A New Meshless Method for Solving 3D Inverse Conductivity Issues of Highly Nonlinear Elliptic Equations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Problem Statement and the Homogenization Functions Method
3. A Single-Parameter Homogenization Function
4. Numerical Algorithm for Inverse Conductivity Issues
5. Numerical Experiments
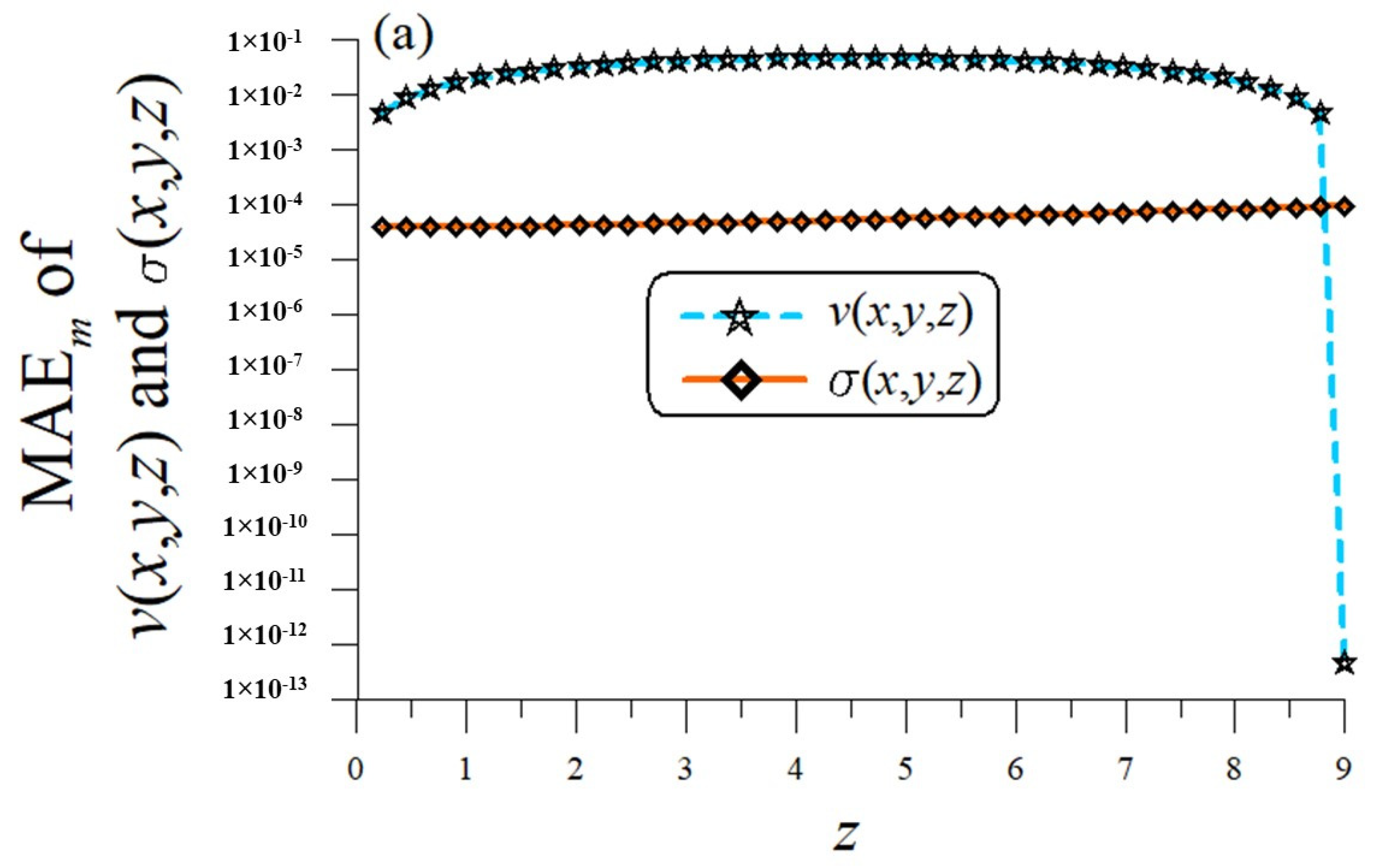
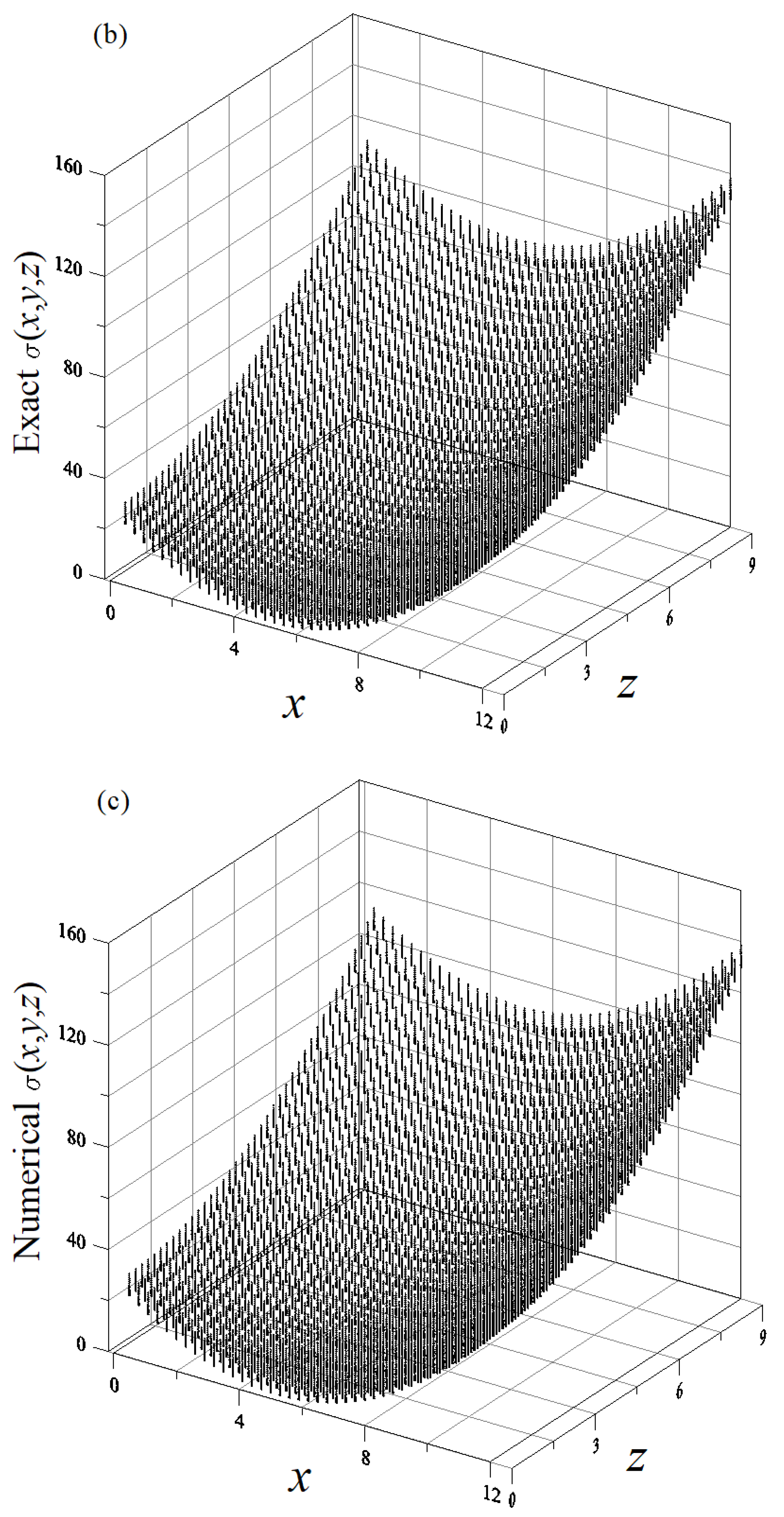
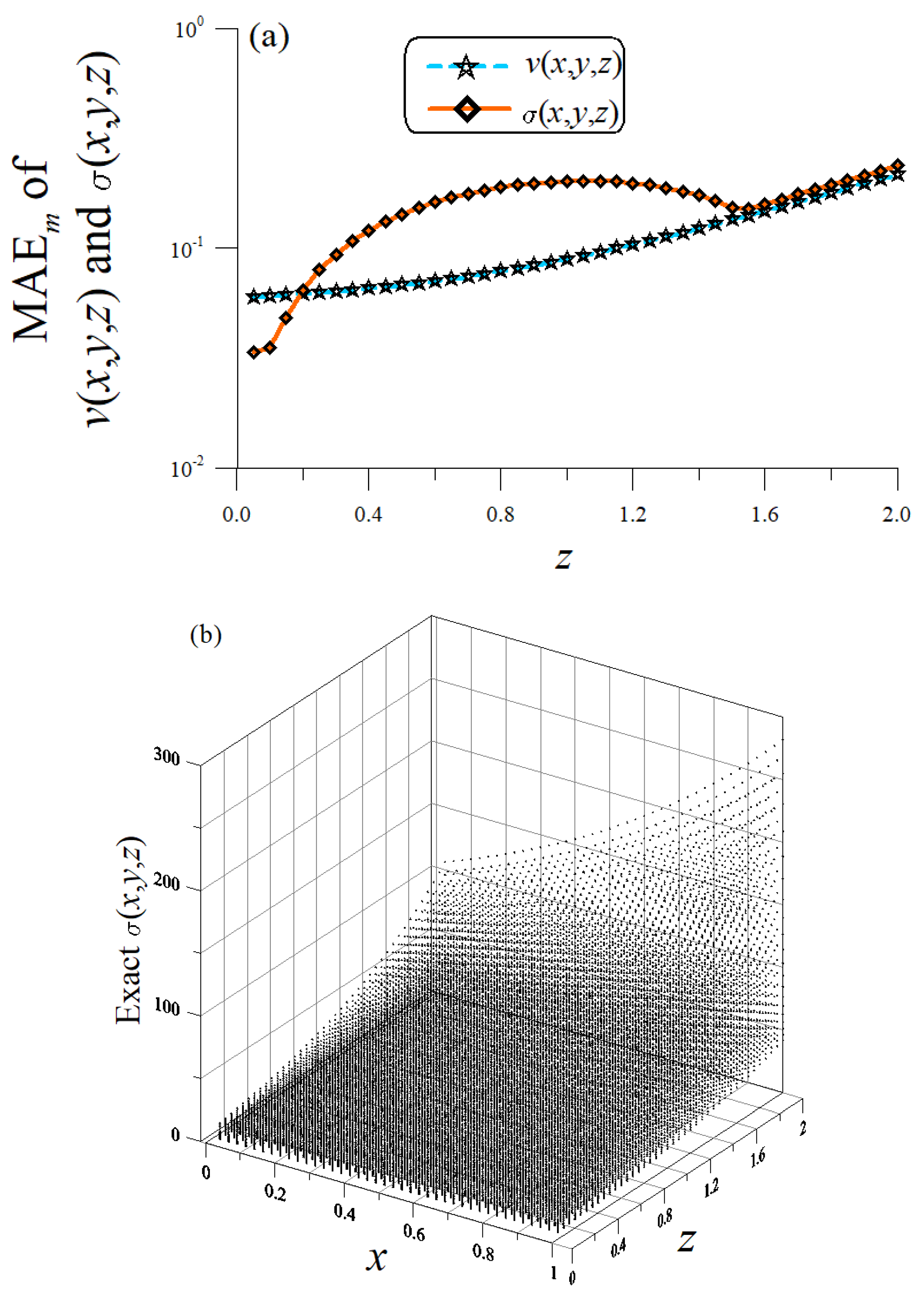
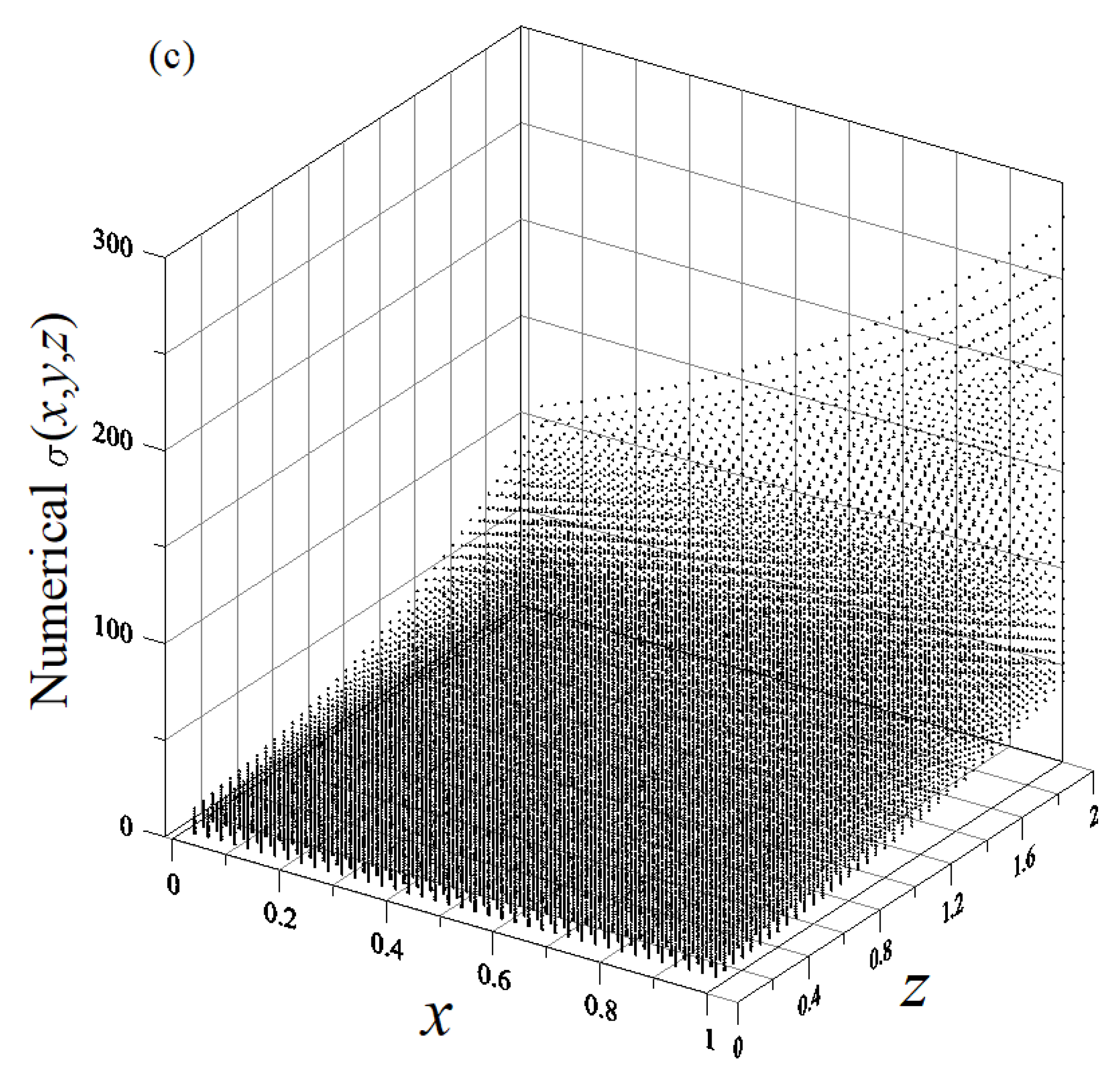
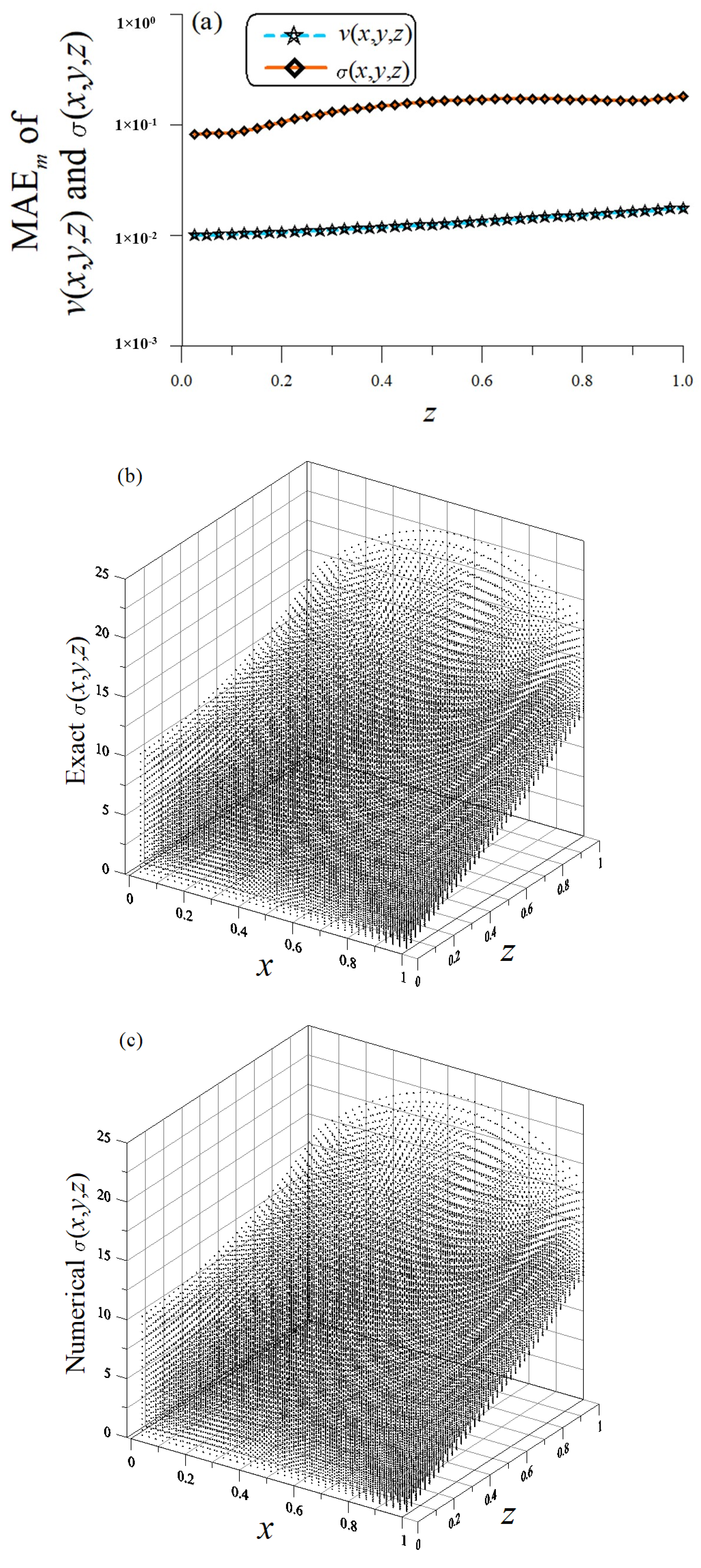
5.1. Example 1
5.2. Example 2
5.3. Example 3
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calderón, A.P. On an Inverse Boundary Value Problem. In Seminar on Numerical Analysis and Its Application to Continuum Physics; Socidade Brasileira de Mathematica: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1980; pp. 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Borcea, L. Electrical impedance tomography. Inverse Probl. 2002, 18, R99–R136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, A.; Guardo, R. A neural network image reconstruction technique for electrical impedance tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 1994, 13, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borcea, L.; Gray, G.A.; Zhang, Y. Variationally constrained numerical solution of electrical impedance tomography. Inverse Probl. 2003, 19, 1159–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brown, R.M.; Uhlmann, G.A. Uniqueness in the inverse conductivity problem for non-smooth conductivities in two dimensions. Commun. Partial. Differ. Equ. 1997, 22, 1009–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francini, E. Recoverning a complex coefficient in a planar domain from the Dirichlet-to-Neumann map. Inverse Probl. 2000, 16, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, I. A variational algorithm for electrical impedance tomography. Inverse Probl. 1998, 14, 1513–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, R.V.; McKenney, A. Numerical implementation of a variational method for electrical impedance tomography. Inverse Probl. 1990, 6, 389–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, S.; Adam, D.; Bresler, Y. Electromagnetic impedance tomography (EMIT): A new method for impedance imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2002, 21, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeson, S.; Killingback, A.L.T.; Blott, B.H. The dependence of EIT images on the assumed initial conductivity distribution: A study of pelvic imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 1995, 40, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, T.; Kagawa, Y. Electrical impedance computed tomography based on a finite element model. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1985, 32, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachman, A.I. Reconstructions from boundary measurements. Ann. Math. 1988, 128, 531–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachman, A.I. Global uniqueness for a two-dimensional inverse boundary problem. Ann. Math. 1996, 143, 71–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siltanen, S.; Mueller, J.; Isaacson, D. An implementation of the reconstruction algorithm of A Nachman for the 2D inverse conductivity problem. Inverse Probl. 2000, 16, 681–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasiak, M.; Sikora, J.; Filipowicz, S.F.; Nita, K. Principal component analysis and artificial neural network approach to electrical impedance tomography problems approximated by multi-region boundary element method. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2007, 31, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvester, J. A convergent layer stripping algorithm for radially symmetric impedance tomography problem. Commun. Partial. Differ. Equ. 1992, 17, 1955–1994. [Google Scholar]
- Wexler, A.; Fry, B.; Neuman, M.R. Impedance-computed tomography algorithm and system. Appl. Opt. 1985, 24, 3985–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorkey, T.J.; Webster, J.G.; Tompkins, W.J. Comparing reconstruction algorithms for electrical impedance tomography. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1987, 34, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlochiver, S.; Rosenfeld, M.; Abboud, S. Induced-current electrical impedance tomography: A 2-D theoretical simulation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2003, 22, 1550–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadehkoochak, M.; Hames, T.K.; Blott, B.H.; George, R.F. A transputer implemented algorithm for electrical impedance tomography. Clin. Phys. Physiol. Meas. 1990, 11, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, A.P. On an inverse boundary value problem. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2006, 25, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-S. Solving the inverse problems of Laplace equation to determine the Robin coefficient/cracks’ position inside a disk. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2009, 40, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.-S.; Atluri, S.N. An iterative and adaptive Lie-group method for solving the Calderón inverse problem. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2010, 64, 299–326. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.-S.; Liu, D. A homogenization boundary function method for determining inaccessible boundary of a rigid inclusion for the Poisson equation. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2018, 86, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-S.; Wang, F. A meshless method for solving the nonlinear inverse Cauchy problem of elliptic type equation in a doubly-connected domain. Comput. Math. Appl. 2018, 76, 1837–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, P.; Ferreira, D.D.S.; Ruiz, A. Stability estimates for the Calderón problem with partial data. J. Diff. Eq. 2016, 260, 2457–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.D.S.; Kenig, C.E.; Salo, M.; Uhlmann, G. Limiting Carleman weights and anisotropic inverse problems. Invent. Math. 2009, 178, 119–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piiroinen, P.; Simon, M. Probabilistic interpretation of the Calderón problem. Inv. Prob. Imag. 2017, 11, 553–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandrini, G.; de Hoop, M.V.; Gaburro, R.; Sincich, E. Lipschitz stability for the electrostatic inverse boundary value problem with piecewise linear conductivities. J. Math. Pures Appl. 2017, 107, 638–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, C.; Uhlmann, G. The Calderón problem for quasilinear elliptic equations. In Annales de l’Institut Henri Poincaré C, Analyse non linéaire; Elsevier Masson: Paris, France, 2020; Volume 37, pp. 1143–1166. [Google Scholar]
- De Moura, B.F.; Martins, M.F.; Palma, F.H.S.; da Silva, W.B.; Cabello, J.A.; Ramos, R. Nonstationary bubble shape determination in electrical impedance tomography combining Gauss–Newton optimization with particle filter. Measurement 2021, 186, 110216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, G.C.; Sato, A.K.; Ueda, E.K.; Takimoto, R.Y.; Martins, T.C.; Tsuzuki, M.S.G. Electrical impedance tomography image reconstruction using convolutional neural network with periodic padding. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2021, 54, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.; Kralovec, C.; Schagerl, M. Evaluation of spatial strain distribution by elastoresistive thin-film sensors using 2D Electrical Impedance Tomography. Mater. Today Proc. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-S.; Chang, C.-W. Solving the inverse conductivity problems of nonlinear elliptic equations by the superposition of homogenization functions method. Appl. Math. Lett. 2019, 94, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, C.-W. A New Meshless Method for Solving 3D Inverse Conductivity Issues of Highly Nonlinear Elliptic Equations. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14051044
Chang C-W. A New Meshless Method for Solving 3D Inverse Conductivity Issues of Highly Nonlinear Elliptic Equations. Symmetry. 2022; 14(5):1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14051044
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Chih-Wen. 2022. "A New Meshless Method for Solving 3D Inverse Conductivity Issues of Highly Nonlinear Elliptic Equations" Symmetry 14, no. 5: 1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14051044
APA StyleChang, C.-W. (2022). A New Meshless Method for Solving 3D Inverse Conductivity Issues of Highly Nonlinear Elliptic Equations. Symmetry, 14(5), 1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14051044





