Effect of Weathering on Cd Mobilization in Different Sedimentary Bedrock Soils
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
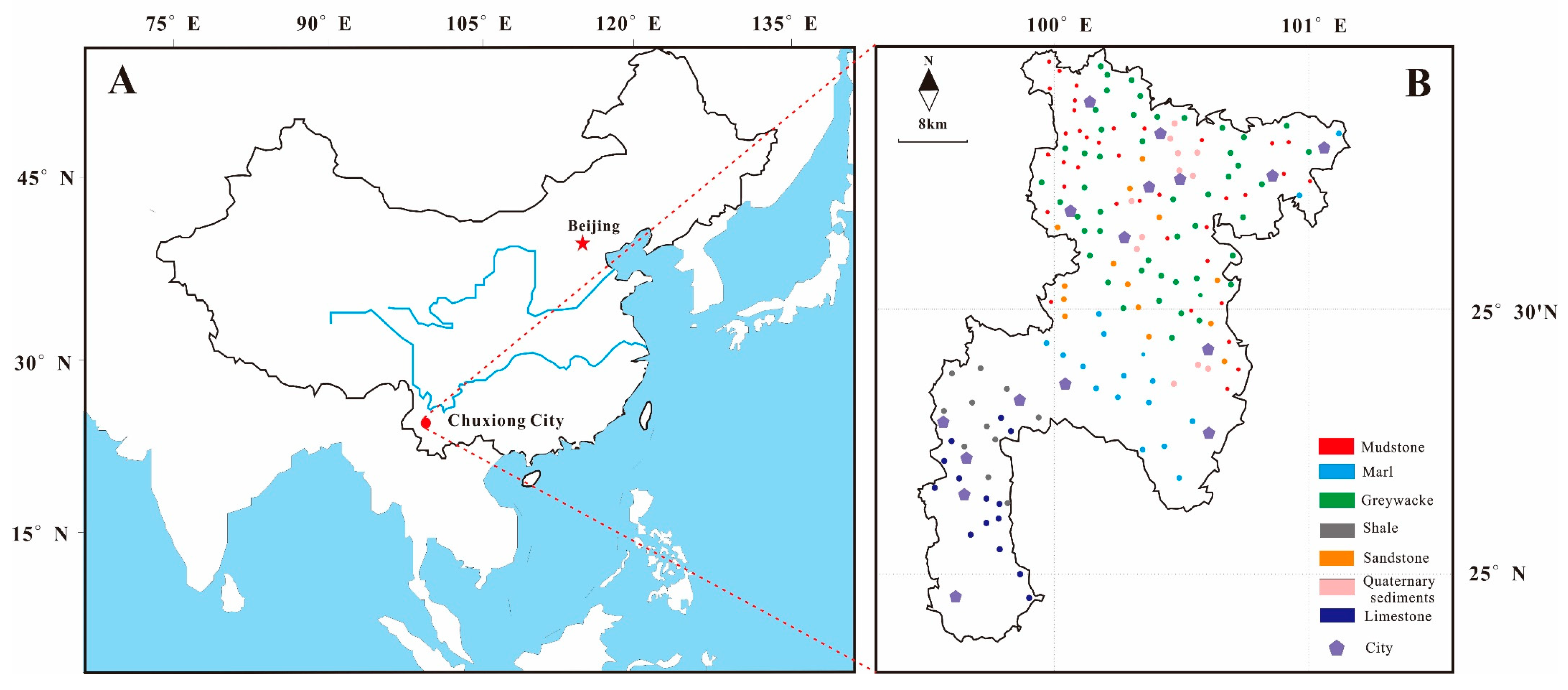
2.1. Study Area and Sample Preparation
2.2. Chemical Analysis
2.3. Assessment of Soil Weathering Degree
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analytical Quality
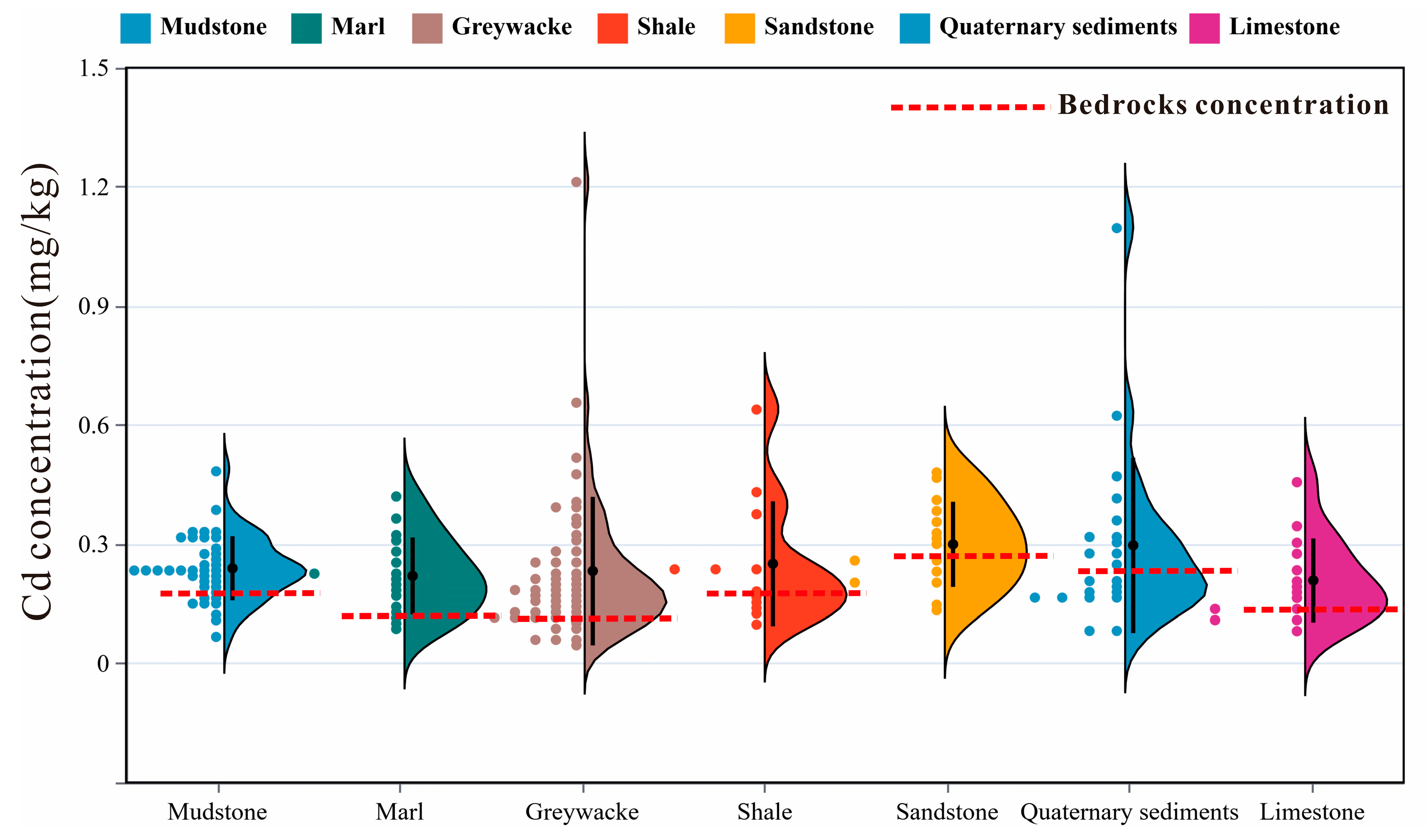
3.2. Distribution of Cd Concentration in Soil of Different Bedrocks
3.3. Sources of Cd in Soil of Different Bedrocks
3.4. Parameters of Wind Erosion Under Varying Geological Parent Material Conditions
3.5. Factors Affecting Cd Concentration in Soil
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kubier, A.; Wilkin, R.T.; Pichler, T. Cd in soils and groundwater: A review. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 108, 104388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Järup, L.; Åkesson, A. Current status of Cd as an environmental health problem. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2009, 238, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imseng, M.; Wiggenhauser, M.; Keller, A.; Müller, M.; Rehkämper, M.; Murphy, K.; Kreissig, K.; Frossard, E.; Wilcke, W.; Bigalke, M. Fate of Cd in agricultural soils: A stable isotope approach to anthropogenic impact, soil formation, and soil-plant cycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1919–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, P.-M.; Gu, Y.; Kopittke, P.M.; Zhao, F.-J.; Wang, P. Iron–manganese (oxyhydro) oxides, rather than oxidation of sulfides, determine mobilization of Cd during soil drainage in paddy soil systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 2500–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.S. Exposure risk assessment and pollution control status of Cd contaminated soil. AGR Technol. 2021, 12, 96–99. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zou, M.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, Z.; Guo, T.; Wang, J. Cd pollution of soil-rice ecosystems in rice cultivation dominated regions in China: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Feng, W.; Wang, S.; Chen, L.; Zheng, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, D. Farmland heavy metals can migrate to deep soil at a regional scale: A case study on a wastewater-irrigated area in China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 281, 116977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Ma, Y.B.; Zhang, S.; Wei, D.; Zhu, Y.-G. An inventory of trace element inputs to agricultural soils in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2524–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Z.; Xiao, T.F.; Ning, Z.P.; Li, H.; Tang, J.; Zhou, G. High Cd concentrations in soil in the Three Gorges region: Geogenic source and potential bioavailability. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 37, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Zhu, J.-M.; Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Qi, M.; Lv, Y.; Gao, T. Cd mobilization in mining-impacted soils with different bedrock lithology: Insights from stable Cd isotopes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, T.; Perkins, R.B.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Ning, Z. Geogenic Cd pollution and potential health risks, with emphasis on black shale. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 176, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pan, Y.P.; Shi, H.D. Cd sources and contribution of atmospheric deposition in farmland soil in North China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2022, 41, 1698–1708. [Google Scholar]
- Quezada-Hinojosa, R.P.; Matera, V.; Adatte, T.; Rambeau, C.; Föllmi, K.B. Cd distribution in soils covering Jurassic oolitic limestone with high Cd concentrations in the Swiss Jura. Geoderma 2009, 150, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Chon, H.-T.; Marton, L. Mobility and accumulation of selenium and its relationship with other heavy metals in the system rocks/soils–crops in areas covered by black shale in Korea. J. Geochem. Explor. 2010, 107, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.J.; Betty, E.E.; Page, A.L.; Elliott, R.A. Occurrence of naturally high Cd levels in soils and its accumulation by vegetation. J. Environ. Qual. 1981, 10, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.X.; Yang, Z.F.; Xi, X.H.; Zhao, C.D.; Wu, X.M.; Zhuang, G.M.; Liu, Y.H.; Chen, G.G. A research framework for source tracking and quantitative assessment of the Cd anomalies along the Yangtze River Basin. Earth Sci. Front. 2005, 12, 261–272, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ning, Y.; Yang, B.; Yang, S.; Ye, J.; Li, J.; Ren, L.; Liu, Z.; Bi, X.; Liu, J. Application of Pb isotopes and REY patterns in tracing heavy metals in farmland soils from the Upper-Middle area of Yangtze River. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.X.; Peng, B.; Peltola, P.; Tang, X.; Xie, S. Effect of weathering on abundance and release of potentially toxic elements in soils developed on Lower Cambrian black shales, P.R. China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2011, 34, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Ji, J.; Yang, Z.; Han, H.; Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W. Cd risk in the soil-plant system caused by weathering of carbonate bedrock. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, M.L.W.; Breit, G.N.; Goldhaber, M.B. Weathering of the New Albany Shale, Kentucky: II. Redistribution of minor and trace elements. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 1565–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Peng, B.; Wu, N.; Xie, S.; Yang, X.; Fang, X.; Song, Z. Mobility and environmental impact of cadmium (Cd) during weathering of carbonaceous black shales in western Hunan, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 470, 134267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Ji, J. Enrichment and source identification of Cd and other heavy metals in soils with high geochemical background in the karst region, Southwestern China. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, W.; Xinhua, W.; Meihua, G.; Xuyan, X. Impact of climate change on reference crop evapotranspiration in Chuxiong City, Yunnan Province. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2012, 5, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.U.; Wei, L.; Jun, T.A.N.; Bing, T.A.N.G.; Gaozhao, L.V. Evaluation and Analysis of Ecological Climatic Index of Tobacco-growing Areas in Chuxiong. Chin. Tob. Sci. 2012, 33, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Ren, Z.L.; Tian, T.; Cui, J.; Liu, C.; Wu, H. Tectono-thermal evolution and its relationship with petroleum generation in the Chuxiong Basin, southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Chin. J. Geophys. 2023, 66, 5057–5073. [Google Scholar]
- DZ/T 0258-2014; Specification of Multi-Purpose Regional Geochemical Survey (1:250000). Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2014; pp. 1–46. (In Chinese)
- DZ/T 0130-2006; The National Standard Method Used for Chemical Analysis and Its Quality Control Included the Specification of Testing Quality Management for Geological Laboratories. Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 1–17. (In Chinese)
- DD2005-03; Geological Survey Technical Standard. China Geological Survey: Beijing, China; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 1–22. (In Chinese)
- Gjoka, F.; Miho, L.; Spaholli, A.; Kasa, E. Weathering patterns in alluvial soils under Mediterranean climatic conditions in Albania and implications for soil fertility. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 18, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedo, C.M.; Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosols, with implications for paleo-weathering conditions and provenance. Geology 1995, 23, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadłonek, W.; Bojakowska, I. Variability of chemical weathering indices in modern sediments of the Vistula and Odra Rivers (Poland). Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2018, 16, 2453–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.L.; Yang, F.; Xu, C.; Yang, H.; Liu, W. Status of metal accumulation in farmland soils across China: From distribution to risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 176, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Bi, X.; Ning, Y.; Yang, S.; Yang, X. Apportionment of sources of heavy metals to agricultural soils using isotope fingerprints and multivariate statistical analyses. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, F.A.; Smith, S.R.; Alloway, B.J.; Carlton-Smith, C.; Chambers, B.J. Aninventory of heavy metals inputs to agricultural soils in England and Wales. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 311, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramatica, P.; Battaini, F.; Giani, E.; Papa, E.; Jones, R.J.A.; Cenci, R.M. Multivariate analysis of heavy metal concentrations in soils and mosses of two northItaly regions. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2006, 15, 731–737. [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Fedo, C.M.; Young, G.M. Quartz and feldspar stability, steady and non-steady-state weathering, and petrogenesis of siliciclastic sands and muds. J. Geol. 1997, 105, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, S.A.; Tijani, M.N.; Adeyemo, O.M. Influence of bedrock weathering of the shallow ground water system around felsic metasediment and amphibolites of the Ilesha schist bel. Transnatl. J. Sci. Tech. 2013, 3, 36–53. [Google Scholar]
- Janusz, W.; Patkowski, J.; Chibowski, S. Competitive adsorption of Ca2+ and Zn (II) ions at monodispersed SiO2/electrolyte solution interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 266, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Yang, J.; Liang, S.; Li, M.; Gan, Q.; Xiao, K.; Hu, J. Enhanced Cr(VI) removal from acidic solutions using biochar modified by Fe3O4@SiO2-NH2 particles. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 628, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, R.; Gao, S. Composition of the continental crust. In Treatise on Geochemistry; Rudnick, R.L., Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 3, pp. 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong-Altrin, J.S.; Lee, Y.I.; Verma, S.P.; Ramasamy, S. Geochemistry of sandstones from the Upper Miocene Kudankulam For-mation, southern India: Implications for provenance, weathering, and tectonic setting. J. Sediment. Res. 2004, 74, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.-W.; Li, L.-B.; Zhu, Y.-Q.; Ren, M.-Q. Behaviors of Major and Trace Elements in Soils Developed from Weathering Basalt in Western Guizhou, China. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 861, 072006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Yang, S.; Guo, Y. A global temperature control of silicate weathering intensity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQueen, K.G.; Scott, K.M. Rock weathering and structure of the regolith. Regolith Sci. 2008, 1, 105–126. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Rempe, D.M.; Dietrich, W.E.; West, A.J.; Lin, T.-C.; Jin, L.; Brantley, S.L. Chemical reactions, porosity, and microfracturing in shale during weathering: The effect of erosion rate. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2019, 269, 63–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkington, A.V.; Paradise, T.R. Sandstone weathering: A century of research and innovation. Geomorphology 2005, 67, 229–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigatti, S.J. Random forest. J. Insur. Med. 2017, 47, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kicińska, A.; Pomykała, R.; Izquierdo-Diaz, M. Changes in soil pH and mobility of heavy metals in contaminated soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 73, e13203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.S.; Angle, J.S.; Chaney, R.L.; Delorme, T.A.; Reeves, R.D. Soil pH effects on uptake of Cd and Zn by Thlaspi caerulescens. Plant Soil 2006, 281, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, S.; Shan, X.; Luo, L.; Pei, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, T.; Xie, Y.; Gault, A. Characterization of Pb, Cu, and Cd adsorption on particulate organic matter in soil. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 2366–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borggaard, O.K.; Holm, P.E.; Strobel, B.W. Potential of dissolved organic matter (DOM) to extract As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn from polluted soils: A review. Geoderma 2019, 343, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Standard | GBW07403 (GSS-3) | GBW07447 (GSS-18) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 (%) | TFe2O3 (%) | CaO (%) | MgO (%) | Na2O (%) | K2O (%) | SiO2 (%) | Zn (mg/kg) | Cu (mg/kg) | Cd (mg/kg) | Pb (mg/kg) | Hg (mg/kg) | |
| Standard value | 12.2% | 2.00% | 1.27% | 0.58% | 2.71% | 3.04 | 74.72 | 31.0 | 19.5 | 0.15 | 20.0 | 0.015 |
| Mean value | 11.6% | 1.96% | 1.22% | 0.62% | 2.82% | 2.97 | 74.03 | 30.6 | 19.5 | 0.14 | 19.3 | 0.016 |
| RSD% | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 1.07 | 1.26 | 0.9 | 0.04 | 1.91 | 1.10 | 6 | 0.50 | 2.62 |
| Specification RSD% | ≤8 | ≤8 | ≤8 | ≤8 | ≤8 | ≤8 | ≤8 | ≤10 | ≤10 | ≤10 | ≤10 | ≤10 |
| ΔlgC | −0.03 | −0.01 | −0.02 | 0.03 | 0.017 | 0.01 | −0.004 | 0.006 | 0.0004 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| Specification ΔlgC | ≤0.04 | ≤0.04 | ≤0.04 | ≤0.04 | ≤0.04 | ≤0.05 | ≤0.04 | ≤0.05 | ≤0.05 | ≤0.05 | ≤0.05 | ≤0.05 |
| Soil | Pb (mg/kg) | Zn (mg/kg) | Cr (mg/kg) | Cu (mg/kg) | Hg (mg/kg) | K2O (%) | MgO (%) | Na2O (%) | CaO (%) | SiO2 (%) | Fe2O3 (%) | Al2O3 (%) | pH | TC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mudstone | 77.06 | 87.68 | 127.27 | 38.61 | 0.06 | 2.22 | 1.50 | 0.46 | 0.47 | 61.81 | 6.06 | 15.31 | 5.87 | 37.07 |
| Marl | 28.86 | 229.12 | 108.46 | 34.38 | 0.08 | 2.45 | 1.37 | 0.55 | 0.51 | 61.62 | 6.25 | 15.63 | 6.00 | 34.69 |
| Greywacke | 35.09 | 79.10 | 94.17 | 34.14 | 0.06 | 2.09 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 0.53 | 66.03 | 5.43 | 14.92 | 5.46 | 33.01 |
| Shale | 24.92 | 70.58 | 112.49 | 27.89 | 0.04 | 1.87 | 1.31 | 0.72 | 2.33 | 61.18 | 4.88 | 12.60 | 6.94 | 34.16 |
| Sandstone | 34.90 | 95.39 | 114.98 | 39.54 | 0.04 | 2.84 | 1.75 | 0.55 | 0.68 | 61.89 | 6.32 | 15.68 | 6.09 | 32.00 |
| Quaternary | 33.15 | 88.85 | 124.90 | 31.64 | 0.06 | 1.85 | 1.22 | 0.47 | 0.54 | 62.84 | 5.61 | 13.88 | 6.01 | 38.45 |
| Limestone | 24.95 | 74.52 | 110.92 | 35.69 | 0.03 | 2.43 | 1.63 | 1.51 | 0.84 | 61.23 | 5.57 | 14.12 | 6.78 | 19.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ning, Y.; Yang, M.; Liu, C.; Huang, J.; Wang, T.; Pang, Y.; Li, Q. Effect of Weathering on Cd Mobilization in Different Sedimentary Bedrock Soils. Land 2025, 14, 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14010176
Ning Y, Yang M, Liu C, Huang J, Wang T, Pang Y, Li Q. Effect of Weathering on Cd Mobilization in Different Sedimentary Bedrock Soils. Land. 2025; 14(1):176. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14010176
Chicago/Turabian StyleNing, Yongqiang, Minglong Yang, Chutong Liu, Jiazhong Huang, Tianyi Wang, Yong Pang, and Quanheng Li. 2025. "Effect of Weathering on Cd Mobilization in Different Sedimentary Bedrock Soils" Land 14, no. 1: 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14010176
APA StyleNing, Y., Yang, M., Liu, C., Huang, J., Wang, T., Pang, Y., & Li, Q. (2025). Effect of Weathering on Cd Mobilization in Different Sedimentary Bedrock Soils. Land, 14(1), 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14010176






