Ontology-Based Decision Support Tool for Automatic Sleep Staging Using Dual-Channel EEG Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Visual Interpretation
4. Materials and Methods
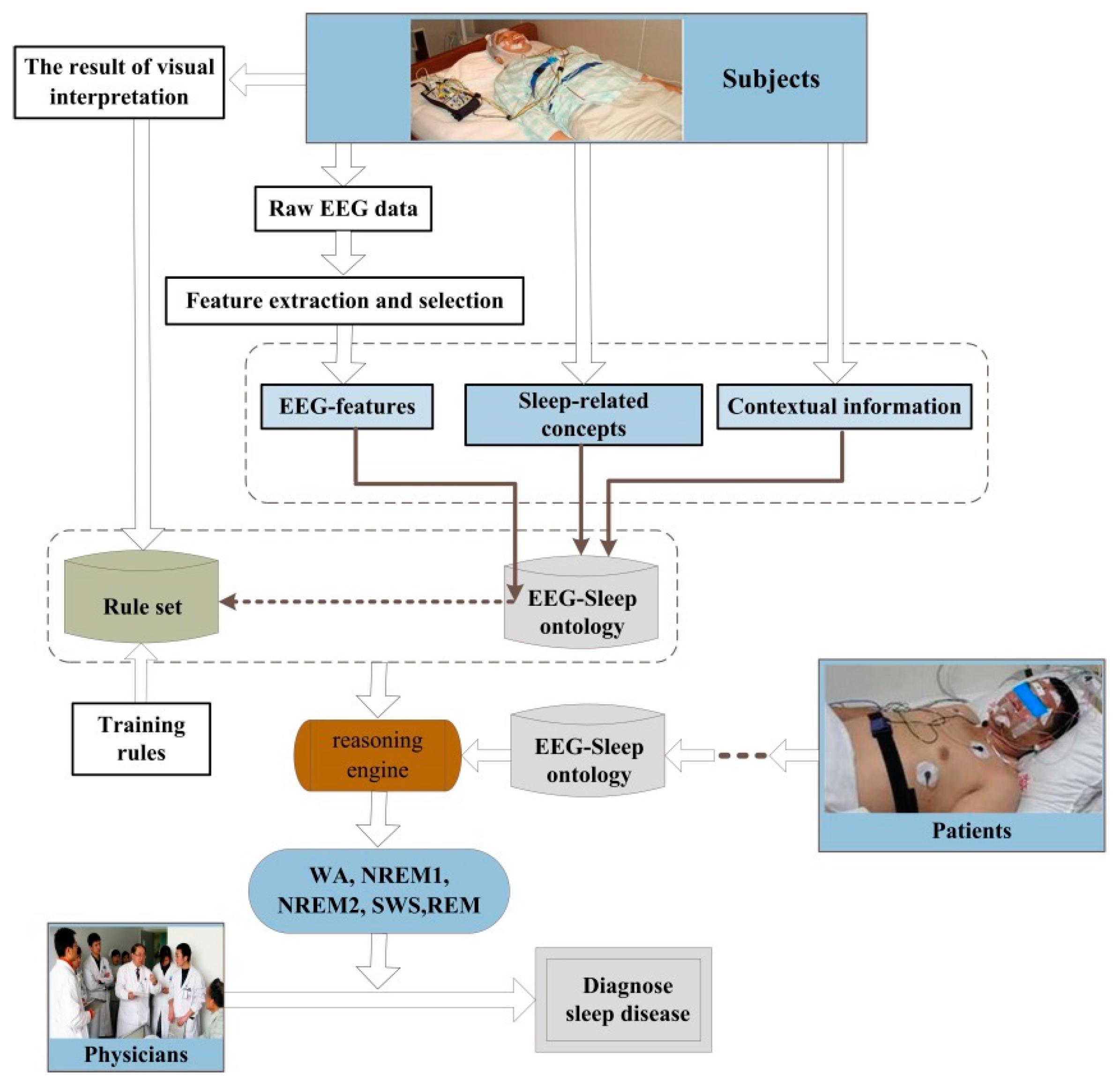
4.1. The Architecture of the Automatic Sleep Staging Tool
4.2. Data Description and Preprocessing
4.2.1. Data Description
4.2.2. Data Preprocessing
4.3. EEG Features Extraction
4.4. EEG Features Selection
4.5. Principal Components of the Automatic Sleep Staging Tool
4.5.1. EEG-Sleep Ontology
4.5.2. Rule Set
4.5.3. Inference Engine
5. Results and Discussions
5.1. Overall Performance of the Difference Classifiers
5.2. Classification Accuracy of the Single Sleep Stage.
5.3. Comparison with Existing Methods
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rechtschaffen, A.; Kales, A. A manual of standardized terminology, techniques and scoring systems for sleep stages of human subjects. Health Inst. 1968, 50, 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Iber, C.; Ancoli-Israel, S.; Chesson, A.; Quan, S.F. The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events: Rules, Terminology and Technical Specifications; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Westchester, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 1–79. [Google Scholar]
- Charbonnier, S.; Zoubek, L.; Lesecq, S.; Chapotot, F. Self-evaluated automatic classifier as a decision-support tool for sleep/wake staging. Comput. Biol. Med. 2011, 41, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahowald, M.W.; Schenck, C.H. Insights from studying human sleep disorders. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 437, 1279–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohayon, M.M. Epidemiology of insomnia: What we know and what we still need to learn. Sleep Med. Rev. 2002, 6, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Hu, B.; Liu, Z.; Yan, L.; Wang, T.; Liu, F.; Kang, H.; Li, X. Investigation of different speech types and emotions for detecting depression using different classifiers. Speech Commun. 2017, 90, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, B.; Sun, S.; Cai, H. EEG-based mild depressive detection using feature selection methods and classifiers. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2016, 136, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carskadon, M.A.; Dement, W.C. Normal human sleep: An overview. Princ. Pract. Sleep Med. 2005, 12, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, R.G.; Pal, I.; Stewart, C.; Walsleben, J.A.; Rapoport, D.M. Interobserver Agreement Among Sleep Scorers from Different Centers in a Large Dataset. Sleep 2000, 23, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderer, P.; Gruber, G.; Parapatics, S.; Woertz, M.; Miazhynskaia, T.; Klösch, G.; Saletu, B.; Zeitlhofer, J.; Barbanoj, M.J.; Danker-Hopfe, H.; et al. An E-Health Solution for Automatic Sleep Classification according to Rechtschaffen and Kales: Validation Study of the Somnolyzer 24 × 7 Utilizing the Siesta Database. Neuropsychobiology 2005, 51, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthomier, C.; Drouot, X.; Herman-Stoïca, M.; Berthomier, M.P.; Prado, J.; Bokar-Thire, D.; Benoit, O.; Mattout, J.; D’Ortho, M.-P. Automatic Analysis of Single-Channel Sleep EEG: Validation in Healthy Individuals. Sleep 2007, 30, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, B.; Moore, P.; Chen, J.; Zhou, L. Emotiono: An Ontology with Rule-Based Reasoning for Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Shanghai, China, 13–17 November 2011; pp. 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, B.; Chen, J.; Moore, P. Ontology-based context modeling for emotion recognition in an intelligent web. World Wide Web 2013, 16, 497–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, B.; Ma, X.; Moore, P.; Chen, J. Ontology driven decision support for the diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2014, 113, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa, A.G.; Laciar, E.; Patino, H.D.; Valentinuzzi, M.E. An automatic sleep-stage classifier using electroencephalographic signals. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2008, 1, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, Y.-L.; Yang, Y.-T.; Wang, J.-S.; Hsu, C.-Y. Automatic sleep stage recurrent neural classifier using energy features of EEG signals. Neurocomputing 2013, 104, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagluk, M.E.; Sezgin, N.; Akin, M. Estimation of Sleep Stages by an Artificial Neural Network Employing EEG, EMG and EOG. J. Med. Syst. 2010, 34, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.-T.; Kuo, C.-E.; Zeng, J.-H.; Liang, S.-F. A transition-constrained discrete hidden Markov model for automatic sleep staging. Biomed. Eng. Online 2012, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanaoka, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Yamazaki, H. Automatic sleep stage scoring based on waveform recognition method and decision-tree learning. Syst. Comput. Jpn. 2002, 33, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Li, Y.; Wen, P.P. Analysis and Classification of Sleep Stages Based on Difference Visibility Graphs from a Single-Channel EEG Signal. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2014, 18, 1813–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Principe, J.; Gala, S.; Chang, T. Sleep staging automaton based on the theory of evidence. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1989, 36, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinero, P.; Garcia, P.; Arco, L.; Alvarez, A.; Garca, M.M.; Bonal, R. Sleep stage classification using fuzzy sets and machine learning techniques. Neurocomputing 2004, 58, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingtao, Z.; Lei, T.; Liu, H.; Cai, H.S. EEG-based automatic sleep staging usingontology and weighting feature analysis. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2018, 6534041, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.-F.; Kuo, C.-E.; Hu, Y.-H.; Pan, Y.-H.; Wang, Y.-H. Automatic Stage Scoring of Single-Channel Sleep EEG by Using Multiscale Entropy and Autoregressive Models. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2012, 61, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakovská, A.; Mezeiová, K. Automatic sleep scoring: A search for an optimal combination of measures. Artif. Intell. Med. 2011, 53, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, T.; Sun, G.N.; Xia, Y.H.; Ma, J.F. Modeling and detection of ontology-based Byzantine attacks. J. Univ. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2011, 28, 696–705. [Google Scholar]
- Orgun, B.; Vu, J. HL7 ontology and mobile agents for interoperability in heterogeneous medical information systems. Comput. Biol. Med. 2006, 36, 817–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soergel, D.; Lauser, B.; Liang, A.; Fisseha, F.; Keizer, J.; Katz, S. Reengineering thesauri for new applications: The AGROVOC Example. J. Digit. Inf. 2004, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Thakor, N.; Tong, S. Advances in Quantitative Electroencephalogram Analysis Methods. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 6, 453–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rector, A.; Rogers, J. Ontological and Practical Issues in Using a Description Logic to Represent Medical Concept Systems: Experience from GALEN. Reason. Web 2006, 4126, 197–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratsas, C.; Koutkias, V.G.; Kaimakamis, E.; Bamidis, P.D.; Pangalos, G.Ι.; Maglaveras, N. KnowBaSICS-M: An ontology-based system for semantic management of medical problems and computerised algorithmic solutions. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2007, 88, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isern, D.; Sánchez, D.; Moreno, A. Ontology-driven execution of clinical guidelines. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2012, 107, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasmahapatra, S.; Dupplaw, D.; Hu, B.; Lewis, P.; Shadbolt, N. Ontology-Mediated Distributed Decision Support for Breast Cancer. Artif. Intell. Med. 2005, 3581, 221–225. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Hu, B.; Xu, L.; Cai, H.; Moore, P.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J. EmotionO+: Physiological signals knowledge representation and emotion reasoning model for mental health monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Belfast, UK, 2–5 November 2014; pp. 529–535. [Google Scholar]
- The Sleep-EDF Database [Expanded]. Available online: http://physionet.org/pn4/sleep-edfx/#sleep-recordings-and-hypnograms-in-european-data-f (accessed on 20 November 2020).
- Kemp, B.; Zwinderman, A.; Tuk, B.; Kamphuisen, H.; Oberye, J. Analysis of a sleep-dependent neuronal feedback loop: The slow-wave microcontinuity of the EEG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 47, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberger, A.L.; Amaral, L.A.N.; Glass, L.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Ivanov, P.C.; Mark, R.G.; Mietus, J.E.; Moody, G.B.; Peng, C.-K.; Stanley, H.E. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet. Circulation 2000, 101, e215–e220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sweden, B.; Kemp, B.; Kamphuisen, H.A.C. Alternative electrode placement in (automatic) sleep scoring (Fpz-Cz/Pz-Oz versus C4-A1/C3-A2). Sleep 1990, 13, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mouze-Amady, M.; Horwat, F. Evaluation of Hjorth parameters in forearm surface EMG analysis during an occupational repetitive task. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1996, 101, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoubek, L.; Charbonnier, S.; Lesecq, S.; Buguet, A.; Chapotot, F. Feature selection for sleep/wake stages classification using data driven methods. Biomed. Signal Process. 2007, 2, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; De Pietro, G. An ontology-based fuzzy decision support system for multiple sclerosis. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2011, 24, 1340–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowa, J.F. Top-level ontological categories. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 1995, 43, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hua, J.; Xiong, Z.; Lowey, J.; Suh, E.; Dougherty, E.R. Optimal number of features as a function of sample size for various classification rules. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 1509–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garner, S. WEKA: The Waikato environment for knowledge analysis. In Proceedings of the New Zealand Computer Science Research Students Conference, Hamilton, New Zealand, 18–21 April 1995; pp. 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Jena, A.P.I. Available online: http://jena.apache.org/ (accessed on 20 November 2020).
- Jensen, F.V. An Introduction to Bayesian Network. Technometrics 1966, 39, 336–337. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Jing, Z.; Hu, B.; Zhu, J.; Zhong, N.; Li, M.; Ding, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L.; Feng, L.; et al. A Resting-State Brain Functional Network Study in MDD Based on Minimum Spanning Tree Analysis and the Hierarchical Clustering. Complexity 2017, 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haykin, S. Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation. Inf. Process. Manag. 1995, 31, 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.; Dai, Y.; Su, Y.; Moore, P.; Zhang, X.; Mao, C.; Chen, J.; Xu, L. Feature Selection for Optimized High-Dimensional Biomedical Data Using an Improved Shuffled Frog Leaping Algorithm. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2016, 15, 1765–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraiwan, L.; Lweesy, K.; Khasawneh, N.; Wenz, H.; Dickhaus, H. Automated sleep stage identification system based on time–frequency analysis of a single EEG channel and random forest classifier. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2012, 108, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himanen, S.-L.; Hasan, J. Limitations of Rechtschaffen and Kales. Sleep Med. Rev. 2000, 4, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsi-Cabrera, M.; Muñoz-Torres, Z.; Del Río-Portilla, Y.; Guevara, M. Power and coherent oscillations distinguish REM sleep, stage 1 and wakefulness. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2006, 60, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Literature | Data Sources | Method | Limitations | Whether to Provide a Feature Management Strategy (Yes or No) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [17] | EEG, EOG, EMG | neural networks | Multiple physiological signal devices limit the subjects’ movement and reduce the quality of physiological signals | no |
| [18] | EEG, EOG, EMG | neural networks | no | |
| [19] | EEG, EOG, EMG | hidden markov models | no | |
| [20] | EEG, EOG, EMG | decision trees | no | |
| [22] | EEG, EOG, EMG | spectral analysis | no | |
| [26] | EEG, EOG, EMG, ECG | optimal combination | no | |
| [15] | EEG | neural networks | Less restriction and interference | no |
| [16] | EEG | neural networks | no | |
| [21] | EEG | visibility graphs | no | |
| [23] | EEG | fuzzy system | no | |
| [24] | EEG | multi-scale entropy | no | |
| [25] | EEG | autoregressive model | no | |
| Our proposed method | EEG | random forest | yes |
| Abbreviation | Full Name |
|---|---|
| α | alpha |
| β | beta |
| θ | theta |
| δ | delta |
| spi | spindle |
| saw | sawtooth |
| Amp | Amplitude |
| var | Variance |
| skew | Skewness |
| kurt | Kurtosis |
| Act | Activity |
| Mob | Mobility |
| Com | Complexity |
| Prel | Relative spectral power |
| Pabs | Absolute spectral power |
| Ent | Entropy |
| spc | Spectral |
| Sleep Stage | Characteristic Wave |
|---|---|
| WA | Alpha, beta |
| NREM1 | Theta |
| NREM2 | K complex, spindle |
| SWS | Delta |
| REM | Alpha, beta, theta, sawtooth |
| Core Concepts | Specific Instances |
|---|---|
| Relative power alpha | Fpz-Cz, Pz-Oz |
| ⋯ | ⋯ |
| Sleep stages | WA, NREM1, NREM2, SWS, REM |
| Stages rule | R&K rules, AASM rules |
| Subject | SC4001E0, ⋯, ST7141J0 |
| Objective Properties | Domain | Range |
|---|---|---|
| is_calculated_on | Relative power alpha | Values range |
| has_Age | Subject | Age range |
| on_Electrode | Kurtosis | Scalp region |
| is_Reflect | EEG feature | Sleep stages |
| Data Properties | Domain | Data Type |
|---|---|---|
| has_feature_values | Relative power alpha | double |
| has_Value | Sleep stages | integer |
| sample_Rate | Sample | float |
| has_Value | has_Value | double |
| Correct Classification | Prediction Classification | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | |
| 1 | true positives (TP) | false negatives (FN) |
| 0 | false positives (FP) | true negatives (TN) |
| Decision Support Tool | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WA | NREM1 | NREM2 | SWS | REM | AC (%) | ||
| Experts | WA | 2193 | 214 | 179 | 39 | 78 | 81.92 |
| NREM1 | 226 | 1512 | 533 | 1 | 340 | 57.86 | |
| NREM2 | 67 | 206 | 14,197 | 517 | 278 | 93.43 | |
| SWS | 9 | 0 | 627 | 6871 | 2 | 91.77 | |
| REM | 41 | 172 | 447 | 10 | 4181 | 87.24 | |
| Average AC (%) | 89.12 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Yang, Z.; Cai, H.; Lian, J.; Chang, W.; Zhang, Z. Ontology-Based Decision Support Tool for Automatic Sleep Staging Using Dual-Channel EEG Data. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1921. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12111921
Zhang B, Yang Z, Cai H, Lian J, Chang W, Zhang Z. Ontology-Based Decision Support Tool for Automatic Sleep Staging Using Dual-Channel EEG Data. Symmetry. 2020; 12(11):1921. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12111921
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bingtao, Zhifei Yang, Hanshu Cai, Jing Lian, Wenwen Chang, and Zhonglin Zhang. 2020. "Ontology-Based Decision Support Tool for Automatic Sleep Staging Using Dual-Channel EEG Data" Symmetry 12, no. 11: 1921. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12111921
APA StyleZhang, B., Yang, Z., Cai, H., Lian, J., Chang, W., & Zhang, Z. (2020). Ontology-Based Decision Support Tool for Automatic Sleep Staging Using Dual-Channel EEG Data. Symmetry, 12(11), 1921. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12111921




