Immune- and Non-Immune-Mediated Adverse Effects of Monoclonal Antibody Therapy: A Survey of 110 Approved Antibodies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
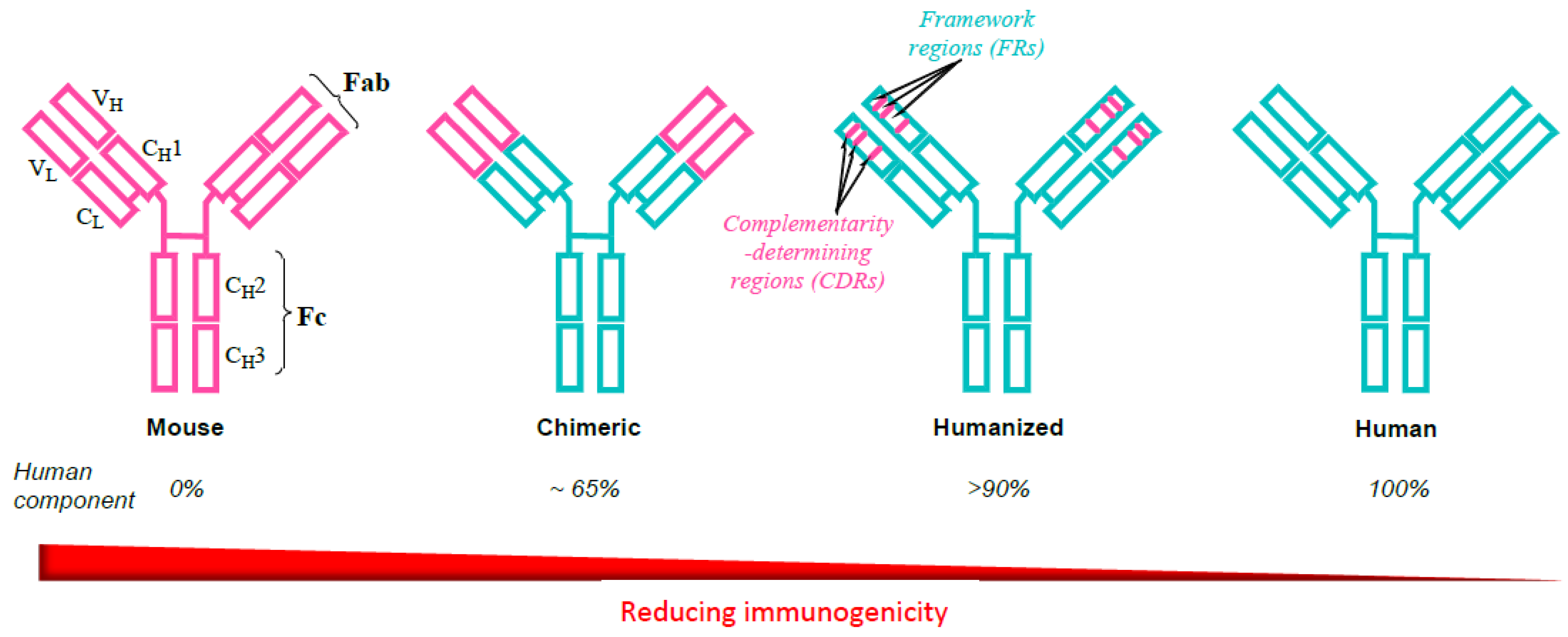
2. Evolution of Monoclonal Antibodies to Avoid Immunogenicity
3. Monoclonal Antibody Targets and Indications
4. Adverse Events to Monoclonal Antibody Therapy
4.1. Immune-Mediated Adverse Responses (Hypersensitivities) to Approved Monoclonal Antibodies
- TypeI hypersensitivity: Warnings for, and reports of, anaphylaxis account for ≈18% of mAbs, 14 used for non-cancer indications and 5 for cancer indications. Reslizumab and obiltoxaximab are covered by a black box warning for anaphylaxis. Urticaria occurs more often with the non-cancer mAbs.
- Serious infusion reactions with signs and symptoms resembling, and sometimes confused with anaphylaxis, occur with some mAbs, for example, alemtuzumab, cetuximab, dinutuximab, ibritumomab tiuxetan, naxitamab-gqgk, panitumumab, rituximab, trastazumab, and vedolizumab. Cytokine release appears to be involved.
- There is as yet no good evidence that many cytopenias are type II hypersensitivities, but these may occur with, for example, abciximab, alemtuzumab for multiple sclerosis and rituximab. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia may be induced by alemtuzumab and rituximab and rituximab-induced early- and late-onset neutropenia may be immune-mediated.
- Type III hypersensitivities, serum sickness-like reactions, cutaneous vasculitis, and hypersensitivity pneumonitis (may be a combined type III and IV hypersensitivity) occur with, for example, infliximab, adalimumab, and alirocumab. Checkpoint inhibitors including ipilimumab, nivolumab, and avelumab (Table 5) may also induce hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chimeric mAbs (e.g., rituximab) and the humanized mAb omalizumab may cause a serum sickness-like reaction.
- Precise mechanisms for immune-mediated colitis, hepatitis, nephritis, hypothyroidism, and endocrinopathies induced by mAbs targeted to PD-1 and PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitors are not yet established.
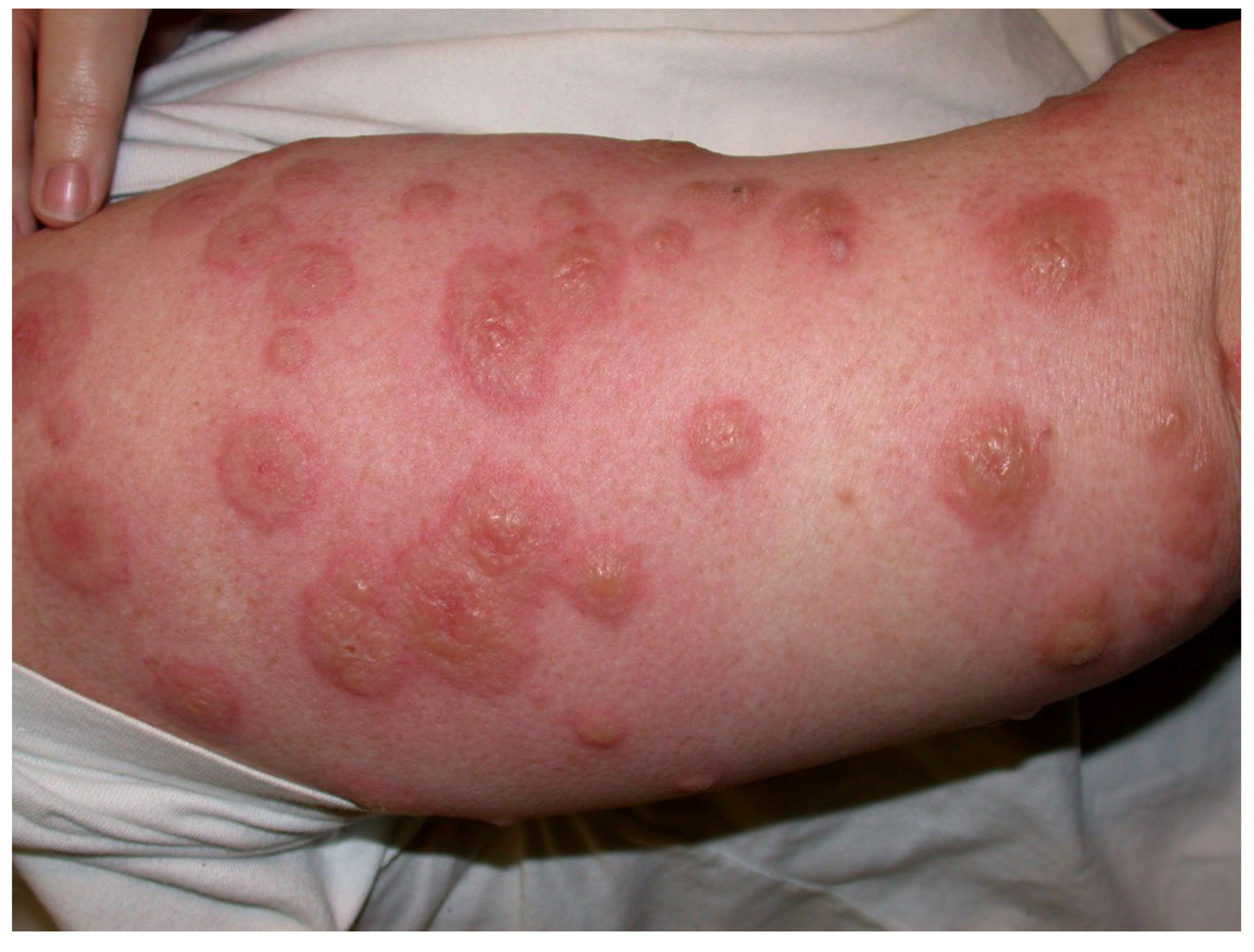
- Type IV hypersensitivities: Rare Stevens–Johnson syndrome reactions have been reported to adalimumab, brentuximab vedotin, infliximab, and rituximab; toxic epidermal necrolysis has been induced by ibritumomab tiuxetan and rituximab. Adalimumab, ibritumomab tiuxetan, infliximab, and naxitamab-gqgk have been implicated in cases of erythema multiforme (EM). Paraneoplastic pemphigus, lichenoid dermatitis, and vesiculobullous dermatitis have occurred after rituximab. Dermatitis may occur after some mAbs, e.g., bevacizumab, catumaxomab, denosumab, and panitumumab. Immune-mediated cutaneous reactions induced by, e.g., cemiplimab-rwlc and durvalumab may be type IV hypersensitivities but mechanisms are not yet unequivocally established. Skin manifestations of rash and pruritus, often seen after many mAbs (Table 4 and Table 5), are generally not true hypersensitivity reactions.
4.2. Non-Immune-Mediated Adverse Responses to Approved Monoclonal Antibodies
- Infusion reactions. Usually mild–moderate or controllable by premedication. Fatal reactions can occur. Reactions have been recorded for almost 50% of approved mAbs. FDA boxed warnings for infusion reactions apply to 8 mAbs used for cancer therapy and 1 mAb used for other therapies.
- Cytopenia: Mechanisms of mAb-induced thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, lymphopenia, and hemolytic anemia are often not investigated/established. Cytopenia seen in more than 30% of the mAbs, especially those used in cancer therapy. Some may be immune-mediated.
- mAb-induced lung disease: Pathogenesis and pathophysiology are generally not known. At least 21 mAbs implicated. Some reactions are known, or suspected, to be immune-mediated.
- Cardiac events: Mechanisms mostly obscure. At least 20 mAbs implicated.
- Liver events: At least 22 mAbs implicated. Immune-mediated hepatitis is seen but other mechanisms often not well understood.
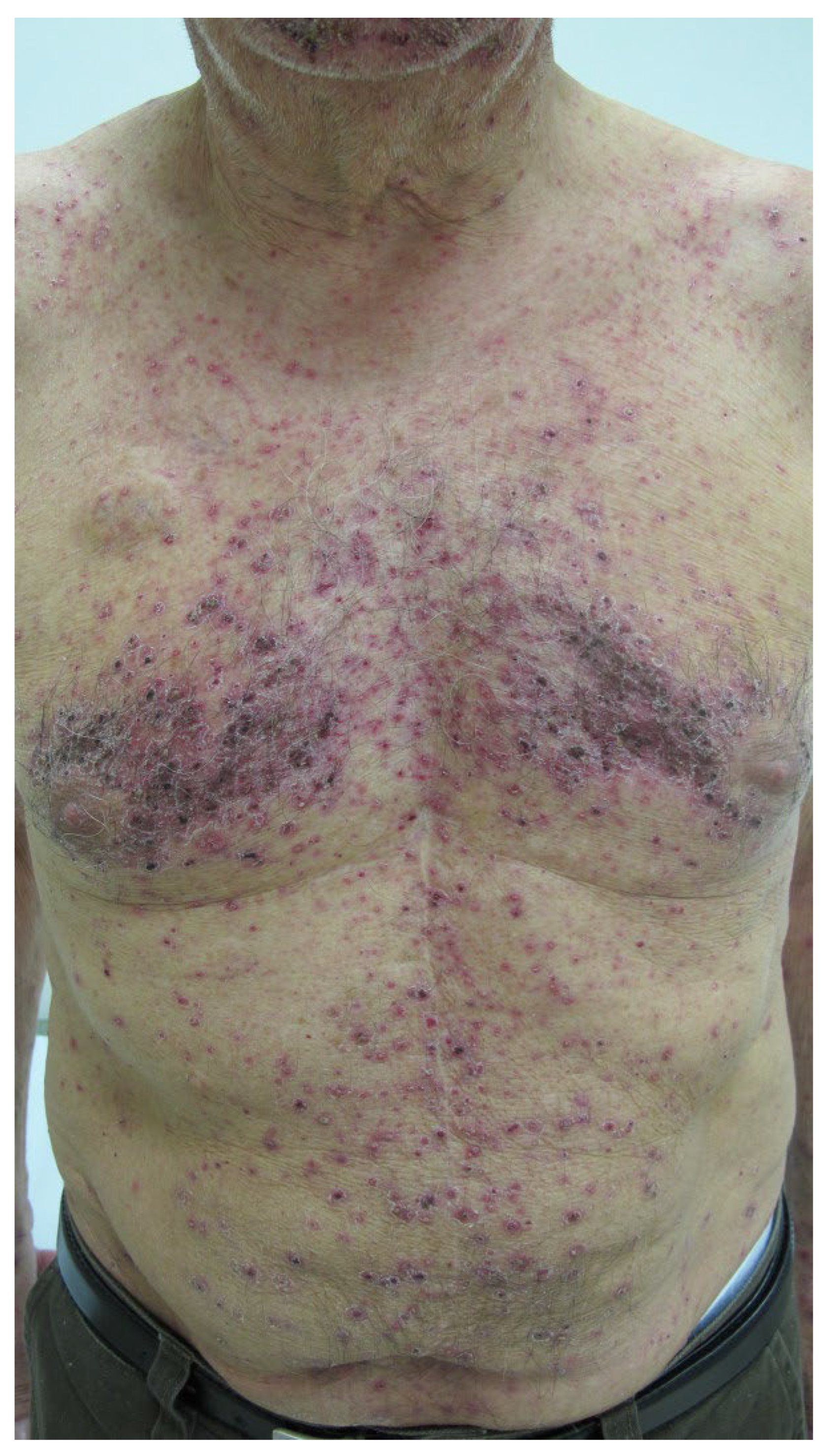
- Dermatologic toxicities: 39 (≈36%) of the mAbs elicited adverse cutaneous reactions of different severity from mild to severe. Rash and/or pruritus are common and were not included in the assessments. Apart from severe toxidermias (see text), papulopustular (acneiform) skin eruptions occur in response to EGFR-targeted antibodies, in particular, cetuximab, necitumumab, and panitumumab. Adverse reactions were seen in ≈29% of the non-cancer group and 50% of the mAbs used for cancer therapy.
- Embryo-fetal toxicity is recognized for 27 (≈25%) of the mAbs, including eight antibody–drug conjugates.
- Cytokine release syndrome (CRS): The distinguishing features between CRS and infusion reactions are often not clear. mAbs implicated include blinatumomab and catumaxomab.
- Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS): Anti-cancer mAbs may destroy large numbers of cells in a short period of time. Seen with brentuximab vedotin, blinatumomab, rituximab, and polatuzumab vedotin-piiq.
- Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML): Rare but occasionally seen after mAbs directed to B cells, e.g., brentuximab vedotin, rituximab, obinutuzumab, vedolizumab, polatuzumab vedotin-piiq, and natalizumab.
- Other syndromes of poorly understood pathogenesis: Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome (RPLS) 1 (cases reported after, e.g., bevacizumb and ramucirumab); immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) (natalizumab); systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) (catumaxomab, eculizumab); capillary leak syndrome (CLS) (bevacizumab, dinutuximab); macrophage activation syndrome (MAS) (canakinumab).
- Mouse antibodies
- ߋ
- Ibrutumomab tiuxetan: hypersensitivity bronchospasm
- Human-mouse chimeric antibodies
- ߋ
- Cetuximab: interstitial pneumonitis
- ߋ
- Infliximab: interstitial lung disease
- ߋ
- Rituximab: ARDS, BOOP, bronchospasm, diffuse alveolar hemorrhage, immune-mediated (hypersensitivity) pneumonitis
- Humanised antibodies
- ߋ
- Ado-trastuzumab: interstitial lung disease, pneumonitis, ARDS, dyspnea, pulmonary infiltrates, radiation pneumonitis
- ߋ
- Alemtuzumab: pneumonitis, bronchospasm, diffuse alveolar hemorrhage, pulmonary infection
- ߋ
- Amivantamab-vmjw: interstitial lung disease, pneumonitis
- ߋ
- Atezolizumab: immune-mediated pneumonitis, dyspnea
- ߋ
- Bevacizumab: anaphylaxis/bronchospasm, pulmonary hemorrhage from tumor site
- ߋ
- Dostarlimab-gxly: immune-mediated pneumonitis
- ߋ
- Fam-trastuzumab deruxtecan-nxki: interstitial lung disease, pneumonitis
- ߋ
- Pembrolizumab: immune-mediated pneumonitis, dyspnea
- ߋ
- Trastuzumab: ARDS, BOOP, dyspnea, interstitial pneumonitis, pleural effusions, pulmonary infiltrates/fibrosis/edema
- Fully human antibodies
- ߋ
- Adalimumab: interstitial lung disease
- ߋ
- Avelumab: immune-mediated pneumonitis
- ߋ
- Cemiplimab-rwlc: immune-mediated pneumonitis
- ߋ
- Durvalumab: immune-mediated pneumonitis, dyspnea
- ߋ
- Golimumab: interstitial lung disease
- ߋ
- Ipilimumab: immune-mediated pneumonitis
- ߋ
- Nivolumab: immune-mediated pneumonitis, dyspnea
- ߋ
- Panitumumab: interstitial lung disease, lung infiltrates, pneumonitis, pulmonary fibrosis
- ߋ
- Tisotumab vedotin-tftv: pneumonitis
4.3. Rare Syndromes Associated with Monoclonal Antibody Therapy
- Cytokine release syndrome (CRS)Alemtuzumab; blinatumomab; catumaxomab; rituximab
- Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH)Alemtuzumab; avelumab; blinatumomab; ipilimumab; nivolumab
- Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS)Adalimumab; ibalizumab-uiyk; infliximab; natalizumab
- Macrophage activation syndrome (MAS)Alemtuzumab; canakinumab; tocilizumab
- Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)Belimumab; brentuximab vedotin; infliximab; eculizumab; natalizumab; ocrelizumab; ofatumumab; polatuzumab vedotin-piiq; rituximab; vedolizumab
- Reversible posterior encephalopathy syndrome (RPLS)Bevacizumab; certolizumab pegol; infliximab; dinutuximab; naxitamab-gqgk; ramucirumab; rituximab; ustekinumab
- Systemic capillary leak syndrome (SCLS)Alemtuzumab; basiliximab; bevacizumab; catumaxomab; dinutuximab; nivolumab; rituximab
- Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)Catumaxomab; eculizumab
- Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS)Alemtuzumab; blinatumomab; brentuximab vedotin; ipilimumab; obinutuzumab; polatuzumab vedotin-piiq; rituximab
5. Concluding Remarks
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ossipow, V.; Fischer, N. (Eds.) Methods and protocols. In Method in Molecular Biology, 2nd ed.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 1131. [Google Scholar]
- Weiner, G.J. Building better monoclonal antibody-based therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baldo, B.A. Safety of Biologics Therapy: Monoclonal Antibodies, Cytokines, Fusion Proteins, Hormones, Enzymes, Coagulation Proteins, Vaccines, Botulinum Toxins; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–215. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Parray, H.A.; Shrivastava, T.; Sinha, S.; Luthra, K. Phage display antibody libraries: A robust approach for generation of recombinant human monoclonal antibodies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Reusch, D. (Eds.) Monoclonal antibodies. In Physicochemical Analysis; Academic Press: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Pedrioli, A.; Oxenius, A. Single B cell technologies for monoclonal antibody discovery. Trends Immunol. 2021, 42, 1143–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondon, P.; Dubreuil, O.; Bouayadi, K.; Kharrat, H. Human antibodies: A race to engineer and explore a larger diversity. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 1117–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Food and Drug Administration. Rare Diseases: Common Issues in Drug Development Guidance for Industry. February 2019. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/rare-diseases-common-issues-drug-development-guidance-industry (accessed on 14 December 2021).
- Mulberg, A.E.; Bucci-Rechtweg, C.; Giuliano, J.; Jacoby, D.; Johnson, F.K.; Liu, Q.; Marsden, D.; McGoohan, S.; Nelson, R.; Patel, N.; et al. Regulatory strategies for rare diseases under current global regulatory statutes: A discussion with stakeholders. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldo, B.A.; Pagani, M. Adverse events to nontargeted and targeted chemotherapeutic agents. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2014, 34, 565–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almagro, J.C.; Fransson, J. Humanization of antibodies. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 1619–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parray, H.A.; Shukla, S.; Samal, S.; Shrivastava, T.; Ahmed, S.; Sharma, C.; Kumar, R. Hybridoma technology a versatile method for isolation of monoclonal antibodies, its applicability across species, limitations, advancement and future perspectives. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 85, 106639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemtrada (alemtuzumab). Highlights of Prescribing Information. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/103948s5158lbl.pdf (accessed on 14 December 2021).
- Campath (alemtuzumab). Highlights of Prescribing Information. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2007/103948s5070lbl.pdf (accessed on 14 December 2021).
- Prolia (denosumab). Highlights of Prescribing Information. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/125320s205lbl.pdf (accessed on 14 December 2021).
- Xgeva (denosumab). Highlights of Prescribing Information. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/125320s094lbl.pdf (accessed on 14 December 2021).
- Scott, A.M.; Wolchok, J.D.; Old, L.J. Antibody therapy of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2012, 12, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldo, B.A.; Pham, N.H. Drug Allergy: Clinical Aspects, Diagnosis, Mechanisms, Structure-Activity Relationships, 2nd ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Baldo, B.A. Adverse events to monoclonal antibodies used for cancer therapy. Focus on hypersensitivity responses. OncoImmunology 2013, 2, e26333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stephens, S.; Emtage, S.; Vetterlein, O.; Chaplin, L.; Bebbington, C.; Nesbitt, A.; Sopwith, M.; Athwal, D.; Novak, C.; Bodmer, M. Comprehensive pharmacokinetics of a humanized antibody and analysis of residual anti-idiotypic responses. Immunology 1995, 85, 668–674. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, J.F.; Bril, V.; Vu, T.; Karam, C.; Peric, S.; Margania, T.; Murai, H.; Bilinska, M.; Shakarishvili, R.; Smilowski, M.; et al. Safety, efficacy, and tolerability of efgartigimod in patients with generalised myasthenia gravis (ADAPT): A multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Colice, G.; Griffiths, J.M.; Almqvist, G.; Ponnarambil, S.; Kaur, P.; Ruberto, G.; Bowen, K.; Hellqvist, Å.; Mo, M.; et al. NAVIGATOR: A phase 3 multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial to evaluate Nthe efficacy and safety of tezepelumab in adults and adolescents with severe, uncontrolled asthma. Respir. Res. 2020, 13, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Corren, J.; Bourdin, A.; Chupp, G.; Israel, E.; Wechsler, M.E.; Brightling, C.E.; Griffiths, J.M.; Hellqvist, Å.; Bowen, K.; et al. Tezepelumab in Adults and Adolescents with Severe, Uncontrolled Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1800–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, B.R.; Swyers, J.; Divgi, A.; McFarland, J.G.; Aster, R.H. Thrombocytopenia after second exposure to abciximab-coated platelets. Blood 2002, 9, 2054–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Bhambi, B.; Nyitray, W.; Sharma, G.; Shambaugh, S.; Antonescu, A.; Shukla, P.; Denny, E. Delayed profound thrombocytopenia presenting 7 days after use of abciximab (ReoPro). J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 7, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuker, A.; Bass, A.D.; Nadj, C.; Agius, M.A.; Steingo, B.; Selmaj, K.W.; Thoits, T.; Guerreiro, A.; Van Wijmeersch, B.; Ziemssen, T.; et al. Immune thrombocytopenia in alemtuzumab-treated MS patients: Incidence, detection, and management. Mult. Scler. J. 2020, 26, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aitken, L.; Patel, R.; D’Rozario, J.; Choi, P. Alemtuzumab induced red cell aplasia and other immune cytopenias—Not so ‘pure’. Immunotherapy 2021, 14, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reickmann, P.; Lenz, A.; Hoffmann, M. Fatal autoimmune hemolytic anemia associated with alemtuzumab in a MS patient with severe relapsing remitting disease course and prior immune therapies (P2.103). Neurology 2016, 86 (Suppl. 16), P2.103. [Google Scholar]
- Desai, P.A.; Romere, C.M.; Nguyen, L.; Saksena, A.; Abdullah, S.J.; Diaz, A.E. Severe Coombs positive autoimmune hemolytic anemia after alemtuzumab infusion for relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. What can we learn? Blood 2018, 132 (Suppl. 1), 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, C.; Spedini, P.; Casari, S.; Re, A.; Tucci, A.; Borlenghi, E.; Ungari, M.; Ruggeri, G.; Rossi, G. Delayed-onset peripheral blood cytopenia after rituximab: Frequency and risk factor assessment in a consecutive series of 77 treatments. Leuk. Lymphoma 2006, 47, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jourdan, E.; Topart, D.; Richard, B.; Jourdan, J.; Sotto, A. Severe autoimmune hemolytic anemia following rituximab therapy in a patient with a lymphoproliferative disorder. Leuk. Lymphoma 2003, 44, 889–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunleavy, K.; Tay, K.; Wilson, W.H. Rituximab-associated neutropenia. Semin. Hematol. 2010, 47, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weissmann-Brenner, A.; Brenner, B.; Belyaeva, I.; Lahav, M.; Rabizadeh, E. Rituximab-associated neutropenia: Description of three cases and an insight into the underlying pathogenesis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2011, 17, CS133–CS137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mantzourani, M.; Gogas, H.; Katsandris, A.; Meletis, J. Severe thrombocytopenia related to trastuzumab infusion. Med. Sci. Monit. 2011, 17, CS85–CS87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anandacoomarasamy, A.; Kannangara, S.; Barnsley, L. Cutaneous vasculitis associated with infliximab in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Intern. Med. J. 2005, 35, 638–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandula, P.; Kouides, P.A. Rituximab-induced leukocytoclastic vasculitis: A case report. Arch. Dermatol. 2006, 142, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Kim, H.O.; Kim, H.Y.; Park, Y.M. Rituximab-induced vasculitis: A case report and review of the medical published work. J. Dermatol. 2009, 36, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arcy, C.A.; Mannik, M. Serum sickness secondary to treatment with the murine-human chimeric antibody IDEC-C2B8 (rituximab). Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 1717–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellerstedt, B.; Ahmed, A. Delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction or serum sickness after rituximab treatment. Ann. Oncol. 2003, 14, 1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finger, E.; Scheinberg, M. Development of serum sickness-like symptoms after rituximab infusion in two patients with severe hypergammaglobulinemia. J. Clin.Rheumatol. 2007, 13, 94–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, L.; Small, E.J. Anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 antibody: The first in an emerging class of immunomodulatory antibodies for cancer treatment. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 5275–5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, T.; Al-Masalmeh, N.; Ambreen, S. Acute pneumonitis due to nivolumab and ipilimumab combination. Am. J. Ther. 2022, 29, e126–e128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J. Pneumonitis induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors: From clinical data to translational investigation. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; Zhu, E.C.; Wu, J.-B.; Li, T.; Hou, Y.-L.; Wang, D.-Y.; Gao, Z.-H. Risk of pneumonitis and pneumonia associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors for solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winkler, U.; Jensen, M.; Manzke, O.; Schulz, H.; Diehl, V.; Engert, A. Cytokine-release syndrome in patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and high lymphocyte counts after treatment with an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (rituximab, IDEC-C2B8). Blood 1999, 94, 2217–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooka, A.K.; Gleason, C.; Ollivierre Sargeant, M.; Walker, M.; Watson, M.; Panjic, E.H.; Lonial, S. Managing infusion reactions to new monoclonal antibodies in multiple myeloma: Daratumumab and elotuzumab. J. Oncol. Pract. 2018, 14, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Xu, Y.; Zang, X.; Wu, C.; Gao, J.; Sun, X.; Xie, M.; Ma, X.; Deng, H.; Song, J.; et al. Beigelman-Aubry, C. Radiographic features and prognosis of early- and late-onset non-small cell lung cancer immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonitis. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzessere, C.; Bouchaab, H.; Jumeau, R.; Letovanec, I.; Daccord, C.; Bourhis, J.; Prior, J.O.; Peters, S.; Lazor, R.; Beigelman-Aubry, C. Relationship between pneumonitis induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors and the underlying parenchymal status: A retrospective study. ERJ Open Res. 2020, 6, 00165–02019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, M.; Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Hatabu, H.; Ramaiya, N.H.; Hodi, F.S. Incidence of programmed cell death 1 inhibitor-related pneumonitis in patients with advanced cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lioté, H.; Lioté, F.; Séroussi, B.; Mayaud, C.; Cadranel, J. Rituximab-induced lung disease: A systematic literature review. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 35, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, S.; Rama, K.; Mallampalli, R.K. The acute respiratory distress syndrome: From mechanism to translation. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meduri, G.U.; Annane, D.; Chrousos, G.P.; Marik, P.E.; Sinclair, S.E. Activation and regulation of systemic inflammation in ARDS: Rationale for prolonged glucocorticoid therapy. Chest 2009, 136, 1631–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounis, N.G.; Soufras, G.D.; Tsigkas, G.; Hahalis, G. Adverse cardiac events to monoclonal antibodies used for cancer therapy. Oncoimmunology 2014, 3, e27987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fabbrocini, G.; Cameli, N.; Romano, M.C.; Mariano, M.; Panariello, L.; Bianca, D.; Monfrecola, G. Chemotherapy and skin reactions. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 31, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maude, S.L.; Barrett, D.; Teachey, D.; Grupp, S.A. Managing cytokine release syndrome associated with novel T cell-engaging therapies. Cancer J. 2014, 20, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daver, N.; McClain, K.; Allen, C.E.; Parikh, S.A.; Otrock, Z.; Rojas-Hernandez, C.; Blechacz, B.; Wang, S.; Minkov, M.; Jordan, M.B.; et al. A consensus review on malignancy-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in adults. Cancer 2017, 123, 3229–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thapa, S.; Shrestha, U. Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK567803/ (accessed on 14 December 2021).
- Malissen, N.; Lacotte, J.; Du-Thanh, A.; Gaudy-Marqueste, C.; Guillot, B.; Grob, J.-J. Macrophage activation syndrome: A new complication of checkpoint inhibitors. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 77, 88–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crayne, C.B.; Albeituni, S.; Nichols, K.E.; Cron, R.Q. The immunology of macrophage activation syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cortese, I.; Reich, D.S.; Nath, A. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and the spectrum of JC virus-related disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feske, S.K. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: A review. Semin. Neurol. 2011, 31, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Druey, K.M.; Greipp, P.R. Narrative review: The systemic capillary leak syndrome. Annals Intern. Med. 2010, 153, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaukonen, K.-M.; Bailey, M.; Pilcher, D.; Cooper, D.J.; Bellomo, R. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome criteria in defining severe sepsis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1629–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Howard, S.C.; Jones, D.P.; Pui, C.-H. The tumor lysis syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 364, 1844–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplon, H.; Reichert, J.M. Antibodies to watch in 2021. MABS 2021, 13, e1860476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Monoclonal Antibody INN and Trade Names | Antibody Type | Target | Approved Indications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human–Mouse Chimeric (-ximab) | |||
| Abciximab (ReoPro®) | Chimeric IgG Fab | Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa | Adjunct therapy for prevention of cardiac ischemic complications |
| Basiliximab (Simulect®) | Chimeric IgG1 | α-chain IL-2 receptor (CD25) | Prevent organ transplant rejection |
| Infliximab (Remicade®) | Chimeric IgG1 | TNF | Crohn’s disease; ulcerative colitis; RA; ankylosing spondylitis; psoriatic arthritis; plaque psoriasis |
| Obiltoxaximab (Anthim®) | Chimeric IgG1 | Bacillus anthracis PA | Inhalational anthrax Bacillus anthracis PA |
| Humanized (-zumab) | |||
| Alemtuzumab (Lemtrada®) | Humanized IgG1 | CD52 | Lemtrada®: multiple sclerosis |
| Benralizumab (Fasenra®) | Humanized IgG1 (afucosylated) | IL-5Rα | Asthma |
| Bimekizumab (Bimzelx®) | Humanized IgG1 | IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-17AF | Plaque psoriasis |
| Brolucizumab (Beovu®) | Humanized single-chain (scFv) fragment | VEGF-A | Neovascular (wet) age-related macular degeneration |
| Caplacizumab-yhdp (Caplivi®) | Humanized bivalent single-domain nanobody | von Willebrand factor (vWF) | Acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura |
| Certolizumab pegol (Cimzia®) | Humanized IgG1 Fab, pegylated | TNF | Crohn’s disease; RA |
| Crizanlizumab-tmca (Adakveo®) | Humanized IgG2 | P-selectin | Sickle cell disease |
| Daclizumab (Zinbryta®) | Humanized IgG2 | α-chain IL-2 receptor (CD25) | Multiple sclerosis |
| Eculizumab (Soliris®) | Humanized IgG2/4 | Complement C5 | Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria; atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome; neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) in adult patients who are anti-aquaporin-4 (AQP4) antibody-positive |
| Emicizumab-kxwh (Hemlibra®) | Humanized IgG4 bispecific | Factors IXa and X | Hemophilia A |
| Eptinezumab-jjmr (Vyepti®) | Humanized IgG1 | CGRP | Migraine |
| Fremanezumab-vfrm (Ajovy®) | Humanized IgG4 | CGRP | Migraine |
| Galcanezumab-gnlm (Emgality®) | Humanized IgG4 | CGRP | Migraine |
| Ibalizumab-uiyk (Trogarzo®) | Humanized IgG4 | CD4 | HIV-1 infection |
| Idarucizumab (Praxbind®) | Humanized IgG1 antibody fragment Fab | Dabigatran | Reversal of anticoagulant effects of dabigatran; life-threatening or uncontrolled bleeding |
| Inebilizumab-cdon (Uplizna®) | Humanized afucosylated IgG1 | CD19 | Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) in adult patients who are anti-aquaporin-4 (AQP4) antibody positive |
| Ixekizumab (Taltz®) | Humanized IgG4 | IL-17A | Plaque psoriasis; psoriatic arthritis |
| Mepolizumab (Nucala®) | Humanized IgG1 | IL-5 | Asthma; eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis |
| Natalizumab (Tysabri®) | Humanized IgG4 | α4 integrin (binds to α4β1 and α4β7 integrins) | Multiple sclerosis; Crohn’s disease |
| Ocrelizumab (Ocrevus®) | Humanized IgG1 | CD20 | Multiple sclerosis |
| Omalizumab (Xolair®) | Humanized IgG1 | IgE | Persistent asthma; chronic idiopathic urticaria |
| Palivizumab (Synagis®) | Humanized IgG1 | RSVF | Prevention of lower respiratory tract disease RSV in children |
| Ranibizumab (Lucentis®) | Humanized IgG1 Fab | VEGF-A | Neovascular (wet) age-related macular degeneration; macular edema following retinal vein occlusion; diabetic macular edema |
| Ravulizumab-cwvz (Ultomiris®) | Humanized IgG2/4 | Complement C5 | Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria |
| Reslizumab (Cinqair®) | Humanized IgG4 | IL-5 | Asthma |
| Risankizumab-rzaa (Skyrizi®) | Humanized IgG1 | IL-23 p19 | Plaque psoriasis |
| Romosozumab-aqqg (Evenity®) | Humanized IgG2 | Sclerostin | Osteoporosis |
| Satralizumab-mwge (Enspryng®) | Humanized IgG2 | IL-6R | Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) in adult patients who are anti-aquaporin-4 (AQP4) antibody-positive |
| Tildrakizumab-asmn (Ilumetri®; Ilumya®) | Humanized IgG1 | IL-23 p19 | Plaque psoriasis |
| Tocilizumab (Actemra®; RoActemra®) | Humanized IgG1 | IL-6R | RA; polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis; systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis |
| Vedolizumab (Entyvio®) | Humanized IgG1 | α4β7 integrin | Adult ulcerative colitis; adult Crohn’s disease |
| Fully human (-umab) | |||
| Adalimumab (Humira®) | Human IgG1 | TNF | RA; psoriatic arthritis; ankylosing spondylitis; plaque psoriasis; Crohn’s disease |
| Aducanumab-avwa (Aduhelm®) | Human IgG1 | Amyloid beta | Alzheimer’s disease |
| Alirocumab (Praluent®) | Human IgG1 | PCSK9 | Heterozygous FH; atherosclerotic CV disease requiring additional ↓ of LDL-C |
| Anifrolumab-fnia (Saphnelo®) | Human IgG1 | Subunit I type I interferon receptor (IFNAR) | Systemic lupus erythematosis |
| Ansuvimab-zykl (Ebanga®) | Human IgG1 | Zaire ebolavirus (EBOV) glycoprotein 1 (GP1) | Zaire ebolavirus infection |
| Atoltivimab, Maftivimab and Odesivimab-ebgn (Inmazeb®) | Human IgG1 | Zaire ebolavirus (EBOV) glycoprotein 1 (GP1) | Zaire ebolavirus infection |
| Belimumab (Benlysta®) | Human IgG1 | BlyS | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| Bezlotoxumab (Zinplava®) | Human IgG1 | Clostridium difficile toxin B | Recurrence of Clostridium difficile toxin B infection |
| Brodalumab (Siliq®; Kyntheum®; Lumicef®) | Human IgG2 | IL-17RA | Plaque psoriasis |
| Burosumab-twza (Crysvita®) | Human IgG1 | FGF23 | X-linked hypophosphatemia |
| Canakinumab (Ilaris®) | Human IgG1 | IL-1β | Cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS) including familial cold autoinflammatory and Muckle–Wells syndromes; SJIA with body weight ≥7.5 kg; NOMID/CINCA; FCAS/FCU; gouty arthritis |
| Casirivimab + Imdevimab (REGEN-COV®; Ronapreve®) | Human IgG1 | The 2 mAbs bind to separate epitopes of the spike protein RBD of SARS-CoV-2, thus preventing its binding to the human ACE2 receptor and subsequent cell entry | COVID-19 disease |
| Denosumab (Prolia®) | Human IgG2 | RANKL | Bone loss—for osteoporosis and to increase bone mass in menopausal women at high risk of fracture |
| Dupilumab (Dupixent®) | Human IgG4 | IL-4Rα subunit | Atopic dermatitis |
| Efgartigimod-alfa-fcab (Vyvgart®) | Human IgG1 Fc fragment | Neonatal Fc receptor FcRn | Generalized myasthenia gravis |
| Emapalumab-lzsg (Gamifant®) | Human IgG1 | IFNγ | HLH |
| Erenumab-zooe (Aimovig®) | Human IgG2 | CGRP receptor | Migraine |
| Evinacumab-dgnb (Evkeeza®) | Human IgG4 | ANGPTL3 (angiopoietin-like 3) | Homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH) |
| Evolocumab (Repatha®) | Human IgG2 | PCSK9 | Primary hyperlipidemia and mixed dyslipidemia; homozygous FH to reduce LDL-C and other lipids |
| Golimumab (Simponi®) | Human IgG1 | TNF | RA; psoriatic arthritis (both in combination with methotrexate); ankylosing spondylitis |
| Guselkumab (Tremfya®) | Human IgG1 | IL-23 | Plaque psoriasis |
| Lanadelumab-flyo (Takhzyro®) | Human IgG1 | Plasma kallikrein | HAE prevention |
| Raxibacumab (ABthrax®) | Human IgG1 | Bacillus anthracis PA | Inhalational anthrax to Bacillus anthracis and prophylaxis in absence of alternative therapies |
| Regdanvirimab (Regkirona®) | Human IgG1 | mAb binds to the spike protein RBD of SARS-CoV-2 preventing its binding to the human ACE2 receptor and subsequent cell entry | COVID-19 disease |
| Sarilumab (Kevzara®) | Human IgG1 | IL-6R | RA |
| Secukinumab (Cosentyx®) | Human IgG1 | IL-17A | Moderate to severe plaque psoriasis |
| Sotrovimab (Xevudy®) 1 | Human IgG1 | Spike protein RBD of SARS-CoV-2 | COVID-19 disease |
| Teprotumumab-trbw (Tepezza®) | Human IgG1 | IGF-1R | Thyroid eye disease |
| Tezepelumab-ekko (Tezspire®) | Human IgG2 | Thymic stromal lymphopoietin | Severe asthma |
| Tralokinumab (Adtralza®) | Human IgG4 | IL-13 | Atopic dermatitis |
| Ustekinumab (Stelara®) | Human IgG1 | IL-12, IL-23 | Plaque psoriasis |
| Monoclonal Antibody INN and Trade Name | Type of mAb | Target | Approved Indications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rat-mouse chimera (-axomab) | |||
| Catumaxomab (Removab®) | Rat IgG2b/Mouse IgG2a bispecfic | EpCAM/CD3 | Malignant ascites |
| Mouse (-omab) | |||
| Blinatumomab (Blincyto®) | Mouse scFvκ-H bispecific | CD19/CD3 epsilon | Philadelphia chromosome-negative relapsed or refractory B cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| Ibritumomab tiuxetan (Zevalin®) | Mouse IgG1 | CD20 | Non-HL |
| Moxetumomab pasudox– tdfk (Lumoxiti®) | ADC immunotoxin. Mouse single chain variable domain (scFv) | CD22 | HCL |
| Human-mouse chimeric (-ximab) | |||
| Brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris®) | Chimeric IgG1 | CD30 | HL after failure of stem cell transplant or chemotherapy; sALCL after failure of chemotherapy; post auto-HSCT consolidation treatment for HL |
| Cetuximab (Erbitux®) | Chimeric IgG1 | EFGR | Colorectal and head and neck cancers |
| Dinutuximab (Unituxin®) | Chimeric IgG1 | GD2 | Pediatric patients with high-risk neuroblastoma |
| Isatuximab-irfc (Sarclisa®) | Chimeric IgG1 with 2 identical H and κ L chains | CD38 | MM |
| Margetuximab-cmkb (Margenza®) | Chimeric IgG1 | HER2 | HER2-positive breast cancer |
| Rituximab (Rituxan®; MabThera®) | Chimeric IgG1 | CD20 | Non-HL; CLL; rheumatoid arthritis; Wegener’s granulomatosis; microscopic polyangiitis |
| Siltuximab (Sylvant®) | Chimeric IgG1 | IL-6 | Multicentric Castelman’s disease in patients negative for HIV and HHV-8 |
| Humanized (-zumab) | |||
| Ado-trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla®) | ADC. Humanized IgG1 | HER2 | HER2-positive breast cancer in patients who previously received trastuzumab or a taxane |
| Alemtuzumab (Campath®; MabCampath®) | Humanized IgG1 | CD52 | Campath, MabCampath: B cell CLL |
| Atezolizumab (Tecentriq®) | Humanised IgG1 | PD-L1 | MUC; NSCLC |
| Bevacizumab (Avastin®) | Humanized IgG1 | VEGF-A | Metastatic colorectal cancer; non-squamous NSCLC; metastatic breast cancer; ovarian cancer; glioblastoma |
| Dostarlimab-gxly (Jemperli®) | Humanized IgG4 | PD-1 | Endometrial cancer |
| Elotuzumab (Empliciti®) | Humanised IgG1 | SLAMF7 | MM |
| Fam-trastuzumab deruxtecan-nxki (Enhertu®) | ADC. Humanised IgG1 | HER2 | HER2-positive breast, gastric, and GE adenocarcinomas |
| Gemtuzumab ozogamicin (Mylotarg®) | ADC. Humanized IgG4 | CD33 | AML |
| Inotuzumab ozogamicin (Besponsa®) | ADC. Humanized IgG4 | CD22 | ALL |
| Loncastumab tesirine-lpyl (Zynlonta®) | ADC. Humanized IgG1 | CD19 with teserine cytotoxic agent | LBCL including DLBCL |
| Mogamulizumab-kpkc (Poteligeo®) | Humanized IgG1 | CCR4 | Mycosis fungoides; Sézary syndrome |
| Naxitamab-gqgk (Danyelza®) | Humanized IgG1 | GD2 | Neuroblastoma—antibody given in combination with GM-CSF |
| Obinutuzumab (Gazyva®; Gazyvaro®) | Humanized IgG1 | CD20 | In combination with chlorambucil for previously untreated CLL |
| Pembrolizumab (Keytruda®) | Humanized IgG4 | PD-1 | Unresectable or metastatic melanoma; refractory metastatic NSCLC tumors that express PD-L1 |
| Pertuzumab (Perjeta®) | Humanized IgG1 | HER2 | Combination with trastuzumab and docetaxel for HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer |
| Polatuzumab vedotin-piiq (Polivy®) | ADC. Humanized IgG1 | CD79b | Diffuse large B cell lymphoma |
| Sacituzumab govitecan-hziy (Trodelvy®) | ADC. Humanized IgG1 | Trop-2 with topoisomerase inhibitor | mTNBC |
| Tafasitamab-cxix (Monjuvi®) | Humanized IgG1/2 with hybrid Fc-modified domain | CD19 | DLBCL |
| Trastuzumab (Herceptin®) | Humanized IgG1 | HER2 | Breast cancer overexpressing HER2, metastatic gastric or GE junction adenocarcinoma overexpressing HER2 |
| Fully human (-umab) | |||
| Amivantamab-vmjw (Rybrevant®) | Bi-specific low fucose human IgG1-based antibody | EGFR and c-MET receptors | NSCLC |
| Avelumab (Bavencio®) | Human IgG1 | PD-L1 | MCC; UC; RCC |
| Belantamab mafodoton-blmf (Blenrep®) | ADC afucosylated IgG1 | BCMA with MMAF microtubule inhibitor | MM |
| Cemiplimab-rwlc (Libtayo®) | Human IgG4 | PD-1 | CSCC |
| Daratumumab (Darzalex®) | Human IgG1 | CD38 | MM |
| Denosumab (Prolia®; Xgeva®) | Human IgG2 | RANKL | Bone loss. Prolia: for osteoporosis and to increase bone mass; Xgeva: for bone metastases from solid tumors and giant cell tumor of bone |
| Durvalumab (Imfinzi®) | Human IgG1 | PD-L1 | UC |
| Enfortumab-vedotin-ejfv (Padcev®) | ADC human IgG1 | Nectin-4 with MMAE microtubule inhibitor | UC |
| Ipilimumab (Yervoy®) | Human IgG1 | CTLA-4 | Metastatic melanoma |
| Necitumumab (Portrazza®) | Human IgG1 | EGFR | Squamous NSCLC |
| Nivolumab (OPDIVO®) | Human IgG4 | PD-1 | Unresectable or metastatic melanoma and disease progression following ipilimumab and, if BRAF V600-positive, a BRAF inhibitor; NSCLC |
| Ofatumumab (Arzerra®) | Human IgG1 | CD20 | CLL refractory to fludarabine and alemtuzumab |
| Olaratumab (Lartruvo®) | Human IgG1 | PDGFR-α | Soft tissue sarcoma |
| Panitumumab (Vectibix®) | Human IgG2 | EGFR | Metastatic colorectal cancer |
| Ramucirumab (Cyramza®) | Human IgG1 | VEGFR2 | Gastric or GE junction adeno- carcinoma; metastatic NSCLC with docetaxel after platinum therapy; HCC; with FOLFIRI for metastatic colorectal cancer |
| Tisotumab vedotin-tftv (Tivdak®) | ADC human IgG1 | TF with MMAE microtubule inhibitor | Cervical cancer |
| Target | Monoclonal Antibodies |
|---|---|
| Monoclonal antibodies for non-cancer therapy | |
| TNF | Adalimumab; certolizumab pegol; golimumab; infliximab |
| PCSK9 | Alirocumab; evolocumab |
| EBOV GP1 | Ansuvimab-zykl; atoltivimab; maftivimab; odesivimab-ebgn |
| IL-2 receptor α chain (CD25) | Basiliximab; daclizumab |
| VEGF-A | Brolocizumab-dbll; ranibizumab |
| ACE2 RBD of SARS-CoV-2 | Casirivimab + imdevimab; regdanvirimab; Sotrovimab |
| Complement C5 | Eculizumab; ravulizumab-cwvz |
| CGRP | Eptinezumab-jjmr; fremanezumab-vfrm; galcanezumab-gnlm |
| IL-17A | Ixekizumab; secukinumab |
| IL-5 | Mepolizumab; reslizumab |
| α4 integrin | Natalizumab; vedolizumab |
| Bacillus anthracis | Obiltoxaximab; raxibacumab |
| IL-23 p19 | Risankizumab-rzaa; tildrakizumab-asmn |
| IL-6R | Sarilumab; satralizumab-mwge; tocilizumab |
| Monoclonal antibodies for cancer therapy | |
| HER2 | Ado-trastuzumab; fam-trastuzumab; margetuximab-cmkb; pertuzumab; trastuzumab |
| PD-L1 | Atezolizumab; avelumab; durvalumab |
| PD-1 | Cemiplimab-rwlc; dostarlimab-gxly; nivolumab; pembrolizumab |
| EGFR | Amivantamab; Cetuximab; necitumumab; panitumumab |
| CD38 | Daratumumab; isatuximab-irfc |
| GD2 | Dinutuximab; naxitamab-gqgk |
| CD20 | Ibritumomab; obinutuzumab; ofatumumab; rituximab |
| CD22 | Inotuzumab ozogamicin; moxetumomab pasudox-tdfk |
| Monoclonal Antibody 2 INN and Trade Names | Target 3 | Warnings, Precautions, Risks and Safety Concerns | Other Adverse Events 4, Serious and Common |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abciximab (ReoPro®) | Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa | Increased risk of bleeding; thrombocytopenia | Systemic: Bleeding; intracranial hemorrhage or stroke; GI; CV; anemia; NS; respiratory; urinary disorders Cutaneous: Pruritus; generalized exanthema |
| Adalimumab (Humira®) | TNF | Boxed warning: Serious infections; malignancy Other: Anaphylaxis, serious allergic reactions; hepatitis B reactivation; demyelinating disease; cytopenias; heart failure; lupus-like syndrome | Systemic: Infections; isr; ILD; sarcoidosis; liver failure Cutaneous: SJS; EM; psoriasis; cutaneous vasculitis; alopecia |
| Aducanumab-avwa (Aduhelm®) | Amyloid beta | Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA); hypersensitivity | Systemic: Headache; ARIA-oedema, -headache, -H microhemorrhage, -H superficial siderosis, fall |
| Alemtuzumab (Lemtrada®) | CD52 | Boxed warning: Autoimmunity; IRs; malignancies Other: Other immune cytopenias; glomerular nephropathies; thyroid disorders; delay therapy in cases of infections; pneumonitis | Systemic: Headache; pyrexia; nausea; UTI; herpes virus infection; extremity and back pain; dizziness; flushing; cough; chills; vomiting; dyspnea Cutaneous: Rash; urticaria; pruritus; dermatitis |
| Alirocumab (Praluent®) | PCSK9 | Allergic reactions (pruritus, urticaria, rash) including some serious (including hypersensitivity vasculitis) | Systemic: Nasopharyngitis; isr; influenza; URTI; cough; sinusitis; bronchitis; diarrhea; myalgia; muscle spasms; musculoskeletal pain; liver enzyme abnormalities |
| Anifrolumab-fnia (Saphnelo®) | IFNAR | Serious infections; hypersensitivity; malignancy; avoid live attenuated vaccines and other biological therapies | Systemic: Nasopharyngitis; URTI; IR; bronchitis; herpes zoster; cough |
| Ansuvimab-zykl (Ebanga®) | EBOV GP1 | Hypersensitivity; IR | Systemic: Pyrexia; tachycardia; diarrhea; vomiting; hypotension; tachypnoea; chills |
| Atoltivimab, Maftivimab, and Odesivimab-ebgn (Inmazeb®) | EBOV GP1 | Hypersensitivity; IR | Systemic: Pyrexia; chills; tachycardia; tachypnoea; vomiting |
| Basiliximab (Simulect®) | IL-2 receptor α-chain (CD25) | Boxed warning: General risk of immunosuppressive therapy Other: Immunogenicity; hypersensitivity | Systemic: GI; viral infection; peripheral oedema; UTI; URTI; dyspnea; wound complications; hypertension; anemia; hypo- and hyperkalemia and hyperuricemia; headache; tremor Cutaneous: Rash; pruritus; hypertrichosis |
| Belimumab (Benlysta®) | BLyS | Mortality; serious infection; malignancy; hypersensitivity including anaphylaxis; IR; depression; immunization | Systemic: Nausea; diarrhea; pyrexia; pain in extremity; bronchitis; depression; migraine Cutaneous: Rash; pruritus |
| Benralizumab (Frasenra®) | IL-5Rα | Hypersensitivity; helminth infections—treat prior; decrease steroids gradually | Systemic: Headache; pharyngitis |
| Bezlotoxumab (Zinplava®) | Clostridium difficile toxin B | Heart failure | Systemic: Nausea; pyrexia; headache |
| Bimekizumab (Bimzelx®) | IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-17AF | Infections; pre-evaluation for tuberculosis; IBD; avoid live vaccines; hypersensitivity | Systemic: Infections and infestations, nervous system disorders; isr Cutaneous: Dermatitis; acne; eczema |
| Brodalumab (Siliq®; Kyntheum®; Lumicef®) | IL-17RA | Boxed warning: Suicidal ideation and behavior. Other: TB; infections; Crohn’s disease; avoid live vaccines | Systemic: Arthralgia; headache; fatigue; diarrhea; oropharyngeal pain; nausea; myalgia; isr, influenza; neutropenia; tinea infections |
| Brolucizumab-dbll (Beovu®) | VEGF-A | Endophthalmitis and retinal detachment; risk of arterial thromboembolic events; increase in intraocular pressure | Systemic: Conjunctival hemorrhage; eye pain; vitreous floaters; cataracts; blurred vision |
| Burosumab-twza (Crysvita®) | FGF23 | Hypersensitivity; isr; hyperphosphatemia and risk of nephrocalcinosis | Systemic: Headache; isr; vomiting; pyrexia; pain in extremity; decreased vitamin D |
| Canakinumab (Ilaris®) | IL-1β | Increased risk of serious infections; immunization; MAS; hypersensitivity; immunosuppression | Systemic: CAPS—Nasopharyngitis; diarrhea; influenza; headache; nausea; dizziness/vertigo; SJIA, URTI, isr, abdominal pain |
| Caplacizumab-yhdp (Cablivi®) | von Willibrand factor | Bleeding | Systemic: Epistaxis; gingival bleeding; headache; isr |
| Casirivimab + Imdevimab (REGEN-COV®; Ronapreve®) | mAbs bind to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein RBD preventing binding to the ACE2 receptor | Hypersensitivity including anaphylaxis; IR | - |
| Certolizumab pegol (Cimzia®) | TNF | Boxed warning: Serious infections; lymphoma and other malignancies Other: Heart failure; serious allergic reactions; hepatitis B reactivation; demyelinating disease; cytopenias; lupus-like syndrome | Systemic: URTI; cardiac disorders; eye disorders; isr; hepatitis and ↑ liver enzymes; nephrotic syndrome; renal failure; thrombophlebitis; vasculitis Cutaneous: Dermatitis; erythema nodosum; urticaria |
| Crizanlizumab-tmca (Adakveo®) | P-selectin | IR | Systemic: Nausea; arthralgia; back pain; pyrexia |
| Daclizumab (Zinbryta®) | IL-2 receptor α-chain (CD25) | Boxed warning: Hepatic injury including autoimmune hepatitis and other immune-mediated disorders Other: Hypersensitivity; infections; depression and suicide | Systemic: Nasopharyngitis; URTI; oropharyngeal pain; bronchitis; eczema; depression; influenza. Cutaneous: Dermatitis, rash |
| Denosumab (Prolia®) | RANKL | Hypersensitivity; hypocalcemia; serious infections; osteonecrosis of jaw; atypical femoral fractures; severe bone, joint, muscle pain; suppression of bone turnover; dermatologic reactions | Systemic: Post-menopausal osteoporosis—back, extremity and musculoskeletal pain; hypercholesterolemia; cystitis; male osteoporosis—back pain; arthralgia; nasopharyngitis Cutaneous: Rash; pruritus; dermatitis; eczema |
| Dupilumab (Dupixent®) | IL-4Rα | Hypersensitivity; conjunctivitis and keratitis; eosinophilic conditions; helminth infections—treat prior; decrease steroids gradually | Systemic: Conjunctivitis; blepharitis; eye pruritus; herpes infections; keratitis; dry eye; oropharyngeal pain; isr; eosinophilia |
| Eculizumab (Soliris®) | Complement C5 | Boxed warning: Serious meningococcal infection | Systemic: PNH—headache; nasopharyngitis; back pain; nausea; AHUS—hypertension; URTI; GI; abdominal pain; anemia; cough; pyrexia; peripheral edema Cutaneous: Rash; pruritus |
| Efgartigimod-alfa-fcab (Vyvgart®) 5 | Neonatal Fc receptor FcRn | See reference below 5 | See reference below 5 |
| Emapalumab-lzsg (Gamifant®) | IFNγ | Infections; IR; avoid live vaccines | Systemic: Infections; pyrexia; hypertension; IR |
| Emicizumab-kxwh (Hemlibra®) | Factors IXa & X | Boxed warning: Thrombotic microangiopathy and thromboembolism. Other: mAb interference with coagulation tests | Systemic: Arthralgia; isr; headache |
| Eptinezumab-jjmr (Vyepti®) | CGRP | Hypersensitivity | Systemic: Nasopharyngitis; hypersensitivity |
| Erenumab-zooe (Aimoig®) | CGRP Receptor | - | Systemic: Constipation; isr |
| Evinacumab-dgnb (Evkeeza®) | ANGPTL3 | Serious hypersensitivity; embryo-fetal toxicity | Systemic: Nasopharyngitis; influenza-like illness; dizziness; rhinorrhea; nausea |
| Evolocumab (Repatha®) | PCSK9 | Patients with renal and hepatic impairments have not yet been adequately studied; cover of prefilled syringe and pen contain latex which may cause allergic reactions | Systemic: Nasopharyngitis; isr; influenza; URTI; back pain; arthralgia; hypertension; nausea Cutaneous: Rash; hives |
| Fremanezumab-vfrm (Ajovy®) | CGRP | Hypersensitivity | Systemic: isr |
| Galcanezumab-gnlm (Emgality®) | CGRP | Hypersensitivity | Systemic: isr |
| Golimumab (Simponi®) | TNF | Boxed warning: Serious infections; lymphoma, and other malignancies Other: Invasive fungal infections; heart failure; hepatitis B reactivation; demyelinating disease; hypersensitivity | Systemic: URTI; viral infections; bronchitis; ↑ liver enzymes; sarcoidosis; ILD; paresthesia Cutaneous: Skin exfoliation; rash |
| Guselkumab (Tremfya®) | IL-23 | Infections; prior evaluation for TB | Systemic: URTI; isr; arthralgia; headache; diarrhea; tinea; gastroenteritis; herpes simplex infections |
| Ibalizumab-uiyk (Trogarzo®) | CD4 | IRIS | Systemic: Diarrhea, nausea; dizziness. Cutaneous: Rash |
| Idarucizumab (Praxbind®) | Dabigatran | Thromboembolic risk; hypersensitivity; risk of adverse reaction in patients with hereditary fructose intolerance; reappearance of bleeding | Systemic: Headache; hypokalemia; delirium; pneumonia; constipation; pyrexia |
| Inebilizumab-cdon (Uplizna®) | CD19 | IR; infections; monitor immunoglobulin levels; fetal risk | Systemic: Urinary tract infection; arthralgia |
| Infliximab (Remicade®) | TNF | Boxed warning: Serious infections; malignancy Other: Hepatitis B reactivation; hepatotoxicity; cytopenias; demyelinating disease; lupus-like syndrome | Systemic: Infections; pancytopenia; anemia; cellulitis; serum sickness; thrombophlebitis; intestinal obstruction; ILD; anaphylaxis; IRs Cutaneous: Cutaneous vasculitis; SJS; EM; psoriasis; |
| Ixekizumab (Taltz®) | IL-17A | Infections: TB—evaluate prior; hypersensitivity; inflammatory bowel disease | Systemic: URTI; isr; nausea; tinea infections |
| Lanadelumab-flyo (Takhzyro®) | Plasma kallikrein | Hypersensitivity | Systemic: URTI; isr; headache; diarrhea; dizziness; myalgia Cutaneous: Rash |
| Mepolizumab (Nucala®) | IL-5 | Hypersensitivity; helminth infections—treat prior; herpes zoster infections—consider prior vaccination; decrease steroids gradually; not to be used for bronchospasm or status asthmaticus | Systemic: Headache; isr; back pain; fatigue |
| Natalizumab (Tysabri®) | α4 integrin (binds to α4β1 and α4β7 integrins) | Boxed warning: PML Other: Hypersensitivity; hepatotoxicity; immunosuppression/infections; IRIS | Systemic: MS—headache; fatigue; arthralgia; urinary tract infection; URTI; gastroenteritis; vaginitis; diarrhea. CD—headache; URTI; nausea Cutaneous: Rash; urticaria |
| Obiltoxaximab (Anthim®) | Bacillus anthracis PA | Boxed warning: Hypersensitivity and anaphylaxis | Systemic: URTI; headache; pruritus; IR pain, swelling, bruise Cutaneous: Urticaria |
| Ocrelizumab (Ocrevus®) | CD20 | Infections; IR; increased risk of malignancy | Systemic: Respiratory tract infections; IR; PML Cutaneous: Skin infections |
| Omalizumab (Xolair®) | IgE | Anaphylaxis; malignancy; acute asthma; decrease CSs gradually; eosinophilia; serum sickness-like reaction; parasitic infection | Systemic: Allergic asthma— arthralgia; pain; dizziness; fracture; earache. CIU—nausea; pharyngitis; URTI; sinusitis; arthralgia; headache; cough; virus infections Cutaneous: Pruritus; dermatitis. |
| Palivisumab (Synagis®) | RSVF | Anaphylaxis; delay administration during moderate–severe infections; give with caution in cases of thrombocytopenia or coagulation disorders | Systemic: isr; pyrexia; apnea; cough; dizziness thrombocytopenia Cutaneous: Rash; itching; erythema |
| Ranibizumab (Lucentis®) | VEGF-A | Endophthalmitis and retinal detachment, increase in intraocular pressure and risk of arterial thromboembolic events after intravitreal injection | Systemic: Conjunctival hemorrhage; eye pain; vitreous floaters; cataracts |
| Ravulizumab-cwvz (Ultomiris®) | Complement C5 | Boxed warning: Serious meningococcal infections | Systemic: URTI; headache; diarrhea; nausea |
| Raxibacumab (ABthrax®) | Bacillus anthracis PA | IR | Systemic: Pain in extremity; somnolence; headache; URTI; nausea; cough; arthralgias. Cutaneous: Rash; pruritus; urticaria |
| Regdanvirimab (Regkirona®) | Binds to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein RBD preventing binding to ACE2 receptor | Hypersensitivity including anaphylaxis; IR | -- |
| Reslizumab (Cinqair®) | IL-5 | Boxed warning: Anaphylaxis Other: Helminth infections—treat prior; decrease steroids gradually; malignancy | Systemic: Oropharyngeal pain |
| Risankizumab-rzaa (Skyrizi®) | IL-23 p19 | Infections; prior evaluation for TB; hypersensensitivity | Systemic: URTI; isr; diarrhea |
| Romosozumab-aqqg (Evenity®) | Sclerostin | Boxed warning: Potential risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, and cardiovascular death Other: Cardiac events; hypersensitivity; hypocalemia; atypical femoral fracture | Systemic: Arthralgia; headache |
| Satralizumab-mwge (Enspryng®) | IL-6R | Infections; elevated liver enzymes (ALT, AST); decreased neutrophils | Systemic: Nasopharyngitis; headache; URTI; gastritis; arthralgia; extremity pain; fatigue; nausea Cutaneous: Rash |
| Sarilumab (Kevzara®) | IL-6R | Boxed warning: Risk of serious infection Other: GI perforation; avoid live vaccines; hypersensitivity; neutropenia; thrombocytopenia | Systemic: increased ALT; isr; URTI; urinary tract infections |
| Secukinumab (Cosentyx®) | IL-17A | Infections; tuberculosis activation; exacerbation of Crohn’s disease; hypersensitivity; avoid live vaccines | Systemic: Nasopharyngitis; diarrhea; URTI; rhinitis Cutaneous: Urticaria |
| Sotrovimab (Xevudy®) 6 | Spike protein RBD of SARS-CoV-2 | Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis | -- |
| Teprotumumab-trbw (Tepezza®) | IGF-1R | IR; exacerbation of pre-existing inflammatory bowel disease; hyperglycemia | Systemic: Muscle spasm; nausea; alopecia; diarrhea; fatigue; hyperglycemia; hearing impairment; dry skin; dysgeusia; headache |
| Tezepelumab-ekko (Tezspire®) 7 | Thymic stromal lymphopoietin | Hypersensitivity; acute asthma and deteriorating disease; reduction of corticosteroid dosage; parasite infection; live attenuated virus vaccines 7 | Systemic: Pharyngitis; arthralgia; back pain 7 |
| Tildrakizumab-asmn (Ilumetri®; Ilumya®) | IL-23 p19 | Infections; prior evaluation for TB; hypersensensitivity | Systemic: URTI; isr; diarrhea |
| Tocilizumab (Actemra®; RoActemra®) | IL-6R | Boxed warning: Serious infections Other: GI perforation; avoid live vaccines; hypersensitivity; laboratory monitoring | Systemic: Nasophraryngitis; nausea; ↑ liver enzymes; IR; hypertension; thrombocytopenia; neutropenia; headache Cutaneous: Dermatologic reactions |
| Tralokinumab (Adtralza®) | IL-13 | Hypersensitivity; conjunctivitis; helminth infection; avoid live and live attenuated vaccines | Systemic: URTI; conjunctivitis; eosinophilia; isr |
| Ustekinumab (Stelara®) | IL-12 IL-23 | Infections; tuberculosis; RPLS; malignancies; anaphylaxis; avoid live vaccines | Systemic: Nasopharyngitis; headache; dental infections; URTI; isr; arthralgia; GI Cutaneous: Pruritus |
| Vedolizumab (Entyvio®) | α4β7 integrin | Hypersensitivity/IR; infections; PML; liver injury | Systemic: Headache; arthralgia; nausea; pyrexia; URTI; cough; bronchitis; influenza; back pain; pain in extremities; nasopharyngitis Cutaneous: Rash; pruritus |
| Monoclonal Antibody 2 INN and Trade Names | Target 3 | Warnings, Precautions, Risks, and Safety Concerns | Other Adverse Events 4: Serious and Common |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ado-trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla®) | HER2 | Boxed warning: Hepatotoxicity; cardiac toxicity; embryo-fetal toxicity Other: IR; pulmonary toxicity; extravasation; hemorrhage; thrombocytopenia; neurotoxicity | Systemic: Pulmonary events; fetal harm; LVD; hypersensitivity/IR; nausea; fatigue; anemia; headache; musculoskeletal pain; increased transaminases; constipation Cutaneous: Rash; pruritus |
| Alemtuzumab (Campath®; MabCampath®) | CD52 | Boxed warning: Cytopenias; IR; immunosuppression/infections Other: Immunization | Systemic: Pulmonary events; immunogenicity; cardiac events; diarrhea; nausea; emesis; insomnia Cutaneous: Rash; urticaria; erythema; pruritus |
| Amivantamab-vmjw (Rybrevant®) | EGFR and c-MET receptors | ILD/pneumonitis; IR; dermatologic (including acneiform dermatitis and TEN); ocular toxicity; embryo-fetal toxicity | Systemic: IR; paronychia; musculoskeletal pain; dyspnea; nausea; fatigue; edema; stomatitis; cough; constipation; vomiting Cutaneous: Rash |
| Atezolizumab (Tecentriq®) | PD-L1 | Immune-mediated pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies (hypophysitis, thyroid disorders, adrenal insufficiency, diabetes mellitus); embryo-fetal toxicity | Systemic: IR; fatigue; nausea; infections; urinary tract infections; decreased appetite; diarrhea; pyrexia; constipation; dyspnea. Cutaneous: Rash; pruritus |
| Avelumab (Bavencio®) | PD-L1 | Immune-mediated pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies, nephritis and renal dysfunction; IR | Systemic: Fatigue; musculoskeletal pain; diarrhea; nausea; decreased appetite; peripheral edema; urinary tract infection Cutaneous: Rash; pruritus |
| Belantamab mafodoton-blmf (Blenrep®) | BCMA with MMAF microtubule inhibitor | Boxed warning: Ocular toxicity Other: Thrombocytopenia; IR; embryo-fetal toxicity | Systemic: Keratopathy; decreased visual acuity, nausea; blurred vision; pyrexia; IR; fatigue; decreased platelets, lymphocytes, hemoglobin; increased creatinine, GGT |
| Bevacizumab (Avastin®) | VEGF-A | Boxed warning: GI perforation; surgery/wound healing; hemorrhage Other: Non-GI fistula; RPLS; IR; CHF; hypertension; arterial/venous thromboembolism; eye disorders; proteinurea; neutropenia/infections; ONJ | Systemic: Pulmonary events; epistaxis; headache; rectal hemorrhage; dry skin; necrotizing fasciitis; taste alteration; lacrimation disorder; ovarian failure Cutaneous: Exfoliative dermatitis; alopecia |
| Blinatumomab (Blincyto®) | CD19/CD3 epsilon | Boxed warning: CRS; neurological toxicities Other: Infections; neutropenia and febrile neutropenia; TLS; elevated liver enzymes; leukoencephalopathy | Systemic: HLH; pyrexia; lymphopenia; leukopenia; chills; headache; CNS symptoms (disorientation, confusion, tremor, speech disorders); hypokalemia; pneumonia; sepsis, constipation, peripheral edema Cutaneous: Rash |
| Brentuximab vedotin(Adcetris®) | CD-30 | Boxed warning: PML Other: Peripheral neuropathy; IR and anaphylaxis; neutropenia; infections; fetal harm; hepatotoxicity; TLS; SJS | Systemic: Cytopenias; immunogenicity; URTI; pyrexia; nausea; vomiting; fatigue; cough; anaphylaxis Cutaneous: Rash; pruritus; SJS; alopecia |
| Catumaxomab (Removab®) | EpCAM/CD3 | Monitor and evaluate for: CRS; SIRS; HAMA/HARA; GI hemorrhage; hepatic disorders; abdominal infection; ileus/intestinal perforation; decreased lymphocyte count | Systemic: Cytopenias; hepatotoxicity; abdominal disorders; pyrexia; chills; nausea; vomiting; infections; immunogenicity; dyspnea Cutaneous: Rash; erythema; allergic dermatitis; hyperhidrosis; pruritus |
| Cemiplimab-rwlc (Libtayo®) | PD-1 | Immune-mediated pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies, nephritis, dermatologic reactions; IR; embryo-fetal toxicity | Systemic: Diarrhea; fatigue; nausea; constipation; musculoskeletal pain Cutaneous: Rash; pruritus |
| Cetuximab (Erbitux®) | EFGR | Boxed warning: Serious IR and cardiopulmonary arrest. Other: Pulmonary toxicity; dermatologic toxicity; hypomagnesemia | Systemic: Electrolyte imbalance; infection; GI; anaphylaxis; headache; diarrhea Cutaneous: Acneiform rash; nail changes; xeroderma; paronychial inflammation; pruritus |
| Daratumumab (Darzalex®) | CD38 | IR; interference with serological testing; neutropenia; thrombocytopenia | Systemic: Neutropenia; thrombocytopenia; fatigue; nausea; diarrhea; constipation; vomiting; muscle spasms; arthralgia; back pain; pyrexia; chills; dizziness; insomnia; cough; dyspnea; peripheral edema; peripheral sensory neuropathy; URTI |
| Denosumab (Prolia®; Xgeva®) | RANKL | Hypocalcemia; ONJ; embryo-fetal toxicity | Systemic: Osteomyelitis; hypophosphatemia; dyspnea; fatigue/asthenia; back pain; nausea; extremity pain Cutaneous: Rash; pruritus; dermatitis; eczema |
| Dinutuximab (Unituxin®) | GD2 | Boxed warning: Serious IR; neuropathy Other: CLS and hypotension; infection; RPLS; neurological disorders of eye; BMS; electrolyte abnormalities; AHUS; embryo-fetal toxicity | Systemic: Hypokalemia; pain; fever; hypocalcemia; hyponatremia; anemia; thrombocytopenia; lymphopenia; neutropenia; increased AST, ALT; GI Cutaneous: Urticaria |
| Dostarlimab-gxly (Jemperli®) | PD-1 | Immune-mediated colitis, pneumonitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies, nephritis, dermatologic adverse reactions; IR; complications of allogeneic HSCT after PD-1/L-1–blocking antibody; embryo-fetal toxicity | Systemic: Fatigue/asthenia; nausea; diarrhea; anemia |
| Durvalumab (Imfinzi®) | PD-L1 | Immune-mediated pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, nephritis, endocrinopathies; dermatologic reactions; embryo-fetal toxicity; infections; IR | Systemic: Fatigue; musculoskeletal pain; diarrhea; nausea; decreased appetite; peripheral edema; urinary tract infection; pneumonitis; dyspnea; URTI; cough Cutaneous: Rash; pruritus |
| Elotuzumab (Empliciti®) | SLAMF7 | IR; infections; second primary malignancies; hepatotoxicity; interference in monitoring M-protein impacting determination of complete response in patients with IgGκ myeloma protein | Systemic: Fatigue; diarrhea; pyrexia; constipation; cough; peripheral neuropathy; nasopharyngitis; URTI; decreased appetite; pneumonia |
| Enfortumab-vedotin-ejfv (Padcev®) | Nectin-4 with MMAE microtubule inhibitor | Hyperglycemia; peripheral neuropathy; ocular disorders; skin reactions; infusion site extravasation; embryo-fetal toxicity | Systemic: Fatigue; peripheral neuropathy; decreased appetite; rash; alopecia; nausea; dysgeusia; diarrhea; dry eye Cutaneous: Pruritus; dry skin |
| Fam-trastuzumab deruxtecan-nxki (Enhertu®) | HER2 | Boxed warning: ILD and pneumonitis; embryo-fetal toxicity Other: Neutropenia; LVD | Systemic: Decreased hemoglobin, white blood cells, neutrophils, lymphocytes, platelets; nausea; vomiting; constipation; fatigue; decreased appetite; anemia; diarrhea; hypokalemia; pyrexia; alopecia; increased blood bilirubin, aspartate aminotransferase, AP, alanine aminotransferase |
| Gemtuzumab ozogamicin (Mylotarg®) | CD33 | Boxed warning: Hepatotoxicity including severe or fatal hepatic veno-occlusive disease Other: IR including anaphylaxis; hemorrhage; embryo-fetal toxicity | Systemic: Hemorrhage; infection; fever; nausea; vomiting; constipation; headache; increased ALT, AST; mucositis Cutaneous: Rash |
| Ibritumomab tiuxetan (Zevalin®) | CD20 | Boxed warning: Serious IR; severe cytopenias; severe mucocutaneous and cutaneous reactions Other: MDS and AML; extravasation; immunization | Systemic: Infections; asthenia; musculoskeletal symptoms; GI; hemorrhage; hypersensitivity Cutaneous: Exfoliative dermatitis; bullous dermatitis; EM; SJS; TEN |
| Inotuzumab ozogamicin (Besponsa®) | CD22 | Boxed warning: Hepatotoxicity including hepatic veno-occlusive disease; increased risk of post- transplant non-relapse mortality Other: myelosuppression; embryo- fetal toxicity; QT interval prolongation | Systemic: IR; cytopenias; nausea; fatigue; hemorrhage; pyrexia; infection; headache; febrile neutropenia; increased transaminases; hyperbilirubinemia |
| Ipilimumab (Yervoy®) | CTLA-4 | Boxed warning: Immune-mediated adverse reactions | Systemic: Diarrhea; fatigue; colitis Cutaneous: Rash; pruritus; dermatitis |
| Isatuximab-irfc (Sarclisa®) | CD38 | IR; neutropenia; second primary malignancies; indirect antiglobulin test and interference with serum electrophoresis and immunofixation tests | Systemic: Neutropenia; IR; pneumonia; URTI; diarrhea; anemia; lymphopenia; thrombocytopenia |
| Loncastumab tesirine-lpyl (Zynlonta®) | CD19 with teserine cytotoxic agent | Effusions (pericardial, pleural, ascites); embryo-fetal toxicity; myelosuppression; infections; cutaneous reactions (including photosensitivity) | Systemic: Thrombocytopenia; increased gamma-glutamyltransferase; neutropenia; nausea; anemia; hyperglycemia; transaminase elevation; fatigue; hypoalbuminemia; edema; musculoskeletal pain Cutaneous: Rash |
| Margetuximab-cmkb (Margenza®) | HER2 | Boxed warning: LVD; embryo-fetal toxicity | Systemic: Fatigue/asthenia; nausea; diarrhea; vomiting; constipation; IR; headache; pyrexia; alopecia; abdominal pain; peripheral neuropathy; arthralgia/myalgia; cough; decreased appetite; dyspnea; extremity pain Cutaneous: PPE |
| Mogamulizumab-kpkc (Poteligeo®) | CCR4 | Dermatologic toxicity; IR; infections; autoimmune reactions; HSCT complications | Systemic: IR; diarrhea; fatigue; URTI; musculoskeletal pain Cutaneous: Rash |
| Moxetumomab pasudox- tdfk (Lumoxiti®) | CD22 | Boxed warning: CLS; hemolytic uremic syndrome Other: Renal toxicity; electrolyte abnormalities; IR | Systemic: Edema; nausea; fatigue; headache; pyrexia; constipation; diarrhea; anemia; increased creatinine, ALT, AST; hypophosphatemia; hypocalcemia |
| Naxitamab-gqgk (Danyelza®) | GD2 | Boxed warning: Serious IR; neurotoxicity including RPLS | Systemic: IR; isr; pain; tachycardia; vomiting; cough; nausea; diarrhea; decreased appetite; hypertension; fatigue; peripheral neuropathy; edema; urticaria; pyrexia; headache; anxiety; irritability; decreased lymphocytes; neutrophils, hemoglobin, platelets, K, Ca, Na, glucose, albumin, phosphate; increased alanine aminotransferase Cutaneous: EM |
| Necitumumab (Portrazza®) | EGFR | Boxed warning: Cardiopulmonary arrest; hypo-magnesemia Other: Venous, arterial thromboembolic events; dermatologic toxicities; embryo-fetal toxicity; ↑ toxicity, mortality in patients with non- squamous NSCLC; IR | Systemic: Diarrhea; vomiting Cutaneous: Rash; dermatitis acneiform |
| Nivolumab (OPDIVO®) | PD-1 | Immune-mediated adverse reactions; embryo-fetal toxicity | Systemic: Increased ALT, AST, AP; hyponatremia; hyper- and hypokalemia; hyper- and hypocalcemia; lymphopenia; fatigue; asthenia; musculoskeletal and abdominal pain; dyspnea; cough; GI. Cutaneous: Rash; pruritus |
| Obinutuzumab (Gazyva®; Gazyvaro®) | CD20 | Boxed warning: Hepatitis B virus reactivation; PML. Other: IR; TLS; neutropenia; thrombocytopeia; infections; immunization | Systemic: Anemia; pyrexia; musculoskeletal disorders; headache; cough |
| Ofatumumab (Arzerra®) | CD20 | IR; Hepatitis B virus reactivation; PML; cytopenias intestinal obstruction; immunization | Systemic: Infections; pneumonia; neutropenia; pyrexia; dyspnea; cough; diarrhea; URTI; nausea; fatigue; bronchitis Cutaneous: Rash; urticaria; hyperhidrosis. |
| Olaratumab (Lartruvo®) | PDGFR-α | IR; embryo-fetal toxicity | Systemic: Olaratumab + doxorubicin: fatigue; musculoskeletal pain; diarrhea; decreased appetite; headache; neuropathy; cytopenias; hyperglycemia; elevated aPTT; hypokalemia; hypophosphatemia Cutaneous: Alopecia |
| Panitumumab (Vectibix®) | EGFR | Boxed warning: Dermatologic toxicity; IR Other: Increased toxicity with bevacizumab and chemotherapy; pulmonary toxicities; electrolyte depletion; ocular events | Systemic: Pulmonary events; pulmonary embolism; GI; fatigue; abdominal pain; hypomagnesemia Cutaneous: Rash; dermatitis ‘acneiform’; erythema; exfoliation; paronychia; skin fissures; photosensitivity; xerosis; pruritus |
| Pembrolizumab (Keytruda®) | PD-1 | Immune-mediated adverse reactions; embryo-fetal toxicity | Systemic: Fatigue; peripheral edema; chills; pyrexia; renal failure; cellulitis; decreased appetite; dyspnea; arthralgia; nausea; diarrhea; cough Cutaneous: Rash; pruritus; vitiligo |
| Pertuzumab (Perjeta®) | HER2 | Boxed warning: Cardiomyopathy; embryo-fetal toxicity. Other: IR; hypersensitivity/anaphylaxis | Systemic: Neutropenias; LVD; peripheral neuropathy; fatigue; GI; asthenia Cutaneous: Rash; paronychia; pruritus; alopecia; PPE (in combination therapy) |
| Polatuzumab vedotin-piiq (Polivy®) | CD79b | Peripheral neuropathy; myelosuppression and related reactions; infections; IR; TLS; PML; hepatotoxicity; embryo-fetal toxicity | Systemic: Cytopenia; fatigue; decreased appetite; diarrhea; pyrexia; pneumonia |
| Ramucirumab (Cyramza®) | VEGFR2 | Boxed warning: Hemorrhage; GI perforation; impaired wound healing. Other: A rterial thromboembolic events; IR; RPLS; hypertension; deterioration in patients with cirrhosis; proteinuria including nephrotic syndrome; thyroid dysfunction; embryo-fetal risk | Systemic: Hypertension; diarrhea; headache; hytremia; neutropenia; epistaxis; stomatitis; immunogenicity |
| Rituximab (Rituxan®; MabThera®) | CD20 | Boxed warning: Fatal IRs; TLS; potentially fatal PML and severe mucocutaneous reactions Other: hepatitis B virus reactivation; infections; cardiac arrhythmias; bowel obstruction and perforation | Systemic: Pulmonary events; renal toxicity; neutropenias; serum sickness; anaphylaxis; fever; lymphopenia; chills; asthenia Cutaneous: Paraneoplastic pemphigus; lichenoid dermatitis; vesicullobullous dermatitis; SJS; TEN |
| Sacituzumab govitecan-hziy (Trodelvy®) | Trop-2 with topoisomerase inhibitor | Boxed warning: Severe neutropenia; severe diarrhea Other: Hypersensitivity; nausea/vomiting; risk of neutropenia increased in individuals with reduced uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyl transferase 1A1; embryo-fetal toxicity | Systemic: Nausea; neutropenia; diarrhea; fatigue; anemia; vomiting; alopecia; constipation; decreased appetite; abdominal pain Cutaneous: Rash |
| Siltuximab (Sylvant®) | IL-6 | Not for patients with severe infections or live vaccines; IR; cautionary use in patients with GI perforation risk | Systemic: Hyperuricemia; URTI; increased weight Cutaneous: Rash; pruritus |
| Tafasitamab-cxix (Monjuvi®) | D19 | IR; myelosuppression; infections; embryo-fetal toxicity | Systemic: Neutropenia; fatigue; anemia; diarrhea; thrombocytopenia; cough; pyrexia; peripheral edema; URTI; decreased appetite |
| Tisotumab vedotin-tftv (Tivdak®) | TF with MMAE microtubule inhibitor | Boxed warning: Ocular toxicity Other: Ocular adverse reactions, e.g., conjunctival reactions, dry eyes, corneal reactions, blepharitis; ulcerative keratitis; peripheral neuropathy; pneumonitis; embryo- fetal toxicity | Systemic: Most serious: ileus; hemorrhage; pneumonia; sepsis; pyrexia; peripheral neuropathy; constipation. Most common: diarrhea; peripheral neuropathy; conjunctival and corneal reactions; fatigue; alopecia; epistaxis; decreased hemoglobin, lymphocytes, and leukocytes; increased creatinine; dry eye; prothrombin international normalized ratio; aPTT prolonged Cutaneous: Rash |
| Trastuzumab (Herceptin®) | HER2 | Boxed warning: Cardiomyopathy; IR; pulmonary toxicity Other: Exacerbation of chemotherapy-induced neutropenia; embryo-fetal toxicity | Systemic: Neutropenia; anemia; thrombocytopenia; pulmonary events; LVD; GI; chills; fever; URTI; anaphylaxis/angioedema; headache; cough; stomatitis; mucosal inflammation Cutaneous: Rash; nail disorders; pruritus |
| Anaphylaxis 1 | Infusion Reactions | Cytopenias | Pulmonary Adverse Events 2 | Cardiac Adverse Events | Hepatotoxicity 2 | Other Immune- Mediated Reactions 3 | Embryo-Fetal Toxicity | Dermatologic Toxicity 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monoclonal Antibodies for non-cancer therapy | ||||||||
| Adalimumab Belimumab Casirivimab+ Imdevimab 4 Certolizumab pegol Evinacumab-dgnb Infliximab Obiltoxaximab Omalizumab Palivisumab Regdanvirimab Reslizumab Tocilizumab Ustekinumab | Alemtuzumab 5 Anifrolumab-fnia Ansuvimab-zykl Atoltivimab 6 Belimumab Casirivimab+ Imdevimab 4 Crizanlizumab-tmca Emapalumab-lzsg Inebilizumab-cdon Infliximab Obiltoxaximab Ocrelizumab Raxibacumab Regdanvirimab Sotrovimab Teprotumumab-trbw Tocilizumab Vedolizumab | Abciximab Adalimumab Alemtuzumab 5 Brodalumab Certolizumab pegol Infliximab Palivisumab Sarilumab Satralizumab-mwge Tocilizumab | Adalimumab Alemtuzumab 5 Golimumab Infliximab | Adalimumab Bezlotoxumab Certolizumab pegol Golimumab Romosozumab-aqqg | Adalimumab Certolizumab pegol Daclizumab Evolocumab Infliximab Natalizumab Vedolizumab | Adalimumab Alemtuzumab Alirocumab Daclizumab Infliximab Omalizumab | Evinacumab-dgnb Inebilizumab-cdon | Abciximab Adalimumab Alemtuzumab 5 Alirocumab Bimekizumab Certolizumab pegol Daclizumab Denosumab 7 Evolocumab Golimumab Infliximab Natalizumab Obiltoxaximab Ocrelizumab Omalizumab Raxibacumab Secukinumab Tocilizumab |
| Monoclonal Antibodies for cancer therapy | ||||||||
| Brentuximab vedotin Cetuximab Gemtuzumab ozogamicin Pertuzumab Rituximab Trastuzumab | Ado-trastuzumab Alemtuzumab 8 Amivantamab-vmjw Atezolizumab Avelumab Belantamab mafodoton-blmf Bevacizumab Brentuximab vedotin Cemiplimab-rwlc Cetuximab Daratumumab Dinutuximab Dostarlimab-gxly Durvalumab Elotuzumab Gemtuzumab ozogamicin Ibritumomab tiuxetan Inotuzumab ozogamicin Isatuximab-irfc Mogamulizumab-kpkc Moxetumomab pasudox-tdfk Naxitamab-gqgk Necitumumab Obinutuzumab Ofatumumab Olaratumab Panitumumab Pertuzumab Polatuzumab vedotin-piiq Ramucirumab Rituximab Siltuximab Tafasitamab-cxix Trastuzumab | Ado-trastuzumab Alemtuzumab 8 Belantamab mafodoton-blmf Blinatumomab Brentuximab vedotin Catumaxomab Daratumumab Dinutuximab Fam-trastuzumab deruxtecan-nxki Ibritumomab tiuxetan Inotuzumab ozogamicin Isatuximab-irfc Loncastumab-tesirine-lpyl Naxitamab-gqgk Obinutuzumab Ofatumumab Olaratumab Pertuzumab Polatuzumab vedotin-piiq Ramucirumab Rituximab Sacituzumab govetican-hziy Tafasitamab-cxix Tisotumab vedotin-tftv Trastuzumab | Ado-trastuzumab Alemtuzumab 8 Amivantamab-vmjw Atezolizumab Avelumab Bevacizumab Cemiplimab-rwlc Cetuximab Dostarlimab-gxly Durvalumab Fam-trastuzumab deruxtecan-nxki Ipilimumab Nivolumab Panitumumab Pembrolizumab Rituximab Tisotumab vedotin-tftv Trastuzumab | Ado-trastuzumab Alemtuzumab 8 Bevacizumab Cetuximab Fam-trastuzumab deruxtecan-nxki Ibritumomab tiuxetan Inotuzumab ozogamicin Margetuximab-cmkb Necitumumab Obinutuzumab Pertuzumab Ramucirumab Rituximab Romosozumab-aqqg Trastuzumab | Ado-trastuzumab Atezolizumab Avelumab Brentuximab vedotin Catumaxomab Cemiplimab-rwlc Dostarlimab-gxly Durvalumab Elotuzumab Gemtuzumab ozogamicin Inotuzumab Ozogamicin Obinutuzumab Ofatumumab Polatuzumab vedotin-piiq Rituximab | Atezolizumab Avelumab Cemiplimab-rwlc Dostarlimab-gxly Durvalumab Ipilimumab Mogamulizumab-kpkc Nivolumab Pembrolizumab | Amivantamab-vmjw Atezolizumab Belantamab mafodoton-blmf Cemiplimab-rwlc Denosumab 9 Dinutuximab Dostarlimab-gxly Durvalumab Enfortumab vedotin-ejfv Fam-trastuzumab Gemtuzumab ozogamicin Inotuzumab ozogamicin Loncastumab tesirine-lpyl Margetuximab-cmkb Necitumumab Nivolumab Olaratumab Pembrolizumab Pertuzumab Polatuzumab vedotin-piiq Ramucirumab Sacituzumab govetican-hziy Tafasitamab-cxix Tisotumab vedotin-tftv Trastuzumab | Alemtuzumab 8 Amivantamab-vmjw Bevacizumab Brentuximab vedotin Catumaxomab Cemiplimab-rwlc Cetuximab Denosumab 9 Dostarlimab-gxly Durvalumab Enfortumab vedotin-ejfv Ibritumomab tiuxetan Ipilimumab Loncastumabtesirine-lpyl Margetuximab-cmkb Mogamulizumab-kpkc Naxitamab-gqgk Necitumumab Panitumumab Pembrolizumab Pertuzumab Rituximab Trastuzumab |
| Cytopenia | Thrombocytopenia | Neutropenia | Lymphocytopenia |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adalimumab | Abciximab | Bevacizumab | Catumaxomab |
| Alemtuzumab 1 | Ado-trastazumab emtansine | Blinatumomab | |
| Certolizumab pegol | Belantamab mafodoton-blmf | Brentuximab vedotin | |
| Ibritumomab tiuxetan 1 | Daratumumab | Daratumumab | |
| Infliximab | Palivisumab | Fam-trastuzumab Deruxtecan-nxki | |
| Ofatumumab | Sarilumab | Isatuximab-irfc | |
| Obinutuzumab | |||
| Sacituzumab govitecan-hziy 1 | |||
| Sarilumab | |||
| Satralizumab-mwge | |||
| Trastuzumab |
| Monoclonal Antibody | Cardiac Adverse Events |
|---|---|
| Adalimumab. | Heart failure |
| Ado-trastuzumab emtansine 1 | Decreased LVEF |
| Alemtuzumab | Cardiomyopathy, decreased LVEF, cardiac arrhythmias associated with infusions |
| Bevacizumab | CHF: incidence of grade 3 reaction for LVD 1% |
| Bezlotoxumab | Heart failure |
| Brentuximab vedotin | Supraventricular arrhythmia in systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma |
| Certolizumab pegol | Heart failure |
| Cetuximab | Cardiopulmonary arrest/sudden death |
| Fam-trastuzumab deruxtecan-nxki | LVD |
| Golimumab | Heart failure |
| Ibritumomab tiuxetan | Cardiac arrest related to infusions |
| Inotuzumab ozogamicin | QT interval prolongation |
| Margetuximab-cmkb 1 | LVD |
| Necitumumab 1 | Cardiopulmonary arrest |
| Obinutuzumab | Worsening of preexisting cardiac conditions leading to fatal cardiac events |
| Pertuzumab 1 | Cardiomyopathy manifesting as CHF and decreased LVEF |
| Ramucirumab | Serious, sometimes fatal, myocardial infarction |
| Rituximab | Cardiac arrhythmias and angina, fatal cardiac failure |
| Romosozumab-aqqg 1 | Myocardial infarction, cardiac events, cardiovascular death |
| Trastuzumab 1 | Cardiomyopathy manifesting as CHF and decreased LVEF |
| Monoclonal Antibody | Liver Adverse Events |
|---|---|
| Adalimumab | Reactivates hepatitis B; liver failure |
| Ado-trastuzumab | Hepatotoxicity |
| Atezolizumab | Immune-mediated hepatitis |
| Avelumab | Immune-mediated hepatitis |
| Brentuximab vedotin | Hepatotoxicity |
| Catumaxomab | Hepatic disorders—hepatotoxicity |
| Cemiplimab-rwlc | Immune-mediated hepatitis |
| Certolizumab pegol | Reactivates hepatitis B |
| Daclizumab | Hepatic injury including autoimmune hepatitis |
| Dostarlimab-gxly | Immune-mediated hepatitis |
| Durvalumab | Immune-mediated hepatitis |
| Elotuzumab | Hepatotoxicity |
| Evolocumab | Hepatic impairment |
| Gemtuzumab ozogamicin | Hepatotoxicity including severe or fatal hepatic veno-occlusive disease |
| Golimumab | Reactivates hepatitis B |
| Infliximab | Hepatotoxicity |
| Inotuzumab ozogamicin | Hepatotoxicity including severe or fatal hepatic veno-occlusive disease |
| Natalizumab | Hepatotoxicity |
| Obinutuzumab | Reactivates hepatitis B |
| Ofatumumab | Reactivates hepatitis B |
| Polatuzumab vedotin-piiq | Hepatotoxicity |
| Rituximab | Reactivates hepatitis B |
| Vedolizumab | Possibility of liver injury suggested by elevated levels of transaminase and/or bilirubin |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baldo, B.A. Immune- and Non-Immune-Mediated Adverse Effects of Monoclonal Antibody Therapy: A Survey of 110 Approved Antibodies. Antibodies 2022, 11, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib11010017
Baldo BA. Immune- and Non-Immune-Mediated Adverse Effects of Monoclonal Antibody Therapy: A Survey of 110 Approved Antibodies. Antibodies. 2022; 11(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib11010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaldo, Brian A. 2022. "Immune- and Non-Immune-Mediated Adverse Effects of Monoclonal Antibody Therapy: A Survey of 110 Approved Antibodies" Antibodies 11, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib11010017
APA StyleBaldo, B. A. (2022). Immune- and Non-Immune-Mediated Adverse Effects of Monoclonal Antibody Therapy: A Survey of 110 Approved Antibodies. Antibodies, 11(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib11010017






