Symmetry in Aerosol Mechanics: Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Aerosol Particle Motion—Similarity Criteria
2.1. Main Similarity Criteria Adopted for the Aerosol Description
2.2. Particle Motion in Disperse Medium
2.2.1. Approximation of Single Particle in Infinite Gas Volume
2.2.2. Uniform Rectilinear Motion of a Particle—The Stokes problem
- the gas medium is considered incompressible;
- the particle movement velocity is low;
- there is no gas slip on the particle surface;
- the particle is solid (tough);
- the particles travel at a constant speed;
- the gas medium has an infinite extension;
- the particle is sphere-shaped.
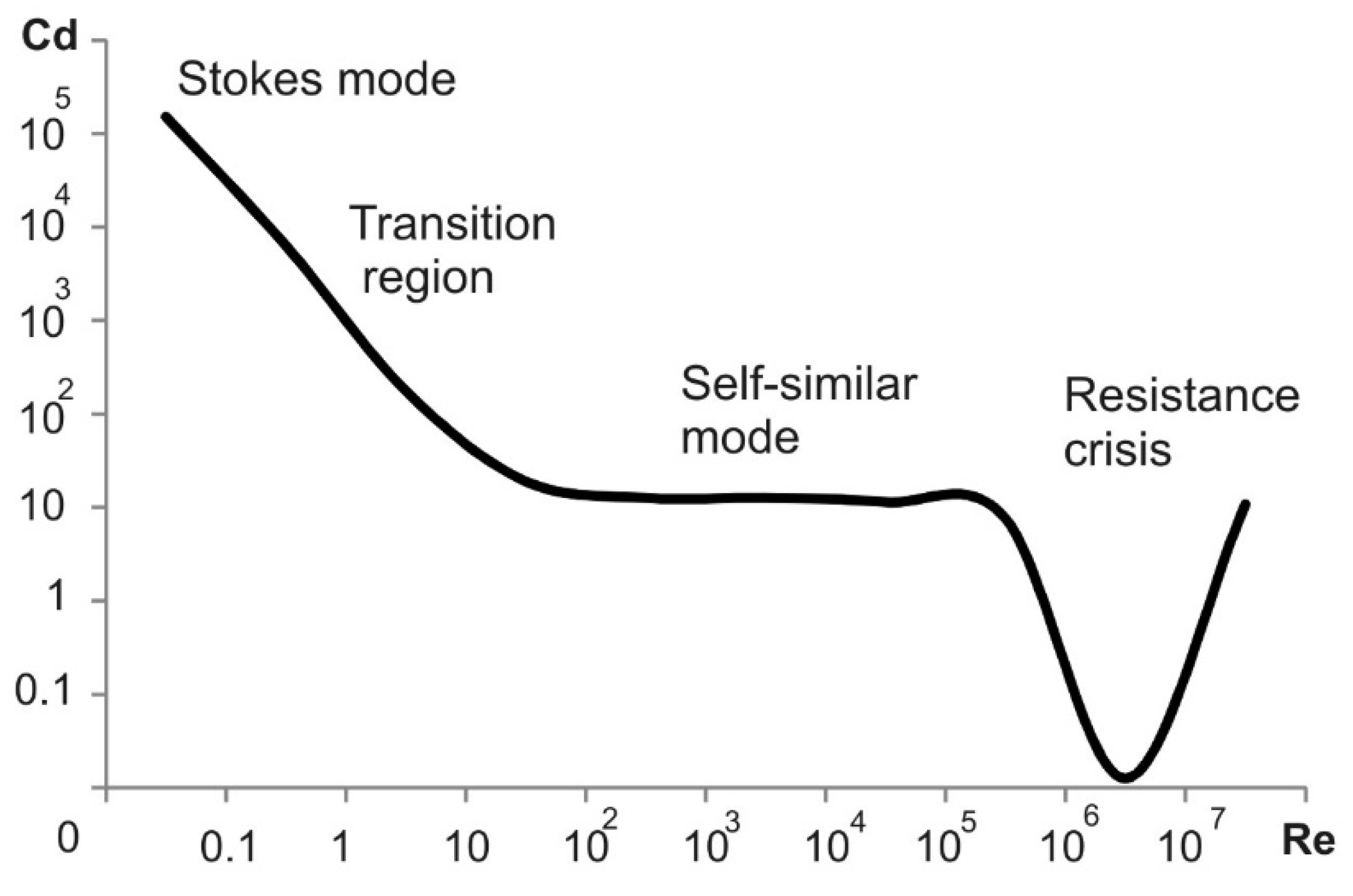
2.2.3. Drag Coefficient
2.2.4. Uniform Rectilinear Motion of a Particle—The Boussinesq Equation
3. Aerosol Particle Motion in External Fields
3.1. Particle Motion under Gravity (the Stokes Mode)
3.1.1. Particle Motion Modes in the Gravitational Field
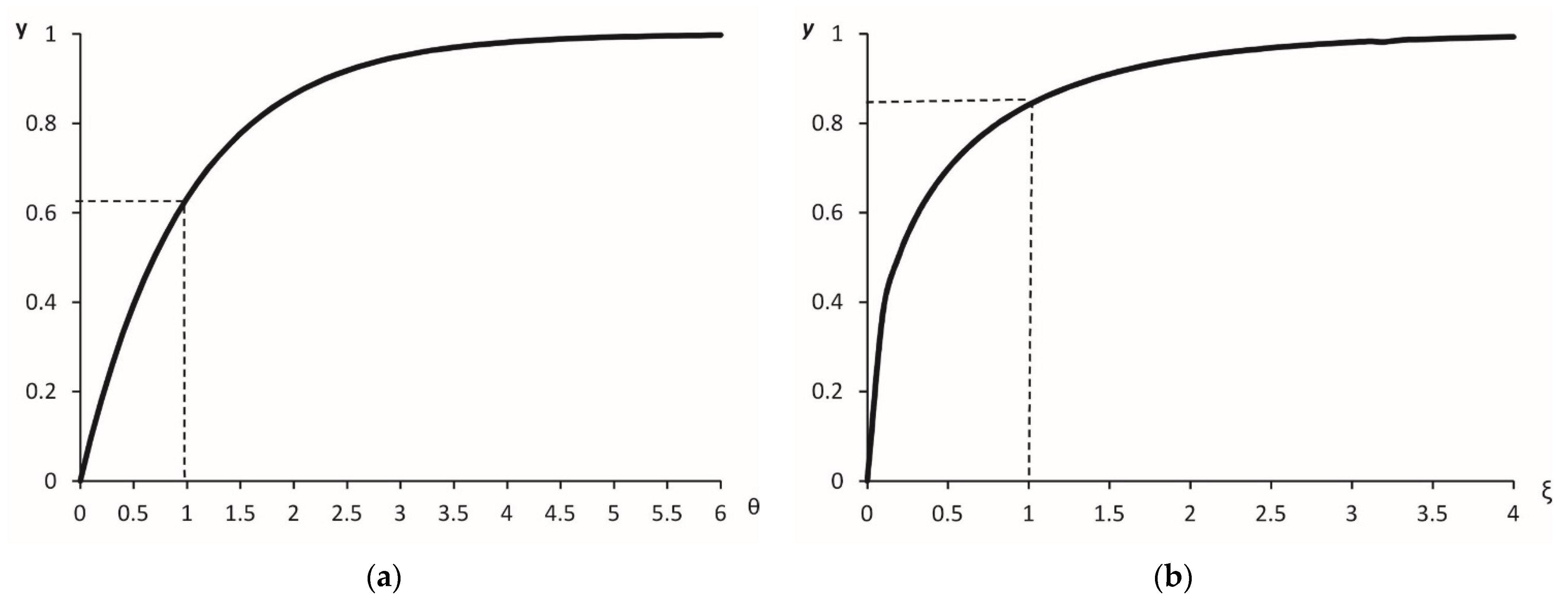
3.1.2. Calculation of Stationary Sedimentation of Particle via Criterion Equation
3.2. Aerosol Particle Coagulation
3.2.1. External Electric Field and Acoustic Wind
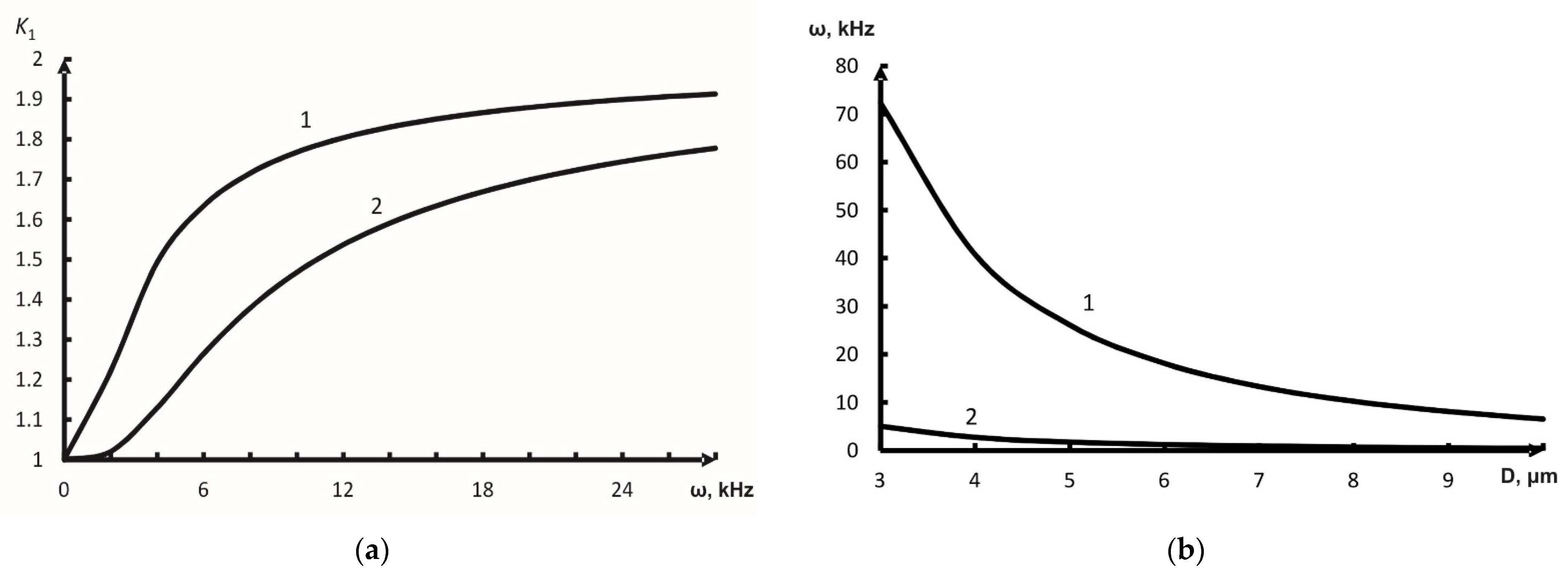
3.2.2. Acoustic Coagulation of Aerosol
- If there is no acoustic field, i.e., = 0, then the collision probability is defined by the Brownian motion (25);
- if the vibrational amplitude rises and hence the velocity up, the collision probability increases;
- the sound field with relatively low frequencies (ω2τ2 << 1) almost does not increase the collision probability as well, (kentr →1, (1– kentr) →0);
- if the sound vibration frequency is ω2τ2 >> 1, the probable collisions and aerosol coagulation take place to maximum effect: kentr →0, (1– kentr) →1.
3.2.3. Aerosol Coagulation with an Additional Dispersed Phase Incorporated
- the collision probability dependence of the particle concentration under electrostatic coagulation is stronger than under the acoustic one;
- the collision probability (and coagulation rate) dependence of the gaseous medium viscosity is also stronger under electrostatic coagulation;
- the greater the electrostatic charge of the particle and the lower the dielectric permittivity, the higher the collision probability in the case of electrostatic coagulation.
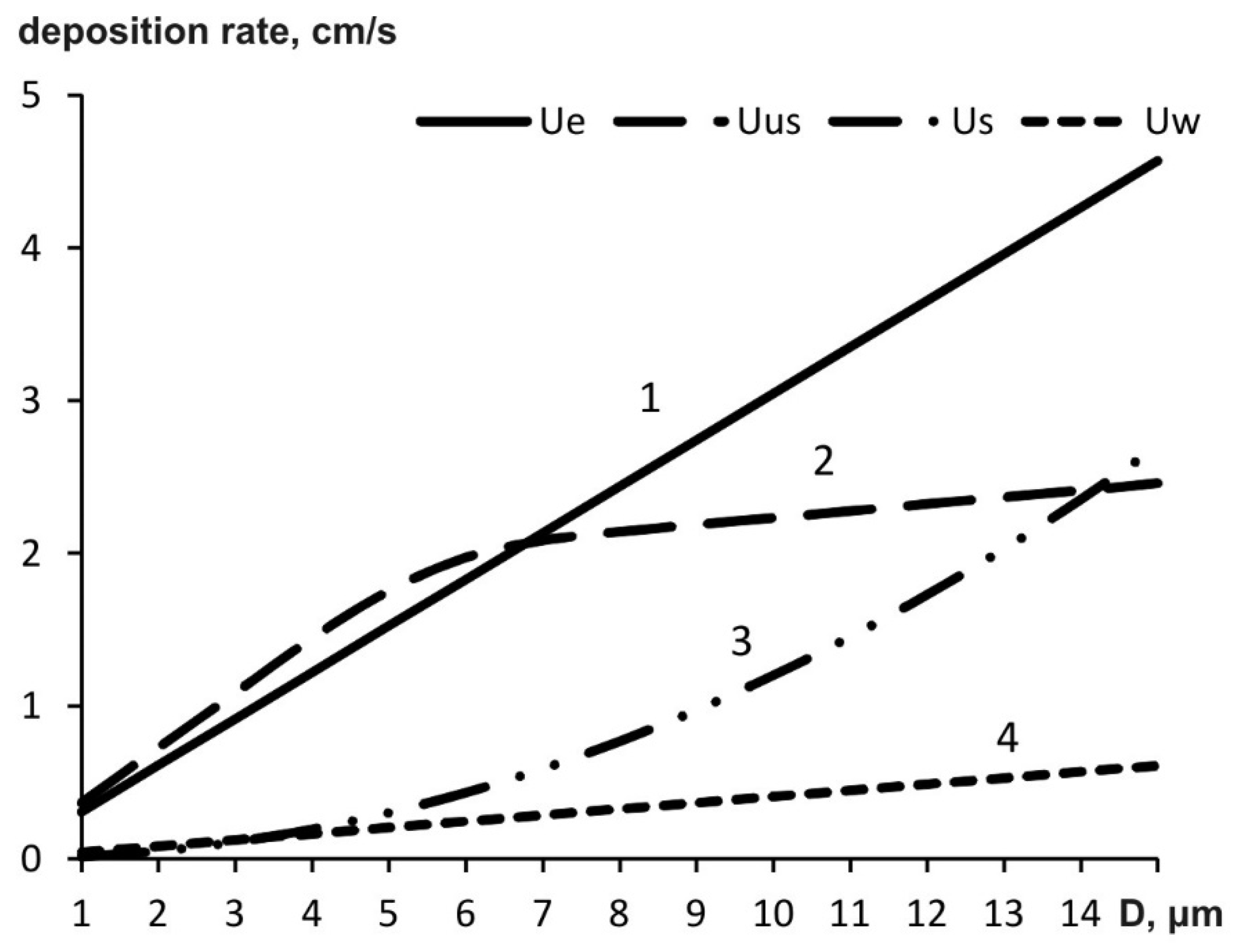
3.3. Aerosol Precipitation Rates in External Fields
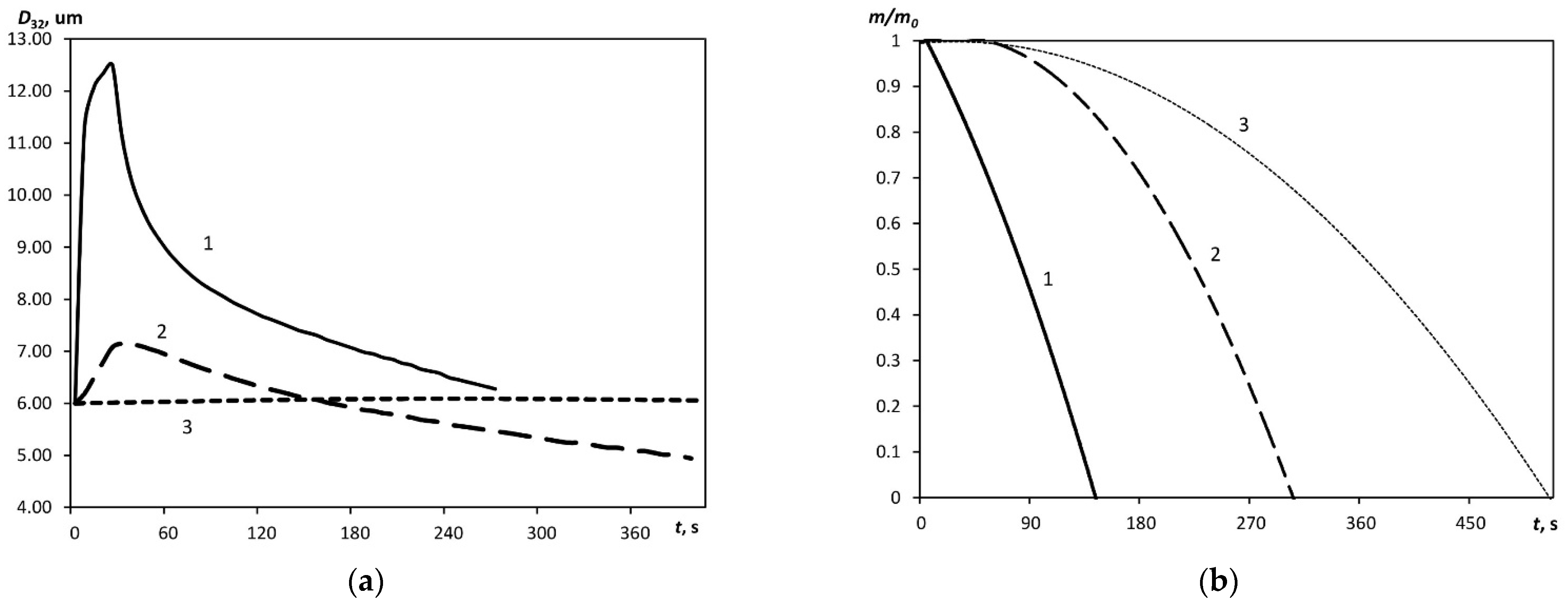
Variations in Particle Sizes and Aerosol Weight in External Fields
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meszaros, E. Fundamental of Atmospheric Aerosol Chemistry; Ak. Kiado: Budapest, Romania, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Pope, C.A., III; Bhatnagar, A.; McCracken, J.P.; Abplanalp, W.; Conklin, D.J.; O’Toole, T. Exposure to Fine Particulate Air Pollution Is Associated with Endothelial Injury and Systemic Inflammation. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Atkinson, R.; Kang, S.; Anderson, H.; Mills, I.; Walton, H. Epidemiological time series studies of PM2. 5 and daily mortality and hospital admissions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Thorax 2014, 69, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xing, Y.F.; Xu, Y.H.; Shi, M.H.; Lian, Y.X. The impact of PM2.5 on the human respiratory system. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, E69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A., III; Burnett, R.T.; Thun, M.J.; Calle, E.E.; Krewski, D.; Ito, K.; Thurston, G.D. Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. JAMA 2002, 287, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, R.; Barth, M.C.; Pfister, G.G.; Delle Monache, L.; Lamarque, J.F.; Archer-Nicholls, S.; Walters, S. How will air quality change in South Asia by 2050? J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 1840–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eber, M. Smoke separators to reduce air pollution. CZ Chem. Tech 1977, 6, 523–527. [Google Scholar]
- Rohilla, M.; Saxena, A.; Dixit, P.K.; Mishra, G.K.; Narang, R. Aerosol forming compositions for fire fighting applications: A review. Fire Technol. 2019, 55, 2515–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altshuller, A.P.; Bufallini, J.J. Photochemical aspects of air pollution. Environm. Sci. Technol. 1971, 5, 39–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, J.P.; Sayer, R.M. Chemistry in the clouds: The role of aerosols in atmospheric chemistry. Sci. Prog. 2002, 85, 263. [Google Scholar]
- Reist, P.C. Introduction to Aerosol Science; Macmillan Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Green, H.L.; Lane, W.R. Particulate Clouds: Dusts, Smokes and Mists. Their Physics and Physical Chemistry and Industrial and Environmental Aspects; E. & F.N. Spon, Ltd.: London, UK, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Sedov, L.I. Similarity and Dimensional Methods in Mechanics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Clift, R.; Grace, J.R.; Weber, M.E. Bubbles, Drops and Particles; Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 1978; p. 380. [Google Scholar]
- Crowe, C.T.; Sommerfeld, M.; Tsuji, Y. Multiphase Flows with Droplets and Particles; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998; p. 471. [Google Scholar]
- Michaelides, E.E. Bubbles, Drops and Particles: Their Motion, Heat and Mass Transfer; World Scientific: Singapore, 2006; p. 410. [Google Scholar]
- Pai, S.I. Two-Phase Flows; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hidy, G.M.; Brock, J.R. The Dynamics of Aerocolloidal Systems: International Reviews in Aerosol Physics and Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Hidy, G.M. (Ed.) Topics in Current Aerosol Research: International Reviews in Aerosol Physics and Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, M.M.R.; Loyalka, S.K. Aerosol Science: Theory and Practice; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Brennen, C.E. Fundamentals of Multiphase Flows; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hinds, W.C. Aerosol Technology: Properties, Behavior, and Measurement of Airborne Particles, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov, G.V.; Strizhak, P.A.; Shlegel, N.E. Interaction of water and suspension droplets during their collisions in a gas medium. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2019, 53, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesin, Y.B. Dimension Theory in Dynamical Systems: Contemporary Views and Applications; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sterrett, S.G. Similarity and dimensional analysis. In Philosophy of Technology and Engineering Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 799–823. [Google Scholar]
- Gukhman, A.A. Introduction to Similarity Theory; Vysshaya Shkola Publisher: Moscow, Russia, 1973; p. 296. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Arkhipov, V.A.; Berezikov, A.P. Theory Bases of Engineering and Physical Experiments; Tomsk Polytechnic University Publisher: Tomsk, Russia, 2008; p. 206. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Beresnev, S.A.; Gryazin, V.I. Physics of Atmospheric Aerosols; Ural University Publisher: Yekaterinburg, Russia, 2008; p. 227. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Nigmatulin, R.I.; Friedly, J.C. Dynamics of Multiphase Media; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Sternin, L.E.; Maslov, B.N.; Shraiber, A.A.; Podvysotskii, A.M. Two-Phase Mono-and Polydisperse Gas Flows Containing Particles; Izdatel Mashinostroenie: Moscow, Russia, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Eiffel, G. Sur la résistance des sphères dans l’air en movement. Comptes Rendus 1912, 155, 1597–1599. [Google Scholar]
- Prandtl, L. Gesammelte Abhandlungen zur Angewandten Mechanik, Hydro-und Aerodynamik: T. Chronologische Folge der Veröffentlichungen. Elastizität, Plastizität, Rheologie. Tragflügel und Luftschrauben; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Stoker, J.J. Garrett Birkhoff, Hydrodynamics, a study in logic, fact, and similitude. Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 1951, 57, 497–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuks, N.A. The Mechanics of Aerosols; Academy of Science Publisher: Moscow, Russia, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Levich, V.G.; Tobias, C.W. Physicochemical hydrodynamics. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1963, 110, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekiel-Jezewska, M.L.; Metzger, B.; Guazzelli, E. Spherical cloud of point particles falling in a viscous liquid. Phys. Fluids 2006, 18, 038104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, X.; Koch, D.L. Hindered settling velocity and microstructure in suspensions of solid spheres with moderate Reynolds numbers. Phys. Fluids 2007, 19, 093302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abade, G.C.; Cunha, F.R. Computer simulation of particles aggregates during sedimentation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2007, 196, 4597–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, G.; Koch, D.L. Evolution of clusters of sedimenting low-Reynolds-number particles with Oseen interactions. J. Fluid Mech. 2008, 603, 63–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, A.A.; Tsuji, T.; Tanaka, T. A new relation of drag force for high Stokes number monodisperse spheres by direct numerical simulation. Adv. Powder Technol. 2014, 25, 1860–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsche, L.C.; Batchelor, G.K. Break-up of a falling drop containing dispersed particles. J. Fluid Mech. 1997, 340, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machu, G.; Meile, W.; Nitsche, L.C.; Schaflinger, U. Coalescence, torus formation and breakup of sedimenting drops: Experiments and computer simulation. J. Fluid Mech. 2001, 447, 299–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Metzger, B.; Nicolas, M.; Guazzelli, E. Falling clouds of particles in viscous fluids. J. Fluid Mech. 2007, 580, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylyk, A.; Meile, W.; Brenn, G.; Ekiel-Jezewska, M.L. Break-up of suspension drops settling under gravity in a viscous fluid close to a vertical wall. Phys. Fluids 2011, 23, 063302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khmelev, V.N.; Shalunov, A.V.; Shalunova, K.V. The acoustical coagulation of aerosols. In 2008 9th International Workshop and Tutorials on Electron Devices and Material; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Stepkina, M.Y.; Kudryashova, O.B.; Antonnikova, A.A.; Zhirnov, A.A. Application of Electrostatic Effect for Cleansing Finely Divided Aerosol from Air. J. Eng. Phys. Thermophys. 2020, 93, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lin, J.; Chan, T. Effect of Fluctuating Aerosol Concentrations on the Aerosol Distributions in a Turbulent Jet. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 1629–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, Z.; Zhou, H. Numerical simulation of condensation of natural fog aerosol under acoustic wave action. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 21, 200361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Fang, M.; He, M.; Liu, S.; Luo, Z. Insights into agglomeration and separation of fly-ash particles in a sound wave field. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 5224–5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khmelev, V.N.; Shalunov, A.V.; Nesterov, V.A. Improving the separation efficient of particles smaller than 2.5 micrometer by combining ultrasonic agglomeration and swirling flow techniques. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khmelev, V.N.; Nesterov, V.A.; Bochenkov, A.S.; Shalunov, A.V. The Limits of Fine Particle Ultrasonic Coagulation. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khmelev, V.N.; Shalunov, A.V.; Golykh, R.N. Increasing the Efficiency of Coagulation of Submicron Particles under Ultrasonic Action. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2020, 54, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzhov, V.N. Cleaning Industrial Gases with Filters; Chemistry: Moscow, Russia, 1967; p. 344. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kudryashova, O.; Korovina, N.; Akhmadeev, I.; Muravlev, E.; Titov, S.; Pavlenko, A. Deposition of Toxic Dust with External Fields. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2575–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kudryashova, O.; Stepkina, M.; Antonnikova, A. New Ways to Use Charged Particles. In Advances in Chemistry Research; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 61. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg, L.L. Physics and Engineering of Powerful Ultrasound. In Powerful Ultrasound Fields; Nauka Publisher: Moscow, Russia, 1968; Volume 2, p. 258. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Titov, S.; Stepkina, M.; Antonnikova, A.; Korovina, N.; Vorozhtsov, B.; Muravlev, E.; Kudryashova, O. Sedimentation of harmful dust by means of ultrasonic waves and additional disperse phase. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 11321–11328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| D, µm | ue/us | uw/us | uus/us |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 46.1 | 6.14 | 55.1 |
| 2 | 23.0 | 3.07 | 27.5 |
| 3 | 15.4 | 2.05 | 18.2 |
| 4 | 11.5 | 1.54 | 13.6 |
| 5 | 9.21 | 1.23 | 10.6 |
| 6 | 7.68 | 1.02 | 8.28 |
| 7 | 6.58 | 0.877 | 6.43 |
| 8 | 5.76 | 0.767 | 5.06 |
| 9 | 5.12 | 0.682 | 4.09 |
| 10 | 4.61 | 0.614 | 3.38 |
| 11 | 4.19 | 0.558 | 2.85 |
| 12 | 3.84 | 0.512 | 2.44 |
| 13 | 3.54 | 0.472 | 2.12 |
| 14 | 3.29 | 0.439 | 1.86 |
| 15 | 3.07 | 0.409 | 1.65 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kudryashova, O.B.; Pavlenko, A.A.; Titov, S.S. Symmetry in Aerosol Mechanics: Review. Symmetry 2022, 14, 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14020363
Kudryashova OB, Pavlenko AA, Titov SS. Symmetry in Aerosol Mechanics: Review. Symmetry. 2022; 14(2):363. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14020363
Chicago/Turabian StyleKudryashova, Olga B., Anatoly A. Pavlenko, and Sergey S. Titov. 2022. "Symmetry in Aerosol Mechanics: Review" Symmetry 14, no. 2: 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14020363
APA StyleKudryashova, O. B., Pavlenko, A. A., & Titov, S. S. (2022). Symmetry in Aerosol Mechanics: Review. Symmetry, 14(2), 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14020363








