Characterization of Co-Formulated High-Concentration Broadly Neutralizing Anti-HIV-1 Monoclonal Antibodies for Subcutaneous Administration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Monoclonal Antibodies
2.1.2. Reagents
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Reverse Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC)
2.2.2. Ion Exchange (IEX)—HPLC
2.2.3. Size-Exclusion High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (SE-HPLC)
2.2.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.2.5. Virus Neutralization Assays
2.2.6. FlowCAM® Imaging
2.2.7. Osmolality
2.2.8. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
3. Results
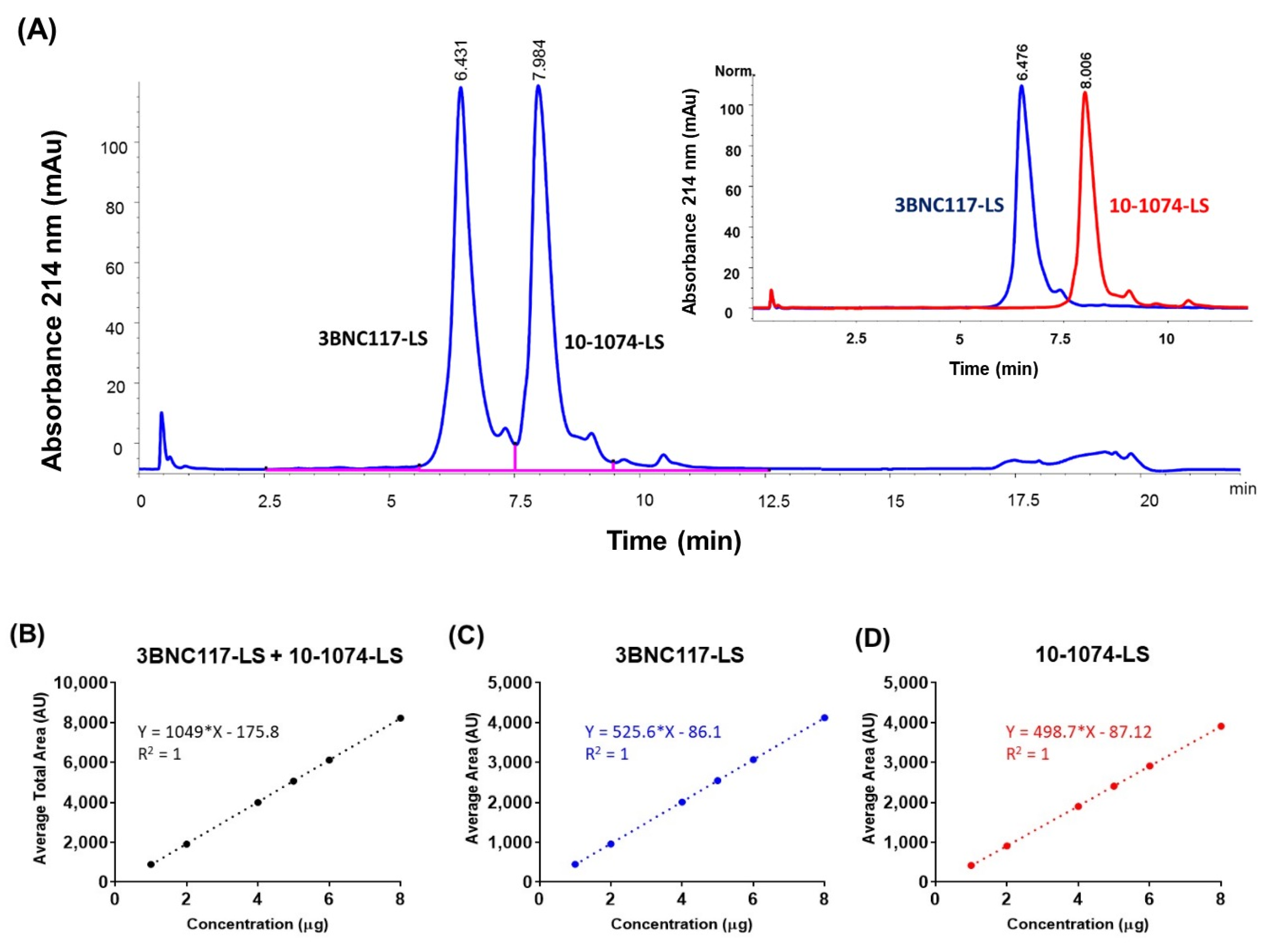
3.1. Chromatographic Separation of Co-Formulated Monoclonal Antibodies
3.2. Reverse Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC)
3.3. Ion Exchange High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (IEX-HPLC)
3.4. Size-Exclusion High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (SE-HPLC)
3.5. Positive Identification of Individual Antibody in the Co-Formulation Sample Using Anti-ID (Idiotype) Based ELISA
3.6. Potency Testing of Individual Antibody in the Co-Formulation Sample Using a Virus Neutralization Assay
3.7. Stability Assessment of Co-Formulated Antibodies
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, S.; Kumar, N.K.; Dwiwedi, P.; Charan, J.; Kaur, R.; Sidhu, P.; Chugh, V.K. Monoclonal Antibodies: A Review. Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 13, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marston, H.D.; Paules, C.I.; Fauci, A.S. Monoclonal Antibodies for Emerging Infectious Diseases—Borrowing from History. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, L.M.; Burton, D.R. Passive immunotherapy of viral infections: ‘super-antibodies’ enter the fray. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeffe, J.R.; Van Rompay, K.K.A.; Olsen, P.C.; Wang, Q.; Gazumyan, A.; Azzopardi, S.A.; Schaefer-Babajew, D.; Lee, Y.E.; Stuart, J.B.; Singapuri, A.; et al. A Combination of Two Human Monoclonal Antibodies Prevents Zika Virus Escape Mutations in Non-human Primates. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geevarghese, B.; Simoes, E.A. Antibodies for prevention and treatment of respiratory syncytial virus infections in children. Antivir. Ther. 2012, 17, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bittner, B.; Richter, W.; Schmidt, J. Subcutaneous Administration of Biotherapeutics: An Overview of Current Challenges and Opportunities. BioDrugs 2018, 32, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoner, K.L.; Harder, H.; Fallowfield, L.J.; Jenkins, V.A. Intravenous versus subcutaneous drug administration. Which do patients prefer? A systematic review. Patient 2015, 8, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stephenson, K.E.; Barouch, D.H. Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies for HIV Eradication. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2016, 13, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pegu, A.; Hessell, A.J.; Mascola, J.R.; Haigwood, N.L. Use of broadly neutralizing antibodies for HIV-1 prevention. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 275, 296–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, P.D.; Mascola, J.R. HIV-1 Vaccines Based on Antibody Identification, B Cell Ontogeny, and Epitope Structure. Immunity 2018, 48, 855–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMichael, A.J.; Haynes, B.F. Lessons learned from HIV-1 vaccine trials: New priorities and directions. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haynes, B.F.; McElrath, M.J. Progress in HIV-1 vaccine development. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2013, 8, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ledgerwood, J.E.; Coates, E.E.; Yamshchikov, G.; Saunders, J.G.; Holman, L.; Enama, M.E.; DeZure, A.; Lynch, R.M.; Gordon, I.; Plummer, S.; et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics and neutralization of the broadly neutralizing HIV-1 human monoclonal antibody VRC01 in healthy adults. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 182, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lynch, R.M.; Boritz, E.; Coates, E.E.; DeZure, A.; Madden, P.; Costner, P.; Enama, M.E.; Plummer, S.; Holman, L.; Hendel, C.S.; et al. Virologic effects of broadly neutralizing antibody VRC01 administration during chronic HIV-1 infection. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 319ra206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caskey, M.; Schoofs, T.; Gruell, H.; Settler, A.; Karagounis, T.; Kreider, E.F.; Murrell, B.; Pfeifer, N.; Nogueira, L.; Oliveira, T.Y.; et al. Antibody 10-1074 suppresses viremia in HIV-1-infected individuals. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- First-in-human Study of 10-1074-LS Alone and in Combination with 3BNC117-LS. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03554408 (accessed on 28 July 2020).
- Scheid, J.F.; Horwitz, J.A.; Bar-On, Y.; Kreider, E.F.; Lu, C.L.; Lorenzi, J.C.; Feldmann, A.; Braunschweig, M.; Nogueira, L.; Oliveira, T.; et al. HIV-1 antibody 3BNC117 suppresses viral rebound in humans during treatment interruption. Nature 2016, 535, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- 3BNC117-LS First-in-Human Phase 1 Study. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03254277 (accessed on 28 July 2020).
- Evaluating the Safety and Pharmacokinetics of VRC01, VRC01LS, and VRC07-523LS, Potent Anti-HIV Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies, in HIV-1-Exposed Infants. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02256631 (accessed on 28 July 2020).
- Safety, PK and Antiviral Activity of PGT121 Monoclonal Antibody in HIV-uninfected and HIV-infected Adults. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02960581 (accessed on 28 July 2020).
- A Clinical Trial of PGDM1400 and PGT121 and VRC07-523LS Monoclonal Antibodies in HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected Adults. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03205917 (accessed on 28 July 2020).
- Bar-On, Y.; Gruell, H.; Schoofs, T.; Pai, J.A.; Nogueira, L.; Butler, A.L.; Millard, K.; Lehmann, C.; Suarez, I.; Oliveira, T.Y.; et al. Safety and antiviral activity of combination HIV-1 broadly neutralizing antibodies in viremic individuals. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1701–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, P.; Gruell, H.; Nogueira, L.; Pai, J.A.; Butler, A.L.; Millard, K.; Lehmann, C.; Suarez, I.; Oliveira, T.Y.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; et al. Combination therapy with anti-HIV-1 antibodies maintains viral suppression. Nature 2018, 561, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halper-Stromberg, A.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Towards HIV-1 remission: Potential roles for broadly neutralizing antibodies. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mueller, C.; Altenburger, U.; Mohl, S. Challenges for the pharmaceutical technical development of protein coformulations. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2018, 70, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, M.; De Mel, N.; Shannon, A.; Prophet, M.; Wang, C.; Xu, W.; Niu, B.; Kim, J.; Albarghouthi, M.; Liu, D.; et al. Charge variants characterization and release assay development for co-formulated antibodies as a combination therapy. MAbs 2019, 11, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.; Gupta, V.; Hickey, J.; Nightlinger, N.S.; Rogers, R.S.; Siska, C.; Joshi, S.B.; Seaman, M.S.; Volkin, D.B.; Kerwin, B.A. Coformulation of Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies 3BNC117 and PGT121: Analytical Challenges During Preformulation Characterization and Storage Stability Studies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 3032–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ko, S.Y.; Pegu, A.; Rudicell, R.S.; Yang, Z.Y.; Joyce, M.G.; Chen, X.; Wang, K.; Bao, S.; Kraemer, T.D.; Rath, T.; et al. Enhanced neonatal Fc receptor function improves protection against primate SHIV infection. Nature 2014, 514, 642–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zalevsky, J.; Chamberlain, A.K.; Horton, H.M.; Karki, S.; Leung, I.W.; Sproule, T.J.; Lazar, G.A.; Roopenian, D.C.; Desjarlais, J.R. Enhanced antibody half-life improves in vivo activity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montefiori, D.C. Measuring HIV neutralization in a luciferase reporter gene assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 485, 395–405. [Google Scholar]
- Sarzotti-Kelsoe, M.; Bailer, R.T.; Turk, E.; Lin, C.L.; Bilska, M.; Greene, K.M.; Gao, H.; Todd, C.A.; Ozaki, D.A.; Seaman, M.S.; et al. Optimization and validation of the TZM-bl assay for standardized assessments of neutralizing antibodies against HIV-1. J. Immunol. Methods 2014, 409, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fekete, S.; Beck, A.; Fekete, J.; Guillarme, D. Method development for the separation of monoclonal antibody charge variants in cation exchange chromatography, Part II: pH gradient approach. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 102, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, S.; Beck, A.; Fekete, J.; Guillarme, D. Method development for the separation of monoclonal antibody charge variants in cation exchange chromatography, Part I: Salt gradient approach. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 102, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbruster, C.; Stiegler, G.M.; Vcelar, B.A.; Jager, W.; Koller, U.; Jilch, R.; Ammann, C.G.; Pruenster, M.; Stoiber, H.; Katinger, H.W. Passive immunization with the anti-HIV-1 human monoclonal antibody (hMAb) 4E10 and the hMAb combination 4E10/2F5/2G12. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 54, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagh, K.; Bhattacharya, T.; Williamson, C.; Robles, A.; Bayne, M.; Garrity, J.; Rist, M.; Rademeyer, C.; Yoon, H.; Lapedes, A.; et al. Optimal Combinations of Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies for Prevention and Treatment of HIV-1 Clade C Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| (A) | ||||||||||
| Samples | ZM249M.PL1 | Q461.e2 | 0013095-2.11 | 62357.14.D3.4589 | ZM53M.PB12 | |||||
| 3BNC117.LS + 10-1074.LS DP | IC50 | IC80 | IC50 | IC80 | IC50 | IC80 | IC50 | IC80 | IC50 | IC80 |
| 0.042 | 0.15 | 0.042 | 0.153 | 1.161 | 15.162 | 0.043 | 0.15 | 0.153 | 0.568 | |
| 3BNC117.LS (control) | 0.037 | 0.13 | 0.039 | 0.143 | 1.396 | >25 | 0.036 | 0.17 | 0.214 | 0.796 |
| 10-1074.LS (control) | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 |
| (B) | ||||||||||
| Samples | C2101.c01 | C4118.c09 | THRO4156.18 | 415.v1.c1 | CNE5 | |||||
| 3BNC117.LS + 10-1074.LS DP | IC50 | IC80 | IC50 | IC80 | IC50 | IC80 | IC50 | IC80 | IC50 | IC80 |
| 0.029 | 0.135 | 0.034 | 0.162 | 1.498 | 8.209 | 0.05 | 0.115 | 0.193 | 0.898 | |
| 3BNC117.LS (control) | 0.044 | 0.15 | 0.051 | 0.183 | 1.939 | 9.815 | 0.048 | 0.142 | 0.193 | 0.911 |
| 10-1074.LS (control) | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 |
| (C) | ||||||||||
| Samples | 1394C9_G1 (Rev-) | ZM247v1 (Rev-) | Du422.1 | 6631.v3.c10 | 377.v4.c9 | |||||
| 3BNC117.LS + 10-1074.LS DP | IC50 | IC80 | IC50 | IC80 | IC50 | IC80 | IC50 | IC80 | IC50 | IC80 |
| 0.02 | 0.077 | 0.02 | 0.099 | 0.032 | 0.114 | 0.157 | 0.796 | 0.418 | 1.397 | |
| 3BNC117.LS (control) | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 |
| 10-1074.LS (control) | 0.033 | 0.119 | 0.036 | 0.162 | 0.045 | 0.161 | 0.189 | 0.968 | 0.433 | 1.515 |
| (D) | ||||||||||
| Samples | 20915593 | T278-50 | 21197826-V1 | Du151.2 | 19715820_A10_H2 | |||||
| 3BNC117-LS + 10-1074-LS DP | IC50 | IC80 | IC50 | IC80 | IC50 | IC80 | IC50 | IC80 | IC50 | IC80 |
| 1.525 | 5.872 | 1.047 | 11.952 | 0.678 | 2.269 | 0.004 | 0.013 | 0.056 | 0.204 | |
| 3BNC117-LS (Control) | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 | >25 |
| 10-1074-LS (control) | 2.02 | 5.817 | 2.174 | 15.13 | 0.613 | 2.188 | 0.005 | 0.015 | 0.074 | 0.253 |
| Test Attributes | Weeks | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
| pH | 5.65 | 5.6 | 5.62 | 5.60 | 5.59 | |
| A280 (mg/mL) | 142 | 137 | 142 | 139 | 149 | |
| Viscosity (cP) | 10.70 | 11.08 | 12.09 | 11.16 | 12.89 | |
| Osmolality (mOsm/Kg) | 345 | 336 | 333 | 336 | 337 | |
| SE-HPLC | HMW (%) | 2.98 | 3.11 | 3.14 | 3.58 | 3.52 |
| Main Peak (%) | 96.90 | 96.81 | 96.84 | 96.41 | 96.46 | |
| CEX-HPLC 3BNC117-LS | Main Peak (%) | 48.78 | 49.08 | 49.15 | 49.27 | 49.71 |
| Pre-Main Peaks (%) | 47.68 | 46.40 | 46.04 | 44.74 | 44.97 | |
| Post-Main Peaks (%) | 3.54 | 4.52 | 4.81 | 5.99 | 5.32 | |
| CEX-HPLC 10-1074-LS | Main Peak (%) | 32.68 | 35.04 | 35.22 | 35.99 | 37.72 |
| Pre-Main Peaks (%) | 61.64 | 59.70 | 59.55 | 59.07 | 57.45 | |
| Post-Main Peaks (%) | 5.68 | 5.26 | 5.23 | 4.94 | 4.83 | |
| RP-HPLC | 3BNC117-LS (mg/mL) | 68.05 | 65.88 | 70.00 | 68.70 | 71.48 |
| 10-1074-LS (mg/mL) | 76.70 | 75.75 | 80.54 | 78.83 | 82.09 | |
| DLS | Z-Average (d.nm) | 10.25 | 10.44 | 10.26 | 10.23 | 10.30 |
| PDI | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.19 | |
| FlowCAM | 2–10 µm (P/mL) | 191 | 101 | 253 | 126 | 475 |
| 10–25 µm (P/mL) | 31 | 23 | 46 | 36 | 107 | |
| 25–50 µm (P/mL) | 15 | 16 | 8 | 9 | 8 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, V.K.; Misra, B.; McManus, K.T.; Avula, S.; Nellaiappan, K.; Caskey, M.; Horowitz, J.; Nussenzweig, M.C.; Seaman, M.S.; Javeri, I.; et al. Characterization of Co-Formulated High-Concentration Broadly Neutralizing Anti-HIV-1 Monoclonal Antibodies for Subcutaneous Administration. Antibodies 2020, 9, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9030036
Sharma VK, Misra B, McManus KT, Avula S, Nellaiappan K, Caskey M, Horowitz J, Nussenzweig MC, Seaman MS, Javeri I, et al. Characterization of Co-Formulated High-Concentration Broadly Neutralizing Anti-HIV-1 Monoclonal Antibodies for Subcutaneous Administration. Antibodies. 2020; 9(3):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9030036
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Vaneet K., Bijay Misra, Kevin T. McManus, Sreenivas Avula, Kaliappanadar Nellaiappan, Marina Caskey, Jill Horowitz, Michel C. Nussenzweig, Michael S. Seaman, Indu Javeri, and et al. 2020. "Characterization of Co-Formulated High-Concentration Broadly Neutralizing Anti-HIV-1 Monoclonal Antibodies for Subcutaneous Administration" Antibodies 9, no. 3: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9030036





