An Assessment of Urban Residential Environment Quality Based on Multi-Source Geospatial Data: A Case Study of Beijing, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
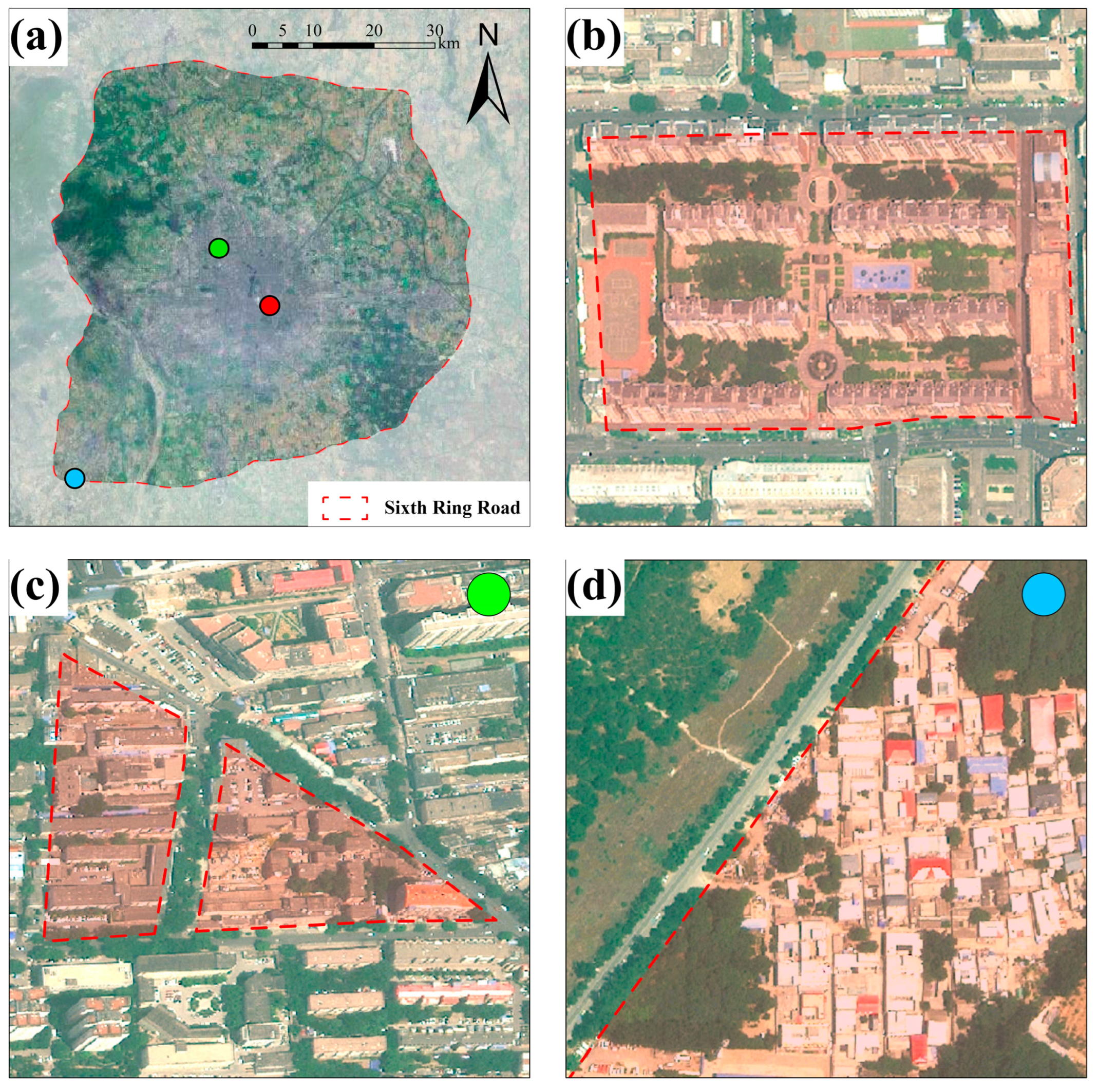
2. Study Area
3. Methods
3.1. Overview of the Assessment Process
3.2. Construction of the REQ Assessment System
3.3. Data Acquisition and Indicator Calculation
- (1)
- For the environmental health and comfort primary indicator, air pollution data are first converted into a grid image with a resolution of 0.01° × 0.01°. Given that some residential blocks are relatively small, making it challenging for the grid images to adequately cover these fine-scale plots, the study employs the Kriging interpolation method for further processing. The interpolated data are then mapped onto every residential block within the study area using zonal statistics. The noise index proximate to residential blocks, predominantly influenced by main roads, is assessed by the shortest distance to these roads. This is measured as the shortest distance between point vector features (the central points of residential blocks) and polyline vector features (the road network). The closer a residential block is to a main road, the higher its noise impact. The street greening rate calculates the NDVI values of the areas of interest using Sentinel-2 images from the Google Earth Engine cloud platform, and then the results were downloaded as TIFF files with a precision of 10 m × 10 m. Higher rates indicate better ecological environments in residential areas. The comfortability of temperatures in July and January is assessed by converting original data into grid data and then calculating the average temperature of those months.
- (2)
- In measuring housing comfort indicators, population density is defined as the ratio of population count grid data to grid area. The housing-price-to-income ratio is derived by dividing the average housing price per unit by the area’s GDP.
- (3)
- For indicators reflecting transportation convenience, road network density is calculated as the ratio of the length of the area’s road network to the area’s size. The nearest distance to subway and bus stations is determined by extracting the central points of residential blocks and POI points. Subsequently, the Amap API is employed to accurately calculate network distances, specifically the shortest distance between two different types of points.
- (4)
- In reflecting city security indicators, the nearest distances to fire stations, police stations, and emergency shelters are accurately obtained via Amap API.
- (5)
- For indicators reflecting life convenience, the distance to commercial centers and the company distribution density are analyzed using kernel density analysis of relevant POI data points. After conducting kernel density analysis on commercial-related POI data, the centers of Beijing’s business districts can be identified from high-density areas, and this serves as a basis for calculating the nearest distance from residential blocks to these business districts. The count of nearby restaurants is determined by tallying establishments within a 1 km buffer zone around the residential block. The nearest distances to various facilities are likewise measured by fetching network distances via the Amap API, with shorter distances indicating better convenience.
3.4. Determination of Indicator Weights
- (1)
- Analytic Hierarchy Process
- (2)
- Entropy Method
- (3)
- Calculation of Composite Weights
3.5. Calculation of the REQ Assessment Indicators
3.6. Pearson Correlation Analysis
4. Results Analysis
4.1. Weight Calculation Results
- (1)
- Environmental health and comfort: The noise index, street greening rate, and comfortability of temperature in July emerge as the most critical factors within this primary indicator. This aligns with Beijing’s ecological conditions characterized by hot and dry summers, heavy traffic volumes, and it reflects the importance of the greening rate.
- (2)
- Housing comfort: Within housing comfort indicators, population density is notably the predominant factor, reflecting Beijing’s dense population and high plot ratios.
- (3)
- Transportation convenience: Road network density and nearest distance to bus stations emerge as the most crucial factors within this primary indicator. Nearest distance to subway stations follows closely, reflecting Beijing’s characteristics with high traffic congestion, long commuting times, and extensive coverage of public transportation.
- (4)
- City security: Nearest distance to fire stations and police stations ranks as the most critical factor within this primary indicator. The impact of nearest distance to emergency shelters follows closely, consistent with Beijing’s low incidence of natural disasters, with emergencies typically handled by fire and police stations, yet it remains significant for city security.
- (5)
- Life convenience: Company distribution density and nearest distance to medical facilities emerge as the most important influencing factors within this primary indicator. This mirrors Beijing’s commuting challenges due to long travel times, the separation of work and residential areas, and the concentrated distribution and uneven allocation of medical resources.
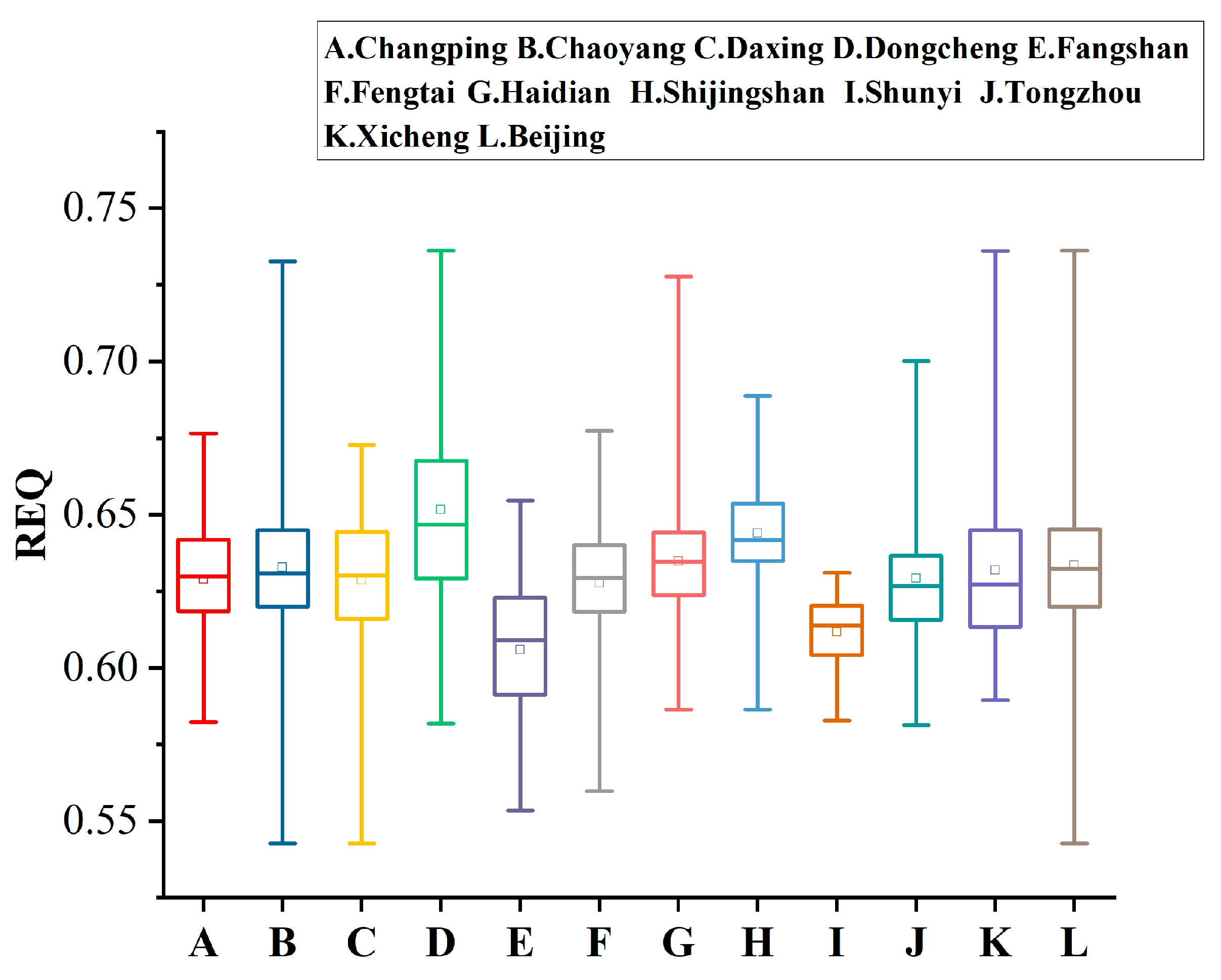
4.2. Overall Evaluation of REQ in Beijing
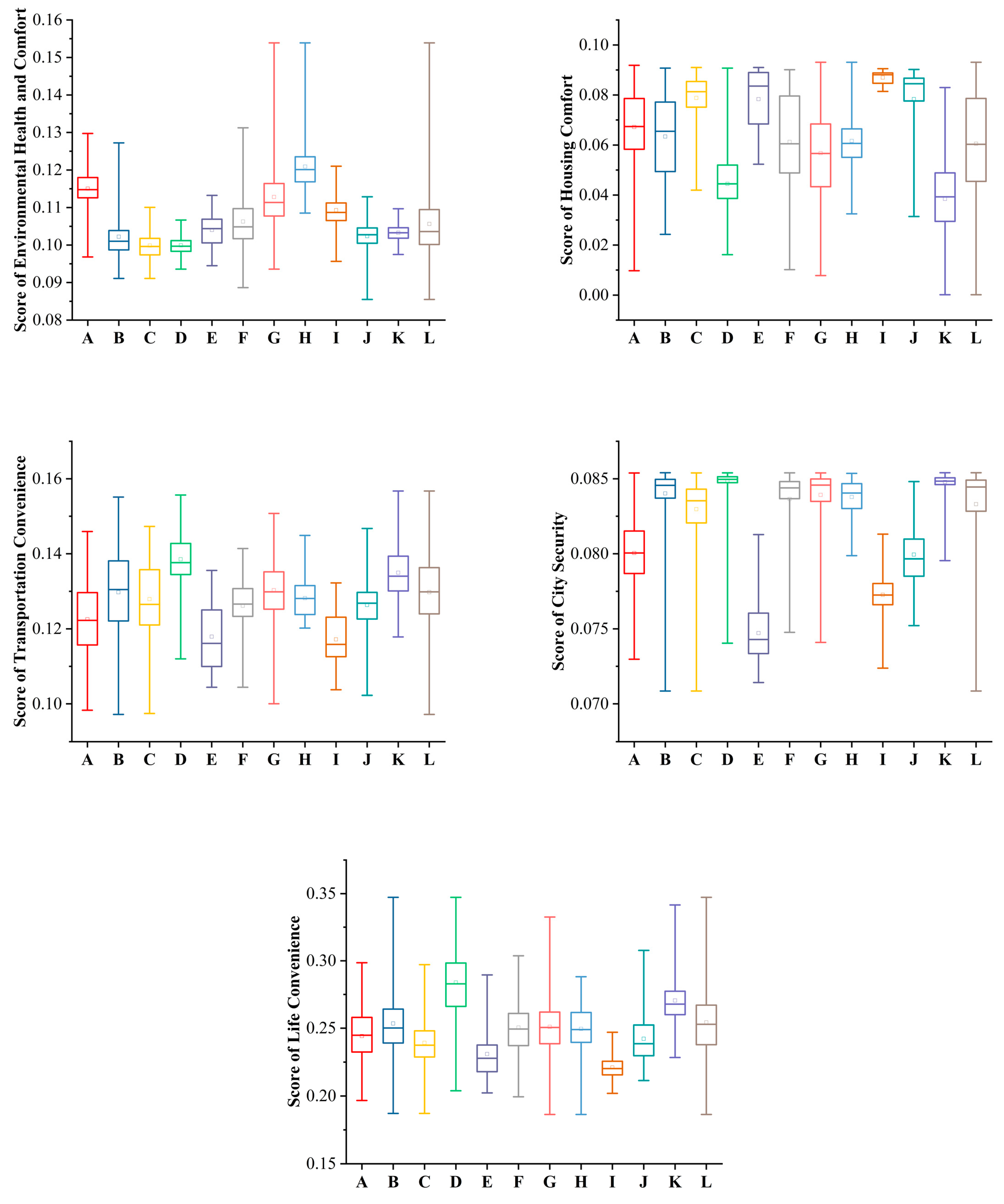
4.3. Evaluation of Primary Indicators for REQ
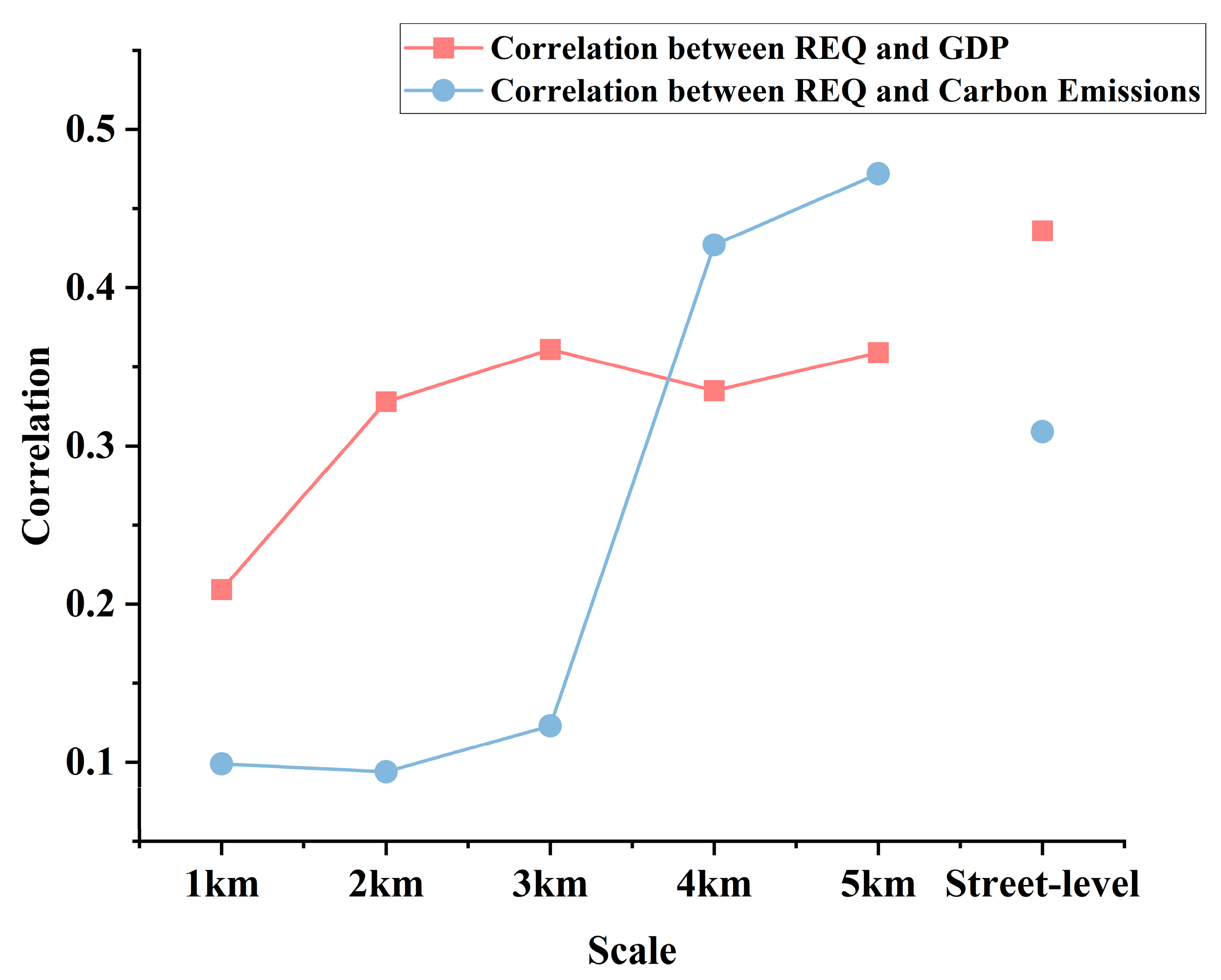
4.4. Analysis of the Correlation between REQ and GDP, Carbon Emissions
5. Discussion
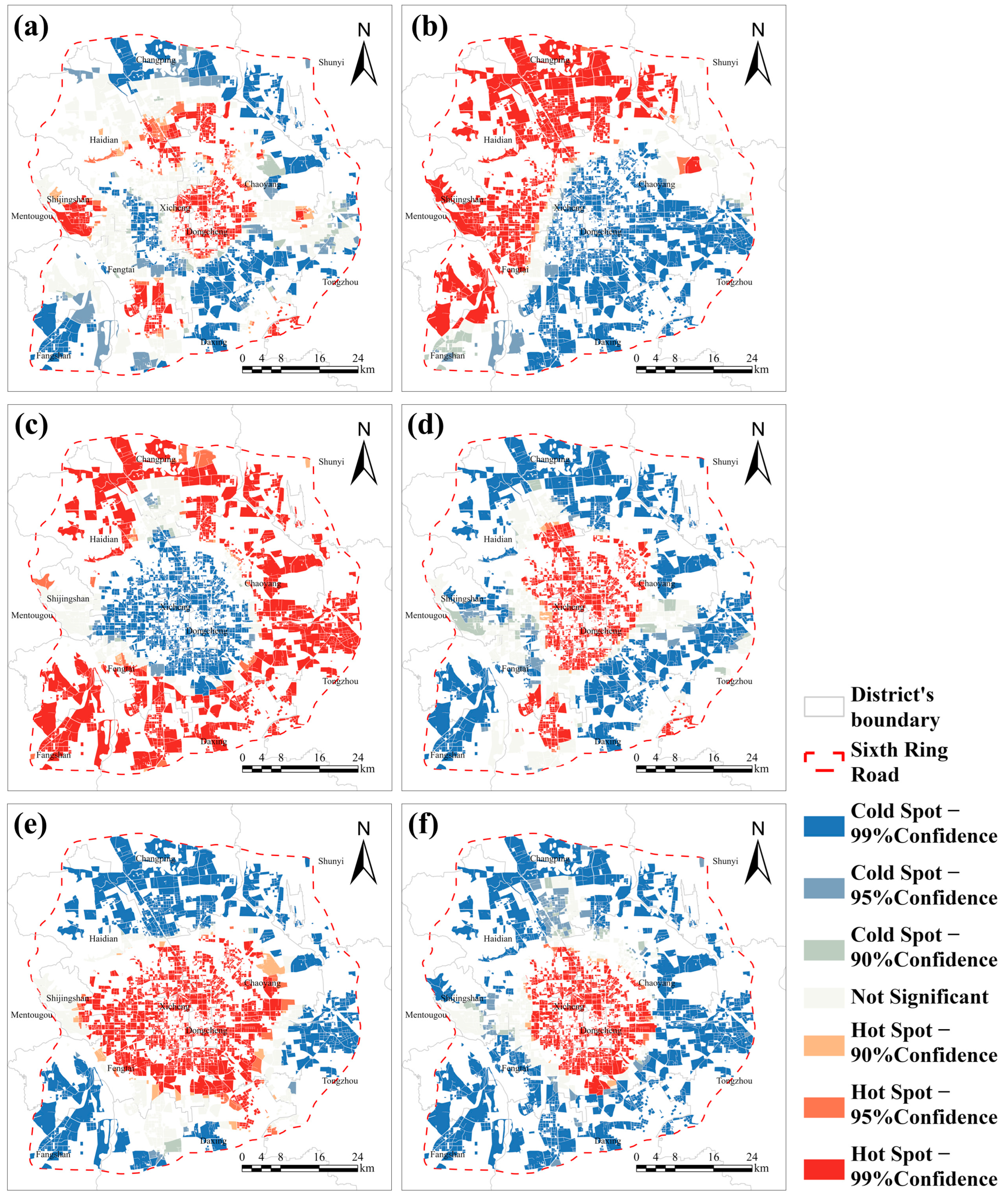
5.1. Hotspot Analysis
5.2. Recommendations for Urban Development
5.3. Pros and Cons
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The overall quality of Beijing’s REQ exhibits a pattern from the center to the edges, from high to low. Environmental health and comfort scores are higher in the northwest and lower in the southeast; housing comfort scores are higher on the edges and lower in the center; transportation convenience, city security, and life convenience scores all show a pattern of being higher in the center and lower on the edges, with a consistent distribution and scores also being higher within the “cross-shaped” area formed around the city center. Additionally, the analysis reveals distinct spatial clustering within Beijing’s REQ, characterized by the widespread distribution of both high-quality (hot spots) and low-quality (cold spots) areas. These characteristics may relate to the different responsibilities assigned to Beijing’s various administrative districts. The government could develop targeted development policies for each district to promote regional economic development, potentially alleviating population density and economic pressure in the central urban areas and comprehensively improving the quality of life for residents in Beijing.
- (2)
- The distribution of environmental health and comfort values is relatively concentrated, with low values being clustered and high values dispersed. The distribution of housing comfort values shows significant differences, with high values more dispersed. The difference in city security is less significant, with values concentrated but low-value data dispersed. The values for transportation convenience, life convenience, and the REQ show a clear pattern of central values being concentrated and edge values being dispersed, overall resembling a “mountain shape”.
- (3)
- The correlation analysis between GDP and the REQ indicates that higher GDP are associated with higher-quality urban environments to a certain extent and within a specific range. The correlation is significant at the street level, and the degree of influence increases with scale. The correlation analysis between carbon emissions and the REQ suggests that regions with higher-quality urban environments tend to exhibit higher levels of carbon emissions to a certain extent. This correlation is similarly significant at the street level and strengthens with scale.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, W.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y. Research Progress on Human Settlement Evolution. Prog. Geogr. 2013, 32, 710–721. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.H. Build Capacity for International Health Agenda on the “Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development”. Health Policy Manag. 2015, 25, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutty, A.A.; Kucukvar, M.; Onat, N.C.; Ayvaz, B.; Abdella, G.M. Measuring sustainability, resilience and livability performance of European smart cities: A novel fuzzy expert-based multi-criteria decision support model. Cities 2023, 137, 104293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodman, P.C.; Mitchel, N.C. Human Settlement and Economy of the Lough Neagh Basin. In Lough Neagh: The Ecology of a Multipurpose Water Resource; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J. A Systematic Review of Big Data-Based Urban Sustainability Research: State-of-The-Science and Future Directions. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 123142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, C.; Meng, J.; Ju, L.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, W. Assessing community-level livability using combined remote sensing and internet-based big geospatial data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khavanin Zadeh, A.R.; Veroustraete, F.; Buytaert, J.A.N.; Dirckx, J.; Samson, R. Assessing Urban Habitat Quality Using Spectral Characteristics of Tilia Leaves. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciach, M.; Faraś, H.; Fröhlich, A.; Fedyń, I. Contrasting Effects of Light and Noise Pollution Interact with Natural Vegetation Remnants: Human-Related Indicators of the Habitat Suitability for Ungulates in the Urban Landscape. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Jin, M.; Liu, X. Evaluation of Urban Habitat Quality Based on Theory of Humanistic-A Case Study of HeFei Metropolitan Circle of China. In International Conference on Green Building, Civil Engineering and Smart City; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 1013–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, D.; Kwan, M.-P.; Zhang, W.; Fan, J.; Yu, J.; Dang, Y. Assessment and Determinants of Satisfaction with Urban Livability in China. Cities 2018, 79, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, A.; Camanho, A.S.; Dias, T.G. The Assessment of Cities’ Livability Integrating Human Wellbeing and Environmental Impact. Ann. Oper. Res. 2015, 226, 695–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Y. Livability assessment of 101,630 communities in China’s major cities: A remote sensing perspective. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2022, 65, 1073–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, Y.; Tang, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, R. Assessing Spatial–Temporal Evolution and Key Factors of Urban Livability in Arid Zone: The Case Study of the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 140, 108995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Du, X.; Huang, H. Community Scale Livability Evaluation Integrating Remote Sensing, Surface Observation and Geospatial Big Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 80, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juntti, M.; Costa, H.; Nascimento, N. Urban environmental quality and wellbeing in the context of incomplete urbanisation in Brazil: Integrating directly experienced ecosystem services into planning. Prog. Plan. 2021, 143, 100433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhang, F. Effect of human settlements on urban thermal environment and factor analysis based on multi-source data: A case study of Changsha city. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 819–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Yu, D.; Zhang, Y. The livable urban landscape: GIS and remote sensing extracted land use assessment for urban livability in Changchun Proper, China. Land Use Policy 2019, 87, 104048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, C.; Lu, M.; Lu, Y. Assessing the Suitability of Regional Human Settlements Environment from a Different Preferences Perspective: A Case Study of Zhejiang Province, China. Habitat Int. 2017, 70, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazauskaitė, D.; Burinskienė, M.; Podvezko, V. Subjectively and objectively integrated assessment of the quality indices of the suburban residential environment. Int. J. Strateg. Prop. Manag. 2015, 19, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Cao, J.; He, J.; Chen, L. City Health Examination in China: A Methodology and Empirical Study. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 951–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Fath, B.D.; Zheng, H.; Xia, L. Analysis of Urban Carbon Metabolic Processes and a Description of Sectoral Characteristics: A Case Study of Beijing. Ecol. Model. 2015, 316, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, J.; Yin, L.; Song, B. Spatio-Temporal Variation and Influencing Factors of Industrial Carbon Emission Effect in China Based on Water-Land-Energy-Carbon Nexus. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 152, 110307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Yan, H.; Zhang, S.; Wei, C. Does urbanization increase residential energy use? Evidence from the Chinese residential energy consumption survey 2012. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 59, 101374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wei, X.; Shen, L. Analysis on the Synchronized Development between Urbanization Process and Eco-Efficiency through the Sustainability Lens. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 80828–80843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Ma, H.; Fang, C. The relationship evolution between urbanization and urban ecological resilience in the Northern Slope Economic Belt of Tianshan Mountains, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 97, 104783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Openshaw, S. A Million or so Correlation Coefficients: Three Experiments on the Modifiable Areal Unit Problem. In Statistical Applications in the Spatial Sciences; Pion: London, UK, 1979; pp. 127–144. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, P.; Chen, B.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Fang, L.; Feng, S.; et al. Mapping Essential Urban Land Use Categories in China (EULUC-China): Preliminary Results for 2018. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W. The core framework of the livable city construction. Geogr. Res. 2016, 35, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouratidis, K. Commute satisfaction, neighborhood satisfaction, and housing satisfaction as predictors of subjective well-being and indicators of urban livability. Travel Behav. Soc. 2020, 21, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Hua, Z.; Li, G.; Qu, J. Assessment of Potentially Toxic Pollutants and Urban Livability in a Typical Resource-Based City, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 18640–18649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, F.; Xi, X.; van Bilsen, D.J.C.; Xu, L. Urban Livability: Agent-Based Simulation, Assessment, and Interpretation for the Case of Futian District, Shenzhen. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 320, 128662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, B.; Chen, H.; Li, Z. Exploring the linkage between greenness exposure and depression among Chinese people: Mediating roles of physical activity, stress and social cohesion and moderating role of urbanicity. Health Place 2019, 58, 102168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Yang, Q.; Jing, W.; Yang, J. Effects of Landscape on Thermal Livability at the Community Scale Based on Fine-Grained Geographic Information: A Case Study of Shenzhen. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, J. Analysis and optimization of 15-min community life circle based on supply and demand matching: A case study of Shanghai. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Donkelaar, A. Satellite-derived PM2.5 - Washington University in St. Louis. Available online: https://sites.wustl.edu/acag/datasets/surface-pm2-5/#V5.GL.02 (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- Muñoz Sabater, J. ERA5-Land monthly averaged data from 1950 to present. Available online: https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- Worldpop. Available online: https://hub.worldpop.org/ (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, G.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, X. Generating Gridded Gross Domestic Product Data for China Using Geographically Weighted Ensemble Learning. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ODIAC Fossil Fuel Emission Dataset|Center for Global Environmental Research. db.cger.nies.go.jp. Available online: https://db.cger.nies.go.jp/dataset/ODIAC/DL_odiac2022.html (accessed on 26 January 2024).
- Yangtze River Delta Science Data Center, National Earth System Science Data Center, National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China. Available online: http://geodata.nnu.edu.cn/ (accessed on 21 January 2024).
- Zhong, C.; Yang, Q.; Liang, J.; Ma, H. Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation with AHP and Entropy Methods and Health Risk Assessment of Groundwater in Yinchuan Basin, Northwest China. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 111956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Xie, D.; Xu, X. Environmental Suitability Evaluation for Human Settlements of Rural Residential Areas in Hengshui. Hebei Province. Land 2022, 11, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Quan, Y. Measuring the Sustainable Development of Marine Economy Based on the Entropy Value Method: A Case Study in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y. The Construction of the Landscape- and Village-Integrated Green Governance System Based on the Entropy Method: A Study from China. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Jin, J. Attribute recognition method of regional ecological security evaluation based on combined weight on principle of relative entropy. Sci. Geogr. Sin 2008, 28, 754–758. [Google Scholar]
- Fieller, E.C.; Pearson, E.S. Tests for Rank Correlation Coefficients. II. Biometrika 1961, 48, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Primary Indicator | Secondary Indicator | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental health and comfort (ecological environment and urban greening) | Air Quality Status | Reflecting PM2.5 Pollution |
| Noise Index | Reflecting Noise Impact from Main Roads | |
| Street Greening Rate | Reflecting Green Space Coverage | |
| Nearest Distance to Parks | Reflecting Proximity to Nature | |
| Nearest Distance to Water Bodies | ||
| Comfortability of Temperature in July | Reflecting Heat Weather Conditions | |
| Comfortability of Temperature in January | Reflecting Cold Weather Conditions | |
| Housing comfort (housing affordability and per capita resource availability) | Population Density | Reflecting Per Capita Resource Availability |
| Housing Price to Income Ratio | Reflecting Economic Burden and Degree | |
| Transportation convenience (the convenience of using vehicle and public transportation) | Road Network Density | Reflecting Convenience of Vehicular Travel |
| Nearest Distance to Subway Stations | Reflecting Convenience of Public Transportation | |
| Nearest Distance to Bus Stations | ||
| City security (the proximity of residential areas to key emergency facilities) | Nearest Distance to Fire Stations | Reflecting Coverage of Fire Stations |
| Nearest Distance to Police Stations | Reflecting Coverage of Police Stations | |
| Nearest Distance to Emergency Shelters | Reflecting Emergency Response Capability | |
| Life convenience (the comprehensiveness of public service infrastructure) | Company Distribution Density | Reflecting Commuting Time to some extent |
| Nearest Distance to Convenience Stores | Reflecting Coverage of Shopping Services | |
| Nearest Distance to Supermarkets | ||
| Nearest Distance to Vegetable Markets | ||
| Nearest Distance to Kindergartens | Reflecting Coverage of Education Services | |
| Nearest Distance to Primary Schools | ||
| Nearest Distance to Middle Schools | ||
| Nearest Distance to Community Hospitals | Reflecting Coverage of Medical Services | |
| Nearest Distance to General Hospitals | ||
| Nearest Distance to Tertiary Hospitals | ||
| Nearest Distance to Pharmacies | ||
| Nearest Distance to Clinics | ||
| Number of Nearby Restaurants | Reflecting Coverage of Dining Services | |
| Nearest Distance to Banks | Reflecting Coverage of Financial Services | |
| Nearest Distance to Sports Facilities | Reflecting Coverage of Sports Facilities | |
| Nearest Distance to Charging Stations | Reflecting Coverage of Automotive Services | |
| Nearest Distance to Gas Stations |
| Data Type | Data Resource | Data Format | Time Range | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land Use Types | Essential Urban Land Use Categories in China (EULUC-China) [27] | ESRI Shapefile | 2018 | / |
| Point of Interest (POI) | Amap Map API Crawling | Microsoft Excel | 2022 | / |
| Air Pollution Levels (PM2.5) | Atmospheric Composition Analysis Group at Washington University in St. Louis [35] | NetCDF | 2020 | 0.01° × 0.01° |
| Temperature Data (2 m) | ERA5-Land Dataset [36] | NetCDF | 2022 | 0.1° × 0.1° |
| Road Network Data | OpenStreetMap | ESRI Shapefile | 2019 | / |
| Urban Green Space Data | Sentinel-2 Satellite Remote Sensing Image | TIFF | 2022 | 10 m × 10 m |
| Water Body Data | Open Street Map | ESRI Shapefile | 2023 | / |
| Population Data | WorldPop | TIFF | 2020 | 100 m × 100 m |
| Housing Price Data | Real Estate Platform | TIFF | 2023 | 200 m × 200 m |
| GDP Data | Yangtze River Delta Science Data Center, National Earth System Science Data Sharing Infrastructure, National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China (http://geodata.nnu.edu.cn/) [40] | TIFF | 2020 | 1 km × 1 km |
| Carbon Emissions Data | ODIAC [39] | TIFF | 2019 | 1 km × 1 km |
| Primary Indicators | Secondary Indicators | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental health and comfort | Air Quality Status | 0.04719 |
| Noise Index | 0.06906 | |
| Street Greening Rate | 0.05424 | |
| Nearest Distance to Parks | 0.00841 | |
| Nearest Distance to Water Bodies | 0.01335 | |
| Comfortability of Temperature in July | 0.07862 | |
| Comfortability of Temperature in January | 0.01860 | |
| Housing comfort | Population Density | 0.09449 |
| Housing Price to Income Ratio | 0.01177 | |
| Transportation convenience | Road Network Density | 0.06044 |
| Nearest Distance to Subway Stations | 0.04436 | |
| Nearest Distance to Bus Stations | 0.06054 | |
| City security | Nearest Distance to Fire Stations | 0.03342 |
| Nearest Distance to Police Stations | 0.02985 | |
| Nearest Distance to Emergency Shelters | 0.02649 | |
| Life convenience | Distance to Commercial Centers | 0.00410 |
| Company Distribution Density | 0.07063 | |
| Nearest Distance to Convenience Stores | 0.00715 | |
| Nearest Distance to Supermarkets | 0.00736 | |
| Nearest Distance to Vegetable Markets | 0.01272 | |
| Nearest Distance to Kindergartens | 0.01209 | |
| Nearest Distance to Primary Schools | 0.00767 | |
| Nearest Distance to Middle Schools | 0.00967 | |
| Nearest Distance to Community Hospitals | 0.02701 | |
| Nearest Distance to General Hospitals | 0.01966 | |
| Nearest Distance to Tertiary Hospitals | 0.01902 | |
| Nearest Distance to Pharmacies | 0.02428 | |
| Nearest Distance to Clinics | 0.02081 | |
| Number of Nearby Restaurants | 0.05297 | |
| Nearest Distance to Banks | 0.01314 | |
| Nearest Distance to Sports Facilities | 0.01146 | |
| Nearest Distance to Charging Stations | 0.01303 | |
| Nearest Distance to Gas Stations | 0.01640 |
| Variable | Scale | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 km | 2 km | 3 km | 4 km | 5 km | Street-Level | |
| GDP | 0.209 ** | 0.328 ** | 0.361 ** | 0.335 ** | 0.359 ** | 0.436 ** |
| Carbon Emissions | 0.099 ** | 0.094 * | 0.123 * | 0.427 ** | 0.472 ** | 0.309 ** |
| Environmental Health and Comfort | Housing Comfort | Transportation Convenience | City Security | Life Convenience | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moran’s Index | 0.86 | 0.54 | 0.34 | 0.43 | 0.59 |
| z-score | 263.25 | 202.90 | 103.82 | 162.74 | 178.794 |
| p-values | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Xia, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, P.; Du, S. An Assessment of Urban Residential Environment Quality Based on Multi-Source Geospatial Data: A Case Study of Beijing, China. Land 2024, 13, 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13060823
Zhang S, Xia Y, Li Z, Li X, Wu Y, Liu P, Du S. An Assessment of Urban Residential Environment Quality Based on Multi-Source Geospatial Data: A Case Study of Beijing, China. Land. 2024; 13(6):823. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13060823
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shijia, Yang Xia, Zijuan Li, Xue Li, Yufei Wu, Peiyi Liu, and Shouhang Du. 2024. "An Assessment of Urban Residential Environment Quality Based on Multi-Source Geospatial Data: A Case Study of Beijing, China" Land 13, no. 6: 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13060823
APA StyleZhang, S., Xia, Y., Li, Z., Li, X., Wu, Y., Liu, P., & Du, S. (2024). An Assessment of Urban Residential Environment Quality Based on Multi-Source Geospatial Data: A Case Study of Beijing, China. Land, 13(6), 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13060823






