Synthesis Strategy of Reversible Circuits on DNA Computers
Abstract
:Highlights
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
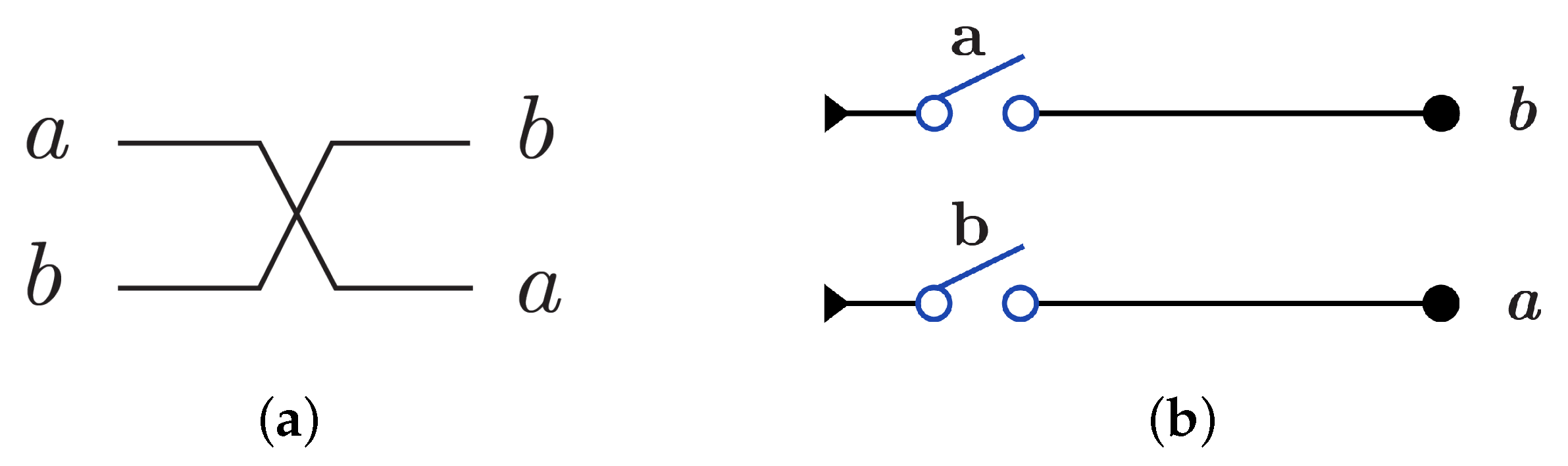
3. Reversible Logic Gates and Circuits Using DNA
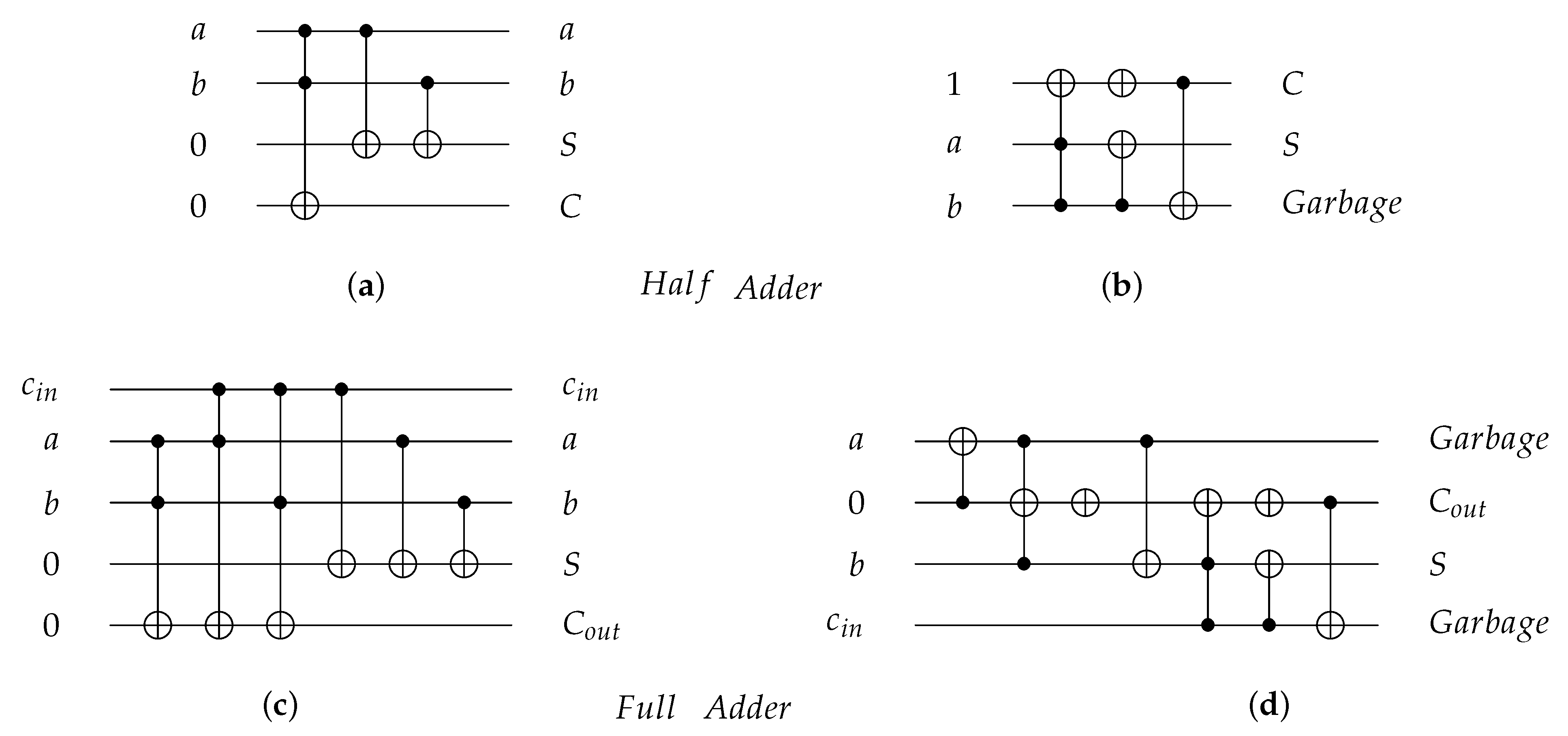
3.1. Reversible Gates and Circuits
3.2. DNA-Based Reversible Gates and Circuits
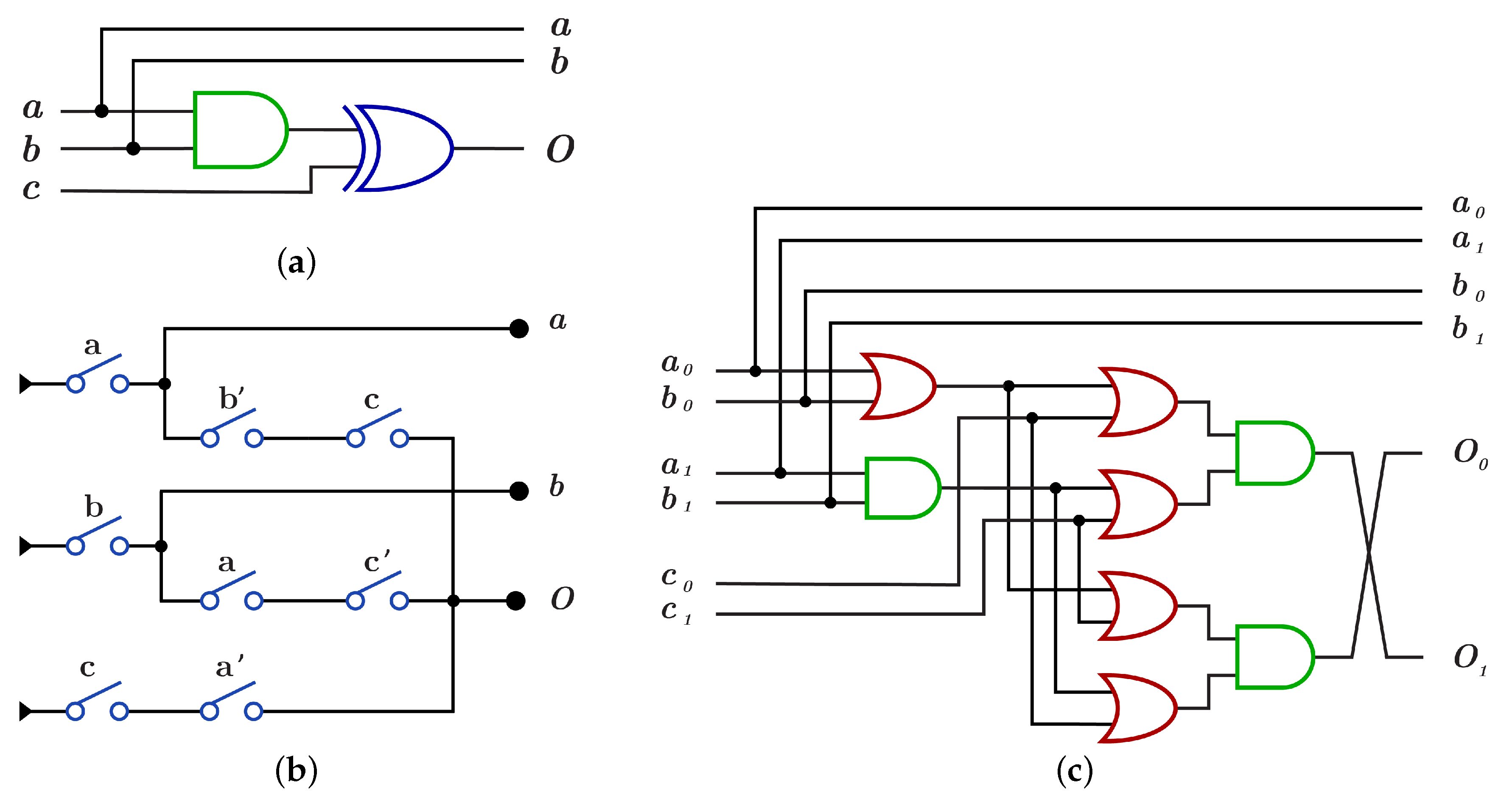
4. Proposed Novel Library of DNA Constructs for Reversible Circuits
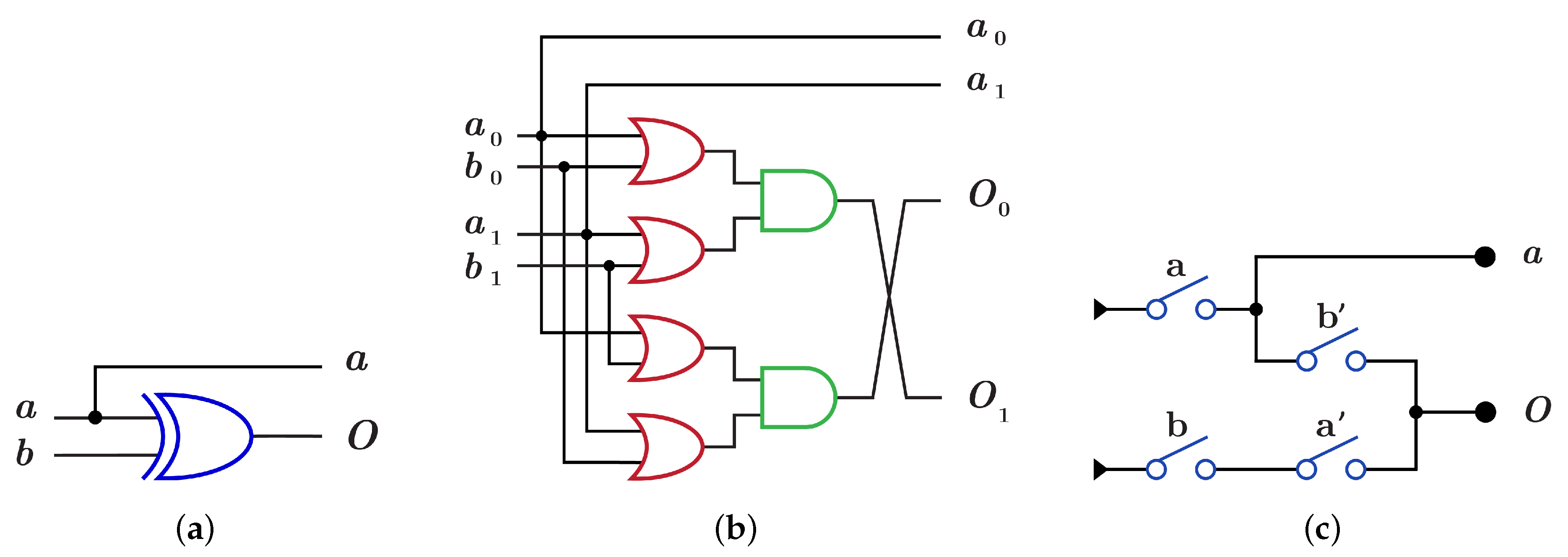
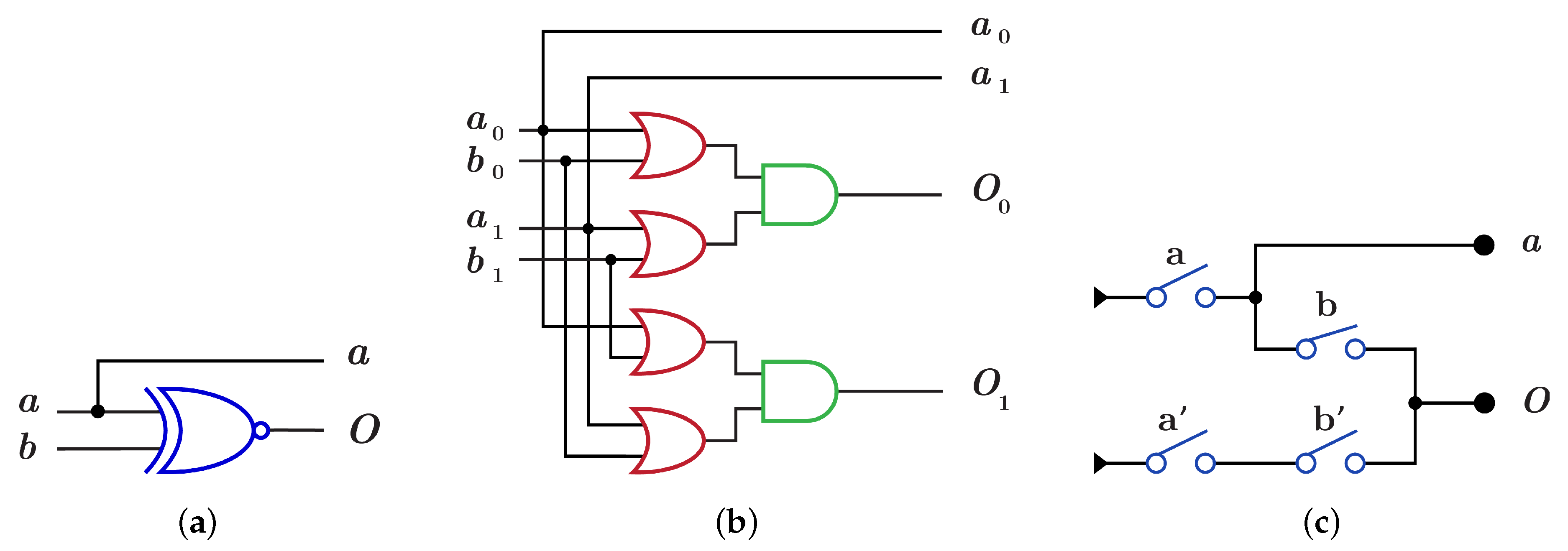
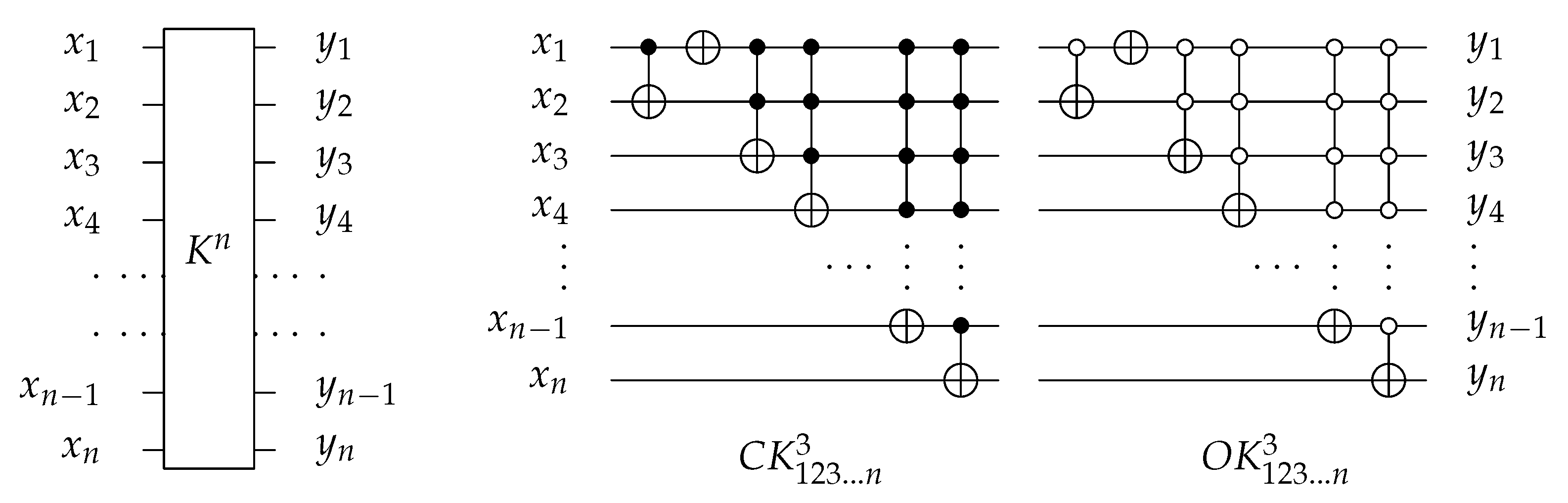
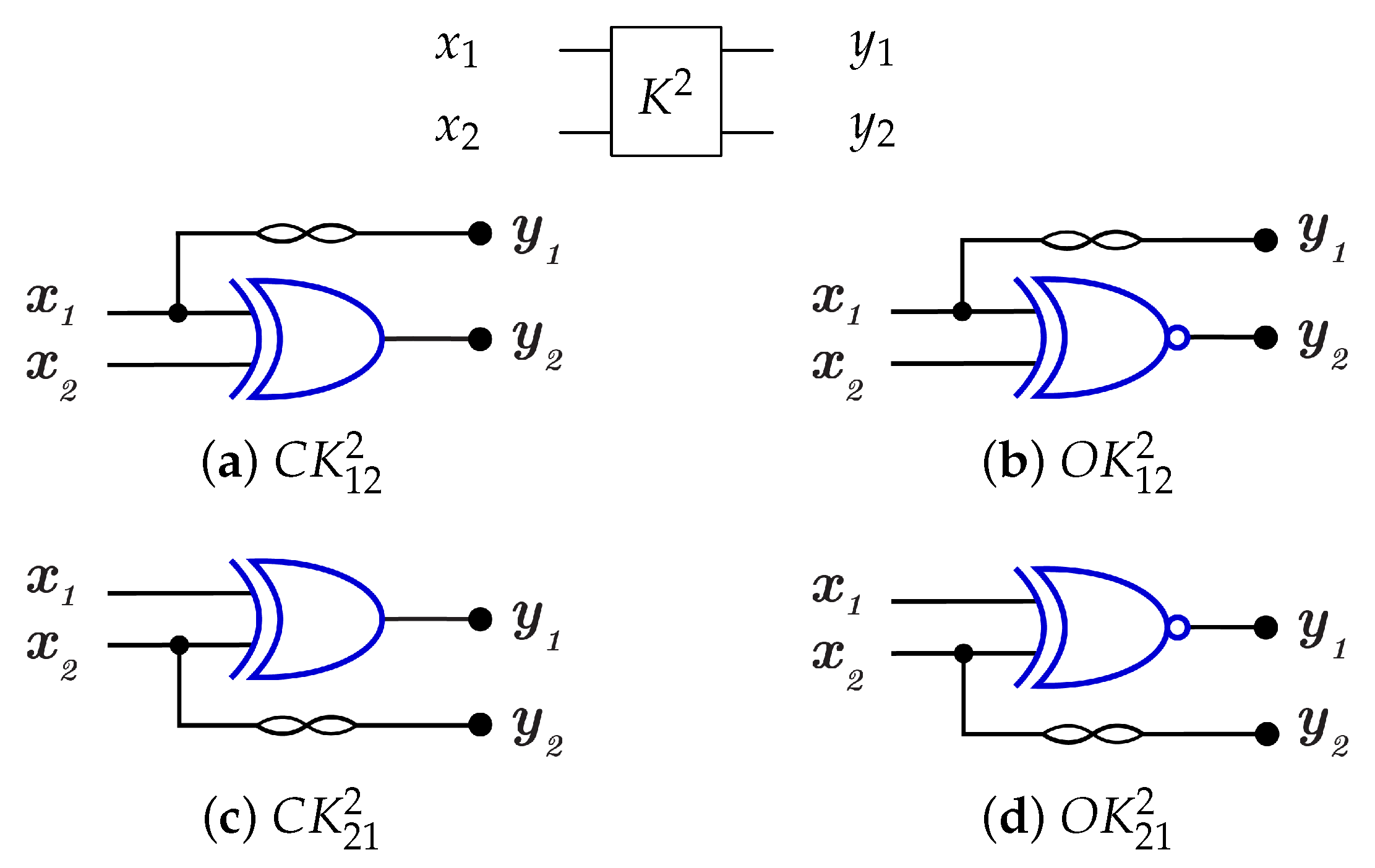
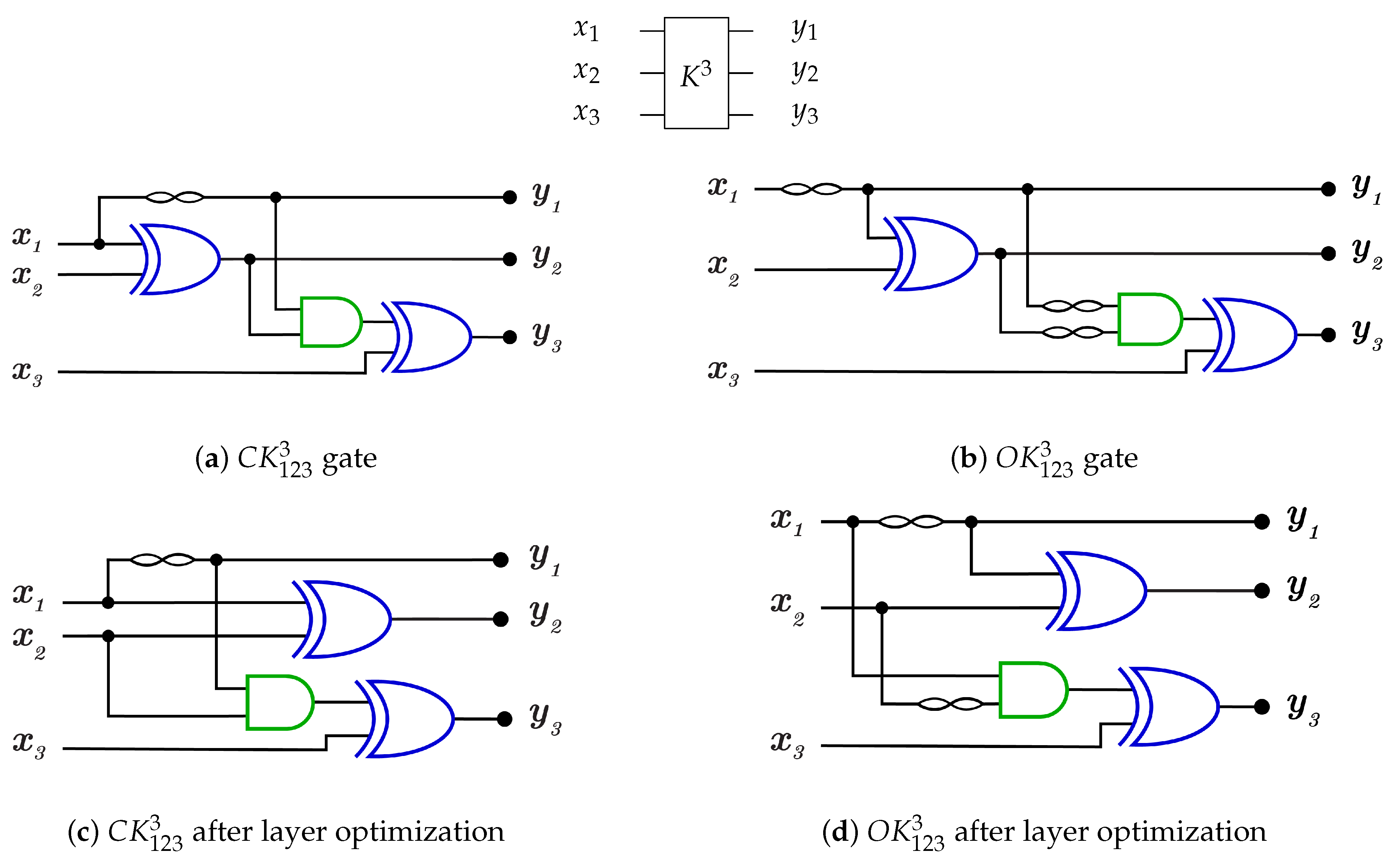
4.1. The Novel Proposed URGL (K Library)
4.1.1. Library
4.1.2. Library
4.1.3. Library
4.1.4. Library
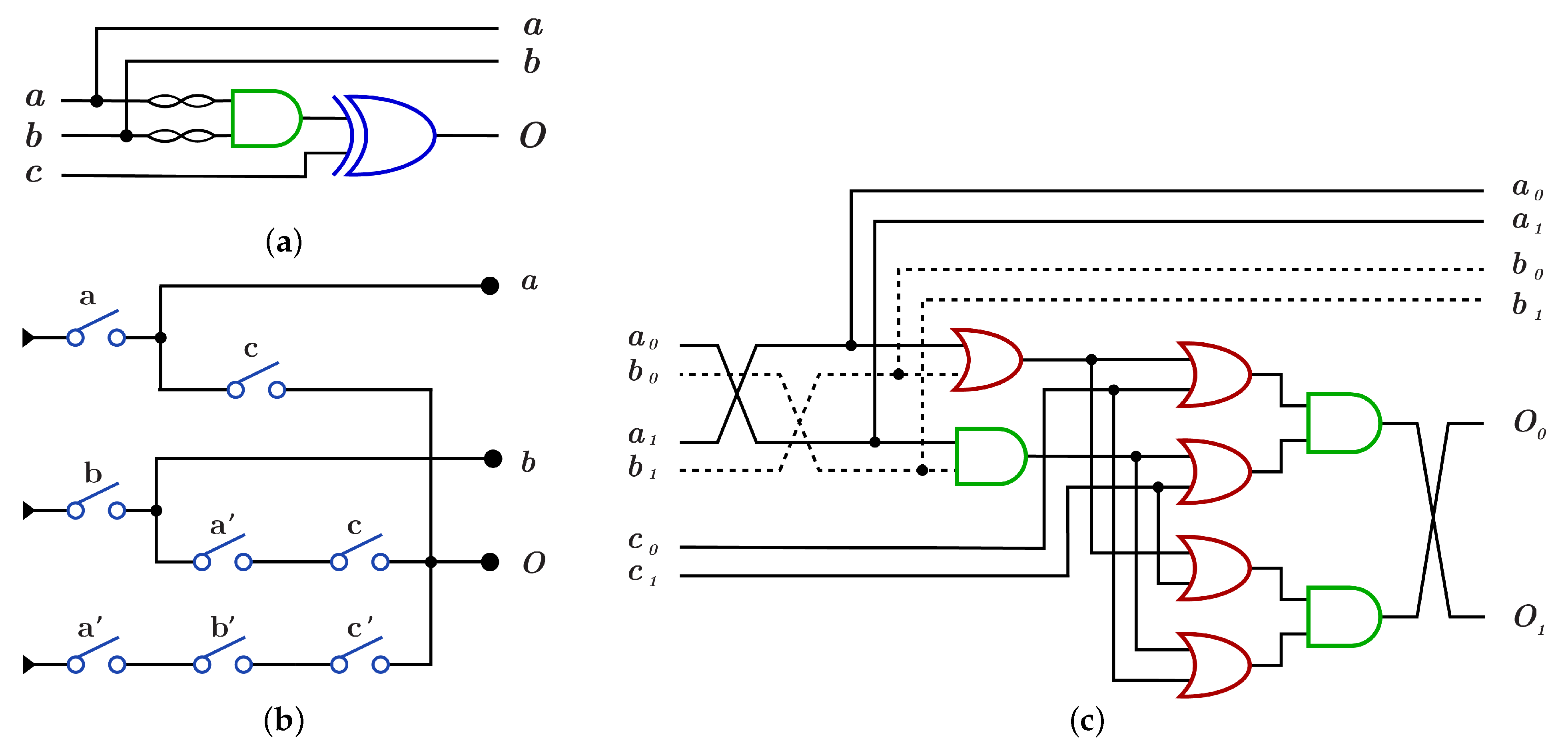
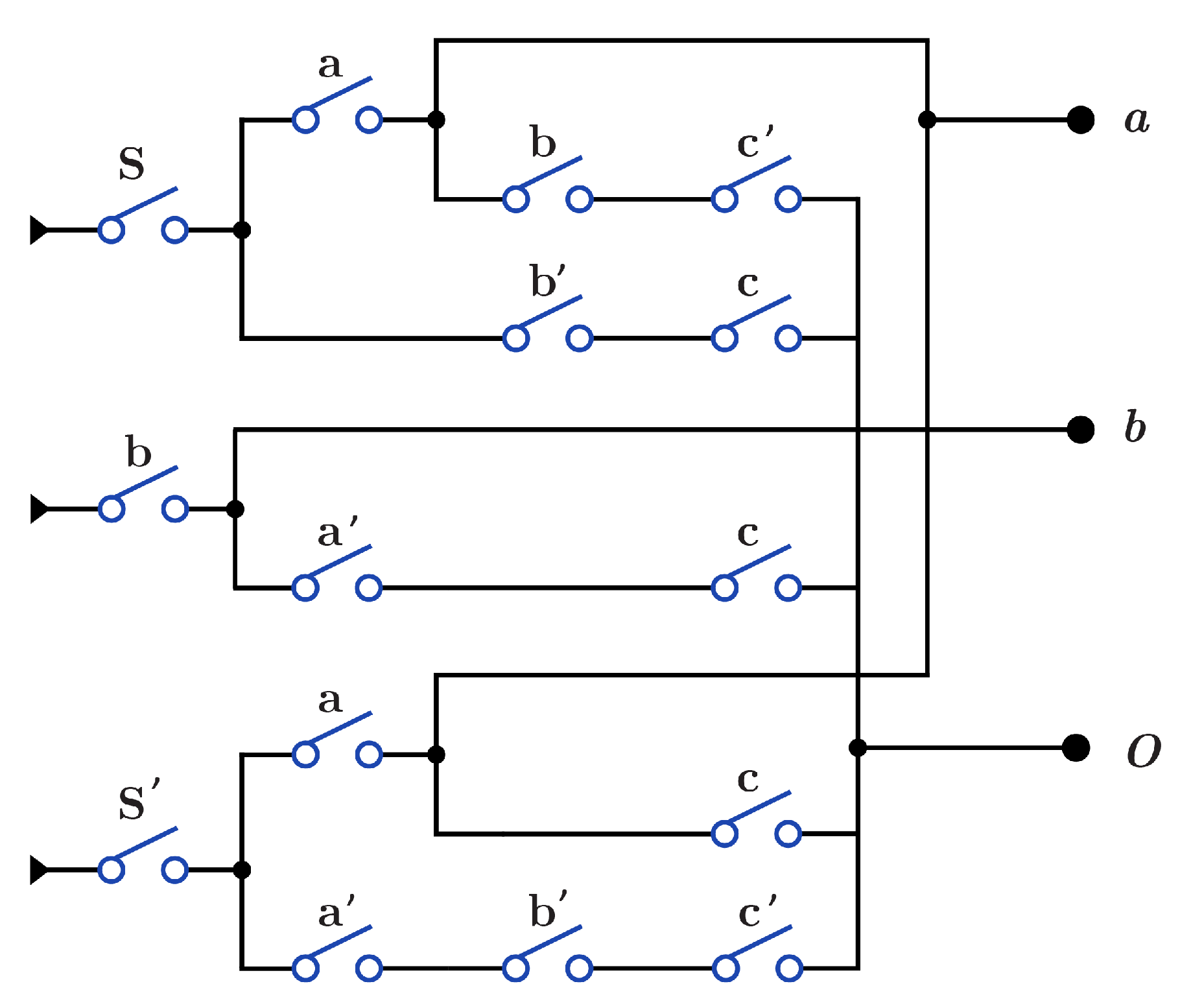
4.2. DNA-Based K Library
4.2.1. Library
4.2.2. Library
4.2.3. Library
4.2.4. Library
5. Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, F.; Lv, H.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Shi, J.; Wang, L.; Fan, C. Implementing digital computing with DNA-based switching circuits. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, N.C.; Pevzner, P. Introduction to Bioinformatics Algorithms; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Watada, J. DNA Computing and Its Application; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 1065–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Adleman, L.M. Molecular computation of solutions to combinatorial problems. Science 1994, 266, 1021–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lipton, R. DNA solution of hard computational problems. Science 1995, 268, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, L.; Winfree, E. A simple DNA gate motif for synthesizing large-scale circuits. J. R. Soc. Interface 2011, 8, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katz, E.; Poghossian, A.; Schöning, M.J. Enzyme-based logic gates and circuits—Analytical applications and interfacing with electronics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshkhahesh, A.; Ebrahimi, S.; Sabbaghi-Nadooshan, R. Designing and Optimizing DNA Reversible Adders and Adder/Subtractors. BioNanoScience 2018, 8, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Eshra, A.; Shah, S.; Bui, H.; Fu, D.; Yang, M.; Mokhtar, R.; Reif, J. Fast and compact DNA logic circuits based on single-stranded gates using strand-displacing polymerase. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, N.; Bertone, P.; Chen, S.; Dessimoz, C.; LeProust, E.M.; Sipos, B.; Birney, E. Towards practical, high-capacity, low-maintenance information storage in synthesized DNA. Nature 2013, 494, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Organick, L.; Ang, S.D.; Chen, Y.J.; Lopez, R.; Yekhanin, S.; Makarychev, K.; Racz, M.Z.; Kamath, G.; Gopalan, P.; Nguyen, B.; et al. Random access in large-scale DNA data storage. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, C.N.; Nguyen, B.H.; Strauss, K.; Ceze, L. Demonstration of End-to-End Automation of DNA Data Storage. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seelig, G.; Soloveichik, D.; Zhang, D.Y.; Winfree, E. Enzyme-Free Nucleic Acid Logic Circuits. Science 2006, 314, 1585–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qian, L.; Winfree, E. Scaling Up Digital Circuit Computation with DNA Strand Displacement Cascades. Science 2011, 332, 1196–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, X.; Eshra, A.; Dwyer, C.; Reif, J. Renewable DNA seesaw logic circuits enabled by photoregulation of toehold-mediated strand displacement. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 28130–28144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yurke, B.; Turberfield, A.J.; Mills, A.P.; Simmel, F.C.; Neumann, J.L. A DNA-fuelled molecular machine made of DNA. Nature 2000, 406, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.H. Logical Reversibility of Computation. IBM J. Res. Dev. 1973, 17, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, A.D. Reversible Computing—Fundamentals, Quantum Computing, and Applications; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Younes, A. On the universality of n-bit reversible gate libraries. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 2015, 9, 2579–2588. [Google Scholar]
- Song, T.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. The design of reversible gate and reversible sequential circuit based on DNA computing. In Proceedings of the 2008 3rd International Conference on Intelligent System and Knowledge Engineering, Xiamen, China, 17–19 November 2008; Volume 1, pp. 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, A.; Ahmed, T.; Rashid, S.M.M.; Anwar, S.; Jaman, L.; Tara, N.; Alam, M.M.; Babu, H.M.H. Realization of Reversible Logic in DNA Computing. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE 11th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering, Taichung, Taiwan, 24–26 October 2011; pp. 261–265. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, M.; Ghosal, P.; Mohanty, S.P. Minimal reversible circuit synthesis on a DNA computer. Nat. Comput. 2017, 16, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratto, B.E.; Lewer, J.M.; Katz, E. An Enzyme-Based Half-Adder and Half-Subtractor with a Modular Design. ChemPhysChem 2016, 17, 2210–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakshi, S.; Zavalov, O.; Halámek, J.; Privman, V.; Katz, E. Modularity of Biochemical Filtering for Inducing Sigmoid Response in Both Inputs in an Enzymatic AND Gate. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 9857–9865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, P.; Dey, D.; Sinha, S.; De, D. Reversible OR Logic Gate Design Using DNA. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Bio-Inspired Computing: Theories and Applications (BIC-TA 2012); Bansal, J.C., Singh, P.K., Deep, K., Pant, M., Nagar, A.K., Eds.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2013; pp. 355–366. [Google Scholar]
- Orbach, R.; Remacle, F.; Levine, R.D.; Willner, I. Logic reversibility and thermodynamic irreversibility demonstrated by DNAzyme-based Toffoli and Fredkin logic gates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 21228–21233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Genot, A.J.; Bath, J.; Turberfield, A.J. Reversible Logic Circuits Made of DNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 20080–20083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A symbolic analysis of relay and switching circuits. Electr. Eng. 1938, 57, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, G.; Song, X.; Hung, W.N.N.; Perkowski, M.A.; Seo, C.J. Synthesis of reversible circuits with minimal costs. Calcolo 2008, 45, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaser, R.; Younes, A.; Abdel-Aty, M. New Design of Reversible Full Adder/Subtractor Using R Gate. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2019, 58, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montaser, R.; Younes, A.; Abdel-Aty, M. Improving the quantum cost of NCT-based reversible circuit. Quantum Inf. Process. 2015, 14, 1249–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaser, R.; Younes, A.; Abdel-Aty, M. New Design of Universal Reversible Gate Library. Quantum Matter 2017, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.; Younes, A.; Ismail, G.; Farouk, R. An Improved Design of n-Bit Universal Reversible Gate Library. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2019, 58, 2531–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GAP System for Computational Discrete Algebra, Version 4.11.0. 2020. Available online: https://www.gap-system.org/ (accessed on 2 June 2021).

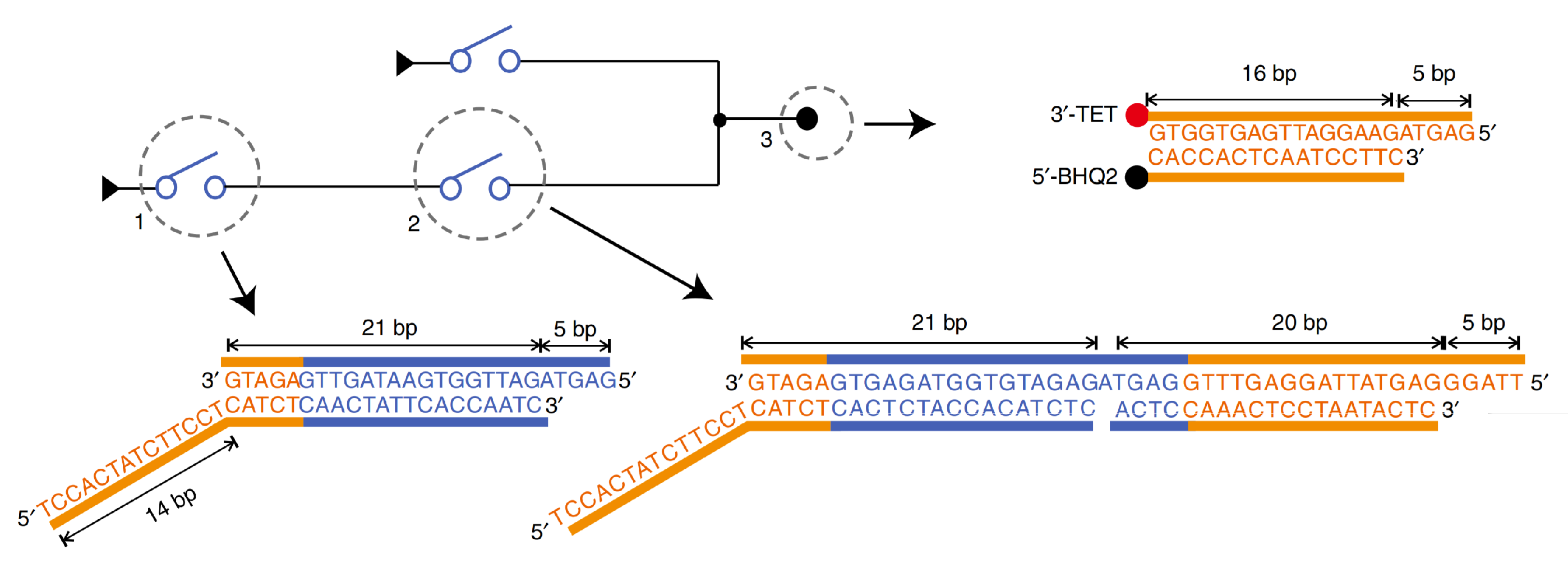

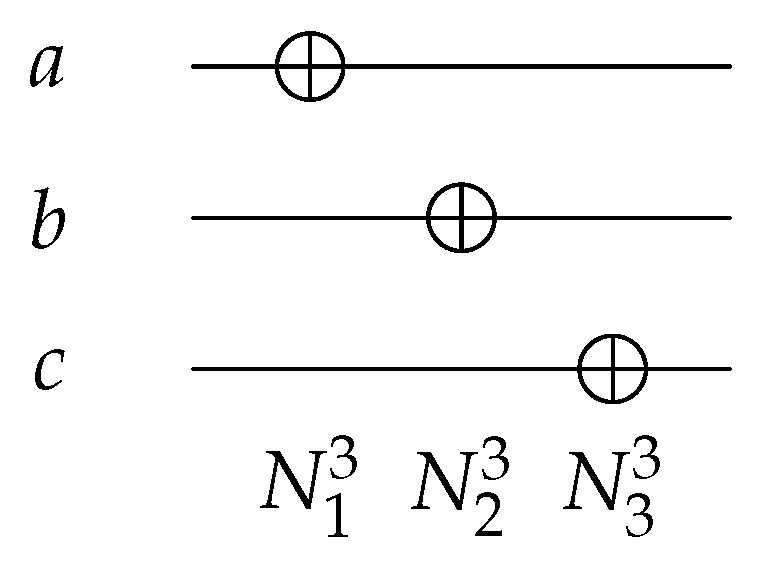

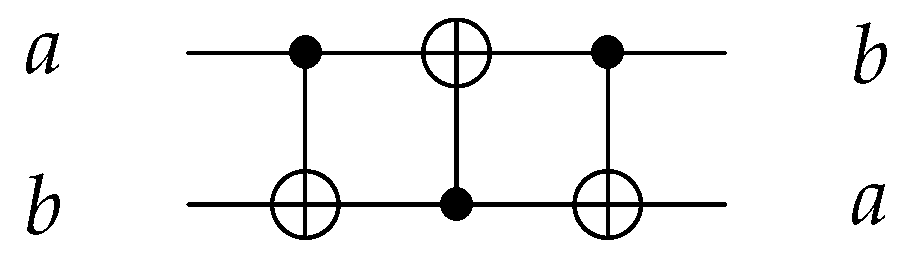
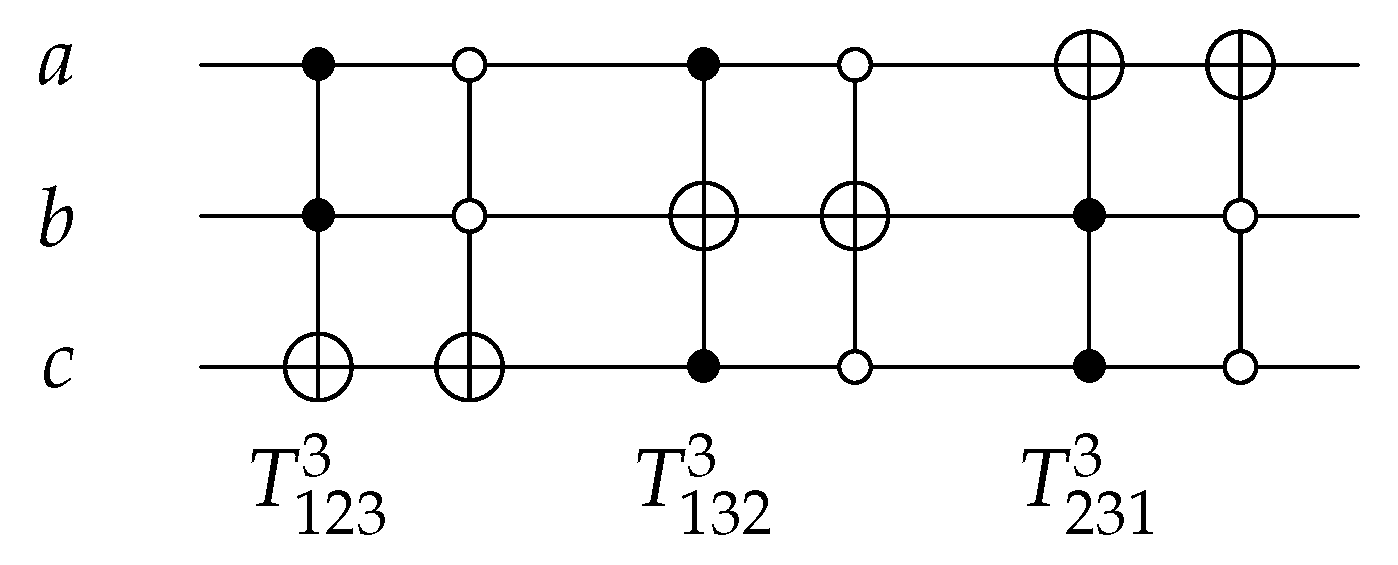
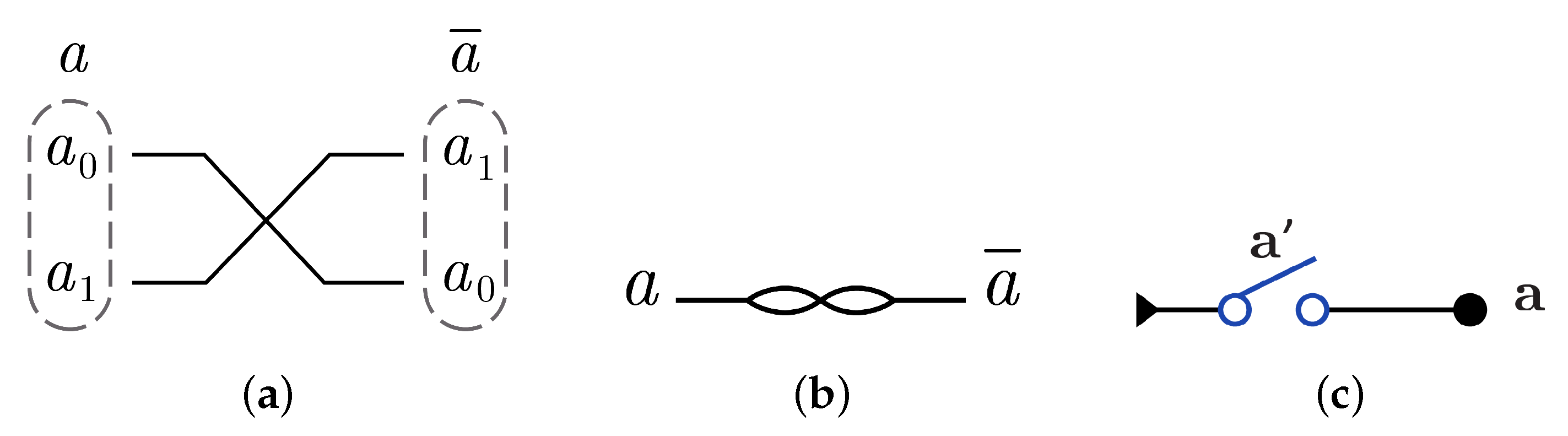

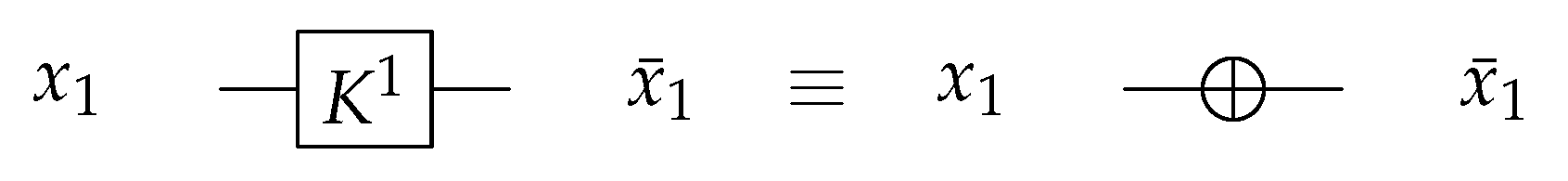

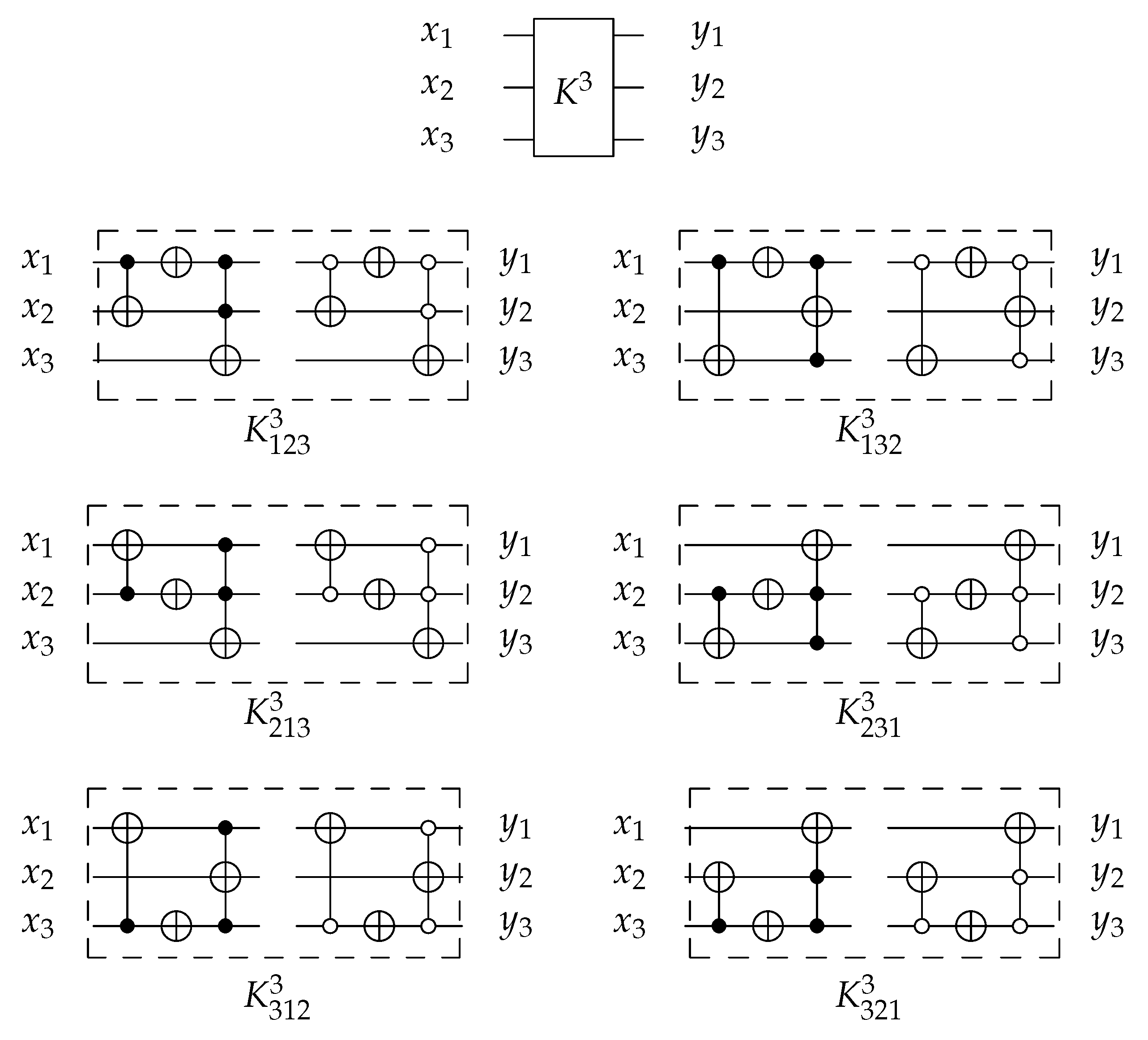

| Gate/Circuit | Figure Number | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N gate | Figure 4 and Figure 9 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| C gate | Figure 5 and Figure 10, Figure 11 and Figure 12 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| T gate | Figure 7 and Figure 14, Figure 15 and Figure 16 | 5 | 3 | 3 |
| Swap gate | Figure 6 and Figure 13 | 3 | 0 | 1 |
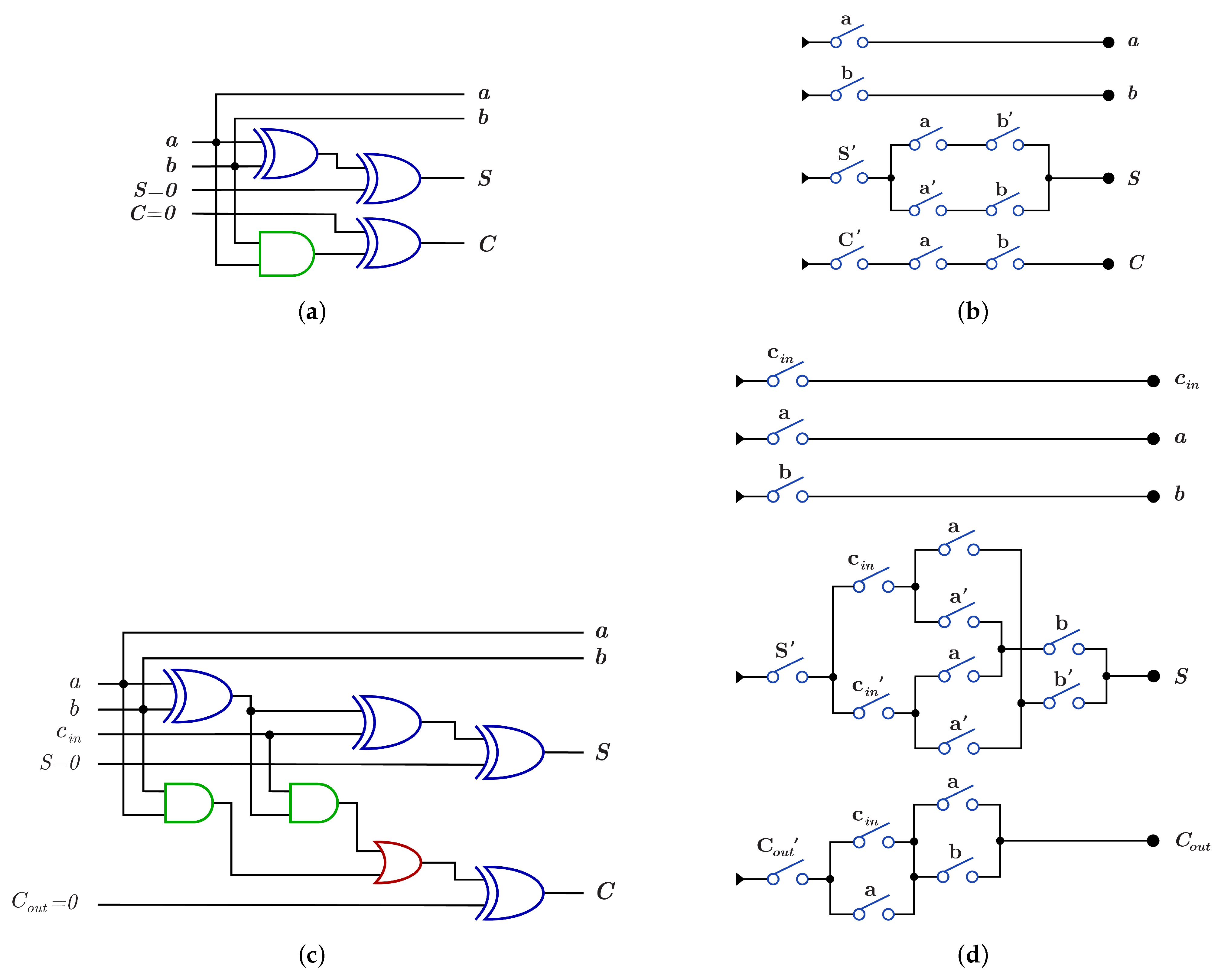
| 1-bit Half Adder | Figure 8a,b and Figure 17a,b | 4 | 4 | 3 |
| 1-bit Full Adder | Figure 8c,d and Figure 17c,d | 8 | 6 | 4 |
| Forward | Backward | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operation (OP) | Action Layer | OP | Action Layer | |
| 1 | 1 | |||
| 1 | 1 | |||
| DNAC | Number of Bits (n) |
|---|---|
| 4 | |
| 5 | |
| 6 | |
| 7 |
| Library | Figure Number | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Figure 18 and Figure 22 | 0 | 0 | |
| Figure 19 and Figure 23 | 1 | 2 | |
| Figure 20 and Figure 24 | 6 | 5 | |
| - | 11 | 9 | |
| - | 16 | 13 | |
| - | 21 | 18 | |
| - | 26 | 23 | |
| - | 31 | 28 | |
| - | 36 | 33 | |
| - | 41 | 39 |
| URGL | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size | 6 | 12 | 6 | 6 | 9 | 6 | 9 | 6 | 12 |
| 25.782 | 12.578 | 32.212 | 44.978 | 29.453 | 44.978 | 29.453 | 37.350 | 29.140 | |
| 15.469 | 11.130 | 19.327 | 44.978 | 29.453 | 44.978 | 29.453 | 31.126 | 24.283 | |
| 18.675 | 14.570 | ||||||||
| Length | 8.500 | 5.866 | 6.442 | 6.425 | 5.326 | 6.425 | 5.326 | 6.225 | 4.857 |
Short Biography of Authors
 | Mirna Rofail obtained her BSc in Computer Science in 2016 from Faculty of Science, Alexandria University. Currently, she is a Computer Science Teaching Assistant in the Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, Alexandria University. She is a member in Alexandria Quantum Computing Group (AleQCG). She is interested in non-standard computation such as DNA computation and quantum computation. |
 | Ahmed Younes is a Professor of Computer Science at Alexandria University and Honorary Research Fellow at School of Computer Science, University of Birmingham, United Kingdom. He is the founder and leader of Alexandria Quantum Computing Group (AleQCG). He obtained his PhD from University of Birmingham, United Kingdom in 2004. He introduced a new technique, now know as ‘Partial Diffusion Operator’ in the field of amplitude amplification and made a contribution in representing Quantum Boolean circuits as Reed-Muller logic. He published many papers in Quantum Algorithms, Quantum cryptography and Reversible Circuits. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rofail, M.; Younes, A. Synthesis Strategy of Reversible Circuits on DNA Computers. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13071242
Rofail M, Younes A. Synthesis Strategy of Reversible Circuits on DNA Computers. Symmetry. 2021; 13(7):1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13071242
Chicago/Turabian StyleRofail, Mirna, and Ahmed Younes. 2021. "Synthesis Strategy of Reversible Circuits on DNA Computers" Symmetry 13, no. 7: 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13071242
APA StyleRofail, M., & Younes, A. (2021). Synthesis Strategy of Reversible Circuits on DNA Computers. Symmetry, 13(7), 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13071242







