SK-PSO: A Particle Swarm Optimization Framework with SOM and K-Means for Inverse Kinematics of Manipulators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Presentation of the SK-PSO
2.1. Standard Particle Swarm Optimization
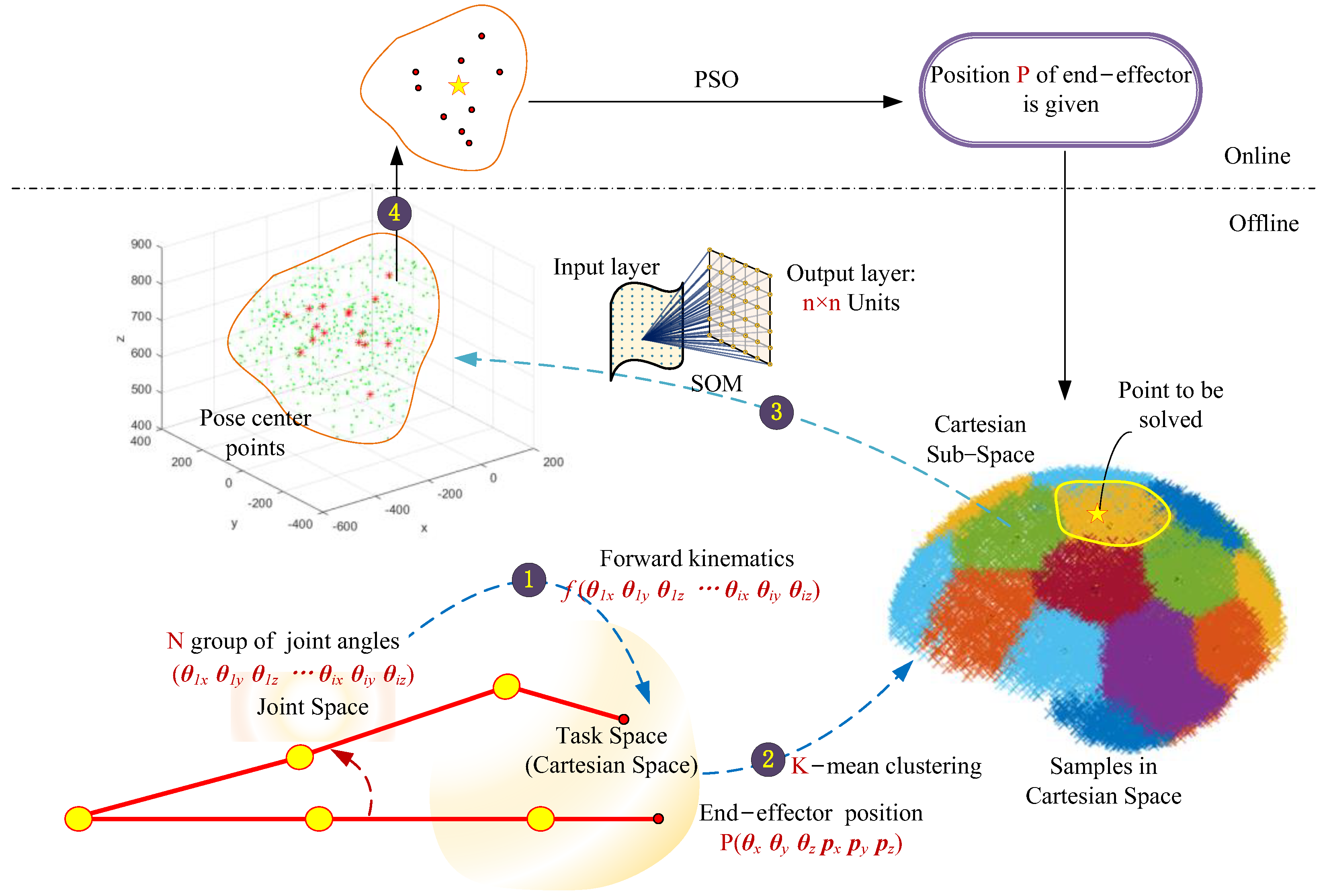
2.2. SK-PSO
3. Kinematic Analysis of Manipulator
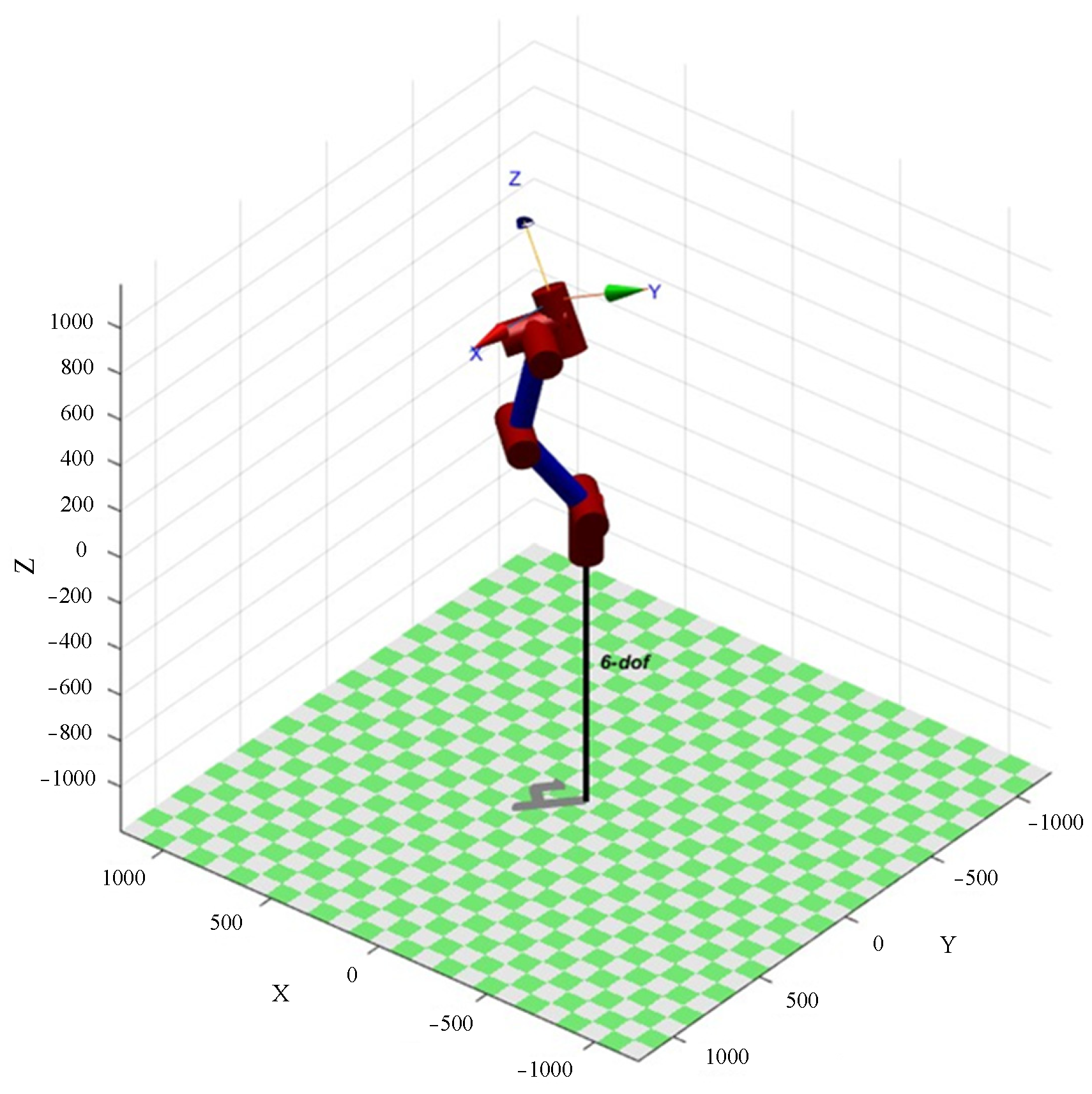
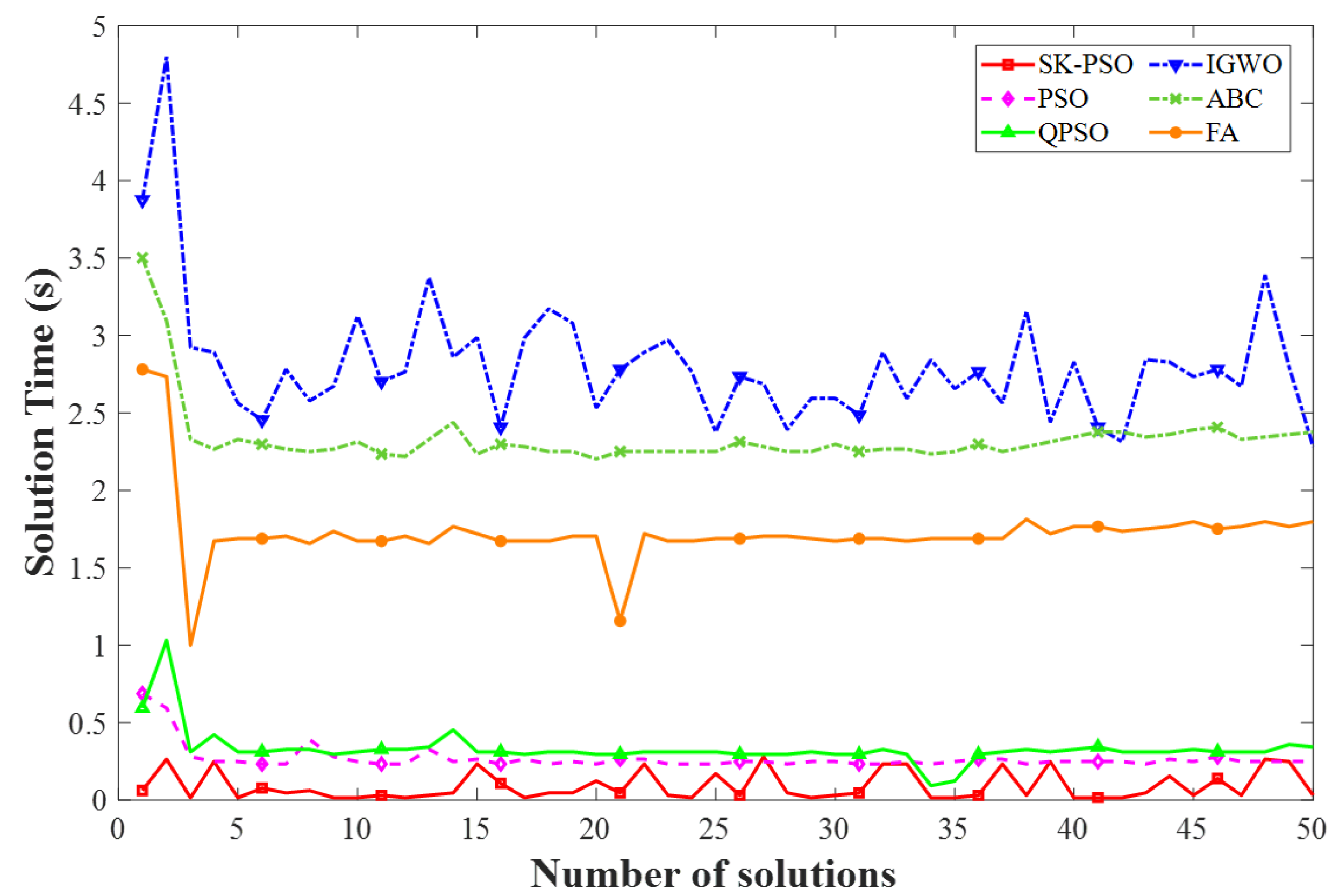
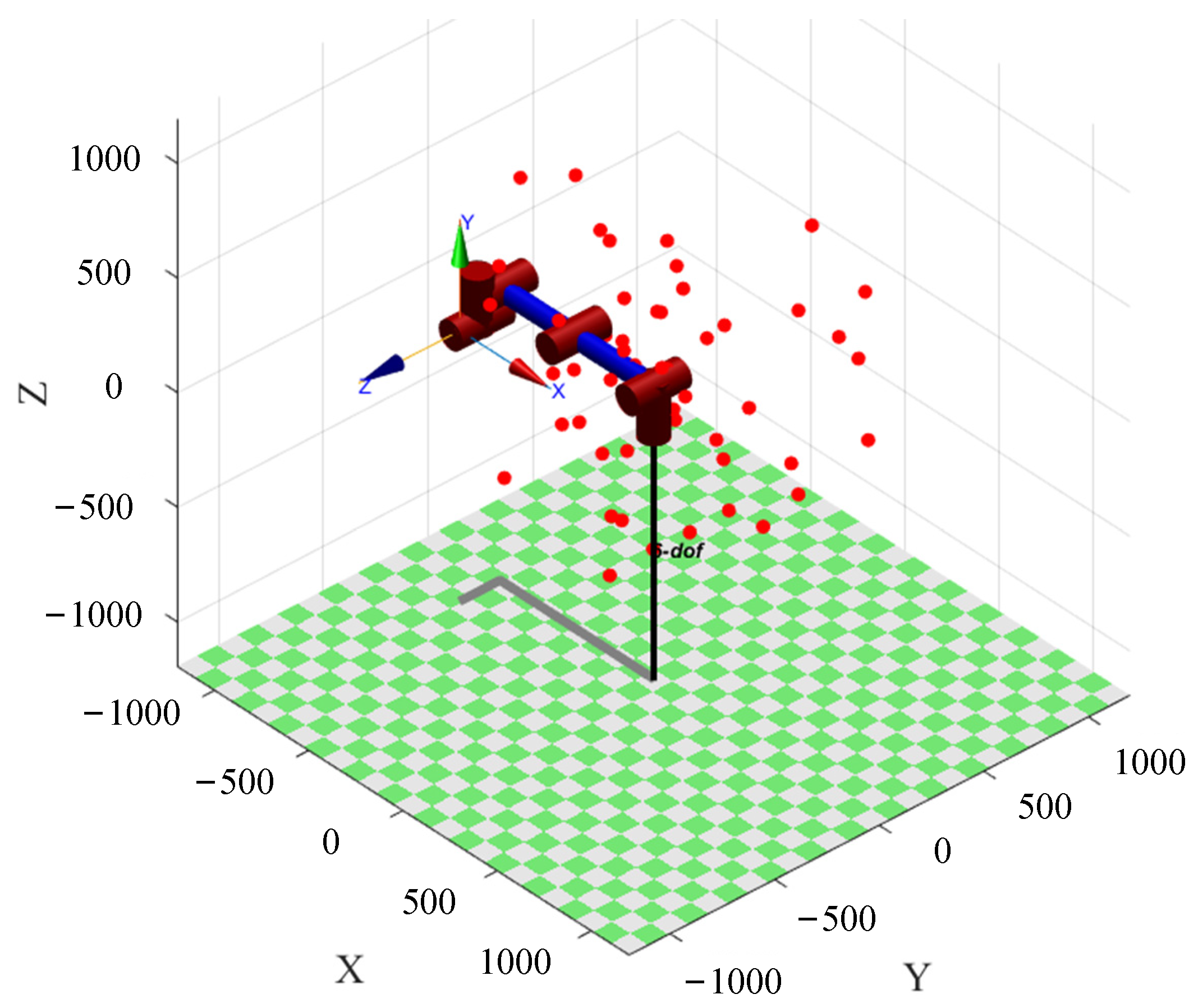
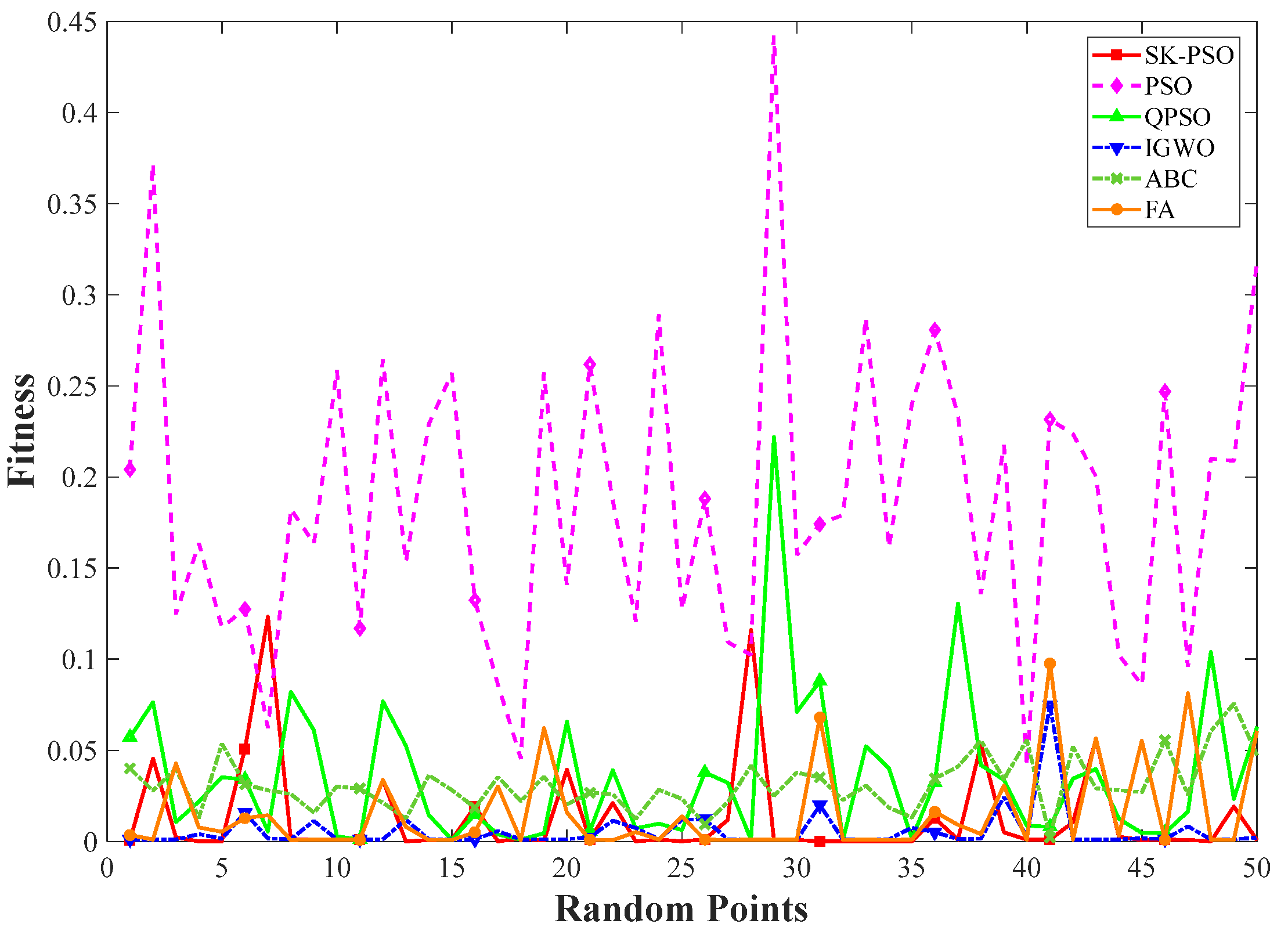
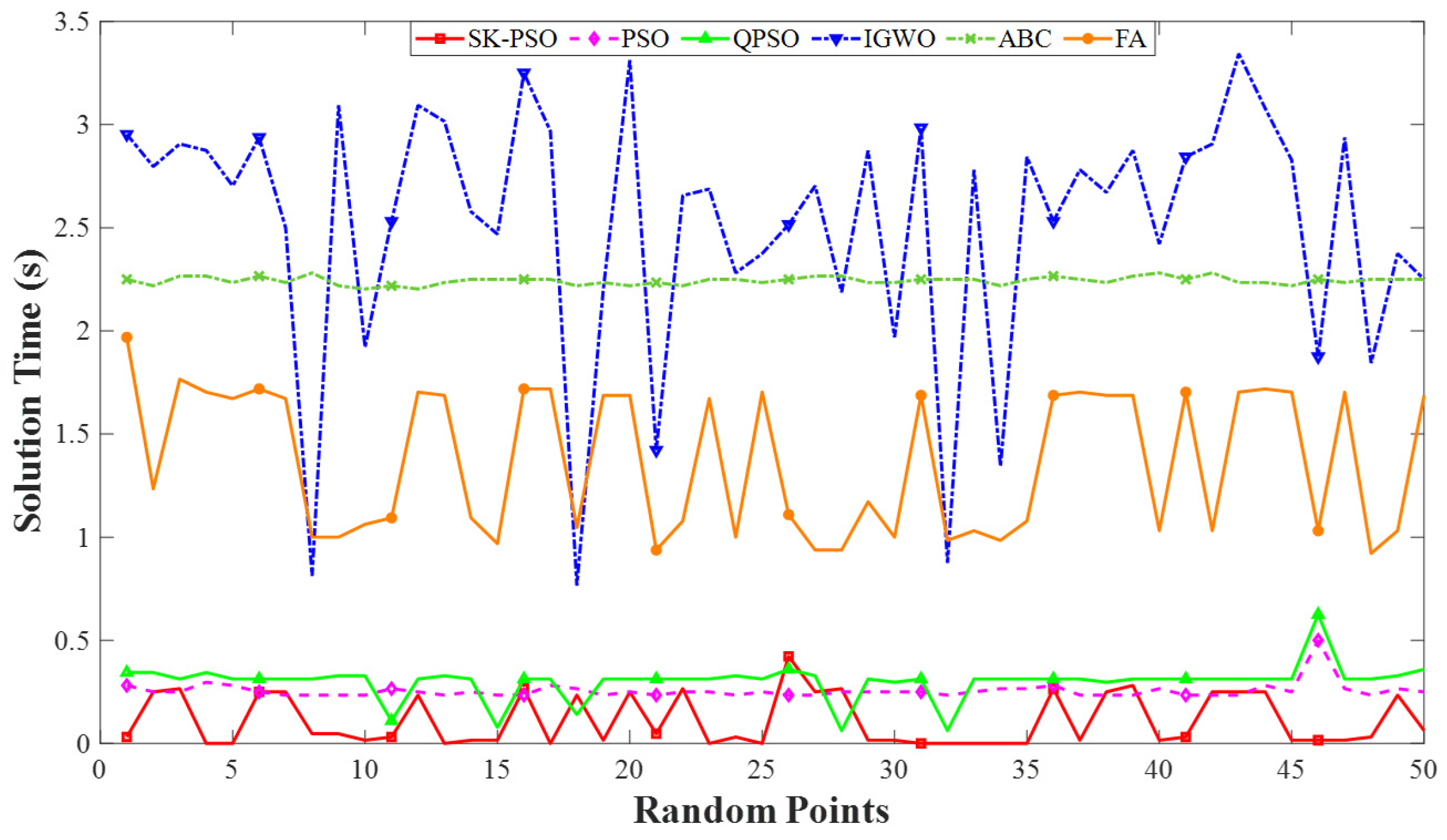
4. Simulation Analysis
4.1. Scenario 1
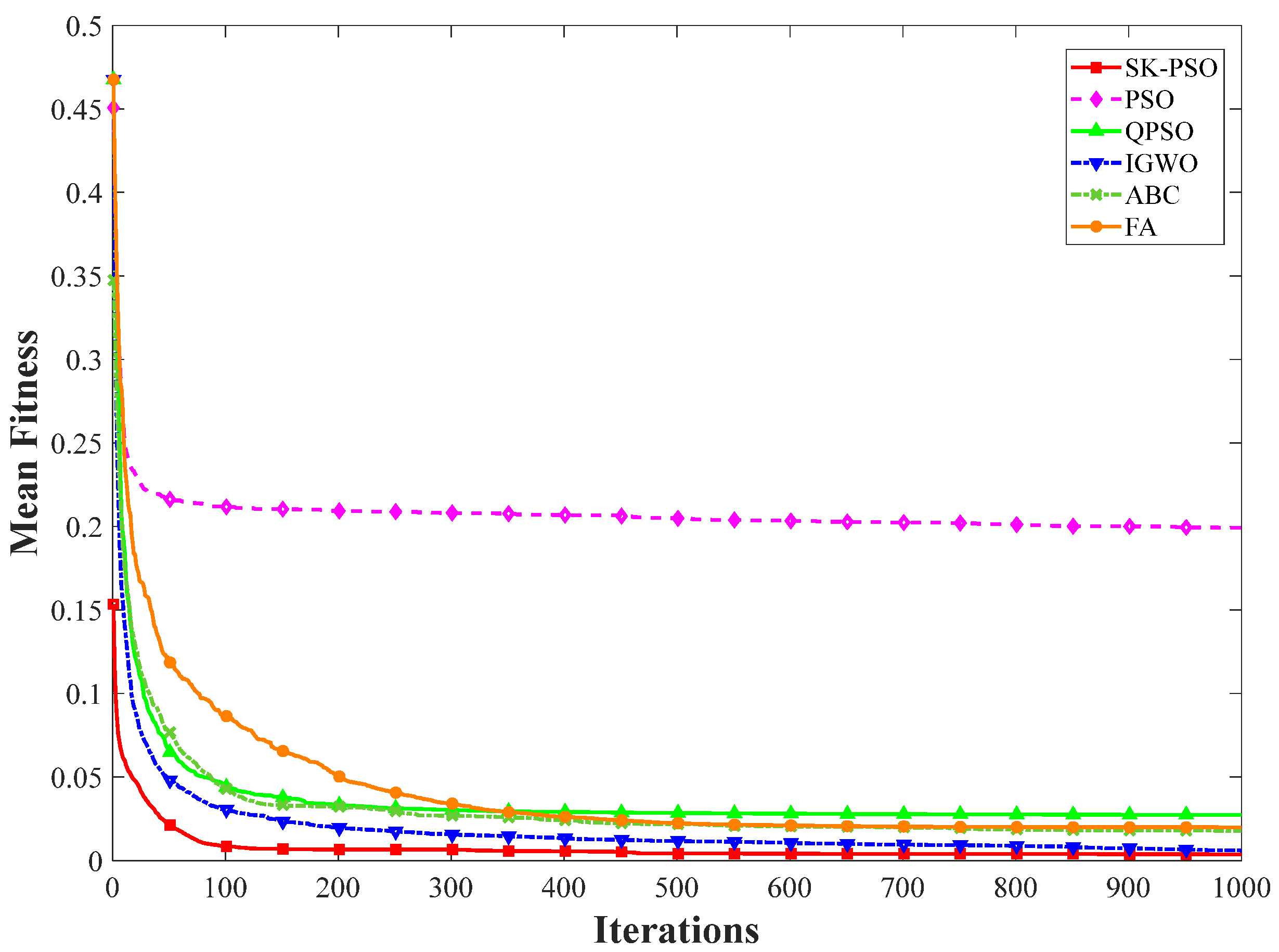
4.2. Scenario 2
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, F.; Xu, W.; Huang, H.; Ning, Y.; Li, B. Design and analysis of a high-payload manipulator based on a cable-driven serial-parallel mechanism. ASME J. Mech. Robot. 2019, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zi, B.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Ding, H. Design and implementation of a 7-DOF cable-driven serial spray-painting robot with motion-decoupling mechanisms. Mech. Mach. Theory 2024, 192, 105549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.; Sadati, S.M.H.; Dong, X.; Mohammad, A.; Walker, I.D.; Bergeles, C.; Xu, K.; Axinte, D.A. Continuum Robots: An Overview. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2023, 5, 2200367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Huang, H.; Li, B.; Xi, F. A parallel learning particle swarm optimizer for inverse kinematics of robotic manipulator. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2021, 36, 6101–6132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulźba, I.; Opalka, M. A comparison of Jacobian-based methods of inverse kinematics for serial robot manipulators. Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. 2013, 23, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, C. The inverse kinematics of a 7R 6-degree-of-freedom robot with non-spherical wrist. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 168781401771498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristidou, A.; Lasenby, J. FABRIK: A fast, iterative solver for the inverse kinematics problem. Graph. Model. 2011, 73, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagigas-Muñiz, D. Artificial Neural Networks for inverse kinematics problem in articulated robots. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 126, 107175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramar, V.; Kramar, O.; Kabanov, A. An artificial neural network approach for solving inverse kinematics problem for an anthropomorphic manipulator of robot SAR-401. Machines 2022, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Luo, M.; Pang, F. An algorithm for solving robot inverse kinematics based on FOA optimized BP neural network. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R. Inverse kinematics solution of Robotics based on neural network algorithms. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2020, 11, 6199–6209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereli, S.; Köker, R. Simulation based calculation of the inverse kinematics solution of 7-DOF robot manipulator using artificial bee colony algorithm. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereli, S. A new modified grey wolf optimization algorithm proposal for a fundamental engineering problem in robotics. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 14119–14131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Mao, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, G.; Liu, P.; Yang, X.; Wang, D. Hybrid mutation fruit fly optimization algorithm for solving the inverse kinematics of a redundant robot manipulator. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.K.; Balamurali, G.; Biswal, B.B. Robotic manipulator trajectory optimisation using an improved modified bat algorithm. Int. J. Mechatron. Autom. 2020, 7, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slim, M.; Rokbani, N.; Neji, B.; Terres, M.A.; Beyrouthy, T. Inverse Kinematic Solver Based on Bat Algorithm for Manipulator Path Planning. Robotics 2023, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L. Grey Wolf Optimizer Based on Nonlinear Adjustment Control Parameter. In Proceedings of the 2016 4th international conference on sensors, mechatronics and automation (ICSMA 2016), Zhuhai, China, 12–13 November 2016; Volume 136, pp. 643–648. [Google Scholar]
- Dereli, S.; Köker, R. Calculation of the inverse kinematics solution of the 7-DOF redundant robot manipulator by the firefly algorithm and statistical analysis of the results in terms of speed and accuracy. Inverse Probl. Sci. Eng. 2020, 28, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omkar, S.N.; Khandelwal, R.; Ananth, T.V.S.; Narayana Naik, G.; Gopalakrishnan, S. Quantum behaved Particle Swarm Optimization (QPSO) for multi-objective design optimization of composite structures. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 11312–11322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkayyali, M.; Tutunji, T.A. PSO-Based Algorithm for Inverse Kinematics Solution of Manipulator Manipulators. In Proceedings of the 2019 20th International Conference on Research and Education in Mechatronics (REM), Wels, Austria, 23–24 May 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shastri, S.; Parvez, Y.; Chauhan, N.R. Inverse kinematics for a 3-R robot using artificial neural network and modified particle swarm optimization. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. C 2020, 101, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Man, W.; Zhang, G.; Ding, W. Application of an Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm in Inverse Kinematics Solutions of Manipulators. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 9th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference (ITAIC), Chongqing, China, 11–13 December 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; Volume 9, pp. 1680–1684. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.; Xie, C. An improved particle swarm optimization algorithm for inverse kinematics solution of multi-DOF serial robotic manipulators. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 13695–13708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xi, J.; Bai, H.; Wang, Z.; Sun, L. A general robot inverse kinematics solution method based on improved PSO algorithm. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 32341–32350. [Google Scholar]
- Rokbani, N.; Neji, B.; Slim, M.; Mirjalili, S.; Ghandour, R. A multi-objective modified PSO for inverse kinematics of a 5-DOF robotic arm. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Jiang, D.; Liu, X.; Tong, X.; Sun, Y.; Tao, B.; Kong, J.; Yun, J.; Liu, Y.; Fang, Z. A Tandem Robotic Arm Inverse Kinematic Solution Based on an Improved Particle Swarm Algorithm. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 832829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Singh, O.; Ray, A.K. Inverse kinematic solution of a 7 DOF robotic manipulator using boundary restricted particle swarm optimization. IFAC -Pap. 2022, 55, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Tao, B.; Jiang, D.; Yun, J.; Fan, H. Improved Bald Eagle Search Optimization Algorithm for the Inverse Kinematics of Robotic Manipulators. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Chu, D.; Li, Q.; He, Y. Inverse Kinematics Solution of 6-DOF Manipulator Based on Multi-Objective Full-Parameter Optimization PSO Algorithm. Front. Neurorobotics 2022, 16, 791796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani Amiri, M.; Ramli, R. Intelligent Trajectory Tracking Behavior of a Multi-Joint Robotic Arm via Genetic–Swarm Optimization for the Inverse Kinematic Solution. Sensors 2021, 21, 3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Xu, Q.; Ju, W.; Zhang, T. Inverse Kinematics of Large Hydraulic Manipulator Arm Based on ASWO Optimized BP Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Luo, M.; Bai, K.; Chen, S. A Precise Positioning Method for a Puncture Robot Based on a PSO-Optimized BP Neural Network Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95—International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohonen, T. Self-organized formation of topologically correct feature maps. Biol. Cybern. 1982, 43, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


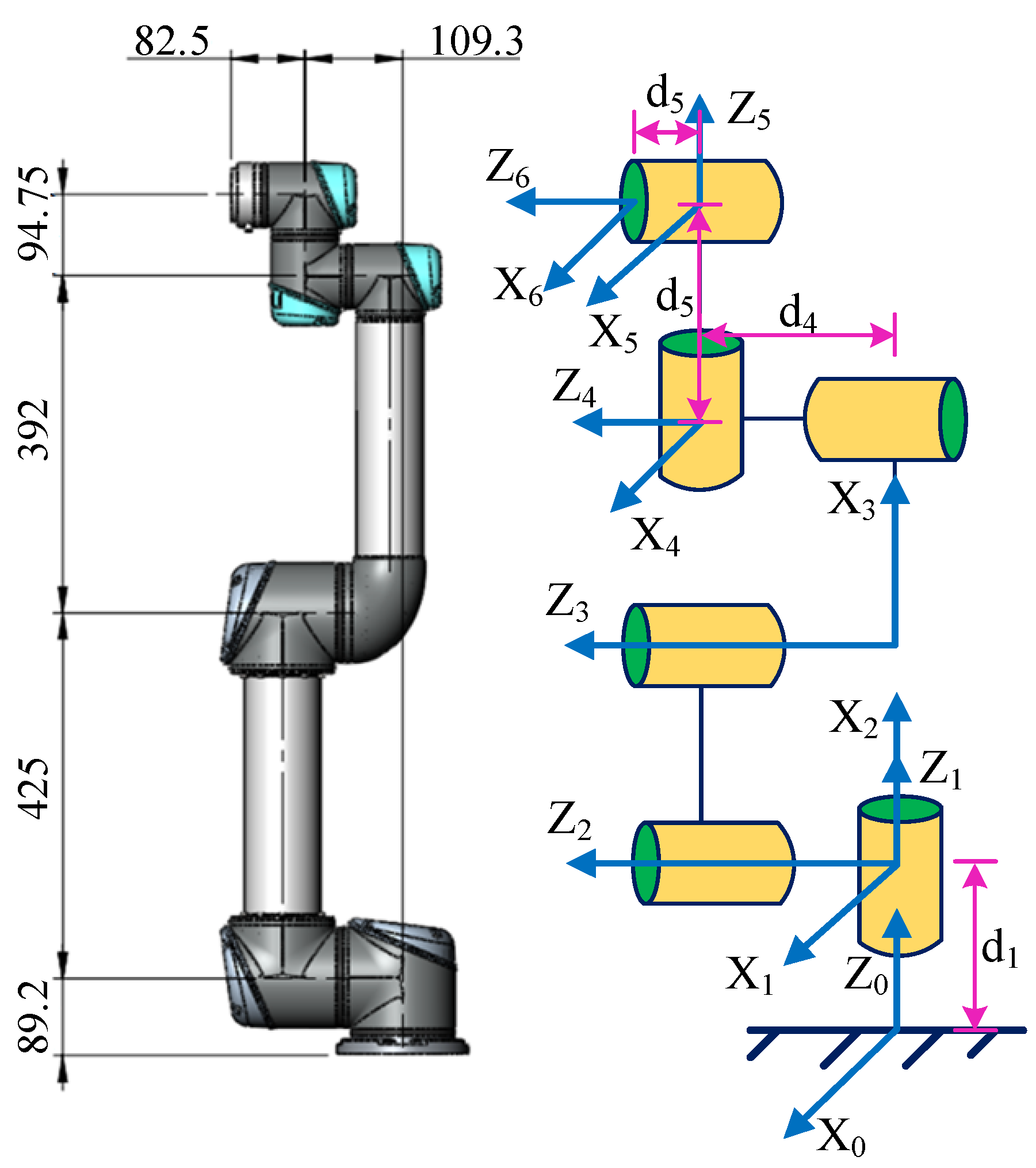

| 1 | 89.2 | 0 | ||
| 2 | 0 | −425 | 0 | |
| 3 | 0 | −392 | 0 | |
| 4 | 109.3 | 0 | ||
| 5 | 94.75 | 0 | ||
| 6 | 82.5 | 0 | 0 |
| Algorithm | Parameter Setting |
|---|---|
| SK-PSO | W = 1 × 0.99, c1 = 2, c2 = 2, a = 0.5, b = 0.5, L = 850 |
| PSO | W = 1 × 0.99, c1 = 1.49445, c2 = 1.49445 |
| QPSO | Beta = (1 − 0.5) × (Maxiterm-iterm)/Maxiterm + 0.5 Mbest = sum(pbest)/popsize |
| IGWO | a = 2 − iterm × ((2)/Maxiterm) |
| ABC | L = round(0.6 × nVar × nPop), a = 1 |
| FA | A = 0.3, β = 0.9, γ = 0.9 |
| Algorithm | Mean Fitness Value | Minimum Fitness Value | Maximum Fitness Value | Variance of Fitness Values | Average Solution Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SK-PSO | 0.004247 | 0.000355 | 0.053310 | 0.011971 | 0.090625 |
| PSO | 0.199249 | 0.063443 | 0.404853 | 0.087894 | 0.269063 |
| QPSO | 0.027334 | 0.000991 | 0.071712 | 0.018888 | 0.33125 |
| IGWO | 0.006844 | 0.001005 | 0.038744 | 0.008514 | 2.81125 |
| ABC | 0.017829 | 0.010741 | 0.029434 | 0.003110 | 2.33375 |
| FA | 0.019890 | 0.000748 | 0.054067 | 0.016522 | 1.728125 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, F.; Gao, C.; Liu, L. SK-PSO: A Particle Swarm Optimization Framework with SOM and K-Means for Inverse Kinematics of Manipulators. Symmetry 2024, 16, 1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym16121667
Liu F, Gao C, Liu L. SK-PSO: A Particle Swarm Optimization Framework with SOM and K-Means for Inverse Kinematics of Manipulators. Symmetry. 2024; 16(12):1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym16121667
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Fei, Changqin Gao, and Lisha Liu. 2024. "SK-PSO: A Particle Swarm Optimization Framework with SOM and K-Means for Inverse Kinematics of Manipulators" Symmetry 16, no. 12: 1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym16121667
APA StyleLiu, F., Gao, C., & Liu, L. (2024). SK-PSO: A Particle Swarm Optimization Framework with SOM and K-Means for Inverse Kinematics of Manipulators. Symmetry, 16(12), 1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym16121667






