Lead Fixation in Sediments of Protected Wetlands in Lithuania
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Importance of Wetlands and Their Functions
1.2. Lead Pollution and Global Trends
1.3. Lead Distribution in Lithuanian Wetland Soils
1.4. Impact of Lead Contamination on Vegetation and Its Role in Wetland Buffer Zones
1.5. Lead Mobility, Bioavailability, and Remediation Strategies in Beaver-Modified Wetlands
1.6. Sediments as Indicators of Lead Contamination and the Role of Beaver Dams in Their Accumulation
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Sample Preparation and Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
- Red marks areas where Pb concentrations exceeded the background level by more than 20%, indicating active Pb input from external sources.
- Yellow represents sites where Pb concentrations remained within ±20% of the background level, suggesting stabilization in relatively immobile forms.
- Green indicates areas where Pb content was lower than the background level, which may be associated with leaching, plant absorption, or sediment transport.
4. Discussion
4.1. Role of Organic Carbon in Lead Fixation
4.2. Impact of Beaver Dams on Lead Distribution
4.3. Spatio-Temporal Variability of Lead Concentrations
4.4. Long-Term Monitoring and Environmental Management
4.5. Future Research Directions: Bioaccumulation and Remediation Strategies
4.6. Implications for Wetland Conservation and Policy Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramsar Convention Secretariat. The Ramsar Convention Manual: A Guide to the Convention on Wetlands, 6th ed.; Ramsar Convention Secretariat: Gland, Switzerland, 2013; Available online: https://www.ramsar.org/document/the-ramsar-convention-manual-6th-edition (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- Racoviceanu, T.; Cazacu, C.; Adamescu, M.; Giuca, R.; Bucur, M.; Fedoriak, M.; Angelstam, P. Agricultural Intensification Reduces the Portfolio of Wetland Ecosystem Services: European Danube River Lowlands as a Global Biodiversity Hotspot. Land 2023, 12, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hook, D.D. Wetlands: History, Current Status, and Future. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1993, 12, 2157–2166. [Google Scholar]
- Greb, S.F.; DiMichele, W.A.; Gastaldo, R.A. Evolution and Importance of Wetlands in Earth History. In Wetlands Through Time; Greb, S.F., DiMichele, W.A., Eds.; Geological Society of America Special Paper; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2006; Volume 399, pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivavičiūtė, G. Change in Lithuanian Wetlands (2002–2021). Rural Environ. Eng. 2022, 37, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, O.; Piatti, G. (Eds.) World Heritage and Buffer Zones; UNESCO World Heritage Centre: Davos, Switzerland, 2009; Volume 25, 120p, Available online: https://portals.iucn.org/library/node/45783 (accessed on 28 March 2025).
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; Volume 1, p. 595. [Google Scholar]
- Mateo-Sagasta, J.; Zadeh, S.M.; Turral, H.; Burke, J. Water Pollution from Agriculture: A Global Review; FAO under UN, IWMI: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Manzetti, S. Heavy Metal Pollution in the Baltic Sea, from the North European Coast to the Baltic States, Finland and the Swedish Coastline to Norway. Technical Reports No. 6:8; Fjordforsk AS: Vangsnes, Norway, 2020; Volume 6, p. 90. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. OECD Environmental Performance Reviews: Lithuania 2021; OECD Environmental Performance Reviews; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zając, E.; Zarzycki, J.; Ryczek, M. Degradation of Peat Surface on an Abandoned Post-Extracted Bog and Implications for Re-Vegetation. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2018, 16, 3363–3380. [Google Scholar]
- Tolunay, D.; Kowalchuk, G.A.; Erkens, G.; Hefting, M.M. Aerobic and Anaerobic Decomposition Rates in Drained Peatlands: Impact of Botanical Composition. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 930, 172639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; 432p. [Google Scholar]
- Dordio, A.; Carvalho, A.J.P.; Pinto, A.P. Wetlands: Water “Living Filters”? In Wetlands: Ecology, Conservation and Restoration; Russo, R.E., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2008; Volume Chapter 1, pp. 15–71. [Google Scholar]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy Metals Toxicity and the Environment; NIH Public Access: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012; Volume 101, pp. 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorham, E. Northern Peatlands: Role in the Carbon Cycle and Probable Responses to Climatic Warming. Ecol. Appl. 1991, 1, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA. Heavy Metals in Europe. European Environment Agency. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/en/analysis/indicators/heavy-metal-emissions-in-europe (accessed on 16 December 2024).
- Alloway, B.J. Heavy Metals in Soils: Trace Metals and Metalloids in Soils and Their Bioavailability, 3rd ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, C.; Flem, B.; Fabian, K.; Birke, M.; Ladenberger, A.; Négrel, P.; Demetriades, A.; Hoogewerff, J.; The GEMAS Project Team. Lead and Lead Isotopes in Agricultural Soils of Europe—The Continental Perspective. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential Extraction Procedure for the Speciation of Particulate Trace Metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W. Determination of Isotope Ratio of Plumbum Pollution Source in Birmingham Urban Soils. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2022, 46, 3871–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, W.; Bakker, D.J. Manual for Calculating Critical Loads of Heavy Metals for Terrestrial Ecosystems; DLO Winand Staring Centre: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume Report 166, 144p. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.; Lee, Y.; Ong, S.K. Heavy Metal Adsorption by Engineered Wetlands. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, I.B.; Palamuleni, L.G. Toxic Heavy Metals in Soil and Plants from a Gold Mining Area, South Africa. In Heavy Metals—Recent Advances; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, G.; Hermann, T.; da Silva, M.R.; Montanarella, L. Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils of the European Union with Implications for Food Safety. Environ. Int. 2016, 88, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Hu, H.; Gao, S.; Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Deng, W.; Li, C. Pb Pollution Stress in Alnus cremastogyne Monitored by Antioxidant Enzymes. Forests 2024, 15, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredina, V.P. Soil Contamination: Textbook; Publishing House of Tomsk State University: Tomsk, Russia, 2015; pp. 32–346. [Google Scholar]
- UNECE. Convention on Long-Range Transboundary Air Pollution: Protocol on Heavy Metals; United Nations Economic Commission for Europe: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. Available online: https://unece.org/environment-policy/air/protocol-heavy-metals (accessed on 16 December 2024).
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; A/RES/70/1; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Joosten, H.; Clarke, D. Wise Use of Mires and Peatlands—Background and Principles Including a Framework for Decision-Making; International Mire Conservation Group and International Peat Society: Saarijärvi, Finland, 2002; Available online: https://www.imcg.net/media/download_gallery/books/wump_wise_use_of_mires_and_peatlands_book.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- Puttock, A.; Graham, H.A.; Carless, D.; Brazier, R.E. Sediment and Nutrient Storage in a Beaver Engineered Wetland. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 2358–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafer, C.U.S. National Park Buffer Zones: Historical, Scientific, Social, and Legal Aspects. Environ. Manag. 1999, 23, 49–73. [Google Scholar]
- Scholz, M. Wetland Systems to Control Urban Runoff; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; 333p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. The Seville Strategy for Biosphere Reserves; United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization: Paris, France, 1996; Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000103849 (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Lithuanian Hygiene Norm HN 60:2004. Maximum Permissible Concentrations of Hazardous Chemicals in Soil. Available online: https://e-seimas.lrs.lt/portal/legalAct/lt/TAD/TAIS.228693 (accessed on 15 November 2024).
- Justification for Investment in the Construction of a Nuclear Power Plant in the Republic of Belarus. Book 11. Environmental Impact Assessment 1588-PZ-OI4. Part 8. EIA Report. Part 8.2. Current Environmental Status. Explanatory Note; Gosatomnadzor: Minsk, Belarus, 2010; Available online: https://am.lrv.lt/uploads/am/documents/files/PAV/10_2%20PAV_ataskaita_RU_%202010_2_dalis.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Taylor, S.R. Abundance of Chemical Elements in the Continental Crust: A New Table. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1964, 28, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedepohl, K.H. The composition of the continental crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1217–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Gao, S. Composition of the continental crust. In Treatise on Geochemistry; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2003; Volume 3, pp. 1–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shia, T.; Maa, J.; Zhanga, Y.; Liub, C.; Hua, Y.; Gonga, Y.; Wua, X.; Jua, T.; Houa, H.; Zhaoa, L. Status of Lead Accumulation in Agricultural Soils across China (1979–2016). Environ. Int. 2019, 129, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Jia, T.; Peng, S.; Yu, X.; She, D. Spatial Distribution, Source Identification, and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Cultivated Soil of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau Region: Case Study on Huzhu County. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 35, e02073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motuzas, A.; Vaisvalavičius, R.; Sabienė, N. Heavy Metal Sorption Capacity and Mobility in the Retisol Profile in Relation to the Contamination. Zemdirbyste-Agriculture 2016, 103, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valskys, V.; Motiejunas, M.; Ignatavicius, G.; Sinkevicius, S. The Contamination of Šventoji River Bottom Sediments by Heavy Metals in Ukmerge, Lithuania. J. Environ. Sci. Int. 2016, 25, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CCME (Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment). Canadian Soil Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Environmental and Human Health: Lead; Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 1999. Available online: https://ccme.ca/en/res/lead-en-canadian-soil-quality-guidelines.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- US EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Soil Screening Guidance: Technical Background Document; EPA/540/R-95/128; Office of Emergency and Remedial Response: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-10/documents/ssg_tech_background.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- Dragović, S.; Mihailović, N.; Gajić, B. Heavy Metals in Soils: Distribution, Relationship with Soil Characteristics and Soil Quality Evaluation. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2008, 43, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibanda, T.; Selvarajan, R.; Tekere, M. Urban Effluents and Their Impact on the Natural Environment: A Need for Legal Framework in South Africa. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorauskienė, V. Mapping of Geochemical Contamination in Urban Areas of Lithuania. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2006, 14, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.; Gochfeld, M.; Jeitner, C.; Donio, M.; Pittfield, T. Lead (Pb) in Biota and Perceptions of Pb Exposure at a Recently Designated Superfund Beach Site in New Jersey. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2012, 75, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alekseev, Y.V. Heavy Metals in Soils and Plants; Agropromizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1987; 142p. [Google Scholar]
- Garmash, G.A.; Garmash, N.Y. Distribution of Heavy Metals in Organs of Cultivated Plants. Agrokhimiya 1987, 5, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Dmitrakov, L.M.; Dmitrakova, L.K.; Abashina, N.A.; Pinsky, D.L. Influence of Lead on Morphometric Indicators of Oats. Agrokhimiya 2004, 8, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Fastovetska, K.; Slepetiene, A.; Vigricas, E.; Urbaitis, G.; Belova, O. Lead Content in Plant Materials in the Buffer Zones of Surface Water Bodies of Northwestern and Central Regions of Lithuania. Zemdirbyste-Agriculture 2022, 109, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedev, I.F.; Derevyagin, S.S. Heavy Metals in Ecosystems; Rakurs: Saratov, Russia, 2017; 178p. [Google Scholar]
- Gromova, V.S. Migration and Accumulation of 137Cs and Heavy Metals in Soil and Plants under Conditions of Dissected Relief. Plodorodie 2007, 4, 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Adriano, D.C. Trace Elements in Terrestrial Environments: Biogeochemistry, Bioavailability, and Risks of Metals, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, F.J. Humus Chemistry: Genesis, Composition, Reactions, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1994; 512p. [Google Scholar]
- Tipping, E. Cation Binding by Humic Substances; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002; 434p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, F.; Ledermann, L.; Schäffer, A.; Snaith, H.J.; Lenz, M. Rapid Sequestration of Perovskite Solar Cell-Derived Lead in Soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 128995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.; Kloas, W. Water Quality and Heavy Metal Monitoring in Water, Sediments, and Tissues of the African Catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822) from the River Nile, Egypt. J. Environ. Prot. 2010, 1, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Tayel, I. Effect of Heavy Metals on Gills of Tilapia ziilli Inhabiting the River Nile Water (Damietta Branch and El-Rahawey Drain), Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2005, 9, 111–128. [Google Scholar]
- Korablina, I.; Barabashin, T.; Katalevsky, N. Heavy Metals in Bottom Sediments of the Shelves in the Northeastern Part of the Black Sea in the Modern Period. Mar. Hydrophys. J. 2021, 37, 591–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikov, M.; Zhilin, A. Distribution Patterns of Heavy Metals in Bottom Sediments of the Barents Sea (Based on Statistical Analysis). Vestn. KRAUNC Earth Sci. 2016, 1, 78–88. [Google Scholar]
- Mejjad, N.; El Aouidi, S.; Laissaoui, A. Assessment of Potential Ecological Risks of Cr, Cd, Pb, and As in Coastal Sediments. Proceedings 2024, 102, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency (EEA). Natura 2000 Network Viewer. Available online: https://natura2000.eea.europa.eu/ (accessed on 19 March 2025).
- Slepetiene, A.; Slepetys, J.; Liaudanskiene, I. Standard and Modified Methods for Soil Organic Carbon Determination in Agricultural Soils. Agron. Res. 2008, 6, 543–554. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Alvyra-Slepetiene-2/publication/228352777_Standard_and_modified_methods_for_soil_organic_carbon_determination_in_agricultural_soils/links/09e41510369912236b000000/Standard-and-modified-methods-for-soil-organic-carbon-determination-in-agricultural-soils.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- Bernardo, B.; Candeias, C.; Rocha, F. Soil Risk Assessment in the Surrounding Area of Hulene-B Waste Dump, Maputo (Mozambique). Geosciences 2022, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavyalova, N.; Korlyakov, K. Content of Heavy Metals in Sod-Podzolic Soil and Vegetation of Forest, Meadow, and Field Phytocenoses. Bull. Perm Fed. Res. Cent. 2018, 1, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Żelazna, A.; Lewandowski, J.; Pawlikowski, A.; Bonisławska, M.; Reindl, A.R.; Szymański, A.; Kowalska-Góralska, M.; Górski, K.; Walczykiewicz, W.; Bajkiewicz-Grabowska, E.; et al. The impact of beaver ponds on heavy metal accumulation in sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čiuldienė, D.; Vigricas, E.; Belova, O.; Aleinikovas, M.; Armolaitis, K. The Effect of Beaver Dams on Organic Carbon, Nutrients, and Methyl Mercury Distribution in Impounded Waterbodies. Wildl. Biol. 2020, 2020, wlb.00678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Como, A.; Deegan, L. Do Abandoned Beaver Dams Act as Natural Water Filters? SES, Lawrence University: Lawrence, MA, USA, 2015; 39p. [Google Scholar]
- Lovering, T.G. (Ed.) Lead in the Environment; Geological Survey Professional Paper 957; United States Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1976; 96p. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/pp/0957/report.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- Sjöberg, G.; Belova, O. Beaver as a Renewable Resource: A Beaver Dam Handbook for the Baltic Sea Region; TMT Tabergs: Jelgava, Latvia, 2020; 133p. [Google Scholar]
- Lamsodis, R.; Ulevičius, A. Geomorphological Effects of Beaver Activities in Lowland Drainage Ditches. Z. Für Geomorphol. 2012, 56, 435–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilkey, M.V.; Nikolaichuk, V.I. The distribution of heavy metals content in the bottom deposits of the trans-border Uzh river system. Biosyst. Divers. 2017, 25, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebregt, A.; De Greve, P. Buffer Zones and Their Management: Policy and Best Practices for Terrestrial Ecosystems in Developing Countries; National Reference Centre for Nature Management: Wageningen, DC, USA, 2000; 64p. [Google Scholar]
- Rambrakash, R.; Singh, A.; Kumari, S. Phytoextraction of Pb and Cr as Influenced by Chelating Agent; LAP Lambert Academic Publication: London, UK, 2013; 101p. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, W.; Cheng, L.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, Y. Exploratory Immobilization Remediation of Hydroxyapatite (HAP) on Lead-Contaminated Soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 26674–26684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, G.; Chibuzo Ugwu, E.; Martínez-Villegas, N.; Sen Gupta, B. Remediation of Lead-Contaminated Soil by Using Saponin Derived from Sapindus Mukorossi. Eur. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 3, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumpiene, J.; Lagerkvist, A.; Maurice, C. Stabilization of As, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn in Soil Using Amendments—A Review. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






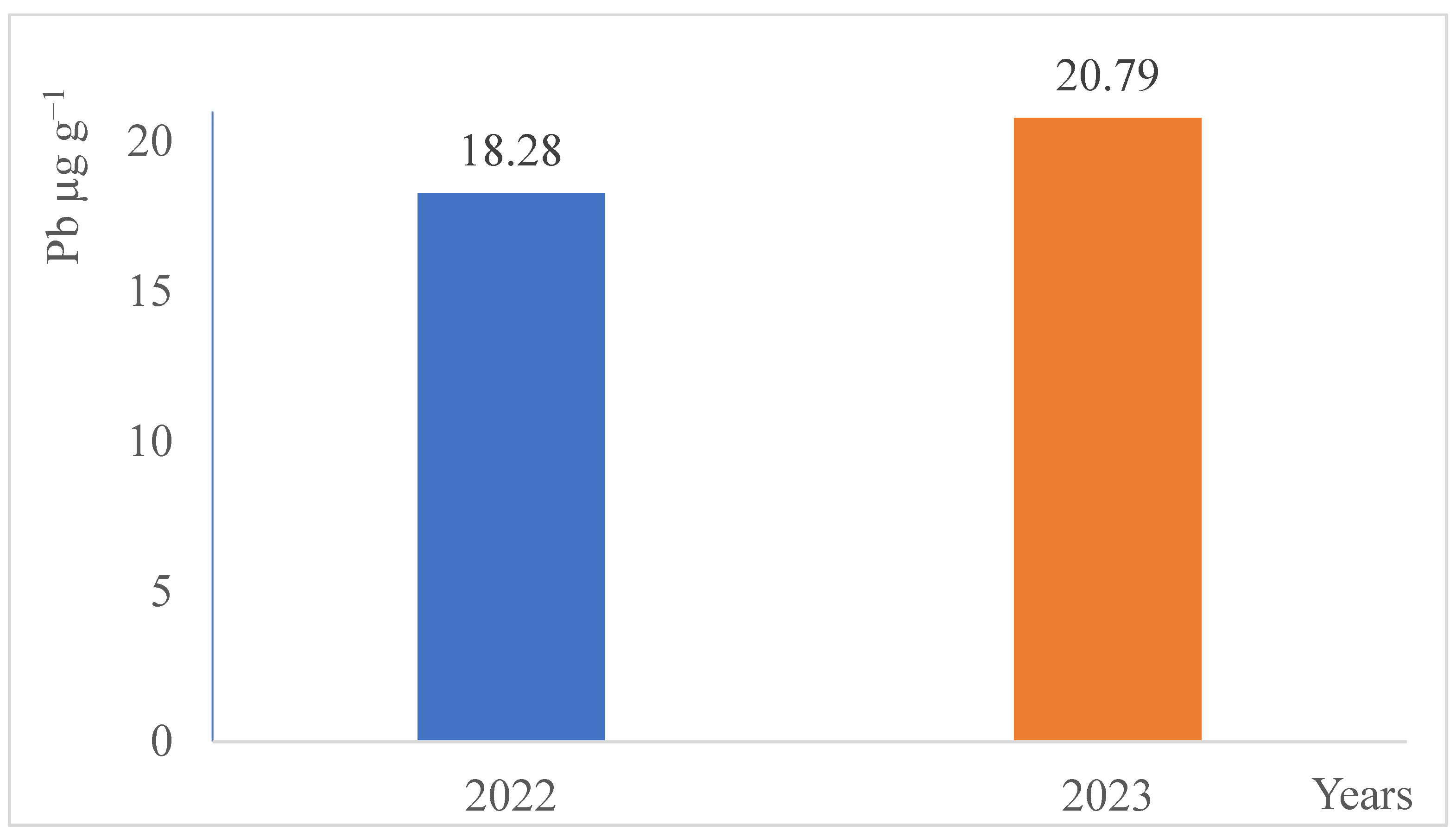




| Location | Pb Concentration (µg g−1) | Possible Source of Contamination | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nile River | 3.1–79.6 | Urban runoff | [60,61] |
| Northern Black Sea | Increase by 1.2 times in 20 years | Industrial and port activities | [62] |
| Barents Sea (coastal sediments) | 30–91.6 | Wastewater discharges from mining | [63] |
| Oualidia Lagoon, Morocco | Moderate levels | Below toxic thresholds for biota | [64] |
| Territories | 1M MMMPV (Plateliai) | 2K Kretinga (Lenkimai) | 3G Dubrava (Girionys) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Lithuania | Northwestern | Northwestern | Central |
| Locality | Žemaitija National Park | The Northern part of the Žemaitija Upland on the border with Latvia | Kauno Marios, Nemunas River |
| Sampling locality and coordinates | |||
| A | Ditch 56.019060868038; 21.865494507859 | Riverside 56.149076; 21.228591 | Ditch 54.793712; 24.078733 |
| B | Stream 56.023279513354; 21.921513405938 | Ditch (former railway) 56.140218; 21.261297 | Pond 54.828811; 24.120541 |
| C | Old “mother” beaver site 56.042144080106; 21.913789218674 | Ditch (meadows) 56.113681; 21.341182 | Lagoon stream 54.856685; 24.035010 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fastovetska, K.; Belova, O.; Slepetiene, A. Lead Fixation in Sediments of Protected Wetlands in Lithuania. Land 2025, 14, 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040737
Fastovetska K, Belova O, Slepetiene A. Lead Fixation in Sediments of Protected Wetlands in Lithuania. Land. 2025; 14(4):737. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040737
Chicago/Turabian StyleFastovetska, Kateryna, Olgirda Belova, and Alvyra Slepetiene. 2025. "Lead Fixation in Sediments of Protected Wetlands in Lithuania" Land 14, no. 4: 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040737
APA StyleFastovetska, K., Belova, O., & Slepetiene, A. (2025). Lead Fixation in Sediments of Protected Wetlands in Lithuania. Land, 14(4), 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040737








