Monitoring of Soil Salinity in the Weiku Oasis Based on Feature Space Models with Typical Parameters Derived from Sentinel-2 MSI Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
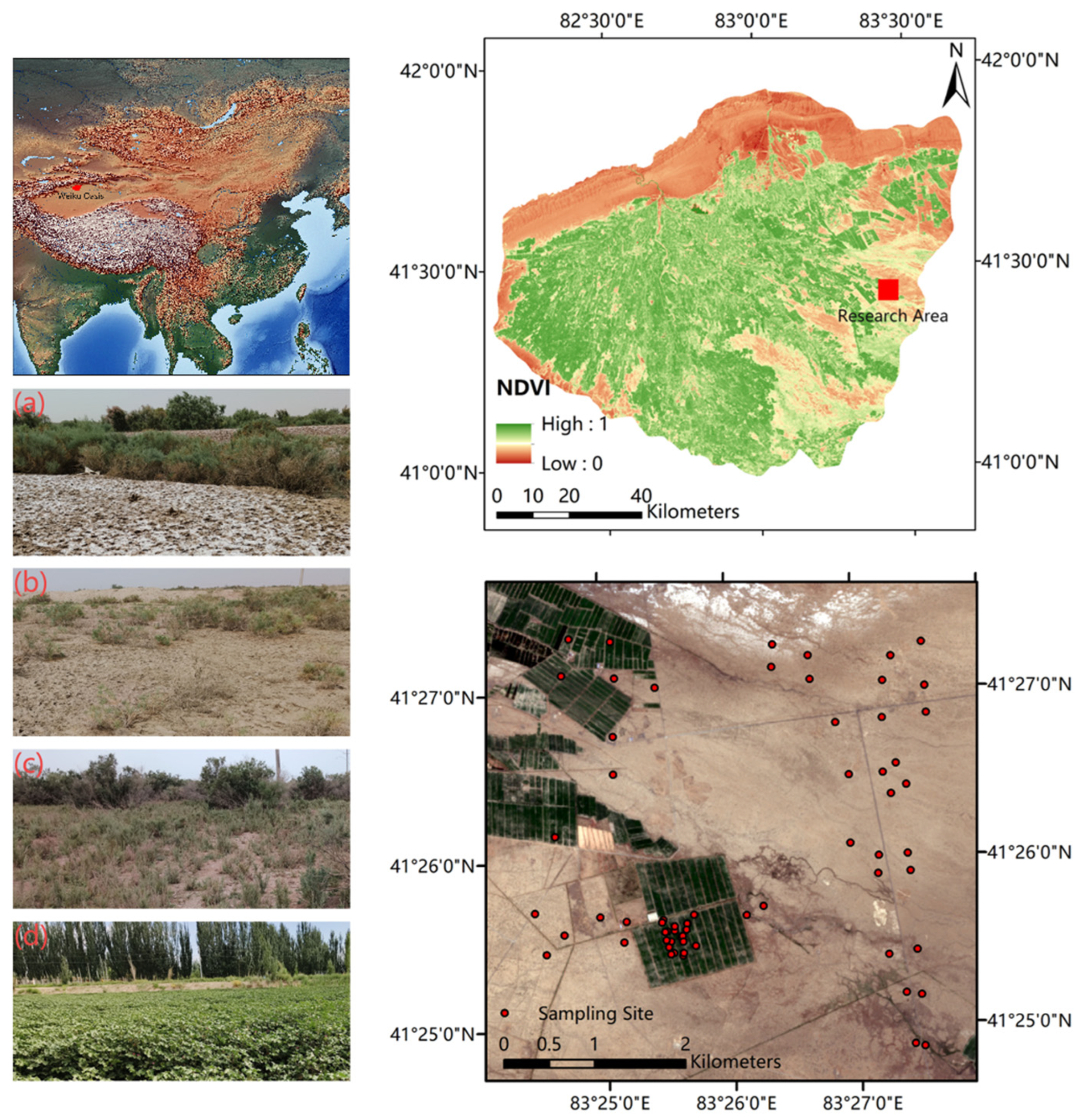
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection and Preprocessing
2.3. Selection of Typical Indices
2.4. Index Standardization
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Feature Space Overview
3. Results
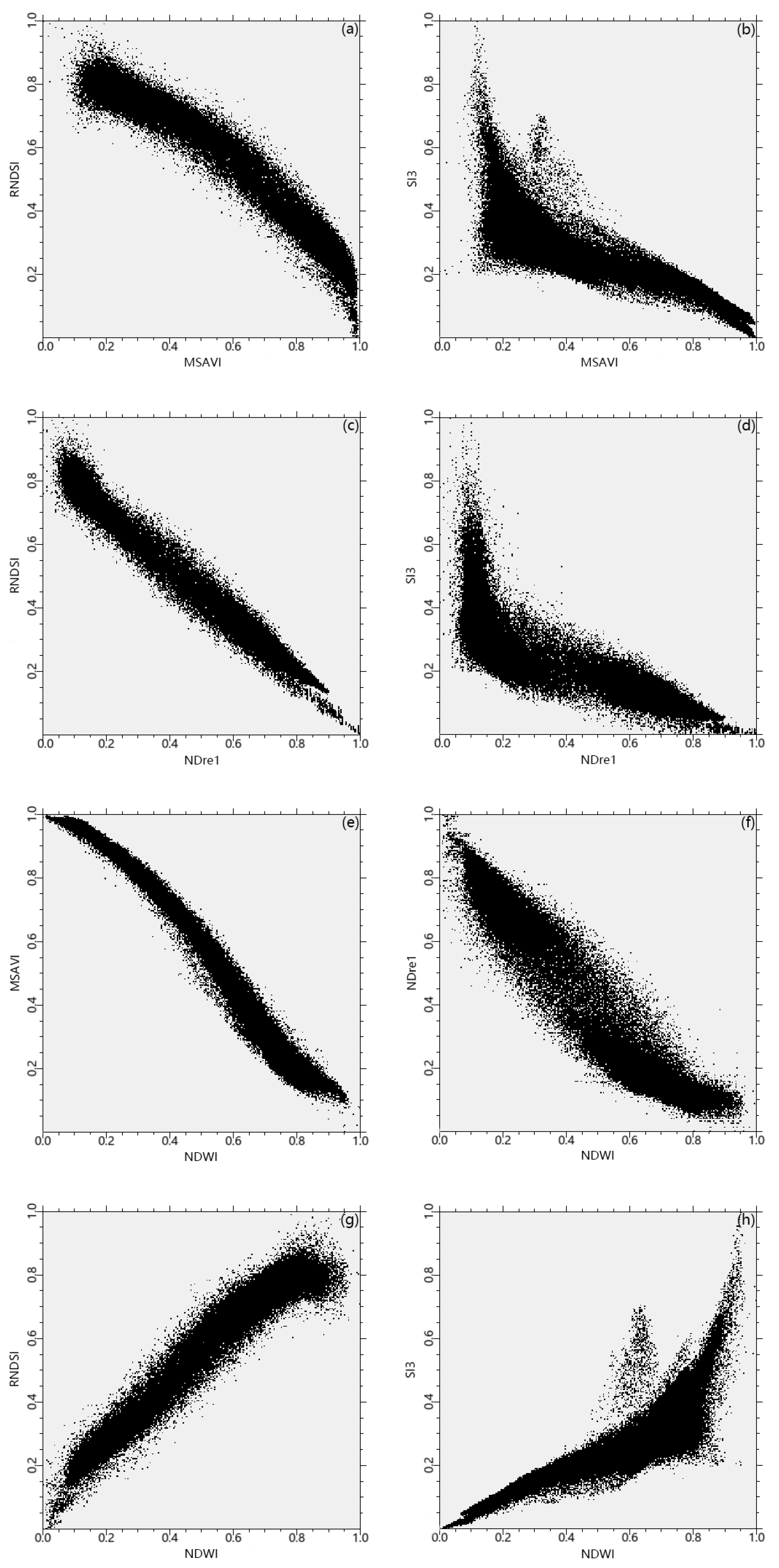
3.1. Sifting the Typical Parameters
3.2. Construction of Feature Spaces
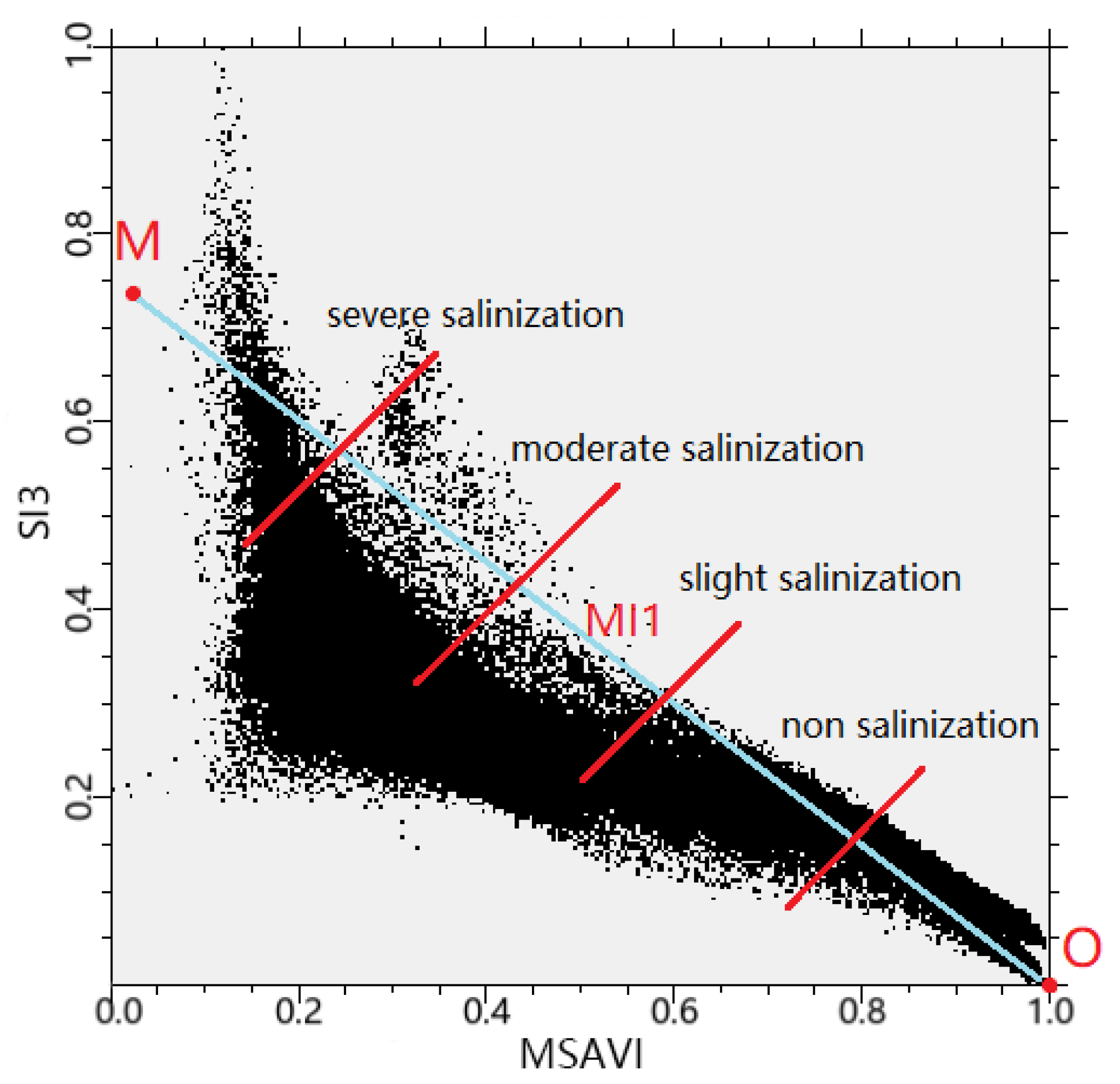
3.3. Establishing the Monitoring Indices of Salinization
3.3.1. Spatial Distribution Rules of Different Levels of Salinization in Feature Space
3.3.2. The Establishment of Monitoring Indices
3.4. Optimal Monitoring Index of Salinization
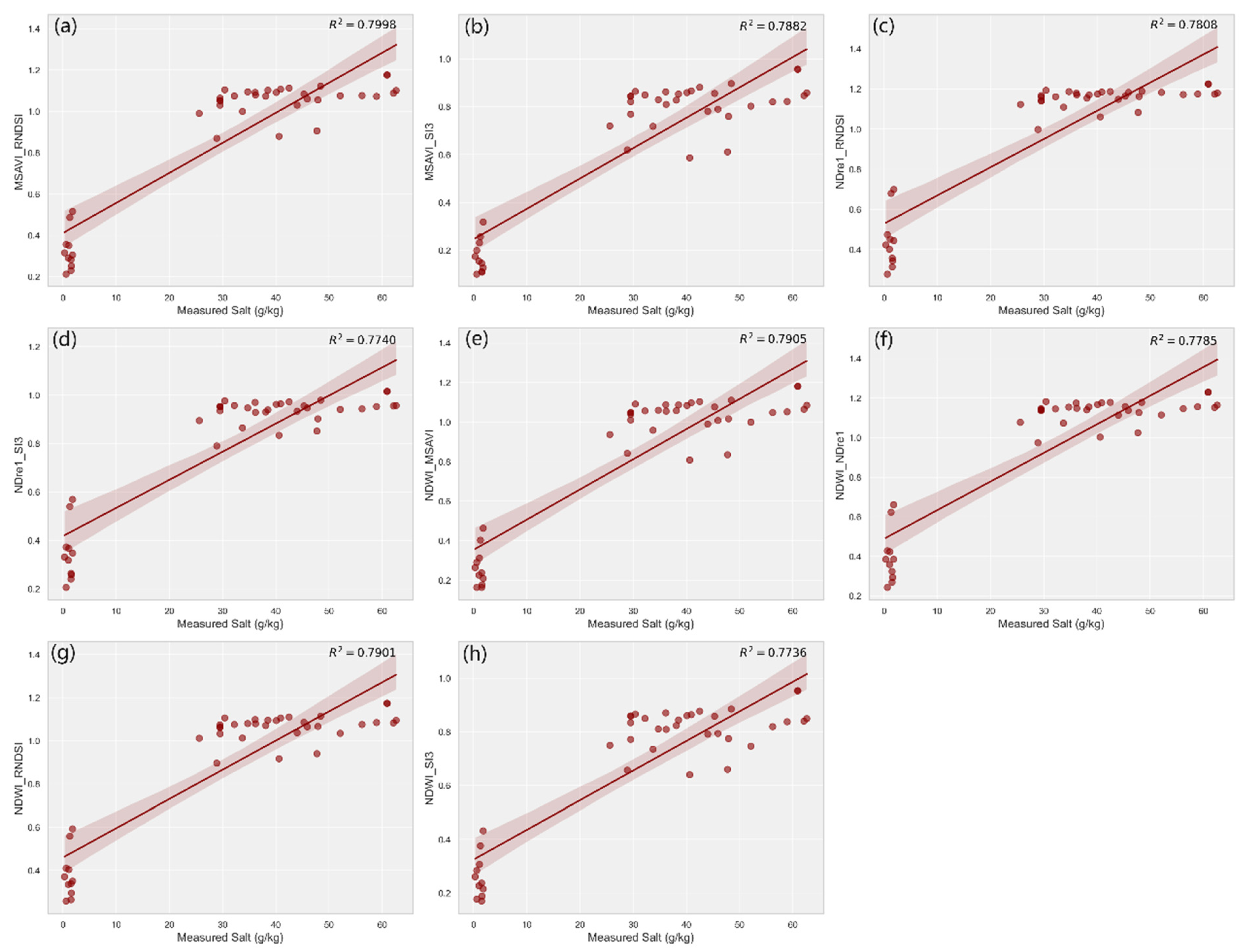
3.4.1. Calculating the Monitoring Indices
3.4.2. Selecting the Optimal Monitoring Index
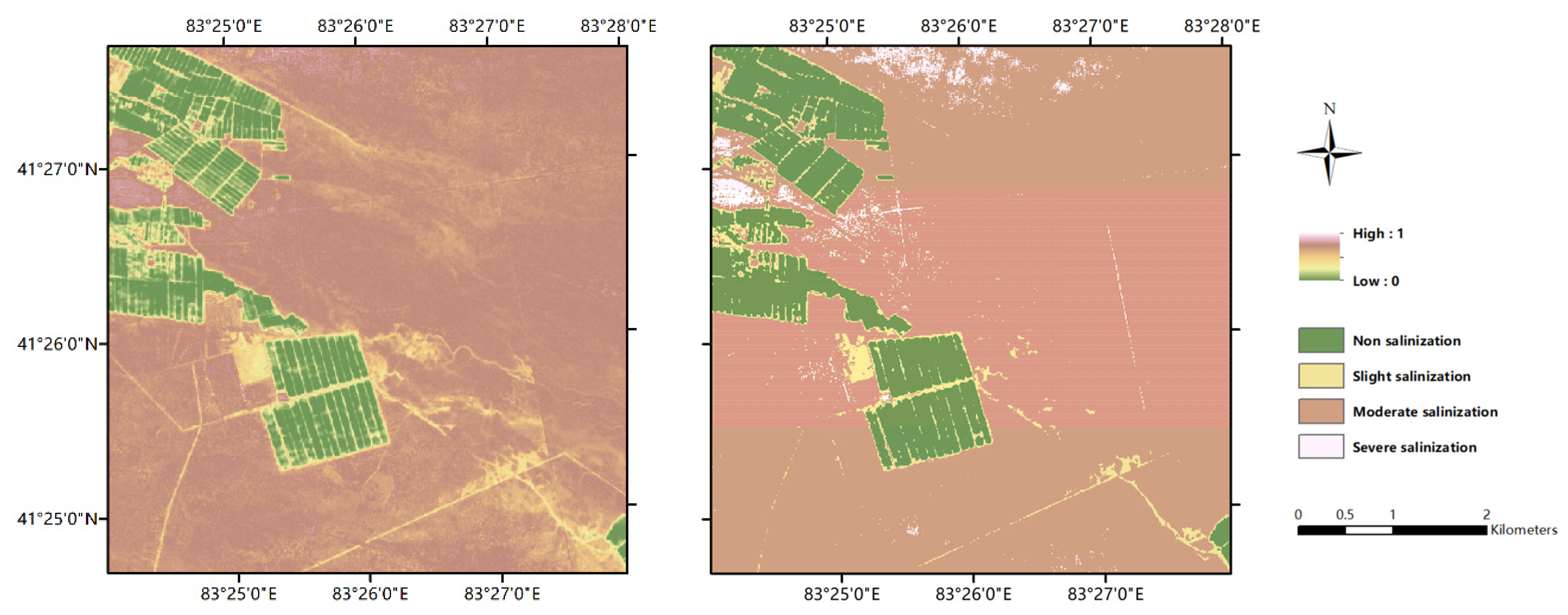
3.5. Spatial Distribution of Salinization in Research Area
4. Discussion
4.1. Advantages of Proposed Model Based on SENTINEL-2 Images and Its Red-Edge Bands
4.2. Spatial Distribution Rule of Salinization in Research Area
4.3. Research Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bian, L.; Wang, J.; Guo, B.; Cheng, K.; Wei, H. Remote Sensing Extraction of Soil Salinity in Yellow River Delta Kenli County based on Feature Space. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2020, 35, 211–218. [Google Scholar]
- Gorji, T.; Sertel, E.; Tanik, A. Monitoring soil salinity via remote sensing technology under data scarce conditions: A case study from Turkey. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 74, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, M.; Geng, R.; Li, X.; Yin, X.; Wei, G. Salinity Characteristics Analysis of Saline Alkali Soil in Yinbei Irrigation District of Ningxia. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2021, 37, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Ruan, B.; Chen, H.; Guan, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, N.; Li, Y. Characterizing the spatiotemporal evolution of soil salinization in Hetao Irrigation District (China) using a remote sensing approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 6805–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yao, R.; Wang, X.; Xie, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, L.; Sun, R. Research on Salt-affected Soils in China: History, Status Quo and Prospect. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2022, 59, 10–27. [Google Scholar]
- Perri, S.; Molini, A.; Hedin, L.O.; Porporato, A. Contrasting effects of aridity and seasonality on global salinization. Nat. Geosci. 2022, 15, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litalien, A.; Zeeb, B. Curing the earth: A review of anthropogenic soil salinization and plant-based strategies for sustainable mitigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ding, X.; Zheng, D.; Shi, N.; Liu, G.; Sun, Z. Effect of Different Plants Plantation on Amelioration of Uncultivated Saline Wasteland, Soils Phosphorus Fraction and Availability in the Yellow River Delta. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 35, 278–284, 293. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, S.Y.; Zheng, Q.H. Responses of NPP of salinized meadows to global change in hyperarid regions. J. Arid Environ. 2002, 50, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Q.; Han, Z.; Wang, G. Research Progress on Soil Salinization in Arid Irrigated Area of Northwestern China. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2011, 27, 246–250. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Ding, J.; Yu, D.; Teng, D.; He, B.; Chen, X.; Ge, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; et al. Machine learning-based detection of soil salinity in an arid desert region, Northwest China: A comparison between Landsat-8 OLI and Sentinel-2 MSI. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 136092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allbed, A.; Kumar, L. Soil salinity mapping and monitoring in arid and semi-arid regions using remote sensing technology: A review. Adv. Remote Sens. 2013, 2, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focardi, S.; Loiselle, S.A.; Mazzuoli, S.; Bracchini, L.; Dattilo, A.M.; Rossi, C. Satellite-based indices in the analysis of land cover for municipalities in the province of Siena, Italy. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 86, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamsi, S.R.F.; Zare, S.; Abtahi, S.A. Soil salinity characteristics using moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) images and statistical analysis. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2013, 59, 471–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ding, J.; Wu, M. Remote sensing model of soil salinization based on NDVI-SI characteristic space. Trans. CSAE 2010, 26, 168–173. [Google Scholar]
- Metternicht, G.I.; Zinck, J.A. Remote sensing of soil salinity: Potentials and constraints. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, x. Study on Soil Salt Inversion Based on Multisource Data and Machine Learning Algorithm in the Ebinur Lake Wetland National Nature Reserve. Master’s Thesis, Xinjiang University, Urumqi, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Biswas, A.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, R.; Hu, J.; Hu, B.; Shi, Z. Estimating soil salinity from remote sensing and terrain data in southern Xinjiang Province, China. Geoderma 2019, 337, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howari, F.M.; Goodell, P.C.; Miyamoto, S. Spectral properties of salt crusts formed on saline soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourati, H.T.; Bouaziz, M.; Benzina, M.; Bouaziz, S. Modeling of soil salinity within a semi-arid region using spectral analysis. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 11175–11182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azabdaftari, A.; Sunar, F. Soil salinity mapping using multitemporal Landsat data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, 41, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Ren, H.; Huang, C. Estimating Soil Salinity in the Yellow River Delta, Eastern China-An Integrated Approach Using Spectral and Terrain Indices with the Generalized Additive Model. Pedosphere 2016, 26, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douaoui, A.E.K.; Nicolas, H.; Walter, C. Detecting salinity hazards within a semiarid context by means of combining soil and remote-sensing data. Geoderma 2006, 134, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wilson, C.; Shannon, M.C. Interpretation of salinity and irrigation effects on soybean canopy reflectance in visible and near-infrared spectrum domain. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 811–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahiaoui, I.; Douaoui, A.; Zhang, Q.; Ziane, A. Soil salinity prediction in the Lower Cheliff plain (Algeria) based on remote sensing and topographic feature analysis. J. Arid Land 2015, 7, 794–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Huang, Y. Desertification remote sensing information extraction from Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and evolution analysis. Arid Land Geogr. 2006, 29, 710–717. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Yao, Y.; Wang, F. Detecting soil salinization in arid regions using spectral feature space derived from remote sensing data. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 4620–4631. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Qian, J.; Yue, H. Comparison and evaluation of different dryness indices based on vegetation indices-land surface temperature/albedo feature space. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 2791–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Ding, J.; Ge, X.; He, B.; Wang, J.; Xie, B.; Zhang, Z. Using spatiotemporal fusion algorithms to fill in potentially absent satellite images for calculating soil salinity: A feasibility study. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 111, 102839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Ding, J.; Han, L.; Ge, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Qin, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y. Exploring PlanetScope Satellite Capabilities for Soil Salinity Estimation and Mapping in Arid Regions Oases. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SentiWiki. Sentinel-2. Available online: https://sentiwiki.copernicus.eu/web/sentinel-2 (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- SentiWiki. S2 Mission. Available online: https://sentiwiki.copernicus.eu/web/s2-mission#S2-Mission-Acquisition-Resolutions (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- European Space Agency. Copernicus Open Access Hub. Available online: https://scihub.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Team of ENVI development. ENVI, version 5.6; Harris Geospatial Solutions: Boulder, CO, USA, 2020.
- European Space Agency. SNAP, version 9.0; ESA: Paris, France, 2022.
- Ge, X.; Ding, J.; Teng, D.; Wang, J.; Huo, T.; Jin, X.; Wang, J.; He, B.; Han, L. Updated soil salinity with fine spatial resolution and high accuracy: The synergy of Sentinel-2 MSI, environmental covariates and hybrid machine learning approaches. Catena 2022, 212, 106054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ding, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q. Sensitivity analysis of soil salinity and vegetation indices to detect soil salinity variation by using Landsat series images:applications in different oases in Xinjiang, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 5007–5022. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Zang, W.; Yang, F.; Han, B.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; He, T.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; et al. Spatial and temporal change patterns of net primary productivity and its response to climate change in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau of China from 2000 to 2015. J. Arid Land 2020, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Lu, M.; Fan, Y.; Wu, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C. A novel remote sensing monitoring index of salinization based on three-dimensional feature space model and its application in the Yellow River Delta of China. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2023, 14, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Tashpolat, N. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Soil Salinity in Weigan River-Kuqa River Delta Oasis Based on Two-Dimensional Feature Space. Water 2023, 15, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Yang, F. A novel feature space monitoring index of salinisation in the Yellow River Delta based on SENTINEL-2B MSI images. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 2303–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Zang, W.; Luo, W.; Wen, Y.; Yang, F.; Han, B.; Fan, Y.; Chen, X.; Qi, Z.; Wang, Z.; et al. Detection model of soil salinization information in the Yellow River Delta based on feature space models with typical surface parameters derived from Landsat8 OLI image. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2020, 11, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wang, L.; Xu, H. A Comparative Study of Different Red Edge Indices for Remote Sensing Detection of Urban Grassland Health Status. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2017, 19, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P. Remote sensing monitoring of desertification in Naiman Banner based on Albedo-MSAVI feature space. Sci. Technol. Innov. Inf. 2021, 32, 78–81. [Google Scholar]
- Team of Anaconda development. Anaconda, Version 3.0; Anaconda Incorporated: Austin, TX, USA, 2014.
- Sandholt, I.; Rasmussen, K.; Andersen, J. A simple interpretation of the surface temperature/vegetation index space for assessment of surface moisture status. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 79, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team of ArcGIS development. ArcGIS, version 10.8; Environmental Systems Research Institute: Redlands, CA, USA, 2016.
- Agricultural and Animal Husbandry Water Resources Division, Water Resources Department of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. Available online: https://slt.xinjiang.gov.cn/xjslt/c114459/zwgk.shtml (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Yao, Y. Evaluation and Scale Effect Analysis of Soil Salinity in Dry and Wet Seasons of the Oasia Using Remote Sensing and Electromagnetic Induction Instruments. Master’s Thesis, Xinjiang University, Urumqi, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Ding, J.; Wei, W. Soil salinization monitoring based on Radar data. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2019, 31, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Yang, F.; Fan, Y.; Han, B.; Chen, S.; Yang, W. Dynamic monitoring of soil salinization in Yellow River Delta utilizing MSAVI-SI feature space models with Landsat images. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, X.; Ye, P.; Wu, H.; Wang, T. Remote sensing monitoring of salinization in Hetao irrigation district based on SI-MSAVI feature space. Remote Sens. Land Resour 2020, 1, 169–175. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Xin, P.; Hong, L. Effect of evaporation on soil salinization caused by ocean surge inundation. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 126200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Ding, J.; Li, X.; Yang, A. Hyperspectral Characteristics Analysis and Modeling of Soil Salinization. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2016, 47, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Zovko, M.; Romic, D.; Colombo, C.; Di Iorio, E.; Romic, M.; Buttafuoco, G.; Castrignano, A. A geostatistical Vis-NIR spectroscopy index to assess the incipient soil salinization in the Neretva River valley, Croatia. Geoderma 2018, 332, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahbeni, G.; Ngabire, M.; Musyimi, P.K.; Szekely, B. Challenges and Opportunities in Remote Sensing for Soil Salinization Mapping and Monitoring: A Review. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez Flores, J.L.; Ramos Rodriguez, M.; Gonzalez Jimenez, A.; Farzamian, M.; Herencia Galan, J.F.; Salvatierra Bellido, B.; Cermeno Sacristan, P.; Vanderlinden, K. Depth-Specific Soil Electrical Conductivity and NDVI Elucidate Salinity Effects on Crop Development in Reclaimed Marsh Soils. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, K.; Qian, H.; Gao, Y.; Fang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, W.; Ren, W. Characterization of soil salinization and its driving factors in a typical irrigation area of Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimi, S.; Ayoubi, S.; Zeraatpisheh, M.; Dematte, J.A.M. Ground Observations and Environmental Covariates Integration for Mapping of Soil Salinity: A Machine Learning-Based Approach. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.; Jin, J.; Han, J.; Wang, X.; Song, Z.; Wei, G. Estimating soil salinity with different fractional vegetation cover using remote sensing. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 597–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Khan, S.; Hussain, N.; Hanjra, M.A.; Akbar, S. Characterizing soil salinity in irrigated agriculture using a remote sensing approach. Phys. Chem. Earth 2013, 55–57, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, C.; Chang, Y. Spatio-temporal Evolution of Saline-alkali Cultivated Land and Its Impact on Productivity in Hetao Plain of Inner Mongolia. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2019, 39, 827–835. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Gao, M.; Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Bi, M. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Soil Salinization and Its Impact on Cultivated Land Productivity in the BOHAI Rim Region. Water 2023, 15, 2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Categories | Typical Indices | Calculations Formulas | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetation indices | ENDVI | [38] | |
| MSAVI | [38] | ||
| NDVI | [39] | ||
| GARI | [40] | ||
| Other indices | IFe2O3 | [39] | |
| Albedo | [39] | ||
| WI | [42] | ||
| NDWI | [40] | ||
| Salinity indices | SI | [40] | |
| SI2 | [40] | ||
| SI3 | [40] | ||
| NDSI | [40] | ||
| Red-edge vegetation indices | NDre1 | [41] | |
| NDre2 | [41] | ||
| IRECI | [43] | ||
| TCARI | [30] | ||
| Red-edge salinity indices | RNDSI | [30] | |
| RSI | [30] | ||
| RS6 | [30] | ||
| RS5 | [30] |
| Typical Parameter | Correlation Coefficient | Typical Parameter | Correlation Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|
| ENDVI | −0.8092 | SI3 | 0.8201 |
| MSAVI | −0.8210 | NDSI | 0.7724 |
| NDVI | −0.8201 | NDre1 | −0.8144 |
| GARI | −0.7878 | NDre2 | −0.8019 |
| IFe2O3 | 0.8206 | IRECI | −0.7793 |
| Albedo | −0.0568 | TCARI | −0.7868 |
| WI | −0.8079 | RNDSI | 0.8213 |
| NDWI | 0.8210 | RSI | 0.7719 |
| SI | 0.7739 | RS6 | −0.8019 |
| SI2 | −0.6523 | RS5 | 0.7718 |
| Feature Space | Formula | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MSAVI_SI3 | 0.7882 | 3.5386 | |
| MSAVI_RNDSI | 0.7998 | 3.3444 | |
| NDWI_MSAVI | 0.7905 | 3.5002 | |
| NDre1_SI3 | 0.7740 | 3.7745 | |
| NDre1_RNDSI | 0.7808 | 3.6614 | |
| NDWI_NDre1 | 0.7785 | 3.7000 | |
| NDWI_SI3 | 0.7736 | 3.7813 | |
| NDWI_RNDSI | 0.7901 | 3.5067 |
| Salinization Level | Features | Soil Salt Content (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| Non-salinization | Farmland, woodland, high-coverage grassland, river | ≪5 |
| Slight salinization | Parts of farmland, grassland, bushwood | 5~25 |
| Moderate salinization | Sparse bushwood and grassland, Gobi | 25~50 |
| Severe salinization | Surface salt crust | ≫50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tashpolat, N.; Reheman, A. Monitoring of Soil Salinity in the Weiku Oasis Based on Feature Space Models with Typical Parameters Derived from Sentinel-2 MSI Images. Land 2025, 14, 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14020251
Tashpolat N, Reheman A. Monitoring of Soil Salinity in the Weiku Oasis Based on Feature Space Models with Typical Parameters Derived from Sentinel-2 MSI Images. Land. 2025; 14(2):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14020251
Chicago/Turabian StyleTashpolat, Nigara, and Abuduwaili Reheman. 2025. "Monitoring of Soil Salinity in the Weiku Oasis Based on Feature Space Models with Typical Parameters Derived from Sentinel-2 MSI Images" Land 14, no. 2: 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14020251
APA StyleTashpolat, N., & Reheman, A. (2025). Monitoring of Soil Salinity in the Weiku Oasis Based on Feature Space Models with Typical Parameters Derived from Sentinel-2 MSI Images. Land, 14(2), 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14020251






