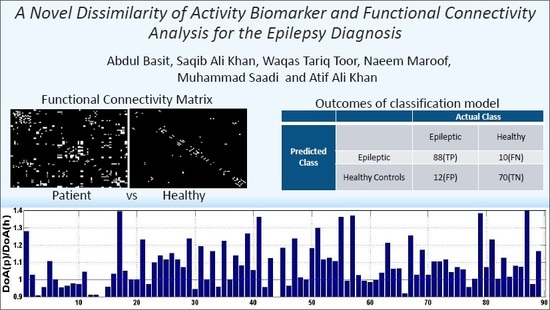
A Novel Dissimilarity of Activity Biomarker and Functional Connectivity Analysis for the Epilepsy Diagnosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Set
3.2. Data Pre-Processing
3.3. Feature Extraction
3.4. Feature Selection
3.5. Classification
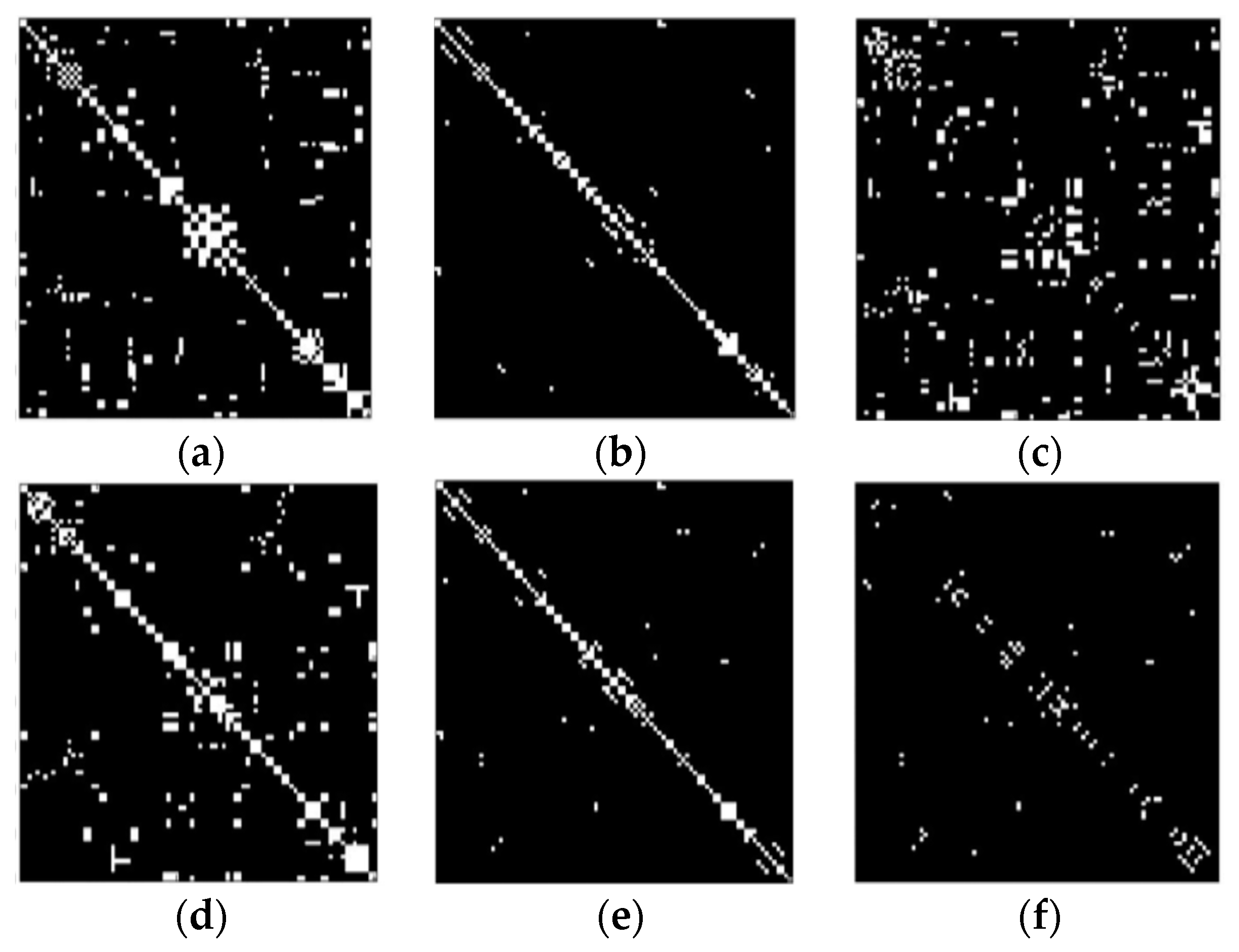
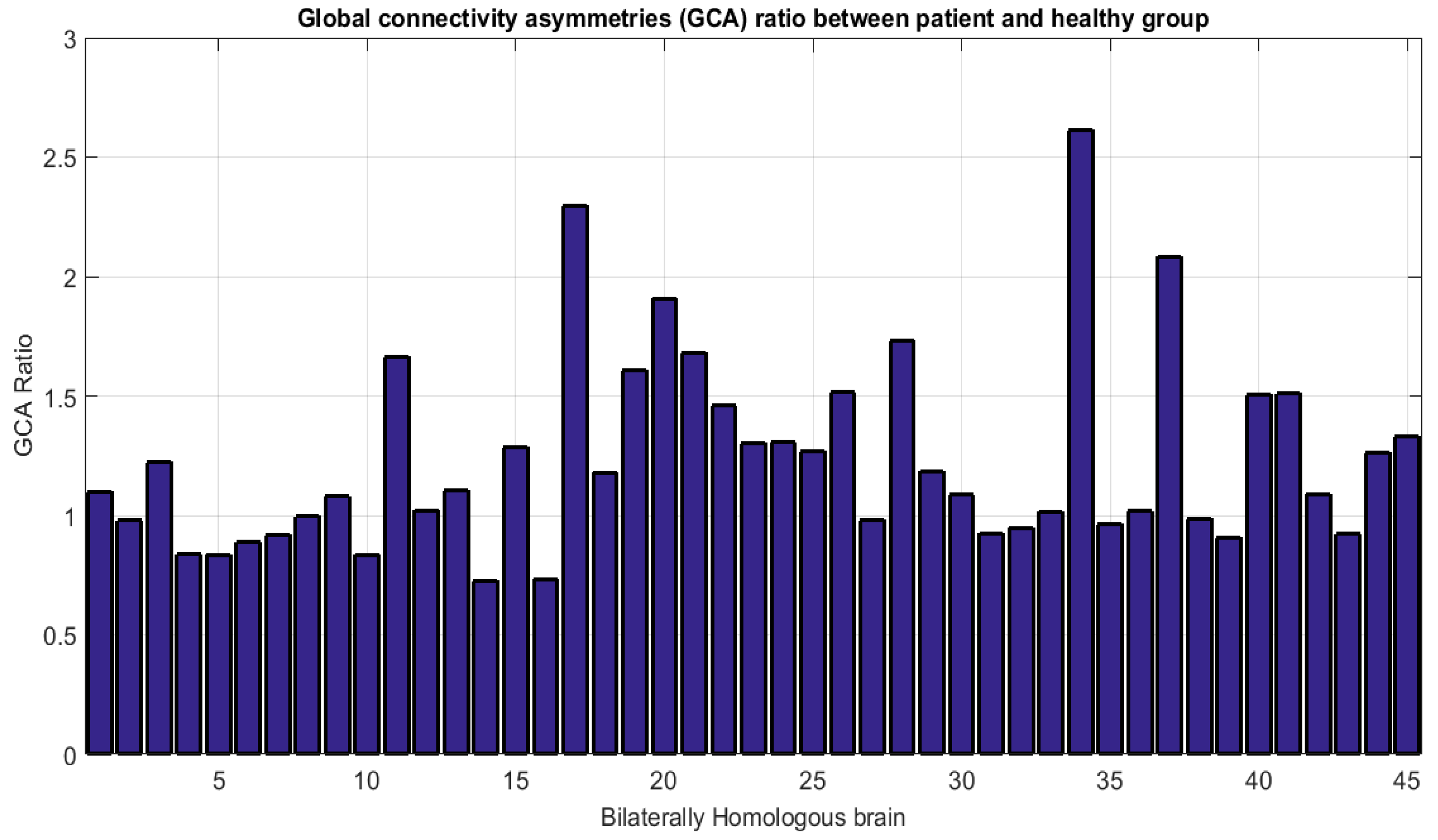
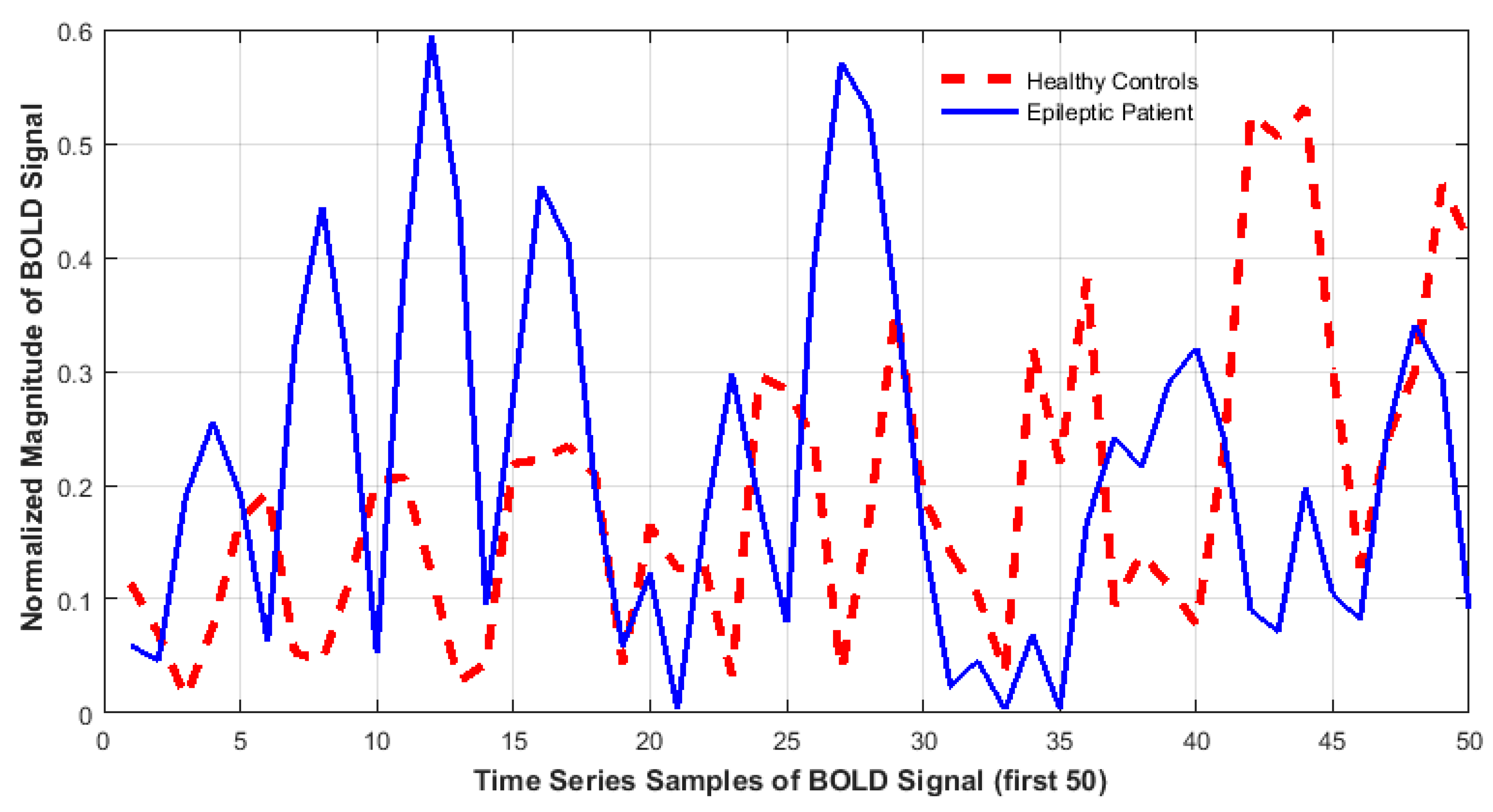
4. Results and Discussion
- (i).
- Better functional connectivity estimation (via partial correlation)
- (ii).
- Accounting for dissimilarity of activity (DoA) in bilaterally homologous regions
- (iii).
- Better feature selection approach
5. Conclusion and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, L.; Zhang, Z.; Mantini, D.; Ding, J.; Duan, X.; Luo, C.; Chen, H. Altered functional connectivity and small-world in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8525. [Google Scholar]
- Logothetis, N. What we can do and what we cannot do with fMRI. Nature 2008, 453, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chkhenkeli, S.A.; Chkhenkeli, I.S. Effects of therapeutic stimulation of nucleus caudatus on epileptic electrical activity of brain in patients with intractable epilepsy. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 1997, 69, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niriayo, Y.L.; Mamo, A.; Kassa, T.D.; Asgedom, S.W.; Atey, T.M.; Gidey, K.; Demoz, G.T.; Ibrhim, S. Treatment outcome and associated factors among patients with epilepsy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elger, C.E.; Hoppe, C. Diagnostic challenges in epilepsy: Seizure under-reporting and seizure detection. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.A.; Eric, D.K.; Heidi, E.K. Emergent network topology at seizure onset in humans. Epilepsy Res. 2008, 79, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apkarian, A.V.; Bushnell, M.C.; Treede, R.D.; Zubieta, J.K. Human brain mechanisms of pain perception and regulation in health and disease. Eur. J. Pain 2005, 9, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodtkorb, E. Common imitators of epilepsy. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 2013, 127, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiglusz, M.S.; Landoski, J.; Cubala, W.J.; Aqius, M. Overlapping phenomena of bipolar disorder and epilepsy–a common pharmacological pathway. Psychiatr Danub 2015, 27, S177–S181. [Google Scholar]
- Ferree, T.C.; Clay, M.T.; Don, M.T. The spatial resolution of scalp EEG. Neurocomputing 2001, 38–34, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alois, S.; Slater, M.; schiller, G.P. Presence research and EEG. In Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Presence, Porto, Portugal, 9–11 October 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Aguirre, G.K.; D’Esposito, M. 30 Experimental Design for Brain fMRI. In Funct. MRI; Springer: Berlin, Gemany, 1999; pp. 369–380. [Google Scholar]
- Hedrich, T.; Pllegrino, G.; Kobayashi, E.; Lina, J.M.; Grova, C. Comparison of the spatial resolution of source imaging techniques in high-density EEG and MEG. NeuroImage 2017, 157, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, P.; Gao, P.; Dai, J.; Niu, G. Research progress on resting state fMRI of epilepsy. Brain Dev. 2012, 34, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B. Resting state fMRI: A personal history. Neuroimage. 2012, 62, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.L.; Shen, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Li, B.; Fang, P.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Hu, D. Identifying major depression using whole-brain functional connectivity: A multivariate pattern analysis. Brain 2012, 135, 1498–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisa, S. The potential of functional MRI as a biomarker in early Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2011, 32, S37–S43. [Google Scholar]
- Magnin, B.; Mesrob, L.; Kinkingn’ehun, S.; P’el´egrini-Issacet, M.; Colliot, O.; Sarazin, M.; Dubois, B.; Lehericy, S.; Benali, H. Support vector machine-based classification of alzheimers disease from whole brain anatomical MRI. Neuroradiology 2009, 51, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Lu, Y.; He, Y.; Tian, L. Regional homogeneity approach to fMRI data analysis. Neuroimage 2004, 22, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laufs, H.; Hamandi, K.; Salek-Haddadi, A.; Kleinschmidt, A.; Duncan, J.; Lemieux, L. Temporal lobe interictal epileptic discharges affect cerebral activity in ‘default mode’ brain regions. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2007, 28, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Li, Q.; Lai, Y.; Xia, Y.; Qin, Y.; Liao, W.; Li, S.; Zhou, D.; Yao, D.; Gong, Q. Altered functional connectivity in default mode network in absence epilepsy: A resting-state fMRI study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2011, 32, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cheng, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, W.; Lu, G.; Feng, J. Pattern classification of large-scale functional brain networks: Identification of informative neuroimaging markers for epilepsy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordes, D.; Haugton, V.; Carew, J.D.; Arfanakis, K.; MaraVilla, K. Hierarchical clustering to measure connectivity in fMRI resting-state data. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2002, 20, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Ven, V.G.; Formisano, E.; Prvulovic, D.; Roeder, C.H.; Linden, D.E. Functional connectivity as revealed by spatial independent component analysis of fMRI measurements during rest. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2004, 22, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltier, S.J.; Thad, A.P.; Douglas, C.N. Detecting low frequency functional connectivity in fMRI using a self-organizing map (SOM) algorithm. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2003, 20, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente, A.; Bing, B.; Hoeschele, I.; Mendes, P. Discovery of meaningful associations in genomic data using partial correlation coefficients. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 3565–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chao, G.Y.; Yu, F.Z. DPARSF: A MATLAB toolbox for ‘pipeline’ data analysis of resting-state fMRI. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Tzourio-Mazoyer, N.; Landeau, B.; Rapathanassiou, D.; Crivello, F.; Etard, O.; Delcroix, N.; Mazoyer, B.; Joliot, M. Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single subject brain. Neuroimage 2002, 15, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.l.; Wesley, K.T.; Greg, S. MATLAB toolbox for functional connectivity. Neuroimage 2009, 47, 1590–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrew, Z.; Fornito, A.; Bullmore, E. On the use of correlation as a measure of network connectivity. Neuroimage 2012, 60, 2096–2106. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, M.J.; Mock, B.J.; Sorenson, J.A. Functional connectivity in single and multislice echoplanar imaging using resting-state fluctuations. Neuroimage 1998, 7, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, A.; Rajpoot, K.; Rajpoot, N. A connectivity difference measure for identification of functional neuroimaging markers for epilepsy. In Proceedings of the 6th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER), San Diego, CA, USA, November 2013; pp. 1517–1520. [Google Scholar]
- Mineichi, K.; Sklansky, J. Comparison of algorithms that select features for pattern classifiers. Pattern Recognit. 2000, 33, 25–41. [Google Scholar]



| Data Acquisition Details | |
|---|---|
| Scanner | Tesla Siemens Trio Tim |
| No. of receiver Coils | |
| Matrix | |
| TR | |
| TE | |
| FOV | |
| Slice thickness | |
| Flip angle | |
| Slice gap | |
| Class Type | Group | Actual Class | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted Class | Epileptic | Healthy Controls | |
| Epileptic | 88(TP) | 10(FN) | |
| Healthy Controls | 12(FP) | 70(TN) | |
| Feature Set (Combination of Biomarkers) | Classification Method | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed Method | Zhang et al. [22] | Correlation Method | |
| Functional Connectivity Matrix (50 edges) | 77.31% | 73.2% | 69.5% |
| Functional Connectivity Matrix (400 edges) FC | 82.57% | 77.6% | 72.11% |
| Global Connectivity Asymmetry (GCA) | 76.1% | 75.57% | 57.61% |
| Dissimilarity of Activity (DoA) | 76.6% | 76.6% | 76.6% |
| FC + GCA | 84.23% | 80.2% | 74.2% |
| FC + DoA | 87.78% | 81.46% | 74.6% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basit, A.; Ali Khan, S.; Tariq Toor, W.; Maroof, N.; Saadi, M.; Ali Khan, A. A Novel Dissimilarity of Activity Biomarker and Functional Connectivity Analysis for the Epilepsy Diagnosis. Symmetry 2019, 11, 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11080979
Basit A, Ali Khan S, Tariq Toor W, Maroof N, Saadi M, Ali Khan A. A Novel Dissimilarity of Activity Biomarker and Functional Connectivity Analysis for the Epilepsy Diagnosis. Symmetry. 2019; 11(8):979. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11080979
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasit, Abdul, Saqib Ali Khan, Waqas Tariq Toor, Naeem Maroof, Muhammad Saadi, and Atif Ali Khan. 2019. "A Novel Dissimilarity of Activity Biomarker and Functional Connectivity Analysis for the Epilepsy Diagnosis" Symmetry 11, no. 8: 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11080979
APA StyleBasit, A., Ali Khan, S., Tariq Toor, W., Maroof, N., Saadi, M., & Ali Khan, A. (2019). A Novel Dissimilarity of Activity Biomarker and Functional Connectivity Analysis for the Epilepsy Diagnosis. Symmetry, 11(8), 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11080979