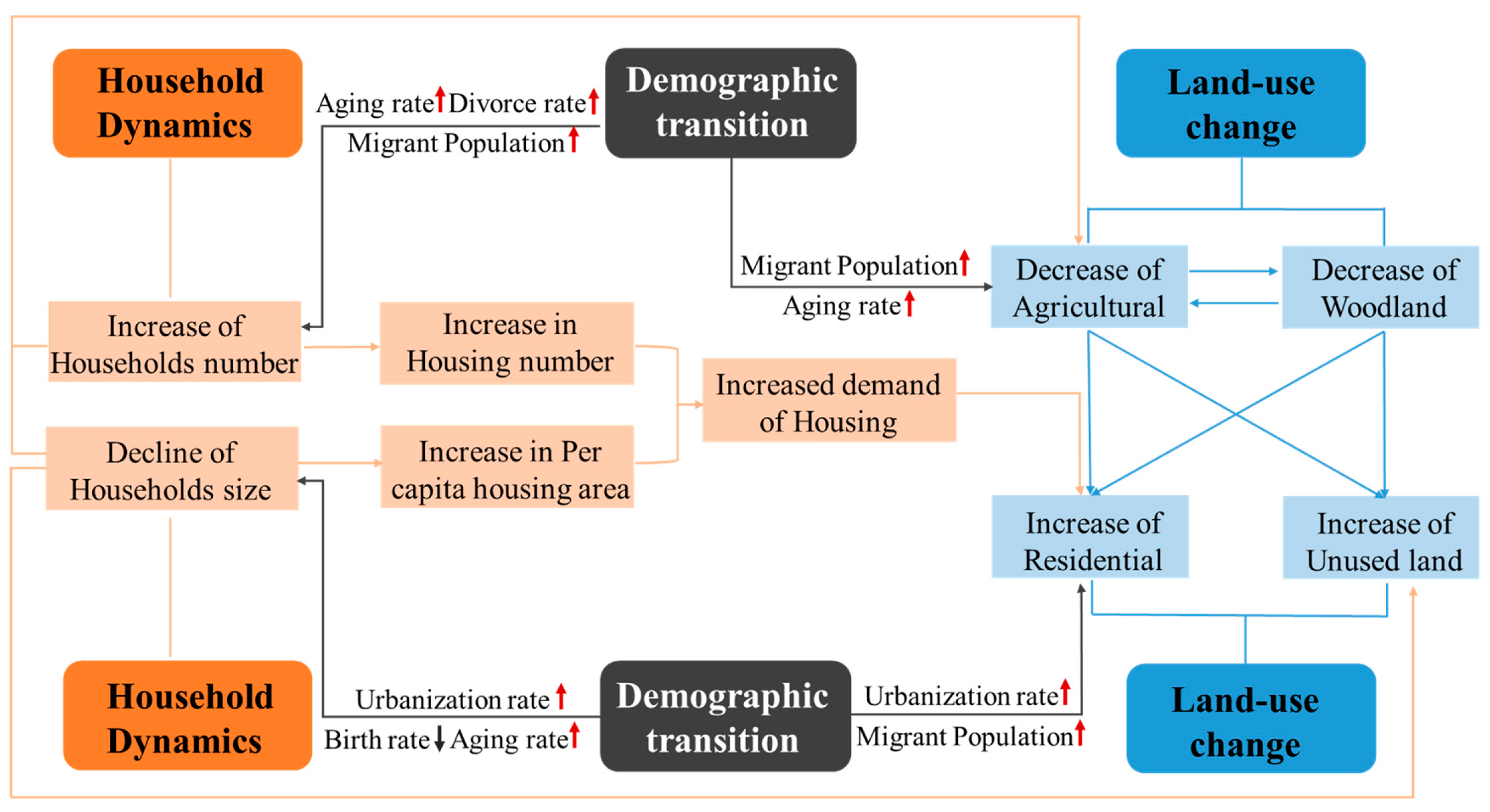
4.1. Demographic Transition and Household Dynamics
4.2. Impact of Household Dynamics on Land-Use Change in China
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stehfest, E.; Van Zeist, W.-J.; Valin, H.; Havlik, P.; Popp, A.; Kyle, P.; Tabeau, A.; Mason-D’Croz, D.; Hasegawa, T.; Bodirsky, B.L.; et al. Key Determinants of Global Land-Use Projections. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Hu, Y. Land Cover Changes and Their Driving Mechanisms in Central Asia from 2001 to 2017 Supported by Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H. Land Use Policy in China: Introduction. Land Use Policy 2014, 40, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilsborrow, R.E.; Okoth-Ogendo, H.W.O. Population-Driven Changes in Land Use in Developing Countries. Ambio J. Hum. Environ. 1992, 21, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council. Population, Land Use, and Environment: Research Directions; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Malthus, T.R.; Winch, D.; James, P. An Essay on the Principle of Population; Cambridge Texts in the History of Political Thought; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1992; ISBN 978-0-521-41954-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich, P.R. The Population Bomb; Ballantine Books: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, W.B.; Turner, B.L. Human Population Growth and Global Land-Use/Cover Change. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1992, 23, 39–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, A. Population Growth and Carbon Dioxide Emission: An Investigation of the Africa Perspective. East Asian J. Bus. Econ. (EAJBE) 2014, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G.; Daily, G.C.; Ehrlich, P.R.; Luck, G.W. Effects of Household Dynamics on Resource Consumption and Biodiversity. Nature 2003, 421, 530–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Liu, J.G.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Linderman, M.; Zhou, S.Q.; Zhang, H.M. Simulating Demographic and Socioeconomic Processes on Household Level and Implications for Giant Panda Habitats. Ecol. Model. 2001, 140, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, M.; Peterson, M.N.; Liu, J.G. Long-Term Dynamics of Household Size and Their Environmental Implications. Popul. Environ. 2014, 36, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellsworth-Krebs, K. Implications of Declining Household Sizes and Expectations of Home Comfort for Domestic Energy Demand. Nat. Energy 2019, 5, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götmark, F.; Cafaro, P.; O’Sullivan, J. Aging Human Populations: Good for Us, Good for the Earth. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2018, 33, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, E.; Liu, J.G. Environmental Impacts of Divorce. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20629–20634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pejchar, L.; Reed, S.E.; Bixler, P.; Ex, L.; Mockrin, M.H. Consequences of Residential Development for Biodiversity and Human Well-Being. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2015, 13, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, K.C.; Güneralp, B.; Hutyra, L.R. Global Forecasts of Urban Expansion to 2030 and Direct Impacts on Biodiversity and Carbon Pools. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16083–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, D.B.; Urquhart, G.; Schmitt, K. Globalization and the Connection of Remote Communities: A Review of Household Effects and Their Biodiversity Implications. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 2897–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mockrin, M.H.; Reed, S.E.; Pejchar, L.; Jessica, S. Balancing Housing Growth and Land Conservation: Conservation Development Preserves Private Lands near Protected Areas. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 157, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Prieto, J.; Martinuzzi, S.; Radeloff, V.C.; Helmers, D.P.; Quiñones, M.; Gould, W.A. Declining Human Population but Increasing Residential Development around Protected Areas in Puerto Rico. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 209, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.L.; Li, Y.R.; Liu, Y.S.; Woods, M.; Zou, J. Accelerated Restructuring in Rural China Fueled by ‘Increasing vs. Decreasing Balance’ Land-Use Policy for Dealing with Hollowed Villages. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, Y.S.; Xu, K.S. Hollow Villages and Rural Restructuring in Major Rural Regions of China: A Case Study of Yucheng City, Shandong Province. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.R.; Liu, Y.S.; Long, H.L. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Population and Residential Land Change in Rural China. J. Nat. Resour. 2010, 10, 1629–1638. [Google Scholar]
- Long, H.L.; Li, T.T. The Coupling Characteristics and Mechanism of Farmland and Rural Housing Land Transition in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 548–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Census Office of the State Council. <<2010 Population Census Of China>>; China Statistical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.S. An Analysis of Changes in the Chinese Family Structure between Urban and Rural Areas: On the Basis of the 2010 National Census Data. Soc. Sci. China 2014, 35, 100–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Yan, C.; Wu, S. China’s Multi-Period Land Use Land Cover Remote Sensing Monitoring Data Set (CNLUCC); Resource and Environment Data Cloud Platform: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.W. Population Change and People’s Livelihood; China Population Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sicard, P.; Mangin, A.; Hebel, P.; Malléa, P. Detection and Estimation Trends Linked to Air Quality and Mortality on French Riviera over the 1990–2005 Period. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 1943–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teferi, E.; Bewket, W.; Uhlenbrook, S.; Wenninger, J. Understanding Recent Land Use and Land Cover Dynamics in the Source Region of the Upper Blue Nile, Ethiopia: Spatially Explicit Statistical Modeling of Systematic Transitions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 165, 98–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bren d’Amour, C.; Reitsma, F.; Baiocchi, G.; Barthel, S.; Güneralp, B.; Erb, K.-H.; Haberl, H.; Creutzig, F.; Seto, K.C. Future Urban Land Expansion and Implications for Global Croplands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 8939–8944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, D. The Nuclear Family Was a Mistake. Atlantic 2020, 325, 54–69. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, J. Ideal Family Size among White Americans: A Quarter of a Century’s Evidence. Demography 1966, 3, 154–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laslett, P. Size and Structure of the Household in England over Three Centuries. J. Demogr. 1969, 23, 199–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindfuss, R.R.; Turner, B.L.; Entwisle, B.; Walsh, S.J. Land Cover/Use and Population. In Land Change Science: Observing, Monitoring and Understanding Trajectories of Change on the Earth’s Surface; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Geist, H.J. Land-Use and Land-Cover Change: Local Processes and Global Impacts; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- MacKellar, L.; Lutz, W.; Prinz, C.; Goujon, A. Population, Households, and CO2 Emissions. Popul. Dev. Rev. 1995, 21, 849–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.G.; Zhu, Y.J.; Zhao, M.F.; Lv, Q.Y. Multi-Dimensional Hollowing Characteristics of Traditional Villages and Its Influence Mechanism Based on the Micro-Scale: A Case Study of Dongcun Village in Suzhou, China. Land Use Policy 2021, 101, 105146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S. The Central Bank’s Survey Shows: Two Suites in 30% of Urban Households with Average Household Assets of 3.18 Million. China Econ. Wkly. 2020, 9, 36–37. [Google Scholar]
- MacKellar, L.; Lutz, W.; Munn, R.E.; Wexler, L.; O’Neill, B.; McMichael, A.; Suhrkre, A. Population and Global Warming; Book Manuscript; International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis: Laxenburg, Austria, 1996. [Google Scholar]










| Data Name | Source | Period |
|---|---|---|
| Household number | ➀➁➂➇ | 1980–2020 |
| Population number | ➈➉ | 1982–2020 |
| Household size | ➀➂➃➇ | 1953–2020 |
| Aging rate | ➀➇ | 1982–2020 |
| Divorce rate | ➀➄➇ | 1980–2020 |
| Birth rate | ➀➇ | 1953–2020 |
| Per-capita-housing area | ➀➂ | 1980–2020 |
| Migrated population | ➀ | 1982–2020 |
| Construction area for housing | ➀➅➆ | 1980–2020 |
| Completed-housing area | ➀➅➆ | 1980–2020 |
| Land-use data (1 km) | ⑪ | 1980–2020 |
| Year | Family Household | Collective Household | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Household Number (Million) | Population Number (Million) | Household Number (Million) | Population Number (Million) | |
| 1982 | 222.08 | 971.09 (96.73%) | 1.07 | 32.82 (3.24%) |
| 1990 | 276.91 | 1097.78 (97.10%) | 1.71 | 32.73 (2.90%) |
| 2000 | 340.49 | 1178.27 (94.82%) | 10.74 | 64.34 (5.12%) |
| 2010 | 401.93 | 1239.98 (93.04%) | 15.79 | 92.83 (6.96%) |
| 2020 | 494.16 | 1292.81 (91.70%) | 28.53 | 116.97 (8.3%) |
| Household Type | 1982 | 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| One generation | 13.77 | 13.53 | 21.70 | 34.18 | 49.50 |
| Two generations | 67.46 | 68.02 | 59.32 | 47.83 | 36.72 |
| Three generations and above | 18.76 | 18.45 | 18.98 | 17.99 | 13.78 |
| Total | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Y.; Chen, R.; Xiong, B.; Jia, N.; Guo, X.; Yin, C.; Song, W. The Impact of Household Dynamics on Land-Use Change in China: Past Experiences and Future Implications. Land 2024, 13, 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13020124
Luo Y, Chen R, Xiong B, Jia N, Guo X, Yin C, Song W. The Impact of Household Dynamics on Land-Use Change in China: Past Experiences and Future Implications. Land. 2024; 13(2):124. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13020124
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Yaxue, Ruishan Chen, Bo Xiong, Nan Jia, Xiaona Guo, Chenglong Yin, and Wen Song. 2024. "The Impact of Household Dynamics on Land-Use Change in China: Past Experiences and Future Implications" Land 13, no. 2: 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13020124
APA StyleLuo, Y., Chen, R., Xiong, B., Jia, N., Guo, X., Yin, C., & Song, W. (2024). The Impact of Household Dynamics on Land-Use Change in China: Past Experiences and Future Implications. Land, 13(2), 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13020124






