Antinuclear Autoantibodies in Health: Autoimmunity Is Not a Synonym of Autoimmune Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Physiological Autoimmunity and Its Bidirectional Pathological Changes
2.1. Physiological Autoimmunity: Historical Perspective and Contemporary Understanding
- Patients with certain ADs show a decrease in the level of certain autoantibodies and/or the strength of antibody-mediated bioeffects in comparison with healthy donors;
- The level of autoantibodies decreases, rather than increases during exacerbations of some ADs;
- Some autoantibodies are associated with a favorable outcome of the disease.
2.2. Transition from Physiological Autoimmune Response to Autoimmune Disease
2.3. Functional Autoantibodies
3. ANA: Detection, Polyspecificity, and Relation to AD Pathogenesis
4. Detection of ANAs in Healthy Individuals
4.1. HEp-2 IFA Cut-Off Titers
4.2. Regional, Social, and Racial-Ethnic Aspects of ANA Prevalence
4.3. Ontogenetic Aspects of Autoimmunity to the Nuclear Antigens
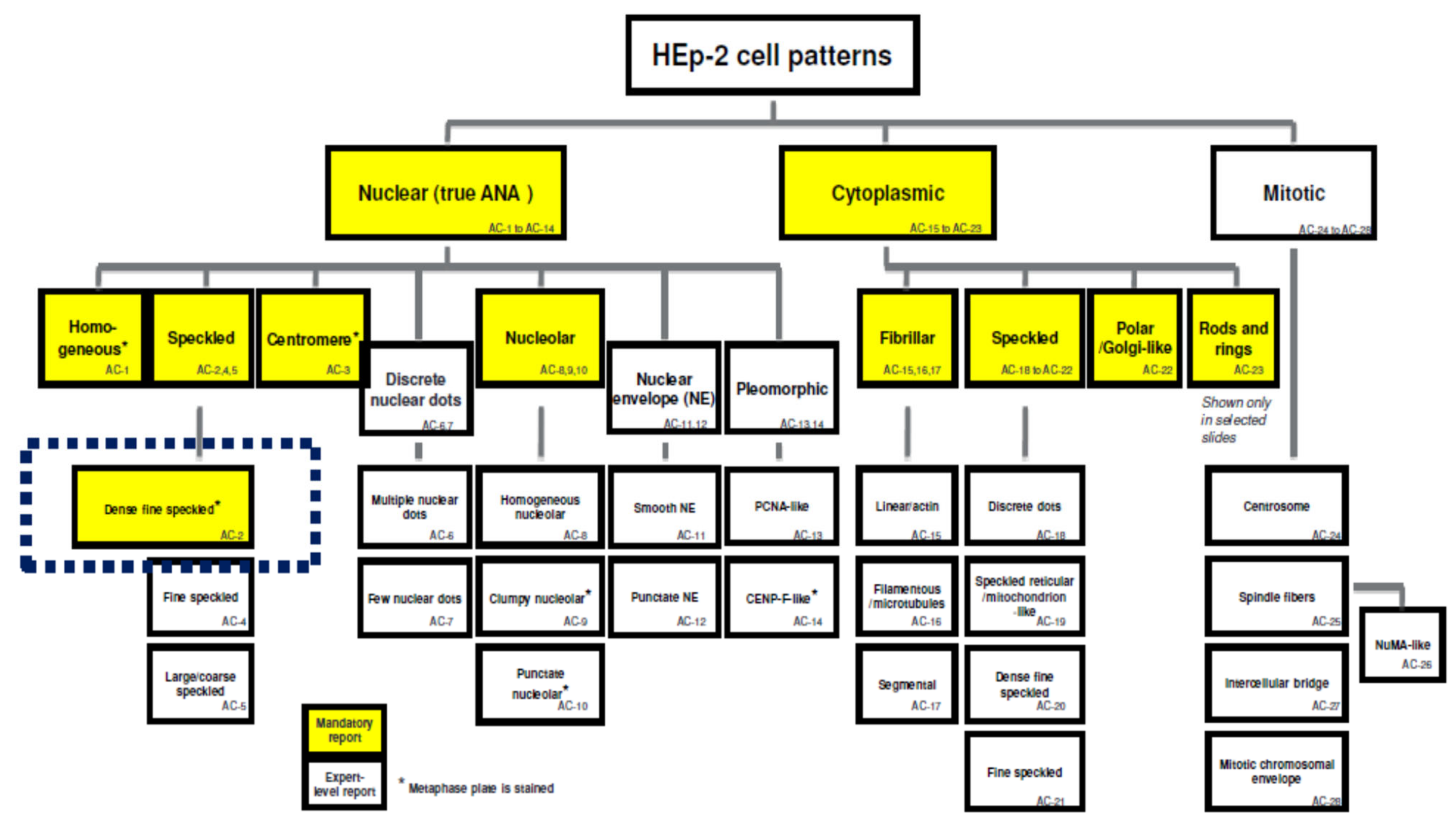
4.4. ANA IFA Patterns in Health
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lerner, À.; Jeremias, P.; Matthias, T. The World Incidence and Prevalence of Autoimmune Diseases is Increasing. Int. J. Celiac Dis. 2015, 3, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Missouma, H.; Alamic, M.; Bachird, F.; Arjid, N.; Bouyahyaa, A.; Rhajaouid, M.; El Aouad, R.; Bakri, Y. Prevalence of autoimmune diseases and clinical significance of autoantibody profile: Data from National Institute of Hygiene in Rabat, Morocco. Hum. Immunol. 2019, 80, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisó-Almirall, A.; Kostov, B.; Martínez-Carbonell, E.; Brito-Zerón, P.; Ramirez, P.B.; Acar-Denizli, N.; Delicado, P.; González-Martínez, S.; Muñoz, C.V.; Àreu, J.B.; et al. The prevalence of 78 autoimmune diseases in Catalonia (MASCAT-PADRIS Big Data Project). Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okoroiwu, I.L.; Obeagu, E.I.; Obeagu, G.U.; Chikezie, C.C.; Ezema, G.O. The prevalence of selected autoimmune diseases. Int. J. Adv. Multidiscip. Res. 2016, 3, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ren, Y.; Liu, D.; Lin, F.; Liang, Y. Prevalence of systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases and clinical significance of ANA profile: Data from a tertiary hospital in Shanghai, China. APMIS 2016, 124, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furst, D.E.; Clarke, A.; Fernandes, A.W.; Bancroft, T.; Gajria, K.; Greth, W.; Iorga, S.R. Medical costs and healthcare resource use in patients with lupus nephritis and neuropsychiatric lupus in an insured population. J. Med. Econ. 2013, 16, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarvin, S.E.; O’Neil, K.M. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Sjogren Syndrome, and Mixed Connective Tissue Disease in Children and Adolescents. Pediatr. Clin. 2018, 65, 711–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, A.; Ravelli, A.; Avcin, T.; Beresford, M.W.; Burgos-Vargas, R.; Cuttica, R.; Ilowite, N.T.; Khubchandani, R.; Laxer, R.M.; Lovell, D.J.; et al. Toward New Classification Criteria for Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: First Steps, Pediatric Rheumatology International Trials Organization International Consensus. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.H.; Lee, H.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, S.S.; Jeong, S.; Hwang, I.S.; Kim, N.; Kim, N.E.; et al. Adrenal insufficiency in systematic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and antiphospholipid syndrome (APS): A systematic review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirouse, A.; Seror, R.; Vicaut, E.; Mariette, X.; Dougados, M.; Fauchais, A.L.; Deroux, A.; Dellal, A.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Denis, G.; et al. Arthritis in primary Sjőgren’s syndrome: Characteristics, outcome and treatment from French multicenter retrospective study. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enocsson, H.; Sjöwall Ch Wirestam, L.; Dahle Ch Kastbom, A.; Rönnelid, J.; Wetterö, J.; Skogh, T. Four Anti-dsDNA Antibody Assays in Relation to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Specificity and Activity. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Infantino, M.; Pregnolato, F.; Bentow, C.; Mahler, M.; Benucci, M.; Li Gobbi, F.; Damiani, A.; Grossi, V.; Franceschini, F.; Bodio, C.; et al. Only monospecific anti-DFS70 antibodies aid in the exclusion of antinuclear antibody associated rheumatic diseases: An Italian experience. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2019, 57, 1764–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomelli, R.; Afeltra, A.; Alunno, A.; Bartoloni-Bocci, E.; Berardicurti, O.; Bombardieri, M.; Bortoluzzi, A.; Caporali, R.; Caso, F.; Cervera, R.; et al. Guidelines for biomarkers in autoimmune rheumatic diseases-evidence based analysis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Aoust, J.; Hudson, M.; Tatibouet, S.; Wick, J.; Mahler, M.; Baron, M.; Fritzler, M.; The Canadian Scleroderma Research Group. Clinical and serologic correlates of anti-PM/Scl antibodies in systemic sclerosis: A multicenter study of 763 patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 1608–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, L.M.; Floca, E.; Sur, D.G.; Colceriu, M.C.; Samasca, G.; Sur, G. Antinuclear Antibodies: Marker of Diagnosis and Evolution in Autoimmune Diseases. Lab. Med. 2018, 49, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Damoiseaux, J.; Andrade, L.E.C.; Carballo, O.G.; Conrad, K.; Francescantonio, P.L.C.; Fritzler, M.J.; De La Torre, I.G.; Herold, M.; Klotz, W.; Cruvinel, W.D.M.; et al. Clinical relevance of HEp-2 indirect immunofluorescent patterns: The International Consensus on ANA patterns (ICAP) perspective. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaichik, A.S.; Poletaev, A.B.; Churilov, L.P. Self-recognition and interaction with self as a main form of adaptive immune system activity. Vestn. St. Petersburg Univ. Med. 2013, 8, 6–27. Available online: https://elibrary.ru/download/elibrary_18943091_27775552.pdf (accessed on 27 December 2020). (In Russian).
- Schwartz, M.; Cohen, I.R. Autoimmunity can benefit self-maintenance. Immunol. Today 2000, 21, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friou, G.J. Identification of the nuclear component of the interaction of lupus erythematosus globulin and nuclei. J. Immunol. 1958, 80, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marin, G.G.; Cardiel, M.H.; Cornejo, H.; Viveros, M.E. Prevalence of antinuclear antibodies in 3 groups of healthy individuals: Blood donors, hospital personnel, and relatives of patients with autoimmune diseases. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2009, 15, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, M.; Chan, E.K.L.; Ho, L.A.; Rose, K.M.; Parks, C.h.G.; Cohn, R.D.; Jusko, T.A.; Walker, N.J.; Germolec, D.R.; Whitt, I.Z.; et al. Prevalence and Sociodemographic Correlates of Antinuclear Antibodies in the United States. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2319–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siloşi, I.; Siloşi, C.A.; Boldeanu, M.V.; Cojocaru, M.; Biciuşcă, V.; Avrămescu, C.S.; Cojocaru, I.M.; Bogdan, M.; FolcuŢi, R.M. The Role of Autoantibodies in Health and Disease. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2016, 57, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peker, B.O.; Şener, A.G.; Tarhan, E.F.; Kaya, S. Investigation of anti-DFS70 antibody in patients with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 3627–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagele, E.P.; Han, M.; Acharya, N.K.; DeMarshall, C.; Kosciuk, M.C.; Nagele, R.G. Natural IgG Autoantibodies Are Abundant and Ubiquitous in Human Sera, and Their Number Is Influenced by Age, Gender, and Disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guilbert, B.; Dighiero, G.; Avrameas, S. Naturally occurring antibodies against nine common antigens in normal humans. 1. Detection, isolation and characterization. J. Immunol. 1982, 128, 2779–2783. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Madi, À.; Bransburg-Zabary, S.; Kenett, D.Y.; Ben-Jacob, E.; Cohen, I.R. The natural autoantibody repertoire in newborns and adults: A current overview. In Naturally Occurring Antibodies (NAbs), 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Chapter 15; pp. 198–212. [Google Scholar]
- Přibylova, J.; Krausova, K.; Kocourkova, I.; Rossmann, P.; Klimesova, K.; Kverka, M.; Tlaskalova-Hogenova, H. Colostrum of Healthy Mothers Contains Broad Spectrum of Secretory IgA Autoantibodies. J. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 32, 1372–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacroix-Desmazes, S.; Kaveri, S.V.; Mouthon, L.; Ayouba, A.; Malanchère, E.; Coutinho, A.; Kazatchkine, M.D. Self-reactive antibodies (natural autoantibodies) in healthy individuals. J. Immunol. Methods 1998, 216, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dighiero, G.; Guilbert, B.; Avrameas, S. Naturally occurring antibodies against nine common antigens in humans sera. II. High incidence of monoclonal Ig exhibiting antibody activity against actin and tubulin and sharing antibody specificities with natural antibodies. J. Immunol. 1982, 128, 2788–2792. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.; Zhao, M.H.; Segelmark, M.; Hellmark, T. Natural autoantibodies to myeloperoxidase, proteinase 3, and the glomerular basement membrane are present in normal individuals. Kidney Int. 2010, 78, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgington, T.S.; Dalessio, D.J. The assessment by immunofluorescent methods of humoral anti-myelin antibodies in man. J. Immunol. 1970, 105, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cabral-Marques, O.; Marques, A.; Giil, L.M.; De Vito, R.; Rademacher, J.; Günther, J.; Lange, T.; Humrich, J.Y.; Klapa, S.; Schinke, S.; et al. GPCR-specific autoantibody signatures are associated with physiological and pathological immune homeostasis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halpert, G.; Amital, H.; Shoenfeld, Y. Dysregulation of G protein-coupled receptors of the autonomic nervous system, adrenergic and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, in patients with autoimmune dysautonomic-related disorders. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2020, 4, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.S.; Kertiles, L.P.; Reichlin, S. Partial purification and characterization of thyrotropin binding inhibitory immunoglobulins from normal human plasma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1983, 56, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risdall, J.E.; Dahlberg, P.O.; Westermark, B. Influence of thyroid autoantibodies on thyroid cellular growth in vitro. J. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1984, 34, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanova, A.K.; Ryabkova, V.A.; Tillib, S.V.; Utekhin, V.J.; Churilov, L.P.; Shoenfeld, Y. Anti-Idiotypic Agonistic Antibodies: Candidates for the Role of Universal Remedy. Antibodies 2020, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Uchida, K.; Nakagaki, K.; Kanazawa, H.; Trapnell, B.C.; Hoshino, Y.; Kagamu, H.; Yoshizawa, H.; Keicho, N.; Goto, H.; et al. Anti-cytokine autoantibodies are ubiquitous in healthy individuals. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 2017–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horn, M.P.; Pachlopnik, J.M.; Vogel, M.; Dahinden, M.; Wurm, F.; Stadler, B.M.; Miescher, S.M. Conditional autoimmunity mediated by human natural anti-Fc(epsilon)RIalpha autoantibodies? FASEB J. 2001, 15, 2268–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaichik, A.S.; Churilov, L.P. Autoimmunity as a system of regulation of the morpho-functional processes. Clin. Pathophysiol. 2002, 2, 8–17. Available online: https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=28342337 (accessed on 27 December 2020). (In Russian).
- Cohen, I.R. Biomarkers, self-antigens and the immunological homunculus. J. Autoimmun. 2007, 29, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poletaev, A.; Osipenko, L. General network of natural autoantibodies as immunological homunculus (Immunculus). Autoimmun. Rev. 2003, 2, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, J.D. Harnessing therapeutic potential of “rogue” antibodies. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 41, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metchnikoff, E. The Evolutionary Biology Papers of Elie Metchnikoff, 1st ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 207–216, originally published in 1892. [Google Scholar]
- Zaichik, A.S.; Churilov, L.P.; Utekhin, V.J. Autoimmune regulation of genetically determined cell functions in health and disease. Pathophysiology 2008, 15, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletaev, A.B.; Churilov, L.P.; Stroev, Y.I.; Agapov, M.M. Immunophysiology versus immunopathology: Natural autoimmunity in human health and disease. Pathophysiology 2012, 19, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleicher, N.; Barad, D.; Weghofer, A. Functional autoantibodies: A new paradigm in Immunology? Autoimmun. Rev. 2007, 7, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral-Marques, O.; Riemekasten, G. Functional autoantibodies directed against cell surface receptors in systemic sclerosis. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2017, 2, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Arguelles, A.; Rivadeneyra-Espinoza, L.; Alarcon-Segovia, D. Antibody penetration into living cells: Pathogenic, preventive and immuno-therapeutic implications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2003, 9, 1881–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuneoka, M.; Imamoto, N.S.; Uchida, T. Monoclonal antibody against non-histone chromosomal protein high mobility group 1 co-migrates with high mobility group 1 into the nucleus. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 1829–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, P.; Bernatsky, S.; Clarke, A.; Isenberg, D.A.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Hansen, J.E. DNA-damaging autoantibodies and cancer: The lupus butterfly theory. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, M.; Redman, R. Effect of antibody to the hemin-controlled translational repressor in rabbit reticulocyte lysate. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1987, 908, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, S.R.; Im, S.W.; Chung, H.Y.; Pravinsagar, P.; Jang, Y.J. Cell- and nuclear-penetrating anti-dsDNA autoantibodies have multiple arginines in CDR3 of VH and increase cellular level of pERK and Bcl-2 in mesangial cells. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 67, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, D.; Westerbergh, J.; Sogkas, G.; Jablonka, A.; Ahrenstorf, G.; Schmidt, R.E.; Heidecke, H.; Wallentin, L.; Riemekasten, G.; Witte, T. Lowered anti-beta1 adrenergic receptor antibody concentrations may have prognostic significance in acute coronary syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, S.; Woodward, M.; Hertel, C.; Vlaicu, P.; Haque, Y.; Kärner, J.; Macagno, A.; Onuoha, S.C.; Fishman, D.; Peterson, H.; et al. AIRE-Deficient Patients Harbor Unique High-Affinity Disease-Ameliorating Autoantibodies. Cell 2016, 166, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poletaev, A.B.; Abrosimova, A.A.; Sokolov, M.A.; Gekht, A.B.; Alferova, V.V.; Gusev, E.I.; Nikolaeva, T.Y.; Selmi, C. Dialectics and implications of natural neurotropic autoantibodies in neurological disease and rehabilitation. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2004, 11, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.C.; Talor, M.V.; Rose, N.R.; Cappola, A.R.; Chiou, R.B.; Weiss, C.; Walston, J.D.; Fried, L.P.; Caturegli, P. Thyroid autoantibodies are associated with a reduced prevalence of frailty in community-dwelling older women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahler, M.; Parker, T.; Peebles, C.L.; Andrade, L.E.C.; Swart, A.; Carbone, Y.; Ferguson, D.J.; Villalta, D.; Bizzaro, N.; Hanly, J.G.; et al. Anti-DFS70/LEDGF antibodies are more prevalent in healthy individuals compared to patients with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 2104–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Infantino, M.; Shovman, O.; Pérez, D.; Grossi, V.; Manfredi, M.; Benucci, M.; Damiani, A.; Gilburd, B.; Azoulay, D.; Serrano, A.; et al. A better definition of the anti-DFS70 antibody screening by IIF methods. J. Immunol. Methods 2018, 461, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Wang, Z.; Mora, R.A.; Liu, A.; Li, C.; Liu, D.; Zhai, F.; Liu, H.; Gong, H.; Zhou, J.; et al. Anti-DFS70 Antibodies Among Patient and Healthy Population Cohorts in China: Results From a Multicenter Training Program Showing Spontaneous Abortion and Pediatric Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases Are Common in Anti-DFS70 Positive Patients. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 562138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conticini, E.; Sota, J.; Falsetti, P.; Bellisai, F.; Bacarelli, M.R.; Al-Khayyat, S.G.; Cantarini, L.; Frediani, B. Anti-dense fine speckled 70 antibodies in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38, 326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Janeway, C. Beneficial autoimmunity? Nature 1982, 299, 396–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechend, R.; Luft, F.C.; Lindheimer, M.D. Agonistic Autoantibody-Mediated Disease. In Chesley’s Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy, 3rd ed.; Academic Press—Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 287–296. [Google Scholar]
- Zaichik, A.M.; Poletaev, A.B.; Churilov, L.P. Natural autoantibodies, immunological theories and preventive medicine. Vestnik of Saint Petersburg University. Medicine 2013, 8, 3–16. Available online: https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=19410140 (accessed on 27 December 2020). (In Russian).
- Churilov, L.P.; Stroev, Y.I.; Zaichik, A.S. Autoimmunity versus Autoallergy in Autoimmune Regulation and Dysregulation. In Physiologic Autoimmunity and Preventive Medicine, 1st ed.; Bentham Science: Oak Park, MI, USA, 2013; pp. 72–166. [Google Scholar]
- Mannoor, K.; Xu, Y.; Chen, C. Natural autoantibodies and associated B cells in immunity and autoimmunity. Autoimmunity 2013, 46, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerne, N.K. The Nobel Lectures in Immunology. The Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine, 1984. The generative grammar of the immune system. Scand. J. Immunol 1993, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, M. T Cell Receptor Signaling in the Control of Regulatory T Cell Differentiation and Function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haspel, M.V.; Onodera, T.; Prabhakar, B.S.; McClintock, P.R.; Essani, K.; Ray, U.R.; Yagihashi, S.; Notkins, A.L. Multiple organ-reactive monoclonal autoantibodies. Nature 1983, 304, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Gennaro, L.A.; Popi, A.F.; Almeida, S.R.; Lopes, J.D.; Mariano, M. B-1 cells modulate oral tolerance in mice. Immunol. Lett. 2009, 124, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amital, H.; Shoenfeld, Y. Natural autoantibodies, heralding, protecting and inducing autoimmunity. In Autoantibodies, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho, A.; Kazatchkine, M.D.; Avrameas, S. Natural autoantibodies. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1995, 7, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notkins, A.L. Polyreactivity of antibody molecules. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkon, K.; Casali, P. Nature and functions of autoantibodies. Nat. Clin. Pract. Rheumatol. 2008, 4, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, Q.; Lan, Q.; Peng, Y.; Cai, J.; Zheng, J.; Dickerson, C.; Xiao, H.; Liu, H.-F. Nature, functions, and clinical implications of IgG4 autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Discov. Med. 2017, 23, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Notley, C.A.; Brown, M.A.; Wright, G.P.; Ehrenstein, M.R. Natural IgM is required for suppression of inflammatory arthritis by apoptotic cells. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 4967–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grabar, P.N. About Autoantibodies. In Problems of Reactivity in Pathology; Meditsina Publishers: Moscow, Russia, 1968; pp. 35–52. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Grabar, P. Hypothesis. Auto-antibodies and immunological theories: An analytical review. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1975, 4, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamov, A.K.; Nikolaev, A.I. On the role of “normal” and autoimmune antibodies in regulation of macromolecular content of the animal cells. Zhurnal Mikrobiol. 1968, 4, 75–80. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ardry, R. Physical heterogeneity of anti-tissue antibodies. Ann. Pharmac. Fr. 1962, 20, 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zaretskaya, I.S.; Saraeva, Z.M.; Tereschenko, N.P. The mechanisms of anti-tumor effect of homologous globulin, containing natural anti-tumor antibodies. Exp. Oncol. 1983, 5, 58–60. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Klemparskaya, N.N.; Shal’nova, G.A. Normal Autoantibodies as Radio-Protecting Factors, 1st ed.; Energoatomizdat Publishers: Moscow, Russia, 1978; 135p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, W.C. Fundamentals of Immunology, 4th ed.; Interscience Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1966; p. 773. [Google Scholar]
- Kovalev, I.E.; Polevaya, O.Y. Biochemical Grounds of Immunity against Low Molecular Chemical Compounds, 1st ed.; Nauka Publisher: Moscow, Russia, 1985; p. 304. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Meroni, P.L.; De Angelis, V.; Tedesco, F. Future trends. In Autoantibodies, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 823–826. [Google Scholar]
- Plotz, P.H. The autoantibody repertoire: Searching for order. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaipl, U.S.; Munoz, L.E.; Grossmayer, G.; Lauber, K.; Franz, S.; Sarter, K.; Voll, R.E.; Winkler, T.; Kuhn, A.; Kalden, J.; et al. Clearance deficiency and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). J. Autoimmun. 2007, 28, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, M.; Ghirardello, A.; Luisetto, R.; Bassi, N.; Fedrigo, M.; Valente, M.; Valentino, S.; Del Prete, D.; Punzi, L.; Doria, A. Immunization with pentraxin 3 (PTX3) leads to anti-PTX3 antibody production and delayed lupus-like nephritis in NZB/NZW F1 mice. J. Autoimmun. 2016, 74, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoch, S.; Schur, P.H.; Schwaber, J. Frequency of anti-DNA antibody producing cells from normal and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1983, 27, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaio, M.P.; Yanase, K. Cellular penetration and nuclear localization of anti-DNA antibodies: Mechanisms, consequences, implications and applications. J. Autoimmun. 1998, 11, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurasov, S.; Wardemann, H.; Hammersen, J.; Tsuiji, M.; Meffre, E.; Pascual, V.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Defective B cell tolerance checkpoints in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Samuels, J.; Ng, Y.S.; Coupillaud, C.; Paget, D.; Meffre, E. Impaired early B cell tolerance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1659–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matzinger, P. The danger model: A renewed sense of self. Science 2002, 296, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shoenfeld, Y.; Isenberg, D.A. The mosaic of autoimmunity. Immunol. Today 1989, 10, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielen, M.M.; van Schaardenburg, D.; Reesink, H.W.; van de Stadt, R.J.; van der Horst-Bruinsma, I.E.; de Koning, M.H.; Habibuw, M.R.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Dijkmans, B.A.C. Specific autoantibodies precede the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis: A study of serial measurements in blood donors. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, A.; Pezeshgi, A.; Karimimoghaddam, A.; Moghimi, Ì.; Kamali, Ê.; Naseri, Ì.; Esmaeilzadeh, A. Evaluation of anti-mutated citrullinated vimentin antibodies, anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in comparison with other rheumatic diseases; a nephrology point of view. J. Nephropharmacol. 2017, 6, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraş, Y.; Meryem, A.B.; Yildiz, F.F.; Atalay, S.G.; Yamçici, S.E.; Bozkurt, S.; Bozkurt, S.; Sezer, N. Laboratory findings in a large population of inflammatory arthritis patients: A retrospective cohort analysis. Biomed. Res. (Aligarh) 2017, 28, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, S.A.V.; Lobo, A.Z.C.; de Oliveira, Z.N.P.; Fukumori, L.M.I.; Périgo, A.M.; Rivitti, E.A. Prevalence of antinuclear autoantibodies in the serum of normal blood donors. Rev. Hosp. Clin. Fac. Med. Sao Paulo 2003, 58, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aho, K.; Koskela, P.; Mäkitalo, R.; Heliövaara, M.; Palosuo, T. Antinuclear antibodies heralding the onset of systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 1992, 19, 1377–1379. [Google Scholar]
- Cabral, D.A.; Petty, R.E.; Fung, M.; Malleson, P.N. Persistent antinuclear antibodies in children without identifiable inflammatory rheumatic or autoimmune disease. Pediatrics 1992, 89, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aygün, E.; Kelesoglu, F.M.; Dogdu, G.; Ersoy, A.; Basbug, D.; Akça, D.; Çam, Ö.N.; Kapici, A.H.; Aydin, N.G.; Karapinar, E.; et al. Antinuclear antibody testing in a Turkish pediatrics clinic: Is it always necessary? Pan Afr. Med. J. 2019, 32, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumuk, Z.; Demir, M. Clinical value of anti-DFS70 antibodies in a cohort of patients undergoing routine antinuclear antibodies testing. J. Immunol. Methods 2020, 480, 112754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gedalia, À.; Garcia, C.O.; Molina, J.F.; Bradford, N.J.; Espinoza, L.R. Fibromyalgia syndrome: Experience in a pediatric rheumatology clinic. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2000, 18, 415–419. [Google Scholar]
- Maddur, M.S.; Lacroix-Desmazes, S.; Dimitrov, J.D.; Kazatchkine, M.D.; Bayry, J.; Kaveri, S.V. Natural Antibodies: From First-Line Defense Against Pathogens to Perpetual Immune Homeostasis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 58, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, P. Croonian Lecture: On immunity with special reference to cell life. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1899, 66, 424–448. [Google Scholar]
- Zaichik, A. Immunological Regulation of the Cellular Functions, 1st ed.; LPMI Publishers: Leningrad, Russia, 1988; p. 128. [Google Scholar]
- Vertosick, F.T.J.; Kelly, R.H. Autoantigens in an immunological network. Med. Hypotheses 1983, 10, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pеtranуi, G. Immunoplasia, immunotrophia, az immunologia masik oldala. Őrv. Hetilap. 1983, 124, 2163–2167. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, M.M.; Goodman, J. Immunoregulation of cellular lifespan: Physiologic autoantibodies and their peptide antigens. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2003, 49, 217–243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nevzorova, T.A.; Vinterm, V.G. Origin and biological role of autoantibodies towards DNA. Uchenye Zap. Kazan. Gos. Univ. 2006, 148, 35–64. Available online: https://kpfu.ru/docs/F549205214/nevzorova_06.pdf (accessed on 25 December 2020). (In Russian).
- Gabibov, A.G.; Ponomarenko, N.A.; Tretyak, E.B.; Paltsev, M.A.; Suchkov, S.V. Catalytic autoantibodies in clinical autoimmunity and modern medicine. Autoimmun. Rev. 2006, 5, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forger, F.; Matthias, T.; Oppermann, M.; Becker, H.; Helmke, K. Clinical significance of anti-dsDNA antibody isotypes: IgG/IgM ratio of anti-dsDNA antibodies as a prognostic marker for lupus nephritis. Lupus 2004, 13, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Hua, X.; Concha, H.; Svenungsson, E.; Cederholm, A.; Frostegård, J. Natural antibodies against phosphorylcholine as potential protective factors in SLE. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grönwall, C.; Akhter, E.; Oh, C.; Burlingame, R.W.; Petri, M.; Silverman, G.J. IgM autoantibodies to distinct apoptosis-associated antigens correlate with protection from cardiovascular events and renal disease in patients with SLE. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 142, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Melero, J.; Tarragó, D.; Núňez-Roldán, A.; Sánchez, B. Human polyreactive IgM monoclonal antibodies with blocking activity against self-reactive IgG. Scand. J. Immunol. 1997, 45, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suurmond, J.; Diamond, B. Autoantibodies in systemic autoimmune diseases: Specificity and pathogenicity. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 2194–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammed, M.E.; Abdelhafiz, K. Autoantibodies in the sera of breast cancer patients: Antinuclear and anti-double stranded DNA antibodies as example. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 11, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, K.; Rasool, A.H.; Hattem, A.; Al-Karboly, T.A.M.; Taher, T.E.; Bystrom, J. Autoantibody profiles in autoimmune hepatitis and chronic hepatitis C identifies similarities in patients with severe disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlagea, A.; Falagan, S.; Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez, G.; Moreno-Rubio, J.; Merino, M.; Zambrana, F.; Casado, E.; Sereno, M. Antinuclear antibodies and cancer: A literature review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2018, 127, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhu, H.-Y.; Miao, Y.; Wu, W.; Liang, J.-H.; Cao, L.; Xia, Y.; Wu, J.-Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. Presence of serum antinuclear antibodies correlating unfavorable overall survival in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Chin. Med. J. 2019, 132, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meridora, K.; Levya, Y. Systemic sclerosis induced by CNS stimulants for ADHD: A case series and review of the literature. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maki, H.; Kubota, K.; Hatano, M.; Minatsuki, S.; Amiya, E.; Yoshizaki, A.; Asano, Y.; Morita, H.; Sato, S.; Komuro, I. Characteristics of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis and Anticentriole Autoantibodies. Int. Heart J. 2020, 61, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holborow, E.J.; Weir, D.M.; Johnson, G.D. A serum factor in lupus erythematosus with affinity for tissue nuclei. Br. Med. J. 1957, 28, 732–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, Y.; Bhatia, A.; Minz, R.W. Antinuclear antibodies and their detection methods in diagnosis of connective tissue diseases: A journey revisited. Diagn. Pathol. 2009, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dema, B.; Charles, N. Autoantibodies in SLE: Specificities, Isotypes and Receptors. Antibodies 2016, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, M.; Fritzler, M.J. Autoantibodies in SLE: Prediction and the p value matrix. Lupus 2019, 28, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebode, M.; Weiler-Normann, C.; Liwinski, T.; Schramm, C. Autoantibodies in Autoimmune Liver Disease-Clinical and Diagnostic Relevance. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morawiec-Szymonik, E.; Foltyn, W.; Marek, B.; Głogowska-Szeląg, J.; Kos-Kudła, B.; Kajdaniuk, D. Antibodies involved in the development of pernicious anemia and other autoimmune diseases. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2020, 130, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.-Y.; Yang, Y.-H.; Chuang, Y.-H.; Chan, P.-J.; Yu, H.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Wang, L.-C.; Chiang, B.-L. The initial manifestations and final diagnosis of patients with high and low titers of antinuclear antibodies after 6 months of follow-up. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2011, 44, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Attilakos, A.; Fotis, L.; Dinopoulos, A.; Alexopoulos, H.; Theofilopoulou, A.V.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Mastroyianni, S.; Karalexi, M.A.; Garoufi, A. Antiphospholipid and Antinuclear Antibodies in Children with Idiopathic Epilepsy: A 2-Year Prospective Study. J. Clin. Neurol. 2020, 16, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.A.; Han, Q.; Hou, X.H.; Peng, X.Z.; Tong, L.; Zheng, X.; Yu, J.-T.; Tan, L. Association of antinuclear antibodies with the risk of intracranial arterial stenosis. Aging 2020, 12, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghrairi, N.; Aouadi, S.; Elhechmi, Y.Z.; Ben Saad, S.; Ben Ali, I.; Yalaoui, S. Antinuclear antibodies in interstitial lung disease: Prevalence and clinical significance. Tunis Med. 2019, 97, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sirota, P.; Firer, M.A.; Schild, K.; Tanay, A.; Elizur, A.; Meytes, D.; Slor, H. Autoantibodies to DNA in Multicase Families with Schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 1993, 33, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilenko, O.V.; Churilov, L.P. Chronic Fatigue of Various Aetiology Shows Different Autoimmunity Spectra. Autoantibodies 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Holborow, E.J. Serum anti-nuclear factor and auto-immunity. Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1960, 53, 625–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallenberg, C.G.; van der Meulen, J.; Pastoor, G.W.; Snijder, J.A.; Feltkamp, T.E.; The, T.H. Human fibroblasts, a convenient nuclear substrate for detection of anti-nuclear antibodies including anti-centromere antibodies. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 1983, 12, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toolan, H.W. Transplantable human neoplasms maintained in cortisone-treated laboratory animals: H.S. No. 1; H.Ep. No. 1; H.Ep. No. 2; H.Ep. No. 3; and H.Emb.Rh. No. 1. Cancer Res. 1954, 14, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moore, A.E.; Sabachewsky, L.; Toolan, H.W. Culture characteristics of four permanent lines of human cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1955, 15, 598–602. [Google Scholar]
- Buchner, C.; Bryant, C.; Eslami, A.; Lakos, G. Anti-nuclear antibody screening using HEp-2 cells. Vis. Exp. 2014, 23, e51211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez, D.; Gilburd, B.; Azoulay, D.; Shovman, O.; Bizzaro, N.; Shoenfeld, Y. Antinuclear antibodies: Is the indirect immunofluorescence still the gold standard or should be replaced by solid phase assays? Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pashnina, I.A.; Krivolapova, I.M.; Tuzankina, I.A.; Chereshnev, V.A. Application of different laboratory methods for antinuclear autoantibodies investigation in patients with autoimmune connective tissue diseases. Acta Biomed. Sci. 2012, 3, 143–147. [Google Scholar]
- Naides, S.J.; Genzen, J.R.; Abel, G.; Bashleben, C.; Ansari, M.Q. Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA) Testing Method Variability: A Survey of Participants in the College of American Pathologists’ (CAP) Proficiency Testing Program. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 47, 1768–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisetsky, D.S.; Bossuyt, X.; Meroni, P.L. ANA as an entry criterion for the classification of SLE. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 102400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebo, A.E. Recent Approaches to Optimize Laboratory Assessment of Antinuclear Antibodies. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2017, 24, e00270-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agmon-Levin, N.; Damoiseaux, J.; Kallenberg, C.; Sack, U.; Witte, T.; Herold, M.; Bossuyt, X.; Musset, L.; Cervera, R.; Plaza-Lopez, A.; et al. International recommendations for the assessment of autoantibodies to cellular antigens referred to as anti-nuclear antibodies. Ann. Rheum Dis. 2014, 73, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herold, M.; Klotz, W.; Andrade, L.E.C.; Conrad, K.; de Melo Cruvinel, W.; Damoiseaux, J.; Fritzler, M.J.; von Muhlen, C.A.; Satoh, M.; Chan, E.K.L.; et al. International consensus on antinuclear antibody patterns: Defining negative results and reporting unidentified patterns. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018, 56, 1799–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, L.E.C.; Klotz, W.; Herold, M.; Conrad, K.; Rönnelid, J.; Fritzler, M.J.; Von Mühlen, C.A.; Satoh, M.; Damoiseaux, J.; Cruvinel, W.D.M.; et al. International consensus on antinuclear antibody patterns: Definition of the ac-29 pattern associated with antibodies to DNA topoisomerase I. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018, 56, 1783–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakespeare, W. Romeo and Juliet. In The Arden Shakespeare, 2nd ed.; Gibbons, B., Ed.; Methuen: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.C.; Dewez, P.; Stuart, L.; Gatenby, P.A.; Sturgess, A. Antinuclear antibodies using HEp-2 cells in normal children and in children with common infections. J. Paediatr. Child Health 1991, 27, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilário, M.O.; Len, C.A.; Roja, S.C.; Terreri, M.T.; Almeida, G.; Andrade, L.E. Frequency of antinuclear antibodies in healthy children and adolescents. Clin. Pediatr. 2004, 43, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapira, Y.; Poratkatz, B.S.; Gilburd, B.; Barzilai, O.; Ram, M.; Blank, M.; Lindeberg, S.; Frostegård, J.; Anaya, J.-M.; Bizzaro, N.; et al. Geographical differences in autoantibodies and anti-infectious agents antibodies among healthy adults. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 42, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeles, A.M.; Abeles, M. The clinical utility of a positive antinuclear antibody test result. Am. J. Med. 2013, 126, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somers, E.C.; Monrad, S.U.; Warren, J.S.; Solano, M.; Schnaas, L.; Hernandez-Avila, M.; Tellez-Rojo, M.M.; Hu, H. Antinuclear antibody prevalence in a general pediatric cohort from Mexico City: Discordance between immunofluorescence and multiplex assays. Clin. Epidemiol. 2017, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abuaf, N. Etude descriptive et comparative des méthodes et techniques utilisées pour la détection des anticorps antinucléaires. Ann. Biol. Clin. 1982, 40, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs, R.N.; Lea, D.J.; Ward, D.J. A fluorimetric assay for human antibodies to all the histones. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermekova, V.M.; Melkonian, O.S.; Nazarova, L.F.; Umanskiy, S.R. Reveal in the sera of intact rabbits the immunoglobulins interacting with chromatin. Biokhimia 1981, 46, 890–896. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zouali, M.; Eyquem, A. Idiotypic anti-idiotypic interactions in SLE. Ann. Immunol. 1983, 1346, 377–397. [Google Scholar]
- Lekakh, I.V.; Poverennyi, A.M. Free and latent antibodies to DNA in immunoglobulin preparations from healthy humans. Mol. Biol. 1996, 30, 422–424. [Google Scholar]
- Lapin, S.V.; Тotolian, A.A. Immunological Laboratory Diagnosis of Autoimmune Diseases; Chelovek Publishers: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2010; p. 272. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ravelli, À.; Felici, Å.; Magni-Manzoni, S.; Pistorio, A.; Novarini, C.; Bozzola, E.; Viola, S.; Martini, A. Patients with antinuclear antibody—Positive juvenile idiopathic arthritis constitute a homogeneous subgroup irrespective of the course of joint disease. Àrthritis Rheum. 2005, 3, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tozzoli, R.; Bizzaro, N.; Tonutti, E.; Villalta, D.; Bassetti, D.; Manoni, F.; Piazza, A.; Pradella, M.; Rizzotti, P. Guidelines for the laboratory use of autoantibody tests in the diagnosis and monitoring of autoimmune rheumatic diseases. J. Clin. Pathol. 2002, 117, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pollock, W.; Toh, B.-H. Routine immunofluorescence detection of Ro/SS-A autoantibody using HEp-2 cells transfected with human 60 kDa Ro/SS-A. J. Clin. Pathol. 1999, 52, 684–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frodlund, M.; Wetterö, J.; Dahle, C.H.; Dahlström, Ö; Skogh, T.; Rönnelid, J.; Sjöwall, C. Longitudinal anti-nuclear antibody (ANA) seroconversion in systemic lupus erythematosus: A prospective study of Swedish cases with recent-onset disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2020, 199, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saikia, B.; Rawat, A.; Vignesh, P. Autoantibodies and their Judicious Use in Pediatric Rheumatology Practice. Indian J. Pediatr. 2016, 83, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariz, H.A.; Sato, E.I.; Barbosa, S.H.; Rodrigues, S.H.; Dellavance, A.; Andrade, L. Pattern on the antinuclear antibody-HEp-2 test is a critical parameter for discriminating antinuclear antibody-positive healthy individuals and patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.M.; Feltkamp, T.E.; Smolen, J.S.; Butcher, B.; Dawkins, R.; Fritzler, M.J.; Gordon, T.; Hardin, J.A.; Kalden, J.R.; Lahita, R.G.; et al. Range of antinuclear antibodies in “healthy” individuals. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciapaglia, F.; Arcarese, L.; Rigon, A.; Vadacca, M.; Valorani, M.G.; Pozzilli, P.; Afeltra, A. Antinuclear antibodies prevalence in Filipinos migrated to Italy. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 12, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Racoubian, E.; Zubaid, R.M.; Shareef, M.A.; Almawi, W.Y. Prevalence of antinuclear antibodies in healthy Lebanese subjects, 2008-2015: A cross-sectional study involving 10,814 subjects. Rheumatol. Int. 2016, 36, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malleson, P.N.; Mackinnon, M.; Sailer-Hoeck, M.; Spencer, C. Review for the generalist: The antinuclear antibody test in children—When to use it and what to do with a positive titer. Pediatric Rheumatol. 2010, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malleson, P.N.; Sailer, M.; Mackinnon, M.J. Usefulness of antinuclear antibody testing to screen for rheumatic diseases. Arch. Dis. Child. 1997, 77, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGhee, J.L.; Kickingbird, L.M.; Jarvis, J.N. Clinical utility of antinuclear antibody tests in children. BMC Pediatr. 2004, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pashnina, I.A.; Krivolapova, I.M.; Kozlova, E.S.; Skorobogatova, O.V.; Tuzankina, I.A.; Chereshnev, V.A. Autoantibodies in children with juvenile arthritis. Russ. J. Immunol. 2013, 7, 437–444. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pashnina, I.A.; Krivolapova, I.M.; Skorobogatova, O.V. The frequency of detection of antinuclear antibodies in children with various forms of systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Ural Med. Acad. Sci. 2010, 2, 186–187. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pollard, K.M. Gender differences in autoimmunity associated with exposure to environmental factors. J. Autoimmun. 2012, 38, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spiewak, R.; Stojek, N. Antinuclear antibodies among eastern-Polish rural inhabitants. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2003, 10, 207–209. [Google Scholar]
- Parks, C.G.; Santos, A.S.E.; Lerro, C.C.; DellaValle, C.T.; Ward, M.H.; Alavanja, M.C.; Berndt, S.I.; Freeman, L.E.B.; Sandler, D.P.; Hofmann, J.N. Lifetime Pesticide Use and Antinuclear Antibodies in Male Farmers From the Agricultural Health Study. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carr, R.I.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Harbeck, R.J. Comparison of DNA binding in normal population, general hospital laboratory personnel and personnel from laboratories studying SLE. J. Rheumatol. 1975, 2, 180–183. [Google Scholar]
- Zarminski, M.A.; Messner, R.P.; Mandel, J.S. Anti-dsDNA antibodies in laboratory workers handling blood from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 1992, 19, 1380–1384. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.-Z.; Karp, D.R.; Quan, J.; Branch, V.K.; Zhou, J.; Lian, Y.; Chong, B.; Wakeland, E.K.; Olsen, N. Risk factors for ANA positivity in healthy persons. Arthritis Res. 2011, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Vlam, K.; De Keyser, F.; Verbruggen, G.; Vandenbossche, M.; Vanneuville, B.; D’Haese, D.; Veys, E.M. Detection and identification of antinuclear autoantibodies in the serum of normal blood donors. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 1993, 11, 393–397. [Google Scholar]
- Wichainun, R.; Kasitanon, N.; Wangkaew, S.; Hongsongkiat, S.; Sukitawut, W.; Louthrenoo, W. Sensitivity and specificity of ANA and anti-dsDNA in the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus: A comparison using control sera obtained from healthy individuals and patients with multiple medical problems. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 31, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.P.; Wang, C.G.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.-Q.; Guo, D.-L.; Jing, X.-Z.; Yuan, C.-G.; Yang, S.; Liu, J.-M.; Han, M.-S.; et al. The prevalence of antinuclear antibodies in the general population of Ñhina: A cross-sectional study. Curr. Ther. Res. Clin. Exp. 2014, 76, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tada, J.; Toi, Y.; Yoshioka, T.; Fujiwara, H.; Arata, J. Antinuclear antibodies in patients with atopic dermatitis and severe facial lesions. Dermatology 1994, 189, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinse, G.E.; Parks, C.G.; Weinberg, C.R.; Co, C.A.; Wilkerson, J.; Zeldin, D.C.; Chan, E.K.L.; Miller, F.W. Increasing Prevalence of Antinuclear Antibodies in the United States. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyave, C.M.; Giambrone, M.J.; Rich, K.C.; Walaszek, M. The frequency of antinuclear antibody (ANA) in children by use of mouse kidney (MK) and human epithelial cells (HEp-2) as substrates. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1988, 82, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivolapova, I.M.; Pashnina, I.A.; Chereshnev, V.A. Prevalence of antinuclear antibodies in healthy children and adults. Russ. J. Immunol. 2019, 13, 816–818. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, M.H.; Erdei, E. Comparative United States autoimmune disease rates for 2010–2016 by sex, geographic region, and race. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, D.; Yung, R. Immune senescence, epigenetics and autoimmunity. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 196, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wananukul, S.; Voramethkul, W.; Kaewopas, Y.; Orrawadee, H. Prevalence of positive antinuclear antibodies in healthy children. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2005, 23, 153–157. [Google Scholar]
- Peréz, D. Anti-DFS70 antibodies: A new protective autoantibodies? In Mosaic of Autoimmunity: The Novel Factors of Autoimmune Diseases, 1st ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 91–92. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, E.K.; Damoiseaux, J.; Carballo, O.G.; Conrad, K.; Cruvinel, W.D.M.; Francescantonio, P.L.C.; Fritzler, M.J.; La Torre, I.G.-D.; Herold, M.; Mimori, T.; et al. Report of the First International Consensus on Standardized Nomenclature of Antinuclear Antibody HEp-2 Cell Patterns 2014–2015. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pashnina, I.A. Analysis of the results of the determination of antinuclear antibodies by various laboratory methods. J. Ural Med. Acad. Sci. 2011, 2, 186–187. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Fotis, L.; Baszis, K.W.; White, A.J.; French, A.R. Four Cases of Anti-PM/Scl Antibody-positive Juvenile Overlap Syndrome with Features of Myositis and Systemic Sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 43, 1768–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Didier, K.; Bolko, L.; Giusti, D.; Toquet, S.; Robbins, A.; Antonicelli, F.; Servettaz, A. Autoantibodies Associated With Connective Tissue Diseases: What Meaning for Clinicians? Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.Y.; Lee, W.I.; Kim, M.H.; La Jeon, Y. Clinical use of anti-DFS70 autoantibodies. Rheumatol. Int. 2019, 39, 1423–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkoğlu, G.; Berkem, R.; Karakoç, A.E. Anti-dense fine speckled 70/lens epithelium derived growth factor p75 otoantikorunun otoimmün hastalıklarda klinik tanıya katkısının araştırılması [Investigation of the diagnostic value of anti-dense fine speckled 70/lens epithelium derived growth factor p75 autoantibody for autoimmune diseases]. Mikrobiyol. Bul. 2018, 52, 413–424. [Google Scholar]
- Slight-Webb, S.; Lu, R.; Ritterhouse, L.L.; Munroe, M.E.; Maecker, H.T.; Fathman, C.G.; Utz, P.J.; Merrill, J.T.; Guthridge, J.M.; James, J.A. Autoantibody-Positive Healthy Individuals Display Unique Immune Profiles That May Regulate Autoimmunity. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slight-Webb, S.; Smith, M.; Bylinska, A.; Macwana, S.; Guthridge, C.; Lu, R.; Merrill, J.T.; Chakravarty, E.; Arriens, C.; Munroe, M.E.; et al. Autoantibody-positive healthy individuals with lower lupus risk display a unique immune endotype. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 1419–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochs, R.L.; Mahler, M.; Basu, A.; Rios-Colon, L.; Sanchez, T.W.; Andrade, L.E.; Fritzler, M.J.; Casiano, C.A. The significance of autoantibodies to DFS70/LEDGFp75 in health and disease: Integrating basic science with clinical understanding. Clin. Exp. Med. 2016, 16, 273–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moroni, L.; Restovic, G.; Cervera, R.; Aldea-Parés, A.; Viñas, O.; García, M.; Sampietro-Colom, L. Economic Analysis of the Use of Anti-DFS70 Antibody Test in Patients with Undifferentiated Systemic Autoimmune Disease Symptoms. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 47, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, T.; Esposito, C.; Pafundi, V.; Carriero, A.; Padula, M.C.; Padula, A.A.; D’Angelo, S. Understanding the Biological Significance of Anti-DFS70 Antibodies: Effect of Biologic Therapies on Their Occurrence in Inflammatory Arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 47, 1295–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo, L.; Shovman, O.; Pérez, D.; Infantino, M.; Cabrera-Marante, O.; Lozano, F.; Gilburd, B.; Manfredi, M.; Serrano, M.; Morillas, L.; et al. Algorithm for antinuclear antibodies in subjects with clinical suspicion of autoimmune diseases. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bossuyt, X.; Claessens, J.; Belmondo, T.; De Langhe, E.; Westhovens, R.; Poesen, K.; Hüe, S.; Blockmans, D.; Fritzler, M.J.; Mahler, M.; et al. Harmonization of clinical interpretation of antinuclear antibody test results by solid phase assay and by indirect immunofluorescence through likelihood ratios. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 102386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robier, C.; Amouzadeh-Ghadikolai, O.; Stettin, M.; Reicht, G. Comparison of the Clinical Utility in the Detection of Anti-Nuclear Antibodies between the Elia CTD Screen and Indirect Immunofluorescence on HEp-2 Cells: A Review of the Literature. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2018, 20, 700–702. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Infantino, M.; Carbone, T.; Manfredi, M.; Grossi, V.; Antico, A.; Panozzo, M.P.; Brusca, I.; Alessio, M.G.; Previtali, G.; Platzgummer, S.; et al. A new diagnostic algorithm for pattern-oriented autoantibody testing according to the ICAP nomenclature: A pilot study. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author(s), Year, (Reference) | Country(ies) | Age, Years | n | Share of ANA Positive Depending on Titers, % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/40 | 1/80 | 1/100 | 1/160 | ≥1/320 | Total | ||||
| Tan E.M. et al., 1997 [165] | International (USA, Europe, Australia, Canada, Japan) | 21–60 | 125 | 31.7 | 1.3 | N/A | 5.0 | 3.3 | 41.3 |
| Fernandez S. et al., 2003 [97] | Brazil | 18–60 | 500 | 14.6 | 4.6 | N/A | 2.0 | 1,4 | 22.6 |
| Cacciapaglia F. et al., 2008 [166] | Italy (Filipinos) | 25–65 | 80 | N/A | N/A | 23.7 | N/A | N/A | 23.7 |
| Italy (Italians) | 25–69 | 60 | N/A | N/A | 8.3 | N/A | N/A | 8.3 | |
| Marin G.G. et al., 2009 [20] | Mexico | 12–72 | 304 | 35.4 | 13.4 | N/A | 3.2 | 1.6 | 53.6 |
| Mariz H. et al., 2011 [164] | Brazil | 18–66 | 918 | N/A | 5.9 | N/A | 1.0 | 5.9 | 12.9 |
| Satoh M. et al., 2012 [21] | USA | 20–29 | 686 | N/A | 13.1 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 13.1 |
| 30–39 | 642 | N/A | 13.4 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 13.4 | ||
| 40–49 | 581 | N/A | 11.5 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 11.5 | ||
| 50–59 | 478 | N/A | 17.4 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 17.4 | ||
| 60–69 | 525 | N/A | 13.8 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 13.8 | ||
| >70 | 625 | N/A | 19.2 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 19.2 | ||
| Racoubian E. et al., 2016 [167] | Lebanon | <20–>70 | 10,814 | N/A | N/A | 20.0 | 3.7 | 2.8 | 26.5 |
| Morawiec-Szymonik E. et al., 2020 [127] | Poland | 18–>60 | 41 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 4.9 |
| Author(s), Year (Reference) | Country(ies) | Age, mo/Years | n | Share of ANA Positive Depending on Titers, % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/40 | 1/80 | 1/160 | ≥1/320 | ≥1/640 | Total | ||||
| Arroyave C. et al., 1988 [184] | USA | 4 months—16 years | 241 | 0.4 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 0.4 |
| Allen R.C. et al., 1991 [148] | Australia | 1–16 years | 100 | 9.0 | N/A | 7.0 | N/A | 2.0 | 18.0 |
| Hilário M.O. et al., 2004 [149] | Brazil | 6 months–5 years | 63 | N/A | 3.2 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 8.0 |
| 5–10 years | 77 | N/A | 9.1 | 5.2 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 19.5 | ||
| 10–15 years | 49 | N/A | 2.0 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 10.0 | ||
| 15–20 years | 25 | N/A | 0.0 | 0.0 | 8.0 | 0.0 | 8.0 | ||
| Wananukul S.et al., 2005 [188] | Thailand | 7–15 years | 207 | 9.6 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 15.4 |
| Satoh M. et al., 2012 [21] | USA | 12–19 years | 1190 | N/A | 11.2 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 11.2 |
| Somers E.C. et al., 2017 [152] | Mexico | 9–17 years | 114 | N/A | 5.3 | 3.5 | 7.0 | N/A | 15.8 |
| Attilakos A. et al., 2020 [129] | Greece | 4–14 years | 40 | N/A | N/A | 5.0 | N/A | N/A | 5.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pashnina, I.A.; Krivolapova, I.M.; Fedotkina, T.V.; Ryabkova, V.A.; Chereshneva, M.V.; Churilov, L.P.; Chereshnev, V.A. Antinuclear Autoantibodies in Health: Autoimmunity Is Not a Synonym of Autoimmune Disease. Antibodies 2021, 10, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib10010009
Pashnina IA, Krivolapova IM, Fedotkina TV, Ryabkova VA, Chereshneva MV, Churilov LP, Chereshnev VA. Antinuclear Autoantibodies in Health: Autoimmunity Is Not a Synonym of Autoimmune Disease. Antibodies. 2021; 10(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib10010009
Chicago/Turabian StylePashnina, Irina A., Irina M. Krivolapova, Tamara V. Fedotkina, Varvara A. Ryabkova, Margarita V. Chereshneva, Leonid P. Churilov, and Valeriy A. Chereshnev. 2021. "Antinuclear Autoantibodies in Health: Autoimmunity Is Not a Synonym of Autoimmune Disease" Antibodies 10, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib10010009
APA StylePashnina, I. A., Krivolapova, I. M., Fedotkina, T. V., Ryabkova, V. A., Chereshneva, M. V., Churilov, L. P., & Chereshnev, V. A. (2021). Antinuclear Autoantibodies in Health: Autoimmunity Is Not a Synonym of Autoimmune Disease. Antibodies, 10(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib10010009







