An Improved Level Set Method on the Multiscale Edges
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Proposed Method
2.1. The Multiscale Edges
- If the target pixel is inside or outside the object, the adjacent pixels should be the object or not due to region connectivity (Figure 2a).
- Suppose the target pixel is located at the object boundary, the adjacent pixels would belong to one of the following cases.
2.2. The Level Set Method
2.3. Segmentation on the Multi Scale Edges
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, C.; Liao, Z.; Yu, Y. Piecewise Flat Embedding for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 41, 1470–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Muchtar, K.; Lin, W.-Y.; Jian, Z.-Y. Moving Object Detection through Image Bit-Planes Representation Without Thresholding. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 21, 1404–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Lee, G.-C. Moving Object Detection Using an Object Motion Reflection Model of Motion Vectors. Symmetry 2019, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, K.S.; Kim, W.-J. Efficient edge-preserved sonar image enhancement method based on CVT for object recognition. IET Image Process. 2019, 13, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Guo, B.; Li, C.; Yan, Y. A Weighted Fourier and Wavelet-Like Shape Descriptor Based on IDSC for Object Recognition. Symmetry 2019, 11, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maqueda, A.I.; Loquercio, A.; Gallego, G.; Garcia, N.; Scaramuzza, D. Event-based Vision meets Deep Learning on Steering Prediction for Self-driving Cars. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/Cvf Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 5419–5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dan, C.C.; Giusti, A.; Gambardella, L.M.; Schmidhuber, J. Deep Neural Networks Segment Neuronal Membranes in Electron Microscopy Images. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 2852–2860. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shelhamer, E.; Long, J.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, T.F.; Vese, L.A. Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D. Hybrid fitting energy-based fast level set model for image segmentation solving by algebraic multigrid and sparse field method. IET Image Process. 2018, 12, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Kao, C.-Y.; Gore, J.C.; Ding, Z. Implicit active contours driven by local binary fitting energy. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Liu, F.; Liu, S. Active contours driven by normalized local image fitting energy. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2014, 26, 1200–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swierczynski, P.; Papiez, B.W.; Schnabel, J.A.; Macdonald, C. A level-set approach to joint image segmentation and registration with application to CT lung imaging. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2018, 65, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Rada, L.; Badshah, N. Image Segmentation for Intensity Inhomogeneity in Presence of High Noise. IEEE Trans Image Process 2018, 27, 3729–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.M.; Xu, C.Y.; Gui, C.; Fox, M.D. Level set evolution without re-initialization: A new variational formulation. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; pp. 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.Y.; Xie, X.; Sazonov, I.; Nithiarasu, P. Segmentation of biomedical images using active contour model with robust image feature and shape prior. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2014, 30, 232–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Yu, X.; Wu, C.; Zhou, W.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, Y. Accurate Optic Disc and Cup Segmentation from Retinal Images Using a Multi-Feature Based Approach for Glaucoma Assessment. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhi, X.-H.; Shen, H.-B. Saliency driven region-edge-based top down level set evolution reveals the asynchronous focus in image segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 80, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osher, S.; Sethian, J.A. Fronts propagating with curvature-dependent speed—Algorithms based on hamilton-jacobi Formulations. J. Comput. Phys. 1988, 79, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akram, F.; Garcia, M.A.; Puig, D. Active contours driven by difference of Gaussians. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khadidos, A.; Sanchez, V.; Li, C.T. Weighted Level Set Evolution Based on Local Edge Features for Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2017, 26, 1979–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, G.; Kornprobst, P. Mathematical Problems in Image Processing: Partial Differential Equations and the Calculus of Variations, Applied Mathematical Sciences; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, T.F.; Osher, S.; Shen, J.H. The digital TV filter and nonlinear denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kristiadi, A.; Pranowo, P. Deep Convolutional Level Set Method for Image Segmentation. J. Ict Res. Appl. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janakiraman, T.N.; Mouli, P.V.S. Image Segmentation Based on Minimal Spanning Tree and Cycles. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Multimedia Applications, Sivakasi, Tamil Nadu, India, 13–15 December 2007; pp. 215–219. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y. PCNN-based level set method of automatic mammographic image segmentation. Optik 2016, 127, 1644–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Acuna, D.; Ling, H.; Kar, A.; Fidler, S. Object Instance Annotation with Deep Extreme Level Set Evolution. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 7492–7500. [Google Scholar]


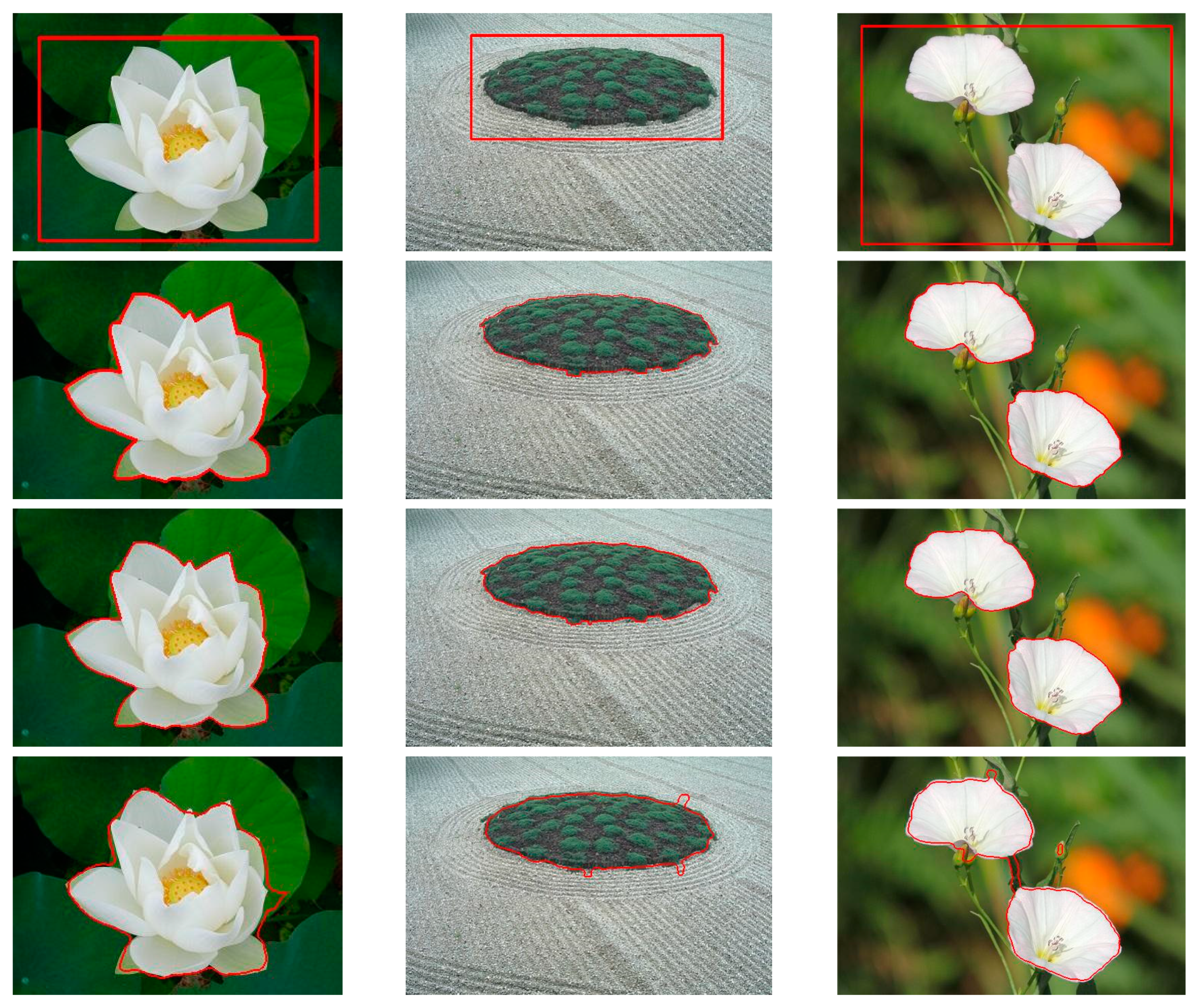







| Method | Figure 3a | Figure 3b | Figure 3c | Figure 4a | Figure 4b | Figure 4c | Figure 5a | Figure 5b | Figure 5c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 320 × 240 | 480 × 320 | 512 × 365 | 220 × 213 | 320 × 221 | 512 × 384 | 400 × 300 | 480 × 320 | 500 × 333 | |
| This method | |||||||||
| Pre. | 1.0 | 0.984 | 0.999 | 1.0 | 0.992 | 0.983 | 0.967 | 0.992 | 0.964 |
| Rec. | 0.965 | 0.972 | 0.993 | 0.938 | 0.940 | 0.998 | 0.988 | 0.834 | 0.979 |
| F-M | 0.982 | 0.978 | 0.996 | 0.968 | 0.965 | 0.990 | 0.987 | 0.906 | 0.970 |
| CPU-t | 3.715 | 8.673 | 26.901 | 3.637 | 7.098 | 20.201 | 4.335 | 7.746 | 6.474 |
| Li’s (Gaussian smoothing + Level Set) | |||||||||
| Pre. | 0.985 | 0.976 | 0.959 | 0.839 | 0.930 | 0.925 | 0.812 | 0.948 | 0.789 |
| Rec. | 0.953 | 0.915 | 0.927 | 0.758 | 0.873 | 0.989 | 0.997 | 0.853 | 0.975 |
| F-M | 0.968 | 0.945 | 0.943 | 0.796 | 0.900 | 0.956 | 0.895 | 0.898 | 0.872 |
| CPU-t | 2.666 | 6.894 | 13.973 | 1.834 | 5.288 | 18.471 | 2.597 | 5.523 | 4.872 |
| IMST | |||||||||
| Pre. | 0.998 | 0.967 | 0.947 | 0.856 | 0.929 | 0.981 | 0.873 | 0.943 | 0.956 |
| Rec. | 0.952 | 0.993 | 0.994 | 0.994 | 0.982 | 0.980 | 0.989 | 0.917 | 0.975 |
| F-M | 0.975 | 0.980 | 0.970 | 0.920 | 0.955 | 0.981 | 0.927 | 0.930 | 0.965 |
| CPU-t | 2.947 | 6.209 | 9.895 | 2.464 | 3.115 | 11.423 | 2.604 | 3.871 | 3.467 |
| DCLSM (CNN + Level Set) | |||||||||
| Pre. | 0.982 | 0.952 | 0.963 | 0.873 | 0.931 | 0.934 | 0.890 | 0.949 | 0.938 |
| Rec. | 0.952 | 0.984 | 0.993 | 0.984 | 0.887 | 0.979 | 0.972 | 0.884 | 0.983 |
| F-M | 0.966 | 0.969 | 0.978 | 0.925 | 0.908 | 0.959 | 0.929 | 0.915 | 0.960 |
| CPU-t | 2.766 | 6.577 | 11.835 | 1.576 | 5.012 | 15.347 | 2.483 | 4.973 | 4.279 |
| SDREL (Saliency Map + Level Set) | |||||||||
| Pre. | 0.872 | 0.959 | 0.737 | 0.846 | 0.786 | 0.849 | 0.825 | 0.853 | 0.991 |
| Rec. | 0.961 | 0.976 | 0.984 | 0.976 | 0.943 | 0.917 | 0.970 | 0.749 | 0.989 |
| F-M | 0.914 | 0.967 | 0.843 | 0.906 | 0.857 | 0.882 | 0.891 | 0.798 | 0.990 |
| CPU-t | 3.423 | 7.823 | 20.715 | 2.979 | 4.357 | 18.542 | 4.011 | 3.824 | 5.348 |
| PSNR (dB) | The Proposed Model | IMST Model | Li Model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | Rec. | F-M. | Pre. | Rec. | F-M. | Pre. | Rec. | F-M | |
| 23.53 | 0.999 | 0.962 | 0.980 | 0.914 | 1.000 | 0.955 | 0.959 | 0.943 | 0.951 |
| 21.94 | 0.998 | 0.962 | 0.980 | 0.915 | 0.984 | 0.948 | 0.951 | 0.943 | 0.947 |
| 20.84 | 0.997 | 0.964 | 0.980 | 0.930 | 0.998 | 0.962 | 0.955 | 0.943 | 0.949 |
| 19.99 | 0.996 | 0.965 | 0.980 | 0.884 | 1.000 | 0.938 | 0.944 | 0.942 | 0.943 |
| 19.39 | 0.992 | 0.963 | 0.977 | 0.920 | 0.996 | 0.957 | 0.945 | 0.941 | 0.943 |
| 18.77 | 0.991 | 0.965 | 0.978 | 0.870 | 1.000 | 0.930 | 0.942 | 0.939 | 0.940 |
| 18.27 | 0.983 | 0.966 | 0.974 | 0.876 | 1.000 | 0.934 | 0.939 | 0.938 | 0.938 |
| 17.84 | 0.980 | 0.967 | 0.973 | 0.934 | 0.981 | 0.957 | 0.929 | 0.940 | 0.934 |
| 16.79 | 0.973 | 0.968 | 0.970 | 0.887 | 0.991 | 0.936 | 0.881 | 0.938 | 0.909 |
| 16.23 | 0.973 | 0.968 | 0.970 | 0.915 | 0.996 | 0.954 | 0.866 | 0.936 | 0.900 |
| 15.77 | 0.972 | 0.970 | 0.971 | 0.866 | 1.000 | 0.928 | 0.854 | 0.935 | 0.893 |
| 15.36 | 0.966 | 0.970 | 0.968 | 0.848 | 0.999 | 0.917 | 0.845 | 0.937 | 0.889 |
| 14.99 | 0.965 | 0.972 | 0.968 | 0.876 | 0.985 | 0.928 | 0.838 | 0.935 | 0.884 |
| 14.40 | 0.960 | 0.972 | 0.966 | 0.856 | 1.000 | 0.922 | 0.826 | 0.933 | 0.876 |
| 13.71 | 0.957 | 0.974 | 0.965 | 0.880 | 0.977 | 0.926 | 0.912 | 0.932 | 0.922 |
| 13.33 | 0.953 | 0.974 | 0.963 | 0.798 | 0.992 | 0.884 | 0.806 | 0.933 | 0.865 |
| 12.87 | 0.953 | 0.976 | 0.964 | 0.828 | 0.989 | 0.902 | 0.790 | 0.930 | 0.854 |
| 11.77 | 0.942 | 0.978 | 0.960 | 0.869 | 1.000 | 0.930 | 0.785 | 0.934 | 0.853 |
| 11.34 | 0.925 | 0.981 | 0.952 | 0.869 | 0.999 | 0.930 | 0.763 | 0.947 | 0.845 |
| 10.92 | 0.907 | 0.984 | 0.944 | 0.805 | 0.988 | 0.877 | 0.730 | 0.954 | 0.827 |
| Original Image | 0.999 | 0.962 | 0.980 | 0.941 | 0.996 | 0.968 | 0.964 | 0.943 | 0.953 |
| Mean | 0.971 | 0.970 | 0.970 | 0.880 | 0.994 | 0.933 | 0.877 | 0.939 | 0.906 |
| Variance | 0.025 | 0.006 | 0.009 | 0.039 | 0.007 | 0.023 | 0.072 | 0.006 | 0.040 |
| 23.53 | 0.999 | 0.962 | 0.980 | 0.914 | 1.000 | 0.955 | 0.959 | 0.943 | 0.951 |
| PSNR (dB) | 9~10 | 10~11 | 11~13 | 13~15 | 15~17 | 17~20 | 20~30 | Original Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The proposed model | 27.5~24.0 | 23.6~20.8 | 20.2~17.8 | 17.6~14.2 | 13.72~10.8 | 10.53~9.0 | 8.96~7.41 | 7.41 |
| The IMST model | 9.66~11.8 | 11.6~10.8 | 10.7~10.4 | 10.4~9.55 | 9.69~9.12 | 9.20~7.74 | 7.52-6.33 | 6.27 |
| The Li’s model | 23..4~20.8 | 20.5~18.5 | 18.3~16.1 | 15.8~12.1 | 11.2~8.5 | 8.43~6.53 | 6.13~5.3 | 5.26 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, Y.; He, K.; Wang, D.; Peng, T. An Improved Level Set Method on the Multiscale Edges. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12101650
Su Y, He K, Wang D, Peng T. An Improved Level Set Method on the Multiscale Edges. Symmetry. 2020; 12(10):1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12101650
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Yao, Kun He, Dan Wang, and Tong Peng. 2020. "An Improved Level Set Method on the Multiscale Edges" Symmetry 12, no. 10: 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12101650
APA StyleSu, Y., He, K., Wang, D., & Peng, T. (2020). An Improved Level Set Method on the Multiscale Edges. Symmetry, 12(10), 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12101650




