Assessment of Pattern and Shape Symmetry of Bilateral Normal Corneas by Scheimpflug Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants and Examination Protocol
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Morphogeometric Symmetry
2.3.2. Axial Symmetry at the Corneal Vertex
- Adjust the point cloud to a general quadric model (ellipsoid) and subsequently transform into a perfect ellipsoid. With the help of some algorithms programmed in Matlab software that use the equations defined in Navarro’s model [34], we adjust the finite and discrete set of spatial data representative of the spatial surfaces (raw data) to an ellipsoid. Then, we perform the algebraic transformation with the matrix equations of the obtained ellipsoid into a perfect ellipsoid at the vertex reference point (V0), whose main axes are the 3 main position and orientation orthogonal axes in 3D space (Figure 2).
2.3.3. Angular-Spatial Symmetry
- Export the raw data CSV files from Sirius. This procedure is the same as in point 1 of Section 2.3.2.
- Identify the singular points for each ring by the elevation coordinate (Zi) and its angular position (αi). The Cartesian coordinate matrix (raw data) size is 20 × 256, where the 20 rows correspond to the projection of the 20 Placido’s discs (radius: 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 1, … 4 mm) on the corneal surface area, so they cover the corneal region for those corneas with a radius equal to 4 mm. Each matrix point i has a Cartesian elevation coordinate (Zi) and an angular position (αi) in relation to the projection ring of the Placido’s disc (anticlockwise). By the algorithm programmed in Matlab, we obtained the uppermost (Zmax) points in relation to the corneal vertex, and their angular positions (αZmax) in relation to the projection ring. This algorithm also helped us to identify each singular point with respect to the 8 defined octants.
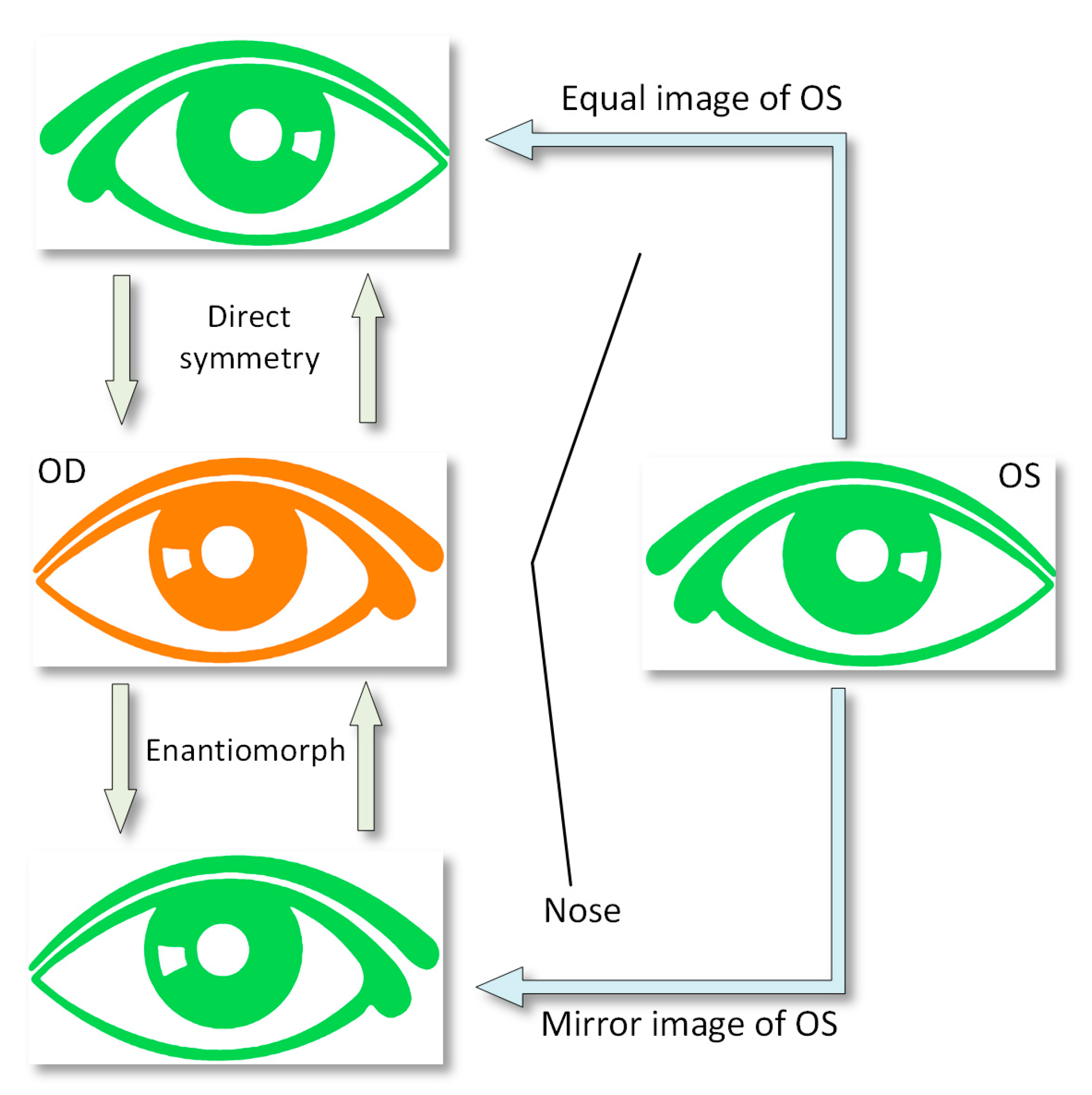
2.3.4. Direct Symmetry (Equal Octants) and Enantiomorphism (Mirror Octants)
- Export the raw data CSV files from Sirius. This procedure is the same as in point 1 of Section 2.3.3. Identify the intersection points (ZX′–OD/ZX″–OD) between the octant axes and the Placido’s discs. For the Cartesian coordinate matrix described in the previous patterns, the points placed on all 8 axes that divide the corneal region are identified. Using another algorithm programmed in Matlab, we identify the 8 points for each Placido’s disc by their angular position, which must coincide with the angles of the octant axes, and obtain the Cartesian elevation coordinates for the right eye (ZA′ … ZH′) and the left eye (ZA″ … ZH″) (Figure 4). Our study considered only the intersection points between the octant axes and the Placido’s discs for radius r = 1, 2, 3, and 4 mm.
- Apply enantiomorph (mirror octants). In this pattern, the octants of the right eye do not coincide with the octants of the left eye. Instead, each right eye (OD) octant has a corresponding octant in the left eye (OS) via its specular image; that is, by its specular image, octant I-OD corresponds to octant IV-OS (Figure 5). As in the previous point, by means of another algorithm programmed in Matlab, the differences between the elevation coordinates for each pair of points are calculated (Table 3).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Morphogeometric Corneal Symmetry
3.2. Analysis of Axial Symmetry at the Corneal Vertex
3.3. Analysis of Angular-Spatial Symmetry
3.4. Analysis of Direct Symmetry (Equal Octants) and Enantiomorphism (Mirror Octants)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hickox, L.J.; Ashby, B.M.; Alderink, G.J. Exploration of the validity of the two-dimensional sagittal plane assumption in modeling the standing long jump. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasuriya, S.A.; Liew, A.W.C.; Law, N.F. Symmetry plane detection in brain image analysis: A survey. Curr. Med. Imaging Rev. 2013, 9, 230–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alterson, R.; Plewes, D.B. Bilateral symmetry analysis of breast mri. Phys. Med. Biol. 2003, 48, 3431–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.; Chen, J.H.; Li, S.; Chang, R.; Yeh, D.C.; Chang, R.F.; Yeh, L.R.; Kwong, J.; Su, M.Y. Evaluation of the association between quantitative mammographic density and breast cancer occurred in different quadrants. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navalho, M.; Resende, C.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Ramos, F.; Gaspar, A.; Pereira Da Silva, J.A.; Fonseca, J.E.; Campos, J.; Canhão, H. Bilateral mr imaging of the hand and wrist in early and very early inflammatory arthritis: Tenosynovitis is associated with progression to rheumatoid arthritis. Radiology 2012, 264, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkau, I.; Prakash, B.; Ananthasubramaniam, A.; Gupta, V.; Aziz, A.; Nowinski, W.L. Quantitative analysis of brain asymmetry by using the divergence measure: Normal-pathological brain discrimination. Acad. Radiol. 2006, 13, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arba Mosquera, S.; Verma, S. Bilateral symmetry in vision and influence of ocular surgical procedures on binocular vision: A topical review. J. Optom. 2016, 9, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, F.; Chen, H.; Yu, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Elsheikh, A. Evaluation of the shape symmetry of bilateral normal corneas in a Chinese population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Bao, F.J. Interocular symmetry analysis of bilateral eyes. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2014, 38, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galletti, J.D.; Vázquez, P.R.R.; Minguez, N.; Delrivo, M.; Bonthoux, F.F.; Pförtner, T.; Galletti, J.G. Corneal asymmetry analysis by pentacam scheimpflug tomography for keratoconus diagnosis. J. Refract. Surg. 2015, 31, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guggenheim, J.A.; Zayats, T.; Prashar, A.; To, C.H. Axes of astigmatism in fellow eyes show mirror rather than direct symmetry. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2008, 28, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myrowitz, E.H.; Kouzis, A.C.; O’Brien, T.P. High interocular corneal symmetry in average simulated keratometry, central corneal thickness, and posterior elevation. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2005, 82, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, G.; Ashok Kumar, D.; Agarwal, A.; Sarvanan, Y.; Jacob, S.; Agarwal, A. Evaluation of bilateral minimum thickness of normal corneas based on fourier-domain optical coherence tomography. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2010, 36, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Dai, E.; Koch, D.D.; Nathoo, A. Optical aberrations of the human anterior cornea. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2003, 29, 1514–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Feng, W.; Han, X.; Cai, J. Evaluation of myopic corneal diameter with the orbscan ii topography system. Graef. Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2013, 251, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñero, D.P. Technologies for anatomical and geometric characterization of the corneal structure and anterior segment: A review. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2015, 30, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Savini, G.; Hoffer, K.J.; Xu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Wen, D.; Hua, Y.; Yang, F.; Pan, C.; Huang, J. A comprehensive assessment of the precision and agreement of anterior corneal power measurements obtained using 8 different devices. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, T.B.; Ribeiro, F.J. Comparability and repeatability of different methods of corneal astigmatism assessment. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2018, 12, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camps, V.J.; Miret, J.J.; García, C.; Tolosa, A.; Piñero, D.P. Simulation of the effect of different presbyopia-correcting intraocular lenses with eyes with previous laser refractive surgery. J. Refract. Surg. 2018, 34, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonini, I.; Angelillo, M.; Pandolfi, A. Theoretical and numerical analysis of the corneal air puff test. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2016, 93, 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-López, D.; Martínez-Finkelshtein, A.; Castro-Luna, G.M.; Piñero, D.; Alió, J.L. Placido-based indices of corneal irregularity. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2011, 88, 1220–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asher, R.; Gefen, A.; Moisseiev, E.; Varssano, D. An analytical approach to corneal mechanics for determining practical, clinically-meaningful patient-specific tissue mechanical properties in the rehabilitation of vision. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 43, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanchares, E.; Buey, M.A.D.; Cristóbal, J.A.; Calvo, B.; Ascaso, F.J.; Malvè, M. Computational simulation of scleral buckling surgery for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment: On the effect of the band size on the myopization. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonini, I.; Pandolfi, A. Customized finite element modelling of the human cornea. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ariza-Gracia, M.Á.; Zurita, J.; Piñero, D.P.; Calvo, B.; Rodríguez-Matas, J.F. Automatized patient-specific methodology for numerical determination of biomechanical corneal response. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 44, 1753–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seven, I.; Vahdati, A.; De Stefano, V.S.; Krueger, R.R.; Dupps, W.J. Comparison of patient-specific computational modeling predictions and clinical outcomes of lasik for myopia. Invest. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci. 2016, 57, 6287–6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bataille, L.; Cavas-Martínez, F.; Fernández-Pacheco, D.G.; Cañavate, F.J.F.; Alio, J.L. A study for parametric morphogeometric operators to assist the detection of keratoconus. Symmetry 2017, 9, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavas-Martínez, F.; Bataille, L.; Fernández-Pacheco, D.G.; Cañavate, F.J.F.; Alio, J.L. Keratoconus detection based on a new corneal volumetric analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavas-Martínez, F.; Bataille, L.; Fernández-Pacheco, D.G.; Cañavate, F.J.F.; Alió, J.L. A new approach to keratoconus detection based on corneal morphogeometric analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Yang, W.; Huang, L.; Wang, J.; Cao, S.; Geraghty, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Bao, F.; Elsheikh, A. Evaluating the repeatability of corneal elevation through calculating the misalignment between successive topography measurements during the follow up of lasik. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; Huang, W.; Geraghty, B.; Wang, Q.; Chen, S.; Bao, F.; et al. Repeatability of corneal elevation maps in keratoconus patients using the tomography matching method. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKendrick, A.M.; Brennan, N.A. The axis of astigmatism in right and left eye pairs. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1997, 74, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohfeld, S.; Barron, V.; McHugh, P.E. Biomodels of bone: A review. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 33, 1295–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, R.; González, L.; Hernández, J.L. Optics of the average normal cornea from general and canonical representations of its surface topography. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2006, 23, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bookstein, F.L. Landmark methods for forms without landmarks: Morphometrics of group differences in outline shape. Med. Image Anal. 1997, 1, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asharlous, A.; Khabazkhoob, M.; Yekta, A.; Hashemi, H. Comprehensive profile of bilateral astigmatism: Rule similarity and symmetry patterns of the axes in the fellow eyes. Ophthal. Physiol. Opt. 2017, 37, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, F.J.; Yu, A.Y.; Kassem, W.; Wang, Q.M.; Elsheikh, A. Biometry of the cornea in myopic chinese patients. J. Refract. Surg. 2011, 27, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durr, G.M.; Auvinet, E.; Ong, J.; Meunier, J.; Brunette, I. Corneal shape, volume, and interocular symmetry: Parameters to optimize the design of biosynthetic corneal substitutes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci. 2015, 56, 4275–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, H.; Asharlous, A.; Yekta, A.; Ostadimoghaddam, H.; Mohebi, M.; Aghamirsalim, M.; Khabazkhoob, M. Enantiomorphism and rule similarity in the astigmatism axes of fellow eyes: A population-based study. J. Optom. 2018, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Bao, F.; Geraghty, B.; Huang, J.; Yu, A.; Wang, Q. High intercorneal symmetry in corneal biomechanical metrics. Eye Vis. 2016, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalban, R.; Pinero, D.P.; Javaloy, J.; Alio, J.L. Intrasubject repeatability of corneal morphology measurements obtained with a new scheimpflug photography-based system. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2012, 38, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saenz-Frances, F.; Bermudez-Vallecilla, M.C.; Borrego-Sanz, L.; Janez, L.; Martinez-de-la-Casa, J.M.; Morales-Fernandez, L.; Santos-Bueso, E.; Garcia-Sanchez, J.; Garcia-Feijoo, J. Anatomical characterization of central, apical and minimal corneal thickness. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 7, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Camarena, J.C.; Chirinos-Saldana, P.; Navas, A.; Ramirez-Miranda, A.; de la Mota, A.; Jimenez-Corona, A.; Graue-Hernindez, E.O. Repeatability, reproducibility, and agreement between three different scheimpflug systems in measuring corneal and anterior segment biometry. J. Refract. Surg. 2014, 30, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savino, G.; Battendieri, R.; Riso, M.; Traina, S.; Poscia, A.; D’Amico, G.; Caporossi, A. Corneal topographic changes after eyelid ptosis surgery. Cornea 2016, 35, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Abad, A.; Pinero, D.P. New perspectives on the detection and progression of keratoconus. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2017, 43, 1213–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Morphogeometric Variable | Acronym | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Corneal volume (mm3) | CV | Volume defined by the solid model generated |
| Anterior/posterior corneal surface area (mm2) | Aant/Apost | Area of the exterior/interior surface |
| Corneal surface area (mm2) | Atot | Area defined by the solid model generated |
| Anterior/posterior apex deviation (mm) | Dapexant/Dapexpost | Distance from the optical axis to the apex of the anterior/posterior corneal surfaces |
| Anterior/posterior minimum thickness point deviation (mm) | Dmctant/Dmctpost | Distance in the XY plane from the optical axis to the minimum thickness points of the anterior/posterior corneal surfaces |
| Shape Parameters | Acronym | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Horizontal/vertical apical radius (mm) | RX/RY | Radius of curvature at apex with respect to x and y axes |
| Horizontal/vertical asphericity | QX/QY | Average variation of instantaneous curvature at each point P along corneal meridian with respect to x and y axes |
| Angular coordinates of rotational displacement (°) | α/β/γ | Rotation in angular coordinates (α, β, γ) of x, y, and z axes with respect to the vertex (V) of a normal cornea (projection in XOY plane of a normal ellipsoid) toward the vertex (V0) of a perfect cornea (projection in XOY plane of a perfect ellipsoid) |
| Cartesian coordinates of translational displacement (mm) | X0/Y0/Z0 | Distance in Cartesian coordinates (x, y, z) of the vertex (V) of a normal cornea (projection in XOY plane of a normal ellipsoid) toward the vertex (V0) of a perfect cornea (projection in XOY plane of a perfect ellipsoid) |
| Parameters of the ellipsoid (mm) | a/b/c | Main parameters of the canonical representation of ellipsoid of major adjustment |
| Equal Octants | Mirror Octants |
|---|---|
| ZA′–ZA″ | ZA′–ZE″ |
| ZB′–ZB″ | ZB′–ZD″ |
| ZC′–ZC″ | ZC′–ZC″ |
| ZD′–ZD″ | ZD′–ZB″ |
| ZE′–ZE″ | ZE′–ZA″ |
| ZF′–ZF″ | ZF′–ZH″ |
| ZG′–Z G″ | ZG′–Z G″ |
| ZH′–ZH″ | ZH′–ZF″ |
| Measurement | Right Eye (OD) | Left Eye (OS) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) Median (Range) | Mean (SD) Median (Range) | ||
| Sphere (D) | −0.03 (3.52) 0.25 (−10.00 to 8.50) | −0.20 (3.78) 0.00 (−12.00 to 8.00) | 0.159 |
| Cylinder (D) | −0.60 (0.54) −0.50 (−2.00 to 0.00) | −0.76 (1.07) −0.50 (−5.75 to 0.00) | 0.316 |
| SE (D) | −0.33 (3.46) 0.00 (−10.00 to 8.12) | −0.58 (3.72) 0.00 (−12.00 to 7.75) | 0.126 |
| Decimal CDVA | 1.00 (0.09) 1.00 (0.60 to 1.20) | 1.00 (0.10) 1.00 (0.60 to 1.20) | 0.892 |
| Q4.5 | −0.11 (0.26) −0.07 (−0.65 to 0.31) | −0.16 (0.24) −0.18 (−0.65 to 0.19) | 0.169 |
| Q8 | −0.27 (0.21) −0.29 (−0.78 to 0.10) | −0.27 (0.18) −0.26 (−0.65 to 0.05) | 0.990 |
| HOA RMS (μm) 6 mm pupil | 0.43 (0.12) 0.42 (0.25 to 0.76) | 0.41 (0.11) 0.39 (0.4 to 0.70) | 0.182 |
| Coma RMS (μm) 6 mm pupil | 0.29 (0.11) 0.30 (0.08 to 0.49) | 0.27 (0.11) 0.27 (0.02 to 0.54) | 0.102 |
| SA (μm) 6 mm pupil | 0.22 (0.05) 0.22 (0.13 to 0.35) | 0.22 (0.06) 0.23 (0.08 to 0.32) | 0.737 |
| MCT (μm) | 539.2 (31.5) 541.9 (479.6 to 610.9) | 540.3 (29.0) 540.5 (485.4 to 609.0) | 0.448 |
| CCT (μm) | 542.8 (31.8) 544.0 (482.0 to 615.0) | 543.9 (29.4) 546.0 (489.0 to 614.0) | 0.458 |
| CV (mm3) | 25.8 (1.6) 26.2 (23.2 to 29.1) | 25.9 (1.5) 26.1 (23.3 to 28.9) | 0.565 |
| Measurement | Right Eye (OD) | Left Eye (OS) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) Median (Range) | Mean (SD) Median (Range) | ||
| Aant (mm2) | 43.09 (0.12) 43.08 (42.84 to 43.34) | 43.10 (0.12) 43.13 (42.83 to 43.32) | 0.055 |
| Apost (mm2) | 44.27 (0.26) 44.29 (43.53 to 44.72) | 44.28 (0.27) 44.28 (43.52 to 44.75) | 0.572 |
| Atot (mm2) | 104.04 (1.24) 104.07 (100.72 to 106.15) | 104.08 (1.23) 104.14 (100.80 to 106.09) | 0.580 |
| Dapexant (mm) | 0.00 (0.00) 0.00 (0.00 to 0.00 | 0.00 (0.00) 0.00 (0.00 to 0.00 | 0.999 |
| Dapexpost (mm) | 0.07 (0.02) 0.08 (0.03 to 0.13) | 0.07 (0.02 to 0.65) 0.87 (0.22) | 0.488 |
| Dmctant (mm) | 0.89 (0.27) 0.89 (0.45 to 1.66) | 0.87 (0.22) 0.88 (0.48 to 1.31) | 0.659 |
| Dmctpost (mm) | 0.81 (0.23) 0.84 (0.40 to 1.53) | 0.79 (0.22) 0.77 (0.40 to 1.24) | 0.606 |
| Measurement | Right Eye (OD) | Left Eye (OS) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) Median (Range) | Mean (SD) Median (Range) | ||
| Rx (mm) | 7.62 (0.21) 7.58 (7.28 to 8.09) | 7.61 (0.23) 7.55 (7.10 to 8.07) | 0.549 |
| Ry (mm) | 7.79 (0.19) 7.79 (7.52 to 8.24) | 7.79 (0.19) 7.76 (7.49 to 8.19) | 0.851 |
| Qx | −0.27 (0.11) −0.27 (−0.51 to −0.05) | −0.27 (0.12) −0.24 (−0.56 to −0.02) | 0.981 |
| Qy | −0.25 (0.11) −0.26 (−0.51 to −0.02) | −0.25 (0.12) −0.23 (−0.49 to 0.00) | 0.999 |
| Alpha (°) | −4.17 (28.62) 1.24 (−161.10 to 13.31) | −3.87 (25.53) −0.39 (−143.08 to 13.49) | 0.814 |
| Beta (°) | −0.05 (11.16) 1.10 (−52.67 to 27.55) | −2.05 (9.59) −1.70 (−49.32 to 18.71) | 0.012 |
| Gamma (°) | −43.08 (91.21) −80.75 (−151.45 to 152.23) | −29.53 (10.50) −80.55 (−176.10 to 173.43) | 0.596 |
| X0 (mm) | 0.20 (0.19) 0.14 (−0.13 to 0.88) | −0.18 (0.26) −0.15 (−1.37 to 0.08) | <0.001 |
| Y0 (mm) | −0.003 (0.219) −0.016 (−0.630 to 0.560) | 0.036 (0.204) −0.001 (−0.470 to 0.690) | <0.001 |
| Z0 (mm) | 10.61 (1.70) 10.43 (8.12 to 15.25) | 10.65 (1.86) 10.00 (8.19 to 15.99) | 0.325 |
| a (mm) | 8.98 (0.68) 9.00 (8.00 to 10.64) | 8.98 (0.72) 8.80 (8.16 to 10.69) | 0.994 |
| b (mm) | 9.07 (0.68) 9.08 (8.17 to 10.84) | 9.08 (0.77) 8.86 (8.22 to 11.46) | 0.345 |
| c (mm) | 10.63 (1.69) 10.43 (8.27 to 15.26) | 10.67 (1.87) 10.01 (8.25 to 16.11) | 0.845 |
| Measurement | Right Eye (OD) | Left Eye (OS) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) Median (Range) | Mean (SD) Median (Range) | ||
| Rx (mm) | 6.21 (0.29) 6.25 (5.74 to 6.90) | 6.22 (0.30) 6.27 (5.75 to 6.94) | 0.466 |
| Ry (mm) | 6.49 (0.29) 6.49 (6.00 to 7.06) | 6.50 (0.27) 6.48 (6.00 to 7.13) | 0.535 |
| Qx | −0.35 (0.21) −0.33 (−0.99 to −0.08) | −0.34 (0.19) −0.30 (−0.79 to−0.07) | 0.606 |
| Qy | −0.32 (0.22) −0.30 (−0.98 to −0.05) | −0.31 (0.19) −0.28 (−0.75 to −0.04) | 0.685 |
| Alpha (°) | 6.15 (30.07) −1.59 (−14.15 to 132.15) | 4.70 (23.66) −3.46 (−9.19 to 86.79) | 0.562 |
| Beta (°) | −8.80 (19.68) −3.87 (−73.89 to 7.58) | −6.30 (15.42) −5.24 (−59.11 to 40.24) | 0.506 |
| Gamma (°) | −22.62 (87.81) −75.31 (−98.32 to 120.09) | −78.51 (45.54) −90.51 (−108.98 to 86.76) | 0.004 |
| X0 (mm) | 1.49 (7.81) 0.06 (−0.62 to 44.91) | −0.23 (0.54) −0.09 (−2.37 to 0.26) | 0.229 |
| Y0 (mm) | 1.09 (4.64) 0.17 (−0.10 to 26.81) | 0.31 (0.42) 0.19 (−0.16 to 2.14) | 0.335 |
| Z0 (mm) | 22.39 (67.41) 9.97 (6.59 to 397.35) | 10.99 (4.28) 9.34 (6.63 to 26.71) | 0.331 |
| a (mm) | 9.08 (7.14) 7.63 (6.04 to 48.19) | 7.95 (1.42) 7.57 (6.10 to 12.24) | 0.342 |
| b (mm) | 9.28 (7.35) 7.73 (6.16 to 49.58) | 8.13 (1.52) 7.71 (6.21 to 13.32) | 0.345 |
| c (mm) | 22.00 (67.99) 9.48 (6.32 to 400.21) | 10.51 (4.29) 8.83 (6.34 to 26.39) | 0.330 |
| Right Eye (OD) | Left Eye (OS) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement | Mean (SD) Median (Range) Most Common Position | Mean (SD) Median (Range) Most Common Position | |
| Radius 1 mm Anterior Zmax (mm) | 0.07 (0.02) 0.07 (0.06 to 0.13) Octants 7 (27.3%) and 3 (18.2%) | 0.07 (0.01) 0.07 (0.06 to 0.13) Octants 7 (33.3%) and 6 (18.2%) | 0.984 |
| Posterior Zmax (mm) | 0.63 (0.03) 0.64 (0.57 to 0.71) Octants 2 (60.6%) and 1 (27.3%) | 0.63 (0.03) 0.64 (0.58 to 0.70) Octants 3 (69.7%) and 4 (21.2%) | 0.247 |
| Radius 2 mm Anterior Zmax (mm) | 0.27 (0.03) 0.27 (0.25 to 0.39) Octants 3 (24.2%) and 7 (21.2%) | 0.27 (0.03) 0.27 (0.25 to 0.38) Octants 7 (30.3%) and 3 (15.2%) | 0.950 |
| Posterior Zmax (mm) | 0.88 (0.04) 0.89 (0.81 to 0.97) Octants 2 (72.7%) and 3 (24.2%) | 0.89 (0.04) 0.90 (0.81 to 0.97) Octants 3 (84.8%) and 2 (9.1%) | 0.171 |
| Radius 3 mm Anterior Zmax (mm) | 0.62 (0.05) 0.61 (0.57 to 0.79) Octants 3 (36.4%) and 7 (18.2%) | 0.62 (0.04) 0.62 (0.57 to 0.78) Octants 2 (24.2%) and 7 (18.2%) | 0.900 |
| Posterior Zmax (mm) | 1.31 (0.05) 1.32 (1.18 to 1.42) Octants 2 (57.6%) and 3 (27.3%) | 1.32 (0.05) 1.33 (1.18 to 1.40) Octants 3 (72.7%) and 2 (15.2%) | 0.560 |
| Radius 4 mm Anterior Zmax (mm) | 1.05 (0.27) 1.12 (0.00 to 1.18) Octants 3 (27.3%) and 2 (21.2%) | 1.05 (0.27) 1.12 (0.00 to 1.18) Octants 2 (24.2%) and 8 (24.2%) | 0.936 |
| Posterior Zmax (mm) | 1.93 (0.07) 1.94 (1.71 to 2.05) Octants 7 (30.3%) and 3 (24.2%) | 1.93 (0.07) 1.94 (1.73 to 2.05) Octants 3 (36.4%) and 6 (27.3%) | 0.745 |
| Radius 1 mm | Radius 2 mm | Radius 3 mm | Radius 4 mm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZX′ (OD) – ZX″ (OS) (Equal Octants) | Mean (SD) Median (Range) | Mean (SD) Median (Range) | Mean (SD) Median (Range) | Mean (SD) Median (Range) | p-Value (1 mm vs. 4 mm) |
| Anterior Corneal Surface | |||||
| A′–A″ (µm) | −0.09 (10.56) −0.25 (−29.70 to 30.83) | −1.16 (21.56) −1.39 (−63.46 to 63.42) | −5.48 (35.12) -4.39 (-111.02 to 99.96) | −16.90 (384.25) −10.15 (−1128.54 to 1061.36) | 0.80 |
| B′–B″ (µm) | −0.07 (10.29) −0.05 (−30.10 to 29.59) | −0.33 (20.53) −0.02 (−63.00 to 58.30) | −0.58 (31.59) 0.33 (−95.62 to 91.05) | −2.92 (386.91) 2.90 (−1110.24 to 1088.41) | 0.97 |
| C′–C″ (µm) | 0.09 (9.76) 0.17 (−28.74 to 28.38) | 0.98 (18.94) 1.34 (−54.76 to 55.54) | 4.75 (28.78) 4.73 (−75.78 to 86.28) | 11.19 (387.67) 6.41 (−1109.13 to 1098.68) | 0.87 |
| D′–D″ (µm) | 0.17 (10.06) 0.07 (−27.72 to 30.11) | 0.79 (20.04) 0.30 (−54.64 to 60.80) | 3.83 (31.91) 3.25 (−83.97 to 97.74) | 12.57 (384.88) 15.39 (−1108.79 to 1085.62) | 0.86 |
| E′–E″ (µm) | −0.01 (10.53) −0.01 (−29.09 to 30.68) | −0.27 (21.47) −0.09 −58.18 to 62.89) | 0.25 (34.58) 1.54 (−92.19 to 100.23) | 1.41 (387.93) 5.13 (−1128.11 to 1092.12) | 0.98 |
| F′–F″ (µm) | −0.22 (10.34) −0.22 (−29.25 to 29.88) | −1.14 (20.42) −1.22 (−58.06 to 57.71) | −3.08 (31.37) −2.92 (−89.28 to 85.70) | −10.02 (394.50) −4.20 (−1164.97 to 1094.93) | 0.89 |
| G′–G″ (µm) | −0.01 (10.02) −0.16 (−28.37 to 28.96) | −0.75 (19.56) −0.93 (−57.28 to 56.69) | −3.68 (30.24) −2.25 (−91.96 to 85.11) | −15.21 (388.90) −14.95 (−1147.93 to 1072.35) | 0.83 |
| H′–H″ (µm) | 0.13 (22.37) −0.13 (−62.49 to 65.21) | −0.58 (42.56) −1.48 (−119.22 to 126.11) | −4.16 (65.42) −5.10 (−189.76 to 193.95) | −20.20 (381.52) −19.01 (−1128.63 to 1048.49) | 0.77 |
| Posterior Corneal Surface | |||||
| A′–A″ (µm) | 6.47 (14.79) 7.17 (−34.30 to 34.07) | 16.40 (21.20) 17.39 (−37.99 to 54.74) | 24.59 (28.43) 27.42 (−46.15 to 79.81) | −0.80 (50.65) 2.81 (−153.69 to 97.13) | 0.43 |
| B′–B″ (µm) | −1.96 (11.86) −3.13 (−36.25 to 18.43) | −1.81 (13.51) −2.61 (−37.95 to 26.85) | −0.78 (16.93) −0.79 (−46.78 to 35.16) | −5.75 (35.00) −3.18 (−97.58 to 94.60) | 0.54 |
| C′–C″ (µm) | −9.43 (13.38) −8.70 (−48.50 to 12.81) | −16.81 (20.07) −17.29 (−68.24 to 30.00) | −21.44 (30.21) −27.50 (−86.19 to 40.59) | 0.40 (46.52) −2.52 (−90.91 to 103.92) | 0.22 |
| D′–D″ (µm) | −16.97 (16.73) −18.04 (−60.09 to 18.51) | −30.09 (27.06) −33.49 (−92.33 to 41.95) | −43.19 (39.46) −49.00 (−130.73 to 62.94) | −45.62 (58.76) −54.94 (−185.60 to 81.02) | <0.01 |
| E′–E″ (µm) | −12.02 (14.19) −11.53 (−53.86 to 16.79) | −23.78 (21.59) −27.86 (−79.60 to 30.69) | −37.76 (31.63) −44.22 (−113.25 to 43.88) | −47.13 (46.55) −52.98 (−148.28 to 74.72) | <0.01 |
| F′–F″ (µm) | −4.03 (12.16) −3.13 (−39.68 to 12.03) | −5.85 (13.13) −4.84 (−49.54 to 12.84) | −7.74 (16.81) −4.66 (−68.22 to 16.58) | −9.24 (24.93) −3.74 (−88.05 to 33.27) | 0.20 |
| G′–G″ (µm) | 5.45 (14.90) 5.75 (−32.47 to 30.66) | 14.99 (21.18) 15.17 (−33.76 to 49.16) | 26.09 (31.88) 26.32 (−35.20 to 91.49) | 34.39 (44.94) 36.42 (−58.31 to 135.05) | <0.01 |
| H′–H″ (µm) | 11.15 (17.61) 10.94 (−29.37 to 43.27) | 24.40 (27.58) 23.86 (−50.35 to 73.36) | 39.14 (40.38) 41.86 (−63.25 to 115.43) | 44.10 (56.82) 53.20 (−84.18 to 136.37) | <0.01 |
| Radius 1 mm | Radius 2 mm | Radius 3 mm | Radius 4 mm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZX′ (OD)– ZX″ (OS) (Mirror Octants) | Mean (SD) Median (Range) | Mean (SD) Median (Range) | Mean (SD) Median (Range) | Mean (SD) Median (Range) | p-Value (1 mm vs 4 mm) |
| Anterior Corneal Surface | |||||
| A′–E″ (µm) | 0.58 (10.32) 0.40 (−27.33 to 30.89) | 1.77 (20.54) 0.74 (−53.01 to 62.89) | 3.14 (32.21) 0.87 (−84.19 to 99.34) | 5.72 (381.94) 8.53 (−1108.79 to 1061.36) | 0.94 |
| B′–D″ (µm) | 0.50 (10.02) 0.27 (−28.03 to 29.46) | 2.58 (19.31) 2.03 (−52.23 to 58.00) | 7.84 (29.07) 8.44 (−73.10 to 91.29) | 13.75 (386.94) 15.69 (−1109.13 to 1088.41) | 0.84 |
| D′–B″ (µm) | −0.33 (10.21) −0.29 (−30.15 to 30.03) | −2.42 (21.03) −2.21 (−65.08 to 61.32) | −5.73 (35.17) −5.30 (−110.80 to 98.36) | 10.23 (380.81) −8.30 (−1128.5 to 1085.6) | 0.88 |
| E′–A″ (µm) | −1.62 (17.15) 0.12 (−62.01 to 31.01) | −2.29 (33.19) −0.04 (−116.23 to 64.37) | −2.45 (52.18) −0.19 (−180.32 to 105.19) | 2.16 (386.87) −0.66 (−1128.63 to 1092.12) | 0.96 |
| F′–H″ (µm) | 0.30 (10.19) 0.14 (−27.81 to 30.23) | 0.48 (20.22) −0.39 (−54.80 to 59.90) | 0.02 (31.73) −2.51 (−83.85 to 94.17) | −5.74 (391.77) −6.42 (−1147.93 to 1094.93) | 0.93 |
| H′–F″ (µm) | 1.74 (17.62) −0.26 (−29.22 to 65.39) | 1.44 (33.94) −2.50 (−61.17 to 124.64) | −1.46 (52.06) −5.17 (−101.63 to 188.99) | −20.95 (382.57) −17.90 (−1128.11 to 1048.49) | 0.75 |
| Posterior Corneal Surface | |||||
| A′–E″ (µm) | 1.30 (13.15) 3.53 (−35.48 to 30.05) | 9.27 (16.09) 10.75 (−39.66 to 47.90) | 19.23 (23.57) 21.42 (−60.39 to 61.40) | 3.03 (43.54) 1.46 (−122.71 to 88.32) | 0.80 |
| B′–D″ (µm) | −2.07 (12.42) −0.41 (−39.52 to 19.39) | 2.50 (16.74) 2.37 (−46.78 to 40.59) | 11.73 (23.89) 8.10 (−54.86 to 61.41) | 19.70 (35.15) 23.77 (−83.97 to 75.25) | <0.01 |
| D′–B″ (µm) | −1.18 (12.10) −9.28 (−47.86 to 9.28) | −2.29 (14.93) −19.59 (−59.99 to 2.77) | −3.78 (21.35) −38.66 (−85.13 to 3.66) | −4.94 (32.51) −51.41 (−134.6 to 35.74) | <0.01 |
| E′–A″ (µm) | −3.15 (11.82) −1.86 (−38.47 to 16.47) | −2.04 (13.41) 1.18 (−36.67 to 21.08) | 1.98 (18.06) 4.25 (−47.29 to 45.80) | 11.07 (30.47) 11.78 (−69.37 to 95.99) | <0.01 |
| F′–H″ (µm) | 1.44 (13.00) 1.84 (−35.00 to 18.67) | 10.58 (16.16) 8.61 (−25.13 to 45.23) | 22.22 (22.23) 22.50 (−29.92 to 77.71) | 29.84 (37.33) 34.44 (−56.98 to 115.93) | <0.01 |
| H′–F″ (µm) | 2.29 (13.48) 2.30 (−35.86 to 24.85) | 2.67 (15.91) 2.29 (−44.93 to 36.23) | −0.60 (21.62) 1.71 (−69.32 to 44.15) | −14.09 (34.85) −7.11 (−126.26 to 43.76) | <0.01 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cavas-Martínez, F.; Piñero, D.P.; Fernández-Pacheco, D.G.; Mira, J.; Cañavate, F.J.F.; Alió, J.L. Assessment of Pattern and Shape Symmetry of Bilateral Normal Corneas by Scheimpflug Technology. Symmetry 2018, 10, 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10100453
Cavas-Martínez F, Piñero DP, Fernández-Pacheco DG, Mira J, Cañavate FJF, Alió JL. Assessment of Pattern and Shape Symmetry of Bilateral Normal Corneas by Scheimpflug Technology. Symmetry. 2018; 10(10):453. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10100453
Chicago/Turabian StyleCavas-Martínez, Francisco, David P. Piñero, Daniel G. Fernández-Pacheco, Jorge Mira, Francisco J. F. Cañavate, and Jorge L. Alió. 2018. "Assessment of Pattern and Shape Symmetry of Bilateral Normal Corneas by Scheimpflug Technology" Symmetry 10, no. 10: 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10100453
APA StyleCavas-Martínez, F., Piñero, D. P., Fernández-Pacheco, D. G., Mira, J., Cañavate, F. J. F., & Alió, J. L. (2018). Assessment of Pattern and Shape Symmetry of Bilateral Normal Corneas by Scheimpflug Technology. Symmetry, 10(10), 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10100453









