Anthropogenic Impact on the Terrestrial Environment in the Lake Dian Basin, Southwestern China during the Bronze Age and Ming–Qing period
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Regional Setting
2.1. Present Climate and Vegetation in the Lake Dian Basin
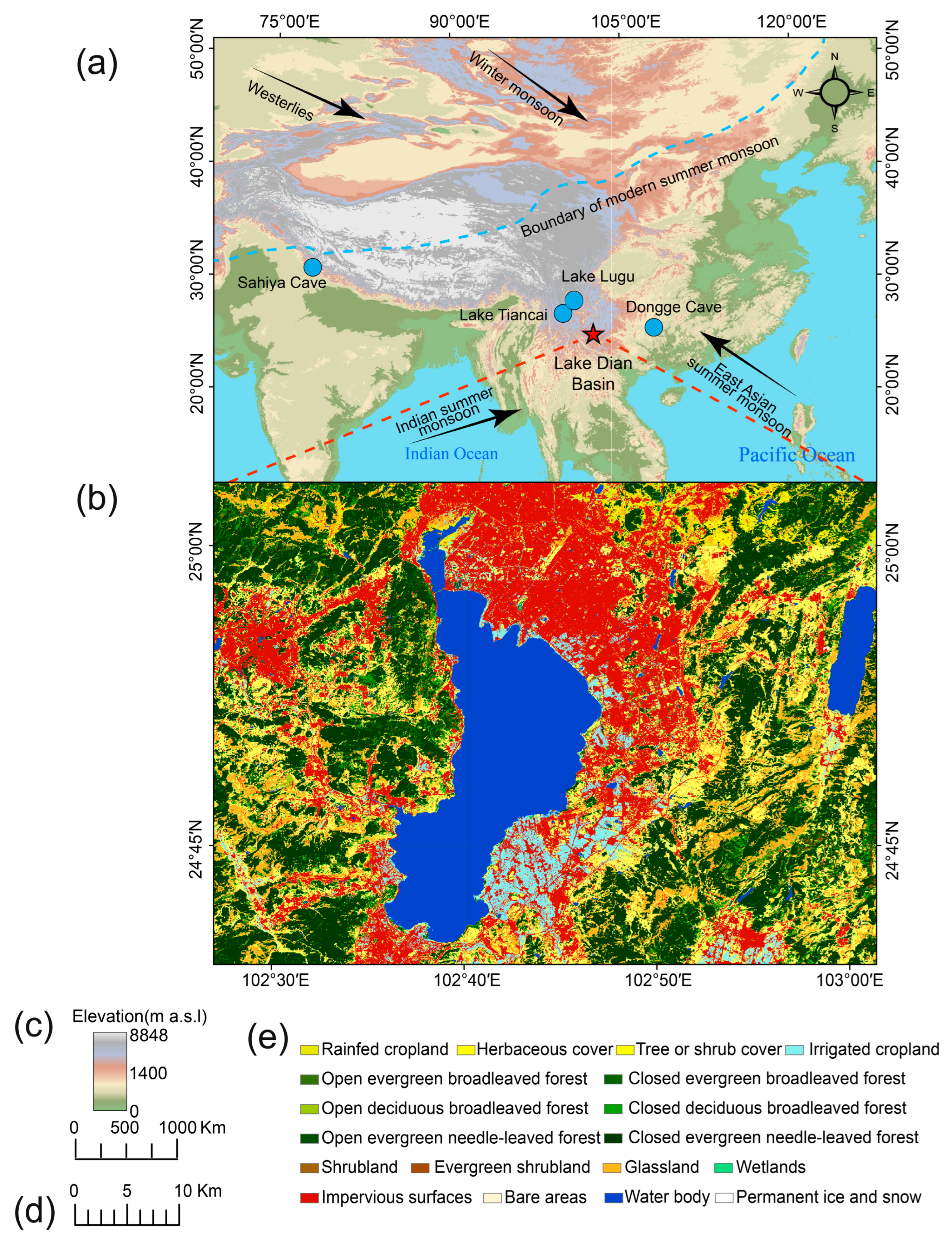
2.2. History of Cultural Evolution in the Lake Dian Basin
2.3. The Anjiangbei Site
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Section Collection and Dating Method
3.2. Elemental Content and Sporopollen Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Chronology
4.2. Element Content
4.3. Sporopollen Records
5. Discussion
5.1. History of Anthropogenic Impacts on the Terrestrial Environment in the Lake Dian Basin during the Bronze Age and the Ming–Qing Period
5.2. Human Activity Intensity and Its Influencing Factors in the Lake Dian Basin during the Bronze Age and the Ming–Qing Period
5.2.1. Natural Factors Influencing Human Activity Intensity in the Lake Dian Basin during the Bronze Age
5.2.2. Social Factors Influencing Human Activity Intensity in the Lake Dian Basin during the Ming–Qing Period
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steffen, W.; Grinevald, J.; Crutzen, P.; McNeill, J. The Anthropocene: Conceptual and historical perspectives. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2011, 369, 842–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.H. Understanding past human-environment interaction from an interdisciplinary perspective. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 1023–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frachetti, M.; Cosmo, N.D.; Esper, J.; Khalidi, L.; Mauelshagen, F.; Oppenheimer, C.; Rohland, E.; Büntgen, U. The dahliagram: An interdisciplinary tool for investigation, visualization, and communication of past human-environmental interaction. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadj3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crutzen, P.J. Geology of mankind. Science 2002, 415, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenny, J.P.; Koirala, S.; Gregory-Eaves, I.; Francus, P.; Niemann, C.; Ahrens, B.; Brovkin, V.; Baud, A.; Ojala, A.E.K.; Normandeau, A.; et al. Human and climate global-scale imprint on sediment transfer during the Holocene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22972–22976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.J.; Liu, H.; Li, G.; Zhang, Z.P.; Chen, X.T.; Shi, Z.L.; Zhou, A.F.; Dong, G.H. Warfare impact overtakes climate-controlled fires in the eastern Silk Roads since 2000 B.P. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Nexus 2023, 2, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottl, O.; Flantua, S.G.A.; Bhatta, K.P.; Felde, V.A.; Giesecke, T.; Goring, S.; Grimm, E.C.; Haberle, S.; Hooghiemstra, H.; Ivory, S.; et al. Global acceleration in rates of vegetation change over the past 18,000 years. Science 2021, 372, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.H.; Zhang, S.J.; Yang, Y.S.; Chen, J.H.; Chen, F.H. Agricultural intensification and its impact on environment during Neolithic Age in northern China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 2913–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.Q.; Chen, J.H.; Yan, H.Y.; Zhang, S.R.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, A.F.; Ji, P.P.; Chen, S.Q.; Lv, F.Y.; Zhang, W.S.; et al. Late Holocene transition from natural to anthropogenic forcing of vegetation change in the semi-arid region of northern China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2023, 287, 106561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.J.; Weng, C.Y.; Steinke, S.; Mohtadi, M. Anthropogenic modification of vegetated landscapes in southern China from 6000 years ago. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 111, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Li, X.; Dodson, J.; Zhang, K.; Atahan, P.; Sun, N.; Yang, Q. Land degradation during the bronze age in Hexi corridor (Gansu, China). Quat. Int. 2012, 254, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.W.; Zhang, S.J.; Zhang, H.C.; Dong, G.H. Detecting anthropogenic impact on forest succession from the perspective of wood exploitation on the northeast Tibetan Plateau during the late prehistoric period. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2022, 65, 2068–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Storozum, M.J.; Li, H.; Cui, Y.; Dong, G. Copper smelting and sediment pollution in Bronze Age China: A case study in the Hexi corridor, Northwest China. Catena 2017, 156, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.H.; Xu, Q.H.; Chen, J.H.; Birks, H.J.B.; Liu, J.B.; Zhang, S.R.; Jin, L.Y.; An, C.B.; Telford, R.J.; Cao, X.Y.; et al. East Asian summer monsoon precipitation variability since the last deglaciation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Rolett, B.V.; Zheng, Z.; Zong, Y.Q. Holocene coastal evolution preceded the expansion of paddy field rice farming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 24138–24143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.P.; Liu, J.B.; Chen, J.; Chen, S.Q.; Shen, Z.W.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.K.; Wu, D.; Sheng, Y.W.; Chen, F.H. Holocene climatic optimum in the East Asian monsoon region of China defined by climatic stability. Ear. Sci. Rev. 2021, 212, 103450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Alpoim Guedes, J.; Bocinsky, R.K. Climate change stimulated agricultural innovation and exchange across Asia. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.H.; Dong, G.H.; Zhang, D.J.; Liu, X.Y.; Jia, X.; An, C.B.; Ma, M.M.; Xie, Y.W.; Barton, L.; Ren, X.Y.; et al. Agriculture facilitated permanent human occupation of the Tibetan Plateau after 3600 B.P. Science 2015, 347, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Li, B.; Chen, W.; Liu, P.; Xie, M.X.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.C.; Dong, G.H. The alteration from agricultural to nomadic regimes resulted in human livelihood transformation in North-Central China during the 12th century: The archaeobotanical evidence. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 978147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.H.; Chen, X.M.; Chen, J.H.; Zhou, A.F.; Wu, D.; Tang, L.Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Huang, X.Z.; Yu, J.Q. Holocene vegetation history, precipitation changes and Indian Summer Monsoon evolution documented from sediments of Xingyun Lake, south-west China. J. Quat. Sci. 2014, 29, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.Y.; Yao, A.; Hillman, A.; Shen, J.; Haberle, S.G. Vegetation, climate and human impact since 20 ka in central Yunnan Province based on high-resolution pollen and charcoal records from Dianchi, southwestern China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2020, 236, 106297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.P.; Scuderi, L.A.; Wang, X.L.; Scuderi, L.J.; Zhang, D.G.; Li, H.W.; Forman, S.; Xu, Q.H.; Wang, R.C.; Huang, W.W.; et al. Groundwater sapping as the cause of irreversible desertification of Hunshandake sandy lands, Inner Mongolia, northern China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mischke, S.; Liu, C.L.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhang, C.J.; Zhang, H.; Jiao, P.C.; Plessen, B. The world’s earliest Aral-Sea type disaster: The decline of the Loulan Kingdom in the Tarim Basin. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.A. A Brief History of Early Sino-Indian Transportation as Seen in Shizaishan Cultural Artifacts. Sichuan Cult. Relics 2004, 6, 28–33. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.M.; Lu, Y.X.; Dong, G.H.; Ren, L.L.; Min, R.; Kang, L.H.; Zhu, Z.H.; Li, X.R.; Li, B.; Yang, Z.J.; et al. Understanding the transport networks complex between South Asia, Southeast Asia and China during the late. Holocene 2023, 33, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.M.; Lu, M.X.; Sun, R.; Zhu, Z.H.; Fuller, D.Q.; Guo, J.X.; Yang, X.M.; Tan, L.L.; Dong, J.J.; Liu, R.L.; et al. Forager-farmer transition at the crossroads of East and Southeast Asia 4900 years ago. Sci. Bull. 2023, 69, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.Y.; Haberle, S.G.; Li, Y.L.; Liu, E.F.; Shen, J.; Zheng, E.L.; Yin, J.J.; Wang, S.M. Evidence of Holocene climatic change and human impact in northwestern Yunnan Province: High-resolution pollen and charcoal records from Chenghai Lake, southwestern China. Holocene 2017, 28, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, A.L.; Yao, A.; Abbott, M.B.; Bain, D.J. Two millennia of anthropogenic landscape modification and nutrient loading at Dian Lake, Yunnan Province, China. Holocene 2019, 29, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Wu, D.; Li, Z.H.; Yuan, Z.J.; Niu, L.L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Zhou, A.F. Holocene-Anthropocene transition in northwestern Yunnan revealed by records of soil erosion and trace metal pollution from the sediments of Lake Jian, southwestern China. J. Paleolimnol. 2022, 68, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.S.; Li, P.C.; Yang, L.J.; Zhu, M. Yunnan Archaeology Bulletin; Yunnan University Press: Kunming, China, 2019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yao, A.; Jiang, Z.L. Rediscovering the settlement system of the ‘Dian’ kingdom, in Bronze Age southern China. Antiquity 2012, 86, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Zhao, F.Z.; Xia, H.Y. Research of climate characteristics over Dianchi Lake Basin. Environ. Sci. Sur. 2009, 28, 8–10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.L.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Q.G.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.S.; Wang, L.X. Modern sedimentation rates and dry-humid change inferred from grain size records in Dianchi Lake, Yunnan Province. Geogra. Res. 2011, 30, 161–171. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.L.; Peng, Y.Q.; Dai, M.; Kou, X.D. Observed (1961–2014) and Projected (2016-2100) Climate Change and Its Influence on Water Environment in the Dianchi Lake Basin. Environ. Sci. Sur. 2017, 36, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, T.R.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, T. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments from a hypertrophic plateau lake Dianchi, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 1219–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Fang, L.; Xiang, Q.Q.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.D.; Ding, Z.C.; Chen, L.Q. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in fish from the Dianchi Lake, China using the integrated biomarker response approach. Environ. Sci. Pollu. Res. 2020, 27, 45712–45721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.H.; Li, C.; Xu, P.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Du, J.S.; Han, Y.P.; Hu, H.Y. Identifying major contributors to algal blooms in Lake Dianchi by analyzing river-lake water quality correlations in the watershed. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F. Future directions for management and treatment of algal blooms: A case study of filamentous-Cyanobacteria in Dianchi Lake. Proceedings of the International Conference on Modern Medicine and Global Health. Theore. Natur. Sci. 2023, 6, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.S.; Sun, X.J. A preliminary study on the relationship between the pollen percentages in forest surface samples and surrounding vegetation on West Mountain of Kunming, Yunnan. Acta Bot. Sin. 1987, 29, 204–211. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Q.Z.; Wei, X.F.; Kong, D.C.; Lai, X.H.; Li, S.C.; Din, F.H. An evaluation on the ecological service function of the forests in Dianchi watershed. J. Yunnan Univ. 2010, 32, 365–372. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.P.; Zhang, X.; Liu, A.R. Study on aquatic vegetation change in Dianchi Lake. J. Southwest For. Univ. 2004, 24, 27–30. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.Y.; Chen, X.D.; Gao, Y.; Xie, S.; Mi, J. GLC_FCS30: Global land-cover product with fine classification system at 30 m using time-series Landsat imagery. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 2753–5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M. Brief review on the paleolithic archaeology in Kunming. In Proceedings of the Sixteenth Annual Meeting of the Chinese Society of Vertebrate Paleontology, Hefei, China, 10–11 November 2018; Volume 8, pp. 345–352. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Yao, A.; Jiang, Z.L.; Chen, X.X.; Yin, L. Bronze Age wetland/scapes: Complex political formations in the humid subtropics of southwest China, 900–100 BC. J. Anthropol. Archaeol. 2015, 40, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.G.; Huang, M. Yunnan region administrative centers eatablishing and its influence at Dianchi Lake area in Han dynasty. J. Wenshan Univ. 2010, 23, 34–38. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H.Y. On the Three Transfers of the Political, Economic and Cultural Center of Yunnan in History. Southwest Front. Ethn. Stud. 2013, 1, 12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.B. Saidianchi zhansiding and the exploitation of irrigation in Yunnan Province. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. 1989, 4, 330–332. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.G.; Cui, Z.M. The reasons why Yunnan administrative center returns to Dian Lake area once more. J. Wenshan Univ. 2012, 25, 51–56. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R. The distribution and development of the Han immigrant’s settlement in Yunnan during the Ming Dynasty. J. Chin. Hist. Geogr. 2006, 3, 74–83. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. Study on the Nonnative Ethic Minorities Immigration to Yunnan Province in the Dynasties of Yuan, Ming and Qing. Ph.D. Thesis, Yunnan University, Kunming, China, 2015. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Reimer, P.J.; Austin, W.E.; Bard, E.; Bayliss, A.; Blackwell, P.G.; Ramsey, C.B.; Butzin, M.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Friedrich, M.; et al. The IntCal20 Northern Hemisphere radiocarbon age calibration curve (0–55 cal kBP). Radiocarbon 2020, 62, 725–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insitute of Botany and South China Institute of Botany, Academia Sinica. Angiosperm Pollen Flora of Tropic and Subtropic China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1982. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.H. Pollen Morphology of Common Cultivated Plants in China—A Reference to the Search for Human Traces in the Stratigraphy; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.Y.; Mao, L.M.; Shu, J.W.; Li, C.H.; Sheng, C.M.; Zhou, Z.Z. An Illustrated Handbook of Quaternary Pollen and Spores in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2016. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Grimm, E.C. CONISS: A FORTRAN 77 program for stratigraphically constrained cluster analysis by the method of incremental sum of squares. Comput. Geosci. 1987, 13, 13–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, E.C. Tilia Software, Version 1.7.16; Illinois State Museum, Research and Collection Center: Springfield, IL, USA, 2011.
- Shu, J.W.; Huang, X.Z.; Xu, D.K.; Chen, Y.; Song, B.; Cui, A.N.; Grimm, E. The latest Tilia software: Chinese manual and practise skills. Acta Palaeontol. Sin. 2018, 57, 260–272. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Makohonienko, M.; Płóciennik, M.; Papiernik, P.; Kittel, P.; Gałka, M.; Mroczkowska, A.; Apolinarska, K.; Okupny, D.; Panfil, M.; Kotrys, B.; et al. Environmental changes during mesolithic-neolithic transition in kuyavia lakeland, central poland. Quater. Int. 2023, 20, 196–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffolo, M.B.; Regev, L.; Mintz, E.; Dubernet, S.; Berna, F.; Chaddwick, J.R.; Maeir, A.; Boaretto, E. Micro-contextual characterization of pyrogenic aragonite diagenesis in archaeological ash: Implications for radiocarbon dating of calcium carbonate in combustion features. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2023, 15, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, C.N.; Zalasiewicz, J.; Summerhayes, C.; Barnosky, A.D.; Poirier, C.; Gałuszka, A.; Cearreta, A.; Edgeworth, M.; Ellis, E.C.; Ellis, M. The Anthropocene is functionally and stratigraphically distinct from the Holocene. Science 2016, 351, aad2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.L.; Maslin, M.A. Defining the Anthropocene. Nature 2015, 519, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.Q.; Liu, J.B.; Wang, X.; Zhao, S.; Chen, J.H.; Qiang, M.R.; Liu, B.; Xu, Q.H.; Xia, D.S.; Chen, F.H. Holocene dust storm variations over northern China: Transition from a natural forcing to an anthropogenic forcing. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 2516–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.R.; Gaillard, F.J.; Cao, X.Y.; Herzschuh, U.; Sugita, C.; Tarasov, P.E.; Wagner, M.; Xu, Q.H.; Ni, J.; Wang, W.M. Towards quantification of Holocene anthropogenic land-cover change in temperate China: A review in the light of pollen-based REVEALS reconstructions of regional plant cover. Ear. Sci. Rev. 2020, 203, 103119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, A.M.; Montecchi, M.C.; Pellacani, G.; Florenzano, A.; Rattighieri, E.; Cardarelli, A. Environment, human impact and the role of trees on the Po plain during the Middle and Recent Bronze Age: Pollen evidence from the local influence of the terramare of Baggiovara and Casinalbo. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2015, 218, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Jones, R.T.; Yang, X.D.; Dearing, J.A.; Wang, S.M. The Holocene vegetation history of Lake Erhai, Yunnan province southwestern China: The role of climate and human forcings. Holocene 2006, 2, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.Y.; Haberle, S.G.; Shen, J.; Xue, B.; Burrows, M.; Wang, S.M. Postglacial fire history and interactions with vegetation and climate in southwestern Yunnan Province of China. Clim. Past. 2017, 13, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, H.M.; deMenocal, P.B.; Henmming, S.; Hemming, T.G.; Brown, F.H.; Guilderson, T.; Sirocko, F. Climate change and the collapse of the Akkadian empire: Evidence from the deep sea. Geology 2000, 4, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.C.; Dong, G.H.; An, Z.S.; Edwards, R.L.; Li, H.M.; Li, D.; Spengler, R.; Cai, Y.J.; Cheng, H.; Lan, J.H.; et al. Megadrought and cultural exchange along the proto-silk road. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, G.H.; Gunther, D.; Peterson, L.C.; Sigman, D.M.; Hughen, K.A.; Aeschlimann, B. Climate and the Collapse of Maya Civilization. Science 2003, 299, 1731–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.X.; Liu, D.S. 4000aB.P. event and its implications for the origin of ancient Chniese civilizatio. Quat. Sci. 2001, 21, 443–451. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gignoux, C.R.; Henn, B.M.; Mountain, J.L. Rapid, global demographic expansions after the origins of agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6044–6049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.W.; Yang, Y.S.; Chen, G.K.; Zhang, S.J.; Zhang, H.C. Changes in Wood Utilization Due to Iron Age Jade Mining in the Western Hexi Corridor: Wood Charcoal Investigations. Fron. Ear. Sci. 2022, 9, 636534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, L.; Li, K.S.; Jiang, J.L.; Chen, G. Varying levels of the Dian Lakes and the Dian Lakes culture. Bull. Indo-Pac. Prehistory Assoc. 2011, 31, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.D.; Wünnemann, B.; Jiang, Z.L. Hydrological variations of a lake-catchment and human interaction during the last 6 ka in Yunnan, China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 587, 124932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, A.L.; Q’Quinn, R.F.; Abbott, M.B.; Bain, D.J. A Holocene history of the Indian monsoon from Qilu Lake, southwestern China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2020, 227, 106051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, H.; Courty, M.A.; Wetterstrom, W.; Guichard, F.; Senior, L.; Meadow, L.; Curnow, A. The Genesis and Collapse of Third Millennium North Mesopotamian Civilization. Science 1993, 261, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.L.; Jiang, Z.L.; Yao, H.Y.; Chen, X.X. A study on the agricultural structure of the Shizhaishan culture in Dian Lake area, Yunnan Province, China: From the perspective of the plant remains at Hebosuo Site. Agric. Hist. China 2021, 40, 36–47+102. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Lan, J.H.; Sheng, E.G.; Liu, B.; Yu, K.K.; Ye, Y.D.; Shi, Z.G.; Cheng, H.; Wang, X.L.; Zhou, X.Y.; et al. Hydroclimatic contrasts over Asian monsoon areas and linkages to tropical Pacific SSTs. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.P.; Zhao, C.; D’Andra, W.J.; Liang, J.; Zhou, A.F.; Shen, J. Temperature fluctuations during the Common Era in subtropical southwestern China inferred from brGDGTs in a remote alpine lake. Earth Plant. Sci. Lett. 2017, 510, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunming Water Work Bureau. Kunming Song Hua Ba Dam-Graphy; Yunnan Scientific Press: Kunming, China, 1996. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kathayat, G.; Cheng, H.; Sinha, A.; Yi, L.; Li, X.L.; Zhang, H.W.; Li, H.Y.; Ning, Y.F.; Edwards, L. The Indian monsoon variability and civilization changes in the Indian subcontinent. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; He, Y.Q.; Kong, X.G.; An, Z.S.; Wu, J.Y.; Kelly, M.J.; Dykoski, J.A.; Li, X.D. The Holocene Asian monsoon: Links to solar changes and North Atlantic climate. Science 2005, 308, 854–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.L.; Xie, S.J. History of Population in China; People’s Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1988. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- The State Administration of Cultural Heritage. The State Administration of Cultural Heritage. The Atlas of Chinses Cultural Relics: Yunan Branch. In The Atlas of Chinses Cultural Relics; The State Administration of Cultural Heritage: Beijing, China, 1999. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, G.H.; Qiu, M.H.; Li, R.; Chen, F.H. Using the fulcrum cognitive model to explore the mechanism of past human-land co-evolution. Acta Geographica. Sin. 2021, 76, 15–28. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, B.M.; Thornton, C.P.; Pigott, V.C. Development of metallurgy in Eurasia. Antiquity 2009, 83, 1012–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, N.F.; Spengler, R.N.; Frachetti, M. Millet cultivation across Eurasia: Origins, spread, and the influence of seasonal climate. Holocene 2016, 26, 1566–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.H.; Du, L.Y.; Yang, L.; Lu, M.X.; Qiu, M.H.; Li, H.M.; Ma, M.M.; Chen, F.H. Dispersal of crop-livestock and geographical-temporal variation of subsistence along the Steppe and Silk Roads across Eurasia in prehistory. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2022, 65, 1187–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, N.D. Small game, the younger dryas, and the transition to agriculture in the southern levant. Mitteilungen Ges. Für Urgesch. 2003, 12, 43–71. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.Y.; Wan, Z.W.; Perry, L.; Lu, H.Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, C.H.; Li, J.; Xie, F.; Yu, J.C.; Cui, T.X.; et al. Early millet use in northern China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3726–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staubwasser, M.; Sirocko, F.; Grootes, P.M.; Segl, M. Climate change at the 4.2 ka BP termination of the Indus valley civilization and Holocene south Asian monsoon variability. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhu, C.; Ma, C.M.; Li, F.; Meng, H.P.; Liu, H.; Li, L.Y.; Wang, X.C.; Sun, W.; Song, Y.G. Mid-Holocene palaeoflood events recorded at the Zhongqiao Neolithic cultural site in the Jianghan Plain, middle Yangtze River Valley, China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2017, 173, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.P. A study on the historical rural settlements and the man- land relationshop in Dianchi basin from 16th to 20th century: A case of Chai river delta plain. J. Chin. Historical. Geopra. 2016, 27, 37–46. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.J.; Yuan, D.X.; Cheng, H.; Yu, T.; Shen, C.C.; Edwards, R.L.; Wu, Y.; Xiao, S.Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; et al. Human activity and climate change triggerred the expansion of rocky desertification in the Karst areas of Southwestern China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 1761–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample ID | Depth (cm) | Material | 14C Age (a BP) | ±(y) | Calibrated Age (AD) (95.4%) | Medium Age (AD) | σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LZU20654 | 79 | Charcoal | 390 | 20 | 1447–1621 | 1479 | 55 |
| LZU20655 | 90 | Charcoal | 340 | 20 | 1479–1635 | 1568 | 47 |
| Beta 583919 | 143 | Charcoal | 640 | 30 | 1285–1397 | 1352 | 34 |
| LZU20657 | 151 | Charcoal | 580 | 20 | 1311–1410 | 1346 | 30 |
| Beta 583920 | 194 | Charcoal | 610 | 30 | 1299–1404 | 1348 | 31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, P.; Liu, F.; Li, G.; Li, Y.; Cao, H.; Li, X. Anthropogenic Impact on the Terrestrial Environment in the Lake Dian Basin, Southwestern China during the Bronze Age and Ming–Qing period. Land 2024, 13, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13020228
Liu P, Liu F, Li G, Li Y, Cao H, Li X. Anthropogenic Impact on the Terrestrial Environment in the Lake Dian Basin, Southwestern China during the Bronze Age and Ming–Qing period. Land. 2024; 13(2):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13020228
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Peilun, Fengwen Liu, Gang Li, Yuejiao Li, Huihui Cao, and Xiaorui Li. 2024. "Anthropogenic Impact on the Terrestrial Environment in the Lake Dian Basin, Southwestern China during the Bronze Age and Ming–Qing period" Land 13, no. 2: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13020228
APA StyleLiu, P., Liu, F., Li, G., Li, Y., Cao, H., & Li, X. (2024). Anthropogenic Impact on the Terrestrial Environment in the Lake Dian Basin, Southwestern China during the Bronze Age and Ming–Qing period. Land, 13(2), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13020228






