Traversable Wormhole in f(Q) Gravity Using Conformal Symmetry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Basic Field Equations in f(Q) Gravity
- where is a red-shift function.
- , where is a shape function.
- The wormhole throat joins two asymptotic regions and is placed at the radial coordinate , where .
- The flaring-out requirement,, which should be valid at or near the throat, must be satisfied by the shape function . This reduces to near the wormhole’s throat.
- The shape function should meet the condition for the radial coordinates in order to maintain the proper signature of the metric.
- The metric functions must obey the requirements and tend to zero as r approaches to ∞ in order to have asymptotically flat geometries. For non-asymptotically flat wormholes, these criteria can obviously be relaxed.
3. Linear Equation of State and Wormhole
4. Traceless Fluid and Wormhole
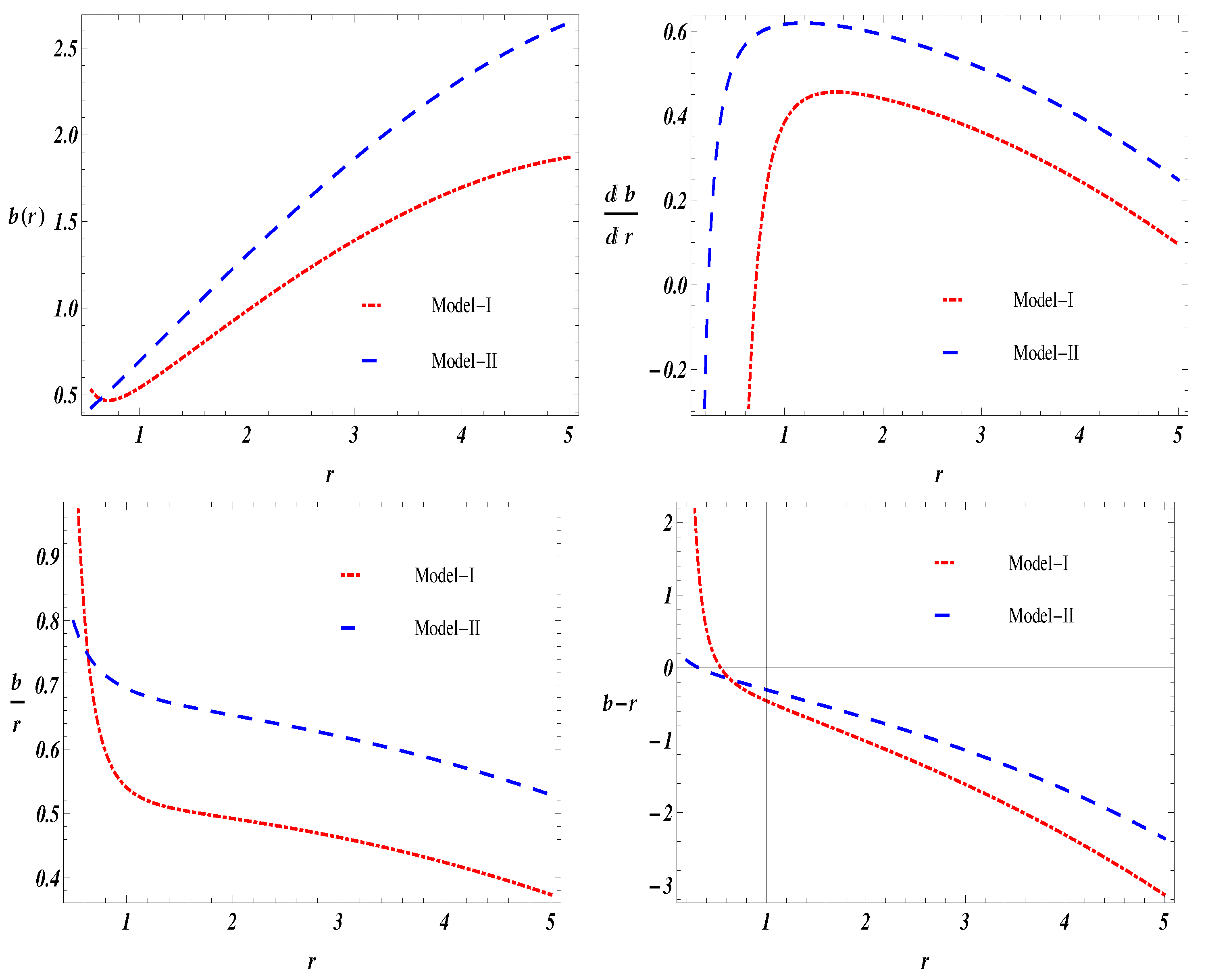
- Both the calculated shape functions are seen as positive with increasing behavior, this kind of behavior can be confirmed from the left penal of the first row of Figure 1. The positive behavior of both the shape function confirms physically compatibility of conformal symmetry with the linear equation of state and traceless fluid matter in the background of gravity.
- Flaring out condition, i.e., derivative of the obtained shape functions with respect to radial coordinate is seen less than one. The graphical behavior of can be seen from the right part of the first row of Figure 1.
- It is noted from the left part of the second row of Figure 1 that the flatness condition is satisfied for both investigated shape functions for model-I and model-II. The physical behavior for flatness condition, i.e., as is required for the wormhole existence.
- It is verified that the difference of calculated shape functions for both the models (I-II) with radial coordinate r, i.e., cut the x-axis and provide us the wormhole throat location. It is realized and for model-I and model-II respectively.
- It can be checked from Figure 2 that energy density remains positive for the negative values of parameter and it remains negative for the positive values of parameter .
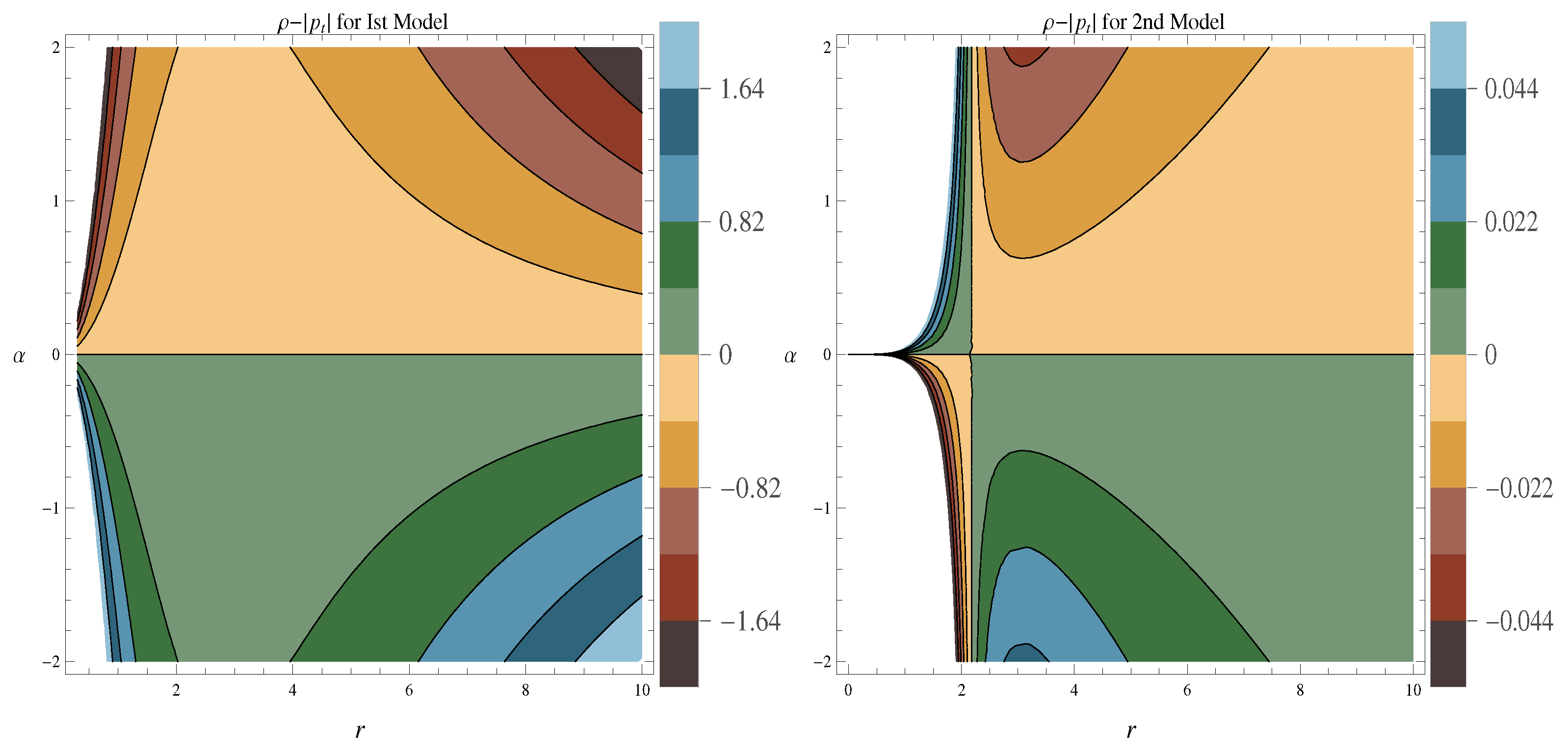
- The graphical behavior of NEC, i.e., and is provided in Figure 3 and Figure 4 respectively. It is noticed from both figures that NEC is violated for model-I and model-II against the different ranges of parameter . The negative values of and confirm the presence of exotic matter, which is necessarily required for the existence of a viable wormhole.
- Strong energy condition, i.e., with graphical development is provide in Figure 7. It is interesting to mention that, is also violated in the current analysis against the different ranges of parameter under the effect of conformal symmetry within the linear equation of state and traceless fluid.
5. Final Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flamm, L. Beiträge zur Einsteinschen Gravitationstheorie. Phys. Z. 1916, 17, 448. [Google Scholar]
- Einstein, A.; Rosen, N. The particle problem in the general theory of relativity. Phys. Rev. 1935, 48, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.S.; Thorne, K.S. Wormholes in spacetime and their use for interstellar travel: A tool for teaching general relativity. Am. J. Phys. 1988, 56, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visser, M. Lorentzian Wormholes: From Einstein to Hawking; American Institute of Physics: Woodbury, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.; Jafferis, D.L.; Wall, A.C. Traversable wormholes via a double trace deformation. J. High Energy Phys. 2017, 2017, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maldacena, J.; Qi, X.L. Eternal traversable wormhole. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.00491. [Google Scholar]
- Caceres, E.; Kundu, A.; Patra, A.K.; Shashi, S. A Killing vector treatment of multiboundary wormholes. J. High Energy Phys. 2020, 2020, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armendariz-Picon, C. On a class of stable, traversable Lorentzian wormholes in classical general relativity. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 65, 104010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolis, A.; Rattazzi, R.; Trincherini, E. Energy’s and amplitudes’ positivity. J. High Energy Phys. 2010, 2010, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visser, M. Traversable wormholes from surgically modified Schwarzschild spacetimes. Nucl. Phys. B 1989, 328, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuhfittig, P.K. A wormhole with a special shape function. Am. J. Phys. 1999, 67, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehmer, C.G.; Harko, T.; Lobo, F.S. Wormhole geometries in modified teleparallel gravity and the energy conditions. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 044033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lobo, F.S.; Oliveira, M.A. Wormhole geometries in f(R) modified theories of gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 80, 104012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capozziello, S.; Pincak, R.; Saridakis, E.N. Constructing superconductors by graphene Chern–Simons wormholes. Ann. Phys. 2018, 390, 303–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; Pinčák, R.; Bartoš, E. Chern-Simons current of left and right chiral superspace in graphene wormhole. Symmetry 2020, 12, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; Francaviglia, M. Extended theories of gravity and their cosmological and astrophysical applications. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2008, 40, 357–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capozziello, S.; Nojiri, S.i.; Odintsov, S.; Troisi, A. Cosmological viability of f(R)-gravity as an ideal fluid and its compatibility with a matter dominated phase. Phys. Lett. B 2006, 639, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capozziello, S.; Cardone, V.F.; Troisi, A. Reconciling dark energy models with f(R) theories. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 71, 043503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; Stabile, A.; Troisi, A. Spherically symmetric solutions in f(R) gravity via the Noether symmetry approach. Class. Quantum Gravity 2007, 24, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capozziello, S.; De Laurentis, M.; Odintsov, S.; Stabile, A. Hydrostatic equilibrium and stellar structure in f(R) gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 064004. [Google Scholar]
- Capozziello, S.; Luongo, O.; Mauro, L. Traversable wormholes with vanishing sound speed in f(R) gravity. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2021, 136, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Capozziello, S.; Godani, N. Non-local gravity wormholes. Phys. Lett. B 2022, 835, 137572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, J.B.; Heisenberg, L.; Koivisto, T. Coincident general relativity. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 044048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mandal, S.; Sahoo, P.; Santos, J.R. Energy conditions in f(Q) gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 024057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frusciante, N. Signatures of f(Q) gravity in cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 044021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D. Covariant formulation of f(Q) theory. Eur. Phys. J. C 2022, 82, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soudi, I.; Farrugia, G.; Said, J.L.; Gakis, V.; Saridakis, E.N. Polarization of gravitational waves in symmetric teleparallel theories of gravity and their modifications. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 044008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lazkoz, R.; Lobo, F.S.; Ortiz-Baños, M.; Salzano, V. Observational constraints of f(Q) gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 104027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayuso, I.; Lazkoz, R.; Salzano, V. Observational constraints on cosmological solutions of f(Q) theories. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 063505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, B.J.; Barreiro, T.; Koivisto, T.; Nunes, N.J. Testing F(Q) gravity with redshift space distortions. Phys. Dark Universe 2020, 30, 100616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulos, F.K.; Basilakos, S.; Saridakis, E.N. First evidence that non-metricity f(Q) gravity could challenge ΛCDM. Phys. Lett. B 2021, 822, 136634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harko, T.; Koivisto, T.S.; Lobo, F.S.; Olmo, G.J.; Rubiera-Garcia, D. Coupling matter in modified Q gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 084043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khyllep, W.; Paliathanasis, A.; Dutta, J. Cosmological solutions and growth index of matter perturbations in f(Q) gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 103521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, R.; De, A.; Mandal, S.; Sahoo, P. Accelerating expansion of the universe in modified symmetric teleparallel gravity. Phys. Dark Universe 2022, 36, 101053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esculpi, M.; Aloma, E. Conformal anisotropic relativistic charged fluid spheres with a linear equation of state. Eur. Phys. J. C 2010, 67, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, R.; Sahoo, P.K. Statefinder Analysis of Symmetric Teleparallel Cosmology. Ann. Der Phys. 2022, 534, 2200076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambrosio, F.; Fell, S.D.; Heisenberg, L.; Kuhn, S. Black holes in f(Q) gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 105, 024042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.H.; Zhai, X.H. Spherically symmetric configuration in f(Q) gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 124001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, H.; Katsuragawa, T. Static and spherically symmetric solutions in f(Q) gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 105, 024060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, G.; Hassan, Z.; Moraes, P.; Sahoo, P. Wormhole solutions in symmetric teleparallel gravity. Phys. Lett. B 2021, 821, 136612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzá, M.; Sebastiani, L. A class of static spherically symmetric solutions in f(Q)-gravity. Eur. Phys. J. C 2023, 83, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, G.; Hassan, Z.; Sahoo, P. Traversable wormhole inspired by non-commutative geometries in f(Q) gravity with conformal symmetry. Ann. Phys. 2022, 437, 168751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokoliuk, O.; Hassan, Z.; Sahoo, P.K.; Baransky, A. Traversable wormholes with charge and non-commutative geometry in the f(Q) gravity. Ann. Phys. 2022, 443, 168968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Mustafa, G.; Hassan, Z.; Sahoo, P. A study of anisotropic spheres in f(Q) gravity with quintessence field. Phys. Dark Universe 2022, 35, 100934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhar, P.; Rahaman, F.; Ray, S.; Chatterjee, V. Possibility of higher-dimensional anisotropic compact star. Eur. Phys. J. C 2015, 75, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, A.; Rahaman, F.; Guha, B.; Ray, S. Relativistic compact stars in f(T) gravity admitting conformal motion. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2015, 358, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, G.; Abbas, G.; Xia, T. Wormhole solutions in F (T, TG) gravity under Gaussian and Lorentzian non-commutative distributions with conformal motions. Chin. J. Phys. 2019, 60, 362–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, G.; Waheed, S.; Zubair, M.; Xia, T.C. Non-commutative wormholes exhibiting conformal motion in Rastall gravity. Chin. J. Phys. 2020, 65, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, G.; Waheed, S.; Zubair, M.; Xia, T. Gaussian distributed wormholes exhibiting conformal motion in f(T) gravity. Int. J. Geom. Methods Mod. Phys. 2019, 16, 1950143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, G.; Maurya, S.; Hussain, I. Relativistic Wormholes in Extended Teleparallel Gravity with Minimal Matter Coupling. Fortschritte der Physik 2023, 2200119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, J.; Heisenberg, L.; Koivisto, T. The Geometrical Trinity of Gravity. Universe 2019, 5, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saiedi, H.; Nasr Esfahani, B. Time-dependent wormhole solutions of f(R) theory of gravity and energy conditions. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2011, 26, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharif, M.; Rani, S. f(T) gravity and static wormhole solutions. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2014, 29, 1450137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


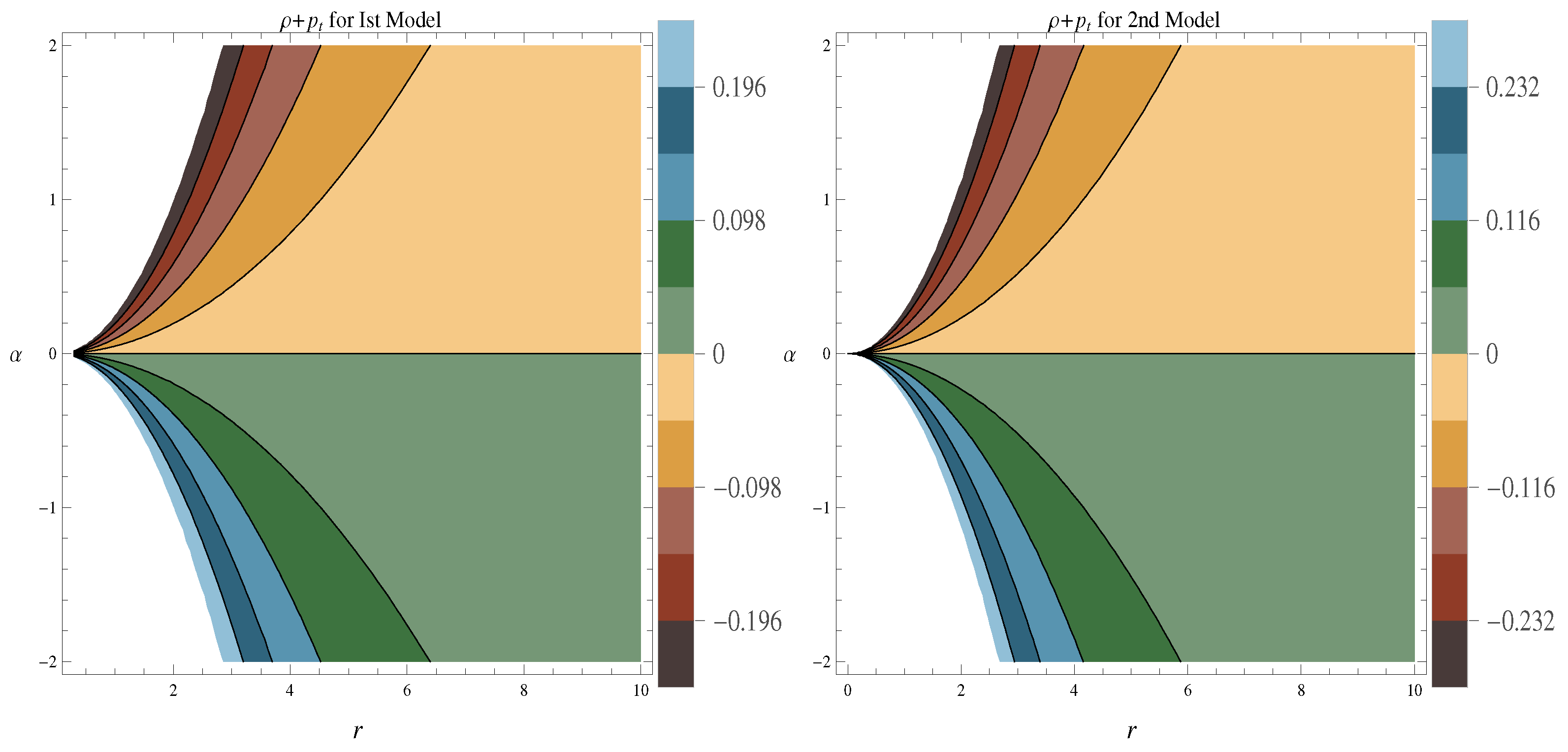
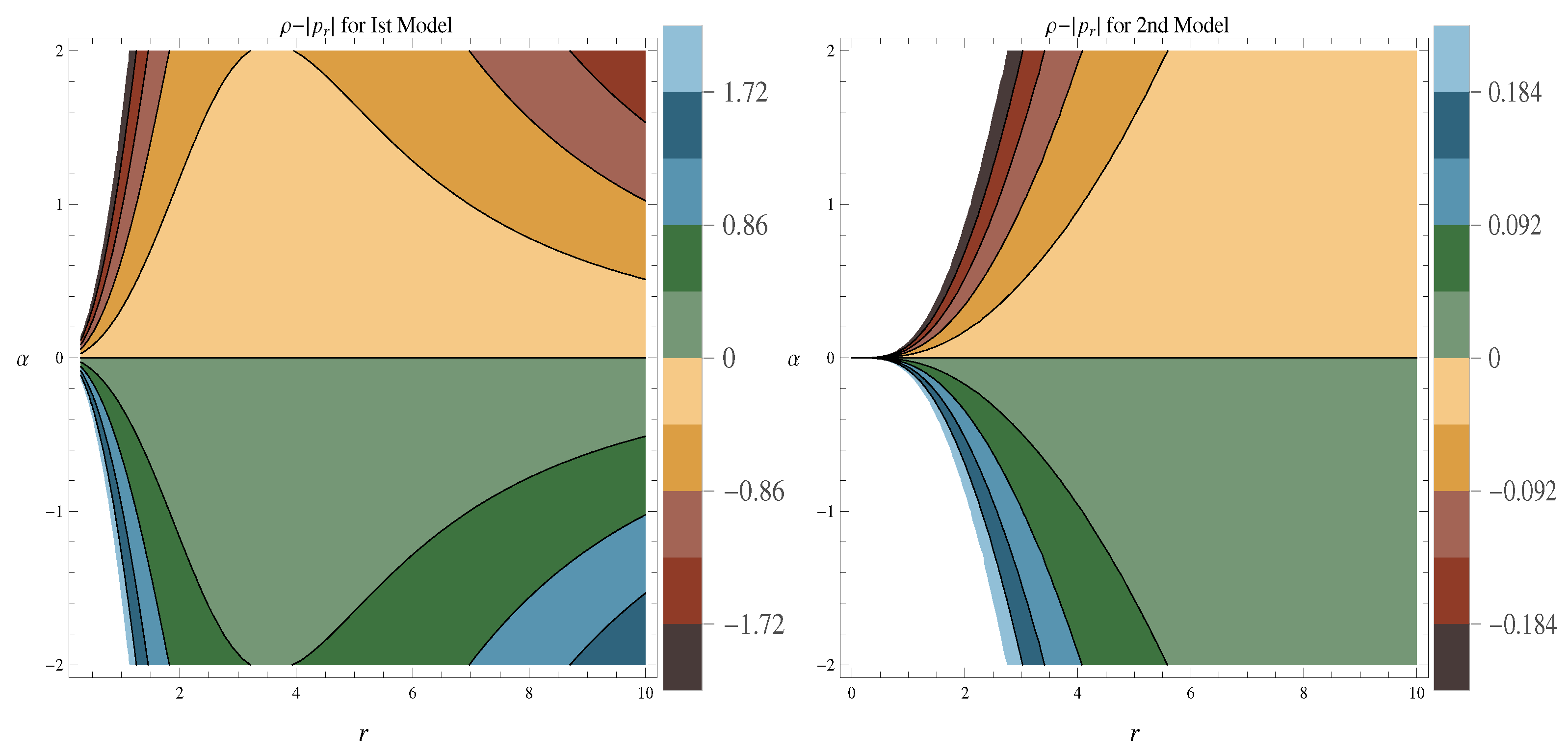

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jan, M.; Ashraf, A.; Basit, A.; Caliskan, A.; Güdekli, E. Traversable Wormhole in f(Q) Gravity Using Conformal Symmetry. Symmetry 2023, 15, 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15040859
Jan M, Ashraf A, Basit A, Caliskan A, Güdekli E. Traversable Wormhole in f(Q) Gravity Using Conformal Symmetry. Symmetry. 2023; 15(4):859. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15040859
Chicago/Turabian StyleJan, Munsif, Asifa Ashraf, Abdul Basit, Aylin Caliskan, and Ertan Güdekli. 2023. "Traversable Wormhole in f(Q) Gravity Using Conformal Symmetry" Symmetry 15, no. 4: 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15040859
APA StyleJan, M., Ashraf, A., Basit, A., Caliskan, A., & Güdekli, E. (2023). Traversable Wormhole in f(Q) Gravity Using Conformal Symmetry. Symmetry, 15(4), 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15040859





