Abstract
Arid central Asia (ACA) is dominated by mid-latitude westerlies and characterized by a climate optimum (a relatively humid climate that has supported the development of human culture) in clear contrast with the climate of monsoonal Asia during the Holocene. Significantly, whether the onset of the Holocene Climate Optimum (HCO) had an impact on cultural exchanges along the ancient Silk Road remains unknown. In this study, we compared the onset of the HCO in different parts of the vast ACA region by referring to a variety of previously established paleo-moisture/precipitation records. Intriguingly, we found significant differences in the onset of the HCO between the western and eastern parts of ACA. The onset of the HCO in the western part of ACA (i.e., to the west of the Tianshan Mountains) mainly occurred at ~8 ka BP (1 ka = 1000 cal yr BP). In contrast, the onset of the HCO occurred at ~6 ka in northern Xinjiang and even as late as ~5 ka in southern Xinjiang; this is a delay of 2–3 thousand years compared with the western part of ACA. These results likely indicate that the onset of the HCO occurred in a time-transgressive manner in ACA, namely, ‘early in the west but late in the east’. On the other hand, we found that the onset of the HCO in the western part of ACA may have resulted in the inception of wheat planting and the development of agricultural civilization and that the onset of the HCO in northern Xinjiang may have prompted the southward migration of Afanasievo culture after ~5 ka. Additionally, the initiation of the HCO in southern Xinjiang could provide an environmental basis for the spread and planting of wheat and millet in this area after ~4.5 ka. We speculate that the spatial differences in the onset of the HCO in ACA are mainly related to temporal changes in the intensity and position of the mid-latitude westerly jet. Although the increase in insolation and reduction in the global ice volume would have led to an increase in the water vapor feeding the western part of ACA around 8 ka, the climate in the eastern part of ACA (namely, the Xinjiang region) could have only become humid after 6 ka when the westerlies were intensified and became positioned in the south. Moreover, the delayed HCO in southern Xinjiang probably benefited from the stronger westerly winds that appeared around 5 ka, which could have overcome the influence of the tall topography of the Tianshan Mountains. Therefore, in addition to external forcing (i.e., insolation), the ocean–atmospheric teleconnection, the regional topography, and their connection to the climate system are important in determining the spatial differences in the time-transgressive onset of the HCO in ACA. Our findings contribute to understanding the spatio-temporal characteristics of the hydroclimate in regions with complex eco-environmental systems and a diverse history of human activity.
1. Introduction
The Holocene (since ~11,700 yr BP) is a geological epoch that has seen the rapid development and prosperity of human civilization [1,2,3]. Previous studies have shown that the global or hemispheric temperature changes that have occurred since the Holocene are partly significant [4,5,6,7,8,9,10], but there are significant differences in the evolution patterns of humidity and precipitation in different regions, e.g., Europe [11], Africa [12], America [13], and Asia [14,15,16,17]. Generally, the Holocene has been characterized by a relatively warm and humid period, which is referred to as the Holocene Climate Optimum (HCO). During this period, the humidity/precipitation increased, and the climate was relatively stable, thus providing the basis for the rise and development of ancient cultures and civilizations [18,19,20,21]. Therefore, clarifying the onset and potential spatial differences in the HCO is essential for understanding the role of climate in the succession of human cultures and civilizations. Since the Holocene, it is possible that temperature changes have held a supra-regional pattern, but this continues to be intensely debated [22,23,24]; we prefer to discuss the onset and duration of the HCO from the perspective of humidity/precipitation evolution.
Mid-latitude arid central Asia (ACA) mainly includes the northeast of Iran, the five Central Asian countries, and the northwest of China. It is the largest non-zonal arid area in the world, possesses large areas of deserts, mountains, and a small number of oases, and has a fragile eco-environment system. Meanwhile, ACA also encompasses the main routes of the Silk Road, a passage that enables cultural exchange between the East and the West. The trade and cultural exchange that has materialized along the Silk Road not only reached unprecedented prosperity in modern times, but it also flourished several thousand years ago. The onset of the HCO in the ACA region remains an important topic of interest, as many studies have suggested that the climate evolution that occurred in the Holocene in ACA is remarkably inconsistent with that of monsoonal Asia [25,26,27]. It has been demonstrated that the ACA region was broadly characterized by a dry climate in the early Holocene, but it has been characterized by a wet climate since the mid-late Holocene [17,25,28]; however, the onset of the HCO in different parts of the ACA region has not been thoroughly addressed in previous studies. This is because ACA is a relatively broad region and is composed of different geomorphic units (basins, mountains, etc.), which lead to spatial differences in the hydroclimate changes that occur within this vast region. Furthermore, some studies have shown that cultural exchanges in ACA are characterized by evidently different stages [29,30], which may correspond to the stages of changes in the hydroclimate. Therefore, it is important to determine whether there are spatial differences in the onset of the HCO in the ACA region in order to establish the relationship between climate change and trans-Eurasian cultural exchange.
By referring to a variety of high-quality paleoclimate records that have been collected by scholars from lakes, loess sections, and cave stalagmites in recent years, we attempt to deepen our understanding of the pattern of evolution in the climate of the Holocene in the ACA region with regard to the spatial difference in the onset of the HCO. In total, we collected 37 records that were reconstructed from the study area; of these, 10 high-quality records were used to characterize the onset of the HCO. The spatial differences in the onset of the HCO were clearly observed, and its association with cultural exchange was further explored. We also explored the possible forcing mechanism that is responsible for the spatial asynchrony of the humid climate in different parts of the ACA region. Our findings can be used to understand the potential role of the regional climate in regulating cultural exchange along the ancient Silk Road, which could provide a reference for the adaptation of human strategies to future environmental changes.
2. Date and Methods
2.1. Study Area
ACA is located in the inland of the Eurasian continent, spanning approximately between 34.33°–55.45° N and 46.49°–107.29° E. It includes northeastern Iran, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and China’s Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. With an average elevation of about 1000 m, the terrain gradually slopes higher in the southeast and lower in the northwest. The landscape is predominantly characterized by mountains and basins. Notably, basins are primarily distributed in the northwest of China, including the Tarim Basin and the Junggar Basin. Correspondingly, tall mountains and plateaus lie in the middle of the ACA, including the Tianshan Mountains and the Pamirs. These characteristics eventually constitute the unique topography of ACA.
Due to its special geographical location and complex terrain, the area is limited in its exposure to maritime airflow, further obstructed by the surrounding high mountain ranges, making it difficult for maritime airflow to penetrate. As a result, precipitation is relatively low [31]. Generally, the water vapor feeding this region is transported by the mid-latitude westerly jet from the North Atlantic Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Caspian Sea [32]. However, due to topographic barriers and airflow uplift, precipitation is predominantly concentrated in mountainous areas, with basins and plains receiving scant rainfall. The average annual precipitation across the entire region is less than 150 mm, with significant spatial disparities [33], exhibiting pronounced characteristics of temperate and continental climates [34].
2.2. Collection of Paleoclimatic Records
In recent years, researchers have established many paleoclimatic records in ACA using various geological documents, including those relating to lake sediments, loess–paleosol sections, peatbogs, and cave stalagmites. For instance, Chen et al. presented a compilation of 36 records regarding the moisture evolution during the Holocene in ACA that are supported by reliable chronologies, revealing an overall long-term trend of wetting (31 out of 36 records) during the Holocene [35]. In addition to Chen’s compilation dataset, we added a newly published quantitative reconstruction of regional precipitation (Pann) using pollen records from Tolbo Lake in the Mongolian Altai Mountains to further support our research [36]. Therefore, in this study, we can reliably investigate the onset of the HCO in the ACA region based on the 37 records primarily collected. High-quality paleoclimatic records were selected using the following criteria: (1) Firstly, the proxies had to be unambiguous indicators of changes in precipitation/moisture; otherwise, they were excluded. (2) The age control of the record had to be reliable, and the selected proxy records needed an average of at least one date per 1 kyr. (3) The duration of the record needed to be a minimum of two-thirds the length of the Holocene epoch. Ten proxy records met these criteria, and detailed information about them is presented in Table 1 and Figure 1. Meanwhile, it is worth noting that there are few studies that focus on the central part of ACA, which may have increased uncertainty regarding the evolution of the Holocene climate in this area.

Table 1.
List of paleoclimatic records used in this study.
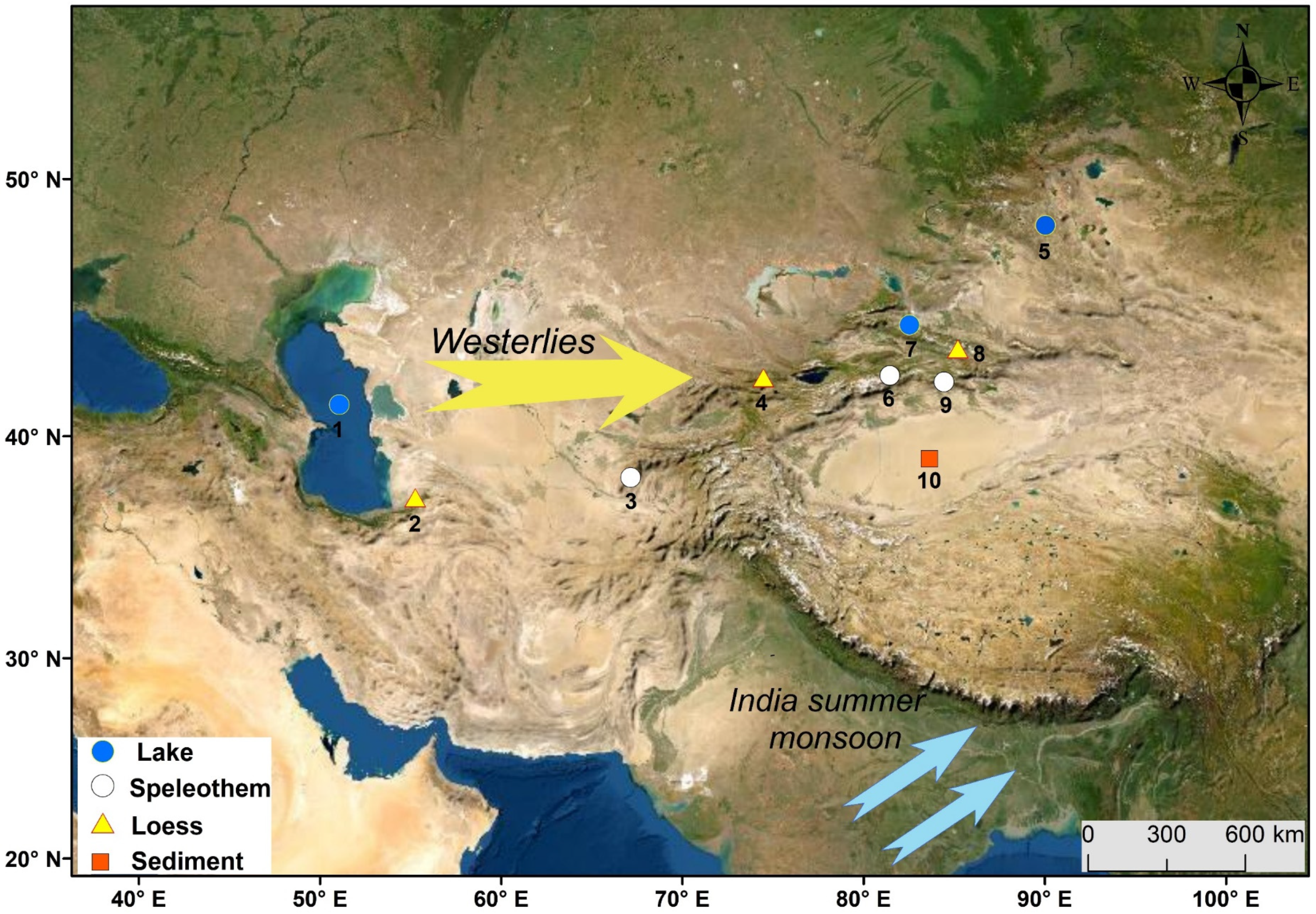
Figure 1.
Map showing the study area and locations of the eight high-quality moisture/precipitation records in ACA that were used in this study. The arrows illustrate the main trajectories of the westerlies and the Indian summer monsoon (ISM). See Table 1 for details of these proxy records.
2.3. Interpretations of Paleoclimatic Proxies
2.3.1. Lake Sediments (Mainly Pollen and Quantitatively Reconstructed Precipitation)
Pollen records from lake sediments are widely used to reconstruct vegetation and climate history, especially those verified by modern datasets to quantitatively reconstruct paleo-rainfall changes [16,36]. The climate characteristics of a region can determine the main types of vegetation to a certain extent. Therefore, the growth, development, prosperity, and decline in plants are closely related to the climate characteristics of the region [44,45]. For example, a warm and humid climate is conducive to the growth of palm trees and tropical rainforests, while a cold and dry climate is suitable for grasslands and coniferous forests [46]. Consequently, by comparing the distribution of spores and pollen types at different times and locations, the climate conditions of a region during different periods, such as humidity and precipitation, can be inferred.
2.3.2. Loess–Paleosoal Sections
Loess is a widely distributed sediment known for its good continuity, rapid deposition rate, and rich environmental information, making it an excellent carrier for recording Quaternary environments. In this study, proxies including δ13Corg, lightness (L*), and χfd from loess sections were used to reflect changes in paleo-moisture/precipitation. First, overlying vegetation is the main source of soil organic matter, so δ13Corg values largely depend on the overlying vegetation [47]. In dry conditions, C3 plants partially close their stomata, resulting in decreased stomatal conductance, increased CO2 concentration gradient inside and outside leaf cells, decreased Ci/Ca, and ultimately an increase in δ13Corg, and vice versa [48]. Therefore, in ecosystems dominated by C3 plants, δ13Corg values are negatively correlated with precipitation [49,50]. Second, lightness (L*) is closely related to the concentration of organic matter, mainly because soil organic matter is the primary factor causing the darkening of color [51]. In general, the smaller the organic matter content, the larger the L* value, indicating a drier climate [52]. Third, magnetic susceptibility is often used to represent the concentration of magnetic minerals in loess sediments, with χfd used to assess the contribution of superparamagnetic (SP) particles. Previous studies show that during loess deposition periods, weak pedogenesis leads to fewer magnetic particles, resulting in low magnetic susceptibility, whereas during the development of paleosols, strong pedogenesis leads to more superparamagnetic particles, resulting in high magnetic susceptibility [53,54]. Therefore, under humid climate conditions, strong pedogenesis leads to an increase in χfd values, whereas under arid climate conditions, weak pedogenesis leads to a decrease in χfd values. Furthermore, sedimentary facies of sedimentary profiles can also reflect regional paleoclimate changes. Sedimentary facies represent the material manifestation of sedimentary environments, with different sedimentary environments forming distinct sedimentary facies. Therefore, based on sedimentary facies characteristics such as bedding, structure, grain size, and color, the environmental conditions of the sediment at that time can be inferred [55]. For instance, river deposits typically exhibit horizontal bedding and coarse grain size, while sandy sedimentation presents a rough surface with possible wind erosion features [43]. Hence, sedimentary facies of sediment profiles can serve as another indicator of paleoclimate.
2.3.3. Speleothems
Cave stalagmites, as carriers for paleoclimate research, possess key advantages such as precise dating, high resolution, and wide distribution, making them the fourth pillar of paleoclimate research [39,56]. Modern observations and laboratory simulations indicate that the variation in trace elements (Sr/Ca) in stalagmites is primarily controlled by prior calcite precipitation (PCP) and water–rock interactions (WRIs) [57,58]. Specifically, under drier conditions, reduced recharge of the karst aquifer leads to intensified degassing of carbon dioxide from water into surface karst voids, as well as water infiltration into caves, resulting in a gradual enrichment in Sr relative to Ca in percolating water. Subsequently, this enrichment is reflected in stalagmites, leading to an increase in Sr/Ca ratios. In contrast, under wetter conditions, PCP is less pronounced, leading to a relatively lower Sr concentration in percolating water compared with Ca [59]. Consequently, we use trace elemental ratios (i.e., Sr/Ca) as reliable indicators of precipitation changes around the cave sites in this study.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Spatial Difference in the Onsets of HCOs in ACA
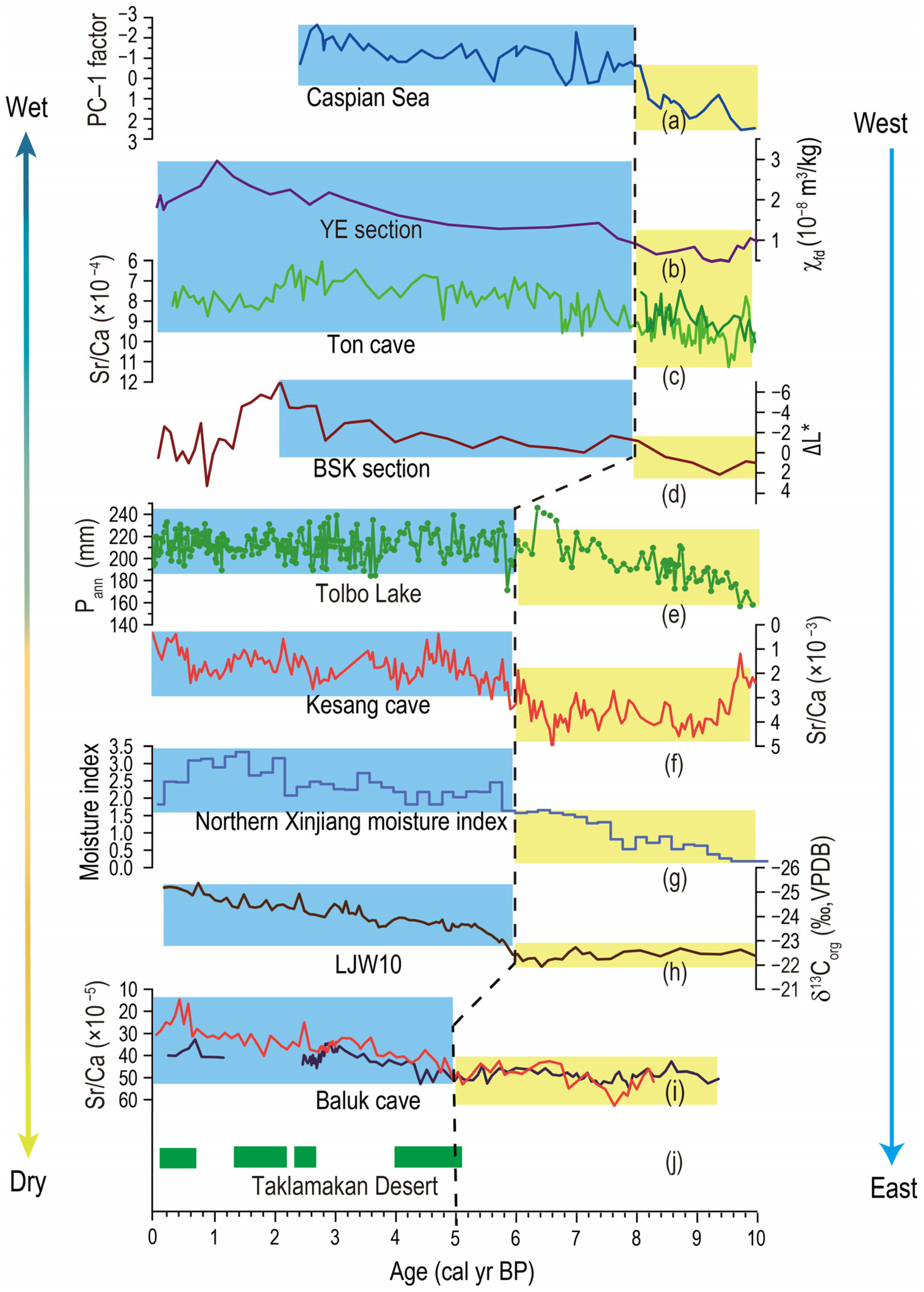
There are significant differences in the onset of the HCO in ACA, as shown by the nine paleo-moisture/precipitation records (Figure 2). According to these records, ACA can be divided into three regions as follows: the western part of ACA (west of the Tianshan Mountains), northern Xinjiang, and southern Xinjiang, which is characterized by inconsistency in the onset of the HCO.
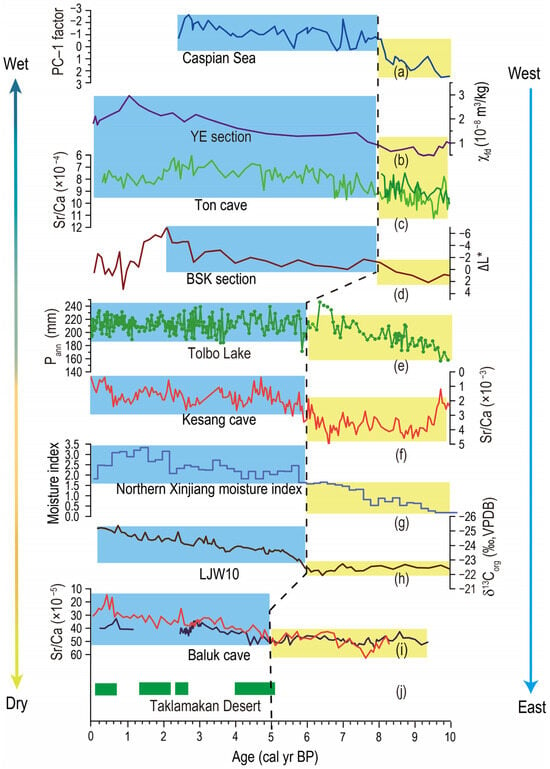
Figure 2.
Spatial difference in the Holocene climatic optimum as reflected in various paleoclimatic records from arid central Asia. (a) Pollen record from the Caspian Sea [37]; (b) record of χfd of the YE loess section in NE Iran [38]; (c) stalagmite Sr/Ca record from Ton Cave, Uzbekistan [39]; (d) lightness record from the BSK loess section, Kyrgyz [40]; (e) pollen-based Pann record from Tolbo Lake, Altai Mountains [36]; (f) stalagmite Sr/Ca record from Kesang Cave [39]; (g) integrated moisture index from north Xinjiang [41]; (h) δ13Corg record of the LJW10 section [42]; (i) stalagmite Sr/Ca record from the Baluk Cave [28]; and (j) wet records reflected by nine sedimentary profiles from the Taklimakan Desert, with green rectangle indicating the humid climate [43].
Firstly, the Caspian Sea pollen record in the western part of the ACA shows that the area was dominated by desert vegetation and that the climate was dry before 8 ka; meanwhile, after 8 ka, the number of trees gradually increased, and the climate began to become significantly more wet [37] (Figure 2a). Similarly, the stalagmite Sr/Ca ratio observed in the Ton cave in Uzbekistan shows notably high values before 8 ka [39] (Figure 2c). In general, the stalagmite Sr/Ca ratio has been regarded as a reliable indicator of regional changes in the precipitation/moisture at various timescales [28,39,60], with lower ratios reflecting a relatively elevated level of humidity around the cave site. Therefore, it can be seen that the onset of the HCO in the western ACA may have occurred at ~8 ka. In addition, two loess section records from the same area also support this proposed time point. The magnetic parameters of the YE profile in northeastern Iran showed low values at 10~8 ka, indicating that the climate was dry at this stage, the soil formation was weak, and no paleosol was formed [38] (Figure 2b). However, the magnetic parameters continue to increase after 8 ka. This is because, when the climate becomes humid, the soil formation is intensified, and secondary fine-grained magnetite minerals are formed during the development of paleosols, resulting in an increase in the magnetic parameters [53,54]. During the same period, the brightness index of the BSK profile was also low [40] (Figure 2d), indicating that the organic matter content and level of precipitation during this period were higher. Furthermore, the pollen record of Lake Van in the western Caspian Sea also supports this conclusion; this suggests that, after 8.2 ka, the effective water content in this area increased significantly and the deciduous oak forest expanded significantly [61]. The above-mentioned results indicate that the moisture/precipitation in the western part of ACA significantly increased around 8 ka, which demonstrates the onset of the HCO at around 8 ka.
Secondly, the onset of the HCO in Xinjiang is clearly later than that in the western part of ACA, and the area can be divided into two parts as follows: northern and southern Xinjiang. The value of the stalagmite Sr/Ca ratio of the Kesang cave in northern Xinjiang was high at 10–6 ka and began to decrease gradually after 6 ka [39] (Figure 2f), indicating that the climate in this area became wetter after 6 ka. Similarly, Wang et al. used the regional average method to reconstruct a synthesized humidity index to be applied to the lakes in northern Xinjiang [41]; the index was remarkably low during 10–6 ka, while it increased significantly after 6 ka (Figure 2g). In addition, the carbon isotope of organic matter and reconstructed precipitation in the LJW10 section in northern Xinjiang shows the time node at which the climate becomes wetter [42,62] (Figure 2h); this is consistent with the stalagmite Sr/Ca ratio and the synthesized humidity index. Lastly, the pollen-based quantitative annual precipitation reconstruction (Pann) record from Tolbo Lake in the Mongolian Altai Mountains also supports this conclusion, which demonstrates the expansion of forest vegetation and high and stable Pann after 6 ka [36]. These characteristics indicate that the onset of the HCO in northern Xinjiang occurred at 6 ka.
Thirdly, the stalagmite Sr/Ca ratio of the Baluk cave in southern Xinjiang was high during 10–5 ka, which suggests that there was a relatively dry climate before 5 ka and a humid climate afterward [28] (Figure 2i). In addition, the sedimentary facies and paleoenvironmental proxies of the nine sedimentary strata in the Taklimakan Desert in southern Xinjiang indicate that they experienced rivers, lakes, and still waters during 5–2 ka [43] (Figure 2j); this indicates that the climate of the southern Xinjiang region changed from dry to humid at ~5 ka. Therefore, it is likely that the onset of the HCO in southern Xinjiang occurred at 5 ka, which is ~1 ka later than in northern Xinjiang and ~3 ka later than in the western part of ACA.
In summary, there are significant differences in the onset of the HCO between the western and eastern parts of ACA. Specifically, the onset of the HCO in the western part of ACA (i.e., to the west of the Tianshan Mountains) mainly occurred at ~8 ka. In contrast, the HCO occurred at about 6 ka in northern Xinjiang and even as late as ~5 ka in southern Xinjiang; this is a delay of 2–3 thousand years compared with the western part of ACA. These results likely indicate that the onset of the HCO occurred in a time-transgressive manner in ACA, namely, ‘early in the west but late in the east’.
3.2. The Impact of the Time-Transgressive Onset of the HCO on Cultural Exchange
The Silk Road originally referred to a trade channel that spanned from Chang’an in the east to Central Asia, Iran, and other countries in the west, and finally, to Rome. It greatly promoted trade and cultural exchange between the East and the West and promoted the diversified development of Eastern and Western civilizations. However, before the birth of the Silk Road, various routes that promoted the exchange of prehistoric civilizations already existed [1,2,63,64], these are commonly known as the ancient Silk Road. Along these prehistoric paths, crops such as wheat that originated in the West were spread eastward, and crops such as millet that originated in the East were spread westward [29,65,66]. According to the existing archaeological records, wheat and millet were domesticated at about 10 ka in the Crescent Valley of Western Asia and the Yellow River Basin of Eastern Asia, where they began to be planted as a crop [67,68]. Since then, they have spread in opposite directions. According to their possible routes of propagation and frequency of occurrence in the ACA region (Figure 3), they can be roughly divided into two stages as follows: the spread of wheat was mainly limited to the west of ACA, while the spread of millet was mainly limited to the west of the Chinese Loess Plateau and the Hexi Corridor before 4.5 ka [69,70,71].
In contrast, the spread of wheat and millet to southern Xinjiang and the frequency of their occurrence increased significantly after 4.5 ka [71,72]. Although wheat was found to have existed in Tongtiandong in northern Xinjiang at around 5 ka [73], it is often considered to have reached northern Xinjiang via the Eurasian Steppe Road [74,75,76]. In the above process, wheat was confined to the west of ACA before 4.5 ka, which may be related to the humid environment in the area. More specifically, wheat spread to the eastern Caspian Sea at 7.5 ka [77] and to the western end of the Tianshan Mountains in Tajikistan at around 6 ka, to where it was confined for a long time [78]. This may be because the onset of the HCO in the western part of ACA occurred at 8 ka. After this, the precipitation increased, the amount of river water increased, and an earlier humid environment formed; this, in turn, provided the water required for wheat growth and suitable climatic conditions. During this period, the climate in Xinjiang was relatively arid, and it was not suitable for wheat planting. At the same time, the western region of ACA gradually transitioned from a hunting and gathering society to a farming society after entering the Neolithic Age [79]. During this period, agricultural civilizations, represented by the Dzheytun culture (8–6.2 ka) and Anau culture (6.2–5.5 ka), appeared successively [80]. Wheat has been found in the remains of both cultures, with agriculture being the main mode of production [77,79]. Therefore, the humid environment of ACA may have also played a crucial role in the birth and development of ACA’s early agricultural culture.
Subsequently, the onset of the HCO in southern Xinjiang may have played an important role in the spread and cultivation of wheat and millet in the region after 4.5 ka. According to previous research, the human migration and cultural exchange of ACA often occurred along the piedmont oasis [65,81,82,83]. Southern Xinjiang is primarily characterized by the Taklamakan Desert and numerous piedmont oases. After the onset of the HCO in this region at 5 ka, precipitation increased, and the climate became humid. This humid environment enabled the piedmont oases to continue to develop and extend, further expanding the scope of human activities and providing a basis for human migration. At the same time, the humid climate also provided suitable environmental conditions for crop planting. Therefore, wheat and millet spread to Xinjiang after 4.5 ka as human migration increased and the climate became suitable for planting.
In addition, a recent study revealed that the genomic data obtained from human remains in the Junggar Basin indicate that the ancestors of the region came from the Afanasievo culture population [84]. The Afanasievo culture was mainly distributed in the south-central part of Siberia and the Minusinsk Basin, with animal husbandry being its main mode of production. It spread southward to the Jungar Basin at around 5 ka, and there remains controversy over whether it continued to migrate southward to the Tarim Basin [84,85,86]. In this process, the onset of the HCO at 6 ka in northern Xinjiang may have promoted the southward migration of the Afanasievo culture. Northern Xinjiang is mainly composed of the Junggar Basin and the surrounding grasslands. The climate of this area gradually became humid after 6 ka, and the area and scope of the grasslands increased significantly after about 1 ka of development. Superior animal husbandry conditions may have attracted the Afanasievo population, prompting the Afanasievo population to start migrating to the south. The arrival of the Afanasievo population, which would have brought Indo-European languages and animal husbandry into the region, could be regarded as the beginning of China’s practice of animal husbandry.
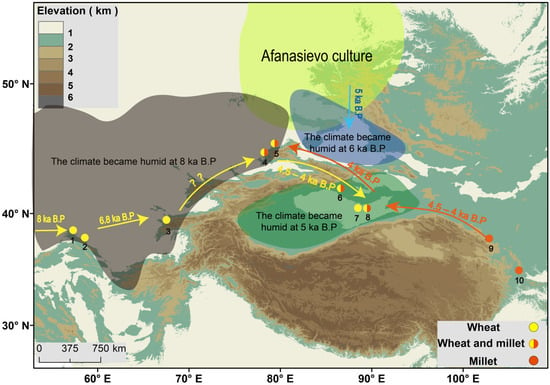
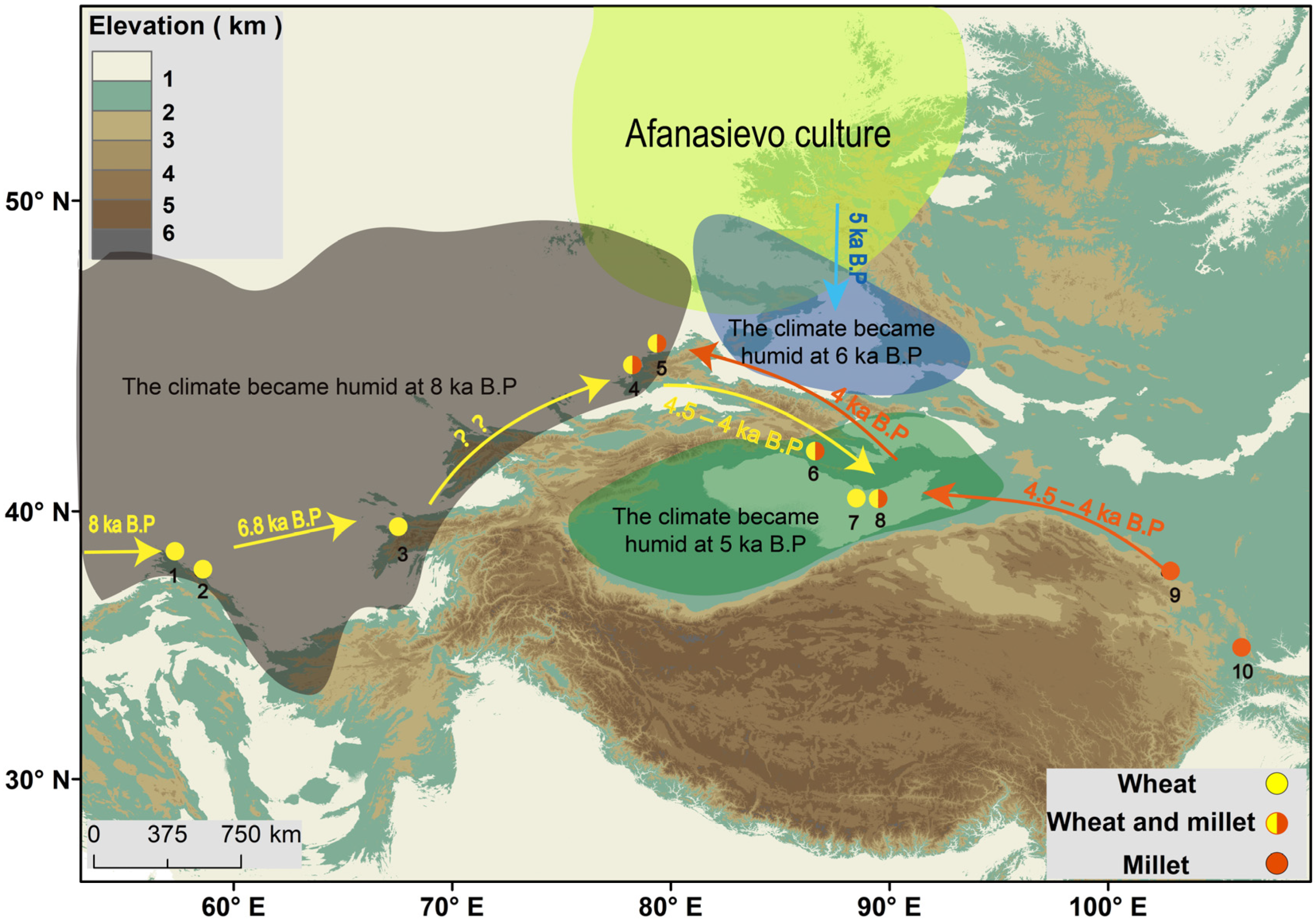

Figure 3.
The relics of wheat and millet and the earliest time at which they appeared in the study area. 1. Jeitun (8.5~7.5 ka) [77]; 2. Anau (6.5~5 ka) [2]; 3. Sarazm (6.5~5 ka) [87]; 4. Begash (4.5~4 ka) [88]; 5. Tasbas (5~4.5 ka) [89]; 6. Xintala (4~3.5 ka) [90]; 7. Xiaohe cemetery (4~3.5 ka) [91]; 8. Gumugou cemetery (4~3.5 ka) [92]; 9. Dadiwan (4.5~4 ka) [93]; and 10. Mozuizi (8~4.5 ka) [69]. The yellow arrow indicates the possible propagation path of wheat. The orange arrow indicates the possible propagation path of millet, and the blue arrows indicate the direction of cultural migration. The question marks mean that the migration of wheat in this region is uncertain.
Figure 3.
The relics of wheat and millet and the earliest time at which they appeared in the study area. 1. Jeitun (8.5~7.5 ka) [77]; 2. Anau (6.5~5 ka) [2]; 3. Sarazm (6.5~5 ka) [87]; 4. Begash (4.5~4 ka) [88]; 5. Tasbas (5~4.5 ka) [89]; 6. Xintala (4~3.5 ka) [90]; 7. Xiaohe cemetery (4~3.5 ka) [91]; 8. Gumugou cemetery (4~3.5 ka) [92]; 9. Dadiwan (4.5~4 ka) [93]; and 10. Mozuizi (8~4.5 ka) [69]. The yellow arrow indicates the possible propagation path of wheat. The orange arrow indicates the possible propagation path of millet, and the blue arrows indicate the direction of cultural migration. The question marks mean that the migration of wheat in this region is uncertain.

3.3. The Forcing Mechanism of the Time-Transgressive Onset of the HCO in ACA
The time-transgressive onset of the HCO in ACA could be attributed to the mechanism via which the water vapor carried by the mid-latitude westerly circulation is distributed. Specifically, this can be discussed from three aspects. First, on the orbital scale, the precipitation in ACA during the Holocene is mainly affected by the intensity of solar radiation. Since the mid-Holocene (approximately 8 ka), the solar radiation observed during winter has increased (Figure 4a); this has led to an increase in the evaporation of the Caspian Sea, the Mediterranean Sea, and the North Atlantic, which are the main sources of the water vapor transported by the westerly circulation [42]. In addition, the increase in insolation in the winter and the strong summer insolation that occurred during the early Holocene prompted the retreat of the Northern Hemisphere ice sheet, which increased the meltwater injected into the Pacific Ocean [94]. As a result, the westerly circulation carries more water vapor, which further increases the moisture/precipitation in the areas controlled by the westerly circulation; this has formed a large pattern of continuous wetting in ACA since the mid-Holocene. Second, on the suborbital scale, the moisture/precipitation of ACA is also regulated by the internal air–sea systems of the earth, such as the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) and circumglobal teleconnection (CGT) [42,95]. When the NAO is in the positive phase, the westerly circulation moves northward; otherwise, it moves southward. When the CGT changes from the positive phase to the negative phase, the evaporation of the Indian Ocean is strengthened, and the excess water vapor reaches Xinjiang along the northeast of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau; this increases precipitation in the region [96,97]. Moreover, the North Sea Caspian Pattern (NCP) and the Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) may also have an impact on precipitation in ACA. Specifically, when the NCP is in its positive (negative) phase, it may lead to increased northward (southward) circulation near the Caspian Sea [98,99], potentially affecting precipitation in ACA. Similarly, during the positive phase of the IOD, the stronger summer monsoon over the Indian Ocean could result in the transportation of more moisture from the Indian Ocean towards ACA, consequently leading to increased precipitation in that region [100,101]. Lastly, the influence of local topography on precipitation in ACA cannot be ignored [102,103,104]. The Tianshan Mountains, which are located within ACA and have an average altitude of more than 4000 m, can not only block the movement of water vapor from the westerly circulation but can also block the north–south airflow. Therefore, the Tianshan Mountains can not only divide ACA into the west of the Tianshan Mountains and the east of the Tianshan Mountains (Xinjiang) but also separate southern and northern Xinjiang.
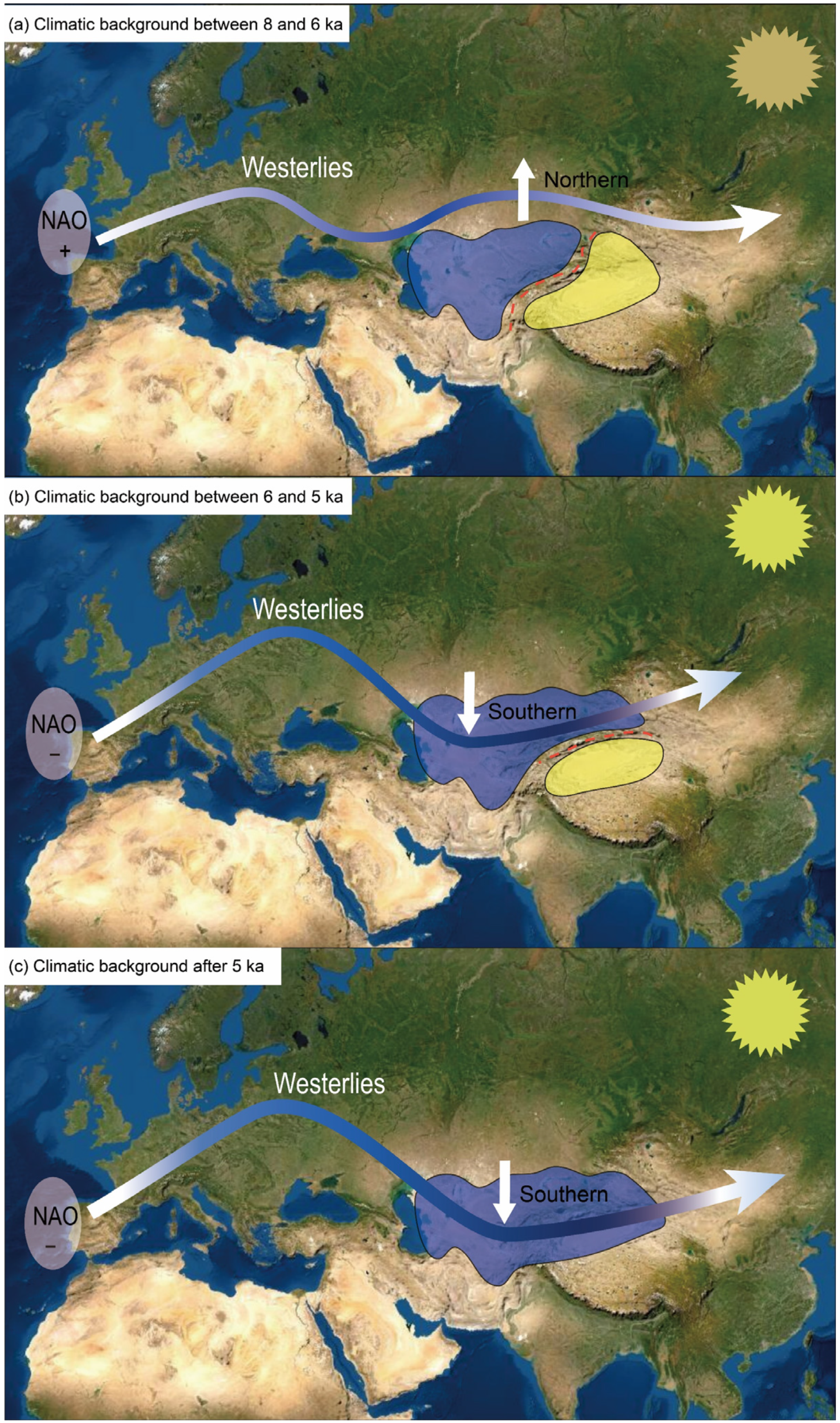
Based on the above factors, we speculate that, at around 8 ka, the increase in the water vapor carried by the westerly circulation resulted in an increase in the moisture/precipitation in the west part of ACA and the climate became wet (indicated by the sites 1~4 in Figure 1). Therefore, the onset of the HCO in the west part of ACA occurred at ~8 ka. During this period, due to the barrier created by the tall Tianshan Mountains in Xinjiang, the water vapor carried by the westerly circulation could not reach the region (Figure 5a); thus, the climate remained dry. This pattern lasted until about 6~5 ka, when the NAO began to change into a negative phase (Figure 4f) and the westerly circulation intensified and became positioned to the south. Under such a situation, the water vapor carried by the westerly circulation overcame the block created by the northern Tianshan Mountains and was transported to the northern part of Xinjiang (Figure 5b). The moisture/precipitation began to increase (indicated by sites 5~8 in Figure 1), and the onset of the HCO in northern Xinjiang occurred at ~6 ka. The result of TraCE21 climate model simulation showed that the intensity of the westerly circulation increased sharply after 6 ka and that the boundary gradually expanded southward [105]. After that, until about 5 ka, with the continuous southward movement of the westerly circulation and the stronger intensity of the westerly circulation compared with 6 ka (Figure 4d), the water vapor crossed the southern Tianshan Mountains and reached southern Xinjiang (Figure 5c), resulting in climate humidification (indicated by sites 9 and 10 in Figure 1). The onset of the HCO in southern Xinjiang thus occurred at 5 ka. In addition, the CGT also transitioned from a positive phase to a negative phase between 6 and 5 ka (Figure 4b). This resulted in water vapor reaching Xinjiang along the northeastern Tibetan Plateau, thus contributing to increased precipitation in the region. This also prompted the onset of the HCO in Xinjiang at 6–5 ka.
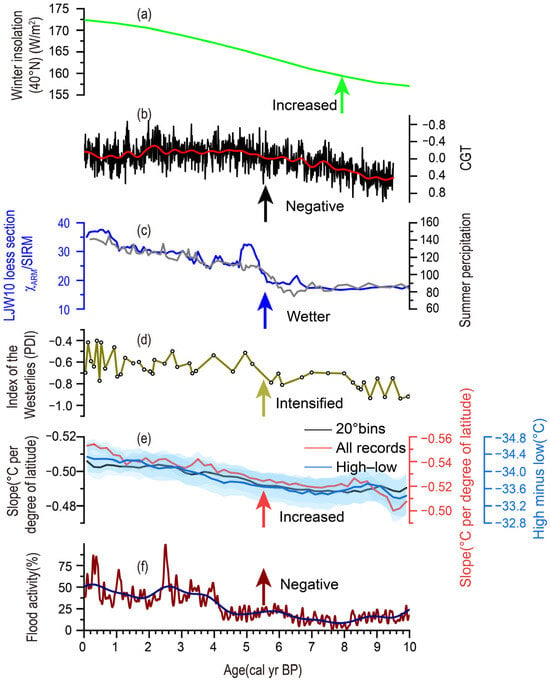
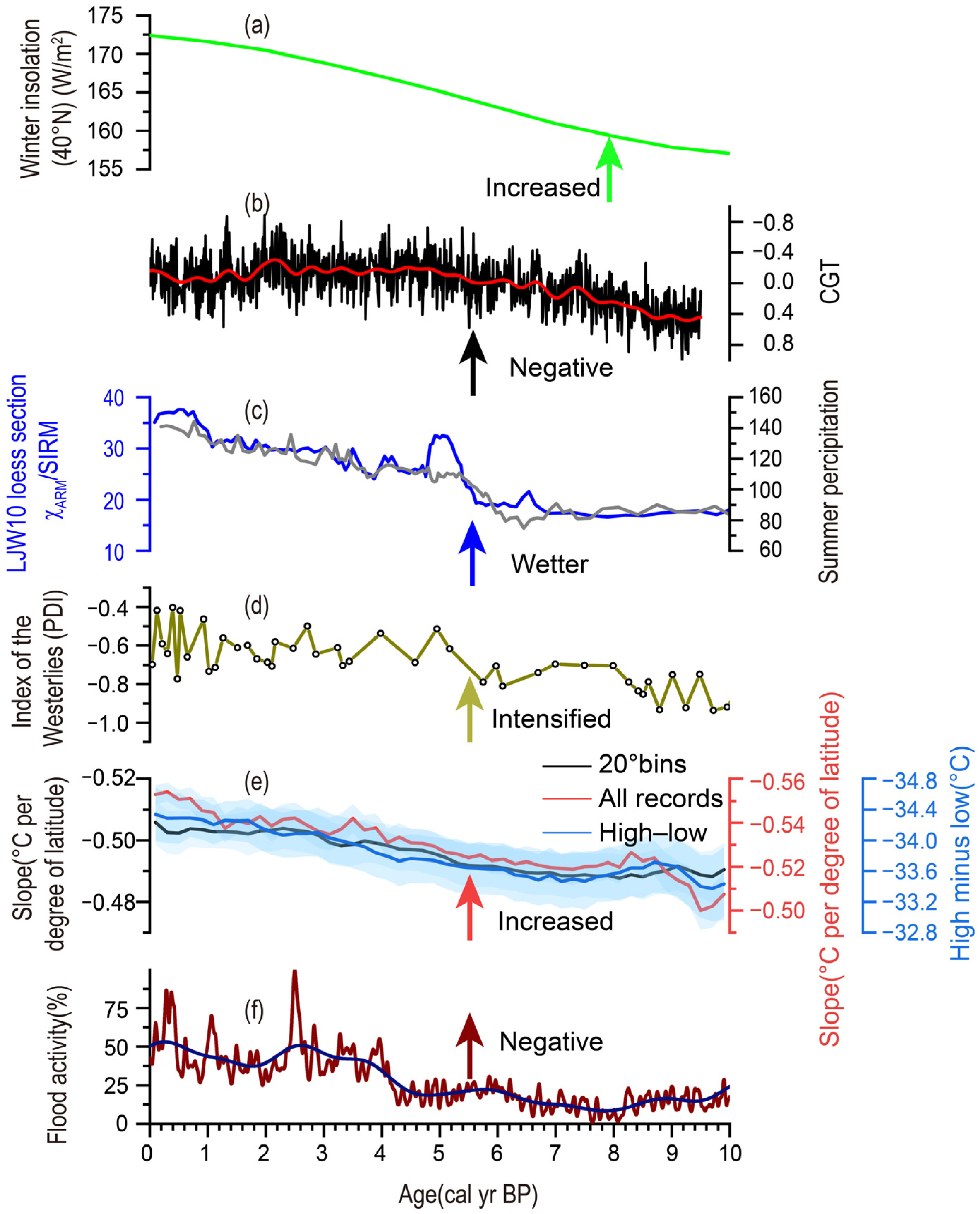

Figure 4.
The possible mechanism implicated in the spatial difference in the onset of the HCO. (a) Northern Hemisphere winter insolation [106]; (b) the z-score of the simulated circumglobal teleconnection (CGT) index [97]; (c) the Holocene moisture evolution in the westerlies-dominated area. The blue curve represents the moisture change reflected by the environmental magnetic χARM/SIRM from the LJW10 loess section [42], and the grey curve represents the moisture change reflected by the summer precipitation reconstructed by the LJW10 loess section [62]; (d) pollen discrimination index (PDI) reflecting the intensity of the westerlies (dots and spline curve) from Lake Namco on the central Tibetan Plateau [107]; (e) latitudinal temperature gradient (LTG) in the Northern Hemisphere, calculated using three different methods, including regression across temperatures averaged into 20° zonal bands (black), regression on all records (red), and high latitudes minus low latitudes (purple) [108]; and (f) reconstruction of the NAO index based on flood activity [109].
Figure 4.
The possible mechanism implicated in the spatial difference in the onset of the HCO. (a) Northern Hemisphere winter insolation [106]; (b) the z-score of the simulated circumglobal teleconnection (CGT) index [97]; (c) the Holocene moisture evolution in the westerlies-dominated area. The blue curve represents the moisture change reflected by the environmental magnetic χARM/SIRM from the LJW10 loess section [42], and the grey curve represents the moisture change reflected by the summer precipitation reconstructed by the LJW10 loess section [62]; (d) pollen discrimination index (PDI) reflecting the intensity of the westerlies (dots and spline curve) from Lake Namco on the central Tibetan Plateau [107]; (e) latitudinal temperature gradient (LTG) in the Northern Hemisphere, calculated using three different methods, including regression across temperatures averaged into 20° zonal bands (black), regression on all records (red), and high latitudes minus low latitudes (purple) [108]; and (f) reconstruction of the NAO index based on flood activity [109].

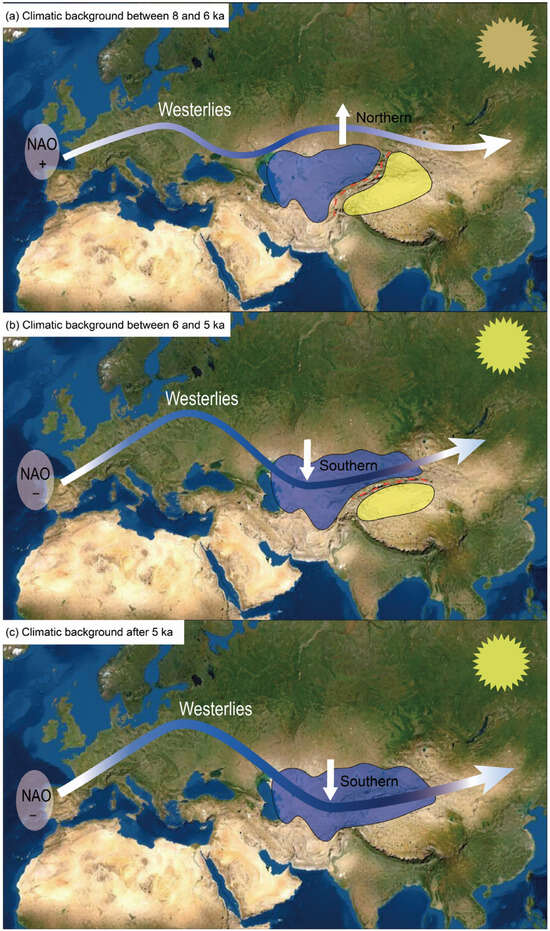
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of the main changes in the westerly circulation caused by the NAO phase changes at different times. (a) When NAO is in the positive phase between 8 and 6 ka, the westerly belt moves northward. (b) As the NAO changes to a negative phase between 6 and 5 ka, the westerlies are strengthened and move southward. (c) The westerly belt continues to move southward after 5 ka. The red dotted line indicates the possible influence of topography on the water vapor carried by the westerly circulation. The light-blue areas represent the humid environment, while the light-yellow areas indicate the dry environment.
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
In this study, we compared the onset of the HCO in different parts of the vast ACA region by evaluating a variety of paleo-moisture/precipitation records. The results generally demonstrate that the onset of the HCO in ACA occurred in a time-transgressive manner, namely, ‘early in the west (~8 ka) but late in the east (6–5 ka)’. The onset of the HCO in Xinjiang was generally delayed by 2–3 thousand years compared with the western part of ACA. Intriguingly, we found that the onset of the HCO in ACA corresponded to the promotion of cultural exchange along the ancient Silk Road. Specifically, the onset of the HCO in the western part of ACA resulted in the formation of a humid environment in the region; this provided a prerequisite for wheat planting and the development of agricultural civilization. Similarly, with the onset of the HCO in northern Xinjiang at 6 ka, the humid climate led to an increase in the area and scope of grasslands, which subsequently prompted the migration of the Afanasievo culture to the south. The onset of the HCO in southern Xinjiang could have also led to the development of piedmont oases, which would have provided an environmental basis for the spread and planting of wheat and millet in this area after 4.5 ka. We speculate that the time-transgressive onset of the HCO in ACA may be attributed to the combined effects of solar radiation, air–sea internal systems, and the local topography. Here, the circulation of the westerlies and related water vapor transport would have played a primary role in the regulation of the spatial differences in the hydroclimate of ACA; meanwhile, the role of the regional topography cannot be ignored due to its connection with climate. Finally, our findings provide new evidence that enhances our understanding of the spatio-temporal characteristics and forcing mechanisms of the hydroclimate of ACA, which is characterized by complex eco-environmental systems and a diverse history of human activity.
Based on the available data, this paper analyzes the spatial differences in the onset of the wetting trend that was observed during the Holocene in the ACA region. However, there is still some uncertainty about the current results, especially due to the lack of high-quality records that have been derived from the central part of the ACA region (steppe route). We believe that the current research direction and objectives are clear; this is crucial for the establishment of the possible link between the phases of climate evolution and the phases of transcontinental cultural exchange. More research that focuses on cultural exchange and its correlation with climate evolution over time is needed. We suggest that further research should focus not only on the establishment of more high-quality climate records but also on cultural exchange and its correlation with climate evolution throughout the Holocene. Furthermore, we also noted the potential influence of seasonality on hydroclimate changes in the ACA region; however, the paleoclimate records currently used can hardly resolve seasonal changes. This remains a challenge in paleoclimate research, which should be addressed in future research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.L. and H.X.; Methodology, Z.W., X.L., H.X., S.C., J.C. and H.W.; Validation, X.L.; Investigation, S.C., H.W. and M.M.; Resources, X.L. and J.C.; Data curation, S.C.; Writing—original draft, Z.W.; Writing—review & editing, X.L.; Supervision, X.L., J.C. and F.C.; Funding acquisition, X.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41901099), the Open Foundation of MOE Key Laboratory of Western China’s Environmental System, Lanzhou University, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (lzujbky-2022-kb04), the Open Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Loess and Quaternary Geology, Institute of Earth Environment, CAS (SKLLOG2316), the Fund of China Scholarship Council, and a Project funded by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021T140686).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Christian, D. Silk roads or steppe roads? The silk roads in world history. J. World Hist. 2000, 11, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmina, E.E. The Prehistory of the Silk Road; University of Pennsylvania Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, G.; Wang, L.; Zhang, D.D.; Liu, F.; Cui, Y.; Li, G.; Shi, Z.; Chen, F. Climate-driven desertification and its implications for the ancient Silk Road trade. Clim. Past 2021, 17, 1395–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmshurst, J.M.; McGlone, M.S.; Leathwick, J.R.; Newnham, R.M. A pre-deforestation pollen-climate calibration model for New Zealand and quantitative temperature reconstructions for the past 18 000 years BP. J. Quat. Sci. Publ. Quat. Res. Assoc. 2007, 22, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, M.; Bleskie, C.; Walker, I.R.; Gavin, D.G.; Hu, F.S. Midge-inferred Holocene summer temperatures in southeastern British Columbia, Canada. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2008, 257, 244–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Rosas, C.; Guiot, J.; Penalba, M.; Ortiz-Acosta, M. Biomization and quantitative climate reconstruction techniques in northwestern Mexico—With an application to four Holocene pollen sequences. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 61, 242–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomis, S.E.; Russell, J.M.; Ladd, B.; Street-Perrott, F.A.; Damsté, J.S.S. Calibration and application of the branched GDGT temperature proxy on East African lake sediments. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2012, 357, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, M.; Magyari, E.K.; Buczkó, K.; Braun, M.; Panagiotopoulos, K.; Heiri, O. Chironomid-inferred Holocene temperature changes in the South Carpathians (Romania). Holocene 2015, 25, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Deng, C.; Xiao, J.; Li, J.; Paterson, G.A.; Chang, L.; Yi, L.; Qin, H.; Pan, Y.; Zhu, R. Insolation driven biomagnetic response to the Holocene Warm Period in semi-arid East Asia. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhan, T.; Zhou, X.; Wu, H.; Li, Q.; Zhao, C.; Qiao, Y.; Jiang, S.; Tu, L.; Ma, Y. Late onset of the Holocene rainfall maximum in northeastern China inferred from a pollen record from the sediments of Tianchi Crater Lake. Quat. Res. 2019, 92, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fohlmeister, J.; Schröder-Ritzrau, A.; Scholz, D.; Spötl, C.; Riechelmann, D.F.C.; Mudelsee, M.; Wackerbarth, A.; Gerdes, A.; Riechelmann, S.; Immenhauser, A.; et al. Bunker Cave stalagmites: An archive for central European Holocene climate variability. Clim. Past 2012, 8, 1751–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, A.J.; Verschuren, D.; Peterse, F.; Miralles, D.G.; Martin-Jones, C.M.; Maitituerdi, A.; Van der Meeren, T.; Van Daele, M.; Lane, C.S.; Haug, G.H.; et al. Reversed Holocene temperature-moisture relationship in the Horn of Africa. Nature 2023, 620, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, J.P.; Cruz, F.W.; Stríkis, N.M.; Wang, X.; Deininger, M.; Catunda, M.C.A.; Ortega-Obregón, C.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Auler, A.S. High-resolution Holocene South American monsoon history recorded by a speleothem from Botuverá Cave, Brazil. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2016, 450, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Porter, S.C.; Kutzbach, J.E.; Xihao, W.; Suming, W.; Xiaodong, L.; Xiaoqiang, L.; Weijian, Z. Asynchronous Holocene optimum of the East Asian monsoon. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2000, 19, 743–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Herzschuh, U. Asynchronous evolution of the Indian and East Asian Summer Monsoon indicated by Holocene moisture patterns in monsoonal central Asia. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2010, 103, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Xu, Q.; Chen, J.; Birks, H.J.B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Jin, L.; An, C.; Telford, R.J.; Cao, X. East Asian summer monsoon precipitation variability since the last deglaciation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chen, J.; Huang, W.; Chen, S.; Huang, X.; Jin, L.; Jia, J.; Zhang, X.; An, C.; Zhang, J. Westerlies Asia and monsoonal Asia: Spatiotemporal differences in climate change and possible mechanisms on decadal to sub-orbital timescales. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 192, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yang, X.; Ye, M.; Liu, K.-B.; Xia, Z.; Ren, X.; Cai, L.; Wu, N.; Liu, T.-S. Millet noodles in late Neolithic China. Nature 2005, 437, 967–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, M.; Liu, R.; Li, X.; Du, L.; Ruan, Q.; Pollard, A.M.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, X.; Liu, F.; Li, G. Earliest systematic coal exploitation for fuel extended to ~3600 BP. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadh0549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Li, G.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, A.; Dong, G.; Moran, E. Warfare impact overtakes climate-controlled fires in the eastern Silk Roads since 2000 B.P. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Nexus 2023, 2, pgad408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Liu, J.; Jia, H.; Lu, H.; Xia, X.; Zhou, L.; Mu, G.; Xu, Q.; Jiao, Y.J.T.H. New evidence of agricultural activity and environmental change associated with the ancient Loulan kingdom, China, around 1500 years ago. Holocene 2012, 22, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhu, J.; Rosenthal, Y.; Zhang, X.; Otto-Bliesner, B.L.; Timmermann, A.; Smith, R.S.; Lohmann, G.; Zheng, W.; Elison Timm, O. The Holocene temperature conundrum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E3501–E3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, J.; Jungclaus, J.; Krivova, N.; Lorenz, S.; Maycock, A.; Raddatz, T.; Schmidt, H.; Toohey, M.; Wu, C.J.; Claussen, M. Global temperature modes shed light on the Holocene temperature conundrum. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Duan, Y.; Hao, S.; Chen, J.; Feng, X.; Hou, J.; Cao, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, T. Holocene thermal maximum mode versus the continuous warming mode: Problems of data-model comparisons and future research prospects. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2023, 66, 1683–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Yu, Z.; Yang, M.; Ito, E.; Wang, S.; Madsen, D.B.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sato, T.; Birks, H.J.B. Holocene moisture evolution in arid central Asia and its out-of-phase relationship with Asian monsoon history. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2008, 27, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Schneider, B.; Park, W.; Latif, M.; Khon, V.; Zhang, X. The spatial–temporal patterns of Asian summer monsoon precipitation in response to Holocene insolation change: A model-data synthesis. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2014, 85, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Jia, J.; Xia, D.; Lu, C.; Lu, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Li, K. Asynchronous Holocene Climate Optimum across mid-latitude Asia. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2019, 518, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Shen, C.-C.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Wu, C.-C.; Chen, F. Inconsistency between records of δ18O and trace element ratios from stalagmites: Evidence for increasing mid–late Holocene moisture in arid central Asia. Holocene 2020, 30, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Yang, Y.; Han, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, F. Exploring the history of cultural exchange in prehistoric Eurasia from the perspectives of crop diffusion and consumption. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2017, 60, 1110–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Li, R.; Lu, M.; Zhang, D.; James, N. Evolution of human–environmental interactions in China from the Late Paleolithic to the Bronze Age. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2020, 44, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Guan, X.; Zhang, Y. Atmospheric Circulation Characteristics of Precipitation Anomaly in Arid Regions in Central Asia. Arid. Zone Res. 2018, 35, 249–259. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizen, E.M.; Aizen, V.B.; Melack, J.M.; Nakamura, T.; Ohta, T. Precipitation and atmospheric circulation patterns at mid-latitudes of Asia. Int. J. Climatol. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 21, 535–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, X.; Qian, C.; Wang, S.; Li, J. Variations and changes of annual precipitation in Central Asia over the last century. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Spatial distribution, temporal variation, and transport characteristics of atmospheric water vapor over Central Asia and the arid region of China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2019, 172, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Lv, F.; Liu, X.; Huang, W.; Wang, T.; Liu, J.; Hou, J.; Chen, F. Holocene moisture variations in arid central Asia: Reassessment and reconciliation. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2022, 297, 107821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Huang, X.; Demberel, O.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, L.; Gundegmaa, V.; Huang, C.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, J.; Qiang, M. Quantitative reconstruction of precipitation changes in the Mongolian Altai Mountains since 13.7 ka. Catena 2024, 234, 107536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, S.A.G.; López-Merino, L.; Tudryn, A.; Chalié, F.; Gasse, F. Late Pleistocene and Holocene palaeoenvironments in and around the middle Caspian basin as reconstructed from a deep-sea core. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2014, 101, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wei, H.; Khormali, F.; Wang, L.; Yan, H.; Xie, H.; Wang, X.; Huang, W.; Chen, J.; Chen, F. Holocene Moisture Variations in Western Arid Central Asia Inferred From Loess Records From NE Iran. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2020, 21, e2019GC008616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Spotl, C.; Breitenbach, S.F.; Sinha, A.; Wassenburg, J.A.; Jochum, K.P.; Scholz, D.; Li, X.; Yi, L.; Peng, Y.; et al. Climate variations of Central Asia on orbital to millennial timescales. Sci. Rep. 2016, 5, 36975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Orozbaev, R.; Dong, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, J. Moisture evolution in Central Asia since 26 ka: Insights from a Kyrgyz loess section, Western Tian Shan. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2020, 249, 106604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Feng, Z.; Ran, M.; Zhang, C. Holocene climate and vegetation changes inferred from pollen records of Lake Aibi, northern Xinjiang, China: A potential contribution to understanding of Holocene climate pattern in East-central Asia. Quat. Int. 2013, 311, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Jia, J.; Chen, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, X.; Xie, H.; Xia, D.; Huang, W.; An, C. A persistent Holocene wetting trend in arid central Asia, with wettest conditions in the late Holocene, revealed by multi-proxy analyses of loess-paleosol sequences in Xinjiang, China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 146, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Du, J.; Liang, P.; Zhang, D.; Chen, B.; Rioual, P.; Feng, Z.; Hongwei, L.; XUlong, W. Palaeoenvironmental changes in the central part of the Taklamakan Desert, northwestern China since the late Pleistocene. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 3205–3218. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.V.; Paez, M.M.; Prieto, A.R.; Stutz, S.; Tonello, M.; Vilanova, I. Mid-Holocene climatic variability reconstruction from pollen records (32–52 S, Argentina). Quat. Int. 2005, 132, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, S. Theory of quantitative reconstruction of vegetation I: Pollen from large sites REVEALS regional vegetation composition. Holocene 2007, 17, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Yuan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, D.; Li, Z. Jurassic spora-pollen assemblages and paleoclamate in Inner Mongolia, GanSu, QingHai, China. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2006, 17, 634–639. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cerling, T.E.; Quade, J.; Wang, Y.; Bowman, J. Carbon isotopes in soils and palaeosols as ecology and palaeoecology indicators. Nature 1989, 341, 138–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melillo, J.M.; Aber, J.D.; Linkins, A.E.; Ricca, A.; Fry, B.; Nadelhoffer, K. Carbon and nitrogen dynamics along the decay continuum: Plant litter to soil organic matter. Plant Soil 1989, 115, 189–198. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, Z.; Guo, W.; Cao, J.; Shi, F.; Jiang, H.; Li, C. Relationship between the stable carbon isotopic composition of modern plants and surface soils and climate: A global review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 165, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Wei, H.; Khormali, F.; Xie, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F. Climatic significance of the stable carbon isotopic composition of surface soils in northern Iran and its application to an Early Pleistocene loess section. Org. Geochem. 2019, 127, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Fang, X.; Li, J.; An, Z.; Chen, S.; Hitoshi, F. Transformation functions of soil color and climate. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2001, 44, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, R.; Schulze, D.; Coffin, D.; Van Scoyoc, G. Color, organic matter, and pesticide adsorption relationships in a soil landscape. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1988, 52, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Oldfield, F.; Wintle, A.; Robinson, S.; Wang, J. Partly pedogenic origin of magnetic variations in Chinese loess. Nature 1990, 346, 737–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Jackson, M.J.; Banerjee, S.K.; Maher, B.A.; Deng, C.; Pan, Y.; Zhu, R. Mechanism of the magnetic susceptibility enhancements of the Chinese loess. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.-Z. A review on the definitions of terms of sedimentary facies. J. Palaeogeogr. 2019, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-J.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; An, Z.; Wu, J.; Shen, C.-C.; Dorale, J.A. A high-resolution absolute-dated late Pleistocene monsoon record from Hulu Cave, China. Science 2001, 294, 2345–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.I.; Banner, J.L.; Musgrove, M. Seasonal dripwater Mg/Ca and Sr/Ca variations driven by cave ventilation: Implications for and modeling of speleothem paleoclimate records. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 3514–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, T.-Y. Seasonal and interannual variations of hydrochemical characteristics and stable isotopic compositions of drip waters in Furong Cave, Southwest China based on 12 years’ monitoring. J. Hydrol. 2019, 572, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairchild, I.J.; Borsato, A.; Tooth, A.F.; Frisia, S.; Hawkesworth, C.J.; Huang, Y.; McDermott, F.; Spiro, B. Controls on trace element (Sr–Mg) compositions of carbonate cave waters: Implications for speleothem climatic records. Chem. Geol. 2000, 166, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Griffiths, M.L.; Chiang, J.C.; Kong, W.; Wu, S.; Atwood, A.; Huang, J.; Cheng, H.; Ning, Y.; Xie, S. East Asian hydroclimate modulated by the position of the westerlies during Termination I. Science 2018, 362, 580–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wick, L.; Lemcke, G.; Sturm, M. Evidence of Lateglacial and Holocene climatic change and human impact in eastern Anatolia: High-resolution pollen, charcoal, isotopic and geochemical records from the laminated sediments of Lake Van, Turkey. Holocene 2003, 13, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Zhang, H.; Ma, J.; Li, G.; Wang, Q.; Rao, Z.; Huang, W.; Huang, X.; Chen, F. Trend of increasing Holocene summer precipitation in arid central Asia: Evidence from an organic carbon isotopic record from the LJW10 loess section in Xinjiang, NW China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2018, 509, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Duan, F.; Wang, X.; Chen, F. The Holocene environmental change in Xinjiang and its impact on prehistoric cultural exchange. Sci. Sin. 2020, 50, 677–687. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, G.; Du, L.; Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Chen, F. continental scales in mid-latitude Eurasia during 6000–3000 years ago. Innovation 2023, 1, 100038. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z. Eastward spread of wheat into China–New data and new issues. Chin. Archaeol. 2009, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Frachetti, M.D. Multiregional Emergence of Mobile Pastoralism and Nonuniform Institutional Complexity across Eurasia. Curr. Anthropol. 2012, 53, 2–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.K.; Liu, X. Origins of agriculture in East Asia. Science 2009, 324, 730–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wan, Z.; Perry, L.; Lu, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Li, J.; Xie, F.; Yu, J.; Cui, T. Early millet use in northern China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3726–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, X.; John, D.; Zhao, K. Rapid agricultural transformation in the prehistoric Hexi corridor, China. Quat. Int. 2016, 426, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z.; Fuller, D.Q.; Chu, X.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, L.; Lu, H. Assessing the occurrence and status of wheat in late Neolithic central China: The importance of direct AMS radiocarbon dates from Xiazhai. Veg. Hist. Archaeobot. 2020, 29, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Agriculture and palaeoeconomy in prehistoric Xinjiang, China (3000–200 bc). Veg. Hist. Archaeobot. 2020, 30, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Du, L.; Yang, L.; Lu, M.; Qiu, M.; Li, H.; Ma, M.; Chen, F. Dispersal of crop-livestock and geographical-temporal variation of subsistence along the Steppe and Silk Roads across Eurasia in prehistory. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2022, 65, 1187–1210. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yu, J.; Spengler, R.N.; Shen, H.; Zhao, K.; Ge, J.; Bao, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, Q.; Chen, G. 5,200-year-old cereal grains from the eastern Altai Mountains redate the trans-Eurasian crop exchange. Nat. Plants 2020, 6, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J. The three stages of early sino-western cultural interactions. Acta Archaeol. Sin. 2021, 3, 317–338. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tan, L.; Dong, G.; An, Z.; Lawrence Edwards, R.; Li, H.; Li, D.; Spengler, R.; Cai, Y.; Cheng, H.; Lan, J.; et al. Megadrought and cultural exchange along the proto-silk road. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Huang, X.; Sun, M.; Panizzo, V.N.; Huang, C.; Zheng, M.; Chen, X.; Chen, F. Prehistoric population expansion in Central Asia promoted by the Altai Holocene Climatic Optimum. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, D.R.; Masson, V.; Berezkin, Y.E.; Charles, M.; Gosden, C.; Hillman, G.; Kasparov, A.; Korobkova, G.; Kurbansakhatov, K.; Legge, A. Investigating early agriculture in Central Asia: New research at Jeitun, Turkmenistan. Antiquity 1993, 67, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spengler, R.N.; Willcox, G. Archaeobotanical results from Sarazm, Tajikistan, an Early Bronze Age Settlement on the edge: Agriculture and exchange. Environ. Archaeol. 2013, 18, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarianidi, V. Excavations at southern Gonur. Iran 1993, 31, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coolidge, J.W. Southern Turkmenistan in the Neolithic: A Petrographic Case Study; University of Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z. Archaeobotanical Data for Research on the Introduction of Wheat into China. Chin. Ann. Hist. Sci. Technol. 2017, 1, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Wang, W.; Duan, F.; Huang, W.; Chen, F. Environmental changes and cultural exchange between East and West along the Silk Road in arid Central Asia. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 875–891. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- An, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Duan, F.; Dong, W. The pattern of Xinjiang physical geography and its relationship with the temporal-spatial distribution of agriculture and husbandry. Sci. Sin. 2020, 50, 295–304. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Ning, C.; Scott, A.; Fu, Q.; Bjorn, R.; Li, W.; Wei, D.; Wang, W.; Fan, L.; Abuduresule, I.; et al. The genomic origins of the Bronze Age Tarim Basin mummies. Nature 2021, 599, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ning, C.; Hagelberg, E.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, W.; Abuduresule, I.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, H. Analysis of ancient human mitochondrial DNA from the Xiaohe cemetery: Insights into prehistoric population movements in the Tarim Basin, China. BMC Genet. 2015, 16, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xiang, L.; Lei, G.; Sun, M.; Qiu, M.; Storozum, M.; Huang, C.; Munkhbayar, C.; Demberel, O.; Zhang, J. Sedimentary Pediastrum record of middle–late Holocene temperature change and its impacts on early human culture in the desert-oasis area of northwestern China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2021, 265, 107054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isakov, A.; Kohl, P.L.; Lamberg-Karlovsky, C.; Maddin, R. Metallurgical analysis from Sarazm, Tadjikistan SSR. Archaeometry 1987, 29, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frachetti, M.D.; Spengler, R.N.; Fritz, G.J.; Mar’yashev, A.N. Earliest direct evidence for broomcorn millet and wheat in the central Eurasian steppe region. Antiquity 2010, 84, 993–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doumani, P.N.; Frachetti, M.D.; Beardmore, R.; Schmaus, T.M.; Spengler III, R.N.; Mar’yashev, A.N. Burial ritual, agriculture, and craft production among Bronze Age pastoralists at Tasbas (Kazakhstan). Archaeol. Res. Asia 2015, 1, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, J.R.; Li, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, K.; Sun, N.; Atahan, P. Origin and spread of wheat in China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2013, 72, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flad, R.; Shuicheng, L.; Xiaohong, W.; Zhijun, Z. Early wheat in China: Results from new studies at Donghuishan in the Hexi Corridor. Holocene 2010, 20, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, S.; Ferguson, D.K.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Jiang, H. Ancient plant use and palaeoenvironmental analysis at the Gumugou Cemetery, Xinjiang, China: Implication from desiccated plant remains. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2017, 9, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Ji, D.; Chen, F.; Dong, G.; Wang, H.; Dong, W.; Zhao, X. Evolution of prehistoric agriculture in central Gansu Province, China: A case study in Qin’an and Li County. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 1925–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, A.E.; Clark, P.U. Ice sheet sources of sea level rise and freshwater discharge during the last deglaciation. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Wang, B. Circumglobal teleconnection in the Northern Hemisphere summer. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 3483–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Feng, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, F. Physical mechanisms of summer precipitation variations in the Tarim Basin in northwestern China. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 3579–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jin, L. Association of the Northern Hemisphere circumglobal teleconnection with the Asian summer monsoon during the Holocene in a transient simulation. Holocene 2016, 26, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raziei, T.; Mofidi, A.; Santos, J.A.; Bordi, I. Spatial patterns and regimes of daily precipitation in Iran in relation to large-scale atmospheric circulation. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 1226–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çağlar, F.; Yetemen, O.; Chun, K.P.; Sen, O.L. The merit of the North Sea-Caspian pattern in explaining climate variability in the Euro-Mediterranean region. Int. J. Climatol. 2023, 43, 4648–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Mu, M. The influence of the Indian Ocean dipole on atmospheric circulation and climate. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 18, 831–843. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Z.; Yamagata, T. The unusual summer of 1994 in East Asia: IOD teleconnections. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZHANG, Z.; HE, X.; LIU, L.; LI, Z.; WANG, P. Spatial distribution of rainfall simulation and the cause analysis in China’s Tianshan Mountains area. Adv. Water Sci. 2015, 26, 500–508. [Google Scholar]
- Rugenstein, J.K.C.; Chamberlain, C.P. The evolution of hydroclimate in Asia over the Cenozoic: A stable-isotope perspective. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 185, 1129–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, K.; Voigt, S.; Verestek, V.; Appel, E.; Albert, R.; Gerdes, A.; Arndt, I.; Raddatz, J.; Voigt, T.; Weber, Y. Long-period astronomical forcing of westerlies’ strength in Central Asia during Miocene climate cooling. Paleoceanogr. Paleoclimatology 2019, 34, 1784–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H. Climate Change Characteristics in the Asian Westerlies Dominated Area Recorded by Geochemical Proxies during Late Quaternary. Ph.D. Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, A.; Loutre, M.-F. Insolation values for the climate of the last 10 million years. Quat. Sci. Rev. 1991, 10, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Lu, X.; Wang, J.; Peng, P.; Kasper, T.; Daut, G.; Haberzettl, T.; Frenzel, P.; Li, Q.; Yang, R.; et al. Climate change on the Tibetan Plateau in response to shifting atmospheric circulation since the LGM. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routson, C.C.; McKay, N.P.; Kaufman, D.S.; Erb, M.P.; Goosse, H.; Shuman, B.N.; Rodysill, J.R.; Ault, T. Mid-latitude net precipitation decreased with Arctic warming during the Holocene. Nature 2019, 568, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, S.B.; Glur, L.; Gilli, A.; Anselmetti, F.S. Holocene flood frequency across the Central Alps—Solar forcing and evidence for variations in North Atlantic atmospheric circulation. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2013, 80, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).