Preparation of Enantiomerically Enriched P-Stereogenic Dialkyl-Arylphosphine Oxides via Coordination Mediated Optical Resolution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General
2.2. Resolution of Ethyl-Phenyl-Propylphosphine Oxide (3) with in Situ Prepared Resolving Agents (Representative Procedure)
2.3. Purification of Diastereomeric Complex of (S)-3·Ca(H-DBTA)2
2.3.1. Purification of Diastereomeric Complex of (S)-3·Ca(H-DBTA)2 by Digestion (Purification Method I)
2.3.2. Purification of Diastereomeric Complex of (S)-3·Ca(H-DBTA)2 by Recrystallization (Purification Method II)
2.3.3. Purification of Diastereomeric Complex of (S)-3·Ca(H-DBTA)2 by Repeated Resolution (Purification Method III)
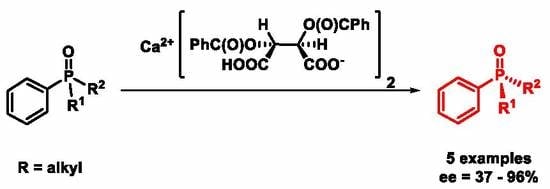
2.4. Resolution of Dialkyl-Arylphosphine Oxides (1, 2, 4–7) with Ca(H-DBTA)2 [(R,R)-8]
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Optical Resolution of Ethyl-Phenyl-Propylphosphine Oxide (3)
3.2. Optical Resolution of Dialkyl-Arylphosphine Oxides (1, 2 and 4–7) with Ca(H-DBTA)2 [(R,R)-8] under Optimized Conditions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Börner, A. (Ed.) Phosphorus Ligands in Asymmetric Catalysis: Synthesis and Applications; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Grabulosa, A. P-Stereogenic Ligands in Enantioselective Catalysis; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dutartre, M.; Bayardon, J.; Jugé, S. Applications and stereoselective syntheses of P-chirogenic phosphorus compounds. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5771–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamer, P.C.J.; Van Leeuwen, P.W.N.M. (Eds.) Phosphorus(III)Ligands in Homogeneous Catalysis: Design and Synthesis; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Imamoto, T. Searching for practically useful P-chirogenic phosphine ligands. Chem. Rec. 2016, 16, 2655–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Guo, H.; Kwon, O. Chiral phosphines in nucleophilic organocatalysis. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2014, 10, 2089–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Fan, Y.C.; Sun, Z.; Wu, Y.; Kwon, O. Phosphine organocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 10049–10293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Chan, W.-L.; Lu, Y. Phosphine-catalyzed asymmetric organic reactions. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 9344–9411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaglia, M.; Rossi, S. Chiral phosphine oxides in present-day organocatalysis. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 3824–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayad, T.; Gernet, A.; Pirat, J.-L.; Virieux, D. Enantioselective reactions catalyzed by phosphine oxides. Tetrahedron 2019, 75, 4385–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Kumatabara, Y.; Shirakawa, S. Chiral quaternary phosphonium salts as phase-transfer catalysts for environmentally benign asymmetric transformations. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golandaj, A.; Ahmad, A.; Ramjugernath, D. Phosphonium salts in asymmetric catalysis: A journey in a decade’s extensive research work. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2017, 359, 3676–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, W.S. Asymmetric Hydrogenations (Nobel Lecture). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 1998–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaud, R.; Phipps, R.J.; Gaunt, M.J. Enantioselective Cu-catalyzed arylation of secondary phosphine oxides with diaryliodonium salts toward the synthesis of P-chiral phosphines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 13183–13186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.-T.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Han, X.-Y.; Sun, S.-P.; Zhang, Q.-W. Ni-Catalyzed asymmetric allylation of secondary phosphine oxides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 16584–16589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korpiun, O.; Lewis, R.A.; Chickos, J.; Mislow, K. Synthesis and absolute configuration of optically active phosphine oxides and phosphinates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1968, 90, 4842–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, N.G.; Ramsden, P.D.; Che, D.Q.; Parvez, M.; Keay, B.A. A simple resolution procedure using the Staudinger reaction for the preparation of P-stereogenic phosphine oxides. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 7478–7486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliana, M.; King, F.; Horton, P.N.; Hursthouse, M.B.; Hii, K.K. Practical synthesis of chiral vinylphosphine oxides by direct nucleophilic substitution. Stereodivergent synthesis of aminophosphine ligands. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 2472–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, H.; Collins, R.C.; Jones, S.; Warner, C.J.A. Enantioselective preparation of P-chiral phosphine oxides. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 6576–6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaux, F.; Frynas, S.; Laureano, H.; Salomon, C.; Morata, G.; Auclair, M.-L.; (Massoud) Stephan, M.; Merdès, R.; Richard, P.; Ondel-Eymin, M.-J.; et al. Enantiodivergent synthesis of P-chirogenic phosphines. C. R. Chim. 2010, 13, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.S.; Goyal, N.; Herbage, M.A.; Sieber, J.D.; Qu, B.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Reeves, J.T.; Desrosiers, J.-N.; Ma, S.; et al. Efficient asymmetric synthesis of P-chiral phosphine oxides via properly designed and activated benzoxazaphosphinine-2-oxide agents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2474–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copey, L.; Jean-Gérard, L.; Framery, E.; Pilet, G.; Robert, V.; Andrioletti, B. Experimental and theoretical investigations of the stereoselective synthesis of P-stereogenic phosphine oxides. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 9057–9061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onofrio, A.; Copey, L.; Jean-Gérard, L.; Goux-Henry, C.; Pilet, G.; Andrioletti, B.; Framery, E. D-Glucosamine as a novel chiral auxiliary for the stereoselective synthesis of P-stereogenic phosphine oxides. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 9029–9034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-G.; Yuan, M.; Topic, F.; Han, Z.S.; Senanayake, C.H.; Tsantrizos, Y.S. Asymmetric library synthesis of P-chiral t-butyl-substituted secondary and tertiary phosphine oxides. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 7291–7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, R.K.; Au-Yeung, T.-L.; Chan, W.-K.; Lam, W.-L.; Li, Z.-Y.; Yeung, L.-L.; Chan, A.S.C.; Li, P.; Koen, M.; Mitchell, C.R.; et al. Reaction of metallated tert-butyl(phenyl)phosphane oxide with electrophiles as a route to functionalized tertiary phosphane oxides: Alkylation reactions. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 2000, 3205–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhao, C.-Q.; Han, L.-B. Stereospecific nucleophilic substitution of optically pure H-phosphinates: A general way for the preparation of chiral P-stereogenic phosphine oxides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12648–12655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.S.; Wu, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, B.; Li, Z.; Caldwell, D.R.; Fandrick, K.R.; Zhang, L.; Roschangar, F.; et al. General and stereoselective method for the synthesis of sterically congested and structurally diverse P-stereogenic secondary phosphine oxides. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 1796–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrzanowski, J.; Krasowska, D.; Urbaniak, M.; Sieroń, L.; Pokora-Sobczak, P.; Demchuk, O.M.; Drabowicz, J. Synthesis of enantioenriched aryl-tert-butylphenylphosphine oxides via cross-coupling reactions of tert -butylphenylphosphine oxide with aryl halides. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 2018, 4614–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiełbasiński, P.; Źurawiński, R.; Pietrusiewicz, K.M.; Zabłocka, M.; Mikołajczyk, M. Enzymatic resolution of racemic phosphinoylacetates having a stereogenic phosphorus atom. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 7081–7084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarczyk, S.; Kwiatkowska, M.; Madalińska, L.; Barbachowska, A.; Rachwalski, M.; Błaszczyk, J.; Sieroń, L.; Kiełbasiński, P. Enzymatic synthesis of enantiopure precursors of chiral bidentate and tridentate phosphorus catalysts. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 2446–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shioji, K.; Ueno, Y.; Kurauchi, Y.; Okuma, K. Lipase-catalyzed kinetic resolution of P-chiral phosphorus compounds: Enantiopreference of Pseudomonas lipase and Candida antarctica lipase. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 6569–6571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, H.; Wang, Q.; Cai, Q. Asymmetric synthesis of chiral P-stereogenic triaryl phosphine oxides via Pd-catalyzed kinetic arylation of diaryl phosphine oxides. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 5308–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Pérez, H.; Vidal-Ferran, A. Stereoselective catalytic synthesis of P-stereogenic oxides via hydrogenative kinetic resolution. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 7019–7023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergin, E.; O’Connor, C.T.; Robinson, S.B.; McGarrigle, E.M.; O’Mahony, C.P.; Gilheany, D.G. Synthesis of P-stereogenic phosphorus compounds. Asymmetric oxidation of phosphines under Appel conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 9566–9567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitin, K.; Rajendran, K.V.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Gilheany, D.G. Turning regioselectivity into stereoselectivity: Efficient dual resolution of P-stereogenic phosphine oxides through bifurcation of the reaction pathway of a common intermediate. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 1906–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, K.V.; Nikitin, K.V.; Gilheany, D.G. Hammond postulate mirroring enables enantiomeric enrichment of phosphorus compounds via two thermodynamically interconnected sequential stereoselective processes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 9375–9381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kortmann, F.A.; Chang, M.-C.; Otten, E.; Couzijn, E.P.A.; Lutz, M.; Minnaard, A.J. Consecutive dynamic resolutions of phosphine oxides. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 1322–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ironmonger, A.; Shipton, M.; Slater, F.; Szeto, P.; Unthank, M.G.; Alexandre, F.R.; Caillet, C.; Dousson, C.B. A highly diastereoselective chloride-mediated dynamic kinetic resolution at phosphorus on-route to a key intermediate in the synthesis of GSK2248761A. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 2154–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Minnaard, A.J.; Hessen, B.; Feringa, B.L.; Duchateau, A.L.L.; Andrien, J.G.O.; Boogers, J.A.F.; de Vries, J.G. Application of monodentate secondary phosphine oxides, a new class of chiral ligands, in Ir(I)-catalyzed asymmetric imine hydrogenation. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 1503–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatineau, D.; Nguyen, D.H.; Hérault, D.; Vanthuyne, N.; Leclaire, J.; Giordano, L.; Buono, G. H-adamantylphosphinates as universal precursors of P-stereogenic compounds. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 4132–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, F.; Mori, K.; Stein, Z.; Goldberg, I. Optical resolution of phosphinates and phosphine oxides by complex formation with optically active 2,2’-dihydroxy-1,1’-binaphthyl and crystallographic study of two diastereomeric complexes with methyl methylphenylphosphinate. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drabowicz, J.; Łyżwa, P.; Omelańczuk, J.; Pietrusiewicz, K.M.; Mikołajczyk, M. New procedures for the resolution of chiral tert-butylphenylphosphine oxide and some of its reactions. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1999, 10, 2757–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, J.; Maj, A.M.; Schudde, E.P.; Pietrusiewicz, K.M.; Sieroń, L.; Wieczorek, W.; Jerphagnon, T.; Arends, I.W.C.E.; Hanefeld, U.; Minnaard, A.J. On the resolution of secondary phosphine oxides via diastereomeric complex formation: The case of tert-butylphenylphosphine oxide. Synthesis 2009, 2009, 2061–2065. [Google Scholar]
- Bagi, P.; Ujj, V.; Czugler, M.; Fogassy, E.; Keglevich, G. Resolution of P-stereogenic P-heterocycles via the formation of diastereomeric molecular and coordination complexes (a review). Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 1823–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bagi, P.; Varga, B.; Szilágyi, A.; Karaghiosoff, K.; Czugler, M.; Fogassy, E.; Keglevich, G. The resolution of acyclic P-stereogenic phosphine oxides via the formation of diastereomeric complexes: A case study on ethyl-(2-methylphenyl)-phenylphosphine oxide. Chirality 2018, 30, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziuba, K.; Lubańska, M.; Pietrusiewicz, K.M. Enantiodivergent synthesis of both PAMPO enantiomers using l-menthyl chloroacetate and stereomutation at P in classical quaternisation reactions. Synthesis 2019. Available online: https://www.thieme-connect.com/products/ejournals/abstract/10.1055/s-0039-1691531 (accessed on 14 January 2020). [CrossRef]
- Faigl, F.; Fogassy, E.; Nógrádi, M.; Pálovics, E.; Schindler, J. Strategies in optical resolution: A practical guide. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2008, 19, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, S. Racemic drug resolution: A comprehensive guide. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 7567–7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagi, P.; Herbay, R. Resolution of phosphine oxides. In Organophosphorus Chemistry—Novel Developments; Keglevich, G., Ed.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 66–90. [Google Scholar]
- Meisenheimer, J.; Casper, J.; Höring, M.; Lauter, W.; Lichtenstadt, L.; Samuel, W. Optisch-aktive Phosphinoxyde. J. Liebig. Ann. Chem. 1926, 449, 213–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozma, D.; Bocskei, Z.; Kassai, C.; Simon, K.; Fogassy, E. Optical resolution of racemic alcohols by diastereoisomeric complex formation with O,O’-dibenzoyl-(2R,3R)-tartaric acid; the crystal structure of the (-)-(1R,2S,5R)-menthol-O,O’-dibenzoyl-(2R,3R)-tartaric acid complex. Chem. Commun. 1996, 635, 753–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mravik, A.; Böcskei, Z.; Katona, Z.; Markovits, I.; Fogassy, E. Coordination-mediated optical resolution of carboxylic acids with O,O′-dibenzoyltartaric acid. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1997, 36, 1534–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Deng, J.; Cun, L.; Cui, X.; Wu, J.; Xu, X.; Wu, Y. Copper(II)-mediated resolution of alpha-halo carboxylic acids with chiral O,O’-dibenzoyltartaric acid: Spontaneous racemization and crystallization-induced dynamic resolution. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2005, 3, 4227–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degenbeck, H.; Felten, A.S.; Etxebarria, J.; Escudero-Adán, E.C.; Benet-Buchholz, J.; Vidal-Ferran, A. Crystallization-induced dynamic resolution of stereolabile biaryl derivatives involving supramolecular interactions. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 2719–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wu, C.; Wu, X.Y.; Li, S.L.; Sun, X.X.; Tang, Z.B. Efficient preparation of (R)-2-chloromandelic acid via a recycle process of resolution. Chirality 2015, 27, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Xie, H.; Ran, K.; Gan, Y. Efficient synthesis and resolution of Tenofovir Alafenamide. Lett. Org. Chem. 2017, 15, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujj, V.; Schindler, J.; Novák, T.; Czugler, M.; Fogassy, E.; Keglevich, G. Coordinative resolution of 1-phenyl- and 1-naphthyl-3-methyl-3-phospholene 1-oxides with calcium hydrogen O,O′-dibenzoyl-(2R,3R)-tartrate or calcium hydrogen O,O′-di-p-toluyl-(2R,3R)-tartrate. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2008, 19, 1973–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagi, P.; Karaghiosoff, K.; Czugler, M.; Hessz, D.; Kállay, M.; Kubinyi, M.; Szilvási, T.; Pongrácz, P.; Kollár, L.; Timári, I.; et al. Synthesis, characterization, and application of platinum(II) complexes incorporating racemic and optically active 4-chloro-5-methyl-1-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydrophosphinine ligand. Heteroatom. Chem. 2016, 27, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faigl, F.; Fogassy, E.; Nógrádi, M.; Pálovics, E.; Schindler, J. Separation of non-racemic mixtures of enantiomers: An essential part of optical resolution. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Entry | Resolving Agent | Eq. | Solvents a | Diastereomeric Complex b | Yield c,g (%) | Eed,g (%) | S e,g (-) | Abs. Config. f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 h | Ca(H-DBTA)2 | 0.5 | 3 × EtOAc/3 × EtOH | (3)∙Ca(H-DBTA)2 | 83 | 44 | 0.36 | (S) |
| 2 i | Ca(H-DBTA)2 | 0.5 | 3 × EtOAc/3 × EtOH/0.3 × H2O | (3)∙Ca(H-DBTA)2 | 62 | 69 | 0.43 | (S) |
| 3 i | Ca(DBTA) | 0.5 | 3 × EtOAc/3 × EtOH/0.3 × H2O | (3)∙Ca(DBTA) | 115 | 19 | 0.22 | (S) |
| 4 i | Ca(H-DPTTA)2 | 0.5 | 3 × EtOAc/3 × EtOH/0.3 × H2O | (3)∙Ca(H-DPTTA)2 | 66 | 38 | 0.25 | (S) |
| 5 i | Ca(DPTTA) | 0.5 | 3 × EtOAc/3 × EtOH/0.3 × H2O | no complex | - | - | - | - |
| Entry | Eq. of Ca(H-DBTA)2 | Solvents a | Diastereomeric Complex b | Yield c,g (%) | Eed,g (%) | S e,g(-) | Abs. Config. f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 h | 0.5 | 3 × EtOAc/3 × EtOH/0.3 × H2O | (3)∙Ca(H-DBTA)2 | 62 | 69 | 0.43 | (S) |
| 2 | 0.5 | 3 × EtOAc/3 × MeOH/0.3 × H2O | (3)∙Ca(H-DBTA)2 | 18 | 79 | 0.14 | (S) |
| 3 | 0.5 | 3 × EtOAc/3 × 2-PrOH/0.3 × H2O | (3)∙Ca(H-DBTA)2 | 66 | 17 | 0.11 | (S) |
| 4 | 0.5 | 3 × BuOAc/3 × EtOH/0.3 × H2O | (3)∙Ca(H-DBTA)2 | 70 | 55 | 0.38 | (S) |
| 5 | 0.5 | 3 × acetone/3 × EtOH/0.3 × H2O | (3)∙Ca(H-DBTA)2 | 62 | 14 | 0.08 | (S) |
| 6 | 0.5 | 3 × MeCN/3 × EtOH/0.3 × H2O | (3)∙Ca(H-DBTA)2 | 42 | 18 | 0.06 | (S) |
| 7 | 0.5 | 3 × toluene/3 × EtOH/0.3 × H2O | (3)∙Ca(H-DBTA)2 | 27 | 0 | 0.00 | (S) |
| 8 | 0.5 | 6 × EtOH/0.3 × H2O | (3)4∙Ca3(H-DBTA)6 | 75 | 44 | 0.33 | (S) |
| 9 | 0.5 | 6 × EtOAc | (3)2∙Ca(H-DBTA)2 | 123 | 12 | 0.15 | (S) |
| 10 | 1 | 3 × EtOAc/3 × EtOH/0.3 × H2O | (3)∙Ca(H-DBTA)2 | 79 | 74 | 0.58 | (S) |
| 11 | 1 | 1.5 × EtOAc/1.5 × EtOH/0.15 × H2O | (3)∙Ca(H-DBTA)2 | 105 | 54 | 0.57 | (S) |
| 12 | 1 | 4.5 × EtOAc/4.5 × EtOH/0.45 × H2O | (3)∙Ca(H-DBTA)2 | 65 | 73 | 0.48 | (S) |
| 13 | 1 | 5 × EtOAc/1 × EtOH/0.3 × H2O | (3)∙Ca(H-DBTA)2 | 132 | 39 | 0.50 | (S) |
| 14 | 1 | 1 × EtOAc/5 × EtOH/0.3 × H2O | (3)∙Ca(H-DBTA)2 | 57 | 71 | 0.41 | (S) |
| 15 | 1 | 3 × EtOAc/3 × EtOH/0.15 × H2O | (3)∙Ca(H-DBTA)2 | 97 | 56 | 0.54 | (S) |
| 16 | 1 | 3 × EtOAc/3 × EtOH/0.6 × H2O | Ca(H-DBTA)2 | - | - | - | - |
| Entry | R1 = Me, R2 = | Diastereomeric Complex a | Number of Crystallizations | Yield b (%) | Eec (%) | S d (-) | Abs. Config. e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Et (1) | (1)2∙Ca(H-DBTA)2 | I. | 109 | 34 | 0.37 | (R) |
| II. | 73 | 66 | 0.48 | ||||
| III. | 46 | 80 | 0.36 | ||||
| IV. | 32 | 85 | 0.27 | ||||
| 2 | Pr (2) | (2)∙Ca(H-DBTA)2 | I. | 16 | 37 | 0.06 | (S) |
| 3 | Bu (4) | (4)∙Ca(H-DBTA)2 | I. | 26 | 75 | 0.20 | (S) |
| II. | 8 | 96 | 0.08 | ||||
| 4 f | Bu (4) | (4)∙Ca(H-DBTA)2 | I. | 69 | 54 | 0.37 | (S) |
| II. | 34 | 86 | 0.29 | ||||
| III. | 17 | 96 | 0.16 | ||||
| 5 | i-Pr (5) | (5)3∙Ca2(H-DBTA)4 | I. | 91 | 32 | 0.29 | (R) |
| II. | 54 | 53 | 0.29 | ||||
| III. | 30 | 69 | 0.21 | ||||
| IV. | 20 | 80 | 0.16 | ||||
| 6 | c-Hex (6) | no complex | - | - | - | - | - |
| 7 | t-Bu (7) | (7)2∙Ca(H-DBTA)2 | I. | 125 | 3 | 0.04 | (R) |
| II. | 79 | 3 | 0.03 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varga, B.; Bagi, P. Preparation of Enantiomerically Enriched P-Stereogenic Dialkyl-Arylphosphine Oxides via Coordination Mediated Optical Resolution. Symmetry 2020, 12, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12020215
Varga B, Bagi P. Preparation of Enantiomerically Enriched P-Stereogenic Dialkyl-Arylphosphine Oxides via Coordination Mediated Optical Resolution. Symmetry. 2020; 12(2):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12020215
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarga, Bence, and Péter Bagi. 2020. "Preparation of Enantiomerically Enriched P-Stereogenic Dialkyl-Arylphosphine Oxides via Coordination Mediated Optical Resolution" Symmetry 12, no. 2: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12020215
APA StyleVarga, B., & Bagi, P. (2020). Preparation of Enantiomerically Enriched P-Stereogenic Dialkyl-Arylphosphine Oxides via Coordination Mediated Optical Resolution. Symmetry, 12(2), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12020215