Spatiotemporal Effects and Driving Factors of Ecosystem Services Trade-Offs in the Beijing Plain Area
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
2.3. Research Approaches
2.3.1. Measurement of ESs
- (1)
- Net Primary Production
- (2)
- Soil Conservation
- (3)
- Water Conservation
- (4)
- Habitat Quality
2.3.2. ESs Analysis of Trade-Offs and Synergies
- (1)
- Method of Evaluation for Trade-offs and Synergies
- (2)
- Trade-offs and Synergies Intensity
- The basic formula is as follows:
- The parameters can be estimated using the following formula:
- The weights are determined using the Gaussian spatial kernel function, expressed as follows:
2.3.3. Analysis of ESs Driving Factors
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity of ESs
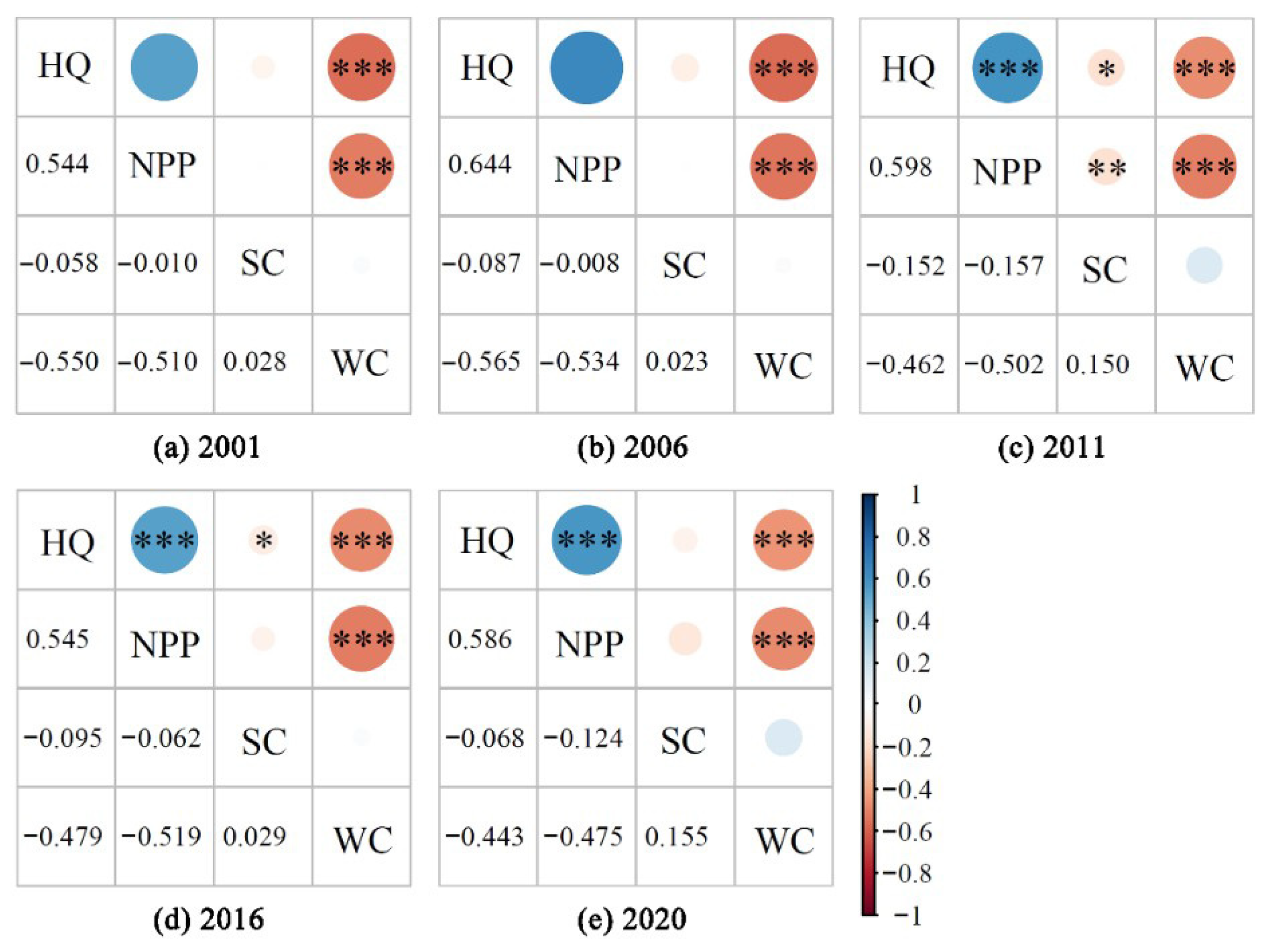
3.2. ESs Trade-Offs and Synergies
3.2.1. Characteristics of Temporal Changes
3.2.2. Characteristics of Spatial Transformations
3.3. Identification of the Determinants of Spatial Heterogeneity in ESs
3.3.1. Single-Factor Detection
3.3.2. Interaction Detector
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatiotemporal Development of ESs in the Plain Area
4.2. Determinants of Spatial Heterogeneity of ESs
4.3. Management and Policy Interventions for ESs
4.4. Uncertainty Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; De Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.J. The Value of the World’s Ecosystem Services and Natural Capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, G.C. Nature’s Services: Societal Dependence on Natural Ecosystems; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bolund, P.; Hunhammar, S. Ecosystem Services in Urban Areas. J. Ecol. Econ. 1999, 29, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Jin, X.; Chen, T.; Wu, J. Understanding Trade-Offs and Synergies of Ecosystem Services to Support the Decision-Making in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region. Land Use Policy 2021, 106, 105446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venalainen, A.; Lehtonen, I.; Laapas, M.; Ruosteenoja, K.; Tikkanen, O.P.; Viiri, H.; Ikonen, V.P.; Peltola, H. Climate Change Induces Multiple Risks to Boreal Forests and Forestry in Finland: A Literature Review. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 4178–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, C.; Hickler, T.; Davis-Reddy, C.; Engelbrecht, F.; Higgins, S.I.; von Maltitz, G.P.; Midgley, G.F.; Pfeiffer, M.; Scheiter, S. Large Uncertainties in Future Biome Changes in Africa Call for Flexible Climate Adaptation Strategies. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 340–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajjur, S.B.; Al-Ghamdi, S.G. Exploring Urban Growth-Climate Change-Flood Risk Nexus in Fast Growing Cities. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Peng, Q.; Fan, Q.; Lin, W.; Su, K. Spatial-Temporal Variation and Driving Forces of Carbon Storage at the County Scale in China Based on a Gray Multi-Objective Optimization-Patch-Level Land Use Simulation-Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Services and Tradeoffs-Optimal Parameter-Based Geographical Detector Model: Taking the Daiyun Mountain’s Rim as an Example. Land 2024, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magle, S.B.; Fidino, M.; Sander, H.A.; Rohnke, A.T.; Larson, K.L.; Gallo, T.; Kay, C.A.M.; Lehrer, E.W.; Murray, M.H.; Adalsteinsson, S.A.; et al. Wealth and Urbanization Shape Medium and Large Terrestrial Mammal Communities. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 5446–5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotze, D.J.; Ghosh, S.; Hui, N.; Jumpponen, A.; Lee, B.P.Y.; Lu, C.; Lum, S.; Pouyat, R.; Szlavecz, K.; Wardle, D.A.; et al. Urbanization Minimizes the Effects of Plant Traits on Soil Provisioned Ecosystem Services across Climatic Regions. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 4139–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Gao, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C. Understanding the Effects of Socio-Ecological Factors on Trade-Offs and Synergies among Ecosystem Services to Support Urban Sustainable Management: A Case Study of Beijing, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 100, 105024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhl, J.B.; Salzman, J.; Arnold, C.A.; Craig, R.; Hirokawa, K.; Olander, L.; Palmer, M.; Ricketts, T.H. Connecting Ecosystem Services Science and Policy in the Field. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2021, 19, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. What Factors Affect the Synergy and Tradeoff between Ecosystem Services, and How, from a Geospatial Perspective? J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wu, T.; Fu, B. The Value of Ecosystem Services in China: A Systematic Review for Twenty Years. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 52, 101365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhao, X.; Wu, P.; Hu, P.; Gao, X. Quantification and Spatially Explicit Driving Forces of the Incoordination between Ecosystem Service Supply and Social Demand at a Regional Scale. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lautenbach, S. A Quantitative Review of Relationships between Ecosystem Services. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assubayeva, A.; Marco, J. Methodological Approaches on Synergies and Trade-Offs within the 2030 Agenda. iScience 2024, 27, 111100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Jiang, C.; Gao, Y.; Du, J. Natural Driving Mechanism and Trade-Off and Synergy Analysis of the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Multiple Typical Ecosystem Services in Northeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 374, 134075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Gao, X.; Zhao, X.; Wu, P. Scale Effect and Spatially Explicit Drivers of Interactions between Ecosystem Services—A Case Study from the Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Gu, Y.; Zou, C.; Xu, D.; Wang, L.; Ye, X.; Yang, Y.; Huang, X. Temporal Variation and Spatial Scale Dependency of the Trade-Offs and Synergies among Multiple Ecosystem Services in the Taihu Lake Basin of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, M.E.; Martone, R.G.; Chan, K.M.A. Human Impacts and Ecosystem Services: Insufficient Research for Trade-Off Evaluation. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 16, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yue, D.; Guo, Z.; Li, Z. Scenario Simulation of Ecosystem Services Based on Land Use/Land Cover Change in the Bailong River Basin, in China. Land 2024, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booi, S.; Mishi, S.; Andersen, O. Ecosystem Services: A Systematic Review of Provisioning and Cultural Ecosystem Services in Estuaries. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Zhao, M.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y. Significant Trade-Off for the Impact of Grain-for-Green Programme on Ecosystem Services in North-Western Yunnan, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirpke, U.; Ghermandi, A.; Sinclair, M.; Van Berkel, D.; Fox, N.; Vargas, L.; Willemen, L. Emerging Technologies for Assessing Ecosystem Services: A Synthesis of Opportunities and Challenges. Ecosyst. Serv. 2023, 63, 101558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, J.; Liang, E. Trade-Offs and Synergies of Ecosystem Services and Their Threshold Effects in the Largest Tableland of the Loess Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 48, e02706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Yang, D.; Jing, W.; Rong, T. Analyzing Spatio-Temporal Changes and Trade-Offs/Synergies among Ecosystem Services in the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Tang, X.; Liu, W. Spatial–Temporal Evolution and Correlation Analysis of Ecosystem Service Value and Landscape Ecological Risk in Wuhu City. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, W. Trade-Offs and Synergies in Ecosystem Services for the Yinchuan Basin in China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 84, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Zhao, W.; Fu, B.; Ding, J.; Wang, S. Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs and Their Influencing Factors: A Case Study in the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 1250–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Luo, H. Trade-Off/Synergistic Changes in Ecosystem Services and Geographical Detection of Its Driving Factors in Typical Karst Areas in Southern China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yin, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Sun, S.; Huang, J. Dynamic Changes and Key Drivers of Ecosystem Service Values in Populous Zones on the Tibetan Plateau: A 35-Year Analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 167, 112620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, J.; Ling, M.; Chen, Z.; Lan, Y.; Huang, Q.; Li, X.; You, H.; Wang, F.; Han, X.; et al. A Framework for Dynamic Assessment of Soil Erosion and Detection of Driving Factors in Alpine Grassland Ecosystems Using the Rusle-Invest (Sdr) Model and Geodetector: A Case Study of the Source Region of the Yellow River. Ecol. Inform. 2025, 85, 102928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Ge, Y.; Xu, C.J. An Optimal Parameters-Based Geographical Detector Model Enhances Geographic Characteristics of Explanatory Variables for Spatial Heterogeneity Analysis: Cases with Different Types of Spatial Data. GISci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnegie Institution of Washington; Willis, B.; Blackwelder, E.; Sargent, R.H.; Hirth, F.; Walcott, C.D.; Weller, S.; Girty, G.H. Research in China …: Systematic Geology, by Bailey Willis; Carnegie Institution of Washington: Washington, DC, USA, 1907. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, K.; Shah, J.A.; Ullah, S.; Raza, S.T. Quantifying Sustainable Urbanization by Predictive Modeling for Better Agricultural Management: A Case Study in the South Asiatic Region. Heliyon 2025, 11, e40978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ma, J.; Sho, K.; Seta, F. Urban Growth Divides: The Inevitable Structure of Shrinking Cities in Urbanization Evolution. Cities 2025, 158, 105638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Lei, X.; Wang, B.; Cui, J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Sui, P. Reducing Carbon Footprint without Compromising Grain Security through Relaxing Cropping Rotation System in the North China Plain. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 318, 128465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yang, J. A Review of Methods for Quantifying Urban Ecosystem Services. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2025, 253, 105215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lu, Z.; Feng Li Crittenden, J.C. Analyzing Spatio-Temporal Changes and Trade-Offs to Support the Supply of Multiple Ecosystem Services in Beijing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Oort, P.A.J.; Wang, G.; Vos, J.; Meinke, H.; Li, B.G.; Huang, J.K.; van der Werf, W. Towards Groundwater Neutral Cropping Systems in the Alluvial Fans of the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 165, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Qin, X.; Zang, H.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. Value of Groundwater Used for Producing Extra Grain in North China Plain. Field Crops Res. 2017, 210, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.L.; Falagán, N.; Hardman, C.A.; Kourmpetli, S.; Liu, L.; Mead, B.R.; Davies, J.A.C. Ecosystem Service Delivery by Urban Agriculture and Green Infrastructure—A Systematic Review. Ecosyst. Serv. 2022, 54, 101405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, L.V.; Inácio, M.; Ferreira, C.S.S.; Ferreira, A.D.; Pereira, P. Ecosystem Services and Well-Being Dimensions Related to Urban Green Spaces—A Systematic Review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 85, 104072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 M Annual Land Cover Dataset and Its Dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, C.S.; Randerson, J.T.; Field, C.B.; Matson, P.A.; Vitousek, P.M.; Mooney, H.A.; Klooster, S.A. Terrestrial Ecosystem Production: A Process Model Based on Global Satellite and Surface Data. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1993, 7, 811–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, J. Estimation of Net Primary Productivity of Chinese Terrestrial Vegetation Based on Remotesensing. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2007, 3, 413–424. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; Mccool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (Rusle); US Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Department of Agriculture, Science and Education Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- United Nations Environment Programme. Globio: Global Methodology for Mapping Human Impacts on the Biosphere: The Arctic 2050 Scenario and Global Application; UNEP-DEWA: Nairobi, Kenya, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, R.; Clarke, K.C.; Zhang, J.; Feng, J.; Jia, X.; Li, J. Spatial Correlations among Ecosystem Services and Their Socio-Ecological Driving Factors: A Case Study in the City Belt Along the Yellow River in Ningxia, China. Appl. Geogr. 2019, 108, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeon, M.; Wana, D. Synergies and Trade-Offs among Key Ecosystem Services in Maze National Park and Its Environs, Southwestern Ethiopia. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2025, 57, e03398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Sun, C.; Fan, F. Multi-Criteria Framework for Identifying the Trade-Offs and Synergies Relationship of Ecosystem Services Based on Ecosystem Services Bundles. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Dang, D.; Li, X.; Lyu, X.; Li, M.; Liu, S. Mapping Ecosystem Services Bundles for Analyzing Spatial Trade-Offs in Inner Mongolia, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunsdon, C.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Charlton, M.E. Geographically Weighted Regression: A Method for Exploring Spatial Nonstationarity. Geogr. Anal. 1996, 28, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Xu, C.D. Geodetector: Principle and Prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Yang, L.; Zhu, Z. Variations in Ecosystem Service Value and Its Driving Factors in the Nanjing Metropolitan Area of China. Forests 2023, 14, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, B. Assessment of Urban Waterlogging-Induced Road Traffic Safety Risk and Identification of Its Driving Factors: A Case Study of Beijing. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2024, 183, 104080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Ma, J.; Liang, E.; Wang, X. Exploring the Natural-Socioeconomic Driving and Response Mechanisms of Ecosystem Services Interactions to Optimize Ecosystem Management: A Case Study in the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, S. Exploring the Spatial–Temporal Patterns of Urban Ecosystem Service Relationships and Their Driving Mechanisms: A Case Study of Wuhu City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 167, 112726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Wang, L.; Hu, R.; Lu, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, G.; Tan, B. Identification of Unique Ecosystem Service Bundles in Farmland—A Case Study in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain of China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Deng, X.; Wang, Y.; Peng, L.; Yu, Z. Impacts of Infrastructure Construction on Ecosystem Services in New-Type Urbanization Area of North China Plain. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 185, 106376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Yi, Y.; Liu, H.; Xu, Q.; Yang, Z. The Relationship between Ecosystem Service Supply and Demand in Plain Areas Undergoing Urbanization: A Case Study of China’s Baiyangdian Basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 289, 112492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Richter, A.; Cong, W.-F.; Xu, Z.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, F.; van der Werf, W.; Groot, J.C.J. Stakeholder Perspectives on Ecosystem Services in Agricultural Landscapes: A Case Study in the North China Plain. Agric. Syst. 2025, 223, 104187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Geng, H.; Luo, G.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q. Multiscale Characteristics of Ecosystem Service Value Trade-Offs/Synergies and Their Response to Landscape Pattern Evolution in a Typical Karst Basin in Southern China. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 81, 102584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Indicator | Factor Description | Classification |
|---|---|---|
| Population density | Reflecting the population distribution within a 1-square-kilometer grid. | natural breakpoint: 7 |
| Land use type | Cropland, Forest, Shrub, Grassland, Water, Sonw/Ice, Barren, Impervious, Wetland. | - |
| NDVI | Vegetation Coverage | equal interval: 7 |
| Elevation | Derived from DEM (Digital Elevation Model) data. | natural breakpoint: 7 |
| Slope | Derived using analysis performed in ArcGIS 10.8. | geometric interval: 7 |
| Annual average temperature | Derived from daily temperature data at surrounding stations, interpolated using the ANUSPLIN model. | natural breakpoint: 7 |
| Annual precipitation | Derived from daily precipitation data at surrounding stations, interpolated using the ANUSPLIN model. | natural breakpoint: 7 |
| Ecosystem Service | Year | Dominant Interaction 1 | Dominant Interaction 2 | Dominant Interaction 3 | Dominant Interaction 4 | Dominant Interaction 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPP-HQ | 2001 | X3∩X4: 0.316NE | X3∩X7: 0.310DE | X3∩X6: 0.296DE | X1∩X3: 0.281DE | X6∩X7: 0.274NE |
| 2006 | X3∩X7: 0.211NE | X3∩X4: 0.193NE | X2∩X7: 0.190NW | X1∩X2: 0.187NW | X1∩X3: 0.187DE | |
| 2011 | X3∩X4: 0.271NE | X1∩X3: 0.261DE | X3∩X6: 0.261DE | X3∩X7: 0.246NE | X3∩X5: 0.238NE | |
| 2016 | X1∩X6: 0.311DE | X1∩X3: 0.276DE | X1∩X4: 0.273NE | X3∩X6: 0.272DE | X4∩X6: 0.266NE | |
| 2020 | X1∩X6: 0.349DE | X1VX4: 0.321NE | X1∩X3: 0.299DE | X1∩X2: 0.295NW | X4∩X6: 0.284NE | |
| NPP-SC | 2001 | X6∩X7: 0.090NE | X4∩X7: 0.0830NE | X4∩X6: 0.0610NE | X1∩X4: 0.053NE | X1∩X6: 0.051NE |
| 2006 | X4∩X6: 0.087NE | X4∩X7: 0.082NE | X3∩X7: 0.074NE | X3∩X6: 0.071NE | X6∩X7: 0.069NE | |
| 2011 | X4∩X6: 0.116NE | X4∩X7: 0.116NE | X6∩X7: 0.105NE | X3∩X7: 0.093NE | X1∩X7: 0.069NE | |
| 2016 | X4∩X6: 0.087NE | X6∩X7: 0.065NE | X4∩X7: 0.064NE | X1∩X4: 0.059NE | X1∩X6: 0.056NE | |
| 2020 | X4∩X6: 0.067NE | X4∩X7:0.042NE | X6∩X7: 0.035DE | X5∩X6: 0.034NE | X3∩X6: 0.031NE | |
| NPP-WC | 2001 | X6∩X7: 0.119NE | X4∩X6: 0.094NE | X1∩X6: 0.085NE | X4∩X7: 0.084NE | X1∩X4: 0.081NE |
| 2006 | X6∩X7: 0.096NE | X4∩X6: 0.090NE | X3∩X6: 0.085NE | X1∩X7: 0.083NE | X1∩X6: 0.082NE | |
| 2011 | X6∩X7: 0.116NE | X4∩X6: 0.102NE | X3∩X6: 0.099NE | X1∩X6: 0.099NE | X5∩X6: 0.096NE | |
| 2016 | X1∩X7: 0.188NE | X6∩X7: 0.185DE | X4∩X7: 0.166NE | X2∩X7: 0.160DE | X3∩X7: 0.160DE | |
| 2020 | X1∩X6: 0.161NE | X6∩X7: 0.161NE | X4∩X6: 0.152NE | X3∩X6: 0.134NE | X2∩X6: 0.131DE | |
| SC-HQ | 2001 | X3∩X4: 0.316NE | X3∩X7: 0.310DE | X3∩X6: 0.296DE | X1∩X3: 0.281DE | X6∩X7: 0.274NE |
| 2006 | X3∩X5: 0.190NE | X2∩X5: 0.186NW | X1VX5: 0.136NE | X1∩X3: 0.132NE | X4∩X5: 0.131NE | |
| 2011 | X3∩X5: 0.203NE | X2∩X5: 0.182NW | X1∩X5: 0.182NE | X5∩X6: 0.158NE | X4∩X5: 0.151NE | |
| 2016 | X3∩X5: 0.175NE | X1∩X5: 0.163NE | X5∩X7: 0.162NE | X4∩X7: 0.160NE | X1∩X7: 0.158NE | |
| 2020 | X5∩X7: 0.214NE | X6∩X7: 0.183NE | X1∩X7: 0.177NE | X3∩X5: 0.171NE | X4∩X7: 0.156NE | |
| SC-WC | 2001 | X5∩X6: 0.234NE | X6∩X7: 0.227NE | X3∩X5: 0.176NE | X4∩X6: 0.173NE | X3∩X4: 0.168NE |
| 2006 | X5∩X7: 0.303NE | X3∩X5: 0.282NE | X5∩X6: 0.277NE | X2∩X5: 0.253NE | X4∩X7: 0.215NE | |
| 2011 | X5∩X7: 0.286NE | X2∩X5: 0.248NE | X3∩X5: 0.246NE | X5∩X6: 0.237NE | X4∩X5: 0.217DE | |
| 2016 | X5∩X7: 0.317NE | X5∩X6: 0.266NE | X3∩X5: 0.252NE | X2∩X5: 0.246NE | X4∩X6: 0.219NE | |
| 2020 | X5∩X6: 0.271NE | X3∩X5: 0.256NE | X2∩X5: 0.251DE | X3∩X4: 0.225NE | X5∩X7: 0.225NE | |
| WC-HQ | 2001 | X3∩X4: 0.455DE | X1∩X4: 0.420NE | X2∩X4: 0.414DE | X4∩X6: 0.409DE | X6∩X7: 0.391NE |
| 2006 | X3∩X4: 0.205NE | X3∩X7: 0.202DE | X1∩X3: 0.199DE | X3∩X5: 0.187NE | X3∩X6: 0.177DE | |
| 2011 | X3∩X4: 0.384DE | X3∩X5: 0.362DE | X1∩X4: 0.355DE | X2∩X4: 0.349DE | X2∩X5: 0.341DE | |
| 2016 | X3∩X4: 0.413DE | X2∩X4: 0.411DE | X2∩X5: 0.401NE | X1∩X4: 0.399DE | X4∩X6: 0.384NE | |
| 2020 | X1∩X4: 0.362DE | X4∩X6: 0.359NE | X3∩X4: 0.352NE | X2∩X4: 0.334DE | X1∩X5: 0.332DE |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bao, L.; Liu, Y. Spatiotemporal Effects and Driving Factors of Ecosystem Services Trade-Offs in the Beijing Plain Area. Land 2025, 14, 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14050949
Bao L, Liu Y. Spatiotemporal Effects and Driving Factors of Ecosystem Services Trade-Offs in the Beijing Plain Area. Land. 2025; 14(5):949. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14050949
Chicago/Turabian StyleBao, Lige, and Yifei Liu. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Effects and Driving Factors of Ecosystem Services Trade-Offs in the Beijing Plain Area" Land 14, no. 5: 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14050949
APA StyleBao, L., & Liu, Y. (2025). Spatiotemporal Effects and Driving Factors of Ecosystem Services Trade-Offs in the Beijing Plain Area. Land, 14(5), 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14050949





