Spatial and Temporal Changes and Influencing Factors of Mercury in Urban Agglomeration Land Patterns: A Case from Changchun Area, Old Industrial Base of Northeast China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
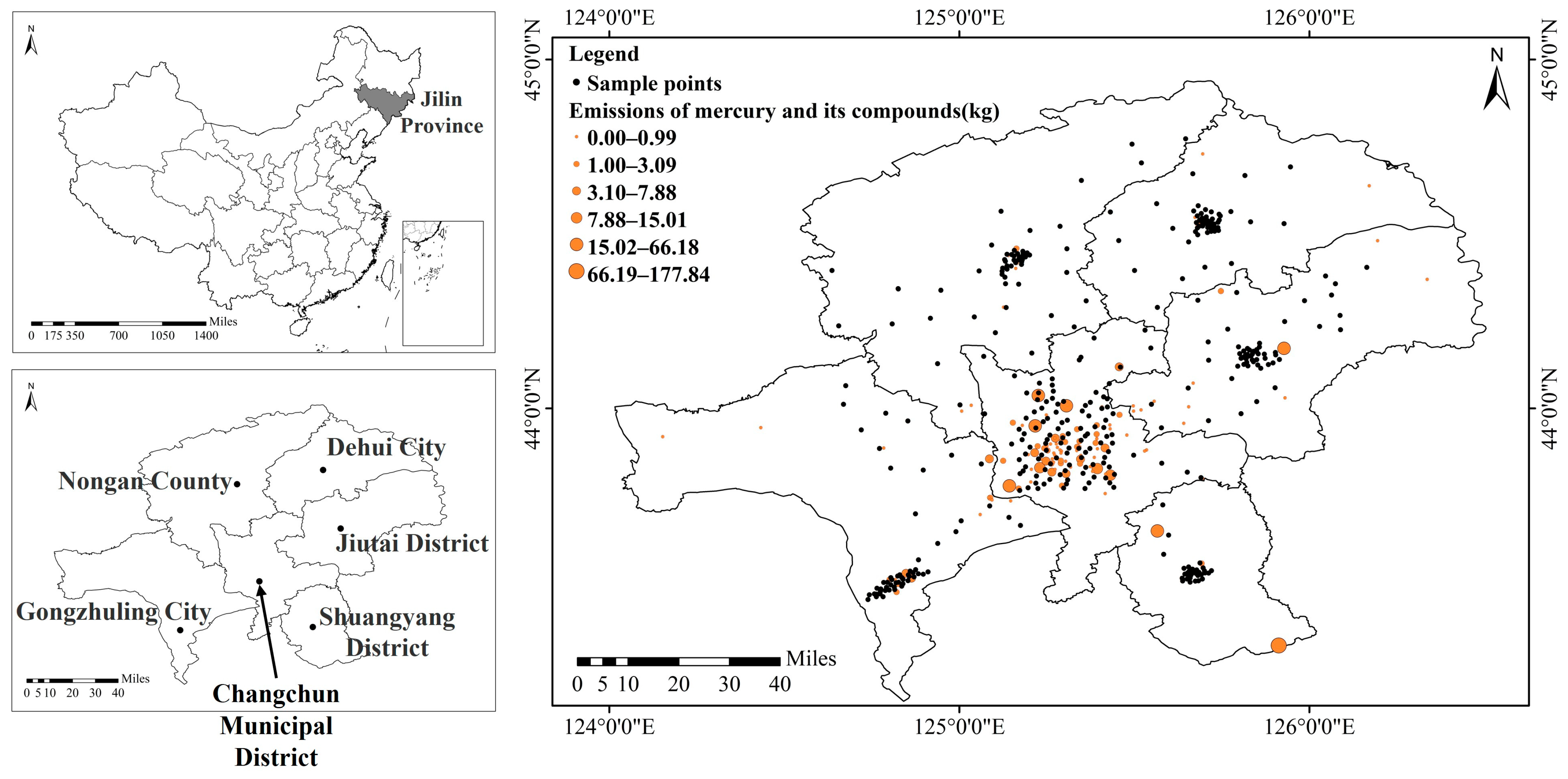
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Point Layout and Processing
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Soil Mercury
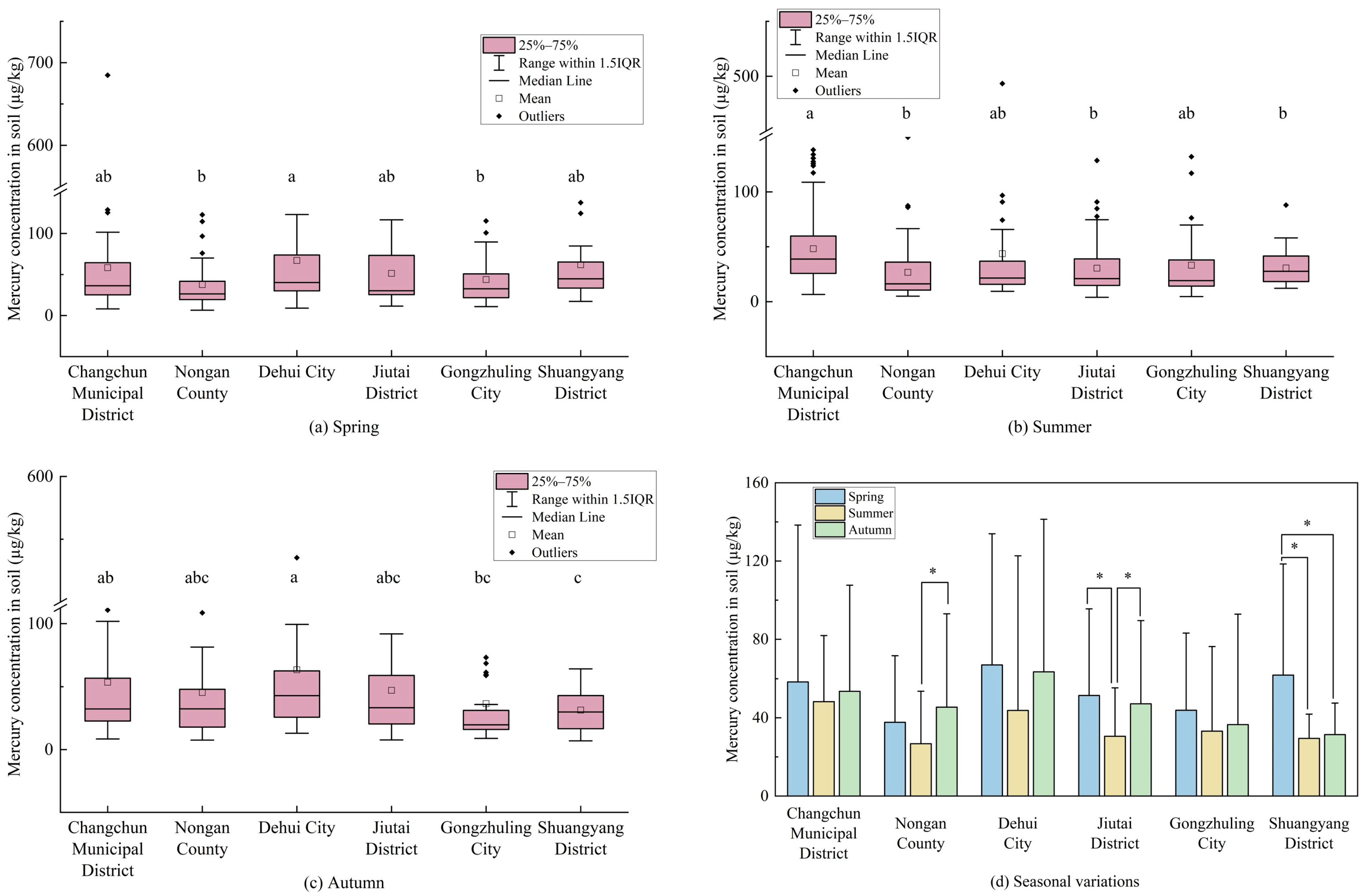
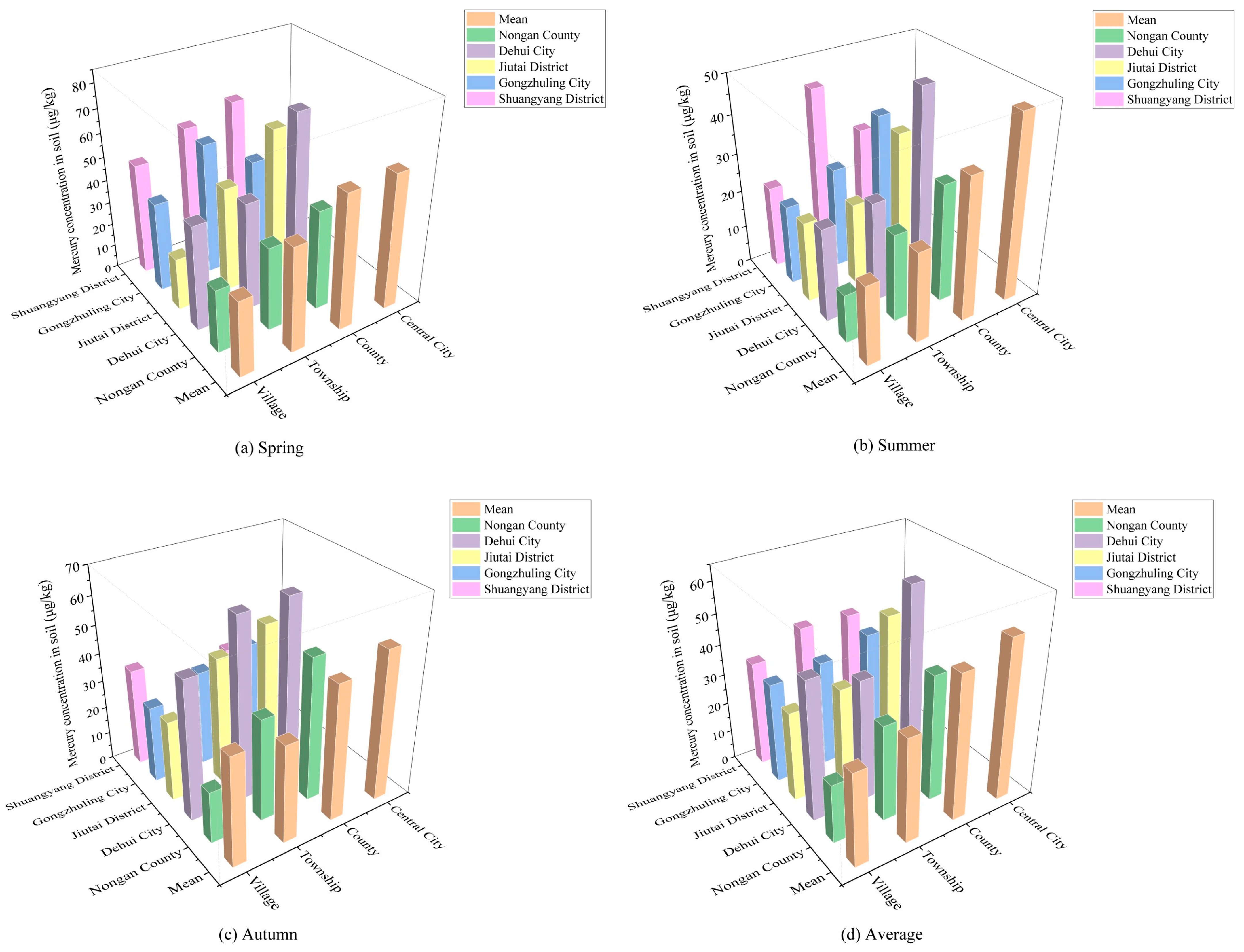
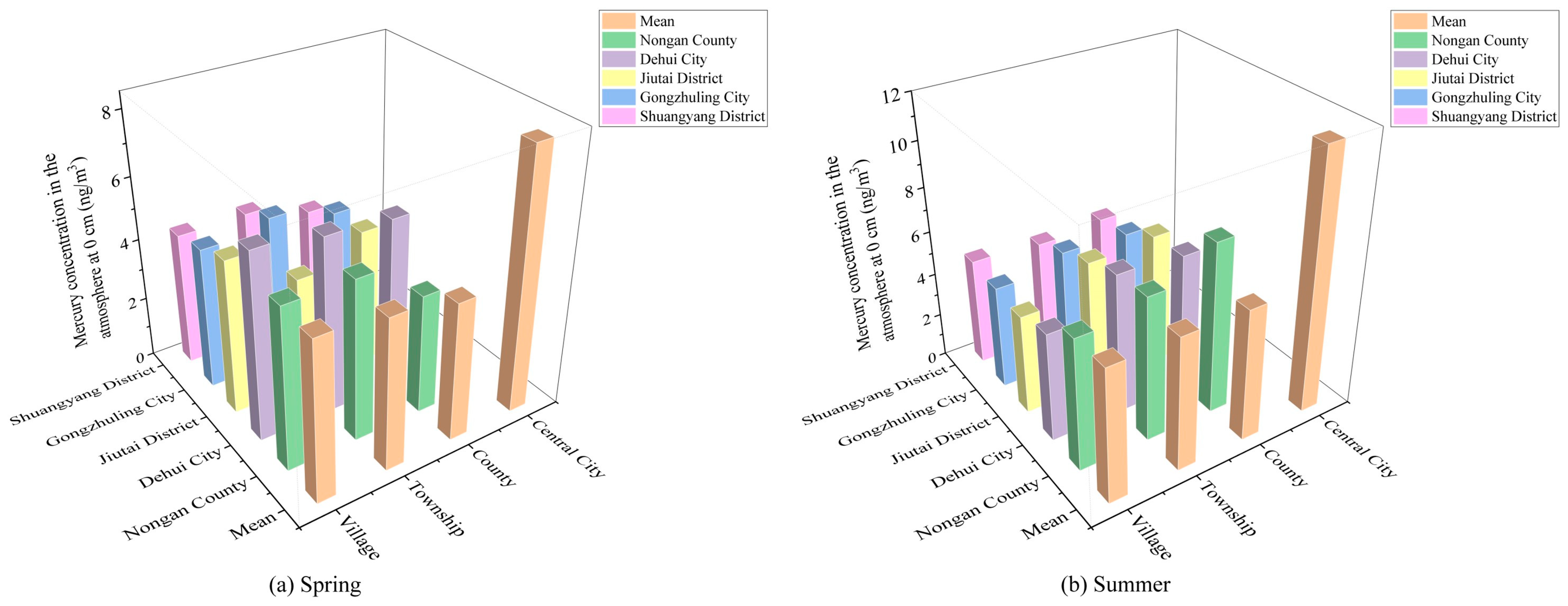
3.1.1. Seasonal Variations in the Soil Mercury Concentration
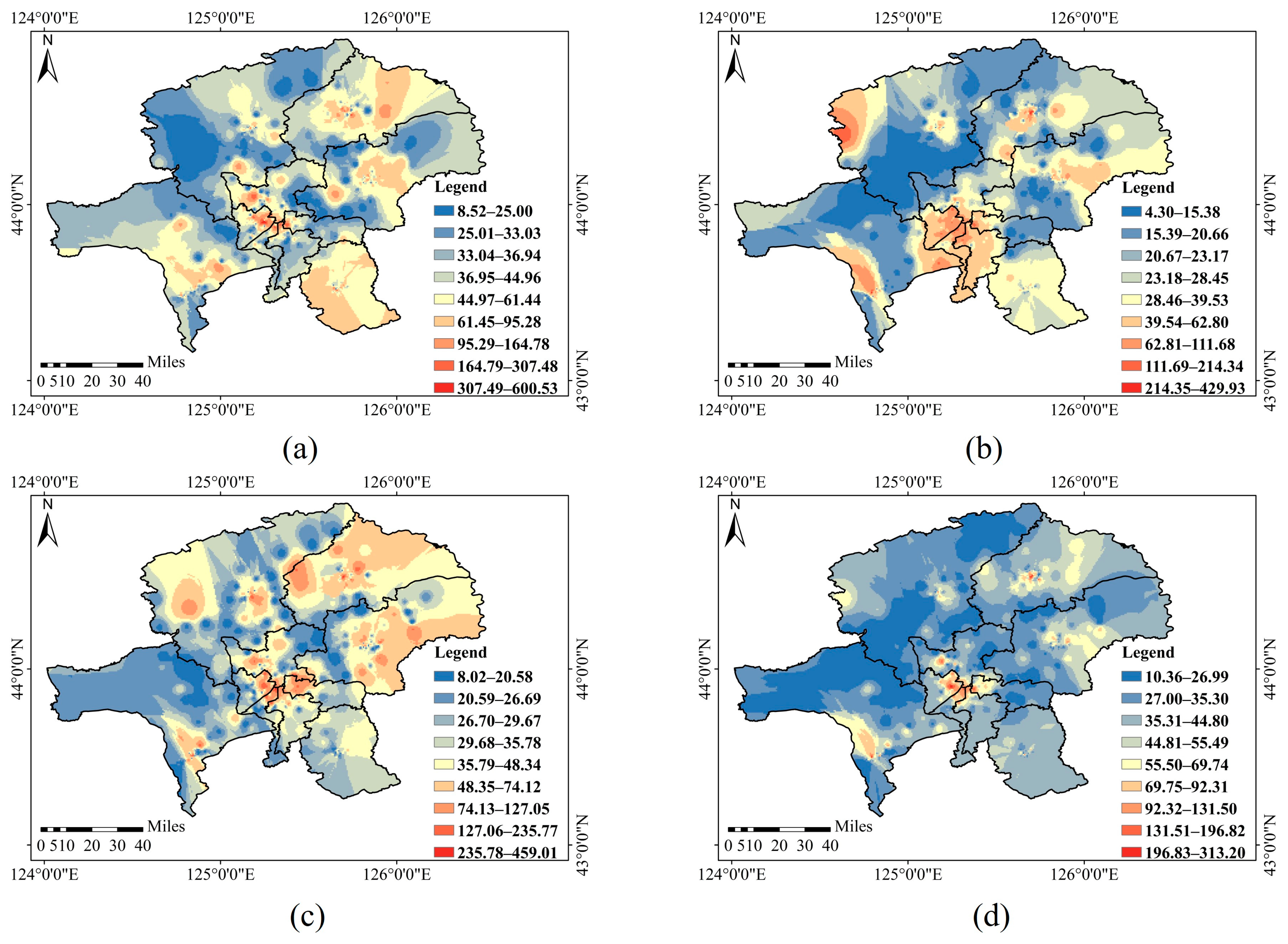
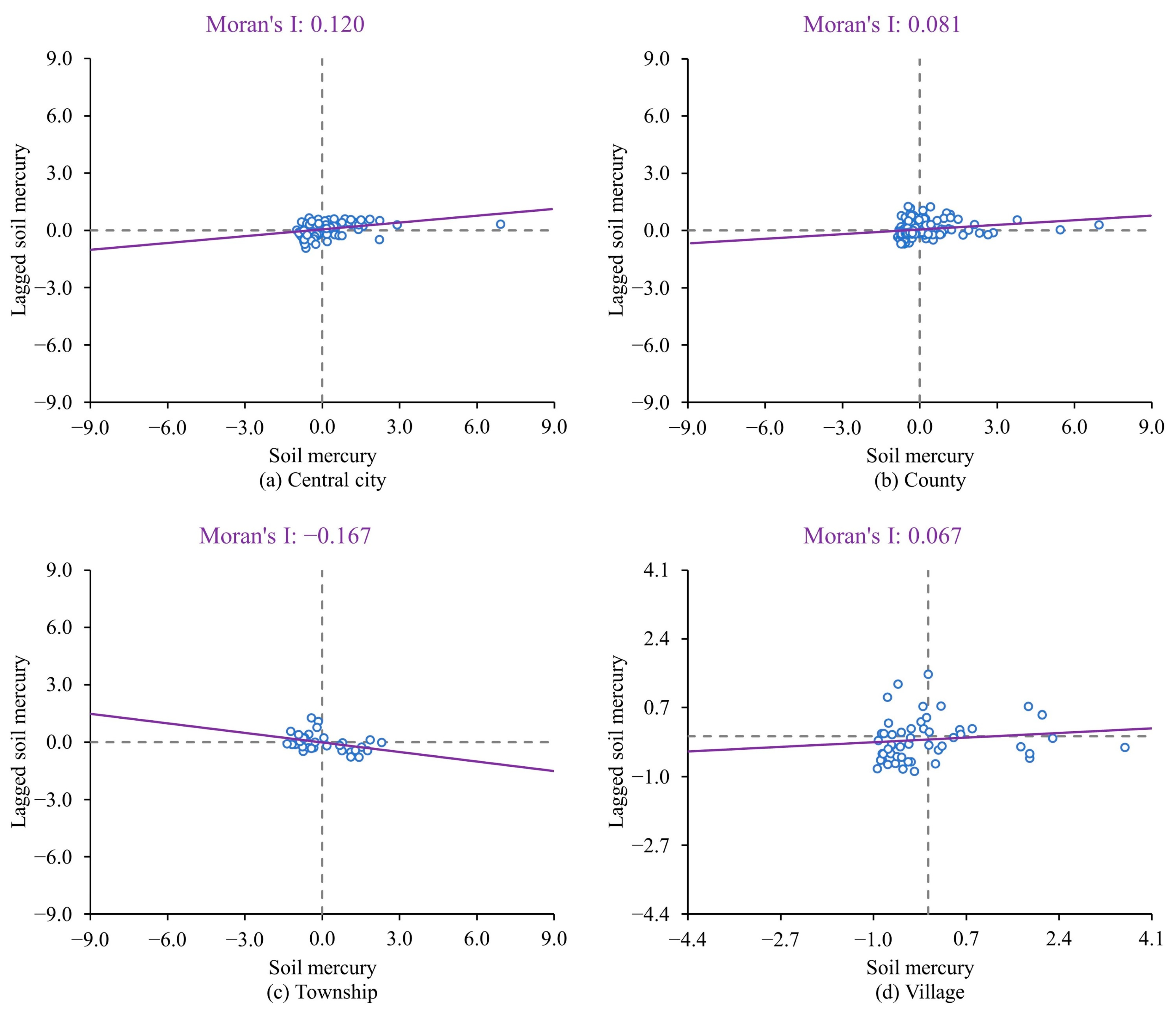
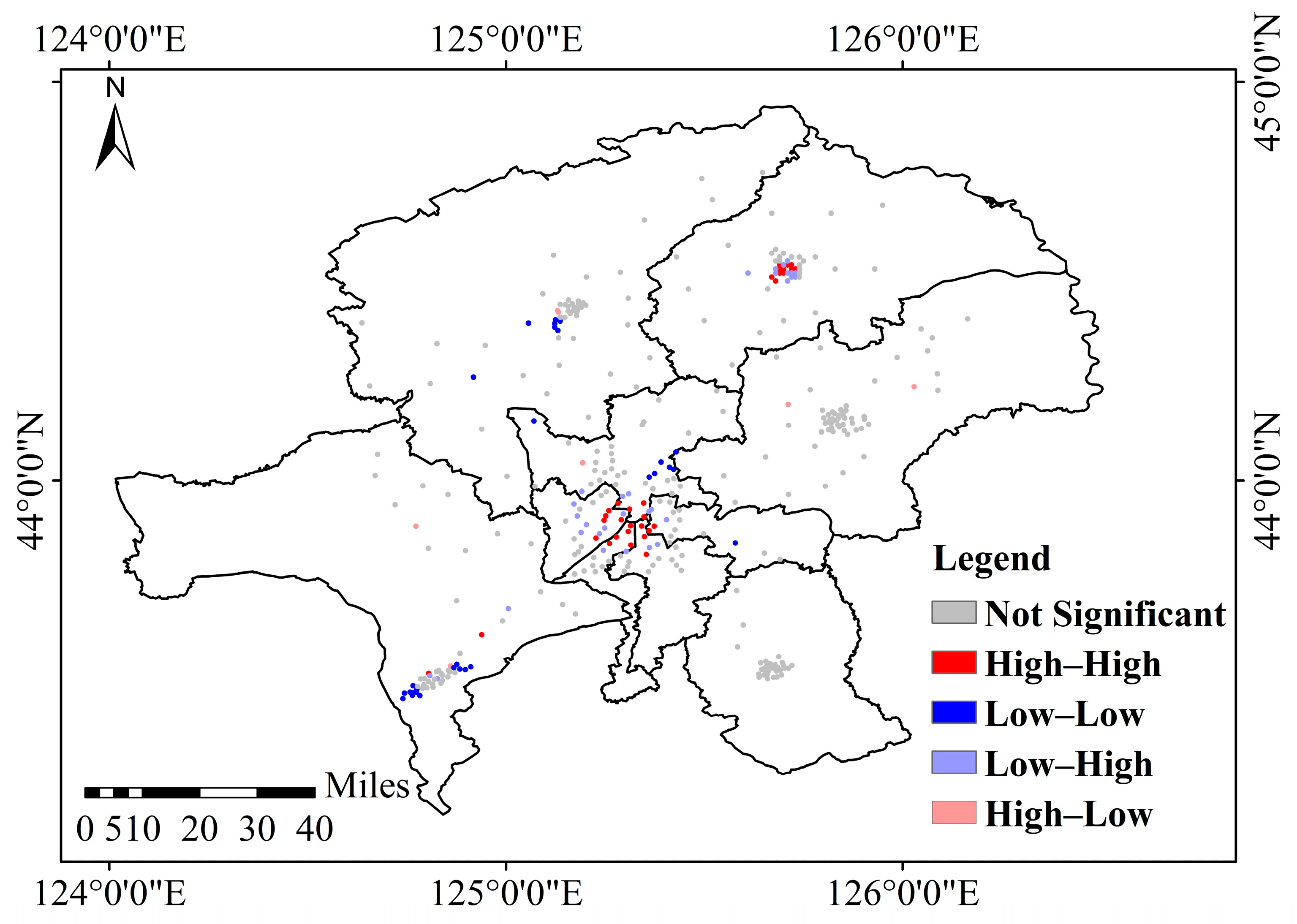
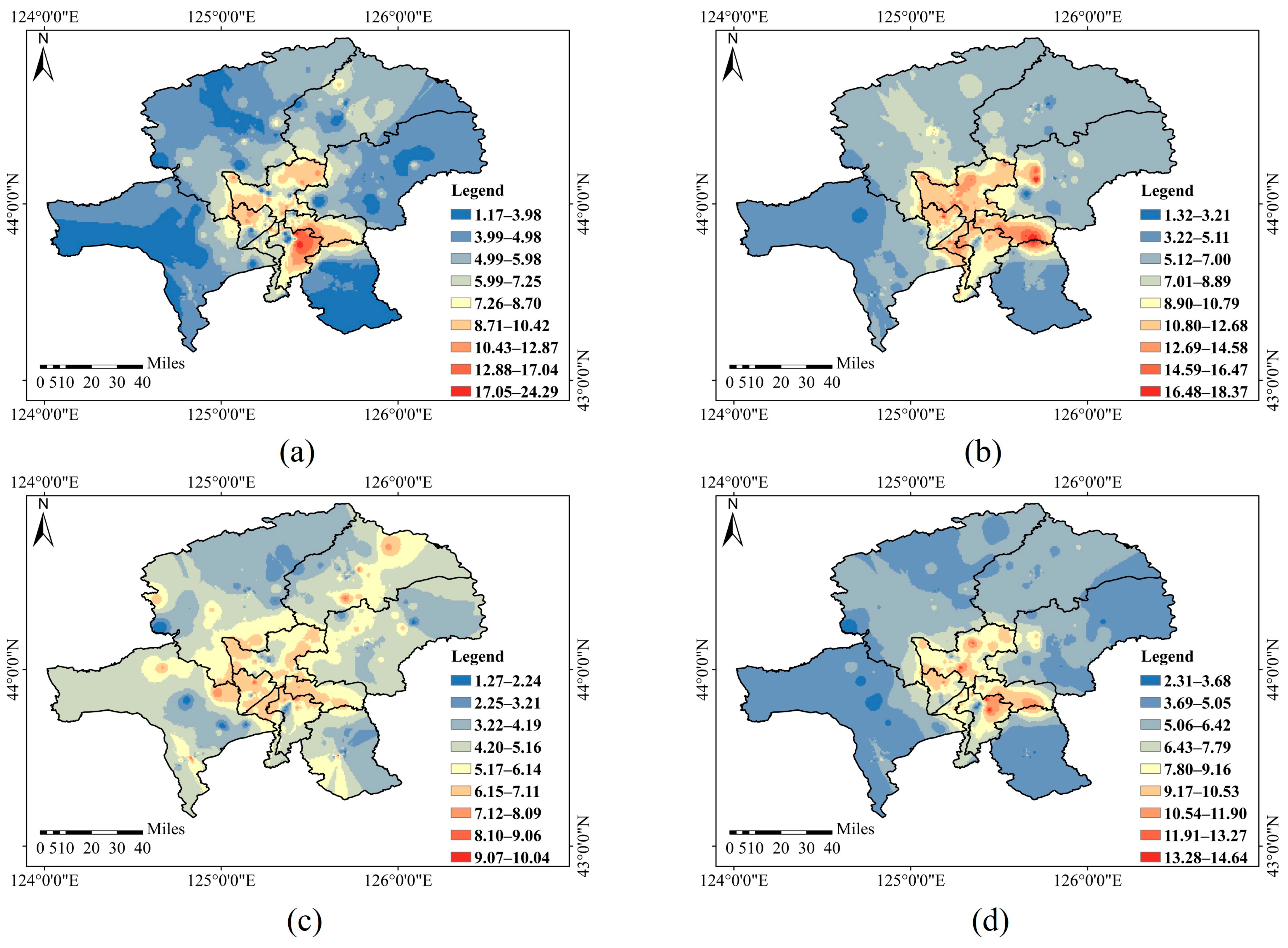
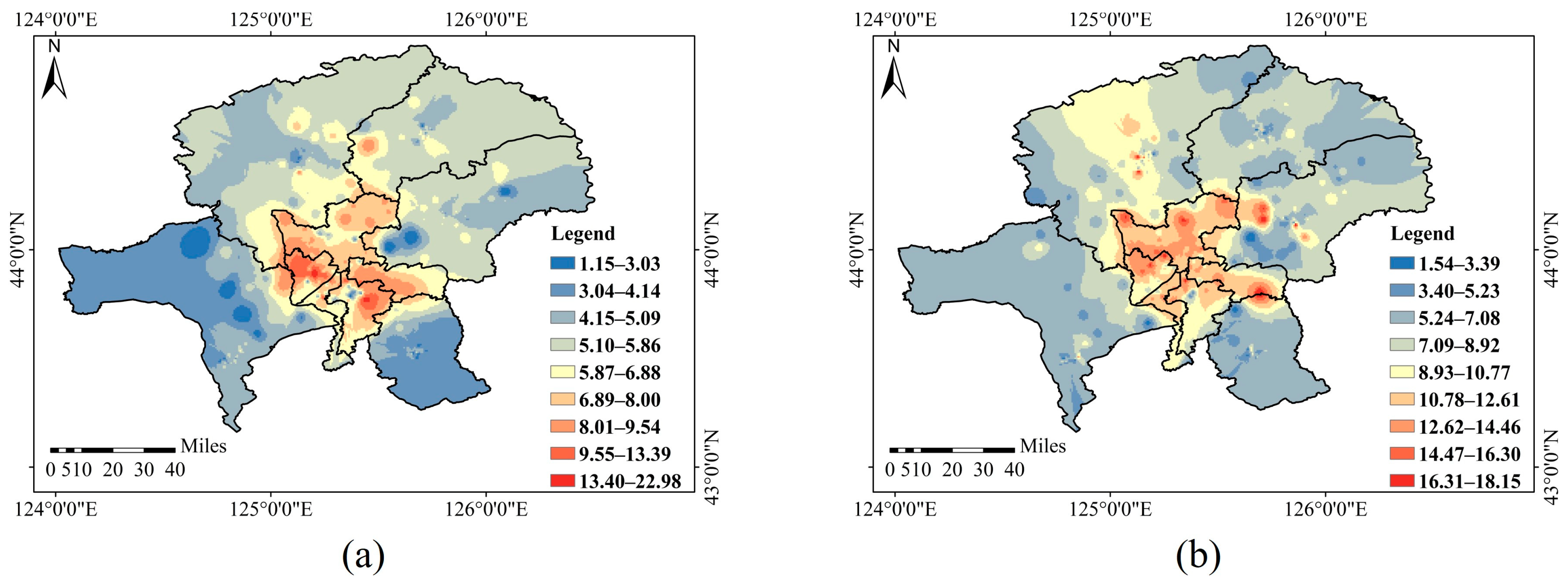
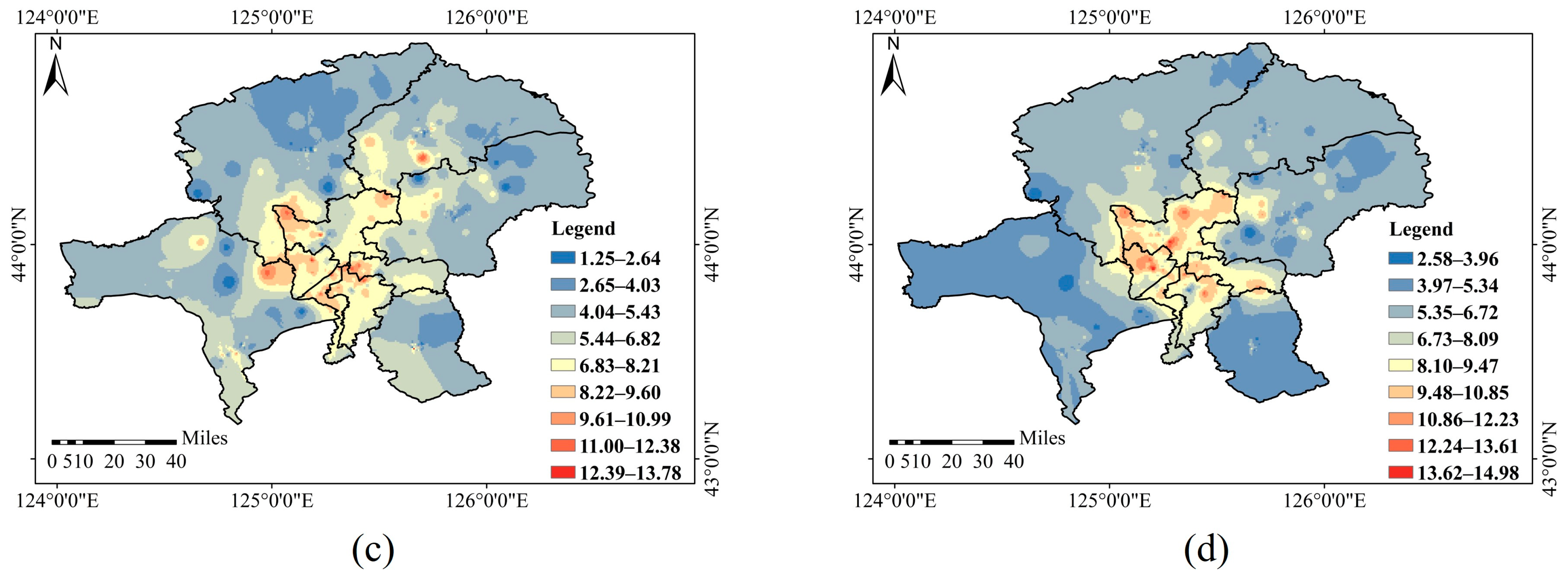
3.1.2. Distribution Characteristics of Soil Mercury in Different Spatial Scales
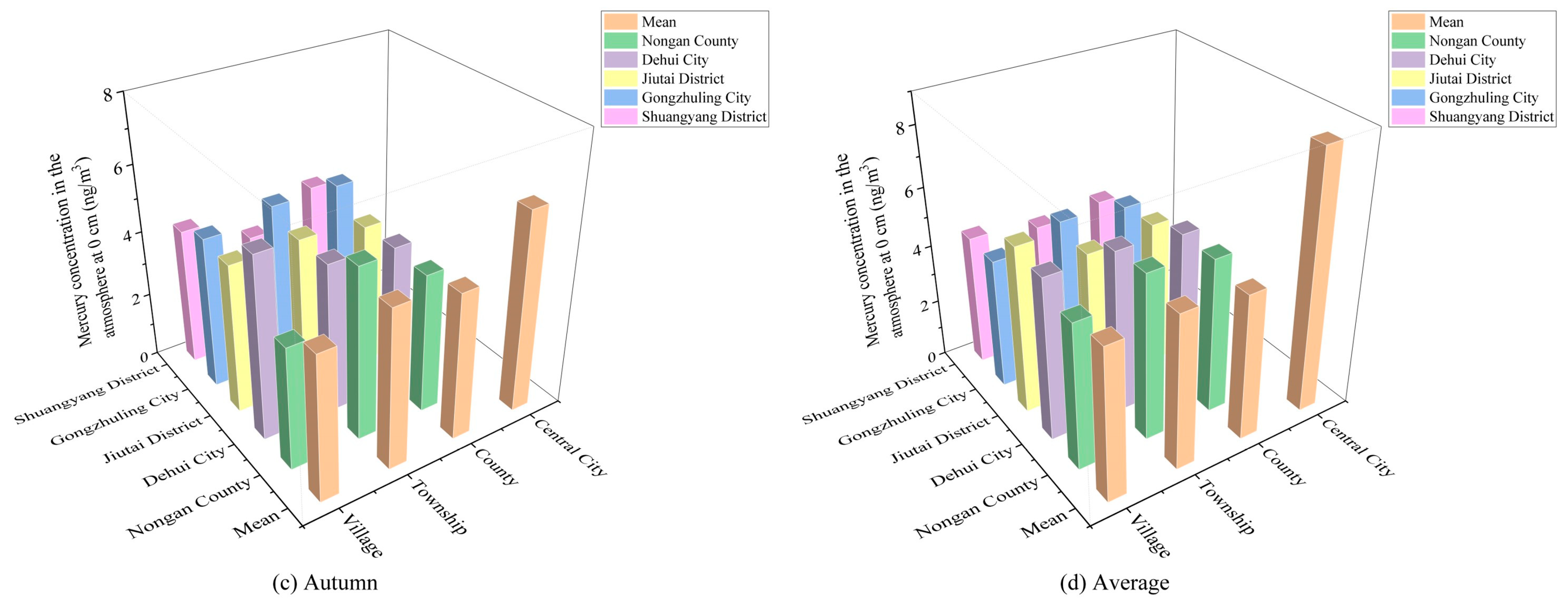
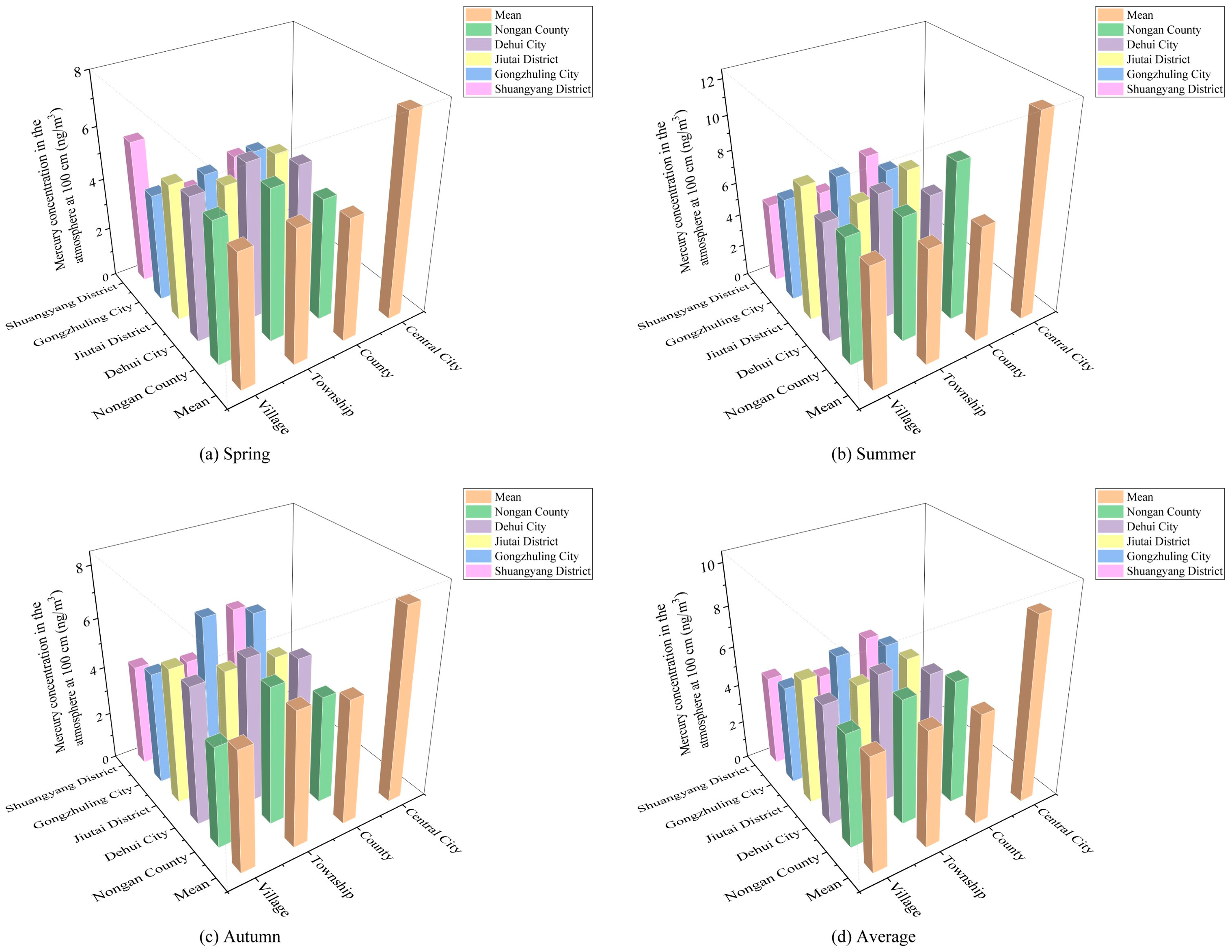
3.2. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics and Distribution of Atmospheric Mercury in Urban Agglomeration
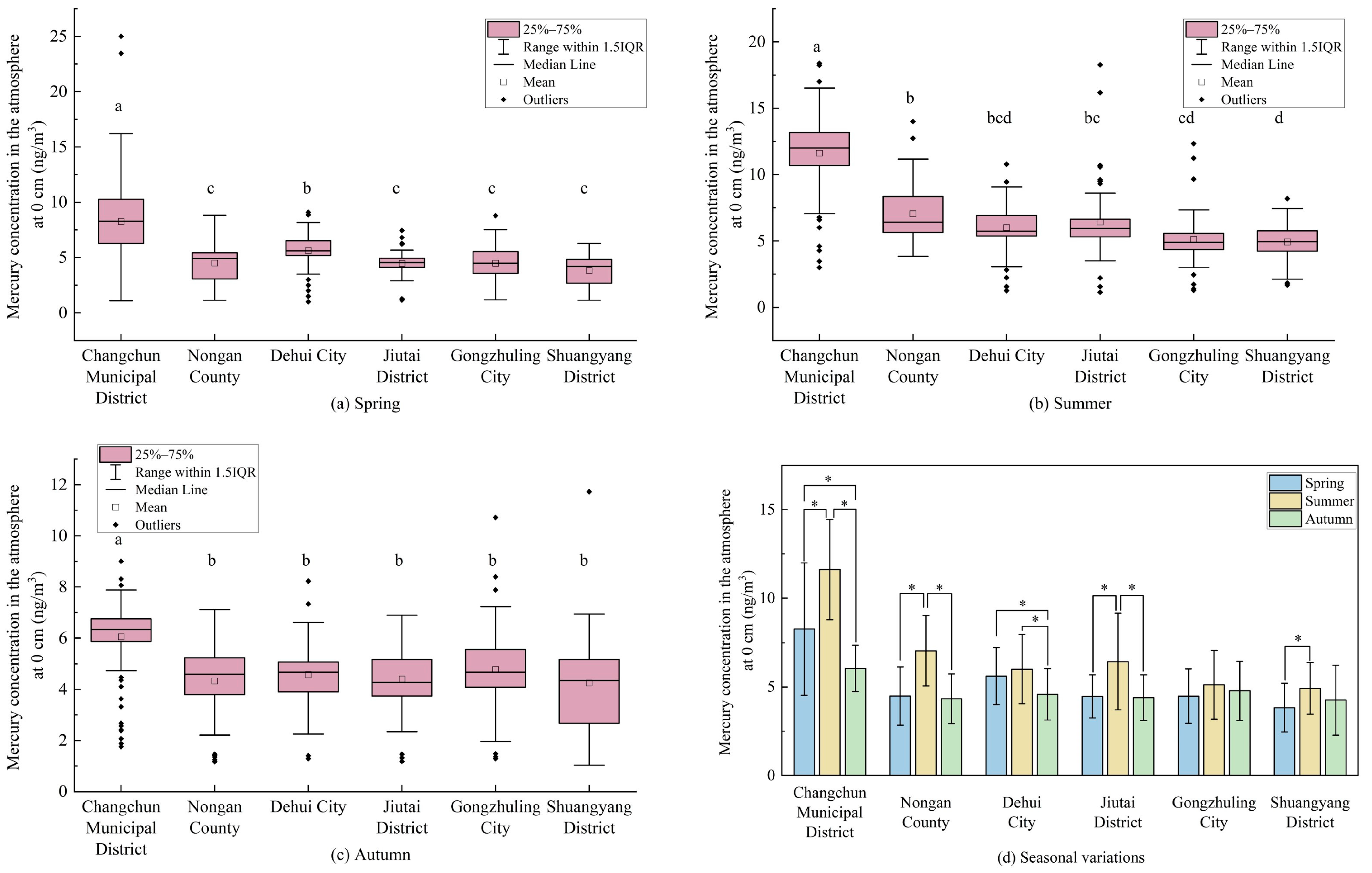
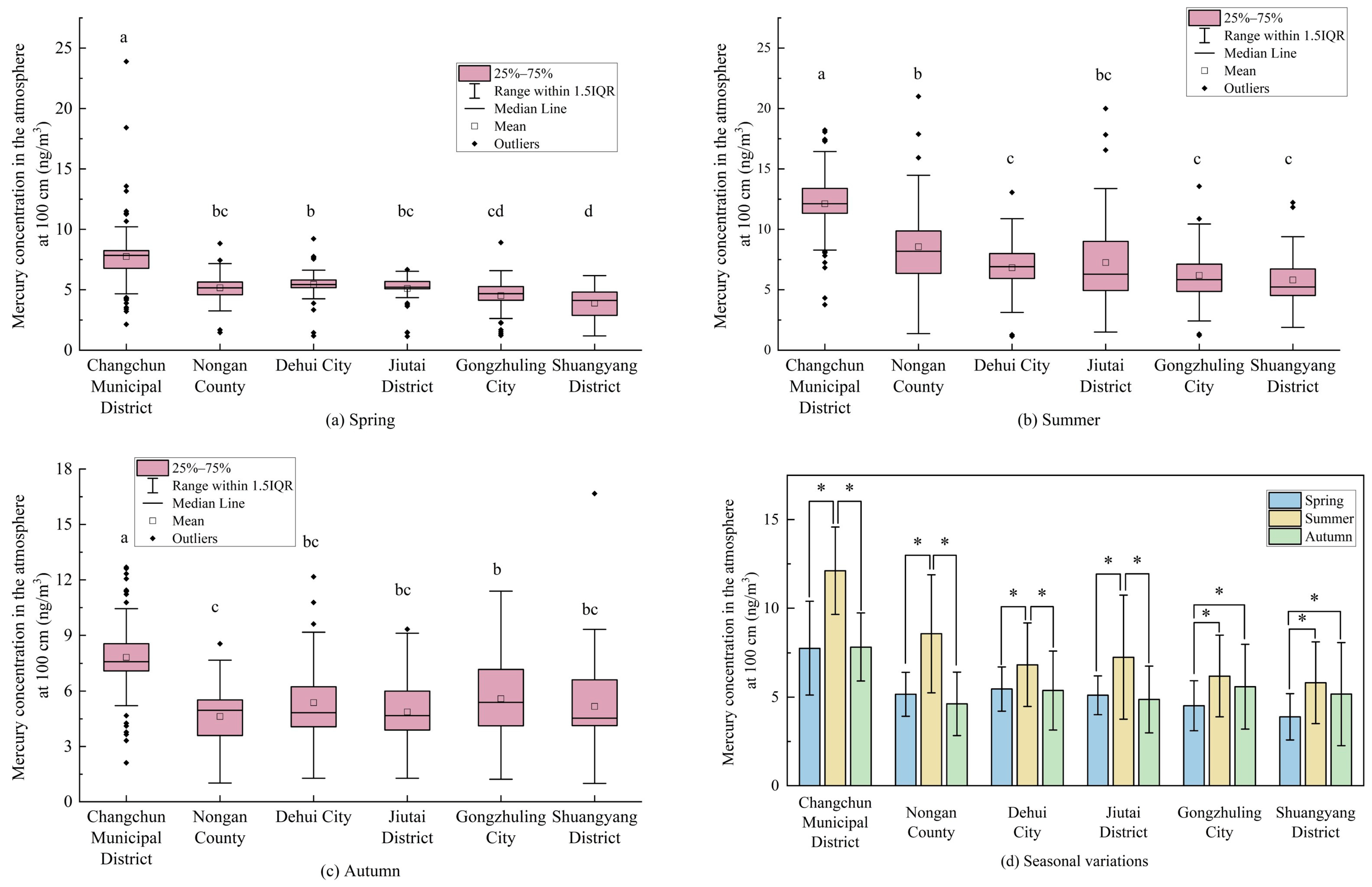
3.2.1. Seasonal Variations in the Atmospheric Mercury Concentration at Different Heights
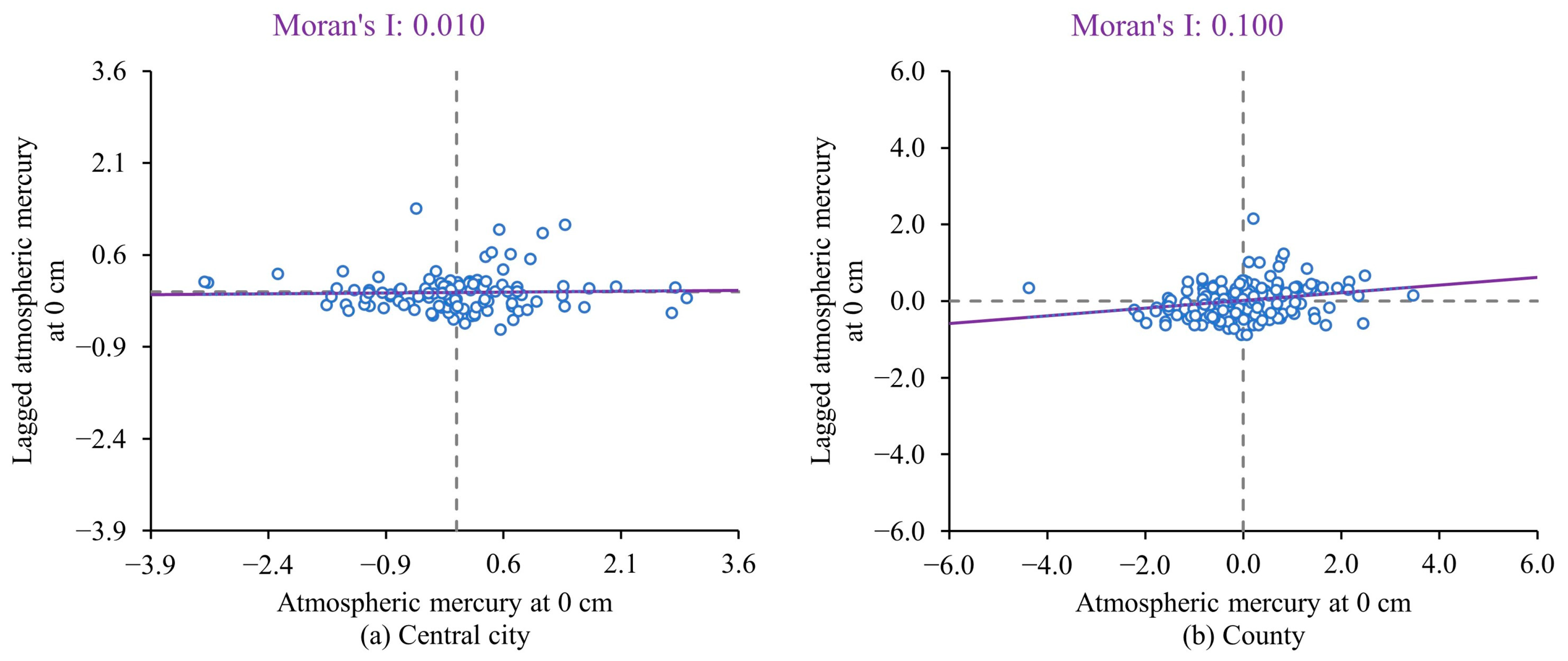
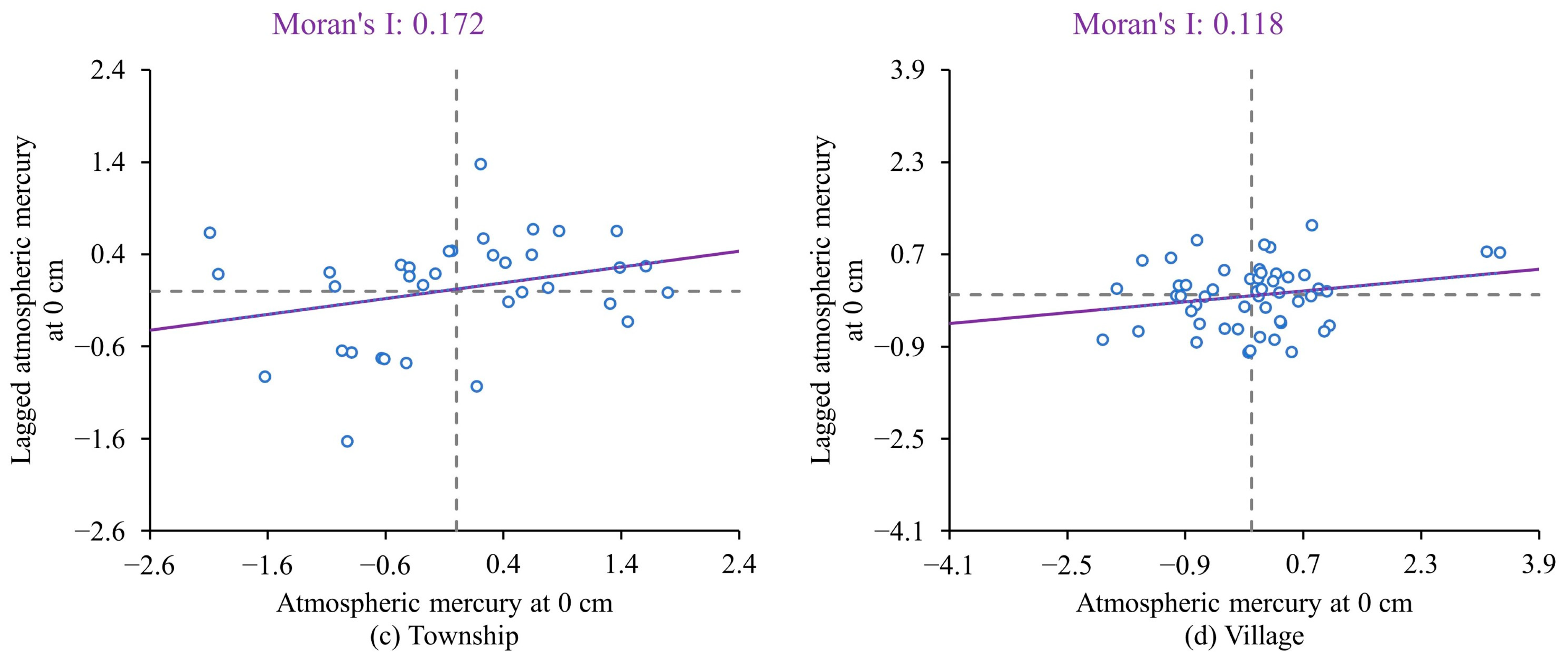
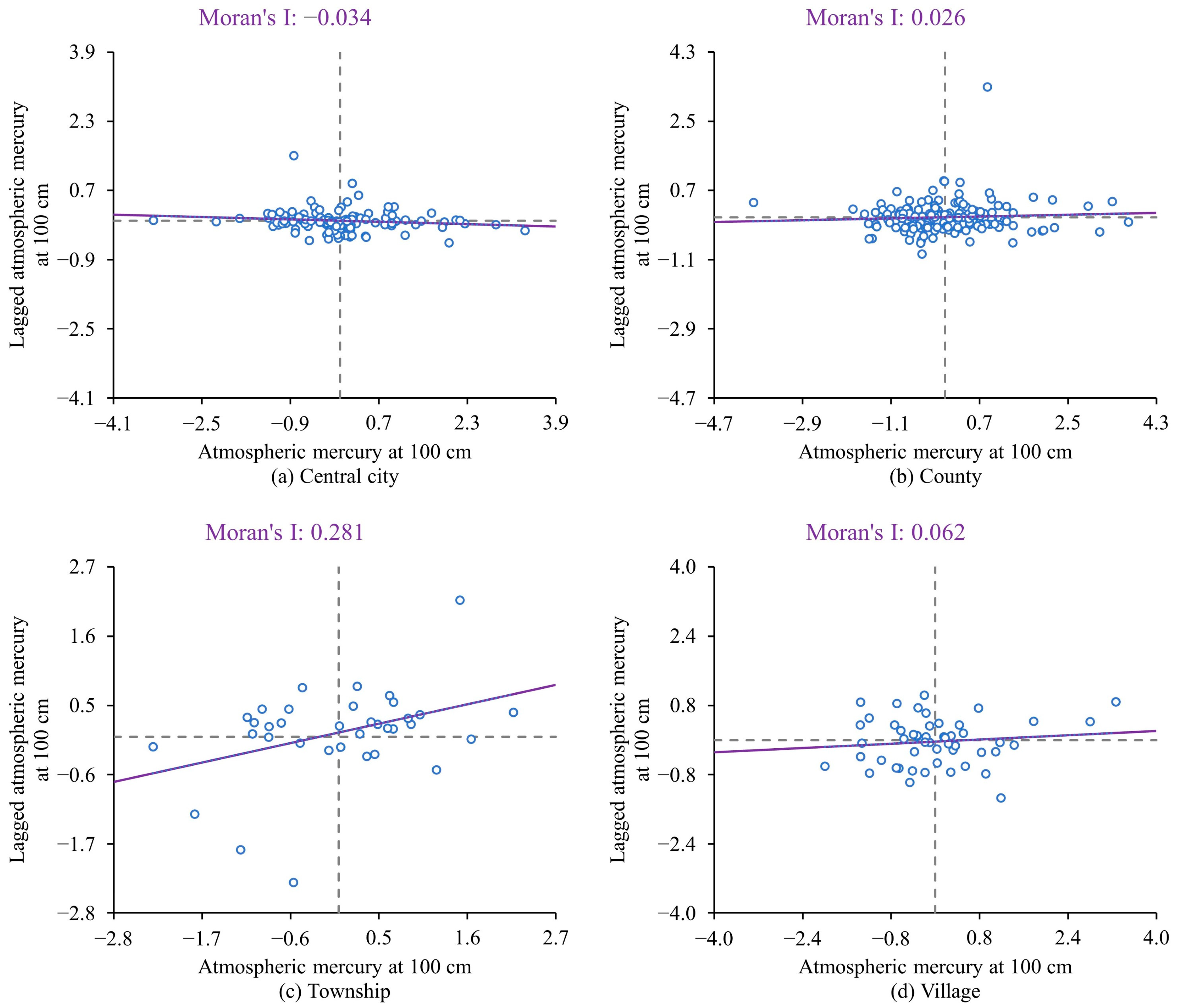
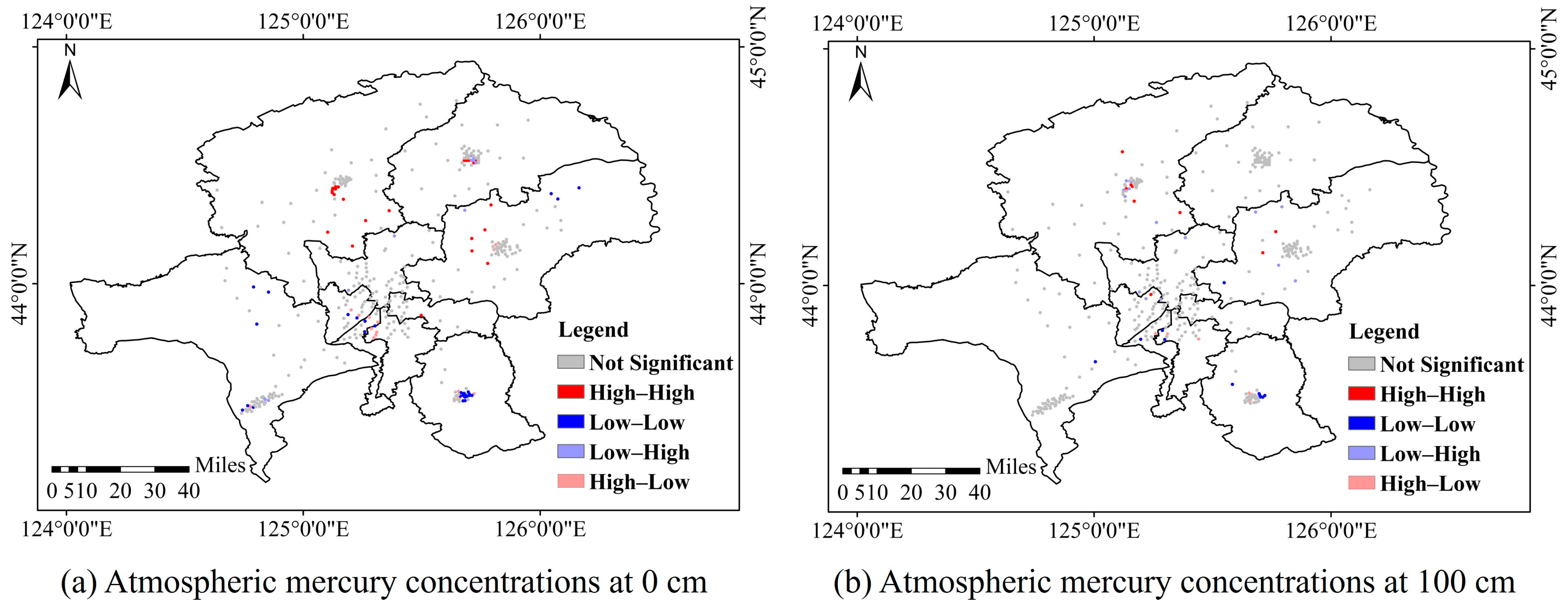
3.2.2. Distribution Characteristics of Atmospheric Mercury in Different Spatial Scales
3.3. Path Analyses of the Main Influencing Factors of Soil Mercury and Atmospheric Mercury in Metropolitan Areas
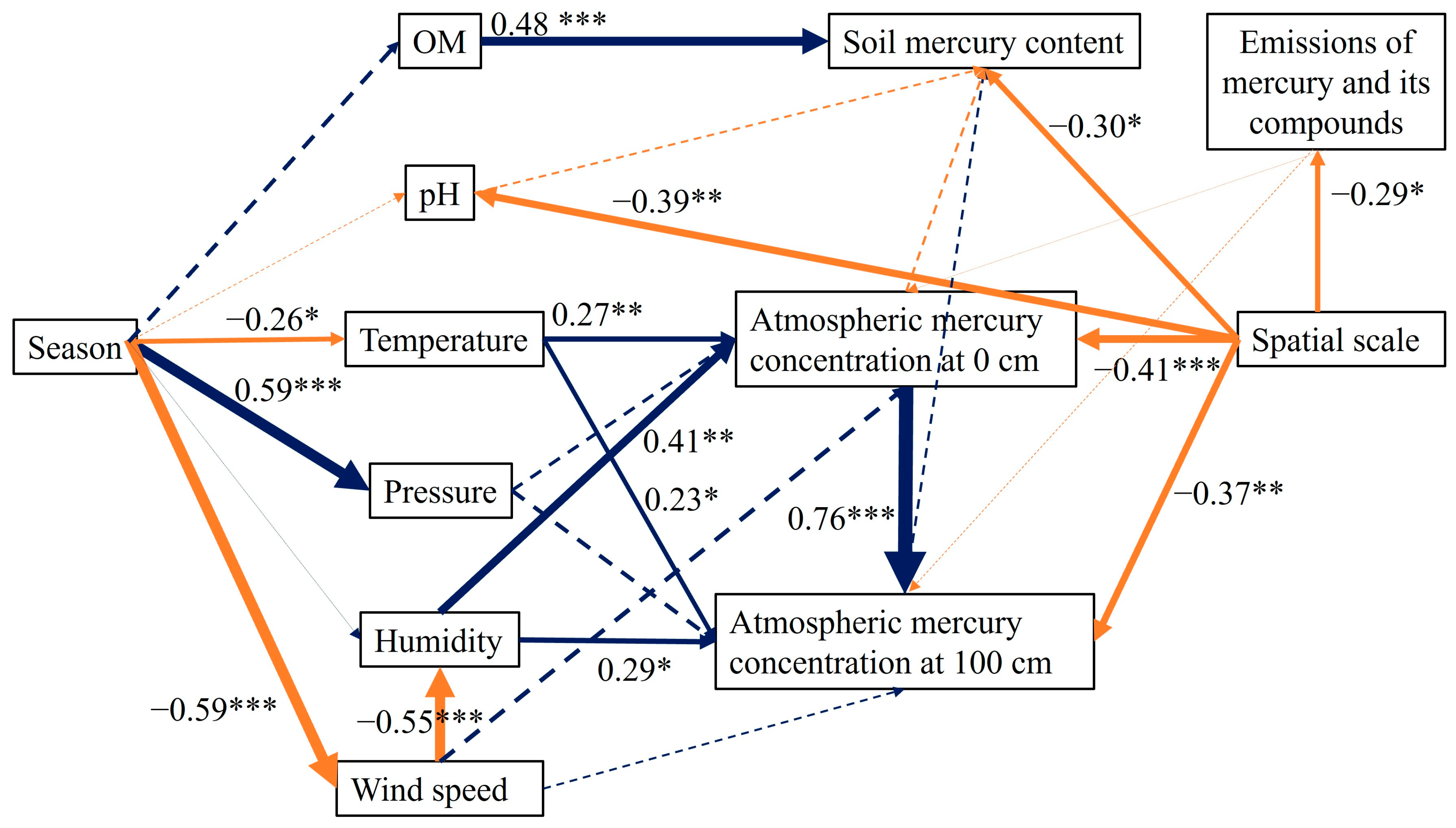
3.3.1. Influencing Factors of Soil Mercury in Changchun Urban Agglomeration
3.3.2. Factors Affecting Atmospheric Mercury in the Changchun Urban Agglomeration
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Mercury Shows Obvious Seasonal Changes in Different Spatial Scales
4.2. Atmospheric Mercury Shows Significant Differences in Different Spatial Scales
4.3. Analysis of the Mechanisms by Which Environmental Factors Significantly Influence Mercury Concentration
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gworek, B.; Dmuchowski, W.; Baczewska-Dąbrowska, A.H. Mercury in the Terrestrial Environment: A Review. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, S.N.; Cheng, I.; Gratz, L.E.; Weiss-Penzias, P.; Zhang, L. An Updated Review of Atmospheric Mercury. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Luo, Z.; Guo, S.; Strähle, U. Toxicity of Mercury: Molecular Evidence. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, L.; Ariya, P. Recent Advances in Atmospheric Chemistry of Mercury. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griggs, T.; Liu, L.; Talbot, R.W.; Torres, A.; Lan, X. Comparison of Atmospheric Mercury Speciation at a Coastal and an Urban Site in Southeastern Texas, USA. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Vogt, R.; Larssen, T. Environmental Mercury in China: A Review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 2431–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acquavita, A.; Brandolin, D.; Cattaruzza, C.; Felluga, A.; Maddaleni, P.; Meloni, C.; Pasquon, M.; Predonzani, S.; Poli, L.; Skert, N.; et al. Mercury Distribution and Speciation in Historically Contaminated Soils of the Isonzo River Plain (NE Italy). J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton-Bermea, O.; Schiavo, B.; Salgado-Martínez, E.; Almorín-Ávila, M.A.; Hernández-Álvarez, E. Gaseous Elemental Mercury (GEM) in the Mexico City Metropolitan Area. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 107, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Duan, Y.; Cheng, N.; Xiu, G. Atmospheric Mercury Speciation in Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xu, L.; Wu, X.; Zhao, G.; Jiao, L.; Chen, J.; Hong, Y.; Deng, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, K.; et al. Characteristics and Sources of Mercury in Precipitation Collected at the Urban, Suburban and Rural Sites in a City of Southeast China. Atmospheric Res. 2018, 211, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Tang, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, K.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Yin, Y.; Liu, G.; Cai, Y.; Li, Y. Spatial and Temporal Variations in the Pollution Status and Sources of Mercury in the Jiaozhou Bay. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 346, 123554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, H.; Zhao, C.; Xu, X. Mercury Contamination in the Topsoil and Subsoil of Urban Areas of Beijing, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 85, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Qin, P.; Ni, H.; Zeng, H. Spatial distribution of mercury contents in surface soil in Shenzhen City. China Environ. Sci. 2010, 30, 1645–1649. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, G.; Feng, X.; Wang, F.; Fu, X. Preliminary Investigation of Soil Mercury Pollution in Wanshan Mercury Mining Area, Guizhou Province. Bull. Miner. Rock. Geochem. 2006, 25, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yuan, W.; Lin, C.-J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Feng, X. Climate and Vegetation As Primary Drivers for Global Mercury Storage in Surface Soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10665–10675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Meng, B.; Feng, X. Mercury Methylation in Rice Paddy and Accumulation in Rice Plant: A Review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 195, 110462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Feng, X.; Larssen, T.; Qiu, G.; Vogt, R.D. In Inland China, Rice, Rather than Fish, Is the Major Pathway for Methylmercury Exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Wang, C.; Ding, L.; Chen, M.; Hu, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, L.; Feng, X. Soil Mercury Pollution Caused by Typical Anthropogenic Sources in China: Evidence from Stable Mercury Isotope Measurement and Receptor Model Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 288, 125687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Feng, X.; Chan, H.-M.; Zhang, X.; Du, B. Human Body Burden and Dietary Methylmercury Intake: The Relationship in a Rice-Consuming Population. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 9682–9689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, B.; Yin, X.; Sharma, C.M.; Tripathee, L.; Truong, M.T.; Tiwari, P.; Kandel, K.; Kang, S.; Zhang, Q. Total Gaseous Mercury in Kathmandu, a South Asian Metropolis: Temporal Variations, Sources Apportionment and Health Risk Assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 483, 136644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.W.; Zhang, H.; Yu, B.; Wang, X.; Lin, C.-J.; Feng, X.B. Observations of Atmospheric Mercury in China: A Critical Review. Atmospheric Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 9455–9476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, L.; Tao, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, L.; Qian, D.; Fan, R. Seasonal and Diurnal Variation of Total Gaseous Mercury in Guangzhou City. China Environ. Sci. 2012, 32, 1554–1558. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Feng, X. Variations of Atmospheric Total Gaseous Mercury Concentrations for the Sampling Campaigns of 2001/2002 and 2009/2010 and Implications of Changes in Regional Emissions of Atmospheric Mercury. Bull. Mineral. Geochem. 2015, 34, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Nadim, F.; Perkins, C.; Carley, R.J.; Hoag, G.E.; Lin, Y.; Chen, L. Atmospheric Mercury Monitoring Survey in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, C.T.; Mason, R.P.; Chan, H.M.; Jacob, D.J.; Pirrone, N. Mercury as a Global Pollutant: Sources, Pathways, and Effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4967–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenberg, S.E.; McKee, L.; Gilbreath, A.; Yee, D.; Connor, M.; Fu, X. Evidence for Short-Range Transport of Atmospheric Mercury to a Rural, Inland Site. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, S.; Ren, X.; Cohen, M.; Luke, W.; Kelley, P.; Artz, R.; Hynes, A.; Landing, W.; Martos, B. Airborne Vertical Profiling of Mercury Speciation near Tullahoma, TN, USA. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 557–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, J.S.; Chen, G.Q.; Wei, W.D.; Yang, Q.; Yao, M.T.; Shao, J.A.; Zhou, M.; Xia, X.H.; Dong, K.Q.; et al. China’s Energy-Related Mercury Emissions: Characteristics, Impact of Trade and Mitigation Policies. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 141, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Ye, H.; Shan, Y.; Chen, B.; Li, J. A City-Level Inventory for Atmospheric Mercury Emissions from Coal Combustion in China. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Feng, X.; Qiu, G.; Wei, Z.; Xiao, T. Mercury Emission to Atmosphere from Lanmuchang Hg–Tl Mining Area, Southwestern Guizhou, China. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 7459–7473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gong, Y. The Association between Carbon Emission and Urban Spatial Form—A Study of Zhuhai, China. Land 2023, 12, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Dong, L.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, L.; Guo, Q.; Liu, Y. Constructing Multi-Level Urban Clusters Based on Population Distributions and Interactions. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2023, 99, 101897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Cheng, H.; Yang, K.; Zhao, C.; Liu, Y.; Peng, M.; Li, K. Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Mercury Exchange Flux between Soil and Air in Guangzhou City. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 139, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, R.; Han, K.; Zhang, Y. Temporal Variation of Gaseous Elemental Mercury in a Northern Coastal City in China: Monsoon and COVID-19 Lockdown Effects. Atmospheric Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Deb, S.; Ghosh, S.; Mandal, S.; Quazi, S.A.; Kushwaha, A.; Hoque, A.; Choudhury, A. Impact of Anthropogenic Pollution on Soil Properties in and around a Town in Eastern India. Geoderma Reg. 2022, 28, e00462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Ma, J.; Hu, Y.; Su, B.; Fang, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Xiang, B. Assessments of Levels, Potential Ecological Risk, and Human Health Risk of Heavy Metals in the Soils from a Typical County in Shanxi Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 19330–19340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Xiao, T.; Yu, T.; Li, X.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, G. Pollution Characteristics and Risk Assessments of Mercury in the Soil of the Main Urban Regions in a Typical Chinese Industrial City: Changchun. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 3829–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DZ/T 0295-2016; Specification of Land Quality Geochemical Assessment. Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Liu, N. Quantifying Mercury Distribution and Source Contribution in Surface Soil of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau Using Mercury Isotopes. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University, Chongqing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Chen, M.; Xiao, J.; Xu, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; Yang, F.; Zhao, C.; Guo, L. Exploring the Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Urban Soil Heavy Metals in Different Levels of Urbanization. Agronomy 2025, 15, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Chen, L.; He, Q.; Ye, Z.; Sun, J. Distribution and pollution assessment of the mercury in soils of Tibet. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2014, 23, 1487–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Jia, Z.; Li, S.; Fu, X.; Yang, X.; Tan, Q.; Ming, L.; Lin, T.; Lin, C.; Li, X.; et al. Risk Assessment and Sources Identification of Soil Heavy Metals in a Typical County of Chongqing Municipality, Southwest China. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 113, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Meng, M.; Shao, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, G. Spatial Distribution of Mercury in Topsoil from Five Regions of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 1756–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, P.; Wang, J.; Feng, X.; Ma, Z.; Lu, A.; Wei, L.; Yan, L. Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soils in Shunyi, Beijing. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2015, 34, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wu, X.; Yan, Z.; Jin, Y.; Bi, K.; Wen, Z. Heavy Metal Content and Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Urban Soils in Nanjing. Urban Environ. Urban Ecol. 2007, 20, 1–4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yi, W.; Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, C.; Dong, F. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of mercury in urban soils of Guangzhou. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2009, 40, 1185–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Hu, L.; Gao, B.; Gao, F.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Yao, H. Spatial–Temporal Variation and Source Analysis of Heavy Metals in Different Land Use Types in Beilun District (2015 and 2022). Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, T. Progress in research on the current status of mercury contamination in the soil environment and its influencing factors. Earth Environ. 2022, 50, 397–414+319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Cui, X.; Zhang, Y. Change of mercury and methylmercury in Yellow River Delta wetlands from autumn to summer. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2017, 37, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustin, M.S.; Lindberg, S.E.; Austin, K.; Coolbaugh, M.; Vette, A.; Zhang, H.; Fu, X.; Yang, X.; Tan, Q.; Ming, L.; et al. Assessing the Contribution of Natural Sources to Regional Atmospheric Mercury Budgets. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 259, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B. Field Measurement of Soil Mercury Emission Flux in Forest. Master’s Thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gustin, M.S.; Biester, H.; Kim, C.S. Investigation of the Light-Enhanced Emission of Mercury from Naturally Enriched Substrates. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 3241–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J. Characteristics of Mercury Exchange at the Soil/Water-Gas Interface in Agricultural Fields in the Hilly Areas of Eastern Sichuan Province. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University, Chongqing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Cheng, H.; Yang, K.; Zhao, C.; Peng, M.; Li, K.; Liu, Y. Exchange flux of mercury on soil/air interface in black soils of Heilongjiang. Earth Sci. Front. 2015, 22, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaditame, F.; LeMonte, J.J.; Siebecker, M.G.; Yu, X.; Fischel, M.; Tappero, R.; Sparks, D.L. Sea−level Rise and Arsenic−rich Soils: A Toxic Relationship. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 472, 134528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zha, T.; Guo, X.; Meng, G.; Zhou, J. Spatial Distribution of Metal Pollution of Soils of Chinese Provincial Capital Cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1502–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, J. The Evolution and Reconstruction of Industrial Space in Changchun Metropolitan Area. Ph.D. Thesis, Northeast normal university, Changchun, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Li, F.; Fu, G.; Feng, H.; Xiong, F. The Spatial-Temporal Distribution Characteristics and Contamination Assessments of Heavy Metals in the Road Dusts of Beijing. Geoscience 2019, 33, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Zhou, W.; Kang, S.; de Foy, B.; Yu, Y.; Xie, J.; Sun, S.; Wu, K.; Zhang, Q. Latest Observations of Total Gaseous Mercury in a Megacity (Lanzhou) in Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, D. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Gaseous Elemental Mercury in Chongqing, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 156, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiu, G.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R. Total Gaseous Mercury in Ambient Air of Shanghai:Its Seasonal Variation in Relation to Meteorological Condition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 35, 155–158+205. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Rybski, D.; Kropp, J.P. The Role of City Size and Urban Form in the Surface Urban Heat Island. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Wang, S.; Jin, S.; Yang, J. Influence of Urban Form and Wind Environment on Surface Temperature in Changchun City. Acta Geofraphica Sin. 2019, 74, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Miao, J. Progress of Urban Heat Island Circulation in China. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2019, 47, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z. Influence of Chimney Height and Night-Time Urban Heat Island Effect on Pollutant Transport and Dispersion. Environ. Sci. 1986, 2, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.S.P.; Pham, T.D.H.; Truong, M.T.; Tran, A.N. Characteristics of Total Gaseous Mercury at a Tropical Megacity in Vietnam and Influence of Tropical Cyclones. Atmospheric Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.-G.; Lee, H.; Kwon, S.Y.; Jo, M.-J.; Hwang, D.-W.; Lim, J.-H.; Choi, S.-D. Isotopic Fractionation of Gaseous Mercury in a Large Industrial City: Spatio-Temporal Variations and Source Apportionment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 487, 137162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Research on Distribution Characteristics and Source of Atmospheric Mercury in Qingdao. Master’s Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S.X.; Wang, L.; Hao, J.M. Atmospheric Mercury Concentration and Chemical Speciation at a Rural Site in Beijing, China: Implications of Mercury Emission Sources. Atmospheric Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 10505–10516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Lyu, X.; Zhang, G.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.; et al. Isotopic Compositions of Atmospheric Total Gaseous Mercury in 10 Chinese Cities and Implications for Land Surface Emissions. Atmospheric Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 6721–6734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Cheng, I.; Lu, J. Annual Atmospheric Mercury Species in Downtown Toronto, Canada. J. Environ. Monit. 2009, 11, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Variation of atmospheric mercury and estimating the mercury exposure dose in residential area of city, China-Sweden. Ph.D. Thesis, Southwest University, Chongqing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- de la Rosa, D.A.; Volke-Sepúlveda, T.; Solórzano, G.; Green, C.; Tordon, R.; Beauchamp, S. Survey of Atmospheric Total Gaseous Mercury in Mexico. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 4839–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phu Nguyen, L.S.; Zhang, L.; Lin, D.-W.; Lin, N.-H.; Sheu, G.-R. Eight-Year Dry Deposition of Atmospheric Mercury to a Tropical High Mountain Background Site Downwind of the East Asian Continent. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, M.; Xu, Z.; Fan, R.; Tao, J.; Chen, D.; Zhang, D.; Xie, D.; Sun, J. Variation Trends and Influencing Factors of Total Gaseous Mercury in the Pearl River Delta—A Highly Industrialised Region in South China Influenced by Seasonal Monsoons. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wang, S.; Qiu, G.; Hou, Y.; Tang, S. Total Gaseous Mercury Emissions from Soil in Guiyang, Guizhou, China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmospheres 2005, 110, D14306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, Q.; Liu, K.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, H.; Li, Z.; et al. Recent Decrease Trend of Atmospheric Mercury Concentrations in East China: The Influence of Anthropogenic Emissions. Atmospheric Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 8279–8291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.S.P.; Sheu, G.-R.; Lin, D.-W.; Lin, N.-H. Temporal Changes in Atmospheric Mercury Concentrations at a Background Mountain Site Downwind of the East Asia Continent in 2006–2016. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, H.; Cheng, I.; Zhang, L. Current Understanding of the Driving Mechanisms for Spatiotemporal Variations of Atmospheric Speciated Mercury: A Review. Atmospheric Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 12897–12924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Yang, X.; Tan, Q.; Lin, T.; Lin, C.; Li, X.; Feng, X. Isotopic Composition of Gaseous Elemental Mercury in the Marine Boundary Layer of East China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 7656–7669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Kumar, B.; Manzoor, S.; Kulshrestha, U. Status of Atmospheric Mercury Research in South Asia: A Review. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 1092–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Cheng, J.; Wang, W. Analysis on the current situation and causes of soil mercury pollution in Lanzhou. Energy Environ. 2006, 1, 69–72. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Han, G.; Chen, Q.; Chu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Meteorological Drivers of Atmospheric Mercury Seasonality in the Temperate Northern Hemisphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL100120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, A.M.; Magand, O.; Laj, P.; Andrade, M.; Moreno, I.; Velarde, F.; Salvatierra, G.; Gutierrez, R.; Blacutt, L.; Aliaga, D.; et al. Seasonal Patterns of Atmospheric Mercury in Tropical South America as Inferred by a Continuous Total Gaseous Mercury Record at Chacaltaya Station (5240 m) in Bolivia. Atmospheric Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 3447–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naccarato, A. Sea Surface Temperature Variation Linked to Elemental Mercury Concentrations Measured on Mauna Loa. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 7751–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X. Speciated Atmospheric Mercury during Haze and Non-Haze Periods in Winter at an Urban Site in Beijing, China: Pollution Characteristics, Sources, and Causes Analyses. Atmospheric Res. 2021, 247, 105209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardè, M.; Barbante, C.; Barbaro, E.; Becherini, F.; Bonasoni, P.; Busetto, M.; Calzolari, F.; Cozzi, G.; Cristofanelli, P.; Dallo, F.; et al. Characterization of Atmospheric Total Gaseous Mercury at a Remote High-Elevation Site (Col Margherita Observatory, 2543 m a.s.l.) in the Italian Alps. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 271, 118917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G. Characteristics and Sources of Atmospheric Mercury in Typical Urban Area of Yunnan Province. Master’s Thesis, Kunming University of Science & Technology, Kunming, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
| Study Area | Season | Soil Mercury Concentration (µg/kg) | Range | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Changchun urban agglomeration | Spring | 53.4 ± 60.2 | 6.5–684.8 | 1.13 |
| Summer | 37.7 ± 42.0 | 4.0–493.3 | 1.12 | |
| Autumn | 48.2 ± 54.4 | 6.9–535.3 | 1.13 | |
| Average | 46.2 ± 39.5 | 9.7–353.5 | 0.86 |
| Study Area | Spring | Summer | Autumn | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Range | CV | Average | Range | CV | Average | Range | CV | ||
| Atmospheric mercury concentration at 0 cm | Changchun MunicipalDistrict | 8.26 ± 3.73 | 1.08–25.00 | 0.45 | 11.62 ± 2.84 | 3.00–18.38 | 0.24 | 6.05 ± 1.32 | 1.76–9.00 | 0.22 |
| Nongan County | 4.49 ± 1.65 | 1.13–8.83 | 0.37 | 7.04 ± 1.98 | 3.84–14.00 | 0.28 | 4.33 ± 1.41 | 1.17–7.11 | 0.33 | |
| Dehui City | 5.61 ± 1.61 | 1.00–9.09 | 0.29 | 6.00 ± 1.95 | 1.25–10.78 | 0.32 | 4.58 ± 1.45 | 1.29–8.23 | 0.32 | |
| Jiutai District | 4.47 ± 1.22 | 1.15–7.44 | 0.27 | 6.43 ± 2.73 | 1.13–18.27 | 0.42 | 4.40 ± 1.29 | 1.18–6.89 | 0.29 | |
| Gongzhuling City | 4.48 ± 1.54 | 1.17–8.78 | 0.34 | 5.12 ± 1.94 | 1.28–12.33 | 0.38 | 4.78 ± 1.67 | 1.29–10.72 | 0.35 | |
| Shuangyang District | 3.83 ± 1.38 | 1.14–6.28 | 0.36 | 4.92 ± 1.46 | 1.68–8.18 | 0.30 | 4.25 ± 1.98 | 1.03–11.72 | 0.47 | |
| Atmospheric mercury concentration at 100 cm | Changchun MunicipalDistrict | 7.75 ± 2.64 | 2.14–23.89 | 0.34 | 12.12 ± 2.46 | 3.77–18.22 | 0.20 | 7.82 ± 1.91 | 2.12–12.68 | 0.24 |
| Nongan County | 5.16 ± 1.24 | 1.46–8.83 | 0.24 | 8.56 ± 3.32 | 1.38–21.99 | 0.39 | 4.62 ± 1.79 | 1.02–8.56 | 0.39 | |
| Dehui City | 5.46 ± 1.25 | 1.18–9.22 | 0.23 | 6.82 ± 2.35 | 1.15–13.06 | 0.34 | 5.37 ± 2.23 | 1.28–12.17 | 0.42 | |
| Jiutai District | 5.11 ± 1.10 | 1.14–6.67 | 0.21 | 7.25 ± 3.49 | 1.50–20.00 | 0.48 | 4.87 ± 1.89 | 1.28–9.33 | 0.39 | |
| Gongzhuling City | 4.51 ± 1.41 | 1.22–8.91 | 0.31 | 6.19 ± 2.30 | 1.22–13.56 | 0.37 | 5.59 ± 2.39 | 1.21–11.39 | 0.43 | |
| Shuangyang District | 3.89 ± 1.31 | 1.18–6.17 | 0.34 | 5.81 ± 2.31 | 1.89–12.22 | 0.40 | 5.17 ± 2.91 | 1.00–16.67 | 0.56 | |
| Study Area | Spring | Summer | Autumn | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | OM | pH | OM | pH | OM | ||||
| Content (g/kg) | Correlation Coefficient | Content (g/kg) | Correlation Coefficient | Content (g/kg) | Correlation Coefficient | ||||
| Changchun Municipal District | 8.2 | 32.98 | 0.491 ** | 8.4 | 34.18 | 0.472 ** | 8.2 | 31.98 | 0.221 * |
| Nongan County | 7.8 | 31.75 | 0.464 ** | 8.6 | 29.26 | 0.523 ** | 8.2 | 30.50 | 0.475 ** |
| Dehui City | 7.5 | 28.87 | 0.549 ** | 8.1 | 30.93 | 0.507 ** | 7.9 | 32.65 | 0.492 ** |
| Jiutai District | 7.0 | 31.36 | 0.632 ** | 7.1 | 30.13 | 0.553 ** | 7.3 | 32.47 | 0.581 ** |
| Gongzhuling City | 7.7 | 33.34 | 0.565 ** | 8.6 | 33.58 | 0.423 ** | 8.1 | 31.21 | 0.371 ** |
| Shuangyang District | 8.0 | 30.98 | 0.501 ** | 8.1 | 31.16 | 0.599 ** | 8.3 | 29.42 | 0.698 ** |
| Study Area | Season | 0 cm | 100 cm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wind Speed | Air Pressure | Temperature | Humidity | Wind Speed | Air Pressure | Temperature | Humidity | ||
| Changchun MunicipalDistrict | Spring | - | - | 0.293 ** | - | −0.193 * | - | 0.235 ** | - |
| Summer | - | - | 0.335 ** | −0.283 ** | - | - | 0.380 ** | −0.394 ** | |
| Autumn | 0.228 * | - | 0.203 ** | - | 0.224 * | - | 0.390 ** | - | |
| Nongan County | Spring | - | - | 0.344 ** | - | - | −0.352 * | 0.381 ** | - |
| Summer | - | 0.300 * | 0.466 ** | - | - | - | 0.497 ** | −0.431 ** | |
| Autumn | 0.278 * | - | 0.235 ** | - | 0.382 * | - | 0.446 ** | - | |
| Dehui City | Spring | - | - | 0.345 * | - | - | - | 0.292 * | - |
| Summer | 0.336 * | - | 0.320 * | −0.345 * | 0.322 * | - | 0.359 * | −0.317 * | |
| Autumn | - | - | 0.319 * | −0.527 ** | - | - | 0.320 * | −0.447 ** | |
| Jiutai District | Spring | - | - | 0.232 ** | - | - | - | 0.423 ** | −0.281 * |
| Summer | - | - | 0.290 ** | - | - | - | 0.355 ** | −0.447 ** | |
| Autumn | - | - | 0.262 ** | - | −0.282 * | - | 0.309 * | −0.445 ** | |
| Gongzhuling City | Spring | - | - | 0.310 * | - | - | - | 0.405 ** | - |
| Summer | - | −0.344 * | 0.425 ** | −0.341 * | - | −0.308 * | 0.419 ** | −0.339 * | |
| Autumn | - | - | 0.327 * | - | −0.267 * | - | 0.369 ** | - | |
| Shuangyang District | Spring | - | - | 0.322 ** | - | - | - | 0.476 ** | - |
| Summer | - | - | 0.373 * | - | - | - | 0.423 ** | −0.419 ** | |
| Autumn | −0.522 ** | - | 0.485 ** | - | −0.580 ** | - | 0.471 ** | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zong, J.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, Z. Spatial and Temporal Changes and Influencing Factors of Mercury in Urban Agglomeration Land Patterns: A Case from Changchun Area, Old Industrial Base of Northeast China. Land 2025, 14, 652. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030652
Zhang Z, Wang Z, Zong J, Zhang H, Hu Y, Xiao Y, Zhang G, Li Z. Spatial and Temporal Changes and Influencing Factors of Mercury in Urban Agglomeration Land Patterns: A Case from Changchun Area, Old Industrial Base of Northeast China. Land. 2025; 14(3):652. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030652
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhe, Zhaojun Wang, Jing Zong, Hongjie Zhang, Yufei Hu, Yuliang Xiao, Gang Zhang, and Zhenxin Li. 2025. "Spatial and Temporal Changes and Influencing Factors of Mercury in Urban Agglomeration Land Patterns: A Case from Changchun Area, Old Industrial Base of Northeast China" Land 14, no. 3: 652. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030652
APA StyleZhang, Z., Wang, Z., Zong, J., Zhang, H., Hu, Y., Xiao, Y., Zhang, G., & Li, Z. (2025). Spatial and Temporal Changes and Influencing Factors of Mercury in Urban Agglomeration Land Patterns: A Case from Changchun Area, Old Industrial Base of Northeast China. Land, 14(3), 652. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030652






