Noise Elimination for Coalcutter Vibration Signal Based on Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition and an Improved Harris Hawks Optimization Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Basic Theory
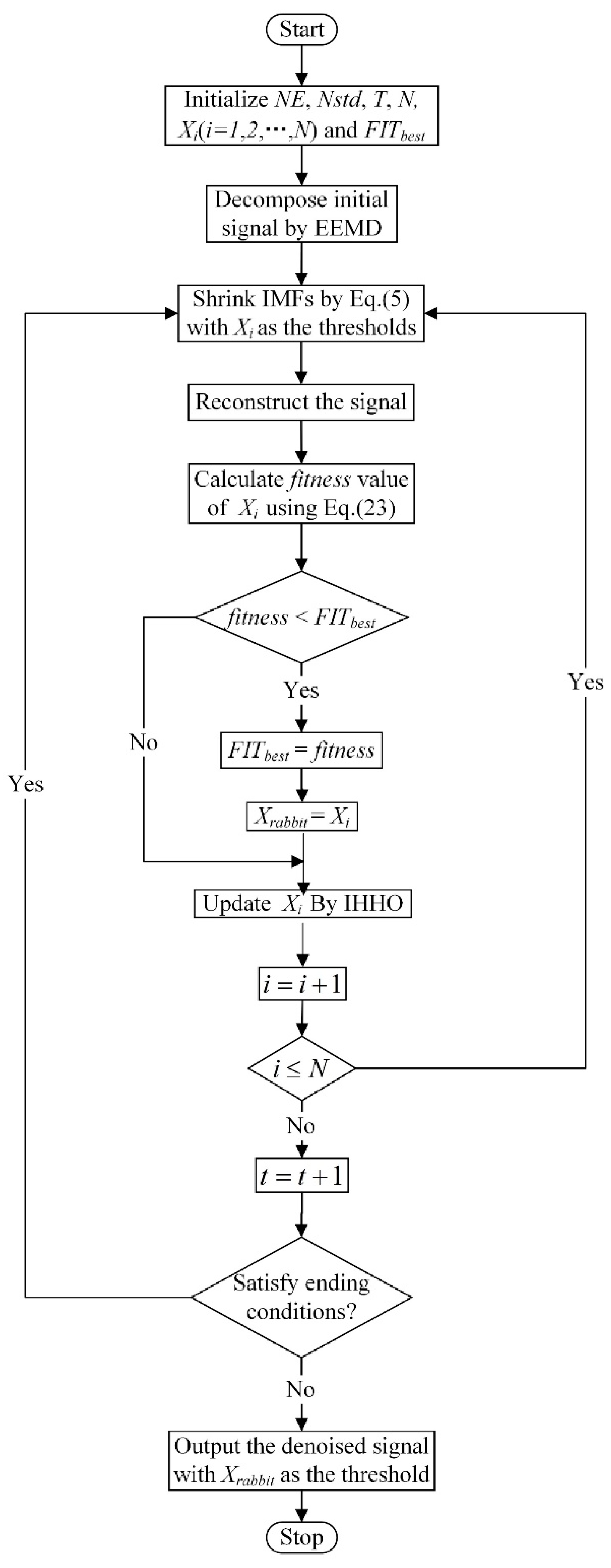
2.1. Denoising Based on EEMD
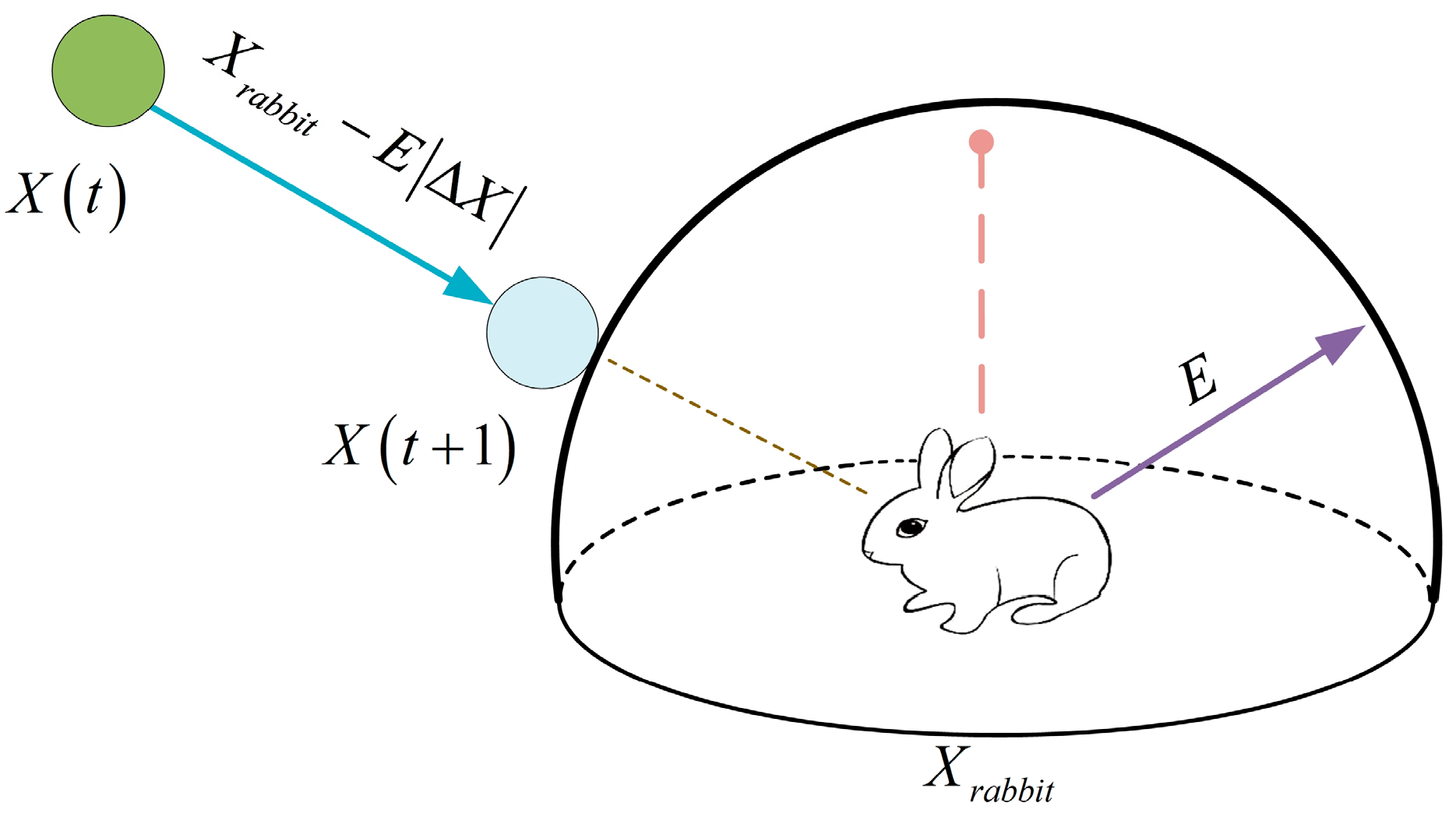
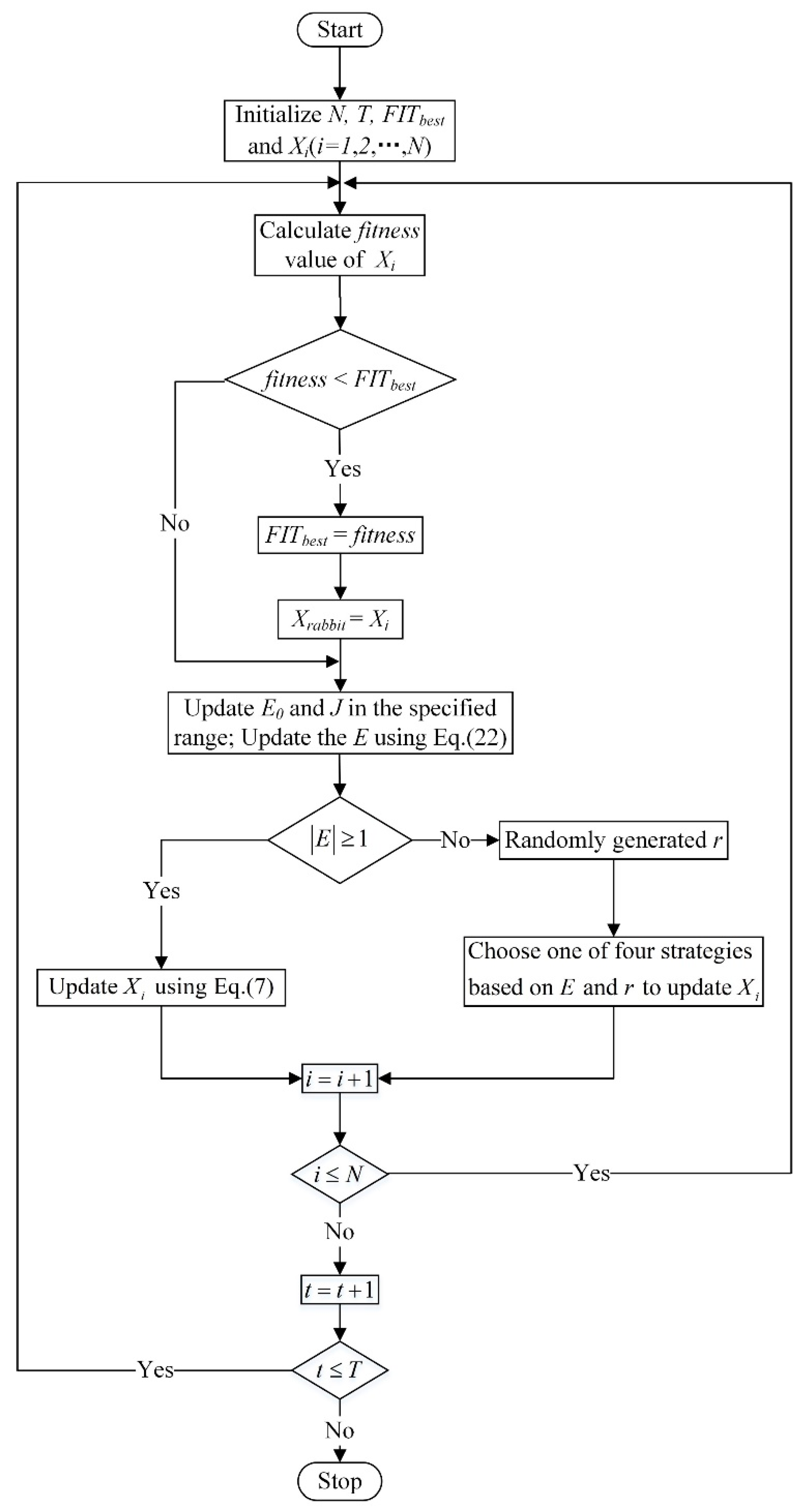
2.2. Harris Hawks Optimization Algorithm
- (1)
- Exploration Stage
- (2)
- Transition Stage
- (3)
- Exploitation Stage
- Soft siege with progressive dive: when and , the energy of the prey is sufficient. The chance of escape is also high. There are two ways to update the position of each Harris’s hawk. One way is simulated by Equation (11).
- b.
- Soft siege: when and , the prey still has sufficient physical strength. At this time, the Harris’s hawks slowly surround the prey to consume their energy. The formula is as follows.
- c.
- Hard siege with progressive dive: when and , the prey does not have enough energy to escape. This strategy has two ways of updating the position, as follows:
- d.
3. Proposed Method
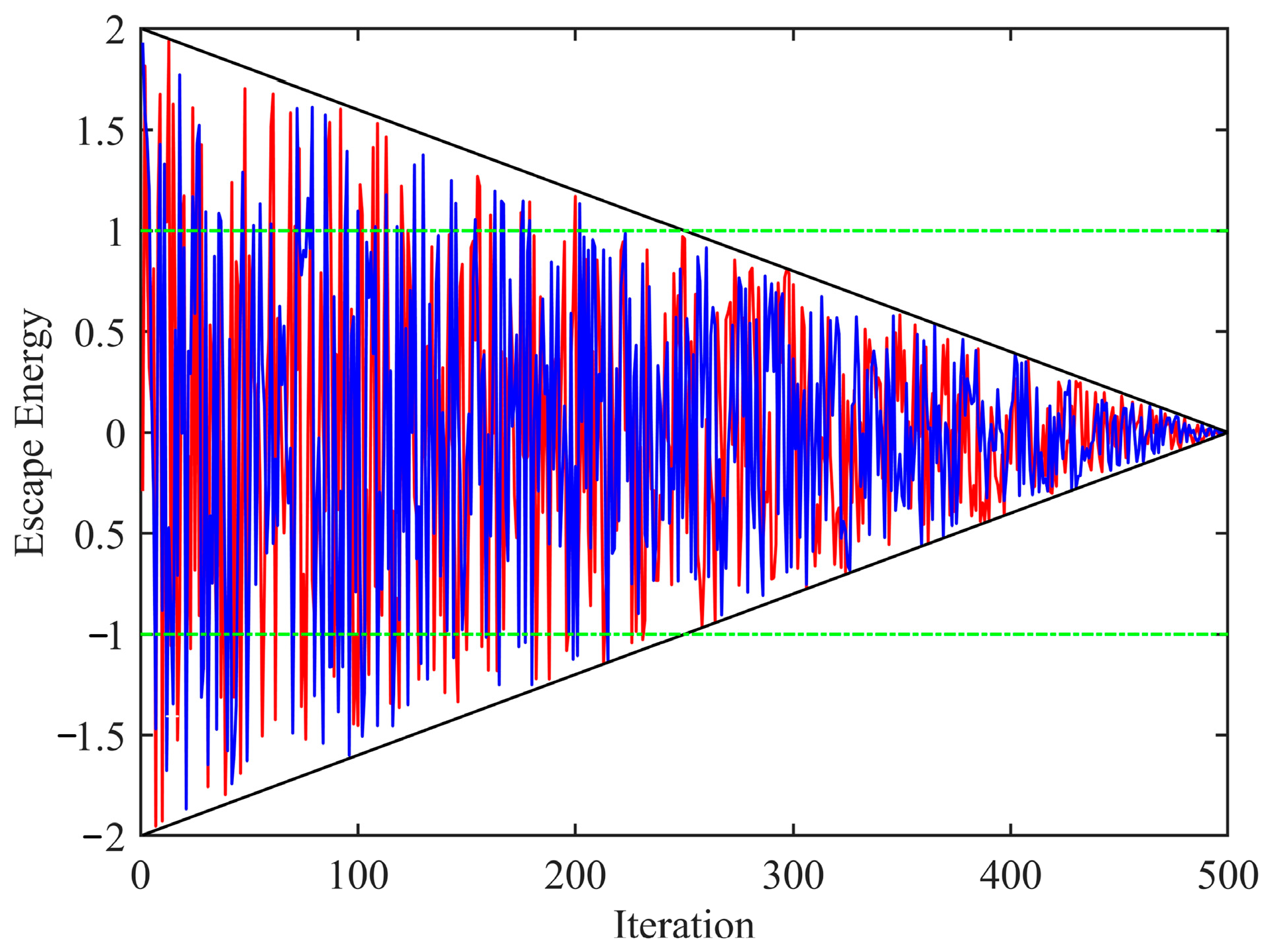
3.1. Improvement of HHO
3.2. Flow of the Proposed Denoising Method
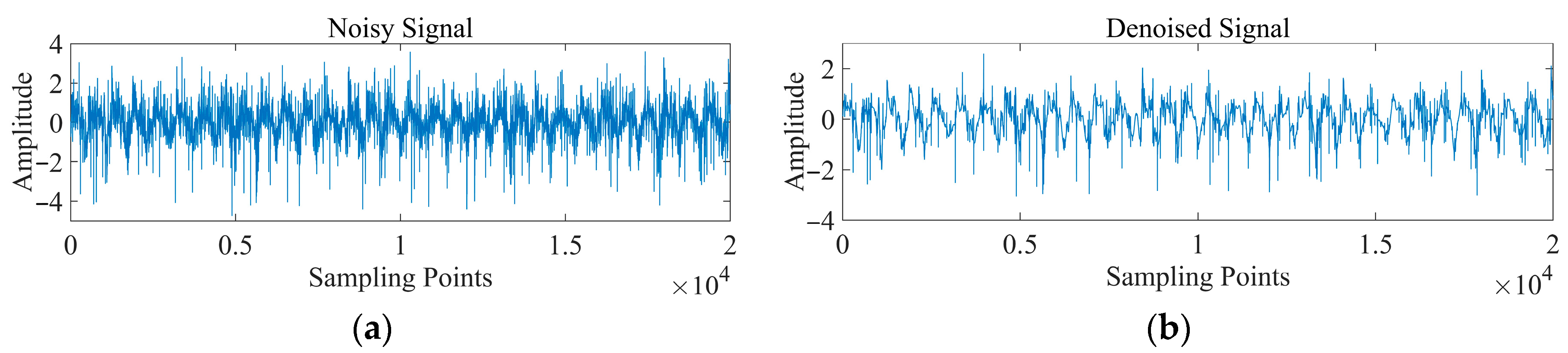
4. Simulation and Analysis
4.1. Experimental Data and Evaluation Indicators
4.2. Comparative Analysis
- (1)
- EEMD denoising: Set the total number of added noise , the ratio of the standard deviation of the added noise to the original noisy signal .
- (2)
- EEMD-PSO denoising: Set the total number of added noise , ratio of the standard deviation of the added noise to the original noisy signal , number of particles , particle maximum speed , and maximum iterations number . Self-learning factor , group-learning factor , and inertia weight [33].
- (3)
- EEMD-HHO denoising and EEMD-IHHO denoising: Set the total number of noise added , the ratio of the standard deviation of the added noise to the original noisy signal , the maximum number of iterations in HHO , and the total number of eagles in the population . In EEMD-IHHO denoising, the escape energy was updated by Equation (25). Where was equal to 5.
- (4)
- EEMD-Grey denoising: Set the total number of added noise , the ratio of the standard deviation of the added noise to the original noisy signal , the resolution coefficient , and the weight coefficient .
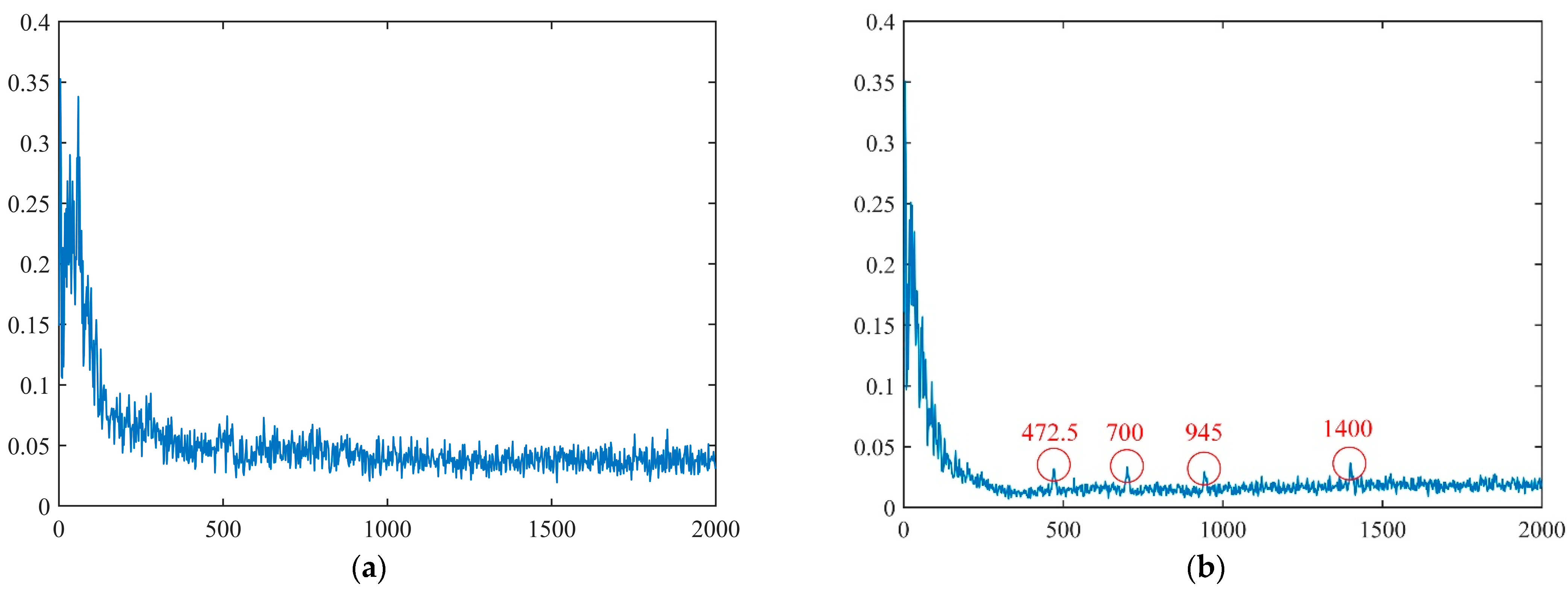
5. Industrial Application
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, F.; Mine, D.C. Discussion on the implementation scheme of unmanned fully mechanized mining face. Shaanxi Coal 2019, 38, 67–71+181. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, D.; Wang, Z.B.; Si, L.; Tan, C.; Lu, X.L. Online shearer-onboard personnel detection method for the intelligent fully mechanized mining face. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2022, 236, 3058–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.Y.; Jiang, L.P.; Pan, H.G.; Yang, J.; Kitipornchai, S. Coupled free vibration of a functionally graded pre-twisted blade-shaft system reinforced with graphene nanoplatelets. Compos. Struct. 2020, 16, 113362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, L.; Wang, Z.B.; Tan, C.; Liu, X.H.; Xu, X.H. A feature extraction method for shearer cutting pattern recognition based on improved local mean decomposition and multi-scale fuzzy entropy. Curr. Sci. 2017, 112, 2243–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.P.; Peng, T.H.; Zhu, Y.M. A Cutting Pattern Recognition Method for Shearers Based on ICEEMDAN and Improved Grey Wolf Optimizer Algorithm-Optimized SVM. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Pan, H.G.; Cai, Y. Free vibration analysis of a rotating graphene nanoplatelet reinforced pre-twist blade-disk assembly with a setting angle. Appl. Math. Model. 2021, 93, 578–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.P.; Peng, Z. Multi-mode separation and nonlinear feature extraction of hybrid gear failures in coal cutters using adaptive nonstationary vibration analysis. Nonlinear Dyn. 2016, 84, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Forero, S.; Pages, R.; Angulo, J. Learnable Empirical Mode Decomposition based on Mathematical Morphology. Siam J. Imaging Sci. 2022, 15, 23–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosh, M.; Singh, P.; Sadhu, A. Empirical mode decomposition and its variants: A review with applications in structural health monitoring. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 093001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.B.W.; Yu, F.H.; Li, Q.L. Soil Temperature Prediction Using Convolutional Neural Network Based on Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 4084–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.P.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, Q.C. Comparison of EEMD-ARIMA, EEMD-BP and EEMD-SVM algorithms for predicting the hourly urban water consumption. J. Hydroinform. 2022, 24, 535–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.; Ma, H.; Saha, T.; Ekanayake, C. Self-adaptive partial discharge signal de-noising based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition and automatic morphological thresholding. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2014, 21, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tong, Y.; Guan, L.; Wu, S.; Li, D. A uv-visible absorption spectrum denoising method based on eemd and an improved universal threshold filter. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 8558–8568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.H.; Xiao, Y.L. Impulse interference processing for mt data based on a new adaptive wavelet threshold de-noising method. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, P.; Kim, J.-M. Adaptive ecg denoising using genetic algorithm-based thresholding and ensemble empirical mode decomposition. Inf. Sci. 2016, 373, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Bajaj, V.; Kumar, A. Effective de-noising of ecg by optimised adaptive thresholding on noisy modes. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 2018, 12, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, T.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, L.; Zhang, M. A dual-adaptive denoising algorithm for brillouin optical time domain analysis sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 22712–22719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Ren, Z.C.; Liu, T.; Tang, J.Y. Improved Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm Based on Harris Hawks Optimization. J. Internet Technol. 2022, 23, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarz, J.C. Cooperative hunting harris’ hawks (parabuteo unicinctus). Science 1988, 239, 1525–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussien, A.G.; Abualigah, L.; Abu Zitar, R.; Hashim, F.A.; Amin, M.; Saber, A.; Almotairi, K.H.; Gandomi, A.H. Recent advances in harris hawks optimization: A comparative study and applications. Electronics 2022, 11, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.W.; He, W.; Peng, X.G.; Peng, X.N. Harris hawks optimization with information exchange. Appl. Math. Model. 2020, 84, 52–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamboj, V.K.; Nandi, A.; Bhadoria, A.; Sehgal, S. An intensify harris hawks optimizer for numerical and engineering optimization problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 89, 106018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, K.; Fu, W.; Tan, J.; Wang, K. Coordinated approach fusing time-shift multiscale dispersion entropy and vibrational harris hawks optimization-based svm for fault diagnosis of rolling bearing. Measurement 2021, 173, 108580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, K.; Zhu, W.; Salleh, M.N.M. Long-term memory harris hawk optimization for high dimensional and optimal power flow problems. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 147596–147616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D.L.; Johnstone, I.M. Ideal spatial adaptation by wavelet shrinkage. Biometrika 1994, 81, 425–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Xiong, Z.Q.; Wang, Z.J.; Zhang, L.J.; Zhang, D.Z.; Li, F.S. Gamma spectrum denoising method based on improved wavelet threshold. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2020, 52, 1771–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.S.; Wang, X.H.; Zhang, Y.H. Study on PD detection for GIS based on autocorrelation coefficient and similar Wavelet soft threshold. Clust. Comput. J. Netw. Softw. Tools Appl. 2019, 22, 6755–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihwail, R.; Omar, K.; Ariffin, K.A.Z.; Tubishat, M. Improved harris hawks optimization using elite opposition-based learning and novel search mechanism for feature selection. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 121127–121145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, A.A.; Mirjalili, S.; Faris, H.; Aljarah, I.; Mafarja, M.; Chen, H. Harris hawks optimization: Algorithm and applications. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 97, 849–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.Z.; Zhang, T.Q. Single-channel blind source separation for vibration signals based on TVF-EMD and improved SCA. IET Signal Process. 2020, 14, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, S.T.; Zhang, X.D. Fuzzy-based learning rate determination for blind source separation. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2003, 11, 375–383. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.C.; Li, G.L.; Dong, X.; He, K. A novel denoising method for vibration signal of hob spindle based on EEMD and grey theory. Measurement 2021, 169, 108490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, F.; Ab Rahim, L.; Mahmood, A.K.; Abed, S.A. A Hybrid Particle Swarm Optimization-Based Wavelet Threshold Denoising Algorithm for Acoustic Emission Signals. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Shi, G.; Wang, F. Vibration response and fault characteristics analysis of gear based on time-varying mesh stiffness. Mech. Mach. Theory 2020, 148, 103786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Fan, H.; Mushayi, K. Accurate fault location method of the mechanical transmission system of shearer ranging arm. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 202260–202273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




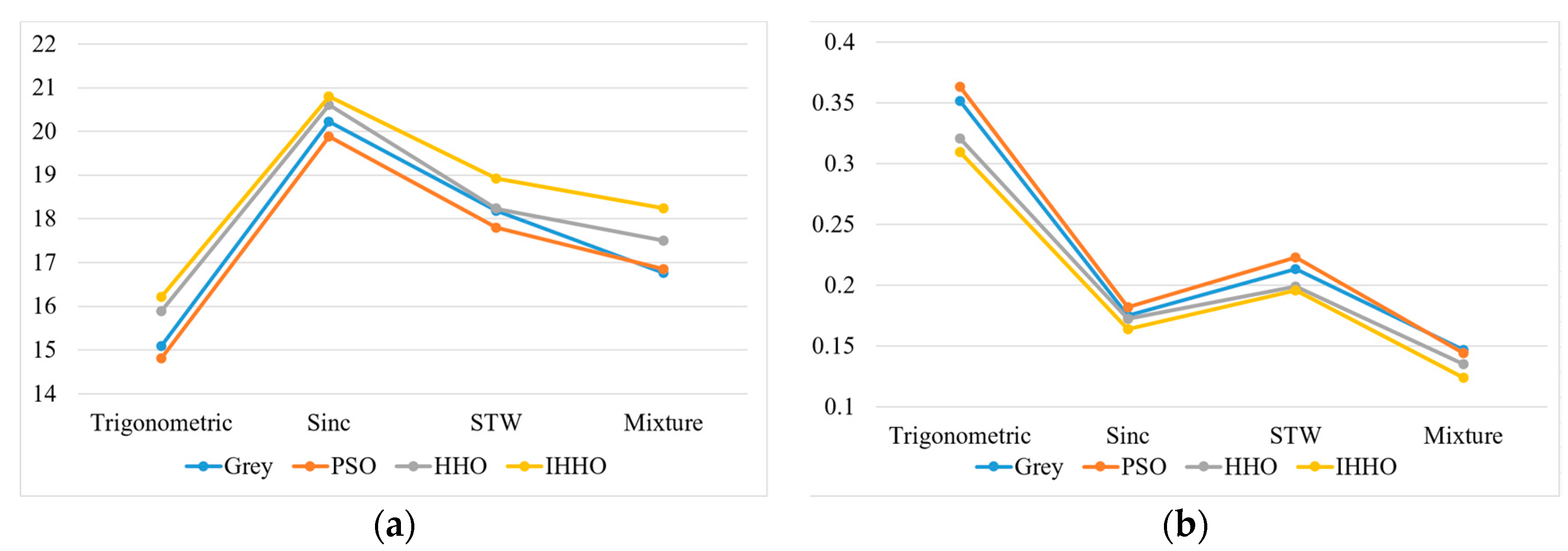


| (a) | (b) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Type | EEMD | EEMD-PSO | EEMD-Grey | EEMD-HHO | EEMD-IHHO | Signal Type | EEMD | EEMD-PSO | EEMD-Grey | EEMD-HHO | EEMD-IHHO |
| Tric | 2.18 | 14.82 | 15.10 | 15.89 | 16.21 | Tric | 1.556 | 0.363 | 0.352 | 0.321 | 0.309 |
| Sinc | 8.96 | 19.87 | 20.22 | 20.61 | 20.80 | Sinc | 0.640 | 0.182 | 0.175 | 0.172 | 0.164 |
| STW | 6.73 | 17.80 | 18.18 | 18.24 | 18.93 | STW | 0.798 | 0.223 | 0.214 | 0.199 | 0.196 |
| Mixture | 4.41 | 16.85 | 16.76 | 17.51 | 18.24 | Mixture | 0.608 | 0.144 | 0.147 | 0.135 | 0.124 |
| (a) | (b) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Type | EEMD | EEMD-PSO | EEMD-Grey | EEMD-HHO | EEMD-IHHO | Signal Type | EEMD | EEMD-PSO | EEMD-Grey | EEMD-HHO | EEMD-IHHO |
| 0 dB | 4.54 | 10.06 | 10.02 | 14.64 | 15.44 | 0 dB | 0.588 | 0.317 | 0.331 | 0.187 | 0.171 |
| 5 dB | 4.43 | 10.81 | 10.35 | 16.50 | 19.14 | 5 dB | 0.606 | 0.291 | 0.297 | 0.151 | 0.111 |
| 10 dB | 4.38 | 11.01 | 10.24 | 17.39 | 17.52 | 10 dB | 0.610 | 0.284 | 0.293 | 0.136 | 0.134 |
| 15 dB | 4.28 | 11.55 | 11.37 | 17.63 | 17.85 | 15 dB | 0.611 | 0.267 | 0.277 | 0.133 | 0.129 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Ren, C.; Liu, Y.; Chang, X. Noise Elimination for Coalcutter Vibration Signal Based on Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition and an Improved Harris Hawks Optimization Algorithm. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14101978
Xu J, Ren C, Liu Y, Chang X. Noise Elimination for Coalcutter Vibration Signal Based on Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition and an Improved Harris Hawks Optimization Algorithm. Symmetry. 2022; 14(10):1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14101978
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jing, Chaofan Ren, Yanxin Liu, and Xiaonan Chang. 2022. "Noise Elimination for Coalcutter Vibration Signal Based on Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition and an Improved Harris Hawks Optimization Algorithm" Symmetry 14, no. 10: 1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14101978
APA StyleXu, J., Ren, C., Liu, Y., & Chang, X. (2022). Noise Elimination for Coalcutter Vibration Signal Based on Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition and an Improved Harris Hawks Optimization Algorithm. Symmetry, 14(10), 1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14101978





