Modeling Neuronal Systems as an Open Quantum System
Abstract
1. Introduction
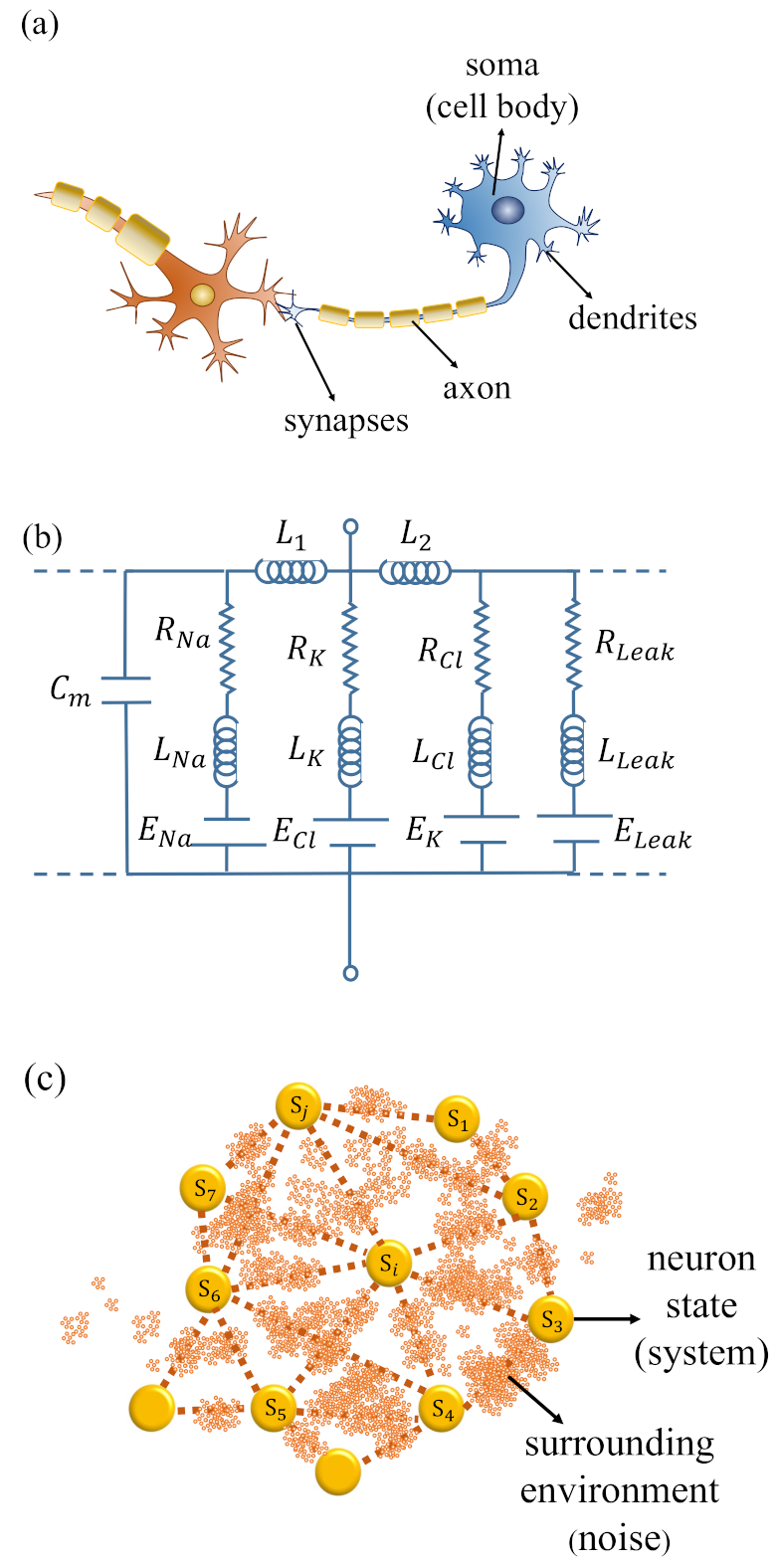
2. Modeling the Neuronal System as an Open Quantum System
3. The Master Equation of the Neuron Dynamics
4. Collective Neural Behavior and Neuron Dynamics Analysis
4.1. Equation of Motion for the Collective Neural States
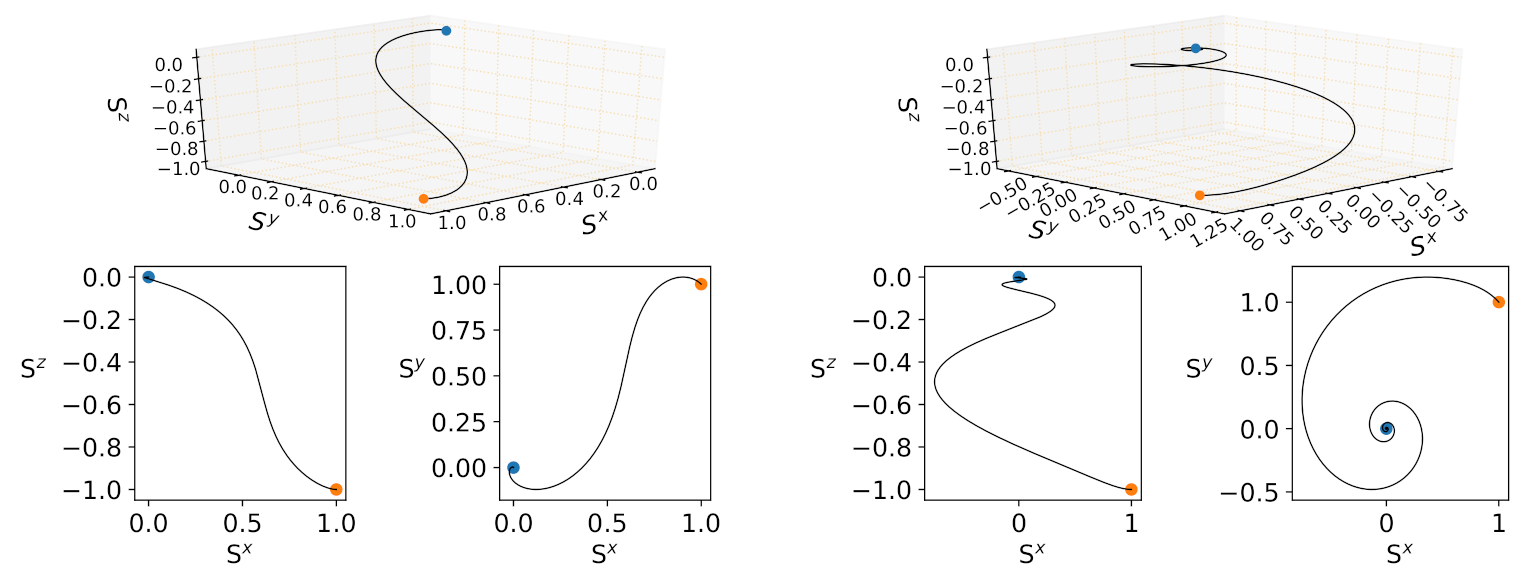
4.2. The Dynamics of Collective Neural States
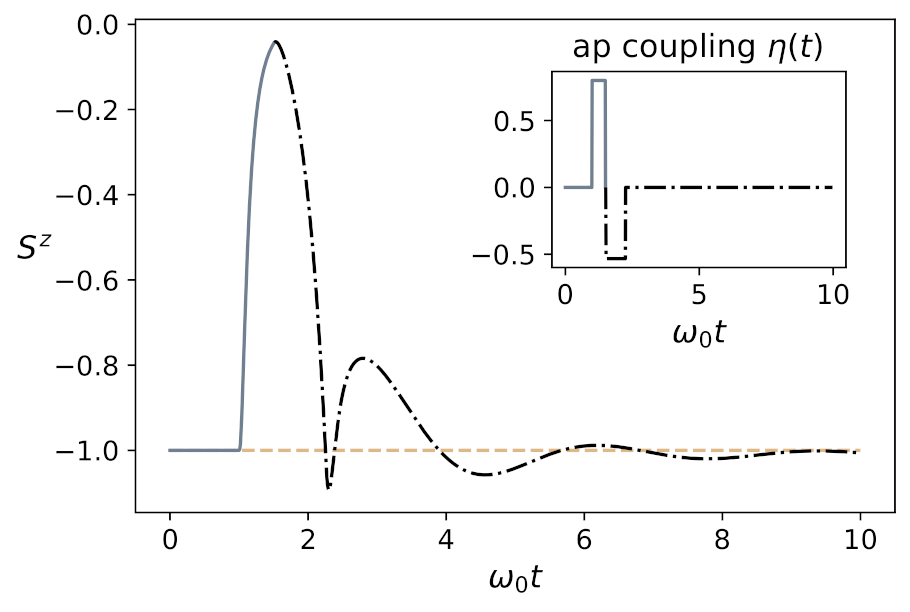
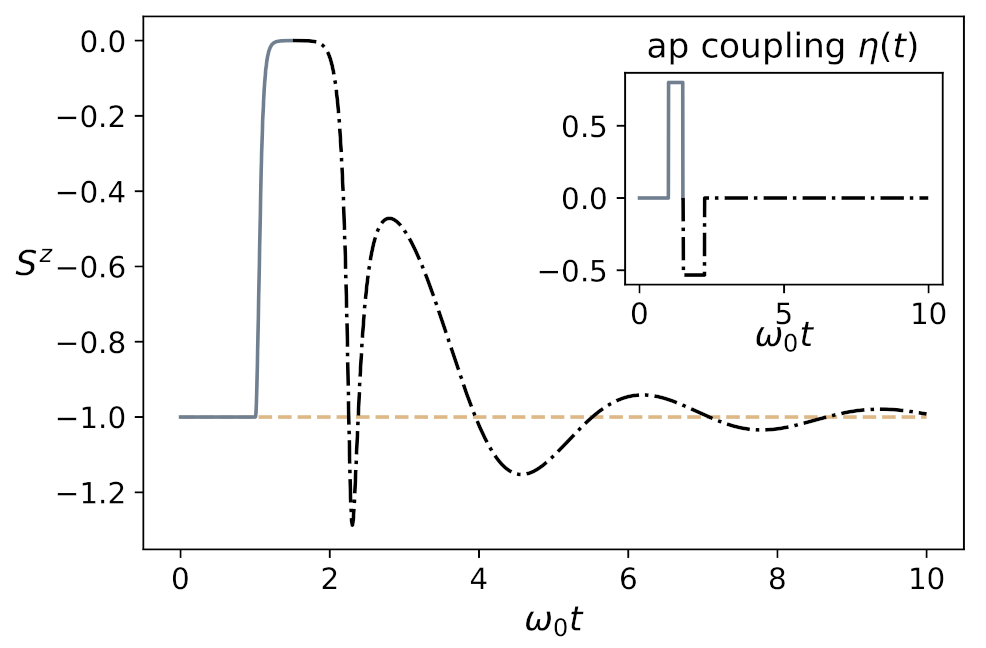
4.2.1. Collective Neural Dynamics at Zero Temperature
4.2.2. Collective Neural Dynamics at Room Temperature
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tortora, G.J.; Derrickson, B.H. Principles of Anatomy and Physiology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voulodimos, A.; Doulamis, N.; Doulamis, A.; Protopapadakis, E. Deep learning for computer vision: A brief review. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassif, A.B.; Shahin, I.; Attili, I.; Azzeh, M.; Shaalan, K. Speech recognition using deep neural networks: A systematic review. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 19143–19165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evgeniou, T.; Pontil, M. Regularized Multi–Task Learning. In Proceedings of the Tenth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD ’04, Seattle, WA, USA, 22–25 August 2004; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Codevilla, F.; Gurram, A.; Urfalioglu, O.; López, A.M. Multimodal end-to-end autonomous driving. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassabis, D.; Kumaran, D.; Summerfield, C.; Botvinick, M. Neuroscience-inspired artificial intelligence. Neuron 2017, 95, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turing, A.M. On computable numbers, with an application to the Entscheidungsproblem. Proc. Lond. Math. Soc. 1937, 2, 230–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turing, A.M. Computing machinery and intelligence. In Parsing the Turing Test; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 23–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloch, W.S.; Pitts, W. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull. Math. Biophys. 1943, 5, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkin, A.L.; Huxley, A.F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. 1952, 117, 500–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, K.S.; Curtis, H.J. Electric impedance of the squid giant axon during activity. J. Gen. Physiol. 1939, 22, 649–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgkin, A.L.; Katz, B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of the giant axon of the squid. J. Physiol. 1949, 108, 37–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keynes, R. The ionic movements during nervous activity. J. Physiol. 1951, 114, 119–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkin, A.L. The Conduction of the Nervous Impulse; Sherrington Lectures; Liverpool University Press: Liverpool, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Bean, B.P. The action potential in mammalian central neurons. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebb, D.O. The organization of behavior: A neuropsychological theory. Wiley Book Clin. Psychol. 1949, 62, 78. [Google Scholar]
- Hopfield, J.J. Neural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational abilities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 2554–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofroniew, M.V.; Vinters, H.V. Astrocytes: Biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 7–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, K.; Hanke, W.; Corcia, A. Ion Channel Fluctuations in Pure Lipid Bilayer Membranes: Control by Voltage; Caruaru, Brazil; 1989. Available online: http://membranes.nbi.dk/Kaufmann/pdf/Kaufmannbook3ed.pdf (accessed on 29 May 2021).
- Pollack, G.H. Cells, Gels and the Engines of Life: A New, Unifying Approach to Cell Function; Ebner & Sons: Seattle, WA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, V.; Makarov, I.; Schäffer, T.; Heimburg, T. Analyzing heat capacity profiles of peptide-containing membranes: Cluster formation of gramicidin A. Biophys. J. 2003, 84, 2427–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Heimburg, T.; Jackson, A.D. On soliton propagation in biomembranes and nerves. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9790–9795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arraut, I. Black-hole evaporation from the perspective of neural networks. EPL 2018, 124, 50002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.C.; Macieszczak, K.; Lesanovsky, I.; Garrahan, J.P. Metastability in an open quantum Ising model. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 94, 052132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotondo, P.; Marcuzzi, M.; Garrahan, J.P.; Lesanovsky, I.; Müller, M. Open quantum generalisation of Hopfield neural networks. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2018, 51, 115301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damanet, F.; Daley, A.J.; Keeling, J. Atom-only descriptions of the driven-dissipative Dicke model. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 99, 033845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glauber, R.J. Time-dependent statistics of the Ising model. J. Math. Phys. 1963, 4, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peretto, P. Collective properties of neural networks: A statistical physics approach. Biol. Cybern. 1984, 50, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, K.S.; Baker, R.F. Longitudinal impedance of the squid giant axon. J. Gen. Physiol. 1941, 24, 771–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Thow, X.Y.; Lee, S.; Peh, W.Y.X.; Ng, K.A.; He, T.; Thakor, N.V.; Chen, C.H.; Lee, C. Inductance in neural systems. bioRxiv 2018, 343905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feynman, R.P.; Vernon, F.L., Jr. The theory of a general quantum system interacting with a linear dissipative system. Ann. Phys. 2000, 281, 547–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, F. Principles of Neurodynamics. Perceptrons and the Theory of Brain Mechanisms; Technical Report; Cornell Aeronautical Lab Inc.: Buffalo, NY, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, L.N.; Liberman, F.; Oja, E. A theory for the acquisition and loss of neuron specificity in visual cortex. Biol. Cybern. 1979, 33, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longuet-Higgins, H.C. The non-local storage of temporal information. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1968, 171, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longuet-Higgins, H.C. Holographic model of temporal recall. Nature 1968, 217, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohonen, T. Associative Memory: A System-Theoretical Approach; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 17. [Google Scholar]
- Amari, S.I. Neural theory of association and concept-formation. Biol. Cybern. 1977, 26, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, S.I.; Takeuchi, A. Mathematical theory on formation of category detecting nerve cells. Biol. Cybern. 1978, 29, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, W.A. The existence of persistent states in the brain. Math. Biosci. 1974, 19, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amit, D.J.; Gutfreund, H.; Sompolinsky, H. Spin-glass models of neural networks. Phys. Rev. A 1985, 32, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, U. Quantum Dissipative Systems; World Scientific: Singapore, 2012; Volume 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leggett, A.J.; Chakravarty, S.; Dorsey, A.T.; Fisher, M.P.; Garg, A.; Zwerger, W. Dynamics of the dissipative two-state system. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1987, 59, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Neumann, J. Mathematical Foundations of Quantum Mechanics: New Edition; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Breuer, H.P.; Petruccione, F. The Theory of Open Quantum Systems; Oxford University Press on Demand: Oxford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.-J.; Zhang, W.-M. Modeling Neuronal Systems as an Open Quantum System. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13091603
Sun Y-J, Zhang W-M. Modeling Neuronal Systems as an Open Quantum System. Symmetry. 2021; 13(9):1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13091603
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yu-Juan, and Wei-Min Zhang. 2021. "Modeling Neuronal Systems as an Open Quantum System" Symmetry 13, no. 9: 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13091603
APA StyleSun, Y.-J., & Zhang, W.-M. (2021). Modeling Neuronal Systems as an Open Quantum System. Symmetry, 13(9), 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13091603






