Abstract
Soil erosion is a major environmental concern, especially in sensitive ecosystems like the Loess Plateau of China, where certain geological and climatic circumstances exacerbate the erosion process. Terracing and mulching are popular soil erosion management strategies in this region. However, their combined effects under varied rainfall intensities are poorly understood. The purpose of this study is to assess the performance of various terracing–mulch combinations in reducing water erosion under different rainfall intensities. The experimental layout included a control plot (C), non-terraced mulch applications (NTr-M), fish-scale pits with mulch (FSPs-M), zig terraces with mulch (ZTr-M), level bench terraces with mulch (LBTr-M), and trench terraces with mulch (TTr-M). Controlled artificial rainfall experiments were carried out under different intensities, and runoff and soil loss data were collected to evaluate the effects of the combinations. The event-based WEPP simulations, calibrated for the Loess Plateau, demonstrated strong predictive accuracy, as evidenced by the high correlation coefficients (R2 = 0.97 for runoff; R2 = 0.86 for soil loss) and Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE = 0.93 for runoff; NSE = 0.89 for soil loss), confirming their reliability in simulating erosion processes when compared to measured values. Our results revealed significant differences (p < 0.05) in mean runoff and soil loss among the treatments, ranked in the order LBTr-M < TTr-M < ZTr-M < FSPs-M < NTr-M < C. Incremental response analysis also revealed that the control plot (C) was the most sensitive to changes in rainfall intensity, followed by FSPs-M and NTr-M. In contrast, LBTr-M was found to be the most stable strategy. These findings highlight the importance of optimizing micro-relief construction and mulch application to enhance erosion control and support the recommendation of LBTr-M, TTr-M, and ZTr-M as effective strategies. Conversely, FSPs-M and NTr-M proved less effective under higher rainfall intensities. These findings emphasize the need to optimize micro-relief construction and mulch application for erosion management, as well as suggest that such strategies could be applied to the Loess Plateau and other erosion-prone regions worldwide with similar climatic and topographic conditions.
1. Introduction
Soil is a fundamental component of the Earth’s surface, playing a critical role in maintaining ecological balance and supporting terrestrial ecosystems. It serves as a primary medium for water, nutrients, temperature regulation, and gas exchange, all of which are necessary for sustaining life [1,2,3]. Beyond these core functions, healthy soil supports agricultural productivity, global food security, and climate change mitigation through its ability to sequester carbon and other greenhouse gases [1,4]. However, soil erosion, particularly in fragile ecosystems, poses a significant threat to the long-term sustainability of this essential resource [5].
The interaction of natural factors and human action has intensified the issue of soil erosion. Slope length and gradient, ground cover, soil properties, and rainfall intensity primarily influence the severity of soil erosion [6,7]. On sparsely vegetated hillslopes, like the Loess Plateau, where the typical slope gradient exceeds 15 degrees (27%) [8], intense rainstorms can generate high-velocity surface runoff, displacing and transporting soil particles [9]. The Loess Plateau of China is recognized as one of the most eroded regions globally, primarily due to its extensive loess deposits, steep terrain, and semiarid climate. Approximately 60% of the plateau, covering 640,000 km2, is severely impacted by soil erosion, with erosion rates ranging from 5000 to 10,000 t/km2/year [10]. In some areas, the soil erosion modulus exceeds 8000 t/km2/year, driven by intense gully erosion, often worsened by drainage basin developments [11]. The region’s vulnerability to erosion is amplified by its complex topography, including numerous gullies and valleys formed by natural processes and human activities. Additionally, frequent land cover and land use changes have worsened soil erosion, leading to the depletion of nutrients and organic matter, reduced soil fertility, and threats to food security [12,13,14]. Furthermore, climate change is expected to exacerbate soil erosion in the Loess Plateau through increased precipitation intensity and variability. Studies indicate that projected changes in rainfall patterns could lead to more frequent and severe rainstorms, which may overwhelm existing soil conservation techniques and increase runoff and erosion rates [15]. For instance, research has shown that every 1% increase in rainfall could lead to a 2% increase in runoff and a 1.7% increase in erosion [16]. This highlights the urgent need to adapt soil conservation practices to account for the impacts of climate change, ensuring their effectiveness in mitigating soil erosion under changing climatic conditions. Therefore, understanding the interplay between climate change and soil conservation strategies is critical for maintaining soil health and agricultural productivity in this vulnerable region.
In response to the critical issue of soil erosion, several conservation practices have been employed on the Loess Plateau of China, including terracing and mulching. Terracing is a highly successful soil and water management approach that entails building stepped, leveled, or slightly inclined platforms along the contours of sloped terrain [1,17,18]. By breaking up extended slopes, these terraces assist in lowering the rate of water flow and promote water infiltration and sediment deposition. Furthermore, creating physical barriers can increase organic matter accumulation and vegetation formation, further strengthening the soil’s resilience to erosion [19,20,21]. Meanwhile, mulching preserves the soil surface, enhances moisture retention, and improves soil structure, thereby mitigating erosion. Mulching involves the application of organic matter or gravel to the soil, safeguarding it from raindrop impact, hence reducing particle disintegration and runoff [22,23]. In addition to preventing erosion, mulching provides several environmental benefits that support sustainable land management, including regulating soil temperatures, reducing crop irrigation needs, minimizing nutrient depletion, and decreasing soil compaction [24,25]. The combination of these practices is critical in the region due to its unique ecological conditions, agricultural practices, and susceptibility to soil erosion.
While terracing is widely acknowledged as an efficient erosion management approach, its effectiveness is affected by many parameters, including terrace type, local rainfall intensity, slope gradient, and ground cover. Each terracing layout responds uniquely to soil type and rainfall, affecting its capacity to regulate runoff and minimize soil loss. In the setting of steep slopes such as the Loess Plateau (about 27%) [8], the design and execution of terracing strategies are essential for efficient soil conservation. Developing a comprehensive erosion control strategy in extremely erosion-prone areas needs a detailed assessment of runoff and soil loss under varied terracing practices, rainfall intensities, and ground cover applications, including mulch.
Field monitoring and modeling techniques are imperative for evaluating soil and water conservation strategies, particularly terracing, as they offer important insights into their efficacy across multiple spatial and temporal dimensions [26]. Process-based models, notably the Water Erosion Prediction Project (WEPP), are effective tools for estimating runoff and soil erosion, applicable across diverse situations [27,28]. The WEPP model’s key advantage lies in its capacity to extrapolate findings to scenarios where direct field testing may not be feasible, allowing for the broader applicability of results [29]. Furthermore, the WEPP model effectively quantifies runoff and soil erosion while improving outcomes by predicting both geographic and temporal variations in soil erosion in a hillslope or small watershed [30].
Terracing and mulching are prevalent soil preservation techniques on the Loess Plateau of China; nevertheless, their synergistic impacts on runoff and sediment control across various rainfall intensities remain insufficiently understood. Existing research has extensively documented the individual effects of terracing and mulch on reducing runoff and sediment under different rainfall events [22,31,32,33,34]. Additionally, several studies have modeled erosion using the WEPP model for various land uses on the Loess Plateau of China [35,36,37], typically through continuous-storm simulations, which can introduce variability and complicate parameter calibration. However, to our knowledge, the analysis of field data combined with the WEPP modeling of different terracing–mulch combinations through a single storm, such as artificial rainfall simulation, has not been adequately addressed in this region. This gap is critical, as single-storm conditions generated through artificial rainfall simulations provide controlled experimental environments that reduce parameter uncertainties and enable a more robust evaluation of the model’s performance [38].
Therefore, this study evaluates the combined effects of terracing and mulch under various rainfall intensities in the Chinese Loess Plateau by integrating single-storm experiments with WEPP modeling. The study aimed to (1) assess the synergistic effects of various terrace and mulch combinations on erosion control under varying rainfall conditions, (2) compare the efficacy and advantages of specific terracing–mulch combinations in reducing water erosion, and (3) formulate and propose optimal terracing–mulch systems to improve water erosion management in the Loess Plateau of China and similar areas worldwide.
2. Methodology
2.1. Study Area
The experiment was carried out at the Dingxi Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, which is situated in Gansu province, China, at the coordinates 35°34′45.88″ N, 104°38′5.67″ E. This region is situated in a semiarid climate characterized by warm, humid summers and cold, dry winters. The mean annual precipitation in this region, was 421 mm, with approximately 78% of it occurring during the growing season [39]. The topography of the area is marked by undulating hills and valleys, with slopes that often exceed 15 degrees, contributing to the susceptibility of the soil to erosion. The soil in this area is primarily composed of loess, a highly erodible material that poses significant challenges to soil conservation [40]. The loess deposits in Gansu province are widely distributed and are particularly vulnerable to erosion due to the region’s climatic conditions and land use practices [41]. Vegetation cover in the Dingxi region has been significantly impacted by agricultural practices and land use changes, leading to a decline in natural grasslands and forests. The predominant land use includes crop cultivation, which is essential for the local economy but also contributes to soil degradation if not managed sustainably [42]. The combination of climatic conditions, topographical features, and land use practices makes the Dingxi area an ideal location for studying soil erosion and the effectiveness of soil conservation techniques, such as terracing and mulching. Furthermore, the Dingxi region is representative of the broader Loess Plateau, making the findings of this study applicable to other areas with similar climatic and topographical conditions.
2.2. Experimental Setup
For this study, six separate experimental plots with 20% slope gradients, which is the average slope gradient of the Loess Plateau [8], and dimensions of 7 m in length and 1.5 m in width were made using cement ridges. The arrangement of these ridges was meticulously planned to direct the flow of runoff and sediment to a collection tank for effective collection. All experimental plots contained uniformly dispersed silt-rich soil, as is typical of the Loess Plateau. Soil samples were collected with three replications at a 300 mm depth from each plot and transferred to the laboratory in plastic bags to determine soil texture. The composition of the experimental soil was 4% sand, 84.5% silt, and 11.5% clay, indicating a predominantly silty texture that is highly susceptible to erosion. The soil bulk density of the experimental soil was also measured three times for each plot using the volumetric ring method. Samples were dried at 105 °C for 24 h to calculate soil bulk density. The soil bulk density was determined to be 1.4 g/cm3. Furthermore, the organic matter content was measured using the wet oxidation method, yielding a value of 2%.
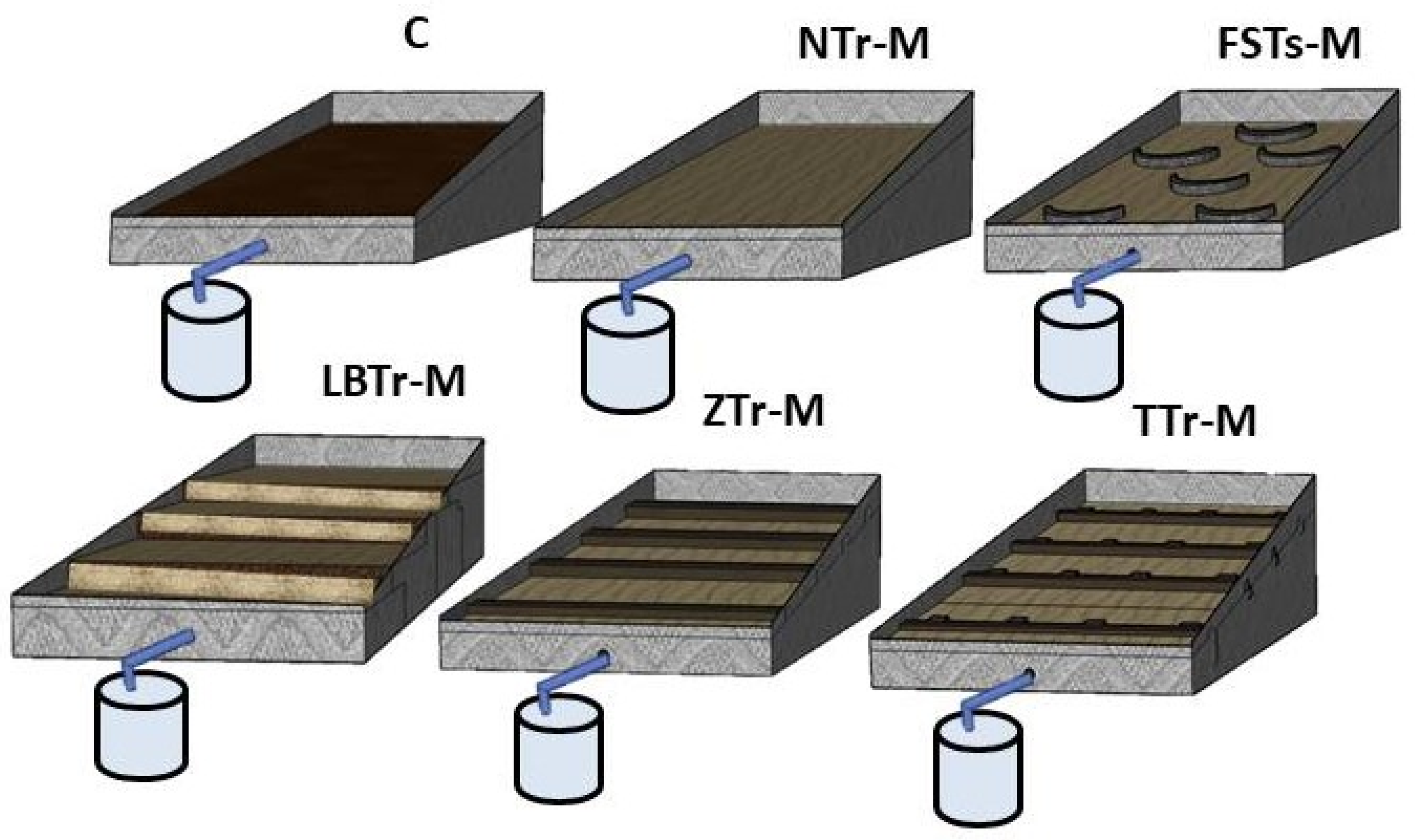
Each plot was designed to feature a specific combination of terracing and mulch treatments (Figure 1). The plots included FSPs-M, ZTr-M, LBTr-M, TTr-M, NTr-M, and C. The design criteria for each terracing style are outlined as follows: The FSPs were organized in a triangle configuration of four rows, forming a unique semicircular shape. The dimensions of this terracing measurement were 120 cm in diameter, 70 cm in length, and 40 cm in width. For the plot with the LBTr system, a plot was transformed into four equal-level bench surfaces, each with dimensions of 2 by 1.2 m. The bench riser measured 0.3 m in height. The four ZTrs were constructed with a consistent height of 0.3 m and dimensions of 2 m in length and 1.5 m in width for the plot that was treated with a ZTr. Similarly, the TTr plot was designed with four terraces that matched the ZTr’s dimensions, which were 2 m long and 1.5 m wide. This terrace consisted of four trenches connected by ditches on a single surface. Each trench was 0.4 m wide and 0.3 m high, with perfect connections to the ditches. Although no ideal mulch application rate applicable under all situations was determined, we used a rate of 500 g/m2 based on previous studies conducted under comparable climatic conditions [43,44].
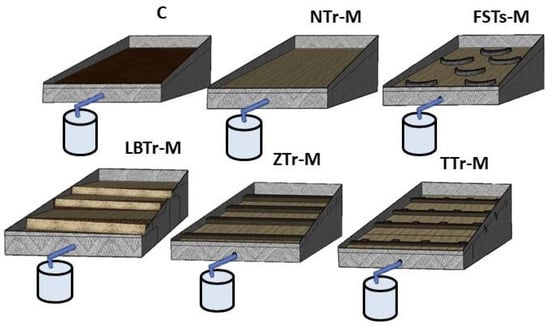
Figure 1.
Terracing and mulch combinations: control plot (C), non-terraced mulch (NTr-M), fish-scale pits with mulch (FSPs-M), zig terrace with mulch (ZTr-M), leveled bench terrace with mulch (LBTr-M), and trench terrace with mulch (TTr-M).
2.3. Rainfall Simulation Experiments
This study used artificial rainfall simulations at intensities of 60, 90, 120, and 150 mm/h to analyze the effect of terracing–mulch combinations on soil erosion dynamics in the Loess Plateau. These intensities were selected to represent a wide range of conditions identified in this ecologically fragile region, where the threshold for runoff initiation is around 30 mm/h, and erosion processes begin at higher rainfall rates [45]. Rainfall intensities of 90–120 mm/h are common during erosive storms in the region [46], which have a considerable effect on soil stability. The incorporation of the maximum intensity of 150 mm/h allows the investigation of severe storms, which are increasingly prevalent because of climate change, highlighting the region’s vulnerability to soil degradation [45]. For this experiment, a total of 72 erosive rainfall events were conducted, with three replications for each rainfall intensity and experimental plot. A Norton ladder-type artificial rainfall simulator [47,48] was installed 3.5 m above the runoff plots (Figure 2). Upon completion of the rainfall simulation on each plot, the simulator was relocated to the next plot for subsequent testing. The spraying system used six Veejet 80,100 nozzles spaced 1.1 m apart and operated at a water pressure of 41 kpa. To ensure the accuracy of the artificial precipitation rates, the system was calibrated before each experiment. Calibration involved adjusting the nozzle settings and water pressure to achieve the desired rainfall intensity, which was systematically varied to simulate the different hydrological conditions appropriate for the experiment. To verify the uniformity of rainfall distribution across all experimental plots, rain gauges were strategically placed at multiple locations within each plot. The rainfall intensity was measured at these gauges during the simulations to assess the spatial distribution of precipitation. The uniformity coefficient was calculated based on the readings from the rain gauges, ensuring that the rainfall distribution met the required standards for experimental accuracy. Additionally, the period between successive rainfalls was set to 48 h for each test phase to maintain consistent moisture conditions similar to the starting moisture level.

Figure 2.
A schematic illustration of field studies with runoff plots and the Norton rainfall simulator.
2.4. Data Collection Procedure and Analysis
To regularly collect runoff and sediment from each plot, we directed the runoff flow into a plastic container positioned below the plots using downstream pipes for each experiment. We employed two 20-L graded plastic water containers to measure the runoff volume effectively. Systematic runoff collection was made possible by carefully switching out these containers as they became full. Afterward, we carefully transferred the collected runoff to a larger container with a capacity of 1000 L, which allowed us to measure sediment concentrations. During each rainstorm simulation, sediment runoff samples were collected at 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 min intervals. These samples were thoroughly collected with a 500 mL graduated flask to ensure precise volume readings. Following collection, the runoff samples were treated to separate the sediment. The isolated sediment was then dried in an oven at 105 °C until it reached a stable mass that could be precisely quantified for analytical purposes. The sediment concentration was estimated by dividing the mass of the dried deposit by the volume of runoff in each sample, and the mean sediment concentration was established across all samples. The sediment data were translated to soil loss in kg m−2, providing a standardized measure to compare the effectiveness of each terracing–mulch combination.
The statistical study was conducted using R. The Shapiro–Wilk test was used to evaluate the normality of the data distribution. ANOVA was performed to identify significant differences between groups, provided that the normality requirements were met. Subsequently, post hoc analysis was utilized to determine significant differences within the groups. The significance level for all tests was set at p < 0.05. Finally, to investigate the sensitivity of runoff and soil loss to increasing rainfall intensity, an incremental analysis was conducted. Incremental changes in runoff and soil loss were calculated for each plot type across successive rainfall intensity transitions (60 → 90, 90 → 120, 120 → 150).
2.5. WEPP Model
The Water Erosion Prediction Project (WEPP) is a comprehensive simulation model intended to predict spatial and temporal patterns of runoff and soil erosion in landscapes with diverse slope gradients and lengths, particularly in steep areas. It accurately estimates the spatial and temporal distribution of sediment output and deposition, enabling exact predictions of erosion occurrences on hillslopes or within watersheds. This facilitates the focused implementation of conservation techniques, ensuring the optimal management of soil erosion [49,50]. Due to the WEPP’s suitability for small-scale applications [51] and its ability to accurately modify slope profiles, it serves as an ideal tool for modeling small-plot terraced systems, where specific slope reshaping is required to properly represent the specific topographic and hydrological dynamics that distinguish these landscapes.
WEPP Model Parameter Files
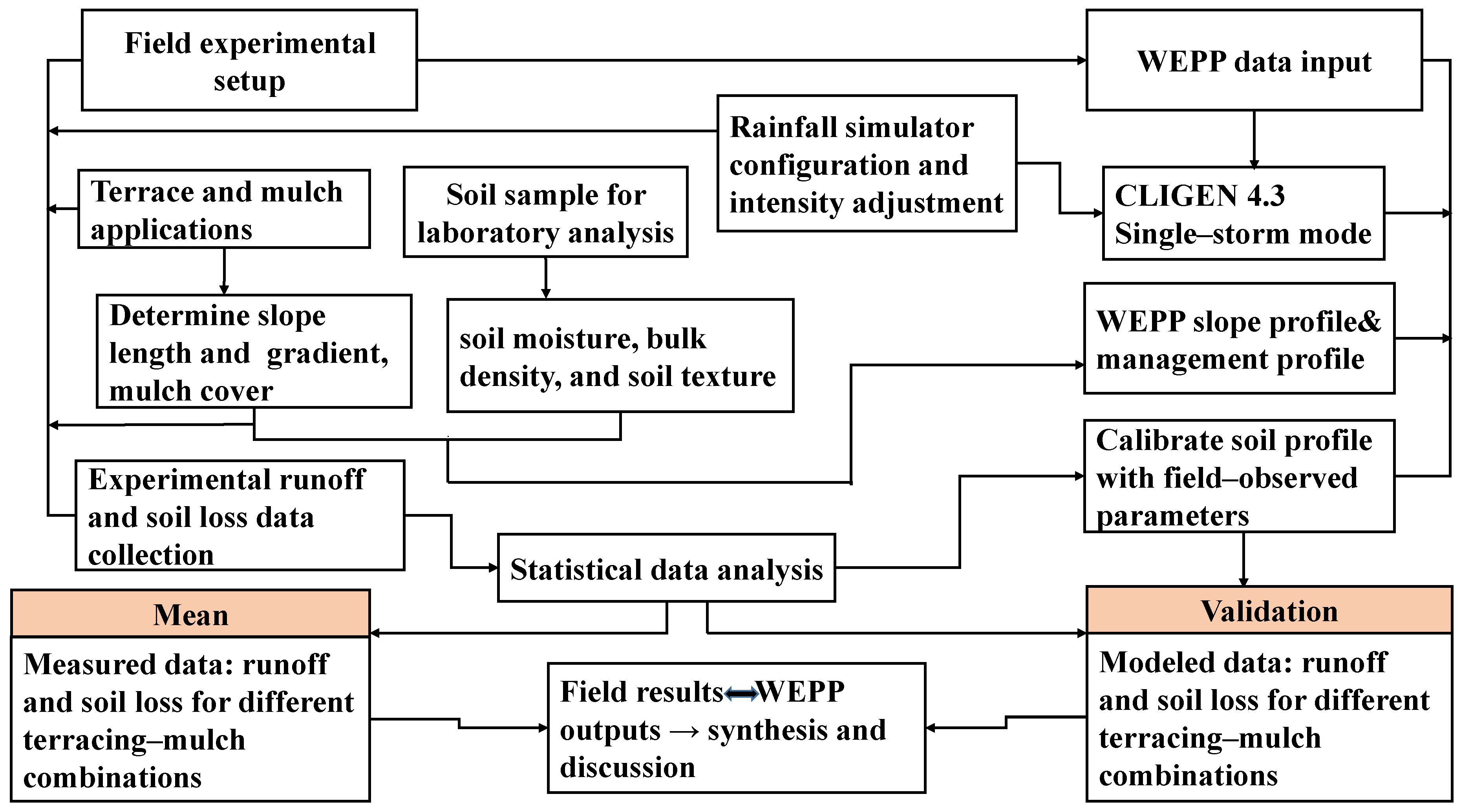
The model’s inputs were supplied utilizing four separate files: climatic data, slope attributes, soil parameters, and vegetation and management techniques. In this study, the climate and slope characteristics of these model components were based on field measurements and surveys, remaining constant without parameter modifications before simulation. The workflow chart, outlining the key steps of field data collection, WEPP data input, calibration, and scenario simulations, is shown in Figure 3.
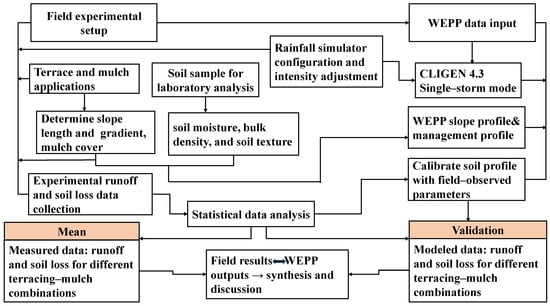
Figure 3.
Workflow illustrating the integration of field data collection, rainfall simulations, soil parameter calibration, and WEPP model predictions for assessing runoff and soil erosion under terracing–mulching combinations.
Climate data files can be produced using the standalone application CLIGEN 4.3, which accommodates either continuous-storm or single-storm modes. It provides three categories of climate data outputs: continuous simulation data utilizing ip/tp, single-event simulation employing ip/tp, and TR-55-design single-storm files incorporating ip/tp data. [28]. This study utilized the single-storm mode, employing intensity (ip) and time-to-peak (tp) data. The depth and intensity of rainfall were regulated using predetermined parameters, and the simulated rainfall events were produced based on these inputs, enabling exact control over precipitation features. The climate file requires certain parameters: storm date, total storm amount, rainfall duration, maximum rainfall intensity, and time to peak intensity. Table 1 displays the experimental outcomes of simulated rainfall with climate data for the WEPP model.

Table 1.
Summary of simulated rainfall events.
For the slope profile, we used detailed field topography data to build a slope file for each experimental plot. Every plot was segmented based on its topographical characteristics, dividing them into distinct sections that reflected changes in slope. For plots featuring level bench terraces, the original 7 m slope length was divided into four equal segments of 1.7 m each. The initial 20% slope gradient was adjusted to four segments of flat sections, accurately representing the terrace design. For the zig terrace plot, the 7 m slope was divided into four 1.7 m parts in the same manner. The slope gradient for these segments was reduced from 20% to 7% as a result of the terrace, directly illustrating the terraced topography. For the trench terrace plot, the same 8 m segmentation was applied, but the slope gradient was reduced from 20% to 4.5%, reflecting the modified topography of the terrace.
For the plot with fish-scale pits, the slope was segmented into seven unique sections to represent the distribution of fish-scale pits and their transitions precisely. Segment 1 is 1.7 m in length and has a gradient of 12%, indicating the slope at the beginning of the plot prior to the fish-scale pits. Segment 2 has a length of 0.3 and a 3% slope, and it represents the first location where water is retained around a fish-scale pit. Segment 3 extends 1.7 m with a 12% slope gradient between the pits in the initial triangle group. Segment 4 then drops the slope to 3% for 0.3 m, reflecting the next pit’s water-retention effect. Segment 5 is the transition between the two triangular groupings of pits, measuring 1.7 m with a 12% slope. Segment 6 replicates the configuration of pit sections, including a 3% slope over 0.3 m, aligning with the third fish-scale pit in the second group. The final segment of the slope after the last fish-scale pit is represented by Segment 7, which returns to a steeper slope of 12% over 1.7 m.
Management input files were created to take into consideration the unique features of the study area. The experimental soil had an average bulk density of 1.4 g/cm2, a value consistently employed in our investigations. All rainfall simulations were conducted on bare soil, establishing the initial plant conditions as ‘no growth’. Days since the last tillage was assigned as zero for all plots. For mulched plots, the interrill cover percentage, initial actual cover, initial total dead root mass, and total submerged residue mass were modified accordingly. All other parameters were defaulted.
The majority of the soil properties, such as texture, cation exchange capacity, organic matter content, albedo, and initial moisture content (SAT), were determined through laboratory analysis of field-collected soil samples (Table 2). The effective hydraulic conductivity (Ke) was determined by measuring the total runoff depth (mm) from precipitation events and calculating the average of three replications for each plot. The interrill erodibility (Ki) was determined by calculating the average soil erosion rates according to the total sediment collected at each plot during rainfall events.

Table 2.
Soil properties used for simulations.
3. Results
3.1. Water Erosion Modeling for Terracing–Mulch Combinations
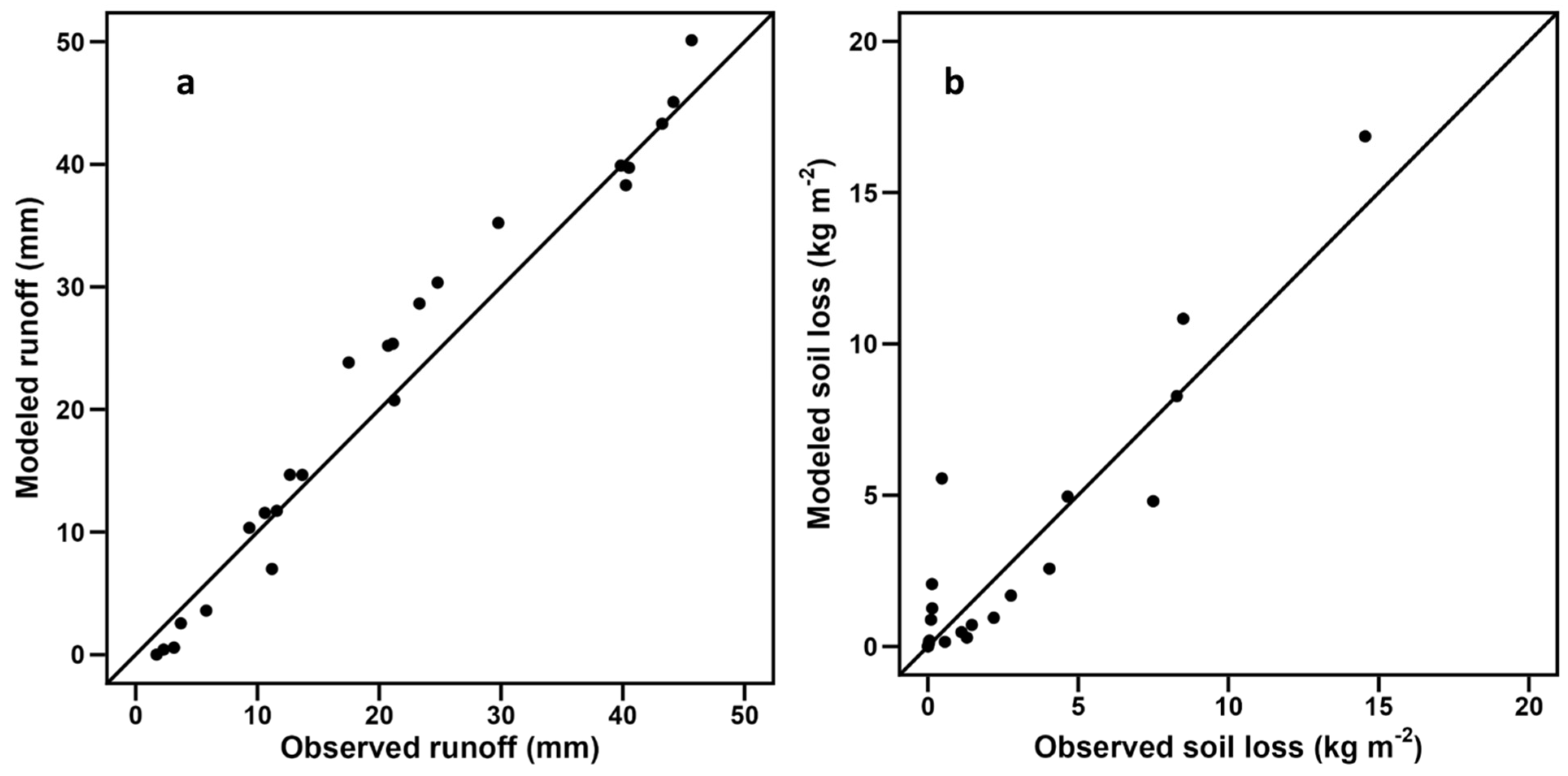
In this study, the WEPP (Water Erosion Prediction Project) model was applied to predict runoff and soil loss under simulated rainfall conditions on the Loess Plateau of China, utilizing input parameters derived from field simulations of various terracing–mulch combinations. Controlled simulations under standardized rainfall conditions provided a precise framework for isolating the impacts of terracing–mulch combinations on runoff and soil loss. The observed and simulated results exhibited considerable agreement, supporting the suitability of the WEPP model for closely replicating the hillslope conditions determined by the field erosion plots (Figure 4). Model performance was evaluated using key metrics, including the correlation coefficient (R2), Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE), root-mean-square error (RMSE), and relative error (Re). The high Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE), low root-mean-square error (RMSE), and minimal relative error (Re) confirm WEPP’s capability to predict erosion dynamics effectively (Table 3).
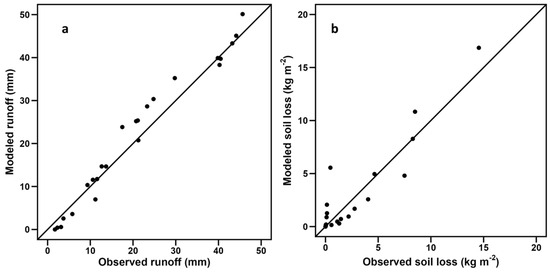
Figure 4.
Comparison of modeled and observed runoff (a) and soil loss (b).

Table 3.
WEPP model performance evaluation using field observed data as a reference.
The WEPP model provides significant advantages in evaluating water erosion under terracing–mulch combinations. Its flexibility allows for detailed adjustments to slope configurations, which is essential for accurately simulating the impacts of terracing practices. Furthermore, the model supports the customization of ground cover parameters, enabling the precise representation of mulching effects. These include reduced raindrop impact, improved infiltration rates, and reduced soil detachment, which are critical factors in erosion control.
3.2. Erosion Response to Terracing and Mulching Combinations
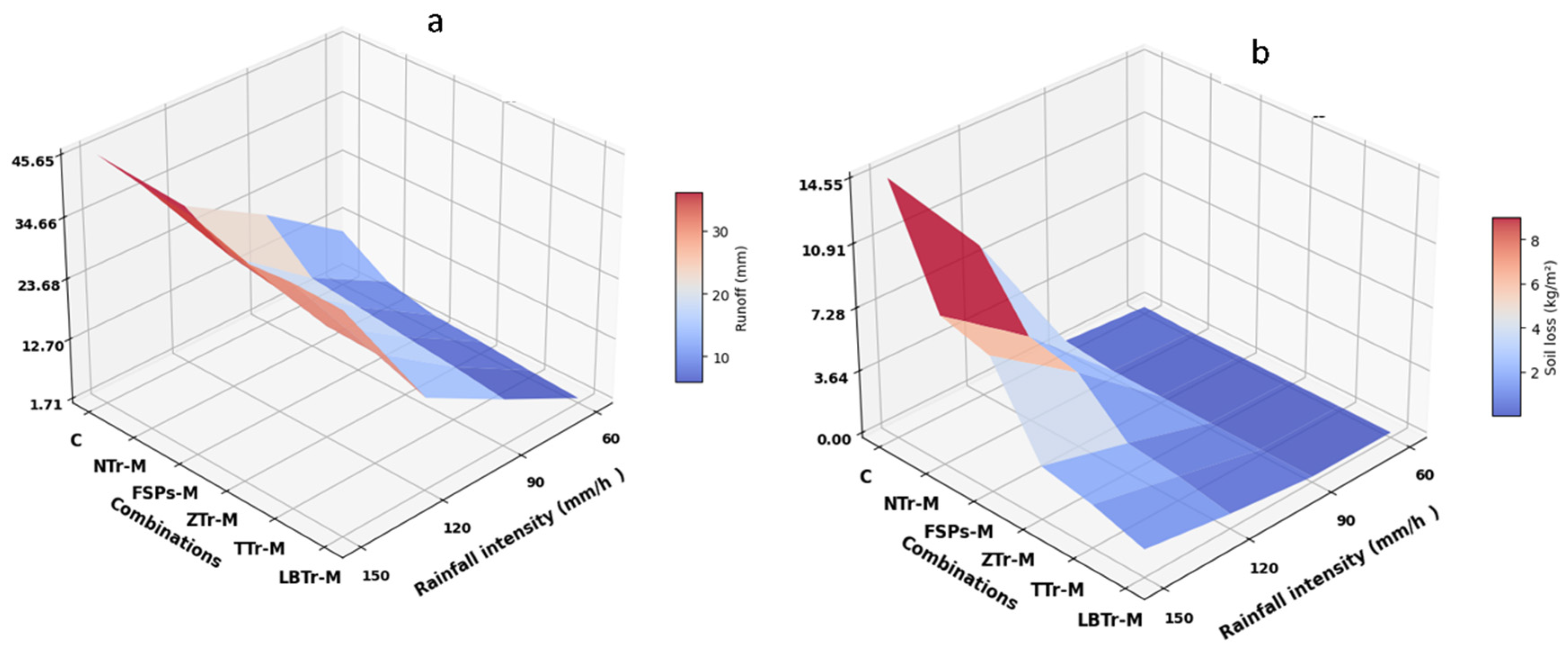
Different responses to simulated rainfall intensities were observed among various terracing–mulch combinations. The observed mean runoff and soil loss, along with their standard deviations and significant differences, are presented in Table 4 and Table 5 for each treatment and rainfall intensity. All combinations and rainfall patterns significantly influenced runoff and erosion dynamics. Figure 5a,b illustrate the three-dimensional relationships among rainfall intensity, terracing–mulch combinations, and their respective impacts on runoff and soil loss. Among the treatments, combinations LBTr-M, TTr-M, and ZTr-M consistently exhibited significantly lower runoff compared to other treatments across all rainfall intensities, with LBTr-M achieving the most substantial reduction. At a rainfall intensity of 120 mm/h, LBTr-M was significantly different from all other treatments; however, at other rainfall intensities, no significant differences were observed among LBTr-M, TTr-M, and ZTr-M (Table 4).

Table 4.
Responses of runoff for different rainfall intensities.

Table 5.
Responses of soil loss for different rainfall intensities.
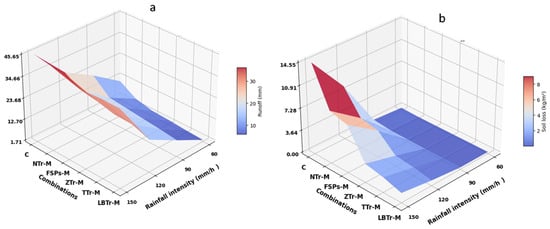
Figure 5.
Three-dimensional relationships among terracing–mulch combinations, rainfall intensity, runoff (a), and soil erosion (b). The plot abbreviations are as follows: control plot (C), non-terraced plot with mulch (NTr-M), fish-scale pits with mulch (FSPs-M), zig terraces with mulch (ZTr-M), trench terraces with mulch (TTr-M), and level bench terraces with mulch (LBTr-M).
FSPs-M recorded the highest runoff among the terrace structures, while NTr-M generated more runoff than all treatments except C, which consistently had the highest runoff. All treatments showed significantly different runoff patterns from C across all rainfall intensities.
Soil erosion demonstrated a similar pattern, with all terracing–mulch combinations resulting in reduced soil loss. Significant differences in soil erosion were seen between C and all other treatments at all rainfall intensities, except for 60 mm/h, where no statistically significant differences were observed (Table 5). At 120 mm/h and 150 mm/h, LBTr-M exhibited significant distinctions from all other treatments, proving the most efficient under storm rainfall conditions. TTr-M and ZTr-M also exhibited notable decreases in soil erosion in this circumstance. Overall, the mean soil loss followed the trend C > NTr-M > FSPs-M > ZTr-M > TTr-M > LBTr-M.
3.3. Incremental Changes in Runoff and Soil Loss Across Rainfall Transitions
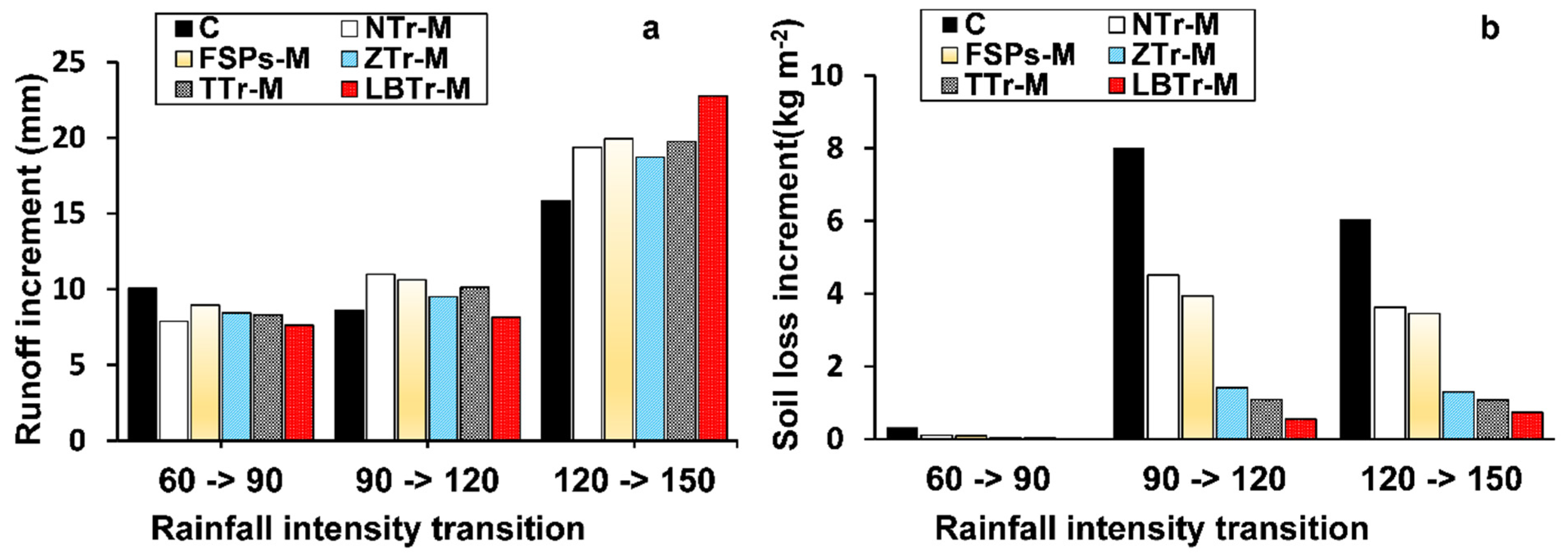
Incremental changes in runoff and soil loss across rainfall transitions indicate terracing practices with various sensitivity levels. LBTr-M showed the smallest increases, with little change between the 60 to 90 mm/h and 90 to 120 mm/h transitions. However, a notable increase in runoff and soil loss was observed during the 120 to 150 mm/h transition, showing lower resilience to higher rainfall intensities (Figure 6a,b). TTr-M and ZTr-M demonstrated moderate sensitivity, with incremental increases in both runoff and soil loss that were larger than LBTr-M but remained relatively stable across transitions. In contrast, FSPs-M and NTr-M exhibited sharp increases in runoff and soil loss, particularly during higher rainfall transitions, highlighting their susceptibility to extreme rainfall conditions. The control plot (C) showed the largest incremental increases in both parameters across all transitions, underscoring its lack of protective mechanisms.
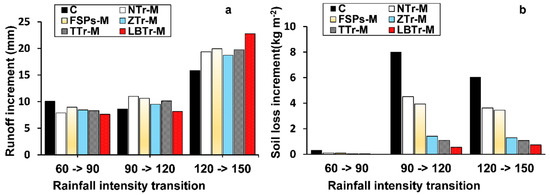
Figure 6.
Incremental analysis (a) runoff and (b) soil loss under varying rainfall intensity transitions for different terrace configurations. The plot abbreviations are as follows: control plot (C), fish-scale pits with mulch (FSPs-M), level bench terraces with mulch (LBTrs-M), non-terraced plot with mulch (NTr-M), trench terraces with mulch (TTrs-M), and zig terraces with mulch (ZTrs-M).
In summary, the incremental analysis highlights LBTr-M as the least sensitive to rainfall transitions, followed by TTr-M and ZTr-M, while FSPs-M, NTr-M, and the control plot exhibited greater sensitivity to rainfall intensity change.
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Effects for Various Terracing–Mulch Combinations Under Different Rainfall Intensities
Terracing is widely acknowledged as an effective intervention for reducing soil erosion; however, its performance can exhibit considerable variability due to a range of influencing factors. Key variables, including slope modification, terrace design, and the presence or absence of structural features such as embankments and ridges, play a pivotal role in determining the efficacy of terracing systems [18]. To ensure the long-term sustainability of terracing systems, it is essential to integrate them with complementary soil conservation practices. Among these, maintaining soil cover—such as mulch—during rainy periods and establishing vegetation for stability are particularly critical. These practices, along with proper terrace maintenance, enhance erosion control, improve soil structure, and promote ecosystem resilience [52]. While these strategies have proven effective in mitigating erosion, their adoption and large-scale implementation depend on economic feasibility, labor requirements, and resource availability in different environmental and socio-economic contexts. Therefore, the adoption of terracing–mulch strategies must consider both initial costs and long-term benefits.
The findings of this comprehensive study provide valuable insights into the efficacy of various terracing and mulching strategies in mitigating soil erosion under various rainfall intensities in the Loess Plateau of China. The comparative analysis of the evaluated configurations, alongside the integration of the WEPP model, demonstrated substantial differences in the efficacy of these practices in controlling runoff and soil erosion, demonstrating the necessity of choosing suitable soil conservation strategies adapted to the specific environmental conditions in the region.
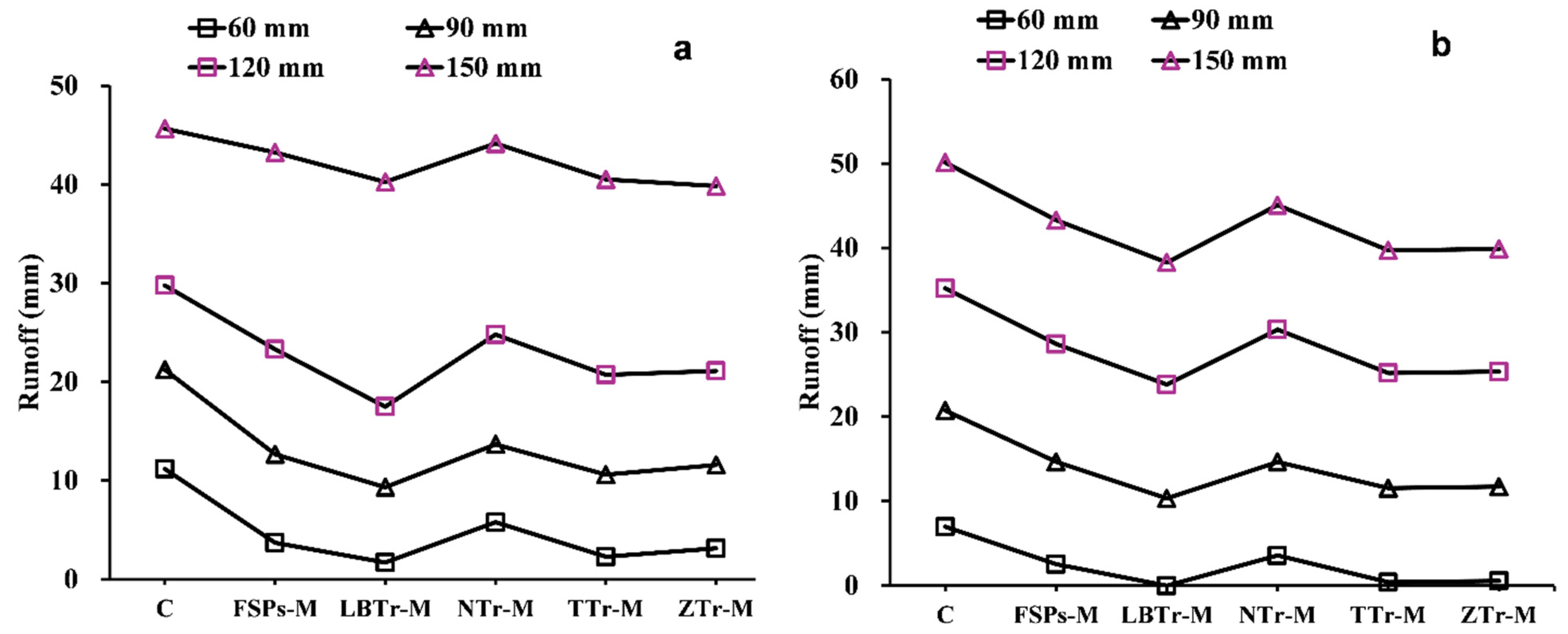
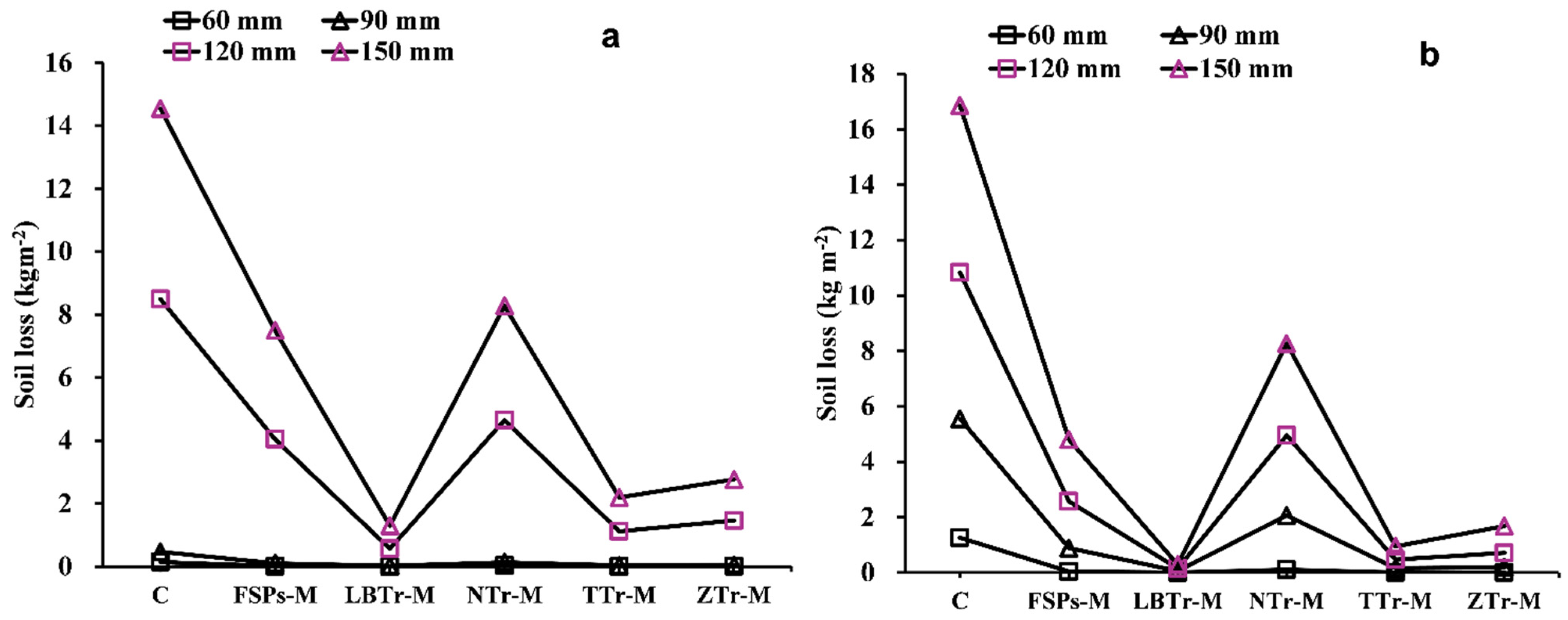
Among the tested configurations, LBTr-M emerged as the most effective strategy, demonstrating the lowest sensitivity to increased rainfall intensity and resulting in the least runoff and soil loss across all tested conditions (Figure 7) and soil loss (Figure 8) across all tested variables. The results of this study align with those of [20,53], demonstrating that level bench terraces are superior to other terrace types in reducing runoff and sediment loss. The reduction can be attributed to the bench design, which minimizes slope length and steepness, thereby limiting the volume, velocity, and energy of surface runoff and effectively hindering sediment loss [20,54]. Wide benches serve as an effective land management strategy by mitigating the erosive impact of rainfall, reducing surface runoff velocity, enhancing water infiltration into the soil, and consequently minimizing soil erosion and preventing land degradation [55]. However, the dramatic increase in runoff observed during the transition from the 120 mm/h to 150 mm/h rainfall intensities in the incremental study (Figure 6a) highlights a reduction in the efficiency of the LBTr-M combination in mitigating runoff under higher rainfall intensities. Despite this, it is important to note that soil loss consistently decreased across all rainfall intensities, underscoring the overall effectiveness of this strategy in controlling erosion under varying conditions (Figure 6b). As a result, level bench terraces not only help improve soil water retention but also provide resilience against extreme drought conditions [20]. However, the development of level bench terraces requires significant labor and high initial costs due to the need for manual work and mechanized equipment to alter the slope topography [55]. Despite these challenges, the long-term benefits, including improved soil water retention and increased agricultural productivity, make them a valuable investment in soil conservation. For instance, Sharda [56] highlighted the economic feasibility of bench terraces through a benefit–cost analysis (BCA) of an inter-crop-based system conducted over 9 years. The study found that the long-term benefits of bench terraces, including increased crop yields and reduced soil loss, outweighed the initial investment costs, resulting in a favorable benefit–cost ratio. This demonstrates that despite the upfront investment, level bench terraces can be both economically viable and sustainable over the long term, making them suitable for large-scale implementation in erosion-prone regions.
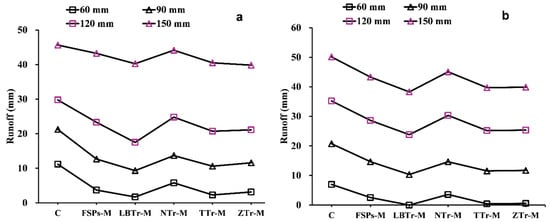
Figure 7.
Observed (a) and predicted (b) runoff for different combinations. The abbreviations of the terracing–mulch combinations are as follows: C for control plot, NTr-M for non-terraced with mulch, FSPs-M for fish-scale pits with mulch, ZTr-M for zig terraces with mulch, LBTr-M for level bench terraces with mulch, and TTr-M for trench terraces with mulch.
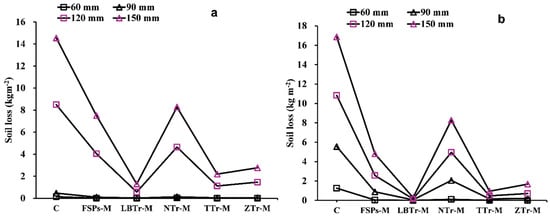
Figure 8.
Observed (a) and predicted (b) soil loss for different combinations. The abbreviations of the terracing–mulch combinations are as follows: C for control plot, NTr-M for non-terraced with mulch, FSPs-M for fish-scale pits with mulch, ZTr-M for zig terraces with mulch, LBTr-M for level bench terraces with mulch, and TTr-M for trench terraces with mulch.
Another effective treatment in this study was the combination of TTr-M, which recorded the second-lowest runoff (Figure 7) and soil loss (Figure 8). These findings align with previous research, such as [57], in which the authors observed significant reductions in runoff coefficients on rangeland (from 0.43 to 0.14) and cropland (from 0.13 to 0.05) due to trench terracing. Similarly, [58] demonstrated the effectiveness of trench terraces in northern Ethiopia for controlling runoff and soil erosion, using P- and C-factors to highlight their utility in arid and semiarid environments. The unique functionality of trench terraces was evident in their integrated ditch-and-embankment design, which effectively reduced runoff and sediment transport. The earthen embankment, positioned downslope and formed from excavated soil, retained excess water and sediment, while the upslope ditch collected runoff and sediment from the inter-trench area, enhancing water infiltration. Even when the ditch reaches capacity, the embankment continues to manage water effectively, ensuring sustained erosion control [57,58,59]. In this study, the trench terrace’s earthen embankment and upslope ditch effectively slowed runoff and captured sediment, further demonstrating the utility of this configuration in reducing soil loss.
ZTr-M is another highly effective method for controlling runoff and soil loss, as evidenced by the low average values presented in Table 4 and Table 5. This finding is within the range of results reported in [55,60], where zig terraces were shown to minimize runoff and sediment yield effectively. The structural traits of zig terraces, including their compacted embankments and channels, significantly alter hydrological processes by slowing runoff, enhancing infiltration, and trapping sediment, thereby increasing rainwater and sediment retention [55]. The incremental analysis in this study (Figure 6) further supports these findings, demonstrating that ZTr-M showed moderate soil loss increments across rainfall intensity transitions.
FSPs-M demonstrated moderate effectiveness in reducing runoff and soil loss under lower rainfall intensities. The pits effectively slowed surface runoff and trapped sediment during mild to moderate storms, aligning with findings that the edges of fish-scale pits restrict surface runoff while storing part of it [61,62]. However, their performance declined significantly under higher rainfall intensities, likely due to exceeding their capacity to manage concentrated runoff and sediment transport.
The small scale and lack of connectivity in fish-scale pits restrict their ability to disrupt runoff pathways or enhance infiltration during high-intensity storms effectively. Once their storage capacity is exceeded under prolonged or heavy rainfall, overflow occurs, reducing sediment interception and increasing downstream erosion. Simulated rainfall experiments on the Loess Plateau have similarly shown that exceeding storage capacity accelerates runoff and sediment transport [55,61]. The incremental analysis in this study revealed sharp increases in soil loss as rainfall intensity transitioned between 90 mm/h and 120 mm/h, where sediment detachment became particularly pronounced (Figure 6). These findings underscore the challenges posed by high-intensity rainfall for systems like FSPs-M, whose discontinuous design limits their resilience.
WEPP simulations further supported these observations, predicting a significant decline in FSPs-M’s effectiveness under extreme rainfall conditions. While the model captured general runoff reduction trends observed in the field, discrepancies emerged at higher rainfall intensities, where soil loss was consistently underestimated. This divergence highlights FSPs-M’s heightened sensitivity to rainfall intensity compared to other terracing systems. Previous studies have similarly suggested that while fish-scale pits can temporarily store runoff and trap sediment, their long-term effectiveness is limited under extreme hydrological conditions [55,63].
4.2. The Effect of Mulching on Water Erosion
Mulch has been widely recognized as an effective measure for erosion control because of its ability to reduce raindrop impact, enhance soil stability, and improve infiltration. Previous studies have demonstrated that mulching reduces runoff velocity and pond water on the soil surface, increasing soil water pressure head and infiltration [33,64,65]. In this investigation, both observed and predicted results confirmed the efficiency of mulch in minimizing runoff and soil loss, particularly under lower rainfall intensities. At 60 mm/h and 90 mm/h, mulch significantly minimized soil detachment and runoff, demonstrating its ability to provide surface protection and enhance water retention. This reduction can be connected to the following features of mulch: (a) the protective function of mulch, which safeguards the soil from direct contact with raindrops [66]; (b) enhanced hydraulic roughness from the straw cover, which slows the surface runoff and promotes infiltration; and (c) water retention by the mulch layer [33,67].
However, the performance of mulch sharply declined under intense rainfall events (120 mm/h and 150 mm/h). Incremental analyses (Figure 6) consistently showed that as rainfall intensity increases, both runoff and soil loss escalate, indicating a reduced protective capacity of mulch under such extreme conditions. This suggests that mulch alone begins to lose its effectiveness under intense storms as the protective layer becomes saturated and less able to buffer raindrop impact or retain water. These findings align with [68], which noted that mulch performance varies significantly with rainfall intensity and environmental factors. Similarly, [69] indicated that straw mulching enhances infiltration capacity and reduces runoff intensity; however, these benefits are less pronounced during heavy rainfall events when the mulch becomes saturated. WEPP simulations also reflected this decline in effectiveness, though slight discrepancies were noted in predicting soil loss under extreme conditions.
5. Conclusions
This study investigates the effectiveness of various terracing–mulching combinations in mitigating water erosion on the Loess Plateau under varying rainfall intensities. Among the strategies assessed, LBTr-M emerged as the most effective solution. At lower rainfall intensities (e.g., 60 mm/h), all treatments significantly reduced water erosion compared to the control plot. However, as rainfall intensity increased, the effectiveness of these treatments varied. Under extreme 150 mm/h conditions, LBTr-M reduced runoff to 40.25 mm and soil loss to 1.3 kg/m2, while the control plot showed 45.65 mm runoff and 14.55 kg/m2 soil loss. Following LBTr-M, TTr-M and ZTr-M recorded runoff values of 40.51 mm and 39.84 mm, respectively, with corresponding soil loss measurements of 2.19 kg/m2 and 2.77 kg/m2 at the 150 mm/h rainfall intensity. While these strategies effectively reduced runoff to levels comparable to LBTr-M, their performance in soil loss reduction was slightly less effective under extreme conditions. In contrast, the performance of FSPs-M and NTr-M significantly declined during high rainfall events, with FSPs-M showing 43.24 mm runoff and 7.5 kg/m2 soil loss, and NTr-M resulting in 44.16 mm runoff and 8.28 kg/m2 soil loss. These treatments exhibited higher sensitivity to rainfall intensity changes.
The Water Erosion Prediction Project (WEPP) model validated these findings, demonstrating strong predictive accuracy with coefficients of determination (R2) of 97% for runoff and 86% for soil loss. This underscores the model’s reliability in simulating erosion processes and evaluating the effectiveness of terracing–mulching strategies under different rainfall conditions.
This study addresses a critical research gap by evaluating the combined effects of terracing and mulching under varying rainfall intensities. While previous studies have modeled terracing or mulching separately, this study integrates both strategies and uses single-storm artificial rainfall simulations in conjunction with the WEPP model to provide more reliable predictions of erosion processes in regions like the Loess Plateau. For decision-makers and farmers, the findings underscore the superiority of LBTr-M for effective erosion control, especially in erosion-prone regions experiencing heavy rainfall. However, the high initial costs and labor-intensive construction associated with LBTr-M may present challenges for resource-limited communities. In such contexts, TTr-M and ZTr-M have demonstrated strong erosion control performance and may serve as practical alternatives. However, further research on the cost-effectiveness of various terrace construction and maintenance practices is crucial to support the broader applicability of these findings. Therefore, future studies should focus on evaluating the long-term performance of these strategies, conducting economic feasibility analyses, and integrating different advanced modeling techniques to enhance the precision and applicability of erosion predictions.
Author Contributions
M.A.A. contributed to the design, methodology, rainfall simulations, data gathering, and manuscript writing. W.W. was in charge of concept creation, article review, project management, and finance. S.Z. designed and carried out the entire experiment and handled data gathering. W.L. helped with rainfall simulations, conception, and article revision. L.C. helped with data analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U21A2011) and National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFF1300403).
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the findings of this study are not publicly available, but can be made available upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors affirm no conflicting interests regarding this research paper.
References
- Chen, D.; Wei, W.; Chen, L. Effects of terracing on soil properties in three key mountainous regions of China. Geogr. Sustain. 2021, 2, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrescu-Mag, R.M.; Petrescu, D.C.; Azadi, H. A social perspective on soil functions and quality improvement: Romanian farmers’ perceptions. Geoderma 2020, 380, 114573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, W.G.; Víctor Hugo Alvarez, V.; Neves, J.C.L. New methods for estimating lime requirement to attain desirable pH values in Brazilian soils. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2020, 44, e0200008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanarella, L. Agricultural policy: Govern our soils. Nature 2015, 528, 32–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuazo, V.D.; Pleguezuelo, C.R.; Peinado, F.M.; De Graaff, J.; Martínez, J.F.; Flanagan, D. Environmental impact of introducing plant covers in the taluses of terraces: Implications for mitigating agricultural soil erosion and runoff. Catena 2011, 84, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.N.; Gong, Y.; Hu, T.; Lal, R.; Zheng, J.; Justine, M.F.; Azhar, M.; Che, M.; Zhang, H. Effect of slope, rainfall intensity and mulch on erosion and infiltration under simulated rain on purple soil of south-western Sichuan province, China. Water 2016, 8, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X. The effect of slope length on sediment yield by rainfall impact under different land use types. Water Resour. 2016, 43, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Zhang, X.J.; Wang, J.; Flanagan, D.C. Assessing applicability of the WEPP hillslope model to steep landscapes in the northern Loess Plateau of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 197, 104492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Wang, S.-J. Effects of land use, land cover and rainfall regimes on the surface runoff and soil loss on karst slopes in southwest China. Catena 2012, 90, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xing, S.; Hou, X. Evaluation of soil erosion and ecological rehabilitation in Loess Plateau region in Northwest China using plutonium isotopes. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 191, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Mu, X.; Holden, J.; Wu, Y.; Irvine, B.; Wang, F.; Gao, P.; Zhao, G.; Sun, W. Comparison of soil erosion models used to study the Chinese Loess Plateau. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 170, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Næss, J.S.; Iordan, C.M.; Huang, B.; Zhao, W.; Cherubini, F. Recent global land cover dynamics and implications for soil erosion and carbon losses from deforestation. Anthropocene 2021, 34, 100291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, D.V.; Silva, M.L.N.; Beniaich, A.; Pio, R.; Gonzaga, M.I.S.; Avanzi, J.C.; Bispo, D.F.A.; Curi, N. Dynamics and losses of soil organic matter and nutrients by water erosion in cover crop management systems in olive groves, in tropical regions. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 209, 104863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, D. Soil erosion: A food and environmental threat. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2006, 8, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarigan, R.A. Impact of Climate Change on Soil Erosion. Agrotekma J. Agroteknologi Dan Ilmu Pertan. 2022, 7, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moges, D.M.; Kmoch, A.; Bhat, H.G.; Uuemaa, E. Future soil loss in highland Ethiopia under changing climate and land use. Reg. Environ. Change 2020, 20, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkel, L. Climatically controlled terraces in uplifting mountain areas. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2003, 22, 2189–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Chen, D.; Wang, L.; Daryanto, S.; Chen, L.; Yu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Sun, G.; Feng, T. Global synthesis of the classifications, distributions, benefits and issues of terracing. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 159, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Qi, J.; Liu, E.; Jiang, Y.; Li, S.; Meng, F.-R. Estimated potential impacts of soil and water conservation terraces on potato yields under different climate conditions. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 74, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wei, W.; Chen, L. Effects of terracing practices on water erosion control in China: A meta-analysis. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 173, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.; Alvi, S.; Kausar, R.; Akram, M.I. The effectiveness of soil and water conservation terrace structures for improvement of crops and soil productivity in rainfed terraced system. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 53, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Wang, X.; Xie, Z.; Wang, Y. Effects of gravel-sand mulch on the runoff, erosion, and nutrient losses in the Loess Plateau of north-western China under simulated rainfall. Soil Water Res. 2021, 16, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y. Gravel–sand mulch for soil and water conservation in the semiarid loess region of northwest China. Catena 2003, 52, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, R.; Raza, M.A.S.; Valipour, M.; Saleem, M.F.; Zaheer, M.S.; Ahmad, S.; Toleikiene, M.; Haider, I.; Aslam, M.U.; Nazar, M.A. Potential agricultural and environmental benefits of mulches—A review. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2020, 44, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader, M.A.; Singha, A.; Begum, M.A.; Jewel, A.; Khan, F.H.; Khan, N.I. Mulching as water-saving technique in dryland agriculture. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2019, 43, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Poesen, J.; Vanmaercke, M.; Ballabio, C.; Hervás, J.; Maerker, M.; Scarpa, S.; Panagos, P. Monitoring gully erosion in the European Union: A novel approach based on the Land Use/Cover Area frame survey (LUCAS). Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2022, 10, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, D.C.; Gilley, J.E.; Franti, T.G. Water Erosion Prediction Project (WEPP): Development history, model capabilities, and future enhancements. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 1603–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, D.; Nearing, M. USDA-Water Erosion Prediction Project: Hillslope profile and watershed model documentation. NSERL Rep. 1995, 10, 1196–47097. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.; Gong, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, R. Analysis and modeling of soil conservation measures in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area in China. Catena 2010, 81, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Himanshu, S.K.; Mishra, S.K.; Singh, V.P. Physically based soil erosion and sediment yield models revisited. Catena 2016, 147, 595–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Seeger, M.; Iserloh, T.; González, J.M.S.; Ruiz-Sinoga, J.D.; Ries, J.B. Rainfall-simulated quantification of initial soil erosion processes in sloping and poorly maintained terraced vineyards-Key issues for sustainable management systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Pan, D.; Yang, Y. Effects of terracing measures on water retention of pinus Tabulaeformis forest in the dryland loess hilly region of China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 308, 108544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, A.d.A.; Abrantes, J.; De Lima, J.; Singh, V.; Santos, T. Impact of mulching on soil and water dynamics under intermittent simulated rainfall. Catena 2013, 109, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Jia, G.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X. The effectiveness of mulching practices on water erosion control: A global meta-analysis. Geoderma 2023, 438, 116643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, D.; Cai, S.; Feng, J.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Evaluating the applicability of the water erosion prediction project (WEPP) model to runoff and soil loss of sandstone reliefs in the Loess Plateau, China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2023, 11, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Fu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Gong, Z. Modeling soil erosion dynamic processes along hillslopes with vegetation impact across different land uses on the Loess Plateau of China. Catena 2024, 243, 108202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Zhang, X.; Yan, S.; Chen, H. Estimating soil erosion response to land use/cover change in a catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2018, 6, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Wang, Y.; Xu, P.; Yan, K. Assessment of the performance of WEPP in purple soil area with simulated rainfall experiments. J. Mt. Sci. 2012, 9, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Chen, L.; Fu, B. Effects of rainfall change on water erosion processes in terrestrial ecosystems: A review. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2009, 33, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xing, Z.; Zhao, C.; Deng, J.; Yang, B.; Tian, Q.; Rees, H.W.; Badreldin, N. Characterizing long-term soil and water erosion and their interactions with various conservation practices in the semi-arid Zulihe basin, Dingxi, Gansu, China. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 106, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, W.; Aydin, A.; Beroya-Eitner, M.A.; Gao, G. Loess genesis and worldwide distribution. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 201, 102947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, Y.; Yin, C.; Yi, X.; Ren, J.; Chien, H. Farmers’ adoption preferences for sustainable agriculture practices in Northwest China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosdocimi, M.; Tarolli, P.; Cerdà, A. Mulching practices for reducing soil water erosion: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 161, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordán, A.; Zavala, L.M.; Gil, J. Effects of mulching on soil physical properties and runoff under semi-arid conditions in southern Spain. Catena 2010, 81, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, P.; Chen, X.; Helmers, M.J.; Zhou, X. Runoff and sediment yield under simulated rainfall on hillslopes in the Loess Plateau of China. Soil Res. 2013, 51, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Li, X.; Jia, L.; Gong, H.; Cai, Q. Experimental study of rill evolution processes and relationships between runoff and erosion on clay loam and loess. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, R.A.; Ziegler, A.D. Hillslope runoff and erosion as affected by rolled erosion control systems: A field study. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2006, 20, 2839–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Feng, Q.; Chen, W.; Wei, W.; Deo, R.C. The influence of structural factors on stormwater runoff retention of extensive green roofs: New evidence from scale-based models and real experiments. J. Hydrol. 2019, 569, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Dong, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X. Effects of different terrace protection measures in a sloping land consolidation project targeting soil erosion at the slope scale. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 53, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Gong, Y.; Li, Y.; Hong, Q.; Xu, L.; Liu, R. A comparison of WEPP and SWAT for modeling soil erosion of the Zhangjiachong Watershed in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.R.; Lane, L.J. User Requirements: USDA, Water Erosion Prediction Project (WEPP) Draft 6.3; NSERL Report (USA). 1987. Available online: https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/full/10.5555/19971913094 (accessed on 16 February 2025).
- Tarolli, P.; Preti, F.; Romano, N. Terraced landscapes: From an old best practice to a potential hazard for soil degradation due to land abandonment. Anthropocene 2014, 6, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutebuka, J.; Uwimanzi, A.M.; Nkundwakazi, O.; Kagabo, D.M.; Mbonigaba, J.J.M.; Vermeir, P.; Verdoodt, A. Effectiveness of terracing techniques for controlling soil erosion by water in Rwanda. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorren, L.; Rey, F. A review of the effect of terracing on erosion. In Briefing Papers of the 2nd SCAPE Workshop; SCAPE: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Wei, W.; Pan, D. Effects of rainfall and terracing-vegetation combinations on water erosion in a loess hilly area, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharda, V.; Dogra, P.; Sena, D. Comparative economic analysis of inter-crop based conservation bench terrace and conventional systems in a sub-humid climate of India. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 98, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taye, G.; Poesen, J.; Wesemael, B.V.; Vanmaercke, M.; Teka, D.; Deckers, J.; Goosse, T.; Maetens, W.; Nyssen, J.; Hallet, V. Effects of land use, slope gradient, and soil and water conservation structures on runoff and soil loss in semi-arid Northern Ethiopia. Phys. Geogr. 2013, 34, 236–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taye, G.; Vanmaercke, M.; Poesen, J.; Van Wesemael, B.; Tesfaye, S.; Teka, D.; Nyssen, J.; Deckers, J.; Haregeweyn, N. Determining RUSLE P-and C-factors for stone bunds and trenches in rangeland and cropland, North Ethiopia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 812–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyssen, J.; Poesen, J.; Descheemaeker, K.; Haregeweyn, N.; Haile, M.; Moeyersons, J.; Frankl, A.; Govers, G.; Munro, N.; Deckers, J. Effects of region-wide soil and water conservation in semi-arid areas: The case of northern Ethiopia. Z. Fur Geomorphol. 2008, 52, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, K.; Li, T.; Li, Y. Regulation effects of reverse-slope level terrace on the runoff and sediment yield in sloping farmland. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 22, 1261. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.; Liu, B.; Zhang, G.; Lu, B.; Ye, Z. Fish-scale pits reduce runoff and sediment. Trans. ASABE 2010, 53, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, B.; Hill, R.L.; Wu, S.; Dong, Q.; Sun, L.; Zhang, K. Fish-scale pit effects on erosion and water runoff dynamics when positioned on a soil slope in the Loess Plateau region, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1813–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-J.; Jiao, J.-Y.; Su, Y.; Chen, Y. The efficiency of large-scale afforestation with fish-scale pits for revegetation and soil erosion control in the steppe zone on the hill-gully Loess Plateau. Catena 2014, 115, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prats, S.A.; Abrantes, J.R.; Crema, I.P.; Keizer, J.J.; de Lima, J.L. Runoff and soil erosion mitigation with sieved forest residue mulch strips under controlled laboratory conditions. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 396, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robichaud, P.R.; Lewis, S.A.; Wagenbrenner, J.W.; Ashmun, L.E.; Brown, R.E. Post-fire mulching for runoff and erosion mitigation: Part I: Effectiveness at reducing hillslope erosion rates. Catena 2013, 105, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabran, K.; Ullah, E.; Hussain, M.; Farooq, M.; Zaman, U.; Yaseen, M.; Chauhan, B. Mulching improves water productivity, yield and quality of fine rice under water-saving rice production systems. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2015, 201, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, P.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X. Effects of tillage and plastic mulch on soil water, growth and yield of spring-sown maize. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 112, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.; Gholami, L.; Sharifi, E.; Khaledi Darvishan, A.; Homaee, M. Scale effect on runoff and soil loss control using rice straw mulch under laboratory conditions. Solid Earth 2015, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Ma, B. The influence of wheat straw mulching and straw length on infiltration, runoff and soil loss. Hydrol. Process. 2022, 36, e14561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).