Spectrum of Primordial Gravitational Waves in Modified Gravities: A Short Overview
Abstract
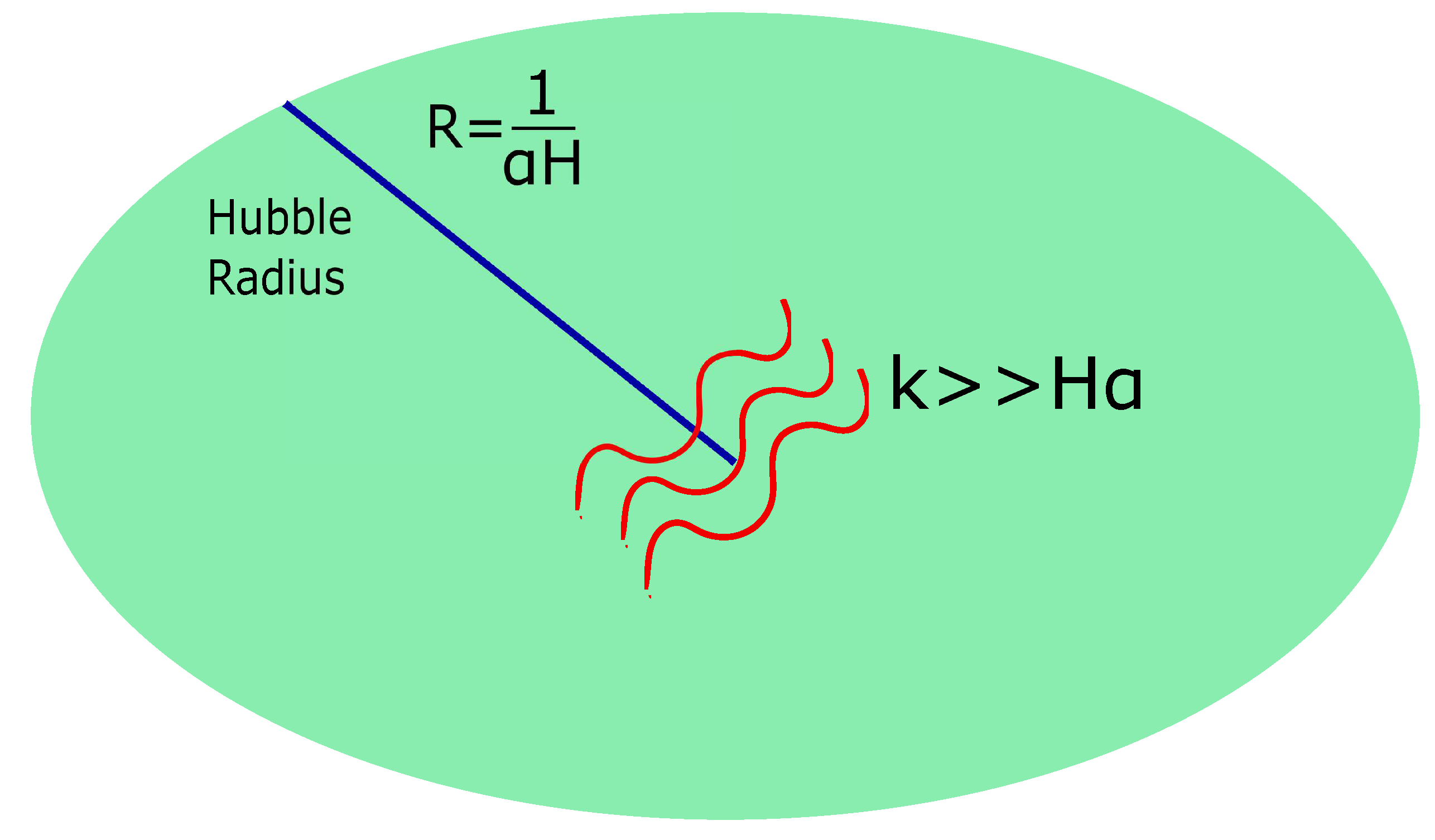
:1. Introduction
2. The Spectrum of Primordial Gravitational Waves in General Relativity and Modified Gravity Effects
The Modified Gravity Effect on the Energy Spectrum of the Primordial Gravitation Waves: A WKB Approach
3. Primordial Gravity Waves in Modified Gravity in its Various Forms
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Linde, A. Inflationary Cosmology. In Lecture Notes in Physics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; Volume 738, pp. 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- Gorbunov, D.S.; Rubakov, V.A. Introduction to the Theory of the Early Universe: Cosmological Perturbations and Inflationary Theory; World Scientific: Hackensack, NJ, USA, 2011; p. 489. [Google Scholar]
- Linde, A. Inflationary Cosmology after Planck; Oxford University Press: England, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lyth, D.H.; Riotto, A. Particle physics models of inflation and the cosmological density perturbation. Phys. Rep. 1999, 314, 1–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D.; Oikonomou, V.K. Modified Gravity Theories on a Nutshell: Inflation, Bounce and Late-time Evolution. Phys. Rep. 2017, 692, 1–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capozziello, S.; De Laurentis, M. Extended Theories of Gravity. Phys. Rep. 2011, 509, 167–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Introduction to modified gravity and gravitational alternative for dark energy. Int. J. Geom. Methods Mod. Phys. 2007, 4, 115–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Unified cosmic history in modified gravity: From F(R) theory to Lorentz non-invariant models. Phys. Rep. 2011, 505, 59–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De la Cruz-Dombriz, A.; Saez-Gomez, D. Black holes, cosmological solutions, future singularities, and their thermodynamical properties in modified gravity theories. Entropy 2012, 14, 1717–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmo, G.J.; Rubiera-Garcia, D. Some Recent Results on Ricci-Based Gravity Theories. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.04116. [Google Scholar]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Modified gravity with negative and positive powers of the curvature: Unification of the inflation and of the cosmic acceleration. Phys. Rev. D 2003, 68, 123512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Unifying inflation with ΛCDM epoch in modified f(R) gravity consistent with Solar System tests. Phys. Lett. B 2007, 657, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Modified f(R) gravity unifying Rm inflation with ΛCDM epoch. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 026007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cognola, G.; Elizalde, E.; Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D.; Sebastiani, L.; Zerbini, S. A Class of viable modified f(R) gravities describing inflation and the onset of accelerated expansion. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 046009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Modified f(R) gravity consistent with realistic cosmology: From matter dominated epoch to dark energy universe. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 086005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Appleby, A.S.; Battye, A.R. Do consistent F(R) models mimic General Relativity plus Λ? Phys. Lett. B 2007, 654, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elizalde, E.; Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D.; Sebastiani, L.; Zerbini, S. Non-singular exponential gravity: A simple theory for early- and late-time accelerated expansion. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 086006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odintsov, S.D.; Oikonomou, V.K. Geometric Inflation and Dark Energy with Axion F(R) Gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 044009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oikonomou, V.K. Unifying inflation with early and late dark energy epochs in axion F(R) gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 044036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, V.K. Rescaled Einstein-Hilbert Gravity from f(R) Gravity: Inflation, Dark Energy and the Swampland Criteria. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 124028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.; Bellovary, J.; Bender, P.L.; Berti, E.; Caldwell, R.; Camp, J.; Conklin, J.W.; Cornish, N.; Cutler, C.; De Rosa, R.; et al. The Laser Interferometer Space Antenna: Unveiling the Millihertz Gravitational Wave Sky. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.06482. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, T.L.; Caldwell, R. LISA for Cosmologists: Calculating the Signal-to-Noise Ratio for Stochastic and Deterministic Sources. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 104055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seto, N.; Kawamura, S.; Nakamura, T. Possibility of direct measurement of the acceleration of the universe using 0.1-Hz band laser interferometer gravitational wave antenna in space. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 221103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, S.; Ando, M.; Seto, N.; Sato, S.; Musha, M.; Kawano, I.; Yokoyama, J.; Tanaka, T.; Ioka, K.; Akutsu, T.; et al. Current status of space gravitational wave antenna DECIGO and B-DECIGO. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.13545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hild, S.; Abernathy, M.; Acernese, F.; Amaro-Seoane, P.; Andersson, N.; Arun, K.; Barone, F.; Barr, B.; Barsuglia, M.; Beker, M.; et al. Sensitivity Studies for Third-Generation Gravitational Wave Observatories. Class. Quant. Gravity 2011, 28, 094013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowder, J.; Cornish, J.N. Beyond LISA: Exploring future gravitational wave missions. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 72, 083005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, T.L.; Caldwell, R. Sensitivity to a Frequency-Dependent Circular Polarization in an Isotropic Stochastic Gravitational Wave Background. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 044036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weltman, A.; Bull, P.; Camera, S.; Kelley, K.; Padmanabhan, H.; Pritchard, J.; Raccanelli, A.; Riemer-Sørensen, S.; Shao, L.; Andrianomena, S.; et al. Fundamental physics with the Square Kilometre Array. Publ. Astron. Soc. Austral. 2020, 37, e002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arzoumanian, Z.; Baker, P.T.; Blumer, H.; Bécsy, B.; Brazier, A.; Brook, P.R.; Burke-Spolaor, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Chen, S.; Cordes, J.M.; et al. The NANOGrav 12.5 yr Data Set: Search for an Isotropic Stochastic Gravitational-wave Background. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 905, L34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pol, N.S.; Taylor, S.R.; Kelley, L.Z.; Vigel, S.J.; Simon, J.; Chen, S.; Arzoumanian, Z.; Baker, P.T.; Bécsy, B.; Brazier, A.; et al. Astrophysics Milestones For Pulsar Timing Array Gravitational Wave Detection. arXiv 2010, arXiv:2010.11950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamionkowski, M.; Kovetz, E.D. The Quest for B Modes from Inflationary Gravitational Waves. Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 54, 227–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denissenya, M.; Linder, E.V. Gravity’s Islands: Parametrizing Horndeski Stability. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2018, 2018, 010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, M.S.; White, M.J.; Lidsey, J.E. Tensor perturbations in inflationary models as a probe of cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 1993, 48, 4613–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boyle, A.L.; Steinhardt, P.J. Probing the early universe with inflationary gravitational waves. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 063504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, W.; Chen, Y.T. Relic gravitational waves in the accelerating Universe. Class. Quant. Gravity 2005, 22, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutz, B.F.; Ricci, F. ‘Gravitational Waves, Sources, and Detectors. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1005.4735. [Google Scholar]
- Sathyaprakash, S.B.; Schutz, F.B. Physics, Astrophysics and Cosmology with Gravitational Waves. Living Rev. Relativ. 2009, 12, 1–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caprini, C.; Figueroa, D.G. Cosmological Backgrounds of Gravitational Waves. Class. Quant. Gravity 2018, 35, 163001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arutyunov, G.; Heinze, M.; Medina-Rincon, D. Superintegrability of Geodesic Motion on the Sausage Model. J. Phys. A 2017, 50, 244002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuroyanagi, S.; Chiba, T.; Sugiyama, N. Precision calculations of the gravitational wave background spectrum from inflation. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 79, 103501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clarke, T.J.; Copel, E.J.; Moss, A. Constraints on primordial gravitational waves from the Cosmic Microwave Background. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2020, 2020, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroyanagi, S.; Takahashi, T.; Yokoyama, S. Blue-tilted Tensor Spectrum and Thermal History of the Universe. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2015, 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakayama, K.; Yokoyama, J. Gravitational Wave Background and Non-Gaussianity as a Probe of the Curvaton Scenario. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2010, 2010, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.L.; Kamionkowski, M.; Cooray, A. Direct detection of the inflationary gravitational wave background. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 73, 023504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giovannini, M. Thermal history of the plasma and high-frequency gravitons. Class. Quant. Gravity 2009, 26, 045004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.H. Detecting Relic Gravitational Waves by Pulsar Timing Arrays: Effects of Cosmic Phase Transitions and Relativistic Free-Streaming Gases. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 024031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.; You, X.P.; Zhu, Z.H. Constraints of relic gravitational waves by pulsar timing arrays: Forecasts for the FAST and SKA projects. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 124012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vagnozzi, S. Implications of the NANOGrav results for inflation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2021, 502, L11–L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Komatsu, E. Improved Calculation of the Primordial Gravitational Wave Spectrum in the Standard Model. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 73, 123515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamionkowski, M.; Kosowsky, A.; Turner, M.S. Gravitational radiation from first order phase transitions. Phys. Rev. D 1994, 49, 2837–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giarè, W.; Renzi, F. Propagating speed of primordial gravitational waves. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 083530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroyanagi, S.; Takahashi, T.; Yokoyama, S. Blue-tilted inflationary tensor spectrum and reheating in the light of NANOGrav results. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2021, 2021, 071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y. Relic gravitational waves and their detection. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 043503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishizawa, A. Generalized framework for testing gravity with gravitational-wave propagation. I. Formulation. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 104037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arai, S.; Nishizawa, A. Generalized framework for testing gravity with gravitational-wave propagation. II. Constraints on Horndeski theory. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 104038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellini, E.; Sawicki, I. Maximal freedom at minimum cost: Linear large-scale structure in general modifications of gravity. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2014, 2014, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, C.R.; Alves, S.E.M.; de Araujo, N.C.J. Primordial gravitational waves in Horndeski gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 084022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Agostino, R.; Nunes, R.C. Probing observational bounds on scalar-tensor theories from standard sirens. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 044041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitra, A.; Mifsud, J.; Mota, D.F.; Parkinson, D. Cosmology with the Einstein Telescope: No Slip Gravity Model and Redshift Specifications. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 502, 5563–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroyanagi, S.; Nakayama, K.; Saito, S. Prospects for determination of thermal history after inflation with future gravitational wave detectors. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 123513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campeti, P.; Komatsu, E.; Poletti, D.; Baccigalupi, C. Measuring the spectrum of primordial gravitational waves with CMB, PTA and Laser Interferometers. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2021, 2021, 012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, A.; Motohashi, H. Constraint on reheating after f(R) inflation from gravitational waves. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 89, 063541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W. Improved calculation of relic gravitational waves. Chin. Phys. 2007, 16, 2894–2902. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.; Qian, T.; Yu, Q.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, Y.R. Wave from Axion-like Particle Inflation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.04242. [Google Scholar]
- Nishizawa, A.; Yagi, K.; Taruya, A.; Tanaka, T. Cosmology with space-based gravitational-wave detectors—Dark energy and primordial gravitational waves. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 044047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chongchitnan, S.; Efstathiou, G. Prospects for direct detection of primordial gravitational waves. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 73, 083511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lasky, P.D.; Mingarelli, C.M.F.; Smith, T.L.; Giblin, J.T.; Reardon, D.J.; Caldwell, R.; Bailes, M.; Bhat, N.D.R.; Burke-Spolaor, S.; Coles, W.; et al. Gravitational-wave cosmology across 29 decades in frequency. Phys. Rev. X 2016, 6, 011035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guzzetti, M.C.; Bartolo, N.; Liguori, M.; Matarrese, S. Gravitational waves from inflation. Riv. Nuovo Cim. 2016, 39, 399–495. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Dayan, I.; Keating, B.; Leon, D.; Wolfson, I. Constraints on scalar and tensor spectra from Neff. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 2019, 007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakayama, K.; Saito, S.; Suwa, Y.; Yokoyama, J. Probing reheating temperature of the universe with gravitational wave background. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2008, 2008, 020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capozziello, S.; De Laurentis, M.; Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Evolution of gravitons in accelerating cosmologies: The case of extended gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 083524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capozziello, S.; De Laurentis, M.; Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. f(R) gravity constrained by PPN parameters and stochastic background of gravitational waves. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2009, 41, 2313–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capozziello, S.; Corda, C.; De Laurentis, F.M. Massive gravitational waves from f(R) theories of gravity: Potential detection with LISA. Phys. Lett. B 2008, 669, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, R.G.; Fu, C.; Yu, W.W. Parity violation in stochastic gravitational wave background from inflation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.04794. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, R.G.; Pi, S.; Sasaki, M. Gravitational Waves Induced by non-Gaussian Scalar Perturbations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 201101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Odintsov, S.D.; Oikonomou, V.K.; Fronimos, F.P. Quantitative predictions for f(R) gravity primordial gravitational waves. Phys. Dark Univ. 2022, 35, 100950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benetti, M.; Graef, L.L.; Vagnozzi, S. Primordial gravitational waves from NANOGrav: A broken power-law approach. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 105, 043520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Gao, S.; Gong, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, F. Primordial black holes and scalar induced secondary gravitational waves from Higgs inflation with non-canonical kinetic term. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.01362. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Lin, J.; Lu, Y. Double-peaked inflation model: Scalar induced gravitational waves and primordial-black-hole suppression from primordial non-Gaussianity. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 063515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odintsov, S.D.; Oikonomou, V.K. Pre-inflationary bounce effects on primordial gravitational waves of f(R) gravity. Phys. Lett. B 2022, 824, 136817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.R.; Kamionkowski, M. Cosmic microwave background fluctuations from gravitational waves: An analytic approach. Ann. Phys. 2005, 318, 2–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Xia, T.; Yuan, Y. Analytic approach to the CMB polarizations generated by relic gravitational waves. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 083006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baskaran, D.; Grishchuk, L.P.; Polnarev, A.G. Imprints of Relic Gravitational Waves in Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 083008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinberg, S. Damping of tensor modes in cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 69, 023503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flauger, R.; Weinberg, S. Tensor Microwave Background Fluctuations for Large Multipole Order. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 75, 123505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breitbach, M.; Kopp, J.; Madge, E.; Opferkuch, T.; Schwaller, P. Dark, Cold, and Noisy: Constraining Secluded Hidden Sectors with Gravitational Waves. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 2019, 007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, J.C.; Noh, H. Classical evolution and quantum generation in generalized gravity theories including string corrections and tachyon: Unified analyses. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 71, 063536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odintsov, S.D.; Oikonomou, V.K.; Fronimos, F.P. Rectifying Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet Inflation in View of GW170817. Nucl. Phys. B 2020, 958, 115135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odintsov, S.D.; Oikonomou, V.K. Swampland implications of GW170817-compatible Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet gravity. Phys. Lett. B 2020, 805, 135437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, V.K.; Fronimos, F.P. A Nearly Massless Graviton in Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet Inflation with Linear Coupling Implies Constant-roll for the Scalar Field. Europhys. Lett. 2020, 131, 30001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, V.K. A refined Einstein–Gauss–Bonnet inflationary theoretical framework. Class. Quant. Gravity 2021, 38, 195025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Modified Gravity Type | |
|---|---|
| Pure | |
| C-S | |
| EGB | |
| H-EGB |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Odintsov, S.D.; Oikonomou, V.K.; Myrzakulov, R. Spectrum of Primordial Gravitational Waves in Modified Gravities: A Short Overview. Symmetry 2022, 14, 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14040729
Odintsov SD, Oikonomou VK, Myrzakulov R. Spectrum of Primordial Gravitational Waves in Modified Gravities: A Short Overview. Symmetry. 2022; 14(4):729. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14040729
Chicago/Turabian StyleOdintsov, Sergei D., Vasilis K. Oikonomou, and Ratbay Myrzakulov. 2022. "Spectrum of Primordial Gravitational Waves in Modified Gravities: A Short Overview" Symmetry 14, no. 4: 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14040729
APA StyleOdintsov, S. D., Oikonomou, V. K., & Myrzakulov, R. (2022). Spectrum of Primordial Gravitational Waves in Modified Gravities: A Short Overview. Symmetry, 14(4), 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14040729








