A Village-Scale Study Regarding Landscape Evolution and Ecological Effects in a Coastal Inner Harbor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
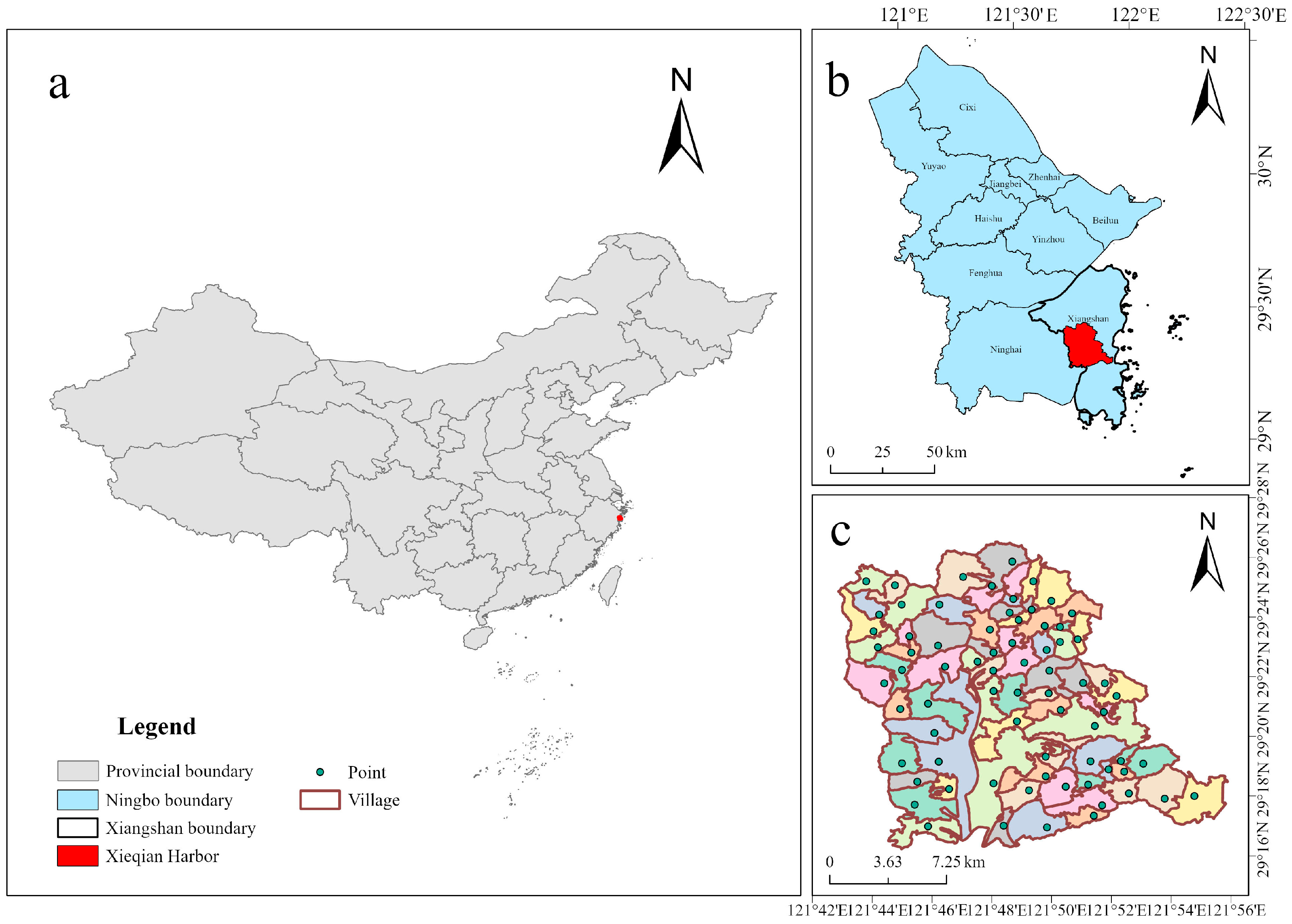
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
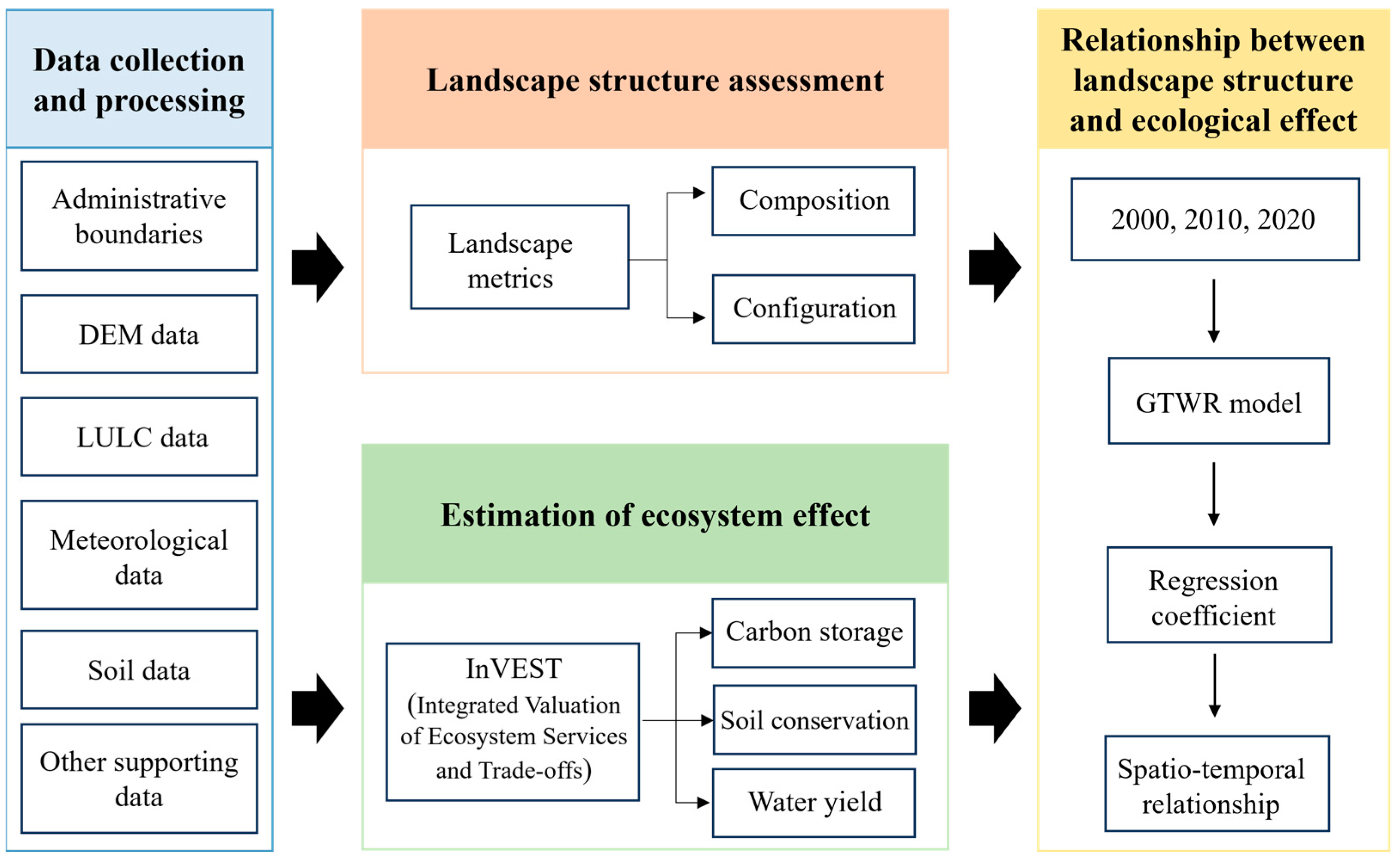
2.3. Research Frameworks
2.4. Research Methods
2.4.1. Quantification of Landscape Patterns
2.4.2. Estimation of Ecological Effects
2.4.3. Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression Model (GTWR)
3. Results
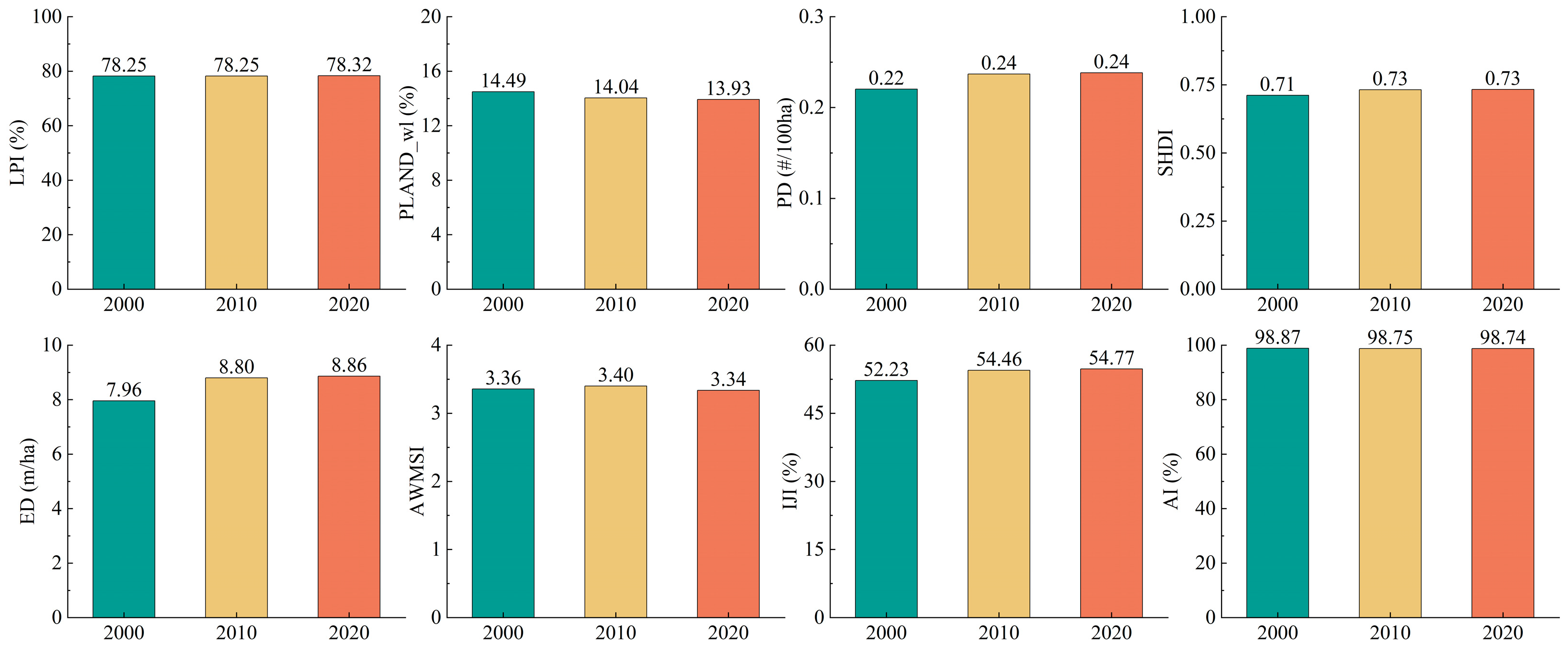
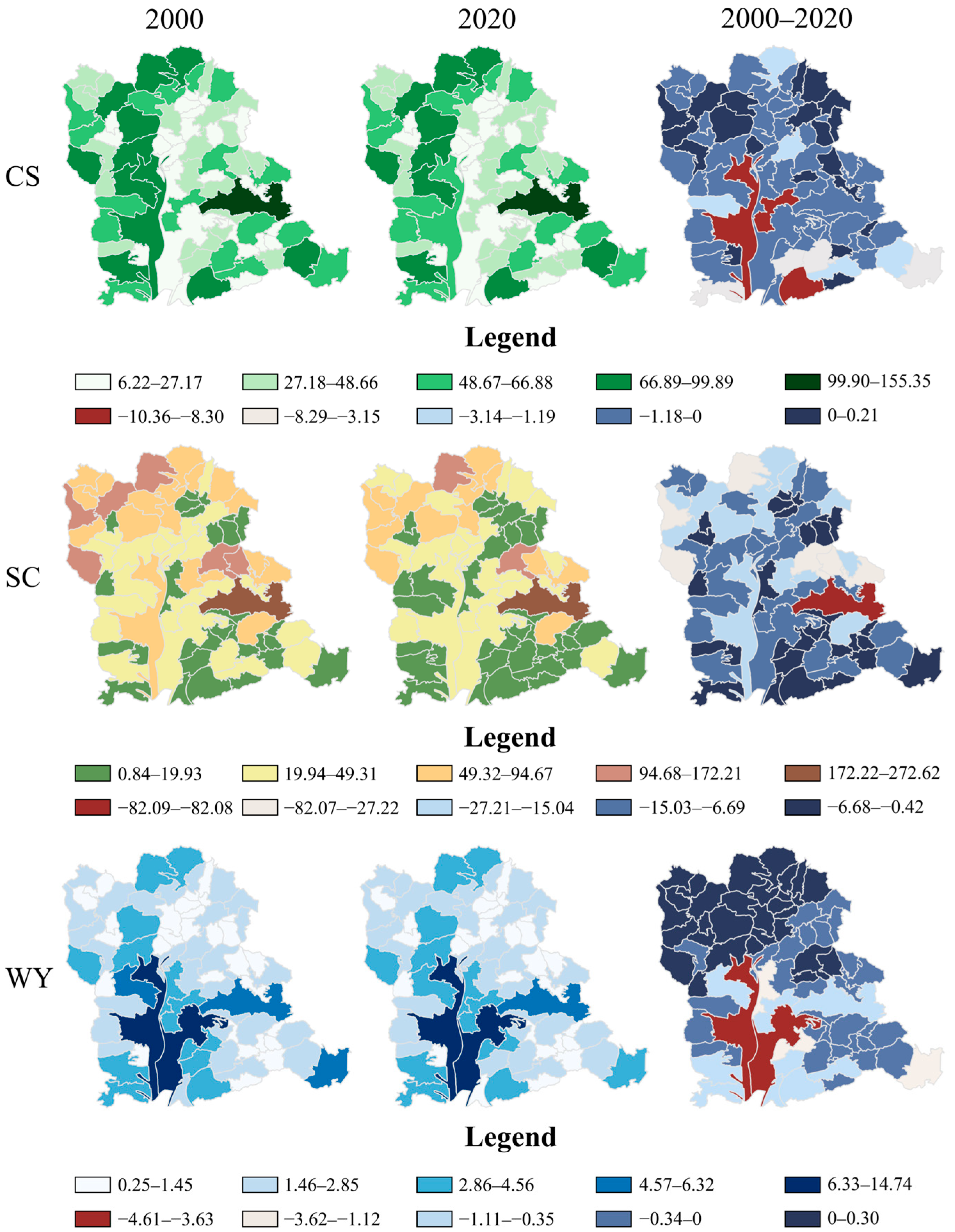
3.1. Changes in Landscape Patterns from 2000 to 2020
3.2. Changes in Ecological Effects from 2000 to 2020
3.3. Spatiotemporal Relationships Between Landscape Structure and Ecological Effects
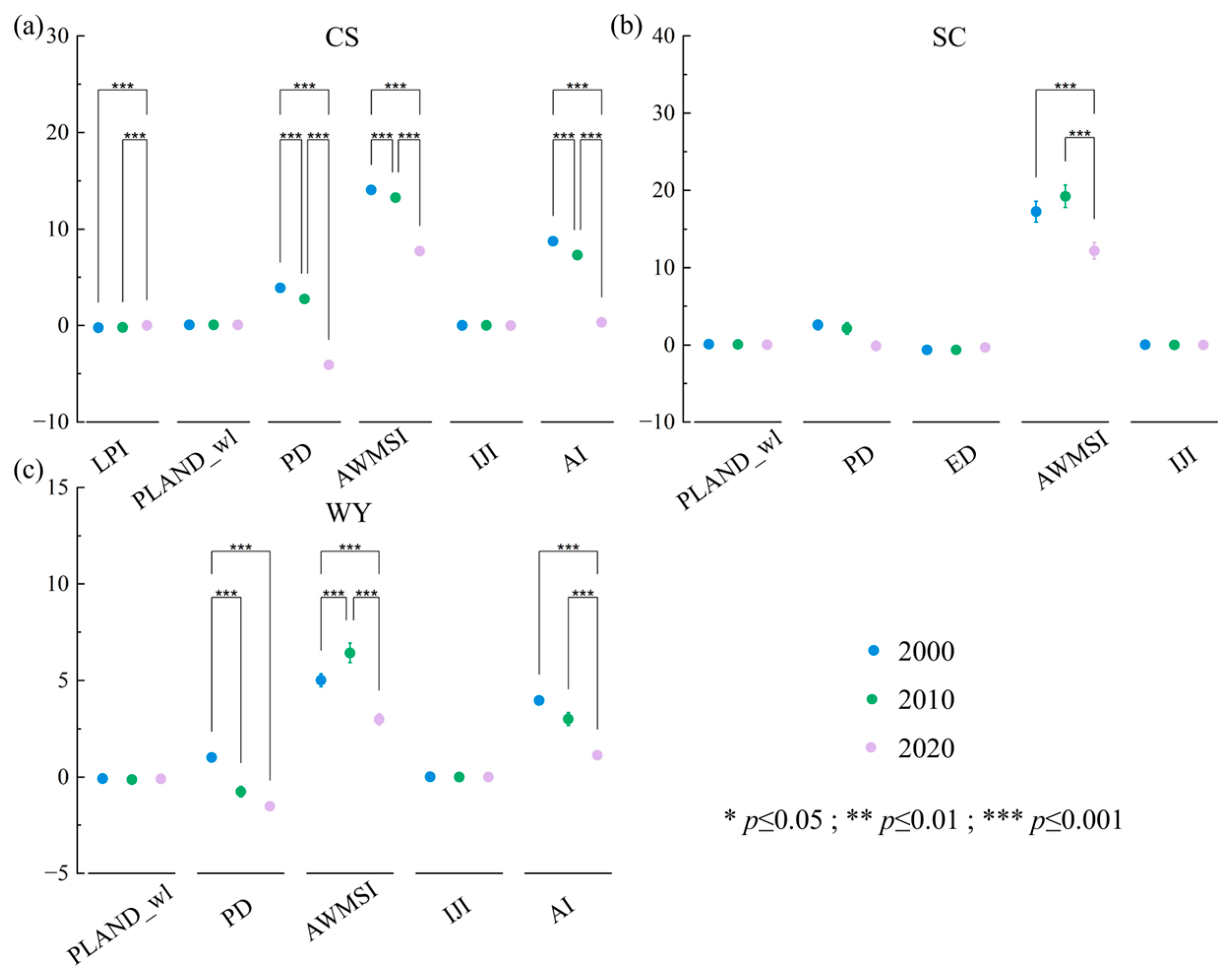
3.3.1. Variable Selection
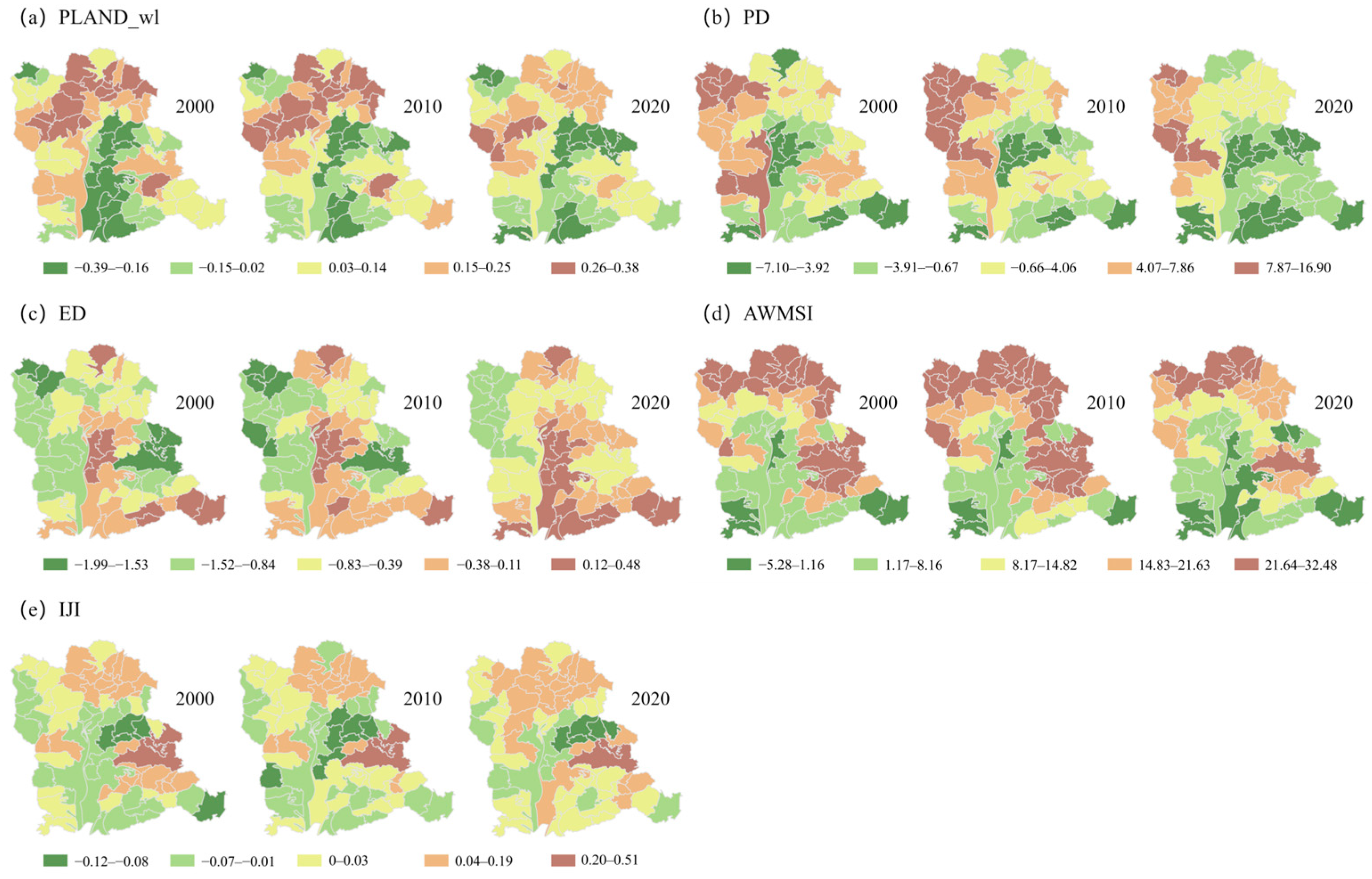
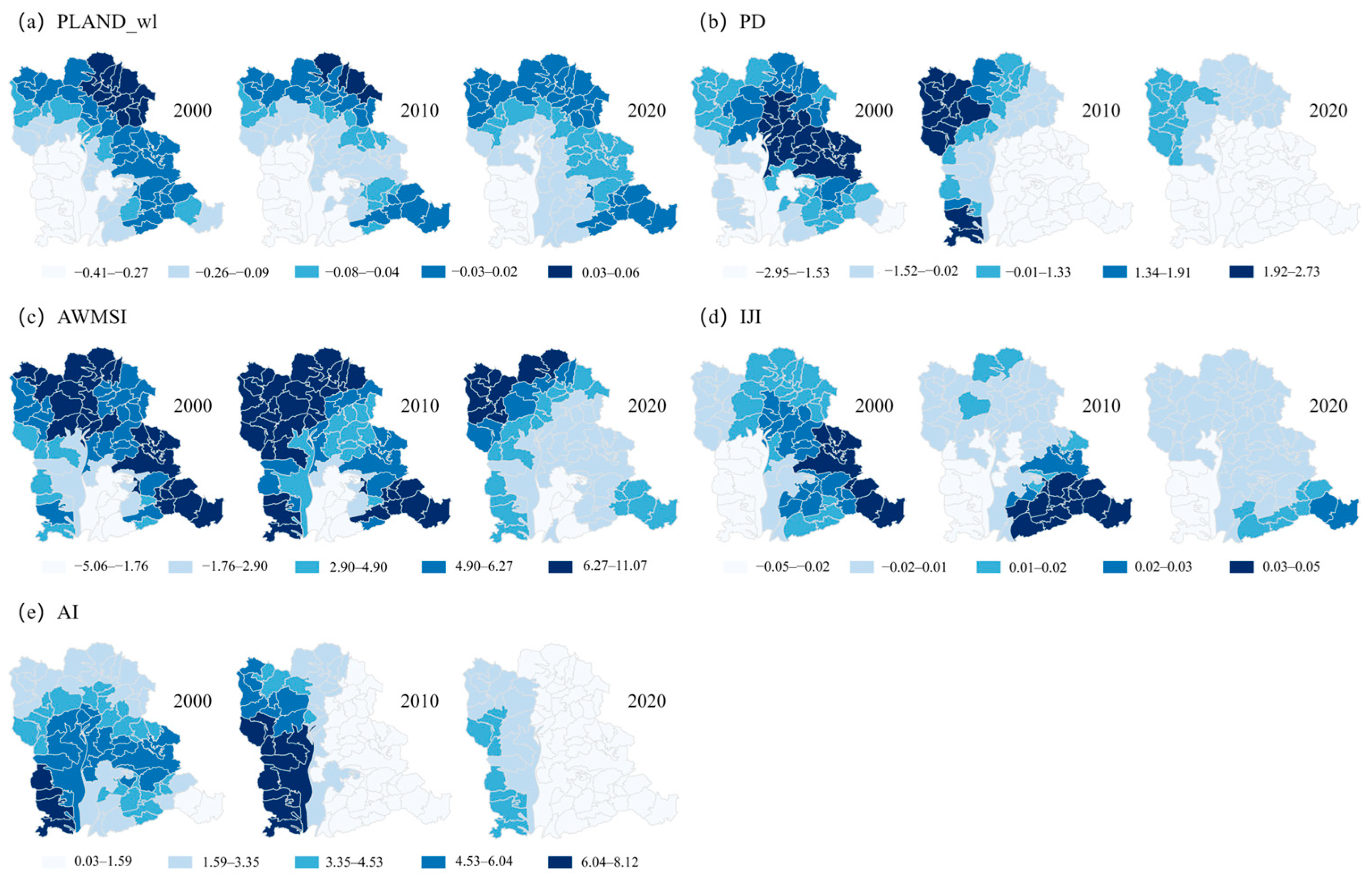
3.3.2. Spatiotemporal Change Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Metrics | Abbreviation (Scale) | Annotation |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Area and Quantity | ||
| Largest Patch Index | LPI (Landscape and Class) | This index expresses the proportion of the largest patch area in a specific landscape type to the total landscape area of the whole region (0 < LPI < 100); if the maximum patch area in a given landscape type gradually shrinks, the LPI tends to 0, whereas if it gradually expands and finally occupies the whole region, the LPI is close to 100 [81,82]. |
| Percentage of Landscape | PLAND (Class) | This index is used to quantify the proportion of the abundance of a particular landscape patch category to that of the regional overall landscape (0 < PLAND < 100) [83]. |
| Patch Density | PD (Class) | This index is used to quantify the number of patches of a particular landscape patch category per unit area of the regional overall landscape (0 < PD < ∞). This index provides insight into the fragmentation and spatial distribution of landscape patches, with higher values indicating greater fragmentation and a more heterogeneous landscape structure [84,85]. |
| (2) Shape and Edge | ||
| Edge Density | ED (Landscape and Class) | This index reflects the length of the edges per unit area [86]. |
| Area-Weighted Mean Patch Shape Index | AWMSI (Class) | This index is used to quantify the complexity of the shape of landscape patches, taking into account the size of each patch. This index provides insight into the geometric complexity and irregularity of patch shapes within a landscape, with higher values indicating more complex shapes [87]. |
| (3) Landscape Diversity | ||
| Shannon’s Diversity Index | SHDI (Landscape) | This index is based on the general knowledge that the degree of regional land exploitation is proportional to that of land diversification; the higher the index, the higher the degree of regional land exploitation and development [88,89,90]. |
| (4) Spatial Distribution | ||
| Interspersion and Juxtaposition Index | IJI (Landscape and Class) | This metric is applied to reflect the distribution of patch adjacency, isolating the interspersion or intermixing of landscape patches (0 < IJI < 100); IJI is close to 0 if the patch is adjacent to only one other patch, whereas it is close to 100 if the patch is equally adjacent to all other patches [43,91]. |
| Aggregation Index | AI (Class) | This index is performed from the adjacency matrix, reflecting the frequency of different landscape patch types occurring side-by-side in a regional landscape (including adjacencies for the same landscape type) (0 ≤ AI ≤ 100); it increases as the focal patch type is increasingly aggregated and tends to 100 when the patch type is maximally aggregated into a single and compact patch [92]. |
| Input Data | Data Source | |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon storage | LULC | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (http://www.resdc.cn/) |
| Carbon pools | Reference to the relevant literature [55] | |
| Soil conservation | DEM | Geospatial data cloud (http://www.gscloud.cn/) |
| Precipitation | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (http://www.resdc.cn/) | |
| Root depth, soil texture, and organic content | Harmonized World Soil Database v 1.2 (https://gaez.fao.org/pages/hwsd) | |
| LULC | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (http://www.resdc.cn/) | |
| Biophysical table | Reference to the relevant literature [93] | |
| Watersheds | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (http://www.resdc.cn/) | |
| Water yield | Precipitation | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (http://www.resdc.cn/) |
| Potential evapotranspiration | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (http://www.resdc.cn/) | |
| Root-restricting layer depth | (http://globalchange.bnu.edu.cn/research/cdtb.jsp, accessed on 7 January 2025) |
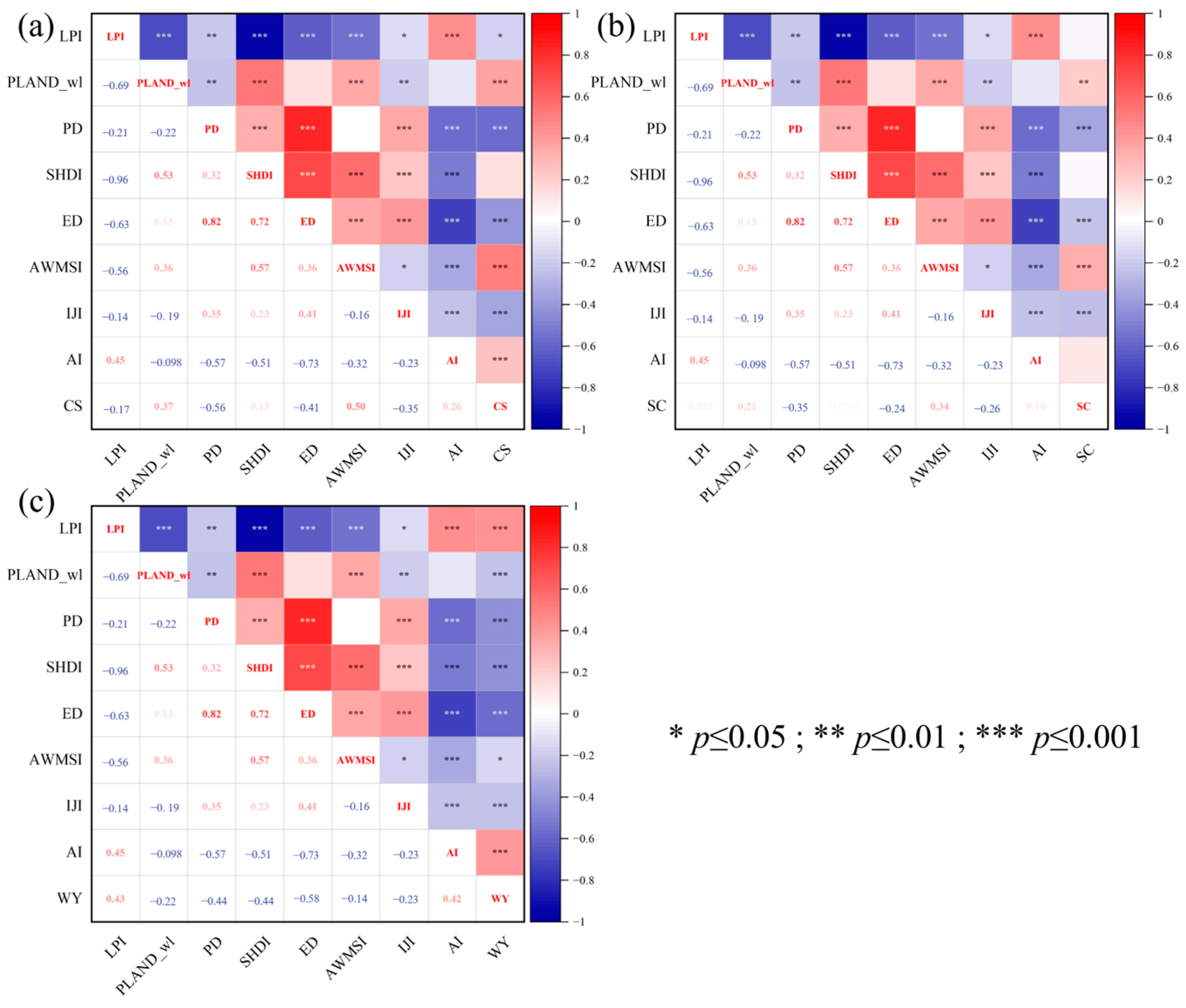
| LPI | PLAND_wl | PD | SHDI | ED | AWMSI | IJI | AI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIF | VIF | VIF | VIF | VIF | VIF | VIF | VIF | |
| CS | 6.250 | 3.034 | 7.263 | NA | 14.724 | 1.945 | 1.613 | 2.189 |
| SC | NA | 1.692 | 6.198 | NA | 8.037 | 1.884 | 1.592 | NA |
| WY | 34.218 | 4.132 | 7.282 | 25.834 | 14.726 | 2.065 | 1.662 | 2.195 |
References
- Hein, C. Port Cities and Urban Waterfronts: How Localized Planning Ignores Water as a Connector. WIREs Water 2016, 3, 419–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Ouyang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X. Construction of an Eco-Island: A Case Study of Chongming Island, China. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2008, 51, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Rao, K.; Ramanathan, A.L. A Systematic Review on the Impact of Urbanization and Industrialization on Indian Coastal Mangrove Ecosystem. In Coastal Ecosystems; Madhav, S., Nazneen, S., Singh, P., Eds.; Coastal Research Library; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 38, pp. 175–199. ISBN 978-3-030-84254-3. [Google Scholar]
- Sempere-Valverde, J.; Guerra-García, J.M.; García-Gómez, J.C.; Espinosa, F. Coastal Urbanization, an Issue for Marine Conservation. In Coastal Habitat Conservation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 41–79. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, J.; Gao, S. Long-Term Reclamation of Tidal Flats of Chongming Island and Ecological Security of Yangtze Estuary, China. Reg. Environ. Change 2024, 24, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Li, R.; Chi, X.; Chen, N.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, F. Island Urbanization and Its Ecological Consequences: A Case Study in the Zhoushan Island, East China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 76, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latimer, J.S.; Boothman, W.S.; Pesch, C.E.; Chmura, G.L.; Pospelova, V.; Jayaraman, S. Environmental Stress and Recovery: The Geochemical Record of Human Disturbance in New Bedford Harbor and Apponagansett Bay, Massachusetts (USA). Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 313, 153–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapin, F.S.; Carpenter, S.R.; Kofinas, G.P.; Folke, C.; Abel, N.; Clark, W.C.; Olsson, P.; Smith, D.M.S.; Walker, B.; Young, O.R. Ecosystem Stewardship: Sustainability Strategies for a Rapidly Changing Planet. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, W.R.; Brandon, K.; Brooks, T.M.; Costanza, R.; Da Fonseca, G.A.; Portela, R. Global Conservation of Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. BioScience 2007, 57, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yan, G.; Ma, M.; Zhou, S.; Qian, Y. Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of China’s Ecological Civilization Progress after Implementing National Conservation Strategy. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 124886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Shi, H.; Zheng, W.; Wang, E. Archipelagic Landscape Patterns and Their Ecological Effects in Multiple Scales. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2018, 152, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Huang, G. Urban Watershed Ecosystem Health Assessment and Ecological Management Zoning Based on Landscape Pattern and SWMM Simulation: A Case Study of Yangmei River Basin. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 95, 106794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Yu, D.; Li, X. Impacts of Changes in Climate and Landscape Pattern on Soil Conservation Services in a Dryland Landscape. Catena 2023, 222, 106869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, S.; Wen, Y.; He, C.; Wang, X.; Sheng, L.; Guo, Y.; Cao, Y. Projecting the Response of Ecological Risk to Land Use/Land Cover Change in Ecologically Fragile Regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 169908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, J.; Deng, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity in Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs and Their Drivers in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, China. Landsc. Ecol. 2024, 39, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Exploring the Spatial and Temporal Driving Mechanisms of Landscape Patterns on Habitat Quality in a City Undergoing Rapid Urbanization Based on GTWR and MGWR: The Case of Nanjing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Adams, J.; Beerling, D.J.; Beringer, T.; Calvin, K.V.; Fuss, S.; Griscom, B.; Hagemann, N.; Kammann, C.; Kraxner, F.; et al. Land-Management Options for Greenhouse Gas Removal and Their Impacts on Ecosystem Services and the Sustainable Development Goals. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2019, 44, 255–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, L.; Ayres, M.P.; Jactel, H. Impact of Stand and Landscape Management on Forest Pest Damage. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2022, 67, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Deng, G.; Wang, L.-J.; Hu, H.; Fang, X.; Jiang, J. Telecoupling between Urban Expansion and Forest Ecosystem Service Loss through Cultivated Land Displacement: A Case Study of Zhejiang Province, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 357, 120695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, D.; Cai, Y.; Liu, M. Coupling Coordination Analysis and Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity between Ecosystem Services and New-Type Urbanization: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J. Quantifying the Spatial Impact of Landscape Fragmentation on Habitat Quality: A Multi-Temporal Dimensional Comparison between the Yangtze River Economic Belt and Yellow River Basin of China. Land Use Policy 2023, 125, 106463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Wu, W.; Yu, L. Effects of Landscape Pattern Change on Ecosystem Services and Its Interactions in Karst Cities: A Case Study of Guiyang City in China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, J.; Xie, Z.; Zhao, M.; Wang, E. Evaluating Landscape Ecological Sensitivity of an Estuarine Island Based on Landscape Pattern across Temporal and Spatial Scales. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wu, B.; Barry, M. Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression for Modeling Spatio-Temporal Variation in House Prices. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Fung, T.; Yu, H.; Mei, C.; Leung, Y.; Zhou, Y. Multiscale Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression with a Unilateral Temporal Weighting Scheme and Its Application in the Analysis of Spatiotemporal Characteristics of House Prices in Beijing. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2021, 35, 2262–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Crespo, R.; Yao, J. Geographical and Temporal Weighted Regression (GTWR): Geographical and Temporal Weighted Regression. Geogr. Anal. 2015, 47, 431–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Zhang, L.; Duan, W.; Zhen, Z. Global and Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression Models for Modeling PM2.5 in Heilongjiang, China from 2015 to 2018. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hong, S. Urban Expansion Patterns and Their Driving Forces Based on the Center of Gravity-GTWR Model: A Case Study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, M.; Huang, X.; Song, X.; Cai, B.; Tang, R.; Sun, J.; Han, Z.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y. Improving Prediction of Soil Heavy Metal (Loid) Concentration by Developing a Combined Co-Kriging and Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression (GTWR) Model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 468, 133745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Xie, Z.; Wu, H.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, B.; Wan, W. Exploring the Interrelations and Driving Factors among Typical Ecosystem Services in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Gao, Y.; Chen, C. CLSER: A New Indicator for the Social-Ecological Resilience of Coastal Systems and Sustainable Management. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 435, 140564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Liang, D.; Lu, N. Landscape Ecology: Coupling of Pattern, Process, and Scale. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Yue, W.; Fang, B.; Feng, S. Spatiotemporal Response Characteristics and Geographic Detection Mechanisms of Ecosystem Service Values in the Dabie Mountains from 1970 to 2015. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 1904–1920. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Turner, M.G. Landscape Ecology In North America: Past, Present, And Future. Ecology 2005, 86, 1967–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjallingii, S.P. Ecology on the Edge: Landscape and Ecology between Town and Country. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2000, 48, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhao, H.; Li, L.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, H.; Bao, C. Spatial Scale Effects of Environmental Impact Assessment in Regional Planning: Case Studies of Gaoqiao Town and Pudong New Area in Shanghai. Prog. Geogr. 2015, 34, 739–748. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Q.; Gao, G.; Xi, H.; Wang, F.; Cheng, X.; Ou, W.; Tao, Y. An Integrated Evaluation Framework for Multiscale Ecological Protection and Restoration Based on Multi-Scenario Trade-Offs of Ecosystem Services: Case Study of Nanjing City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 140, 108962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.D.; Yang, S. Multi-Scale Studies and the Ecological Neighborhood. Curr. Landsc. Ecol. Rep. 2016, 1, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S. China Multi-Period Land Use Remote Sensing Monitoring Dataset (CNLUCC); Resource and Environment Science and Data Center: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wang, H.; Huang, A.; Xu, Y.; Lu, L.; Ji, Z. Identification and Spatial-Temporal Evolution of Rural “Production-Living-Ecological” Space from the Perspective of Villagers’ Behavior–A Case Study of Ertai Town, Zhangjiakou City. Land Use Policy 2021, 106, 105457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Qiao, W.; Gao, B.; Chen, Y. Unveiling Spatial Heterogeneity of Ecosystem Services and Their Drivers in Varied Landform Types: Insights from the Sichuan-Yunnan Ecological Barrier Area. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 442, 141158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Zhang, J.; Han, H.; Cheng, X.; Kang, F. Study on the Impact of Vegetation Change on Ecosystem Services in the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corry, R.C.; Nassauer, J.I. Limitations of Using Landscape Pattern Indices to Evaluate the Ecological Consequences of Alternative Plans and Designs. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2005, 72, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.X.; Li, J. The Correlation Analysis on the Landscape Pattern Index and Hydrological Processes in the Yanhe Watershed, China. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Yang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gao, M. The Spatial Granularity Effect, Changing Landscape Patterns, and Suitable Landscape Metrics in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, 1995–2015. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plexida, S.G.; Sfougaris, A.I.; Ispikoudis, I.P.; Papanastasis, V.P. Selecting Landscape Metrics as Indicators of Spatial Heterogeneity—A Comparison among Greek Landscapes. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 26, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Bo, J.; Li, X.; Fang, F.; Cheng, W. Identifying Key Landscape Pattern Indices Influencing the Ecological Security of Inland River Basin: The Middle and Lower Reaches of Shule River Basin as an Example. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Cai, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q. Analyzing the Influence of Landscape Pattern Change on Ecological Water Requirements in an Arid/Semiarid Region of China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Chang, D.; Xiang, X.; Wang, J. Can Ecological Landscape Pattern Influence Dry-Wet Dynamics? A National Scale Assessment in China from 1980 to 2018. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jing, Y.; Han, S. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Land Use/Land Cover Change and Water Yield Evaluation Coupled with the GMOP-PLUS-InVEST Model: A Case Study of the Nansi Lake Basin in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 110926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-F.; Lin, Y.-P.; Chiang, L.-C.; Huang, T. Assessing Highway’s Impacts on Landscape Patterns and Ecosystem Services: A Case Study in Puli Township, Taiwan. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 128, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qu, M.; Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Cao, Y. Quantifying Landscape Pattern and Ecosystem Service Value Changes: A Case Study at the County Level in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 23, e01110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, E.; Deng, J.; Zhou, M.; Gan, M.; Jiang, R.; Wang, K.; Shahtahmassebi, A. Carbon Emissions Induced by Land-Use and Land-Cover Change from 1970 to 2010 in Zhejiang, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Song, R.; Sun, S.; Li, Y.; Hu, K. Land Use/Land Cover Change and Its Impact on Ecosystem Carbon Storage in Coastal Areas of China from 1980 to 2050. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Liao, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, K. Multiscale Analysis of the Effects of Landscape Pattern on the Trade-Offs and Synergies of Ecosystem Services in Southern Zhejiang Province, China. Land 2023, 12, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.; Boardman, J. The New Assessment of Soil Loss by Water Erosion in Europe. Panagos P. et al., 2015 Environmental Science & Policy 54, 438–447—A Response. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 58, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Lü, Y.; Fu, B.; Zhang, X. Landscape Pattern and Ecosystem Services Are Critical for Protected Areas’ Contributions to Sustainable Development Goals at Regional Scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Ye, X.; Ren, F.; Du, Q. Check-in Behaviour and Spatio-Temporal Vibrancy: An Exploratory Analysis in Shenzhen, China. Cities 2018, 77, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. The Effect of Urbanization on Environmental Pollution in Rapidly Developing Urban Agglomerations. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, C.; Streets, D.G. Analyzing the Spatio-Temporal Variation of the CO2 Emissions from District Heating Systems with “Coal-to-Gas” Transition: Evidence from GTWR Model and Satellite Data in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 150083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, J. Heterogeneous Effects of Climate Change and Human Activities on Annual Landscape Change in Coastal Cities of Mainland China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; He, Q.; Gu, B.; Bai, J.; Liu, X. China’s Coastal Wetlands: Understanding Environmental Changes and Human Impacts for Management and Conservation. Wetlands 2016, 36, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ni, J.; Tenhunen, J. Application of a Geographically-weighted Regression Analysis to Estimate Net Primary Production of Chinese Forest Ecosystems. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2005, 14, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, M.; He, S.; Gan, M.; Yang, L.; Wang, K. Impacts of Urbanization and Landscape Pattern on Habitat Quality Using OLS and GWR Models in Hangzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasher, J.; Mitchell, S.W.; King, D.J.; Fahrig, L.; Smith, A.C.; Lindsay, K.E. Optimizing landscape selection for estimating relative effects of landscape variables on ecological responses. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Propastin, P. Modifying Geographically Weighted Regression for Estimating Aboveground Biomass in Tropical Rainforests by Multispectral Remote Sensing Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 18, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, D.; Futter, M.N.; Bishop, K. On the Forest Cover–Water Yield Debate: From Demand- to Supply-Side Thinking. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 806–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, H.; Liang, J.; Liu, W.; Piao, S.; Tian, H.; Zhou, G.; Lu, C.; You, W.; et al. Maximizing Carbon Sequestration Potential in Chinese Forests through Optimal Management. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Qiao, J.; Li, M.; Huang, M. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of ecosystem service interactions and their drivers at different spatial scales in the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada-Carmona, N.; Sánchez, A.C.; Remans, R.; Jones, S.K. Complex Agricultural Landscapes Host More Biodiversity than Simple Ones: A Global Meta-Analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2203385119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Fang, S.; Geng, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, R.; Sun, W.; Wang, X. Coastal Ecosystem Service in Response to Past and Future Land Use and Land Cover Change Dynamics in the Yangtze River Estuary. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 385, 135601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallarino Castillo, R.; Negro Valdecantos, V.; Del Campo, J.M. Understanding the Impact of Hydrodynamics on Coastal Erosion in Latin America: A Systematic Review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1267402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, K.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Bai, X.; Zhou, Y. Spatial and Temporal Changes of Landscape Patterns and Their Effects on Ecosystem Services in the Huaihe River Basin, China. Land 2022, 11, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrelly, D.J.; Everard, C.D.; Fagan, C.C.; McDonnell, K.P. Carbon Sequestration and the Role of Biological Carbon Mitigation: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 21, 712–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, W.M.; Kwon, K.C. Soil Carbon Sequestration and Land-use Change: Processes and Potential. Glob. Change Biol. 2000, 6, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ren, Y.; Ai, Z.; Qiao, Z.; Ren, Y.; Ma, L.; Yang, Y. Revealing the Spatial Interactions and Driving Factors of Ecosystem Services: Enlightenments under Vegetation Restoration. Land 2024, 13, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, P.; Hu, S.; Frazier, A.E.; Yang, S.; Song, X.; Qu, S. The Dynamic Relationships between Landscape Structure and Ecosystem Services: An Empirical Analysis from the Wuhan Metropolitan Area, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Cao, Y.; Fang, X.; Li, G.; Cao, Y. Identification of the Trade-Offs/Synergies between Rural Landscape Services in a Spatially Explicit Way for Sustainable Rural Development. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 300, 113706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Li, P.; Chen, J.; Chen, C.; Song, W. Spatiotemporal Evolution of the Rural-Urban Interface and Its Effects on Ecological Landscape Structure and Function: A Case Study of Nanjing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, N.; Ma, Q.; Li, J. How Is Human Well-Being Related to Ecosystem Services at Town and Village Scales? A Case Study from the Yangtze River Delta, China. Landsc. Ecol. 2024, 39, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Ding, S. Landscape Pattern Changes at a County Scale: A Case Study in Fengqiu, Henan Province, China from 1990 to 2013. Catena 2016, 137, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Tang, L.; Xu, M.; Yang, X. Landscape Pattern Indices for Evaluating Urban Spatial Morphology—A Case Study of Chinese Cities. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 99, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.-C. Spatiotemporal Changes of Landscape Pattern in Response to Urbanization. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 81, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, W.; Li, Y. Evaluating the Effectiveness of Landscape Metrics in Quantifying Spatial Patterns. Ecol. Indic. 2010, 10, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šímová, P.; Gdulová, K. Landscape Indices Behavior: A Review of Scale Effects. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 34, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Blanchet, F.G.; Koper, N. Measuring Habitat Fragmentation: An Evaluation of Landscape Pattern Metrics. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2014, 5, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, J.-F.; Gao, Y.; Pacheco, J.A.N. Sensitivity of Landscape Pattern Metrics to Classification Approaches. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.-T.; Huang, S.-L. Investigating Spatiotemporal Patterns of Landscape Diversity in Response to Urbanization. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 93, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Wang, Q.; Mi, K.; Peng, Y. Scale-Dependent Effects of Landscape Pattern on Plant Diversity in Hunshandak Sandland. Biodivers. Conserv. 2017, 26, 2169–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, H.; Gao, Y.; Su, X.; Yang, X.; Cheng, F.; Ma, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, L. Spatial-temporal changes and driving force analysis of green space in coastal cities of Southeast China over the past 20 years. Land 2021, 10, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, J.A.; Martinko, E.A.; Price, K.P. Landscape Structure Analysis of Kansas at Three Scales. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2000, 52, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.S.; DeZonia, B.E.; Mladenoff, D.J. An Aggregation Index (AI) to Quantify Spatial Patterns of Landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2000, 15, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Wang, Y.; Fu, B.; Xu, P. Soil Conservation Assessment in the Upper Yangtze River Basin Based on Invest Model. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Symposium on Water Resource and Environmental Protection, Xi’an, China, 20–22 May 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 3, pp. 1833–1836. [Google Scholar]

| Data | Detail | Data Source |
|---|---|---|
| Administrative boundaries | Shapefile, plygon | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (http://www.resdc.cn/) |
| DEM | Rater, 30 m | Geospatial data cloud (http://www.gscloud.cn/) |
| LULC data | Rater, 30 m, 2000, 2010, 2020 | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (http://www.resdc.cn/) |
| Meteorological data | Rater, 1 km, 2000, 2010, 2020 | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (http://www.resdc.cn/) |
| Soil data | Rater, 1 km | Harmonized World Soil Database v 1.2 (https://gaez.fao.org/pages/hwsd, accessed on 7 January 2025) |
| Type | 2000 | 2020 | 2000–2020 | 2000–2020 Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS | 3204.51 | 3147.25 | −57.26 | −1.79 |
| SC | 3188.73 | 2335.61 | −853.12 | −26.75 |
| WY | 172.67 | 153.34 | −19.33 | −11.19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, Q.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Xu, M.; Yang, X. A Village-Scale Study Regarding Landscape Evolution and Ecological Effects in a Coastal Inner Harbor. Land 2025, 14, 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14020319
Pan Q, Li S, Li J, Xu M, Yang X. A Village-Scale Study Regarding Landscape Evolution and Ecological Effects in a Coastal Inner Harbor. Land. 2025; 14(2):319. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14020319
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Qinqin, Saiqiang Li, Jialin Li, Mingshan Xu, and Xiaodong Yang. 2025. "A Village-Scale Study Regarding Landscape Evolution and Ecological Effects in a Coastal Inner Harbor" Land 14, no. 2: 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14020319
APA StylePan, Q., Li, S., Li, J., Xu, M., & Yang, X. (2025). A Village-Scale Study Regarding Landscape Evolution and Ecological Effects in a Coastal Inner Harbor. Land, 14(2), 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14020319






