Brain Extraction Using Active Contour Neighborhood-Based Graph Cuts Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sets
2.2. Graph Cuts
2.3. Active Contour Neighborhood-Based Graph Cuts Model
2.3.1. Description of ACN Model (ACNM)
2.3.2. Edge Weights Assignment in ACNM
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation Metrics
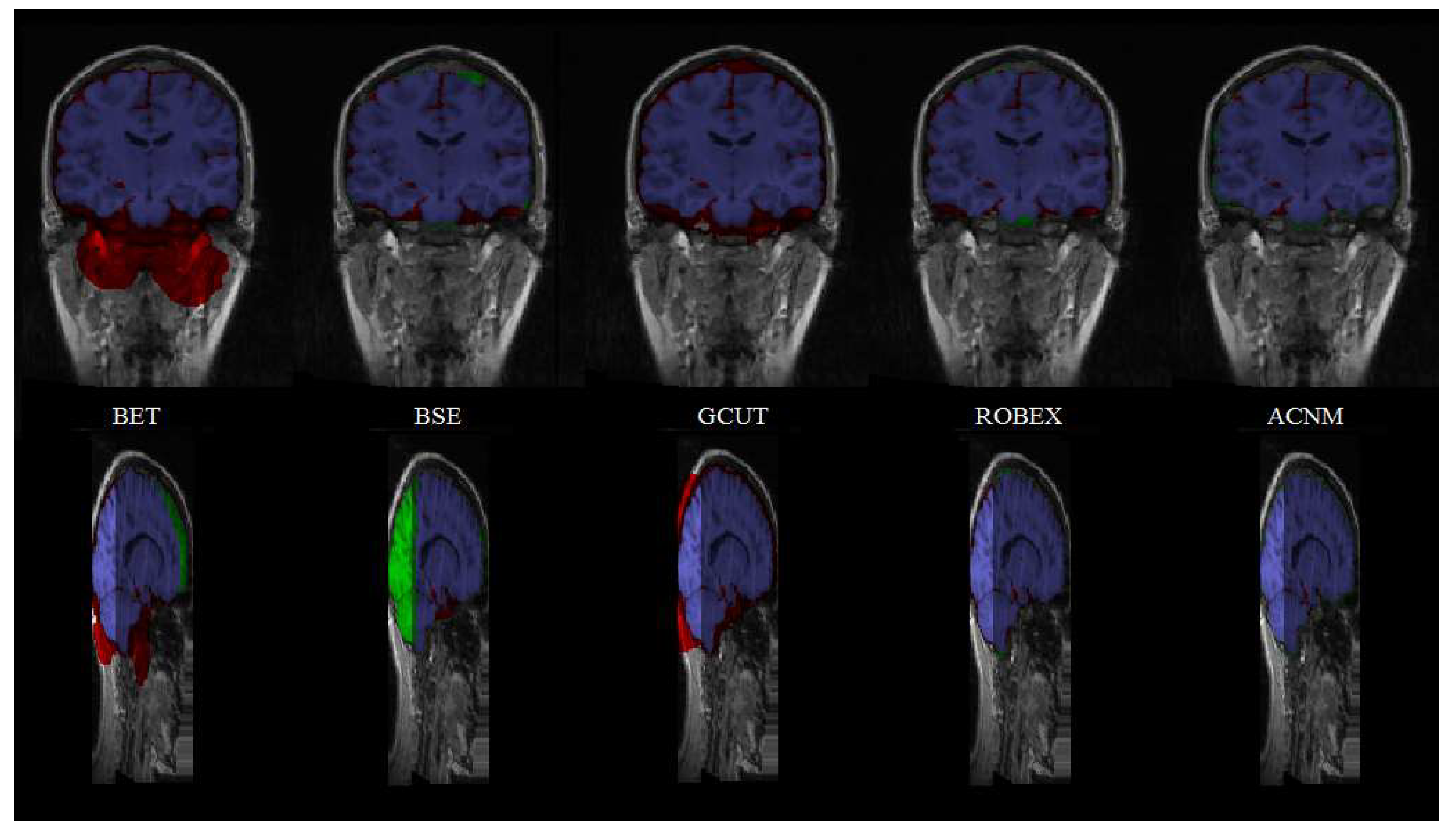
3.2. Comparison to Other Methods
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woods, R.P.; Grafton, S.T.; Watson, J.D.G.; Sicotte, N.L.; Mazziotta, J.C. Automated image registration—Part II: Intersubject validation of linear and nonlinear models. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1998, 22, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.M. Fast robust automated brain extraction. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2002, 17, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholipour, A.; Kehtarnavaz, N.; Briggs, R.; Devous, M.; Gopinath, K. Brain functional localization: A survey of image registration techniques. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2007, 26, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermel, R.A.; Sharma, J.; Tjoa, C.W.; Puli, S.R.; Bakshi, R. A semiautomated measure of whole-brain atrophy in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2003, 208, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.; Srinivasan, P.; Spaeth, R.; Tan, Y.; Kosek, E.; Petzke, F.; Carville, S.; Fransson, P.; Marcus, H.; Williams, S.C. Overlapping structural and functional brain changes in patients with long-term exposure to fibromyalgia. Arthritis. Rheum. 2013, 65, 3293–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shattuck, D.W.; Sandor-Leahy, S.R.; Schaper, K.A.; Rottenberg, D.A.; Leahy, R.M. Magnetic resonance image tissue classification using a partial volume model. Neuroimage 2001, 13, 856–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dale, A.M.; Fischl, B.; Sereno, M.I. Cortical surface-based analysis—Part I: Segmentation and surface reconstruction. Neuroimage 1999, 9, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.W. AFNI:Software for analysis and visualization of functional magnetic resonance neuroimages. Comput. Biomed. Res. 1996, 29, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemieux, L.; Hagemann, G.; Krakow, K.; Woermann, F.G. Fast, accurate, and reproducible automatic segmentation of the brain in T1-weighted volume MRI data. Magn. Reson. Med. 1999, 42, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, H.K.; Peitgen, H.O. The Skull Stripping Problem in MRI Solved by a Single 3D Watershed Transform. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 11–14 October 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, A.H.; Valentino, D.J.; Toga, A.W. Skull-stripping magnetic resonance brain images using a model-based level set. Neuroimage 2006, 32, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, L. Accurate and robust extraction of brain regions using a deformable model based on radial basis functions. J. Neurosci. Methods 2009, 183, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.; Abugharbieh, R.; Ram, R.; Traboulsee, A. MRI brain extraction with combined expectation maximization and geodesic active contours. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 27–30 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Segonne, F.; Dale, A.M.; Busa, E.; Glessner, M.; Salat, D.; Hahn, H.K.; Fischl, B. A hybrid approach to the skull stripping problem in MRI. Neuroimage 2004, 22, 1060–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadananthan, S.A.; Zheng, W.; Chee, M.W.; Zagorodnov, V. Skull stripping using graph cuts. Neuroimage 2010, 49, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z. Brain extraction from cerebral MRI volume using a hybrid level set based active contour neighborhood model. Biomed. Eng. Online 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Nie, J.; Yap, P.T. Knowledge-guided robust MRI brain extraction for diverse large-scale neuroimaging studies on humans and non-human primates. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iglesias, J.; Liu, C.; Thompson, P.; Tu, Z. Robust Brain Extraction Across Data sets and Comparison with Publicly Available Methods. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2011, 30, 1617–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskildsen, S.F.; Coupé, P.; Fonov, V.; Manjón, J.V.; Leung, K.K.; Guizard, N.; Wassef, S.N.; Østergaard, L.R.; Collins, D.L. BEaST: Brain Extraction based on nonlocal Segmentation Technique. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 2362–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Yang, W.; Jiang, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Feng, Q. Brain extraction based on locally linear representation-based classification. Neuroimage 2014, 92, 322–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleesiek, J.; Urban, G.; Hubert, A.; Schwarz, D.; Maier-Hein, K.; Bendszus, M.; Biller, A. Deep MRI brain extraction: A 3D convolutional neural network for skull stripping. Neuroimage 2016, 129, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, S.S.M.; Erdogmus, D.; Gholipour, A. Auto-Context Convolutional Neural Network (Auto-Net) for Brain Extraction in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 2319–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundo, L.; Militello, C.; Russo, G.; Vitabile, S.; Gilardi, M.C.; Mauri, G. GTVcut for neuro-radiosurgery treatment planning: An MRI brain cancer seeded image segmentation method based on a cellular automata model. Nat. Comput. 2017, 17, 521–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.; Rehman, H.Z.U.; Lee, S. 3D U-Net for skull stripping in brain MRI. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, N.; Bansal, R.; Ahuja, N. Object segmentation using graph cuts based active contours. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2003, Madison, WI, USA, 16–22 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Boykov, Y.; Jolly, M.P. Interactive graph cuts for optimal boundary and region segmentation of objects in N-D images. In Proceedings of the ICCV, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–14 July 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Boykov, Y.; Veksler, O.; Zabih, R. Fast Approximate Energy Minimization via Graph Cuts. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2001, 23, 1222–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolmogorov, V.; Zabih, R. What Energy Functions can be Minimized via Graph Cuts? IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2004, 26, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boykov, Y.; Kolmogorov, V. An experimental comparison of min-cut/max-flow algorithms for energy minimization in vision. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2004, 26, 1124–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, S.; Yang, S.; Chen, Z.; Chen, W. Automatic extraction of brain from cerebral MR image based on improved BET method. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Information, Tianjin, China, 17–19 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bezdek, J.C.; Ehrlich, R.; Full, W. FCM: The fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Comput. Geosci. 1984, 10, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Militello, C.; Rundo, L.; Vitabile, S.; Russo, G.; Pisciotta, P.; Marletta, F.; Ippolito, M.; D’Arrigo, C.; Midiri, M.; Gilardi, M.C. Gamma Knife treatment planning: MR brain tumor segmentation and volume measurement based on unsupervised Fuzzy C-Means clustering. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2015, 25, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, G. Deep learning: A critical appraisal. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.00631. preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Rundo, L.; Han, C.; Nagano, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hataya, R.; Militello, C.; Tangherloni, A.; Nobile, M.S.; Ferretti, C.; Besozzi, D.; et al. USE-Net: Incorporating Squeeze-and-Excitation blocks into U-Net for prostate zonal segmentation of multi-institutional MRI datasets. Neurocomputing 2019, 365, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Edge | Weight | for |
|---|---|---|
| K | ||
| 0 | ||
| 0 | ||
| K |
| Edge | Weight | for |
|---|---|---|
| Method | DS Mean (SD) | JS Mean (SD) | FPRATE (%) Mean (SD) | FNRATE (%) Mean (SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BET P*-value | 0.946(0.012) 3.0 × 10−4 | 0.898(0.021) 3.3 × 10−4 | 8.36(2.77) 4.65 × 10−7 | 2.83(2.92) 1.09 × 10−4 |
| BSE P*-value | 0.943(0.039) 5.0 × 10−2 | 0.895(0.066) 4.87 × 10−2 | 7.82(6.20) 8.71 × 10−3 | 3.68(6.30) 2.71 × 10−1 |
| GCUT P*-value | 0.911(0.015) 8.72 × 10−8 | 0.837(0.025) 7.08 × 10−8 | 18.47(3.89) 1.02 × 10−12 | 0.92(0.04) 1.34 × 10−6 |
| ROBEX P*-value | 0.927(0.032) 2.42 × 10−3 | 0.865(0.054) 2.0 × 10−3 | 14.74(8.14) 2.0 × 10−5 | 1.1(0.81) 1.34 × 10−6 |
| ACNM | 0.957(0.013) | 0.917(0.024) | 4.06(1.24) | 4.55(2.48) |
| Method | DS Mean (SD) | JS Mean (SD) | FPRATE (%) Mean (SD) | FNRATE (%) Mean (SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BET P*-value | 0.849(0.076) 2.96 × 10−6 | 0.745(0.110) 9.93 × 10−7 | 22.87(7.95) 1.21 × 10−8 | 9.00(11.30) 2.76 × 10−2 |
| BSE P*-value | 0.933(0.054) 2.02 × 10−2 | 0.878(0.084) 1.58 × 10−2 | 6.43(2.43) 1.27 × 10−8 | 6.57(9.46) 7.41 × 10−2 |
| GCUT P*-value | 0.88(0.015) 1.62 × 10−12 | 0.786(0.024) 1.0 × 10−12 | 27.34(3.91) 1.57 × 10−15 | 0.01(0.02) 1.89 × 10−6 |
| ROBEX P*-value | 0.94(0.012) 1.33 × 10−6 | 0.888(0.021) 9.93 × 10−7 | 11.9(2.75) 6.72 × 10−12 | 0.67(0.46) 1.86 × 10−6 |
| ACNM | 0.960(0.009) | 0.924(0.016) | 4.61(2.08) | 3.40(2.40) |
| Method | DS Mean(SD) | JS Mean(SD) | FPRATE (%)Mean(SD) | FNRATE (%)Mean(SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BET P*-value | 0.931(0.019) 2.64 × 10−2 | 0.871(0.033) 2.54 × 10−2 | 11.0(3.70) 1.14 × 10−35 | 3.45(2.94) 2.95 × 10−33 |
| BSE P*-value | 0.923(0.060) 3.80 × 10−2 | 0.862(0.090) 4.99 × 10−2 | 14.1(18.2) 5.32 × 10−8 | 3.29(2.02) 2.22 × 10−33 |
| GCUT P*-value | 0.950(0.008) 3.57 × 10−8 | 0.904(0.015) 2.90 × 10−8 | 7.55(2.82) 1.13 × 10−40 | 2.76(1.79) 9.57 × 10−6 |
| ROBEX P*-value | 0.955(0.008) 1.02 × 10−21 | 0.914(0.015) 1.36 × 10−22 | 2.54(1.3) 4.22 × 10−10 | 6.23(2.1) 6.16 × 10−23 |
| ACNM | 0.936(0.018) | 0.879(0.031) | 1.95(1.30) | 10.32(3.87) |
| Method | DS Mean | SE Mean | SP Mean |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | 0.958 | 0.943 | 0.994 |
| ACNM | 0.951 | 0.940 | 0.994 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Z.; Yang, S. Brain Extraction Using Active Contour Neighborhood-Based Graph Cuts Model. Symmetry 2020, 12, 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12040559
Jiang S, Wang Y, Zhou X, Chen Z, Yang S. Brain Extraction Using Active Contour Neighborhood-Based Graph Cuts Model. Symmetry. 2020; 12(4):559. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12040559
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Shaofeng, Yu Wang, Xuxin Zhou, Zhen Chen, and Suhua Yang. 2020. "Brain Extraction Using Active Contour Neighborhood-Based Graph Cuts Model" Symmetry 12, no. 4: 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12040559
APA StyleJiang, S., Wang, Y., Zhou, X., Chen, Z., & Yang, S. (2020). Brain Extraction Using Active Contour Neighborhood-Based Graph Cuts Model. Symmetry, 12(4), 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12040559




