Smile Reanimation with Masseteric-to-Facial Nerve Transfer plus Cross-Face Nerve Grafting in Patients with Segmental Midface Paresis: 3D Retrospective Quantitative Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Surgical Procedures
2.3. Physical Therapy
2.4. Facial Animation: Data Collection
2.5. Facial Animations: Data Analysis
2.6. Facial Animations: Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heckmann, J.G.; Urban, P.P.; Pitz, S.; Guntinas-Lichius, O.; Gágyor, I. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Idiopathic Facial Paresis (Bell’s Palsy). Dtsch Arztebl. Int. 2019, 116, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.; Patel, A.; Zhou, S. Bell palsy. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2022, 194, E867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphey, A.W.; Clinkscales, W.B.; Oyer, S.L. Masseteric Nerve Transfer for Facial Nerve Paralysis. JAMA Facial Plast. Surg. 2018, 20, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bruins, T.E.; van Veen, M.M.; Mooibroek-Leeuwerke, T.; Werker, P.M.N.; Broekstra, D.C.; Dijkstra, P.U. Association of Socioeconomic, Personality, and Mental Health Factors With Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients With Facial Palsy. JAMA Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2020, 146, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglioli, F. Facial reanimations: Part II—Long-standing paralyses. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 53, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzis, J.K.; Karypidis, D. Therapeutic Strategies in Post–Facial Paralysis Synkinesis in Adult Patients. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2012, 129, 925e–939e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, K.; Lim, J.-A.; Ko, H.; Kim, T.; Lee, J.-I.; Kim, H.; Han, S.-J.; Kim, J.-S.; Park, S.; et al. Differences in Facial Expressions between Spontaneous and Posed Smiles: Automated Method by Action Units and Three-Dimensional Facial Landmarks. Sensors 2020, 20, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Hiyali, A.; Ayoub, A.; Ju, X.; Almuzian, M.; Al-Anezi, T. The Impact of Orthognathic Surgery on Facial Expressions. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 73, 2380–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawulok, M.; Nalepa, J.; Kawulok, J.; Smolka, B. Dynamics of facial actions for assessing smile genuineness. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0244647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsili, L.; Agostino, R.; Bologna, M.; Belvisi, D.; Palma, A.; Fabbrini, G.; Berardelli, A. Bradykinesia of posed smiling and voluntary movement of the lower face in Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2014, 20, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, R.D. Nonspeech Oral Movements and Oral Motor Disorders: A Narrative Review. Am. J. Speech-Lang. Pathol. 2015, 24, 763–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horen, S.R.; Gantiwala, S.; Jahromi, A.H.; Konofaos, P. A Historical Perspective on the Management of Facial Paralysis. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2022, 88, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.Q.; Hadlock, T.A. Beyond Botox: Contemporary Management of Nonflaccid Facial Palsy. Facial Plast. Surg. Aesthet. Med. 2020, 22, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guerreschi, P.; Labbé, D. Sequelae of Facial Palsy. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 144, 682e–692e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Lee, H.Y. Acute Peripheral Facial Palsy: Recent Guidelines and a Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Choi, K.H.; Lim, B.W.; Kim, M.W.; Kim, J. Half-mirror biofeedback exercise in combination with three botulinum toxin A injections for long-lasting treatment of facial sequelae after facial paralysis. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2014, 68, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglioli, F.; Kutanovaite, O.; Rabbiosi, D.; Colletti, G.; Mohammed, M.; Saibene, A.M.; Cupello, S.; Privitera, A.; Battista, V.M.; Lozza, A.; et al. Surgical treatment of synkinesis between smiling and eyelid closure. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 45, 1996–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglioli, F.; Soliman, M.; El-Shazly, M.; Saadeldeen, W.; Abda, E.A.; Allevi, F.; Rabbiosi, D.; Tarabbia, F.; Lozza, A.; Cupello, S.; et al. Use of the masseteric nerve to treat segmental midface paresis. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 56, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spira, M. Anastomosis of masseteric nerve to lower division of facial nerve for correction of lower facial paralysis preliminary report. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1978, 61, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.M.; Obara, K.; Dias, J.M.; Menacho, M.O.; Lavado, E.L.; Cardoso, J. Facial exercise therapy for facial palsy: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rehabilit. 2011, 25, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamkpah, N.S.; Jeanpierre, L.; Lieu, J.E.C.; Del Toro, D.; Simon, L.E.; Chi, J.J. Physical Therapy for Iatrogenic Facial Paralysis. JAMA Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2020, 146, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, C.A.; Bhama, P.K.; Park, J.; Hadlock, C.R.; Hadlock, T.A. Clinician-Graded Electronic Facial Paralysis Assessment. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 136, 223e–230e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallac, R.R.; Thrikutam, N.; Chou, P.-Y.; Huang, R.; Seaward, J.R.; Kane, A.A. Kinematic Analysis of Smiles in the Healthy Pediatric Population Using 3-Dimensional Motion Capture. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2019, 57, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sforza, C.; Tarabbia, F.; Mapelli, A.; Colombo, V.; Sidequersky, F.V.; Rabbiosi, D.; Annoni, I.; Biglioli, F. Facial reanimation with masseteric to facial nerve transfer: A three-dimensional longitudinal quantitative evaluation. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2014, 67, 1378–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trotman, C.A.; Faraway, J.; Hadlock, T.; Banks, C.; Jowett, N.; Jung, H.J. Facial Soft-tissue Mobility. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2018, 6, e1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotman, C.A.; Faraway, J.; Hadlock, T.A. Facial mobility and recovery in patients with unilateral facial paralysis. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2019, 23, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Xue, Z.; Wu, L.; Yang, R.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Z. Three-Dimensional Dynamic Analysis of the Reproducibility of Verbal and Nonverbal Facial Expressions. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2021, 59, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerós, A.; Horta, R.; Aguiar, P. Facegram—Objective quantitative analysis in facial reconstructive surgery. J. Biomed. Inform. 2016, 61, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavese, C.; Cecini, M.; Lozza, A.; Biglioli, F.; Lisi, C.; Bejor, M.; Toffola, E.D. Rehabilitation and functional recovery after masseteric-facial nerve anastomosis: A case series. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabilit. Med. 2015, 52, 379–388. [Google Scholar]
- Sforza, C.; Frigerio, A.; Mapelli, A.; Tarabbia, F.; Annoni, I.; Colombo, V.; Latiff, M.; Ferreira, C.L.P.; Rabbiosi, D.; Sidequersky, F.V.; et al. Double-powered free gracilis muscle transfer for smile reanimation: A longitudinal optoelectronic study. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2015, 68, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henstrom, D.K.; Skilbeck, C.J.; Weinberg, J.; Knox, C.; Cheney, M.L.; Hadlock, T.A. Good correlation between original and modified house Brackmann facial grading systems. Laryngoscope 2010, 121, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biglioli, F.; Colombo, V.; Rabbiosi, D.; Tarabbia, F.; Giovanditto, F.; Lozza, A.; Cupello, S.; Mortini, P. Masseteric–facial nerve neurorrhaphy: Results of a case series. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 126, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackson, P.; Lafleur, M.F.; Malouin, F.; Richards, C.L.; Doyon, J. Potential role of mental practice using motor imagery in neurologic rehabilitation. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabilit. 2001, 82, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohman, M.H.; Lee, L.N.; Hadlock, T.A. Two-step highly selective neurectomy for refractory periocular synkinesis. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 1385–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volk, G.F.; Pantel, M.; Guntinas-Lichius, O. Modern concepts in facial nerve reconstruction. Head Face Med. 2010, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biglioli, F.; Allevi, F.; Rabbiosi, D.; Cupello, S.; Battista, V.M.A.; Saibene, A.M.; Colletti, G. Triple innervation for reanimation of recent facial paralysis. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 46, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetiser, S.; Karapinar, U. Hypoglossal-Facial Nerve Anastomosis: A Meta-Analytic Study. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2007, 116, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Sekido, M.; Furukawa, H.; Oyama, A.; Tsutsumida, A.; Sasaki, S. Surgical rehabilitation of reversible facial palsy: Facial–hypoglossal network system based on neural signal augmentation/neural supercharge concept. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2007, 60, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y.-C.; Zuker, R.M.; Manktelow, R.T.; Wade, S. A Comparison of Commissure Excursion following Gracilis Muscle Transplantation for Facial Paralysis Using a Cross-Face Nerve Graft versus the Motor Nerve to the Masseter Nerve. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 117, 2407–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takushima, A.; Harii, K.; Okazaki, M.; Ohura, N.; Asato, H. Availability of Latissimus Dorsi Minigraft in Smile Reconstruction for Incomplete Facial Paralysis: Quantitative Assessment Based on the Optical Flow Method. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 123, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boahene, K.D.; Farrag, T.Y.; Ishii, L.; Byrne, P.J. Minimally Invasive Temporalis Tendon Transposition. Arch. Facial Plast. Surg. 2011, 13, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Li, Q. Mini-Temporalis Transposition. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2015, 26, 518–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darby, L.J.; Millett, D.T.; Kelly, N.; McIntyre, G.T.; Cronin, M.S. The effect of smiling on facial asymmetry in adults: A 3D evaluation. Australas. Orthod. J. 2015, 31, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khambay, B.; Lowney, C.; Hsung, T.-C.; Morris, D. Fluctuating asymmetry of dynamic smiles in normal individuals. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 48, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yang, C.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.X. Masseter-to-Facial Nerve Transfer. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2014, 73, S63–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birgfeld, C.; Neligan, P. Surgical Approaches to Facial Nerve Deficits. Skull Base 2011, 21, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quinzi, V.; Polizzi, A.; Ronsivalle, V.; Santonocito, S.; Conforte, C.; Manenti, R.J.; Isola, G.; Giudice, A.L. Facial Scanning Accuracy with Stereophotogrammetry and Smartphone Technology in Children: A Systematic Review. Children 2022, 9, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Patient (M/F) | Age (yrs) | Side (R/L) | Etiology | Surgery | Time between Lesion and Operation (Year) | Time between Operation and 3D Analysis (Months) | M.H.B. Scale (Grade) | First Mimic Muscle Contraction After Surgery-Beginning of Physiotherapy (Months) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preop | Postop | ||||||||
| M1 | 31 | R | Acoustic neurinoma | M-F neurorrhaphy + cross-face sural nerve graft | 10 | 15 | III | II | 3 |
| M2 | 36 | R | Facial trauma | M-F neurorrhaphy + cross-face sural nerve graft (two-step surgery) | 2 | 8 | IV | III | 6 |
| M3 | 18 | L | Congenital palsy | M-F nerve neurorrhaphy | 18 | 27 | III | II | 6 |
| M4 | 51 | L | Facial neurinoma | M-F neurorrhaphy + cross-face sural nerve graft | 2 | 12 | III | II | 4 |
| M5 | 32 | R | Bell’s palsy | M-F neurorrhaphy | 5 | 48 | III | II | 3 |
| F1 | 25 | L | Bell’s palsy | M-F neurorrhaphy | 16 | 16 | III | II | 3 |
| F2 | 35 | L | Ramsay Hunt Syndrome | M-F neurorrhaphy + cross-face sural nerve graft (two-step surgery) | 12 | 39 | IV | III | 4 |
| F3 | 27 | R | Bell’s palsy | M-F neurorrhaphy + cross-face sural nerve graft | 12 | 8 | III | II | 4 |
| F4 | 33 | R | Parotid surgery | M-F nerve neurorrhaphy + cross-face sural nerve graft (two-step surgery) | 30 | 20 | IV | III | 4 |
| F5 | 37 | L | Bell’s palsy | M-F neurorrhaphy + cross-face sural nerve graft | 3 | 25 | III | II | 4 |
| Treatment Timing | Specific Rehabilitative Training |
|---|---|
| 1–3 months |
|
| 3–12 months |
|
| 12–24 months |
|
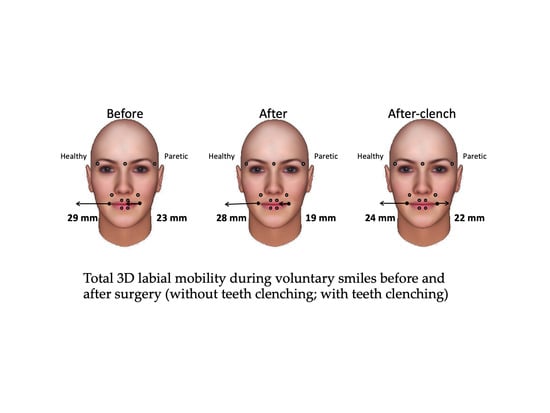
| Variable | Maximum Smile Before Surgery (A) | Maximum Smile after Surgery (B) | Maximum Clenching Smile after Surgery (C) | Friedman Test | Effect Size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | Kendall’s W | |||||
| Healthy side (mm) | Median | 28.7 | 28.1 | 24 | NS (0.104) | 0.323 |
| IQR | 15.4 | 11.2 | 5.2 | |||
| Paretic side (mm) | Median | 23.2 | 18.7 | 22.4 | NS (0.156) | 0.265 |
| IQR | 11.9 | 12.1 | 8.8 | |||
| Ratio (%) | Median | 69 | 65 | 92 | 0.006 B vs. C, p = 0.017 | 0.735 |
| IQR | 31 | 29 | 57 | |||
| Asymmetry index (%) | Median | 18 | 21 | 5 | 0.006 B vs. C, p = 0.017 | 0.735 |
| IQR | 20 | 22 | 30 |
| Healthy Side (mm) | Paretic Side (mm) | Ratio (%) | Asymmetry Index (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spontaneous smile before | Median | 25.1 | 16.8 | 76 | 12 |
| IQR | 18.7 | 9.6 | 26 | 15 | |
| Spontaneous smile after | Median | 17.2 | 12.2 | 75 | 16 |
| IQR | 11.3 | 9.1 | 52 | 13 | |
| Wilcoxon test | p-value | 0.043 | 0.043 | NS (0.465) | NS (0.686) |
| Effect Size | r | 0.561 | 0.561 | 0.211 | 0.112 |
| Kiss before | Median | 34.9 | 27 | 75 | 18 |
| IQR | 19.1 | 25.9 | 52 | 28 | |
| Kiss after | Median | 32.2 | 19.9 | 69 | 18 |
| IQR | 8.1 | 20 | 44 | 33 | |
| Wilcoxon test | p-value | NS (0.091) | 0.028 | NS (0.092) | NS (0.063) |
| Effect Size | r | 0.410 | 0.533 | 0.436 | 0.452 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tarabbia, F.; Bertozzi, F.; Allevi, F.; Dell’Aversana Orabona, G.; Cupello, S.; Dolci, C.; Zago, M.; Sforza, C.; Biglioli, F. Smile Reanimation with Masseteric-to-Facial Nerve Transfer plus Cross-Face Nerve Grafting in Patients with Segmental Midface Paresis: 3D Retrospective Quantitative Evaluation. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14122570
Tarabbia F, Bertozzi F, Allevi F, Dell’Aversana Orabona G, Cupello S, Dolci C, Zago M, Sforza C, Biglioli F. Smile Reanimation with Masseteric-to-Facial Nerve Transfer plus Cross-Face Nerve Grafting in Patients with Segmental Midface Paresis: 3D Retrospective Quantitative Evaluation. Symmetry. 2022; 14(12):2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14122570
Chicago/Turabian StyleTarabbia, Filippo, Filippo Bertozzi, Fabiana Allevi, Giovanni Dell’Aversana Orabona, Silvia Cupello, Claudia Dolci, Matteo Zago, Chiarella Sforza, and Federico Biglioli. 2022. "Smile Reanimation with Masseteric-to-Facial Nerve Transfer plus Cross-Face Nerve Grafting in Patients with Segmental Midface Paresis: 3D Retrospective Quantitative Evaluation" Symmetry 14, no. 12: 2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14122570
APA StyleTarabbia, F., Bertozzi, F., Allevi, F., Dell’Aversana Orabona, G., Cupello, S., Dolci, C., Zago, M., Sforza, C., & Biglioli, F. (2022). Smile Reanimation with Masseteric-to-Facial Nerve Transfer plus Cross-Face Nerve Grafting in Patients with Segmental Midface Paresis: 3D Retrospective Quantitative Evaluation. Symmetry, 14(12), 2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14122570