Warming Effort and Energy Budget Difference of Various Human Land Use Intensity: Case Study of Beijing, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Data
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Land Use Data Reclassification
2.2.2. Surface Energy Balance and Warming Effect
2.2.3. Spatial Analysis and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes in the Surface Energy Intake
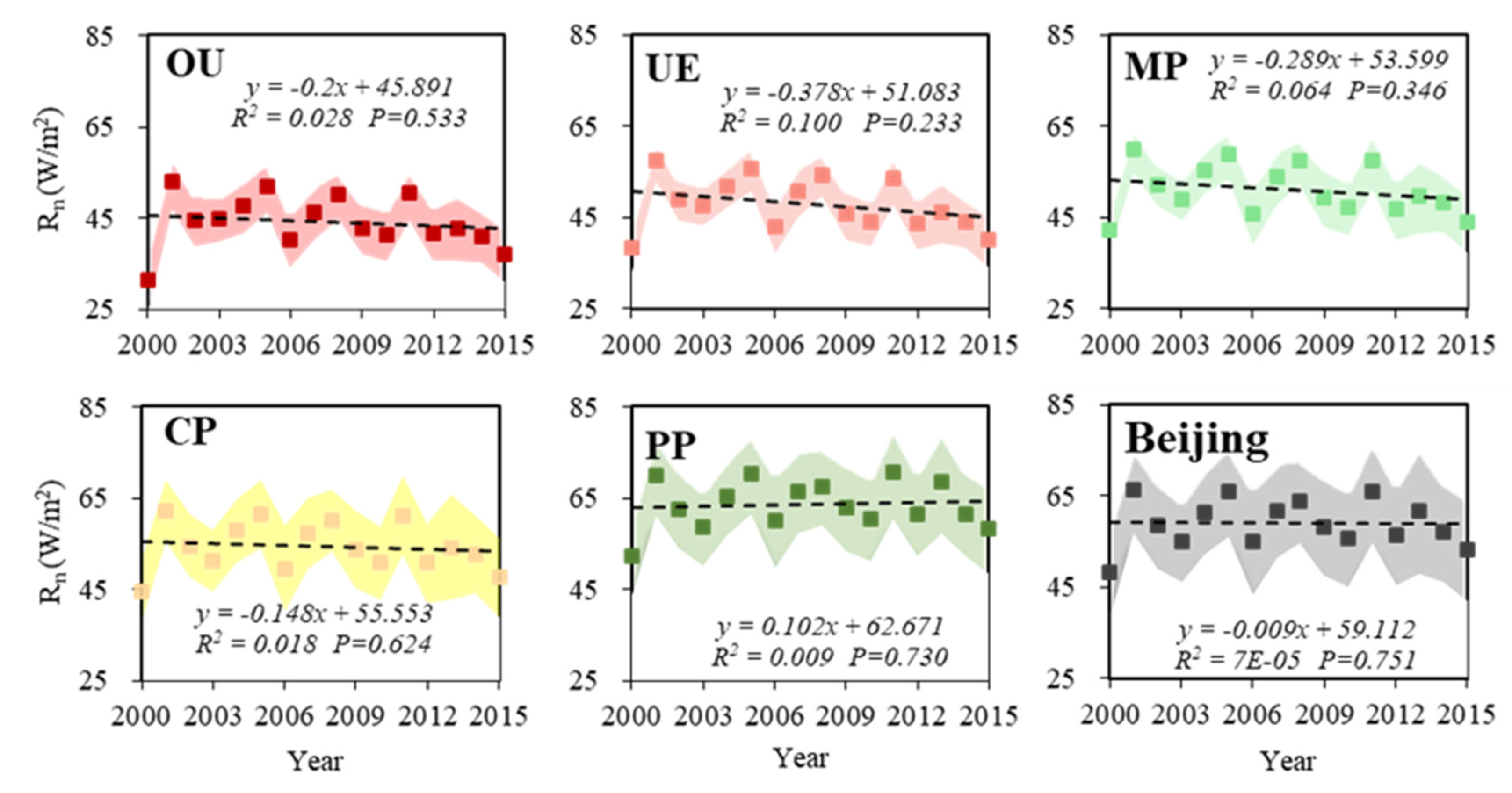
3.1.1. Net Longwave and Shortwave Radiation
3.1.2. Changes in Net Radiation
3.2. Analysis on the Change of the Surface Energy Expenditure
3.3. Comparison of Net Radiation and Latent Heat Flux
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reinhard, R.; Almut, A.; Alberte, B.; Nathalie, N.D.; Thomas, P.; Stephen, S.; Stehfest, E.; Peter, V. Current Challenges of Implementing Anthropogenic Land-Use and Land-Cover Change in Models Contributing to Climate Change Assessments. Earth. Syst. Dynam. 2017, 8, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, W.B.; Turner, B.L.I. Human population growth and global land-use/cover change. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1992, 23, 39–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, W.; Sanderson, R.A.; Tyson, P.D.; Jäger, J.; Matson, P.; Moore, B.; Oldfield, F.; Richardson, K.; Schellnhuber, H.J.; Turner, B.L.; et al. Global Change and the Earth System: A Planet Under Pressure; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; ISBN 978-3-540-26607-5. [Google Scholar]
- Diffenbaugh, N.S. Influence of modern land cover on the climate of the United States. Clim. Dynam. 2009, 33, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Claussen, M.; Brovkin, V.; Ganopolski, A. Biogeophysical versus biogeochemical feedbacks of large-scale land cover change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 1011–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bright, R.; Davin, E.; O’Halloran, T.; Pongratz, J.; Zhao, K.; Alessandro, A. Local temperature response to land cover and management change driven by non-radiative processes. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cui, Y.; Fu, Y.; Li, N.; Tang, X.; Liu, X.; Run, Y. Simulating the Potential Sequestration of Three Major Greenhouse Gases in China’s Natural Ecosystems. Forests 2020, 11, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, D.; Xia, J.; Wan, S. Climate warming and biomass accumulation of terrestrial plants: A meta-analysis. New Phytol. 2010, 188, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, W.; Fu, S. Reforestation makes a minor contribution to soil carbon accumulation in the short term: Evidence from four subtropical plantations. For. Ecol. Manage. 2017, 384, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Meadows, E.M.; Li, N.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, G.; Dong, J. Land Cover Change Intensifies Actual and Potential Radiative Forcing through CO2 in South and Southeast Asia from 1992 to 2015. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Betts, R.A.; Falloon, P.D.; Goldewijk, K.K.; Ramankutty, N. Biogeophysical effects of land use on climate: Model simulations of radiative forcing and large-scale temperature change. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2007, 142, 216–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, M.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, W.; Xiao, W.; Cao, C.; Xu, J. Observed Analysis of Radiation and Energy Fluxes Characteristic sacross Lake Taihu Surface in Summer. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2014, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Gastellu-Etchegorry, J.P. 3D Modeling of satellite spectral images, radiation budget and energy budget of urban landscapes. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2008, 102, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, I.; Castellazzi, M.; Feliciano, D. Comparing path dependence and spatial targeting of land use in implementing climate change responses. Land 2014, 3, 850–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, T.; Wang, L.; Wen, X. Analysis of the characteristics of radiation budget and surface energy balance in the Eling Lake area at the source of the Yellow River. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2013, 35, 112–123. [Google Scholar]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, R.A.; Holtslag, B.A. remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL).1. Formulation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212–213, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Kuang, W. Modeling the radiation balance of different urban underlying surfaces. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Qin, Y.; Dong, J. Modeling urban sprawl effects on regional warming in Beijing-Tianjin-Tangshan urban agglomeration. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 993–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, A.D.; Keenan, T.F.; Migliavacca, M.; Ryu, Y.; Sonnentag, O.; Toomey, M.J.A. Climate change, phenology, and phenological control of vegetation feedbacks to the climate system. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 169, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, G.L.; O’Brien, D.; Webster, P.J.; Pilewski, P.; Kato, S.; Li, J. The albedo of Earth. Rev. Geophys. 2015, 53, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houspanossian, J.; Raul, G.; Esteban, J.; Marcelo, N. Surface albedo raise in the South American Chaco: Combined effects of deforestation and agricultural changes. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 232, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- North, G.R.; Cahalan, R.F.; Coakley, J.A. Energy balance climate models. Rev. Geophys. 1981, 19, 91–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, S.S.; Coauthors. Afforestation in China cools local land surface temperature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2915–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Addas, A.; Goldblatt, R.; Rubinyi, S. Utilizing Remotely Sensed Observations to Estimate the Urban Heat Island Effect at a Local Scale: Case Study of a University Campus. Land 2020, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z. The Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) for estimation of turbulent heat fluxes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 6, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roerink, G.J.; Su, Z.; Menenti, M. S-SEBI: A Simple Remote Sensing Algorithm to Estimate the Surface Energy Balance. Phys. Chem. Earth. 2000, 25, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhai, J.; Sun, C. Biogeophysical Forcing of Land-Use Changes on Local Temperatures across Different Climate Regimes in China. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 7053–7068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, L.; Xu, X.; Tian, W.; He, C. Analysis of evapotranspiration pattern by SEBAL model during the growing season in the agro-pastoral ecotone in Northwest China. Acta Ecol. Sinica. 2020, 40, 2175–2185. [Google Scholar]
- Kirschbaum, M.U.F.; Saggar, S.; Tate, K.R.; Thakur, K.P.; Giltrap, D.L. Quantifying the climate-change consequences of shifting land use between forest and agriculture. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 465, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaab, J.; Bavay, M.; Davin, E.; Hagedorn, F.; Hüsler, F.; Lehning, M.; Schneebeli, M.; Thürig, E.; Bebi, P. Carbon storage versus albedo change: Radiative forcing of forest expansion in temperate mountainous regions of Switzerland. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 467–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J. Modeling urban energy balance and temperature differences of different underlying surfaces. Geogr. Res. 2012, 31, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, J.; Guo, W.; Pitman, A.J.; Kauwe, M.G.; Chen, X.; Fu, C. The Nonradiative Effect Dominates Local Surface Temperature Change Caused by Afforestation in China. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 4445–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, X.; Goulden, M.; Hollinger, D.; Barr, A.; Andrew Black, T.; Bohrer, G.; Bracho, R.; Drake, B.; Goldstein, A.; Gu, L.; et al. Observed increase in local cooling effect of deforestation at higher latitudes. Nature 2011, 479, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duveiller, G.; Forzieri, G.; Robertson, E.; Wei, L.; Cescatti, A. Biophysics and vegetation cover change: A process-based evaluation framework for confronting land surface models with satellite observations. Earth. Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 1265–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duveiller, G.; Hooker, J.; Cescatti, A. The mark of vegetation change on Earth’s surface energy balance. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duveiller, G.; Caporaso, L.; Abad-Viñas, R.; Perugini, L.; Grassi, G.; Arneth, A.; Cescatti, A. Local biophysical effects of land use and land cover change: Towards an assessment tool for policy makers. Land Use Policy 2020, 91, 104382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ge, J.P.F.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Weng, W. Energy flux and balance analysis of Dajiuhu Peatland in Shennongjia. J. Hydroecology 2019, 40, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Cui, Y.; Li, N.; Fu, Y.; Liu, X.; Run, Y.; Li, M.; Zhao, G.; Dong, J. Human activities enhance radiation forcing through surface albedo associated with vegetation in Beijing. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnfield, A.J.; Mills, G.M. An analysis of the circulation characteristics and energy budget of a dry, asymmetric, east-west urban canyon. I. Circulation characteristics. Int. J. Climatol. 1994, 14, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakakibara, Y. A numerical study of the effect of urban geometry upon the surface energy budget. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 1–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson-Teixeira, K.J.; Snyder, P.K.; Twine, T.E.; Cuadra, S.V.; Costa, M.H.; Delucia, E.H. Climate-regulation services of natural and agricultural ecoregions of the Americas. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.D.; Calvin, K.V.; Collins, W.D.; Edmonds, J. Accounting for radiative forcing from albedo change in future global land-use scenarios. Clim. Chang. 2015, 131, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnes, C.A.; Roy, D.P. Radiative forcing over the conterminous United States due to contemporary land cover land use change and sensitivity to snow and interannual albedo variability. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2010, 115, G04033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, G.; Dong, J.; Cui, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhai, J.; He, T.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, X. Evapotranspiration-dominated biogeophysical warming effect of urbanization in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Clim. Dynam. 2019, 52, 1231–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, L.; Sun, G.; Liu, Y. The footprint of urban heat island effect in China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, J.; Qin, Y.; Doughty, R.B.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Qin, Y. Temporal consistency between gross primary production and solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence in the ten most populous megacity areas over years. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Data Items | Time Resolution | Spatial Resolution | Data Resource |
|---|---|---|---|
| Albedo | daily | 500 m | MCD43A3 |
| Temperature (LST) | daily | 1 km | MOD11A1 |
| Latent heat flux (LE) | 8 days | 500 m | MOD16A2 |
| Emissivity | daily | 1 km | MOD11A1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, S.; Wang, K.; Yang, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Fu, Y.; Liu, X.; Run, Y.; Chubwa, O.G.; et al. Warming Effort and Energy Budget Difference of Various Human Land Use Intensity: Case Study of Beijing, China. Land 2020, 9, 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/land9090280
Zhou S, Wang K, Yang S, Li W, Zhang Y, Zhang B, Fu Y, Liu X, Run Y, Chubwa OG, et al. Warming Effort and Energy Budget Difference of Various Human Land Use Intensity: Case Study of Beijing, China. Land. 2020; 9(9):280. https://doi.org/10.3390/land9090280
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Shenghui, Ke Wang, Shiqi Yang, Wenli Li, Yuxuan Zhang, Bin Zhang, Yiming Fu, Xiaoyan Liu, Yadi Run, Oliva Gabriel Chubwa, and et al. 2020. "Warming Effort and Energy Budget Difference of Various Human Land Use Intensity: Case Study of Beijing, China" Land 9, no. 9: 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/land9090280
APA StyleZhou, S., Wang, K., Yang, S., Li, W., Zhang, Y., Zhang, B., Fu, Y., Liu, X., Run, Y., Chubwa, O. G., Zhao, G., Dong, J., & Cui, Y. (2020). Warming Effort and Energy Budget Difference of Various Human Land Use Intensity: Case Study of Beijing, China. Land, 9(9), 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/land9090280









