Anti-RuvBL1/2 Autoantibodies Detection in a Patient with Overlap Systemic Sclerosis and Polymyositis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
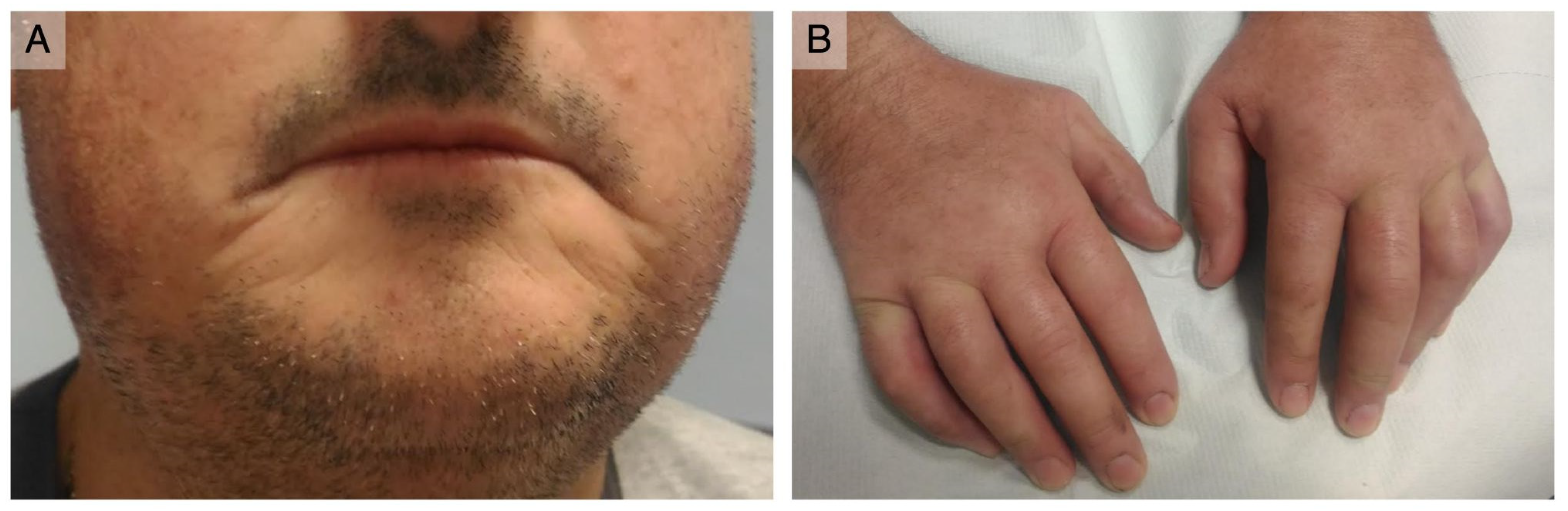
3.1. Case Report
3.2. Review of the Literature
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACAs | Anti-centromere autoantibodies |
| ACE | Angiotensin-converting enzyme |
| ANA | Antinuclear antibody |
| ATAs | Anti-topoisomerase I autoantibodies |
| CREST | Calcinosis, RP, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, and telangiectasia |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| DLCO | Diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide |
| EF | Ejection fraction |
| ESR | Erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
| FVC | Forced vital capacity |
| FEV1 | Forced expiratory volume in one second |
| GAVE | Gastric antral venous ectasia |
| GI | Gastro-intestinal tract |
| HRCT | High-resolution computed tomography |
| ICAP | International Consensus on ANA Patterns |
| IVIG | Intravenous immunoglobulin |
| IIF | Indirect immunofluorescence |
| IIM | Idiopathic inflammatory myopathy |
| ILD | Interstitial lung disease |
| MCTD | Mixed connective tissue disease |
| NSAIDs | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| PAP | Pulmonary arterial pressure |
| PFT | Pulmonary function test |
| PMAT | Particle multi-analyte technology |
| RNAP3 | Anti-RNA polymerase III |
| RP | Raynaud’s phenomenon |
| SSc | Systemic sclerosis |
| TLC | Total lung capacity |
| UCTD | Undifferentiated connective tissue disease |
References
- Tan, E.M.; Rodnan, G.P.; Garcia, I.; Moroi, Y.; Fritzler, M.J.; Peebles, C. Diversity of antinuclear antibodies in progressive systemic sclerosis. Anti-centromere antibody and its relationship to CREST syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1980, 6, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner, E.S.; Earnshaw, W.C.; Senécal, J.L.; Bordwell, B.; Johnson, P.; Rothfield, N.F. Clinical associations of anticentromere antibodies and antibodies to topoisomerase I. A study of 355 patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1988, 31, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Hoogen, F.; Khanna, D.; Fransen, J.; Johnson, S.R.; Baron, M.; Tyndall, A.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Naden, R.P.; Medsger, T.A., Jr.; Carreira, P.E.; et al. 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: An American college of rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domsic, R.T.; Medsger, T.A. Autoantibodies and Their Role in Scleroderma Clinical Care. Curr. Treat. Options Rheum. 2016, 2, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavazzana, I.; Vojinovic, T.; Airo’, P.; Fredi, M.; Ceribelli, A.; Pedretti, E.; Lazzaroni, M.G.; Garrafa, E.; Franceschini, F. Systemic Sclerosis-Specific Antibodies: Novel and Classical Biomarkers. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 18, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroni, S.S.; Santillo, M.; Bevilacqua, F.; Luchetti, M.; Spadoni, T.; Mancini, M.; Fraticelli, P.; Sambo, P.; Funaro, A.; Kazlauskas, A.; et al. Stimulatory autoantibodies to the PDGF receptor in systemic sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2667–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzler, M.J.; Hudson, M.; Choi, M.Y.; Mahler, M.; Wang, M.; Bentow, C.; Milo, J.; Baron, M.; Canadian Scleroderma Research Group. Bicaudal D2 is a novel autoantibody target in systemic sclerosis that shares a key epitope with CENP-A but has a distinct clinical phenotype. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, M.; Raijmakers, R. Novel aspects of autoantibodies to the PM/Scl complex: Clinical, genetic and diagnostic insights. Autoimmun. Rev. 2007, 6, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betteridge, Z.E.; Woodhead, F.; Lu, H.; Shaddick, G.; Bunn, C.C.; Denton, C.P.; Abraham, D.J.; du Bois, R.M.; Lewis, M.; Wells, A.U.; et al. Brief Report: Anti-Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2B Autoantibodies Are Associated with Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2778–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorynia, S.; Bandeiras, T.M.; Pinho, F.G.; McVey, C.E.; Vonrhein, C.; Round, A.; Svergun, D.I.; Donner, P.; Matias, P.M.; Carrondo, M.A. Structural and functional insights into a dodecameric molecular machine-the RuvBL1/RuvBL2 complex. J. Struct. Biol. 2011, 176, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaji, K.; Fertig, N.; Medsger TAJr Satoh, T.; Hoshino, K.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Hasegawa, M.; Lucas, M.; Schnure, A.; Ogawa, F.; Sato, S.; et al. Autoantibodies to RuvBL1 and RuvBL2: A novel systemic sclerosis-related antibody associated with diffuse cutaneous and skeletal muscle involvement. Arthritis Care Res. 2014, 66, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palterer, B.; Vitiello, G.; Carraresi, A.; Giudizi, M.G.; Cammelli, D.; Parronchi, P. Bench to bedside review of myositis autoantibodies. Clin. Mol. Allergy. 2018, 16, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Nakanishi, T.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Fujimoto, N. Case of anti-RuvBL1/2 antibody-positive morphea and polymyositis. J. Dermatol. 2017, 44, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauling, J.D.; Salazar, G.; Lu, H.; Betteridge, Z.E.; Assassi, S.; Mayes, M.D.; McHugh, N.J. Presence of anti-eukaryotic initiation factor-2B, anti-RuvBL1/2 and anti-synthetase antibodies in patients with anti-nuclear antibody negative systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, Y.; Ueda-Hayakawa, I.; Yamazaki, F.; Ozaki, Y.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Takehara, K.; Okamoto, H. A case of anti-RuvBL1/2 antibody-positive systemic sclerosis overlapping with myositis. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2020, 30, 52–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landon-Cardinal, O.; Baril-Dionne, A.; Hoa, S.; Meyer, A.; Leclair, V.; Bourré-Tessier, J.; Mansour, A.M.; Zarka, F.; Makhzoum, J.P.; Nehme, J.; et al. Recognising the spectrum of scleromyositis: HEp-2 ANA patterns allow identification of a novel clinical subset with anti-SMN autoantibodies. RMD Open 2020, 6, e001357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulsteke, J.B.; Piette, Y.; Bonroy, C.; Verschueren, P.; Blockmans, D.; Vanderschueren, S.; Claeys, K.G.; De Haes, P.; Lenaerts, J.L.; Wuyts, W.A.; et al. Anti-RuvBL1/2 autoantibodies in patients with systemic sclerosis or idiopathic inflammatory myopathy and a nuclear speckled pattern. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 742–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranque, B.; Bérezné, A.; Le-Guern, V.; Pagnoux, C.; Allanore, Y.; Launay, D.; Hachulla, E.; Authier, F.J.; Gherardi, R.; Kahan, A.; et al. Myopathies related to systemic sclerosis: A case-control study of associated clinical and immunological features. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 39, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclair, V.; D’Aoust, J.; Gyger, G.; Landon-Cardinal, O.; Meyer, A.; O’Ferrall, E.; Karamchandani, J.; Massie, R.; Ellezam, B.; Satoh, M.; et al. Autoantibody profiles delineate distinct subsets of scleromyositis. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzler, M.J.; Choi, M.Y.; Satoh, M.; Mahler, M. Autoantibody Discovery, Assay Development and Adoption: Death Valley, the Sea of Survival and Beyond. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 679613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, I.E.; Tjärnlund, A.; Bottai, M.; Werth, V.P.; Pilkington, C.; Visser, M.; Alfredsson, L.; Amato, A.A.; Barohn, R.J.; Liang, M.H.; et al. 2017 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for adult and juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and their major subgroups. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Authors, Year [Ref.] (PMID) | No. of Patients | Age | Gender | Anti-RuvBL1/2 Autoabs Prevalence in the Cohort | Other SSc- or IIM-Related Autoabs | ANA Pattern on HEp-2 Cells IIF (Titer) | Organ Involvement | Final Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kaji et al. (2014) [11] (24023044) | Japan cohorts 10 | 58.1 ± 12.1 | 5 F 5 M | 6/316 SSc pts. (1.9%) 4/272 SSc pts. (1.5%) | 11% (4/37: 1 RNAP3/Ku, 1 RNAP3, 1 Ku, 1 Th/To) | Speckled (1:160–1:1280) + in 4/10 cytoplasmic granular | ILD 70%; GI 60%; Muscle 60%; Heart 50%; PAH 10%; Renal crisis 0% | dSSc/IIM 40%; dSSc 27%; lSSc/IIM 19%; lSSc 14% |
| Kaji et al. (2014) [11] (24023044) | Pittsburgh cohort 27 | 46.0 ± 15.1 | 17 F 10 M | 27/485 SSc pts. (5.6%) | n/a | GI 94% *; Muscle 59%; ILD 50% *; PAH 13% *; Heart 22% *; Renal crisis 4% | ||
| Takahashi et al. (2017) [13] (27786369) | 1 | 42 | 1 F | - | SSc: Neg. IIM: AMA | Speckled (1:2560) | Neg | Morphea/IIM overlap |
| Pauling et al. (2018) [14] (29294089) | 2 | n/a | 2 F | 2/128 ANA neg. SSc pts. (1.6%) | SSc: Neg. IIM: n/a | ANA neg | PAH 50%; Muscle 50%; Renal crisis 0%; Others n/a | 1 dSSc/IIM; 1 lSSc/SjS |
| Nomura et al. (2020) [15] (32031537) | 1 | 21 | 1 F | - | Neg. | Speckled (1:1280) | Muscle; Lung; GI; Heart: no; Kidney: n/a | dSSc/IIM |
| Landon-Cardinal et al. (2020) [16] (32892170) | 2 | n/a | n/a | 2/20 seronegative SSc pts. (10%) | Neg. | Fine speckled (1:640) 1/2; Large speckled (1:1280) 1/2 | Muscle 100%; GI 100%; Renal crisis 50%; ILD 0%; Others n/a | dSSc/IIM |
| Vulsteke al. (2022) [17] (35027396) | 8 | 52.6 ± 12 | 2 F 6 M | 8/51 SSc pts. (16%) | Neg. | Fine or large speckled (≥1:80) + in 6/8 cytoplasmic speckled | ILD 88%; Muscle 62%; Heart 50%; GI 25%; PAH 0%; Renal crisis 0% | dSSc/IIM 25%; lSSc/IIM 25%; dSSc 25%; lSSc 12.5%; SSc sine scleroderma/IIM 12.5% |
| Di Pietro et al. (2022); Current case report | 1 | 48 | 1 M | - | Neg. | Fine speckled + cytoplasmic speckled | Muscle, Heart, GI, ILD | SSc/IIM |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Pietro, L.; Chiccoli, F.; Salvati, L.; Vivarelli, E.; Vultaggio, A.; Matucci, A.; Bentow, C.; Mahler, M.; Parronchi, P.; Palterer, B. Anti-RuvBL1/2 Autoantibodies Detection in a Patient with Overlap Systemic Sclerosis and Polymyositis. Antibodies 2023, 12, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib12010013
Di Pietro L, Chiccoli F, Salvati L, Vivarelli E, Vultaggio A, Matucci A, Bentow C, Mahler M, Parronchi P, Palterer B. Anti-RuvBL1/2 Autoantibodies Detection in a Patient with Overlap Systemic Sclerosis and Polymyositis. Antibodies. 2023; 12(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib12010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Pietro, Linda, Fabio Chiccoli, Lorenzo Salvati, Emanuele Vivarelli, Alessandra Vultaggio, Andrea Matucci, Chelsea Bentow, Michael Mahler, Paola Parronchi, and Boaz Palterer. 2023. "Anti-RuvBL1/2 Autoantibodies Detection in a Patient with Overlap Systemic Sclerosis and Polymyositis" Antibodies 12, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib12010013
APA StyleDi Pietro, L., Chiccoli, F., Salvati, L., Vivarelli, E., Vultaggio, A., Matucci, A., Bentow, C., Mahler, M., Parronchi, P., & Palterer, B. (2023). Anti-RuvBL1/2 Autoantibodies Detection in a Patient with Overlap Systemic Sclerosis and Polymyositis. Antibodies, 12(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib12010013







