Informational Measure of Symmetry vs. Voronoi Entropy and Continuous Measure of Entropy of the Penrose Tiling. Part II of the “Voronoi Entropy vs. Continuous Measure of Symmetry of the Penrose Tiling”
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Definition of the Informational Measure of Symmetry
3.2. Informational Measure of Symmetry of the Patterns Generated by the Penrose Tiling
- (i)
- is interpreted as an averaged uncertainty in the presence of symmetry elements from the group G in the given pattern.
- (ii)
- may also be understood as a measure of the average unlikelihood, or unexpectedness of presence of symmetry elements constituting group G in the given 2D pattern.
- (iii)
- The most complicated is the information interpretation of the . It turns out that the quantity provides us with a measure of this information in terms of the minimum number of questions one needs to ask in order to find the presence of elements of symmetry in a given pattern, when , i.e., the probabilities of appearance of the symmetry operation within the pattern are prescribed. It turns out that the quantity provides a minimum measure of information needed to describe a given pattern as a composition of elements of symmetry [5].
- (i)
- The quantification of symmetry of the pattern has a “fine structure” and could not be expressed with a single numerical value.
- (ii)
- The information measure of symmetry, the Voronoi entropy and the continuous measure of symmetry are not necessarily correlated.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shannon, C.E.; Weaver, W. The Mathematical Theory of Communication; The University of Illinois Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Landau, L.D.; Lifshitz, E.M. Statistical Physics, 3rd ed.; Course of Theoretical Physics; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2011; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Kittel, C. Thermal Physics; J. Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Naim, A. Entropy, Shannon’s Measure of Information and Boltzmann’s H-Theorem. Entropy 2017, 19, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ben-Naim, A. Information Theory; World Scientific: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Naim, A. A Farewell to Entropy: Statistical Thermodynamics Based on Information; World Scientific: Singapore, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Naim, A.; Casadei, D. Modern Thermodynamics; World Scientific: Singapore, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Naim, A. Entropy and the Second Law. Interpretation and Misss-Interpretationsss; World Scientific: Singapore, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vstovsky, G.V. Transform information: A symmetry breaking measure. Found. Phys. 1997, 27, 1413–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleiser, M.; Stamatopoulos, N. Information content of spontaneous symmetry breaking. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 045004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bormashenko, E. Entropy, Information, and Symmetry: Ordered is Symmetrical. Entropy 2020, 22, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bormashenko, E. Entropy, Information, and Symmetry: Ordered Is Symmetrical, II: System of Spins in the Magnetic Field. Entropy 2020, 22, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zabrodsky, H.; Peleg, S.; Avnir, D. Continuous symmetry measures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 7843–7851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabrodsky, H.; Peleg, S.; Avnir, D. Continuous symmetry measures. 2. Symmetry groups and the tetrahedron. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 8278–8289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemany, P.; Casanova, D.; Alvarez, S.; Dryzun, C.; Avnir, D. Continuous Symmetry Measures: A New Tool in Quantum Chemistry, Reviews in Computational Chemistry; Parrill, A.L., Lipkowitz, K.B., Eds.; Wliey, Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; Volume 30, pp. 289–353. [Google Scholar]
- Zabrodsky, H.; Avnir, D. Continuous Symmetry Measures. 4. Chirality. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinsky, M.; Avnir, D. Continuous Symmetry Measures. 5. The Classical Polyhedra. Inorg. Chem. 1998, 37, 5575–5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabrodsky, H.; Peleg, S.; Avnir, D. Symmetry as a continuous feature. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intel. 1995, 17, 1154–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinsky, M.; Dryzun, C.; Casanova, D.; Alemany, P.; Avnir, D. Analytical methods for calculating Continuous Symmetry Measures and the Chirality Measure. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 2712–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonjack, M.; Avnir, D. The near-symmetry of protein oligomers: NMR-derived structures. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinai, H.E.; Avnir, D. Adsorption-induced Symmetry Distortions in W@Au12 Nanoclusters, Leading to Enhanced Hyperpo-larizabilities. Israel J. Chem. 2016, 56, 1076–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormashenko, E.; Legchenkova, I.; Frenkel, M.; Shvalb, S. Voronoi Entropy vs Continuous Measure of Symmetry of the Penrose Tiling: Part I. Analysis of the Voronoi Diagrams. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronoi, G. Nouvelles applications des paramètres continus à la théorie des formes quadratiques. Deuxième mémoire. Recherches sur les paralléloèdres primitifs. Reine Angew. Math. 1908, 134, 198–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthélemy, M. Spatial networks. Phys. Rep. 2011, 499, 1–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weaire, D.; Rivier, N. Soap, cells and statistics—Random patterns in two dimensions. Contemp. Phys. 1984, 25, 59–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Tian, Z.; Dong, K.; Xie, Q. Inconsistency of neighborhood based on Voronoi tessellation and Euclidean distance. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 854, 156983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorets, A.A.; Dombrovskyb, L.A. Self-assembled levitating clusters of water droplets: Pattern-formation and stability. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.T.; Tao, C.L.; Zhang, X.; Xia, W.; Shi, D.Q.; Qi, L.; Xu, C.; Sun, R.; Li, X.; Bi, G.Q.; et al. Mesophasic organization of GABAA receptors in hippocampal inhibitory synapses. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fedorets, A.A.; Frenkel, M.; Bormashenko, E.; Nosonovsky, M. Small Levitating Ordered Droplet Clusters: Stability, Symmetry, and Voronoi Entropy. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 5599–5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K. Geometric formulas of Lewis’s law and Aboav-Weaire’s law in two dimensions based on ellipse packing. Philos. Mag. Lett. 2019, 99, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, M.; Arya, P.; Bormachenko, E.; Santer, S. Quantification of ordering in active light driven colloids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 586, 866–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormashenko, E.; Frenkel, M.; Vilk, A.; Legchenkova, I.; Fedorets, A.A.; Aktaev, N.E.; Dombrovsky, L.A.; Nosonovsky, M. Characterization of self-assembled 2D patterns with Voronoi Entropy. Entropy 2018, 20, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frenkel, M.; Fedorets, A.A.; Dombrovsky, L.A.; Nosonovsky, M.; Legchenkova, I.; Bormashenko, E. Continuous Symmetry Measure vs Voronoi Entropy of Droplet Clusters. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 2431–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormashenko, E.; Legchenkova, I.; Frenkel, M. Symmetry and Shannon Measure of Ordering. Entropy 2019, 21, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mebatsion, H.K.; Verboven, P.; Verlinden, B.E.; Hoa, Q.T.; Nguyen, T.A.; Nicolaï, B.M. Microscale modelling of fruit tissue using Voronoi tessellations. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2006, 52, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhardt, P.; Jeong, H.C. A simpler approach to Penrose tiling with implications for quasicrystal formation. Nature 1996, 382, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shechtman, D.; Blech, I.; Gratias, D.; Cahn, J.W. Metallic phase with long-range orientational order and no translational symmetry. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1984, 53, 1951–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yaglom, A.M.; Yaglom, I.M. Probability and Information; Jain, V.K., Reidel, D., Eds.; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Limaye, A.V.; Narhe, R.D.; Dhote, A.M.; Ogale, S.B. Evidence for convective effects in breath figure formation on volatile fluid surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 76, 3762–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, C.P.; Blunt, M.O.; Pauliac-Vaujour, E.; Stannard, A.; Moriarty, P.; Vancea, I.; Thiele, U. Controlling pattern formation in nanoparticle assemblies via directed solvent dewetting. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 116103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dry, M.J. Using relational structure to detect symmetry: A Voronoi tessellation based model of symmetry perception. Acta Psychol. 2008, 128, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
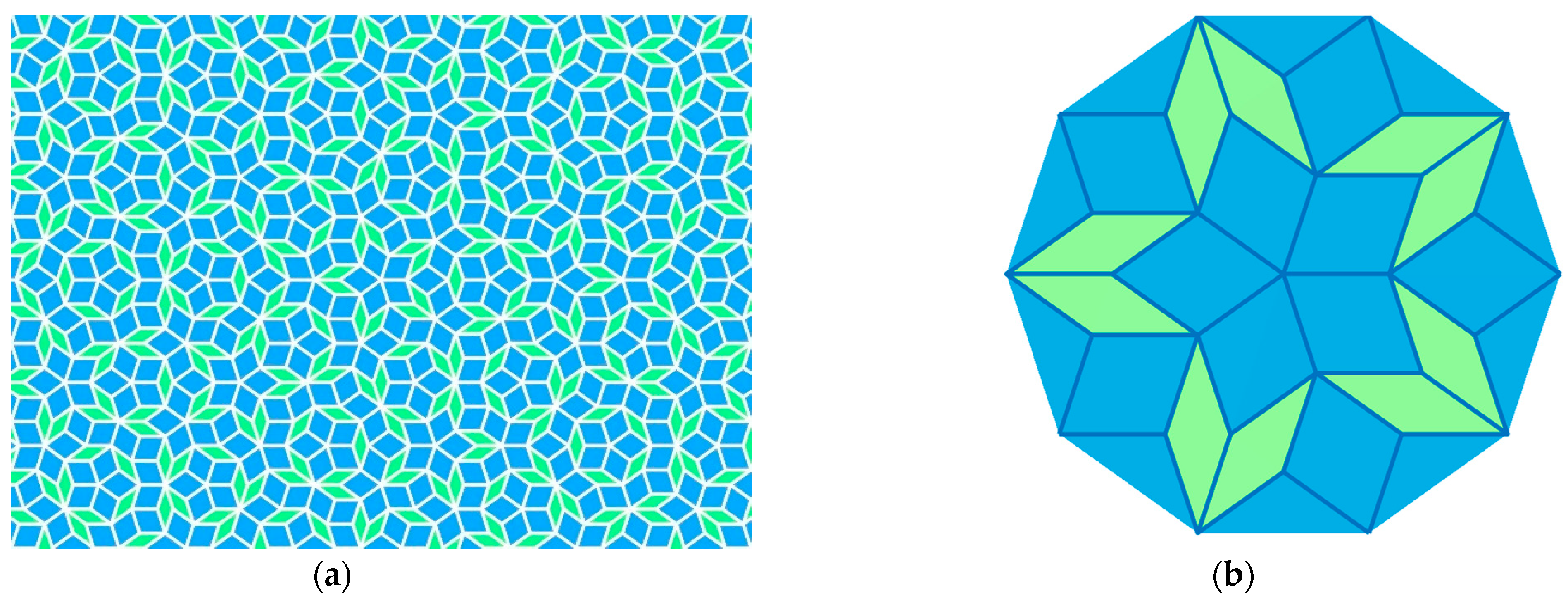
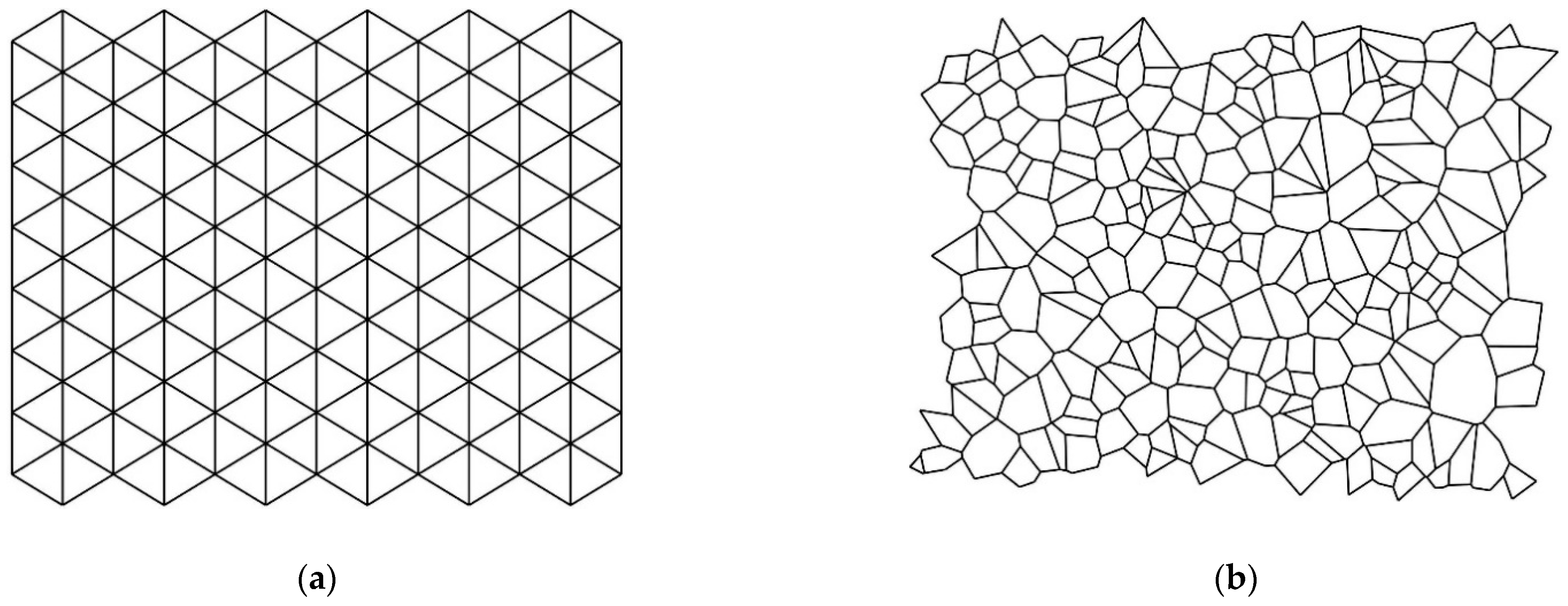
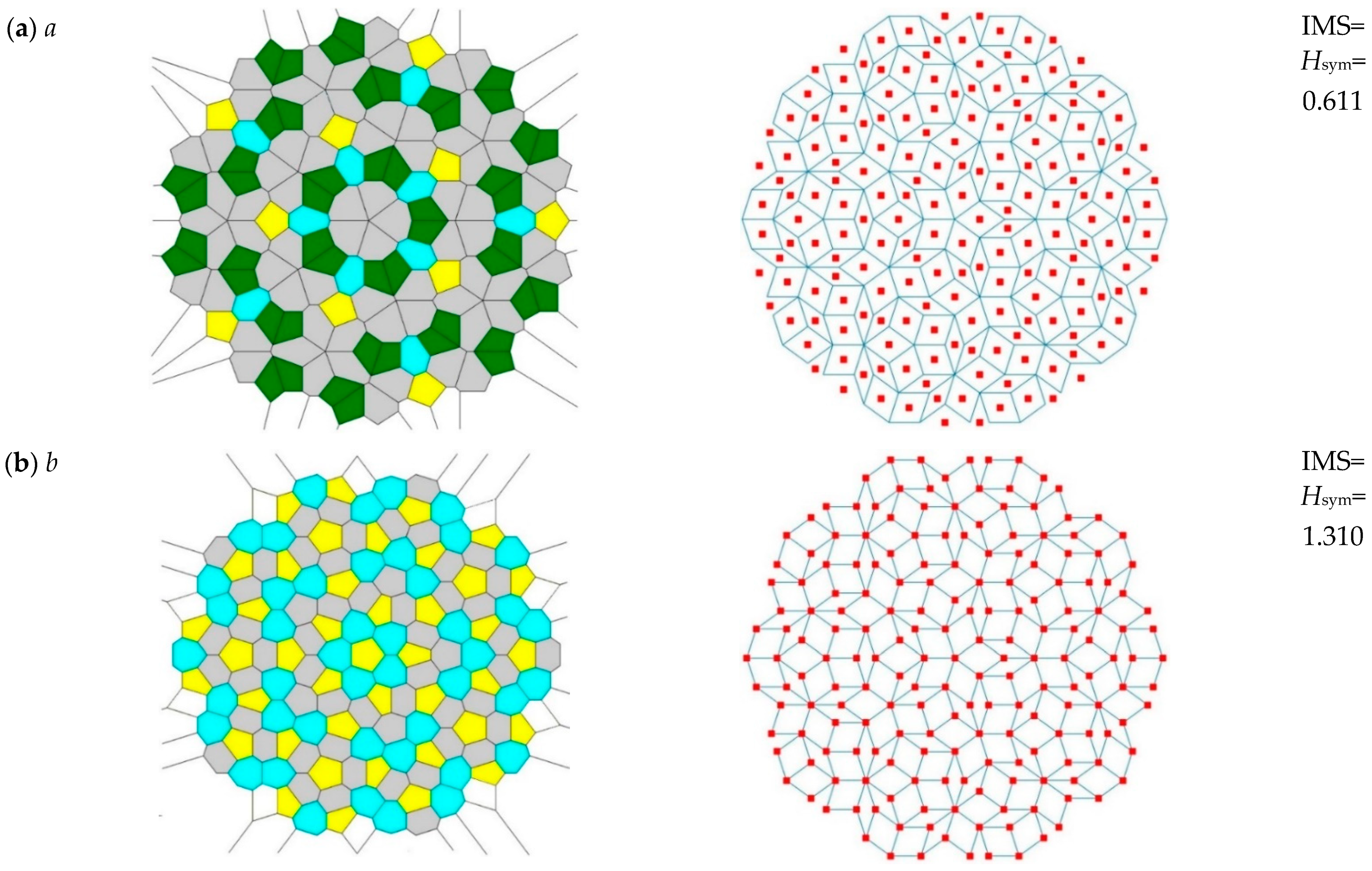
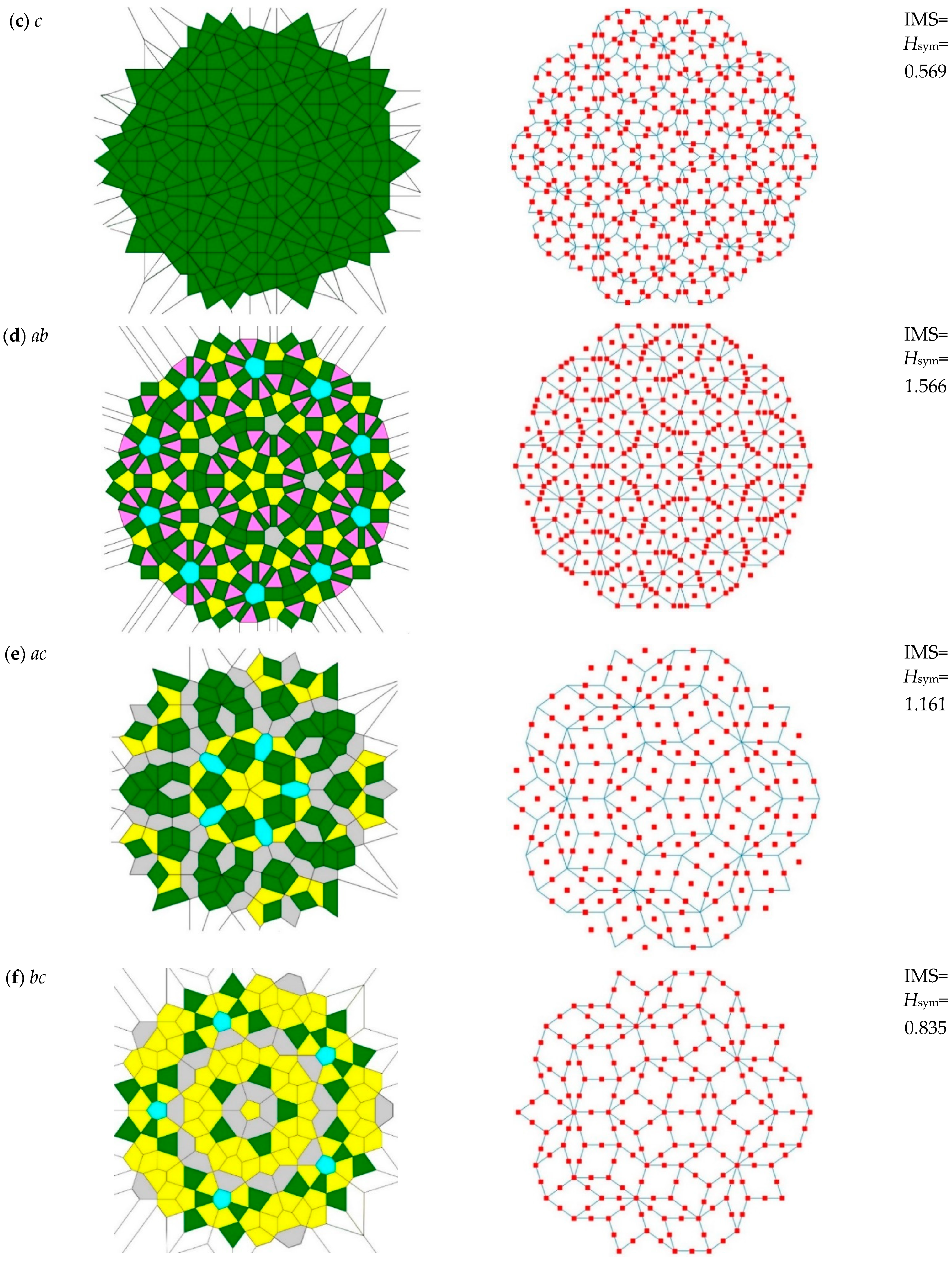
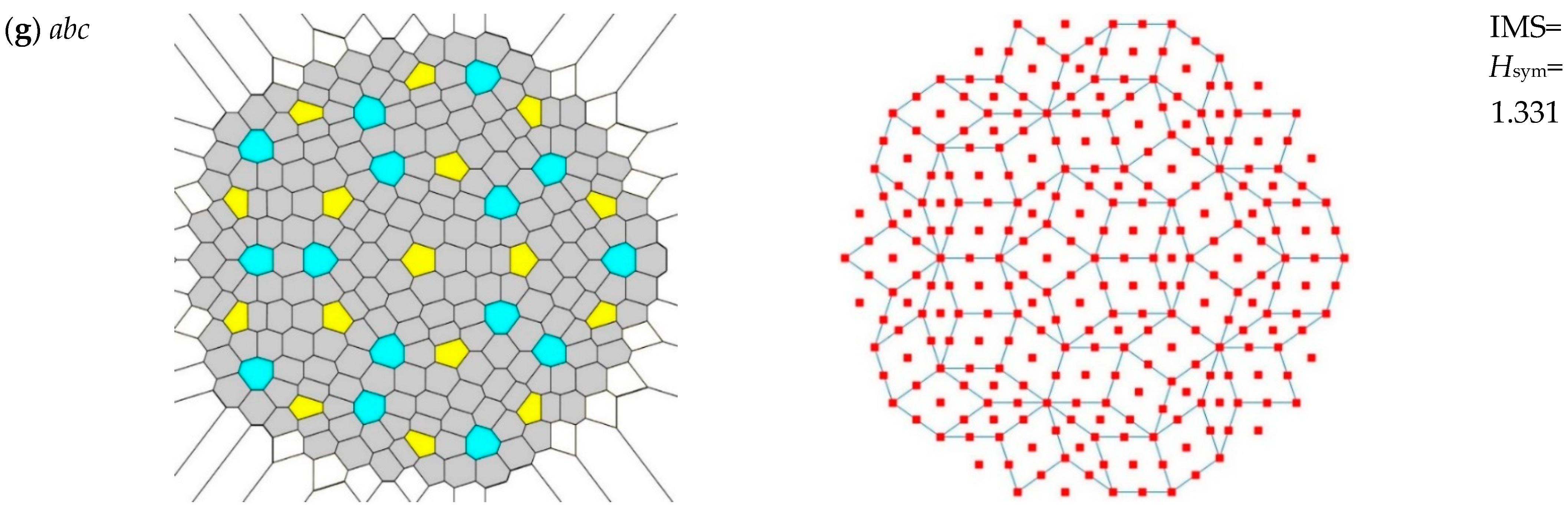
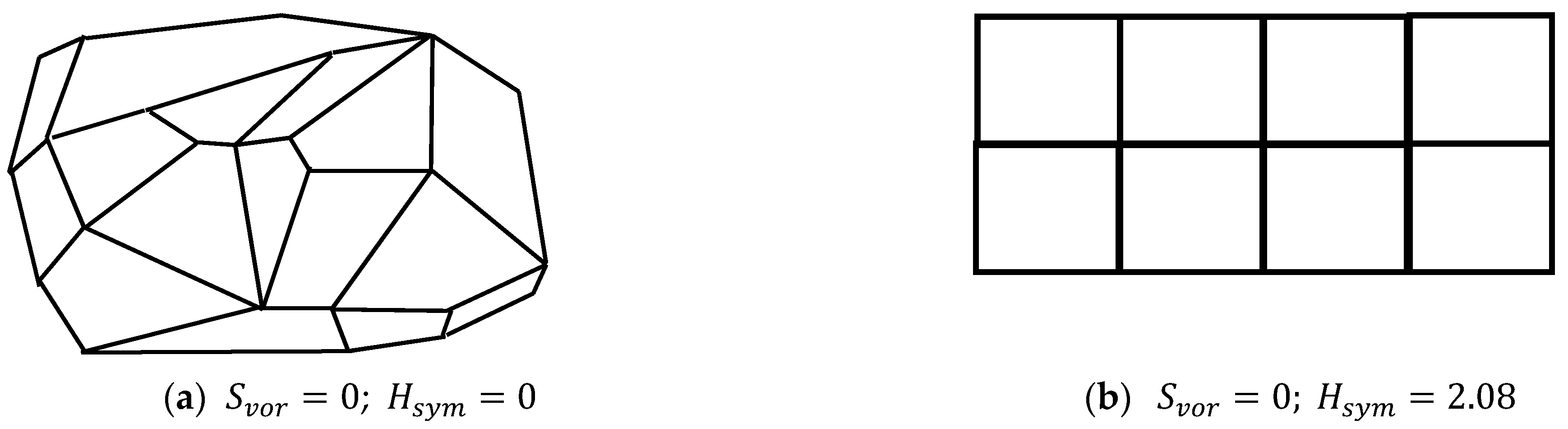
| Diagram Type | Mirror Planes Number () | Number of Rotation Axes () | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (2π) | () | () | () | ( ) | (π) | |||||||
| a | 60 | - | - | - | - | - | 140 | - | - | - | - | - |
| b | 141 | 6 | 6 | 6 | - | 141 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | - | |
| c | 100 | - | - | - | - | - | 290 | - | - | - | - | - |
| ab | 306 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 160 | 311 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 160 |
| ac | 65 | - | - | - | - | 35 | 165 | - | - | - | - | 35 |
| bc | 91 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 161 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - |
| abc | 151 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 60 | 221 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 60 |
| Diagram Type | Polygon Types Number | IMS, | Voronoi Entropy, | CSM | CSM % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 4 | 0.611 | 1.1364 | 0.1138 | 33.74 | 5.37 |
| b | 3 | 1.310 | 1.0847 | 0.0367 | 19.15 | 35.70 |
| c | 1 | 0.569 | 0 | 0.1099 | 33.15 | 5.18 |
| ab | 5 | 1.566 | 1.122 | 0.0619 | 24.87 | 25.30 |
| ac | 4 | 1.161 | 1.1026 | 0.0931 | 30.52 | 12.47 |
| bc | 4 | 0.835 | 1.0371 | 0.0912 | 30.2 | 9.16 |
| abc | 3 | 1.331 | 0.5026 | 0.0515 | 22.7 | 25.84 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bormashenko, E.; Legchenkova, I.; Frenkel, M.; Shvalb, N.; Shoval, S. Informational Measure of Symmetry vs. Voronoi Entropy and Continuous Measure of Entropy of the Penrose Tiling. Part II of the “Voronoi Entropy vs. Continuous Measure of Symmetry of the Penrose Tiling”. Symmetry 2021, 13, 2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13112146
Bormashenko E, Legchenkova I, Frenkel M, Shvalb N, Shoval S. Informational Measure of Symmetry vs. Voronoi Entropy and Continuous Measure of Entropy of the Penrose Tiling. Part II of the “Voronoi Entropy vs. Continuous Measure of Symmetry of the Penrose Tiling”. Symmetry. 2021; 13(11):2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13112146
Chicago/Turabian StyleBormashenko, Edward, Irina Legchenkova, Mark Frenkel, Nir Shvalb, and Shraga Shoval. 2021. "Informational Measure of Symmetry vs. Voronoi Entropy and Continuous Measure of Entropy of the Penrose Tiling. Part II of the “Voronoi Entropy vs. Continuous Measure of Symmetry of the Penrose Tiling”" Symmetry 13, no. 11: 2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13112146
APA StyleBormashenko, E., Legchenkova, I., Frenkel, M., Shvalb, N., & Shoval, S. (2021). Informational Measure of Symmetry vs. Voronoi Entropy and Continuous Measure of Entropy of the Penrose Tiling. Part II of the “Voronoi Entropy vs. Continuous Measure of Symmetry of the Penrose Tiling”. Symmetry, 13(11), 2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13112146









