Physical Crust Formation on Sandy Soils and Their Potential to Reduce Dust Emissions from Croplands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Document the occurrence, structure, and properties of crusts on cropland during the emission season.
- Identify the constraining rainfall conditions that lead to the formation of crusts on sandy cropland soils.
- Assess the potential impact of crusts and their abrasion on dust emissions using a Portable In-Situ Wind Erosion Laboratory (PI-SWERL).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Introduction
2.2. Site Description and Field Measurements
Field Selection and Surface Measurements
2.3. Rainfall Simulation and Crust Formation
2.4. Crust Strength Measurements
2.5. PI-SWERL
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Crust Strength and Structure of Field Crusts
3.2. Crust Formation by Experimental Rainfall
3.3. Dust Emission Thresholds and Fluxes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tegen, I.; Hollrig, P.; Chin, M.; Fung, I.; Jacob, D.; Penner, J. Contribution of different aerosol species to the global aerosol extinction optical thickness: Estimates from model results. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 23895–23915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, O.; Randall, D.; Artaxo, P.; Bretherton, C.; Feingold, G.; Forster, P.; Kerminen, V.M.; Kondo, Y.; Liao, H.; Lohmann, U. Clouds and aerosols. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgle, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 571–657. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.; Wyrwoll, K.H.; Chappell, A.; Huang, J.; Lin, Z.; McTainsh, G.H.; Mikami, M.; Tanaka, T.Y.; Wang, X.; Yoon, S. Dust cycle: An emerging core theme in Earth system science. Aeolian Res. 2011, 2, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, C.; Neff, J. The contemporary physical and chemical flux of Aeolian dust: A synthesis of direct measurements of dust deposition. Chem. Geol. 2009, 267, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, N.; Engelstaedter, S.; Luo, C.; Sealy, A.; Artaxo, P.; Benitez-Nelson, C.; Bonnet, S.; Chen, Y.; Chuang, P.; Cohen, D.; et al. Atmospheric iron deposition: Global distribution, variability, and human perturbations*. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2009, 1, 245–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goudie, A.S. Desert dust and human health disorders. Environ. Int. 2013, 63C, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprigg, W.A. Dust storms, human health and a global early warning system BT. In Extreme Weather, Health, and Communities: Interdisciplinary Engagement Strategies; Steinberg, S.L., Sprigg, W.A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 59–87. ISBN 978-3-319-30626-1. [Google Scholar]
- Chappell, A.; Webb, N.P.; Leys, J.F.; Waters, C.M.; Orgill, S.; Eyres, M.J. Minimising soil organic carbon erosion by wind is critical for land degradation neutrality. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 93, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldeman, L.R. Global Extent of Soil Degradation. In Bi-Annual Report 1991–1992/ISRIC; ISRIC: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 19–36. [Google Scholar]
- Sterk, G.; Herrmann, L.; Bationo, A. Wind-blown nutrient transport and soil productivity changes in southwest Niger. L. Degrad. Dev. 1996, 7, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, E.M.; Oldeman, L.R. Global assessment of human-induced soil degradation. Arid Soil Res. Rehabil. 1999, 13, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, S.M.; Sterk, G. Nutrient dynamics—Wind and water erosion at the village scale in the Sahel. Land Degrad. Dev. 2007, 18, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, N.J. Desert dust hazards: A global review. Aeolian Res. 2017, 24, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginoux, P.; Prospero, J.; Gill, T.E.; Hsu, N.; Zhao, M. Global-scale attribution of anthropogenic and natural dust sources and their emission rates based on MODIS Deep Blue aerosol products. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, 3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegen, I.; Werner, M.; Harrison, S.P.; Kohfeld, K.E. Relative importance of climate and land use in determining present and future global soil dust emission. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prospero, J.M.; Ginoux, P.; Torres, O.; Nicholson, S.E.; Gill, T.E. Environmental characterization of global sources of atmospheric soil dust identified with the Nimbus 7 total ozone mapping spectrometer (TOMS) absorbing aerosol product. Rev. Geophys. 2002, 40, 2–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, J.B.; Seeger, M.; Iserloh, T.; Wistorf, S.; Fister, W. Calibration of simulated rainfall characteristics for the study of soil erosion on agricultural land. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 106, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colazo, J.C.; Buschiazzo, D. The impact of agriculture on soil texture due to wind erosion. L. Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, J.E.; Zobeck, T.M. The Wolfforth field experiment: A wind erosion study. Soil Sci. 1996, 161, 616–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobeck, T.M.; Van Pelt, R.S. Wind-induced dust generation and transport mechanics on a bare agricultural field. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 132, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zobeck, T.M.; Sterk, G.; Funk, R.; Rajot, J.L.; Stout, J.E.; Van Pelt, R.S. Measurement and data analysis methods for field-scale wind erosion studies and model validation. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2003, 28, 1163–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, R.; Reuter, H.; Hoffmann, C.; Engel, W.; Oettl, D. Effect of moisture on fine dust emission from tillage operations on agricultural soils. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2008, 33, 1851–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickery, K.J.; Eckardt, F.D.; Bryant, R.G. A sub-basin scale dust plume source frequency inventory for southern Africa, 2005–2008. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 5274–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eckardt, F.D.; Bekiswa, S.; Von Holdt, J.; Jack, C.; Kuhn, N.J.; Mogane, F.; Murray, J.E.; Ndara, N.; Palmer, A. South Africa’s agricultural dust sources and events from MSG SEVIRI. Aeolian Res. 2020, 47, 100637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, N.P.; Strong, C.L.; Chappell, A.; Marx, S.K.; McTainsh, G.H. Soil organic carbon enrichment of dust emissions: Magnitude, mechanisms and its implications for the carbon cycle. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2013, 38, 1662–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, P.; Bateman, M.; Thomas, D.; Telfer, M.; Barker, C.H.; Lawson, M. A Holocene late Pleistocene aeolian record from lunette dunes in the western free State panfield, South Africa. Holocene 2008, 18, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, P.; Thomas, D.; Bateman, M.; Wiggs, G.F.S.; Rabumbulu, M. Evidence for land degradation from aeolian sediment in the West-Central free state province, South Africa. L. Degrad. Dev. 2012, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggs, G.F.S.; Holmes, P. Dynamic controls on wind erosion and dust generation on west-central free state agricultural land, South Africa. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2011, 36, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Fister, W.; Kuhn, N.J. Temporal variation of SOC enrichment from interrill erosion over prolonged rainfall simulations. Agriculture 2013, 3, 726–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Bissonnais, Y.; Renaux, B.; Delouche, H. Interactions between soil properties and moisture content in crust formation, runoff and interrill erosion from tilled loess soils. CATENA 1995, 25, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belnap, J. Comparative structure of physical and biological soil crusts. In Biological Soil Crusts: Structure, Function, and Management; Belnap, J., Lange, O.L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 177–191. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, M.A.; McEwan, I.K. Crust strength: A wind tunnel study of the effect of impact by saltating particles on cohesive soil surfaces. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2001, 26, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, M.A.; Willetts, B.B.; McEwan, I.K. Wind erosion of crusted soil sediments. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1996, 21, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houser, C.A.; Nickling, W.G. The emission and vertical flux of particulate matter <10 μm from a disturbed clay-crusted surface. Sedimentology 2001, 48, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobeck, T.M. Abrasion of crusted soils: Influence of abrader flux and soil properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1991, 55, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillette, D.A. Threshold friction velocities for dust production for agricultural soils. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1988, 93, 12645–12662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gillette, D.A.; Niemeyer, T.C.; Helm, P.J. Supply-limited horizontal sand drift at an ephemerally crusted, unvegetated saline playa. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 18085–18098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, D. Effect of soil crusting on the emission and transport of wind-eroded sediment: Field measurements on loamy sandy soil. Geomorphology 2004, 58, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharratt, B.; Vaddella, V. Threshold friction velocity of crusted windblown soils in the Columbia plateau. Aeolian Res. 2014, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterk, G.; López, M.V.; Arrúe, J.L. Saltation transport on a silt loam soil in northeast Spain. L. Degrad. Dev. 1999, 10, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillette, D.A.; Adams, J.; Endo, A.; Smith, D.; Kihl, R. Threshold velocities for input of soil particles into the air by desert soils (Mojave). J. Geophys. Res. 1980, 85, 5621–5630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillette, D.A.; Adams, J.; Muhs, D.; Kihl, R. Threshold friction velocities and rupture moduli for crusted desert soils for the input of soil particles into the air. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1982, 87, 9003–9015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Y.; Wu, L.; Xin, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, G. How rain-formed soil crust affects wind erosion in a semi-arid steppe in northern China. Geoderma 2015, 249, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, M.; Gill, T.E.; Etyemezian, V.; Nikolich, G.; Ghodsi Zadeh, Z.; Webb, N.P.; Van Pelt, R.S. Dust emission from crusted surfaces: Insights from field measurements and modelling. Aeolian Res. 2019, 40, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, M.A.; McEwan, I.K.; Mullins, C.E. A conceptual model of wind erosion of soil surfaces by saltating particles. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1999, 24, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajot, J.L.; Alfaro, S.C.; Gomes, L.; Gaudichet, A. Soil crusting on sandy soils and its influence on wind erosion. Catena 2003, 53, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, P.; Ahamed, S.; Carré, F.; Hartemink, A.; Hempel, J.; Huising, J.; Lagacherie, P.; Mcbratney, A.; McKenzie, N.; Mendonça Santos, M.; et al. Digital soil map of the world. Science 2009, 325, 680–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Houyou, Z.; Bielders, C.L.; Benhorma, H.A.; Dellal, A.; Boutemdjet, A. Evidence of strong land degradation by wind erosion as a result of rainfed cropping in the Algerian steppe: A case study at Laghouat. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 1788–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mctainsh, G.H.; Lynch, A.W.; Burgess, R.C. Wind erosion in eastern Australia. Soil Res. 1990, 28, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartemink, A.; Huting, J.R.M. Land cover, extent, and properties of arenosols in Southern Africa. Arid L. Res. Manag. 2008, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Huang, N.; Dong, Z.; Van Pelt, R.; Zobeck, T.M. Wind erosion induced soil degradation in Northern China: Status, measures and perspective. Sustainability 2014, 6, 8951–8966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harper, R.J.; Gilkes, R.J. Evaluation of the 137Cs techniques for estimating wind erosion losses for some sandy Western Australian soils. Soil Res. 1994, 32, 1369–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, L.; Dong, Z.; Xiao, W.; Li, C.; Xiao, N.; Song, S.; Xiao, F.; Du, L. A field investigation of wind erosion in the farming–pastoral ecotone of northern China using a portable wind tunnel: A case study in Yanchi County. J. Arid Land 2018, 10, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goossens, D.; Buck, B. Dust dynamics in off-road vehicle trails: Measurements on 16 arid soil types, Nevada, USA. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 3458–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houser, C.; Nickling, W. The factors influencing the abrasion efficiency of saltating grains on a clay-crusted playa. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2001, 26, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Holdt, J.R.C.; Eckardt, F.D.; Baddock, M.C.; Wiggs, G.F.S. Assessing landscape dust emission potential using combined ground-based measurements and remote sensing data. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2019, 124, 1080–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries. Abstract of Agricultural Statistics 2018; Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries: Pretoria, South Africa, 2018.
- Hu, Y.; Berhe, A.A.; Fogel, M.L.; Heckrath, G.J.; Kuhn, N.J. Transport-distance specific SOC distribution: Does it skew erosion induced C fluxes? Biogeochemistry 2016, 128, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caviezel, C.; Hunziker, M.; Kuhn, N.J. Bequest of the Norseman—The potential for agricultural intensification and expansion in Southern Greenland under climate change. Land 2017, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fister, W.; Goldman, N.; Mayer, M.; Suter, M.; Kuhn, N.J. Testing of photogrammetry for differentiation of soil organic carbon and biochar in sandy substrates. Geogr. Helv. 2019, 74, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Dijk, A.I.J.; Bruijnzeel, L.A.; Rosewell, C.J. Rainfall intensity–kinetic energy relationships: A critical literature appraisal. J. Hydrol. 2002, 261, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, N.J.; Bryan, R.B. Drying, soil surface condition and interrill erosion on two Ontario soils. Catena 2004, 57, 113–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimbone, S.M.; Vickers, A.; Morgan, R.P.C.; Vella, P. Field investigations of different techniques for measuring surface soil shear strength. Soil Technol. 1996, 9, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizuka, M.; Mikami, M.; Leys, J.F.; Yamada, Y.; Heidenreich, S.; Shao, Y.; McTainsh, G.H. Effects of soil moisture and dried raindroplet crust on saltation and dust emission. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Zhibao, D.; Zhenshan, L.; Zuotao, Y. Wind tunnel test of the influence of moisture on the erodibility of loessial sandy loam soils by wind. J. Arid Environ. 1996, 34, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkhtsetseg, E.; Shinoda, M.; Gillies, J.A.; Kimura, R.; King, J.; Nikolich, G. Relationships between soil moisture and dust emissions in a bare sandy soil of Mongolia. Particuology 2016, 28, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Sharratt, B.; Vaddella, V. Windblown soil crust formation under light rainfall in a semiarid region. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 128, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borselli, L.; Biancalani, R.; Giordani, C.; Carnicelli, S.; Ferrari, G.A. Effect of gypsum on seedling emergence in a kaolinitic crusting soil. Soil Technol. 1996, 9, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, J.M.; Grossman, R.B. In-situ measurement of near-surface soil strength by the fall-cone device. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1982, 46, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, D.J. Plastic limit determination using a drop-cone penetrometer. J. Soil Sci. 1976, 27, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhongbao, X.; Wang, L.; Cai, Q.; Wang, X. Effects of wetting rate and simulated rain duration on soil crust formation of red loam. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadiri, H. Crater formation in soils by raindrop impact. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2004, 29, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rice, M.A.; Mullins, C.E.; McEwan, I.K. An analysis of soil crust strength in relation to potential abrasion by saltating particles. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1997, 22, 869–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Okin, G.; Herrick, J.; Belnap, J.; Munson, S.; Miller, M. A simple method to estimate threshold friction velocity of wind erosion in the field. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, M.R.; Mason, J.A. Mechanisms of dust emission from Pleistocene loess deposits, Nebraska, USA. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2013, 118, 1460–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansbo, S. A new approach to determination of shear strength of clay by the fall cone test. Swed. Geotech. Inst. Proc. 1957, 14, 5–47. [Google Scholar]
- Becher, H.H.; Breuer, J.; Klingler, B. An index value for characterizing hardsetting soils by fall-cone penetration. Soil Technol. 1997, 10, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etyemezian, V.; Nikolich, G.; Ahonen, S.; Pitchford, M.; Sweeney, M.; Purcell, R.; Gillies, J.A.; Kuhns, H. The portable in situ wind erosion laboratory (PI-SWERL): A new method to measure PM10 windblown dust properties and potential for emissions. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 3789–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etyemezian, V.; Gillies, J.A.; Shinoda, M.; Nikolich, G.; King, J.; Bardis, A.R. Accounting for surface roughness on measurements conducted with PI-SWERL: Evaluation of a subjective visual approach and a photogrammetric technique. Aeolian Res. 2014, 13, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, C.C.E.; Fister, W.; Vos, H.C.; Cammeraat, L.H.; Kuhn, N.J. A cross-comparison between a traditional portable straight-line wind tunnel and PI-SWERL. Aeolian Res. submitted for publication.
- Shao, Y.; Raupach, M.R.; Findlater, P.A. Effect of saltation bombardment on the entrainment of dust by wind. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1993, 98, 12719–12726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munkhtsetseg, E.; Shinoda, M.; Ishizuka, M.; Mikami, M.; Kimura, R.; Nikolich, G. Anthropogenic dust emissions due to livestock trampling in a Mongolian temperate grassland. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 11389–11401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hiernaux, P.; Bielders, C.L.; Valentin, C.; Bationo, A.; Fernández-Rivera, S. Effects of livestock grazing on physical and chemical properties of sandy soils in Sahelian rangelands. J. Arid Environ. 1999, 41, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Xu, X.; Yang, J. Experimental study on the effect of freezing-thawing cycles on wind erosion of black soil in Northeast China. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2017, 136, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shi, Z.H.; Wu, G.L.; Fang, N.F. Freeze/thaw and soil moisture effects on wind erosion. Geomorphology 2014, 207, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, P.; Fister, W.; Kinnell, P.I.A.; Rüegg, H.-R.; Kuhn, N.J. Developing and testing a precision erosion measurement facility for elucidating mobilization mechanisms in shallow-flow conditions. Desertif. L. Degrad. 2013, 105. [Google Scholar]
- Marticorena, B.; Bergametti, G.; Gillette, D.; Belnap, J. Factors controlling threshold friction velocity in semiarid and arid areas of the United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 23277–23287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langston, G.; Neuman, C.M. An experimental study on the susceptibility of crusted surfaces to wind erosion: A comparison of the strength properties of biotic and salt crusts. Geomorphology 2005, 72, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








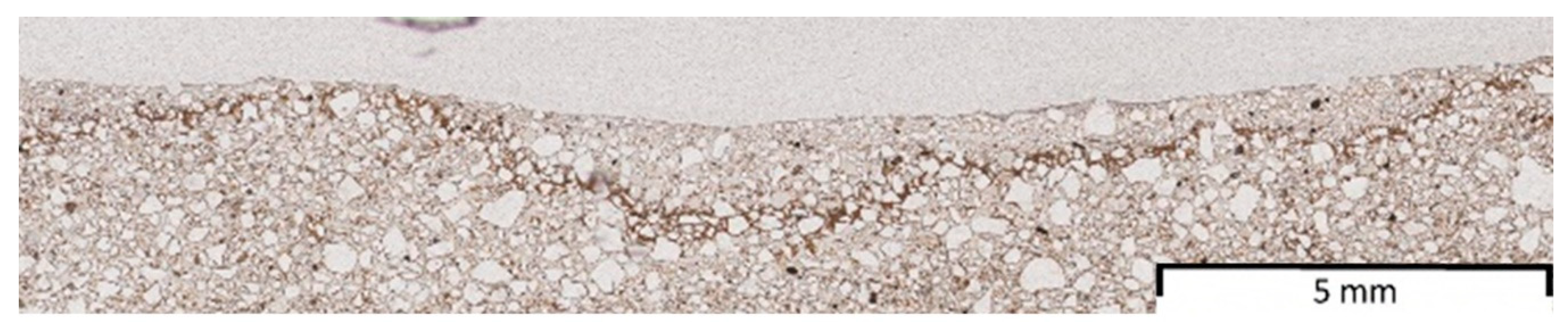





| Field | Soil | Description | Crust Presence | TOC% | pH | Silt/Sand |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Field 1 | Luvisol | Plowed and bare field | No | 0.25 | 6.06 | 0.19 |
| Field 2 | Arenosol | Unharvested maize field | Yes | 0.47 | 6.32 | 0.23 |
| Field 3 | Arenosol | Peanut field, harvested | Yes | 0.19 | 6.30 | 0.09 |
| Field 4 | Arenosol | Maize field, harvested and deep ripped | Yes | 0.18 | 6.32 | 0.12 |
| Field 5 | Arenosol | Sunflower field, harvested | Yes | 0.18 | 6.08 | 0.10 |
| Field 6 | Arenosol | Maize field, unharvested | Yes | 0.32 | 6.81 | 0.19 |
| Field 7 | Arenosol | Harvested maize field, grazed by cattle | Yes | 0.16 | 6.30 | 0.13 |
| Soil | Crust | Abrader Addition | n (Per Soil Type) | Time (s) at 0.59 m s−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AR and LV | Loose soil | No | 6 | 30 |
| Crusted by 15 mm of rainfall | No | 3 | 120 | |
| Yes | 3 | 120 |
| Rainfall Amount | AR versus LV | Single Event versus Sequenced Rainfall | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Event | Sequenced | AR | LV | |
| 5 mm | 0.140 | - | ||
| 10 mm | 0.995 | 0.066 | 0.074 | 0.497 |
| 15 mm | 0.071 | 0.050 | 0.032 | 0.301 |
| 20 mm | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.025 |
| Soil Type | Experiment Type | Average Threshold Friction Velocity (m s−1) | Average Flux (mg m−2 s−1) | Flux Ratio to Loose Run | Relative Abrasion Efficiency | Shear Strength (kPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AR | Loose | 0.305 | 3.872 | - | - | - |
| Crust | - | 0.0053 | 0.14% | - | 68.1 | |
| Abraders | 0.436 | 0.311 | 8.03% | 0.012 | - | |
| LV | Loose | 0.272 | 10.534 | - | - | - |
| Crust | - | 0.0278 | 0.26% | - | 92.0 | |
| Abraders | 0.357 | 0.425 | 4.03% | 0.013 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vos, H.C.; Fister, W.; Eckardt, F.D.; Palmer, A.R.; Kuhn, N.J. Physical Crust Formation on Sandy Soils and Their Potential to Reduce Dust Emissions from Croplands. Land 2020, 9, 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/land9120503
Vos HC, Fister W, Eckardt FD, Palmer AR, Kuhn NJ. Physical Crust Formation on Sandy Soils and Their Potential to Reduce Dust Emissions from Croplands. Land. 2020; 9(12):503. https://doi.org/10.3390/land9120503
Chicago/Turabian StyleVos, Heleen C., Wolfgang Fister, Frank D. Eckardt, Anthony R. Palmer, and Nikolaus J. Kuhn. 2020. "Physical Crust Formation on Sandy Soils and Their Potential to Reduce Dust Emissions from Croplands" Land 9, no. 12: 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/land9120503
APA StyleVos, H. C., Fister, W., Eckardt, F. D., Palmer, A. R., & Kuhn, N. J. (2020). Physical Crust Formation on Sandy Soils and Their Potential to Reduce Dust Emissions from Croplands. Land, 9(12), 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/land9120503




