A Calculation and Optimization Method for the Theoretical Reclamation Timing of Cropland
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Calculation and Optimization Method for TRT
2.1. Calculation Methodology for TRT under Single-Panel Mining Conditions
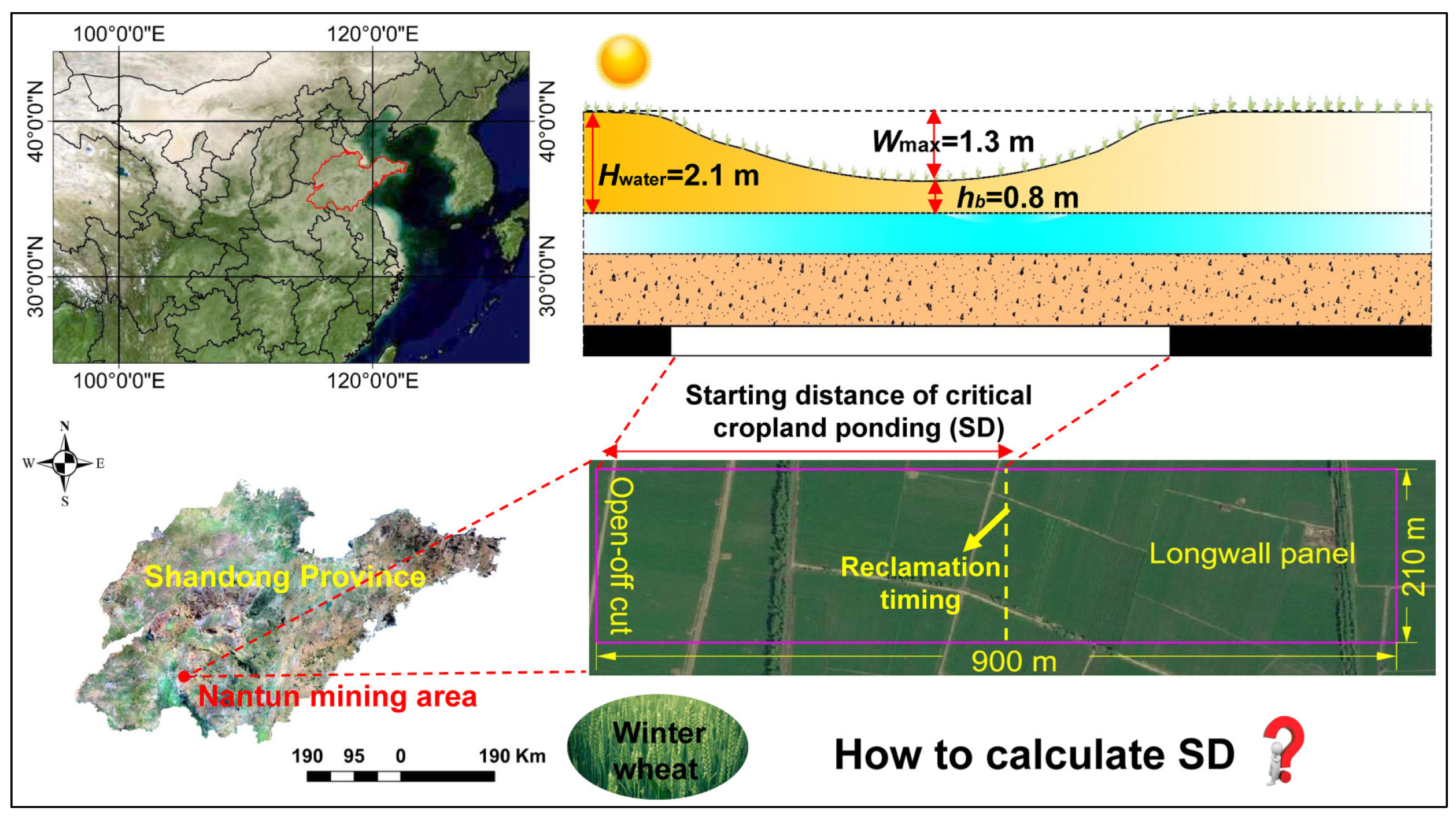
2.1.1. Fundamental Mathematical Model
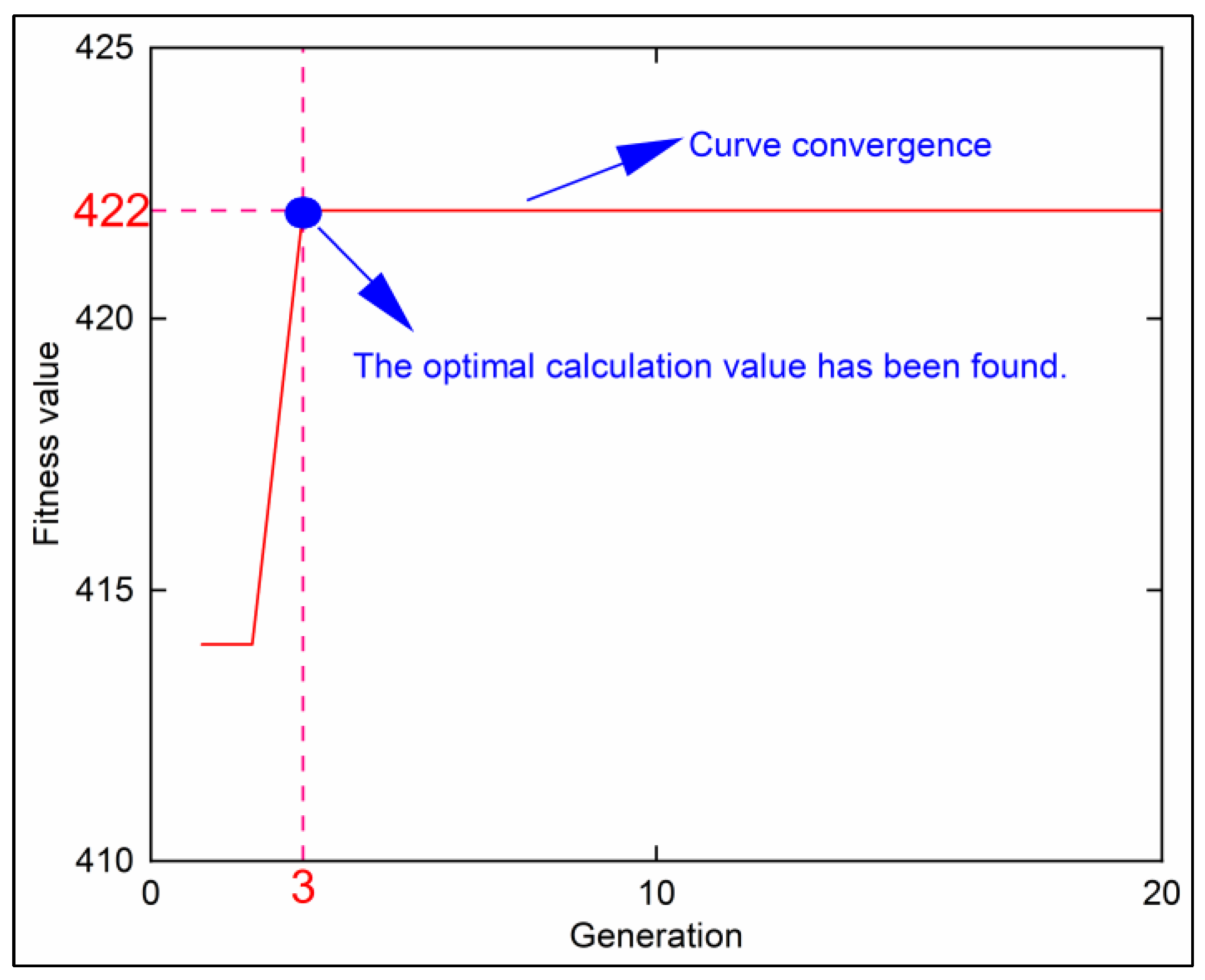
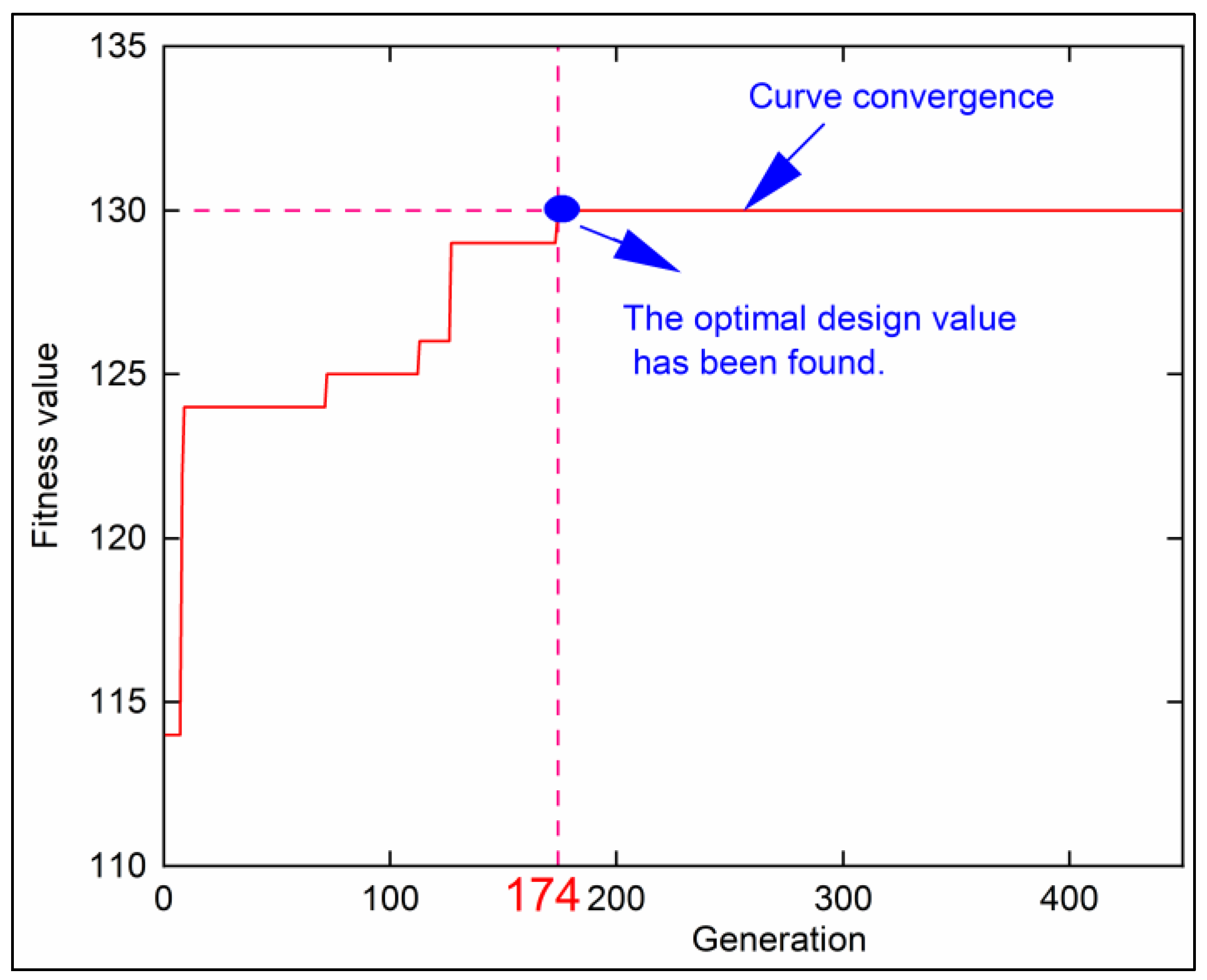
2.1.2. Computational Process of the SD Based on the PSO Algorithm
2.2. Optimization of the TRT of Cropland within a Certain District
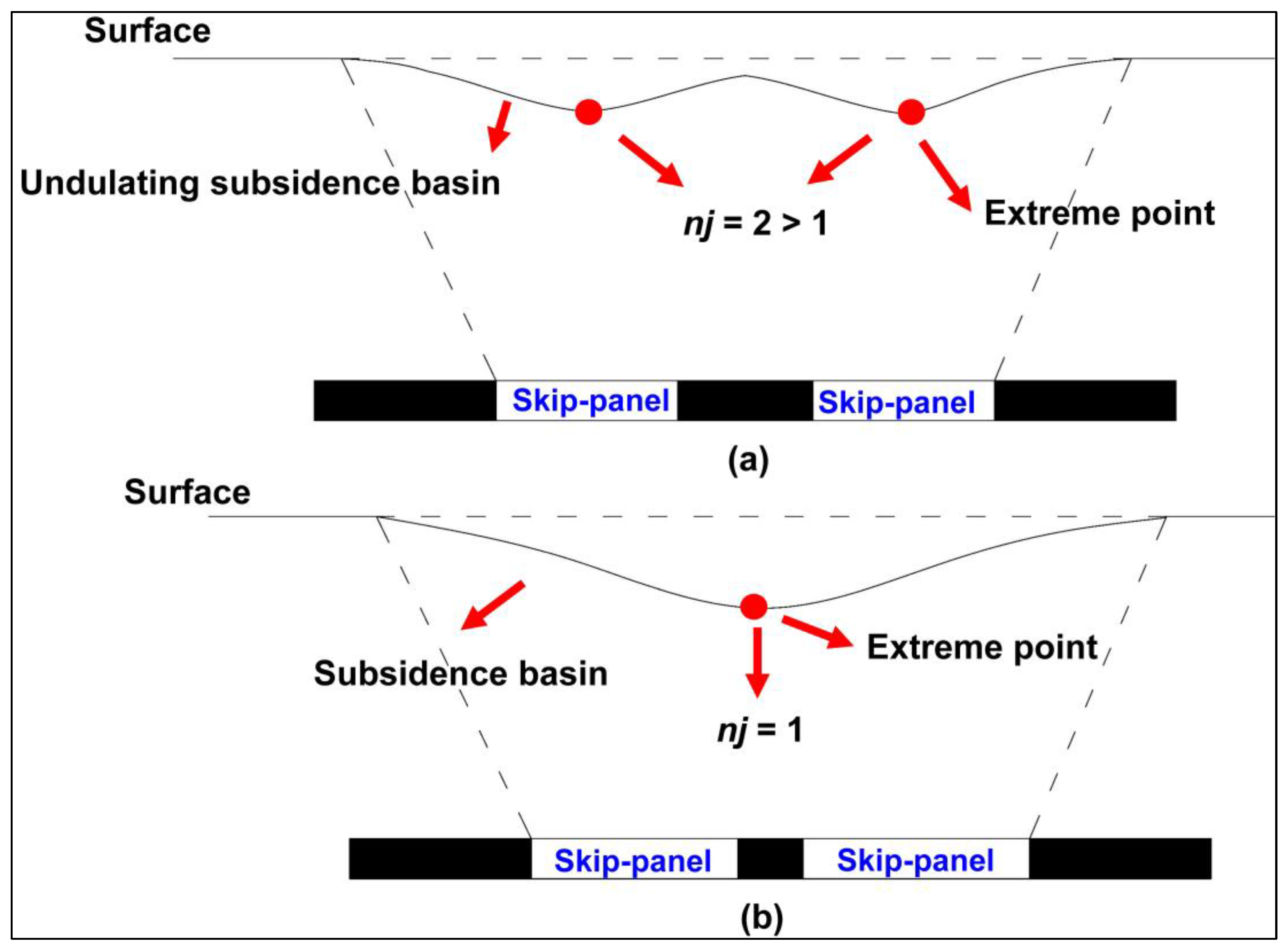
2.2.1. Basic Principles
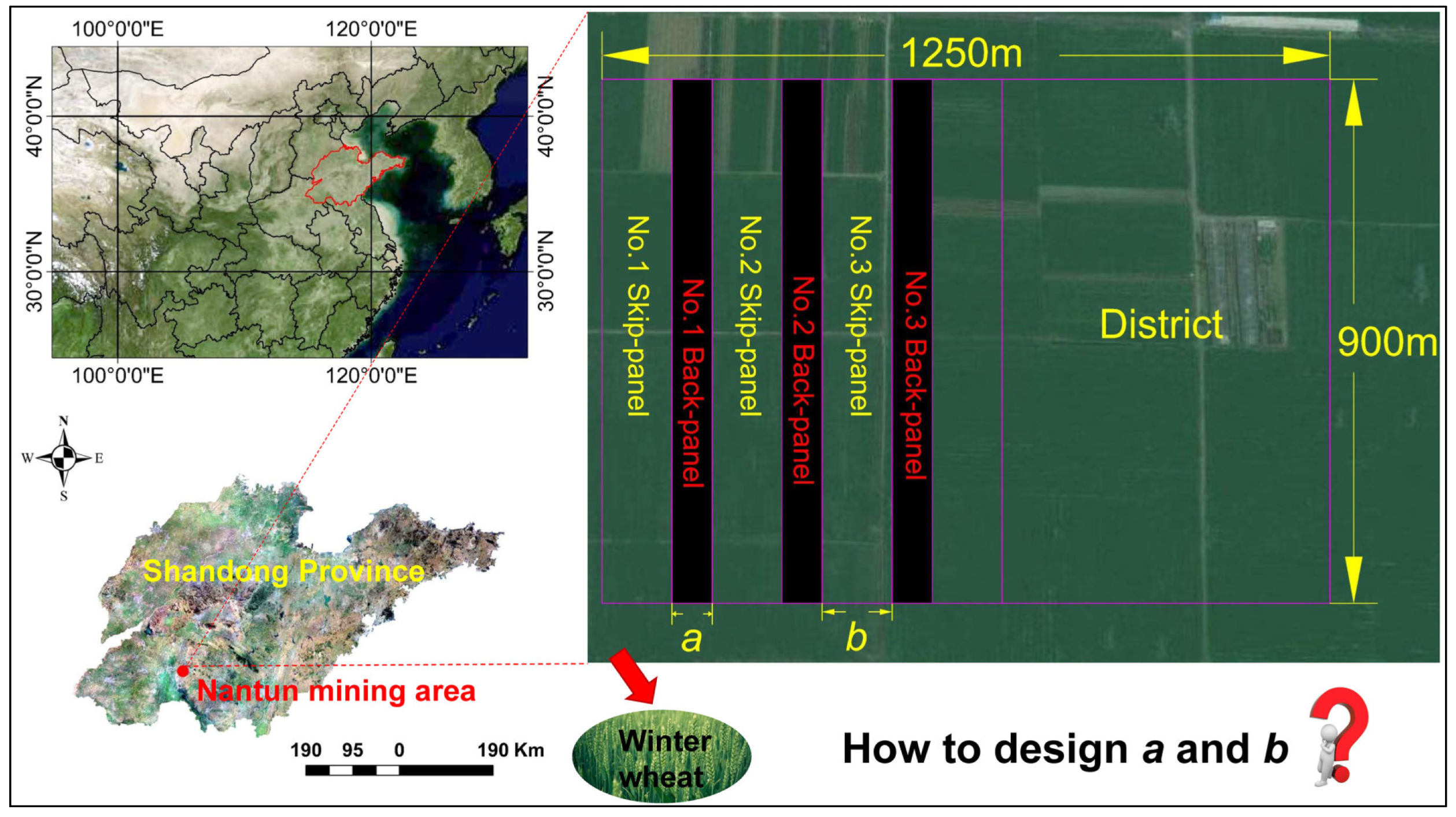
2.2.2. Design Process of Skip-Panel and Back-Panel Widths Based on the CSO Algorithm
3. Method Validation
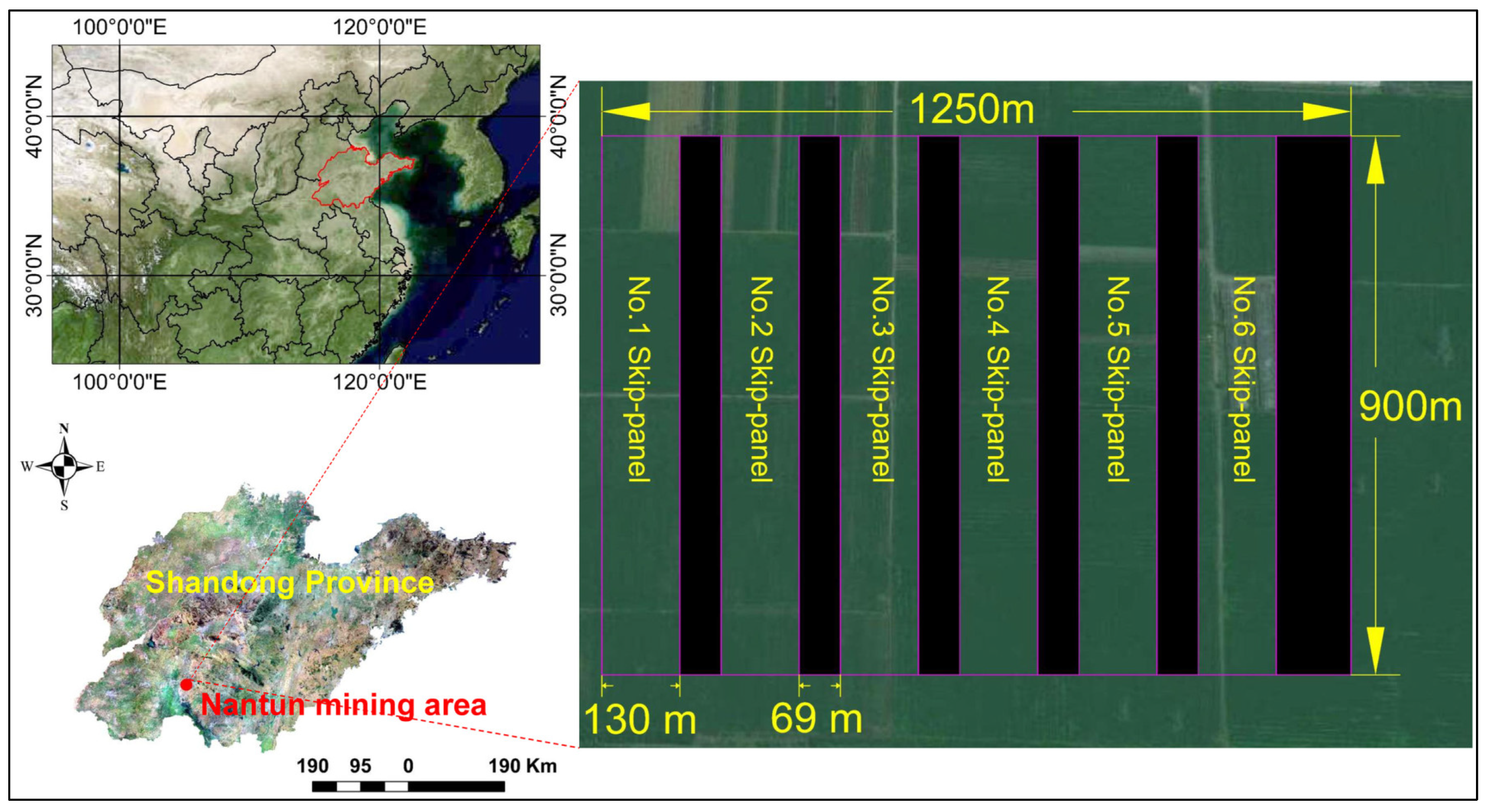
3.1. Calculation Result of TRT for Cropland with Single Panel Simulated Mining in the Nantun Mining Area
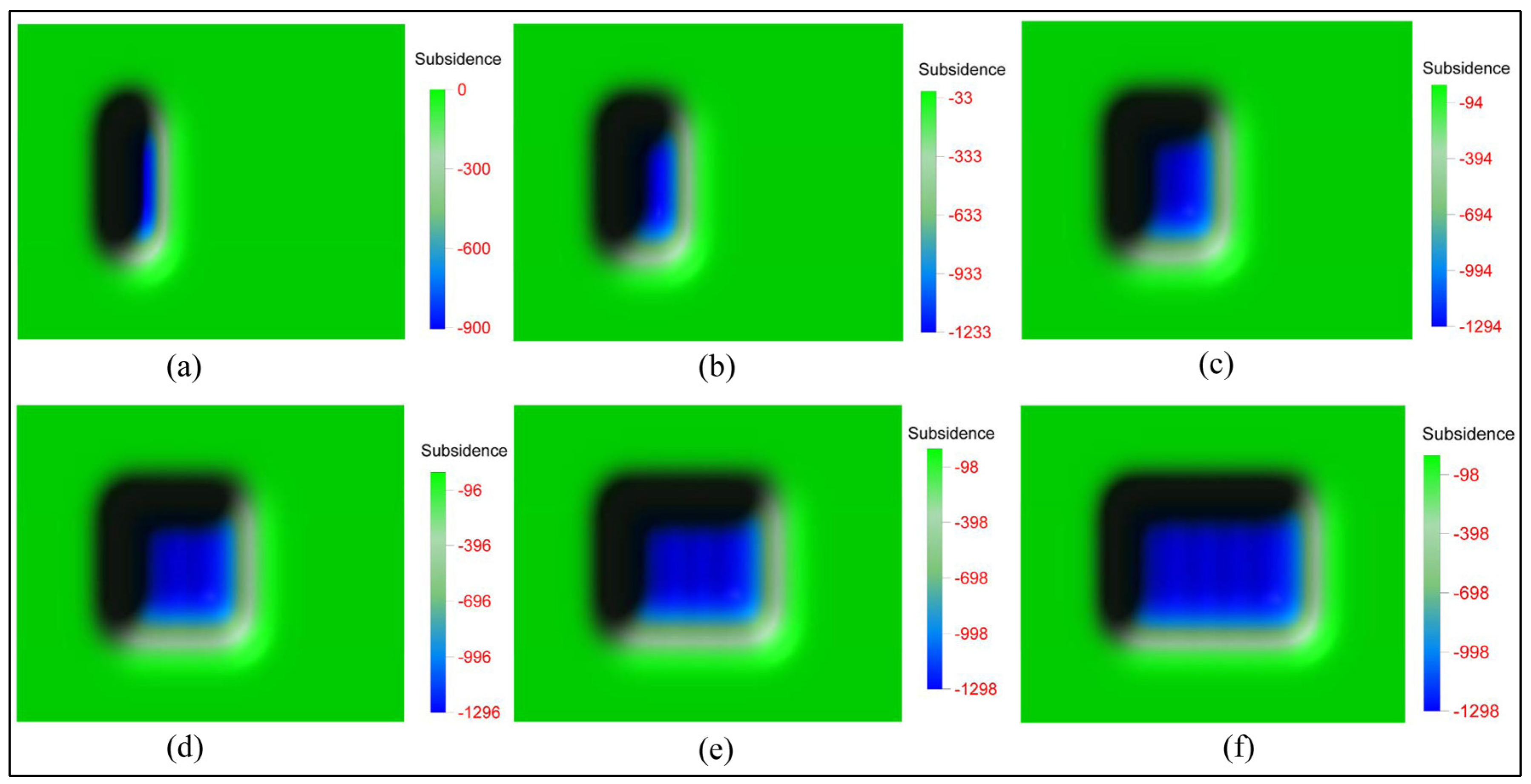
3.2. Optimization of the TRT of Cropland within a District in Nantun Mining Area
4. Discussion
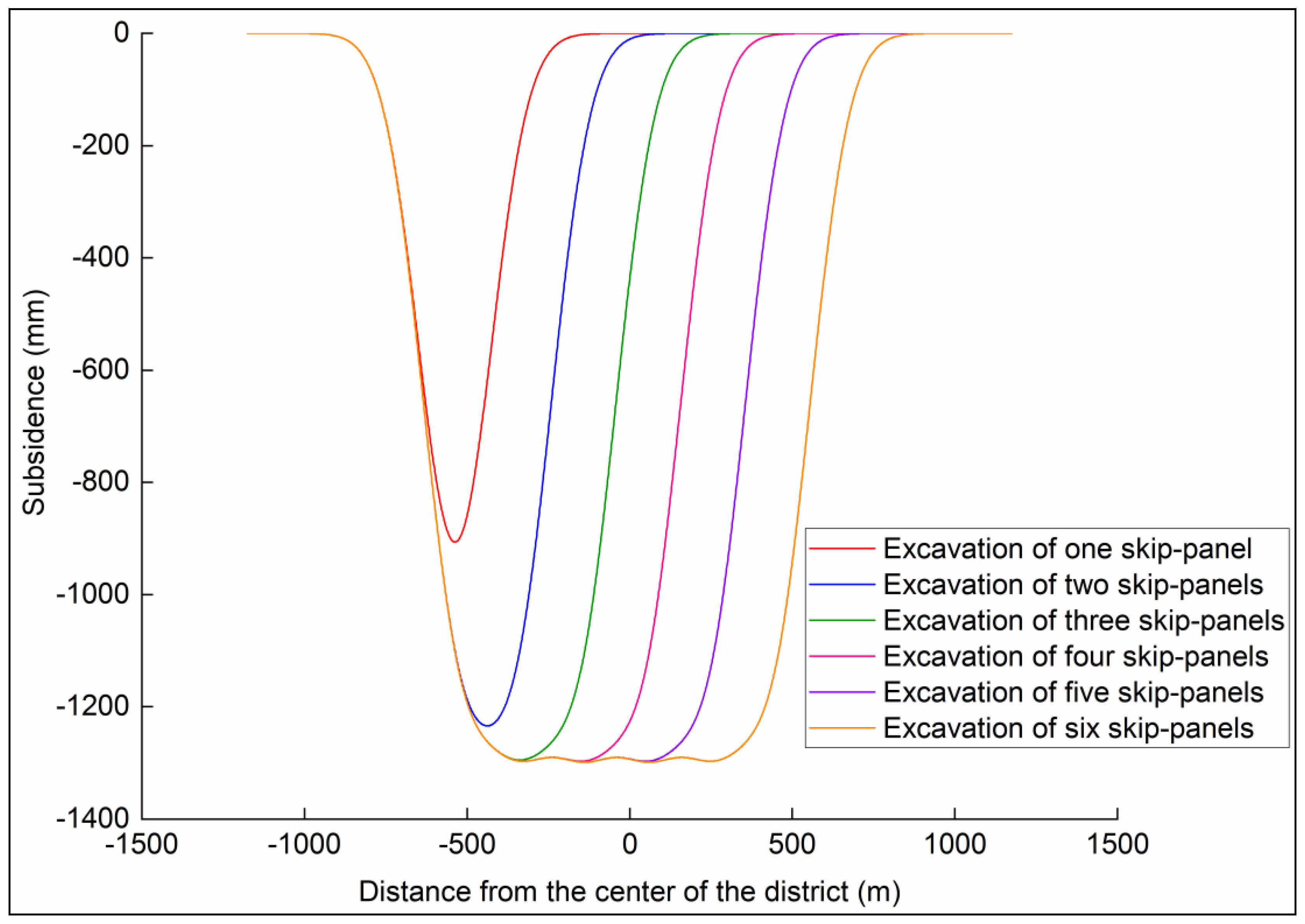
4.1. Influence of Panel Size on the Subsidence of Cropland
4.2. Outlook and Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, G.; Hu, Z.; Li, P.; Yuan, D.; Wang, W.; Yang, K. The optimal framework and model to balance underground coal mining and cropland protection in Jining, eastern China. Resour. Policy 2021, 74, 102307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Hu, Z.; Li, P.; Yuan, D.; Feng, Z.; Wang, W.; Fu, Y. Innovation for sustainable mining: Integrated planning of underground coal mining and mine reclamation. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 351, 131522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics. Statistical Bulletin on National Economic and Social Development of the People’s Republic of China in 2022. China Stat. 2023, 3, 12–29. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Li, G.; Yuan, D. Timing of concurrent mining and reclamation in coal-grain overlapping areas with mining-induced subsidence, Easter China. J. China Coal Soc. 2023, 48, 373–387. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, Z.; Li, P.; Li, G.; Yuan, D.; Guo, J. Assessment and effect of mining subsidence on farmland in coal–crop overlapped areas: A case of shandong Province, China. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, F.; Stacey, T.; Genske, D. Mining subsidence and its effect on the environment: Some differing examples. Environ. Geol. 2000, 40, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmody, R.; Bauer, R.; Barkley, D.; Clarke, S.; Hamilton, D. Agricultural impacts of longwall mine subsidence: The experience in Illinois, USA and Queensland, Australia. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2014, 1, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Hu, Z.; Wang, P.; Yan, Z.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, T. Spatio-temporal evolution and optimization analysis of ecosystem service value—A case study of coal resource-based city group in Shandong, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, K.; Reynolds, J.; Wright, I. Subsidence Fracturing of Stream Channel from Longwall coal mining causing upwelling saline groundwater and metal-Enriched contamination of surface waterway. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignacy, D. Relative elevations of the surface of artificially drained mine subsidence areas as significant aspects in formulating environmental policy. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 1087–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tichavský, R.; Jiránková, E.; Fabiánová, A. Dating of mining-induced subsidence based on a combination of dendrogeomorphic methods and in situ monitoring. Eng. Geol. 2020, 272, 105650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, A.; Agnihotri, A.; Rai, R.; Shrivastva, B.; Mishra, S. Impact assessment of a mine subsidence on native vegetation of South Eastern Coalfields, India. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 5, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrychova’, M.; Svobodova, K.; Kabrna, M. Mine reclamation planning and management: Integrating natural habitats into post-mining land use. Resour. Policy 2020, 69, 101882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.; Parvez, L.; Islam, M.; Dampare, S.; Suzuki, S. Heavy metal pollution of coal mine-affected agricultural soils in the northern part of Bangladesh. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, A.; Baumgartl, T.; Matthew, P.; Glenn, V. The Impact of Underground Longwall Mining on Prime Agricultural Land: A Review and Research Agenda. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 1650–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Zheng, W.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, Z. Examining the relationship between coal mining subsidence and crop failure in plains with a high underground water table. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 2908–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Li, S. The “golden ten years”: Underground coal mining and its impacts on land use and subsequent social problems: A case study on the Jining city region, China. Int. J. Min. Miner. Eng. 2017, 8, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugh, Y. Concurrent mining and reclamation for underground coal mining subsidence impacts in China. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2018, 5, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, X.; Hu, Z. Identification of waterlogging in Eastern China induced by mining subsidence: A case study of Google Earth Engine time-series analysis applied to the Huainan coal field. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 242, 111742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, W.; Deng, X.; Zhang, J. Continues monitoring of subsidence water in mining area from the eastern plain in China from 1986 to 2018 using Landsat imagery and Google Earth Engine. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, Z. Land damage assessment using maize aboveground biomass estimated from unmanned aerial vehicle in high groundwater level regions affected by underground coal mining. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 21666–21679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, W.; Yellishetty, M.; Yang, D. Identifying ecosystem service bundles and the spatiotemporal characteristics of trade-offs and synergies in coal mining areas with a high groundwater table. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Li, G.; Xia, J.; Feng, Z.; Han, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, W.; Li, G. Coupling of underground coal mining and mine reclamation for farmland protection and sustainable mining. Resour. Policy 2023, 84, 103756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Hu, Z.; Yuan, D.; Li, P.; Feng, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, W. A new approach to increased land reclamation rate in a coal mining subsidence area: A case-study of Guqiao Coal Mine, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 33, 866–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojses, M.; Petrovič, F.; Bugár, G. Evaluation of Land-Use Changes as a Result of Underground Coal Mining—A Case Study on the Upper Nitra Basin, West Slovakia. Water 2022, 14, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Xiao, W.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Y. Concurrent mining and reclamation for underground coal mining. J. China Coal Soc. 2013, 38, 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Hu, Z.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H. Improving mine reclamation efficiency for farmland sustainable use: Insights from optimizing mining scheme. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, Y. Re-discussion on coal mine eco-environment concurrent mining and reclamation. J. China Coal Soc. 2020, 45, 351–359. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, R.; Lu, L. Integrated Mining and Reclamation Practices Enhance Sustainable Land Use: A Case Study in Huainan Coalfield, China. Land 2023, 12, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hu, Z. Proper time model for pre-reclamation of unstable subsidence. J. China Coal Soc. 2008, 30, 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Hu, Z.; Yuan, D.; Zhao, H.; Cao, Y. Timing research of concurrent mining and reclamation for single coal face with different mining depths. China Min. Mag. 2019, 28, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hu, Z.; Liu, W.; Yuan, D.; Zhang, R. Simulation of concurrent mining and reclamation for single coal facewith different coal mining thickness. Coal Eng. 2018, 50, 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, W.; Hu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, T. Building and application of topsoil stripping time model in concurrent mining and reclamation technology in underground coal mines. Mine Surv. 2013, 167, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Che, Y.; Malinowska, A. Method and problem for subsidence prediction in entire process induced by underground mining. J. China Coal Soc. 2022, 47, 2170–2181. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Li, Y.; Lin, Y. Intelligent Optimization Algorithms and Emergent Computation, 1st ed.; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 175–354. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle Swarm Optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95—International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Liu, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhang, H. A New Bio-inspired Algorithm: Chicken Swarm Optimization. Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Swarm Intelligence, Hefei, China, 17–20 October 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Guo, G.; Li, H.; Wang, T.; Yuan, Y. Prediction method and research on characteristics of surface subsidence due to mining deeply buried Jurassic coal seams. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Tan, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Dai, H.; Shi, Y.; Xu, L. Deformation Monitoring and Subsidence Engineering, 1st ed.; China University of Mining and Technology Press: Xuzhou, China, 2014; pp. 178–179+290. [Google Scholar]




| Panel Width m | Panel Length m | Mining Height m | Dip Angle of the Coal Seam ° | Mining Depth m | Advance Speed m/day | Hwater m | hb m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 210 | 900 | 5 | 4 | 550 | 4 | 2.1 | 0.8 |
| q0 | tanβ | θ0 ° | S m | c | N | G | c1, c2 | [Llower, Lupper] | rp | Vmax | ω |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.65 | 2.0 | 87.6 | 16 | 0.026886756 | 30 | 20 | 2 | [37, 900] | 1 | 86.3 | 0.7 |
| Mining Height m | Dip Angle of the Coal Seam ° | Mining Depth m | Hwater m | hb m |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 4 | 550 | 2.1 | 0.8 |
| tanβ | θ0 ° | S m | pop | GT | G | NR | NH | NC | NM | [Dlower, Dupper] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.0 | 87.6 | 16 | 120 | 450 | 10 | 24 | 72 | 24 | 7 | [60, 250] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, H.; Guo, G.; Li, H.; Wang, T. A Calculation and Optimization Method for the Theoretical Reclamation Timing of Cropland. Land 2024, 13, 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13050638
Yin H, Guo G, Li H, Wang T. A Calculation and Optimization Method for the Theoretical Reclamation Timing of Cropland. Land. 2024; 13(5):638. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13050638
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Hejian, Guangli Guo, Huaizhan Li, and Tiening Wang. 2024. "A Calculation and Optimization Method for the Theoretical Reclamation Timing of Cropland" Land 13, no. 5: 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13050638
APA StyleYin, H., Guo, G., Li, H., & Wang, T. (2024). A Calculation and Optimization Method for the Theoretical Reclamation Timing of Cropland. Land, 13(5), 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13050638






