Logarithmic Separable Solutions of Force-Free Magnetic Fields in Plane-Parallel and Axial Symmetry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Force-Free Magnetic Fields
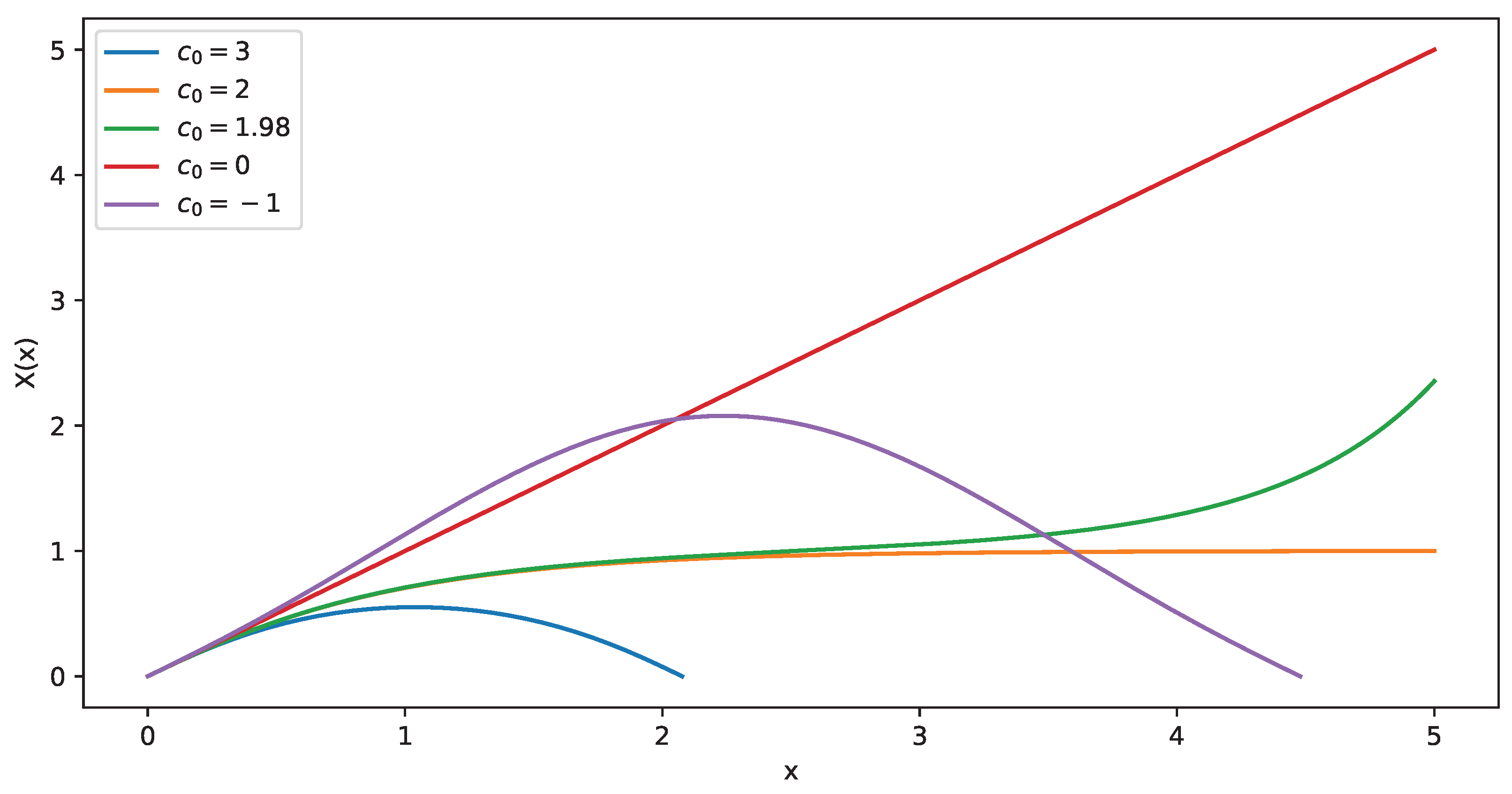
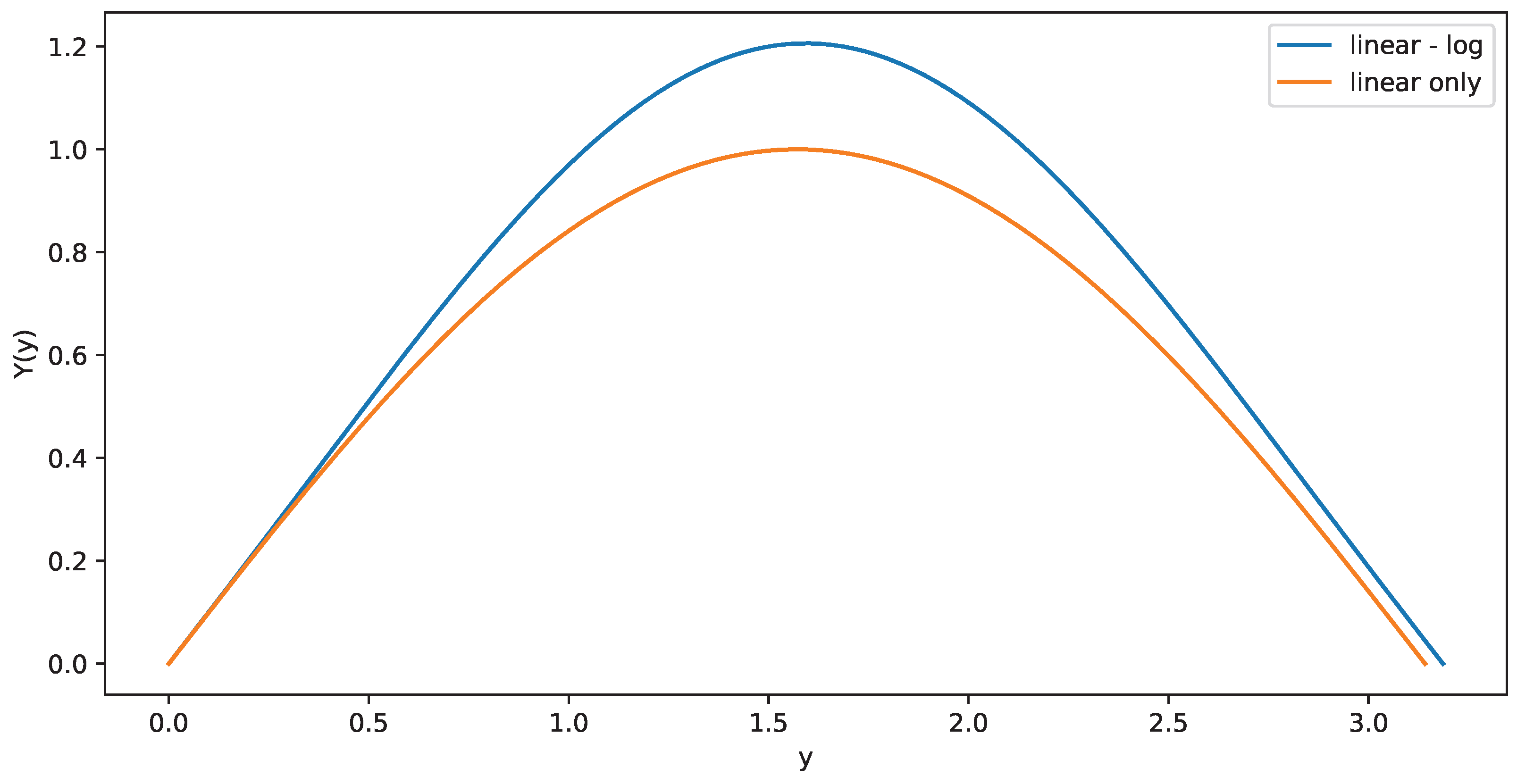
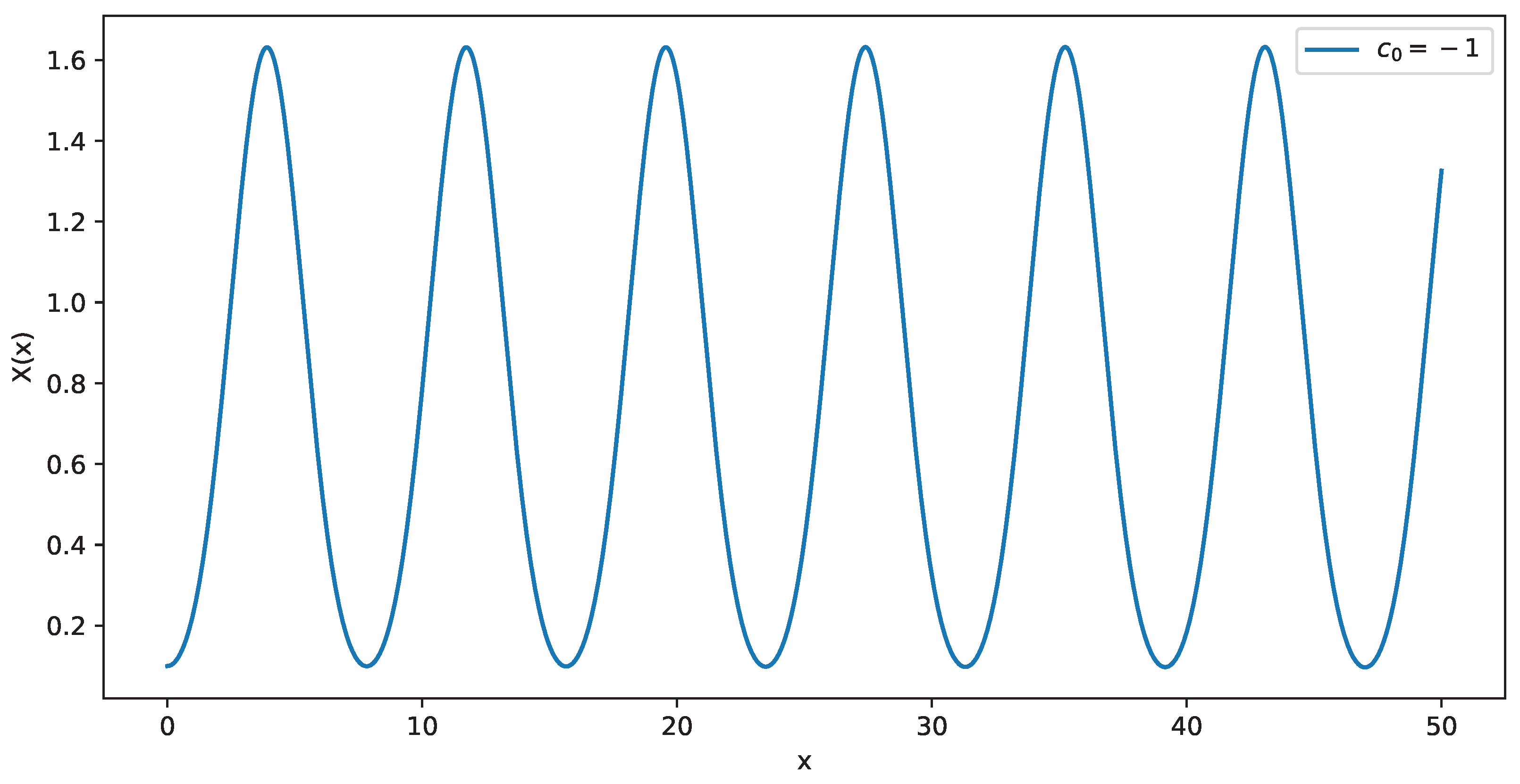
3. Plane Parallel Force-Free Magnetic Fields
4. Cylindrical Fields with Azimuthal Symmetry
5. Discussion
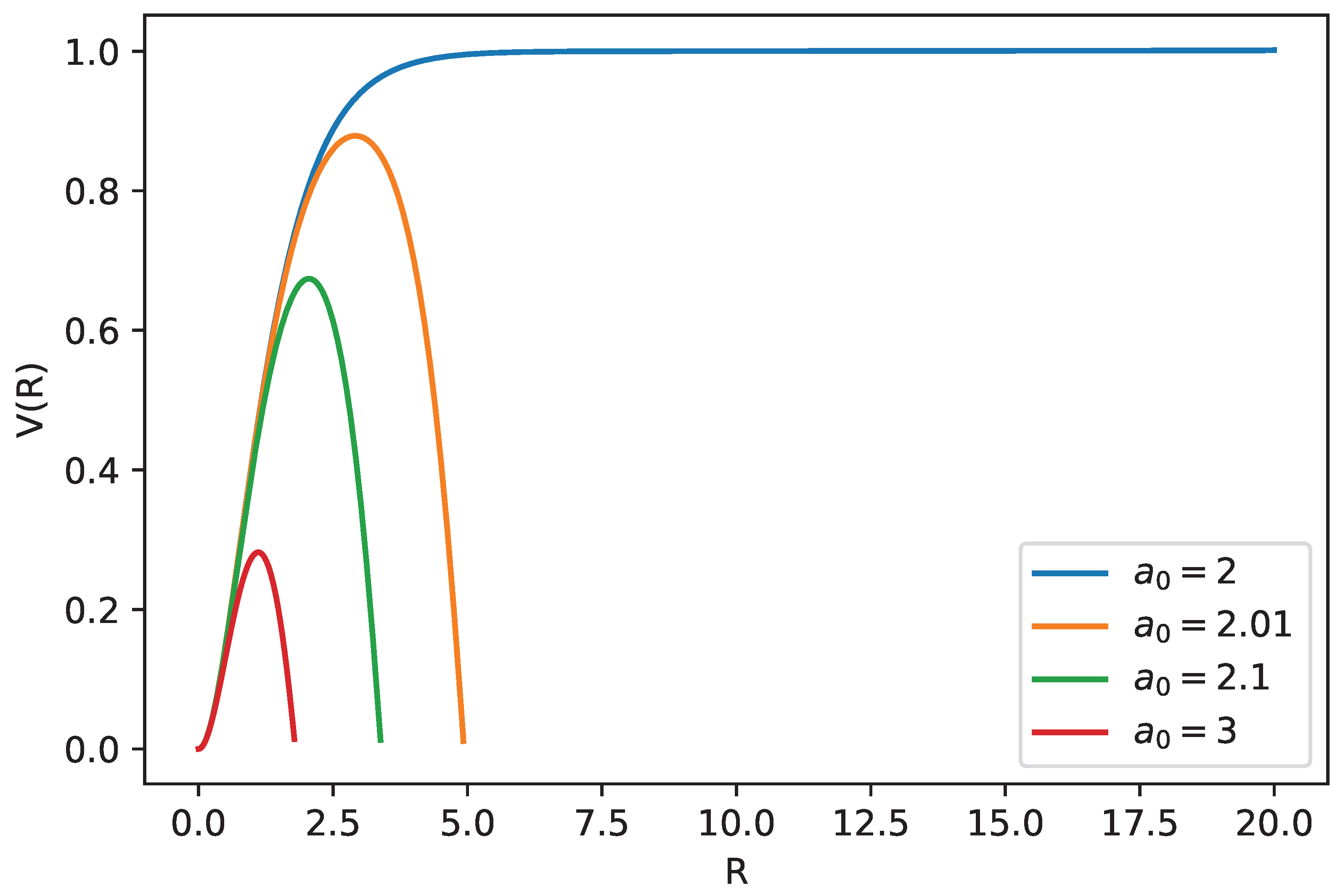
- A single maximum solution where the solution starts from a minimum value, typically zero reaches a maximum and then becomes zero again.
- An unbounded solution where the solution grows indefinitely.
- A solution that reaches an asymptotic value where the field becomes uniform.
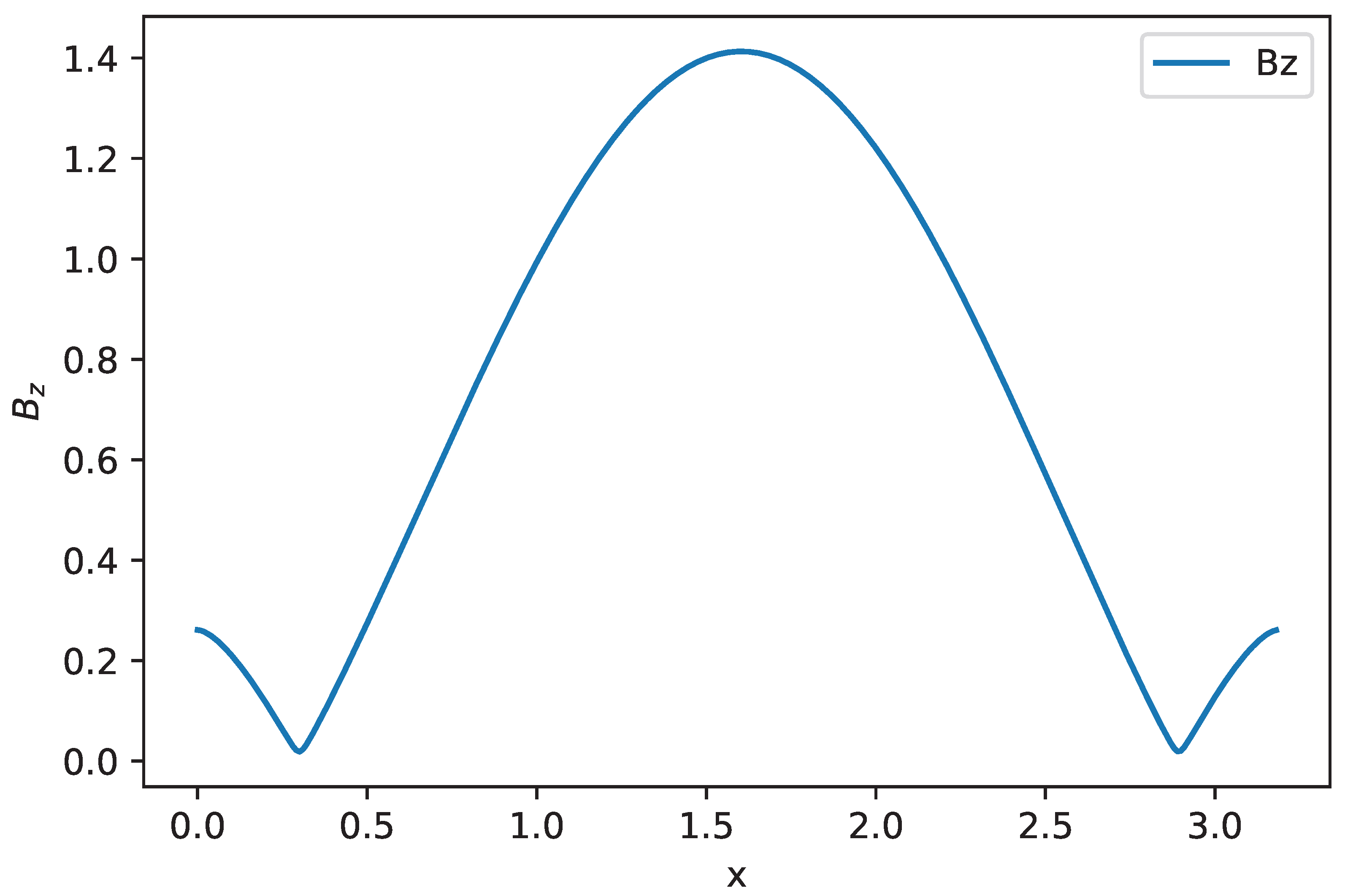
- The periodic solution. In this case, the fields are periodic, while the magnetic flux function never becomes negative.
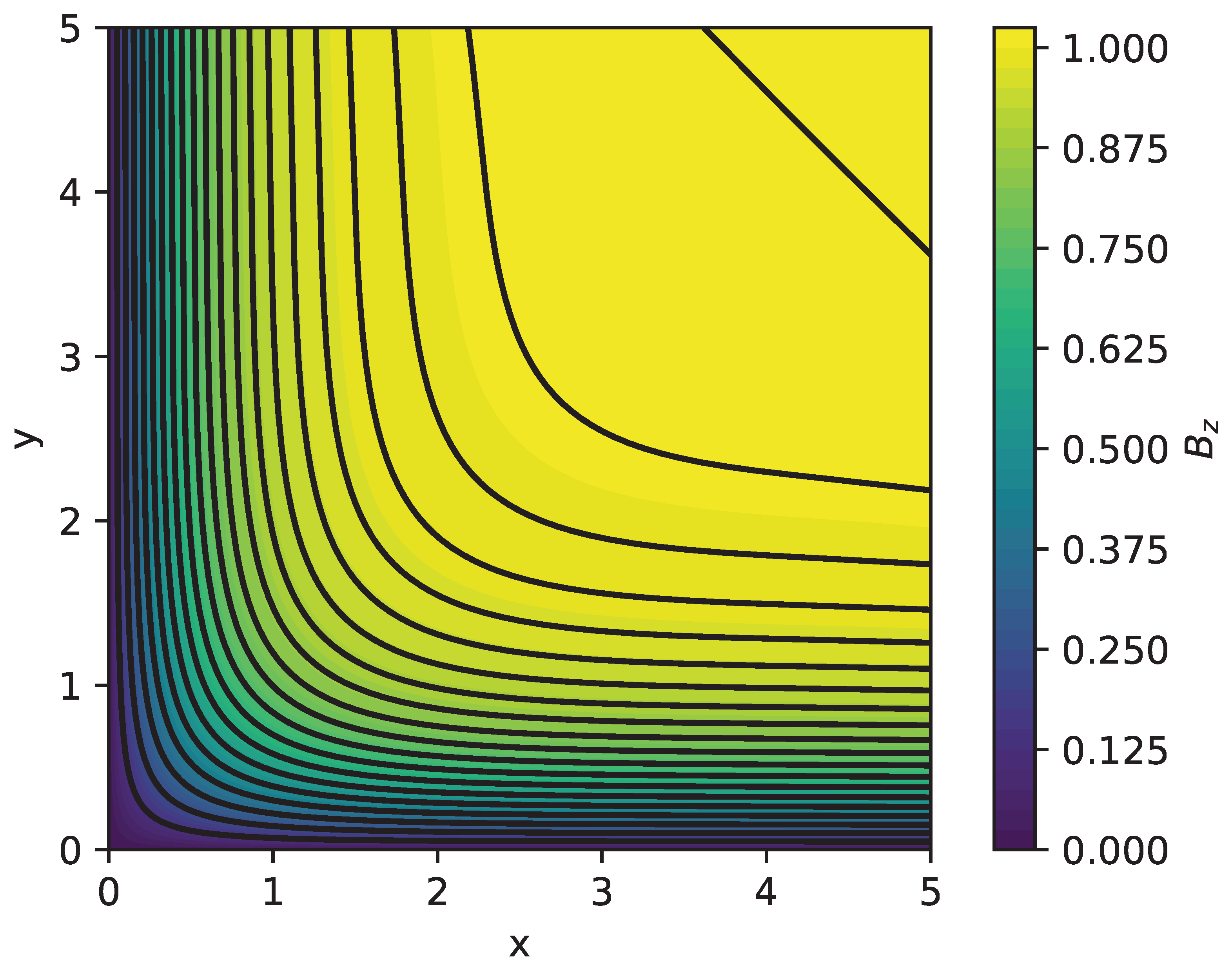
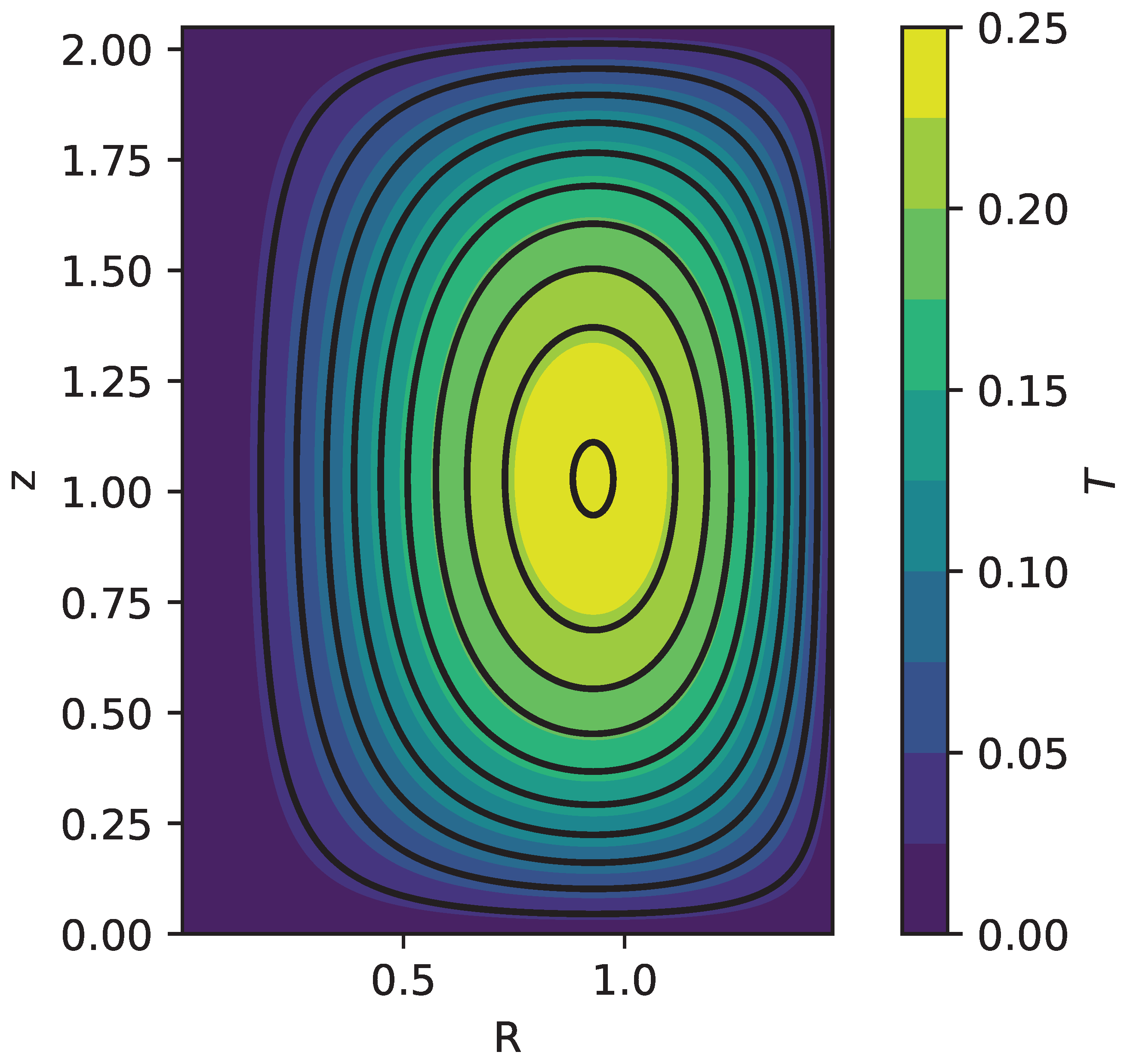
- Fields where the flux function has a single maximum in z and R and become zero at a finite distance, thus, they are confined within a cylinder.
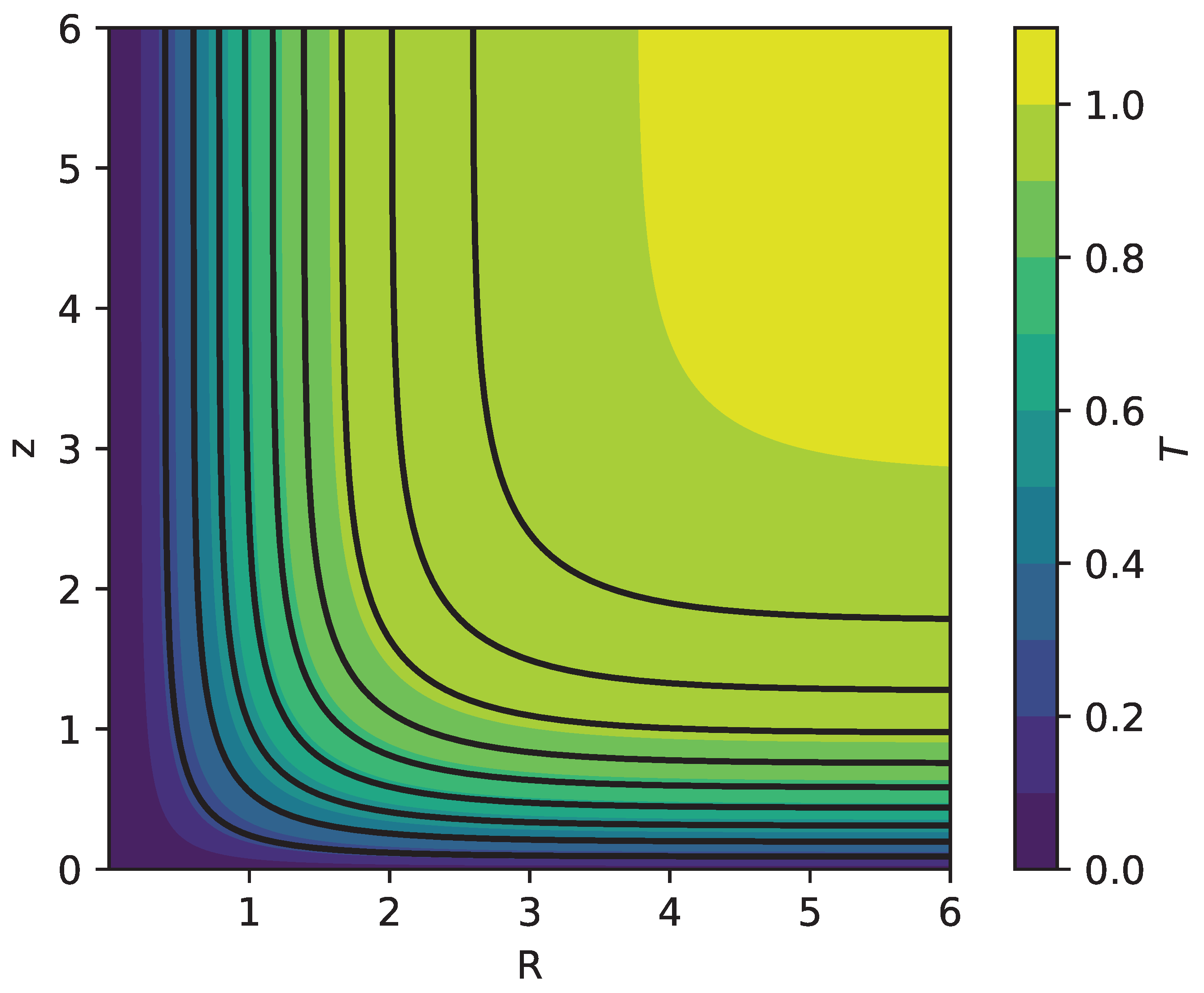
- Fields where the flux function becomes constant for large R, thus, there is no z component of the field for large R.
- Fields where the flux function becomes constant at large z, thus, there is no R component there.
- Fields where the flux function becomes uniform both at large R and z, thus, there is no R and z components at large distances but only .
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. The Form of α
References
- Donati, J.F.; Landstreet, J.D. Magnetic Fields of Nondegenerate Stars. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 47, 333–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutcher, R.M.; Wandelt, B.; Heiles, C.; Falgarone, E.; Troland, T.H. Magnetic Fields in Interstellar Clouds from Zeeman Observations: Inference of Total Field Strengths by Bayesian Analysis. Astrophys. J. 2010, 725, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalidis, R.; Tassis, K. High-accuracy estimation of magnetic field strength in the interstellar medium from dust polarization. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 647, A186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.L. Observing Interstellar and Intergalactic Magnetic Fields. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 55, 111–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepping, R.P.; Jones, J.A.; Burlaga, L.F. Magnetic field structure of interplanetary magnetic clouds at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res. 1990, 95, 11957–11965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babcock, H.W. The Topology of the Sun’s Magnetic Field and the 22-Year Cycle. Astrophys. J. 1961, 133, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bale, S.D.; Goetz, K.; Harvey, P.R.; Turin, P.; Bonnell, J.W.; Dudok de Wit, T.; Ergun, R.E.; MacDowall, R.J.; Pulupa, M.; Andre, M.; et al. The FIELDS Instrument Suite for Solar Probe Plus. Measuring the Coronal Plasma and Magnetic Field, Plasma Waves and Turbulence, and Radio Signatures of Solar Transients. Space Sci. Rev. 2016, 204, 49–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, J.R.P.; Borra, E.F.; Landstreet, J.D. The magnetic fields of white dwarfs. Astrophys. J. Supp. Ser. 1981, 45, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, D.T.; Ferrario, L. The origin of the magnetic fields in white dwarfs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 356, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourgouliatos, K.N.; Esposito, P. Strongly Magnetized Pulsars: Explosive Events and Evolution. In The Physics and Astrophysics of Neutron Stars; Rezzolla, L., Pizzochero, P., Jones, D.I., Rea, N., Vidaña, I., Eds.; Astrophysics and Space Science Library; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2018; Volume 457, p. 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eatough, R.P.; Falcke, H.; Karuppusamy, R.; Lee, K.J.; Champion, D.J.; Keane, E.F.; Desvignes, G.; Schnitzeler, D.H.F.M.; Spitler, L.G.; Kramer, M.; et al. A strong magnetic field around the supermassive black hole at the centre of the Galaxy. Nature 2013, 501, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardall, C.Y.; Prakash, M.; Lattimer, J.M. Effects of Strong Magnetic Fields on Neutron Star Structure. Astrophys. J. 2001, 554, 322–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, S.K. The contrasting magnetic fields of superconducting pulsars and magnetars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 437, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Du, S.; Wang, W.; Hou, S.; Xu, R. Investigating magnetically induced distortions of neutron stars through gamma-ray burst X-ray plateaus. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 666, A138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrijver, C.J.; De Rosa, M.L.; Metcalf, T.R.; Liu, Y.; McTiernan, J.; Régnier, S.; Valori, G.; Wheatland, M.S.; Wiegelmann, T. Nonlinear Force-Free Modeling of Coronal Magnetic Fields Part I: A Quantitative Comparison of Methods. Sol. Phys. 2006, 235, 161–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, T.R.; De Rosa, M.L.; Schrijver, C.J.; Barnes, G.; van Ballegooijen, A.A.; Wiegelmann, T.; Wheatland, M.S.; Valori, G.; McTtiernan, J.M. Nonlinear Force-Free Modeling of Coronal Magnetic Fields. II. Modeling a Filament Arcade and Simulated Chromospheric and Photospheric Vector Fields. Sol. Phys. 2008, 247, 269–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, T.; Aly, J.J.; Luciani, J.F.; Boulmezaoud, T.Z.; Mikic, Z. Reconstructing the Solar Coronal Magnetic Field as a Force-Free Magnetic Field. Sol. Phys. 1997, 174, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharlemann, E.T.; Wagoner, R.V. Aligned Rotating Magnetospheres. General Analysis. Astrophys. J. 1973, 182, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, M.; Kito, M.; Honma, T.; Kaji, I. Stability analysis of a cylindrical surface current plasma confined by a force-free magnetic field using dispersion relations. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 1985, 27, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, G.E. Force-Free Magnetic Fields: Solutions, Topology and Applications; World Scientific: Singapore, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenzel, R.L.; Urrutia, J.M. Force-free electromagnetic pulses in a laboratory plasma. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1990, 65, 2011–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S. On Force-Free Magnetic Fields. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1956, 42, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S.; Kendall, P.C. On Force-Free Magnetic Fields. Astrophys. J. 1957, 126, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S. Axisymmetric Magnetic Fields and Fluid Motions. Astrophys. J. 1956, 124, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundquist, S. On the Stability of Magneto-Hydrostatic Fields. Phys. Rev. 1951, 83, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrant, C.J. Linear force-free magnetic fields and coronal models. Aust. J. Phys. 1989, 42, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheatland, M.S. A Better Linear Force-free Field. Astrophys. J. 1999, 518, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, B.; David Pan, W.; Allen Gary, G.; Hu, Q.; Staudinger, T. Determining the parameter for the linear force-free magnetic field model with multi-dipolar configurations using deep neural networks. Astron. Comput. 2019, 26, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendergast, K.H. Relativistically expanding axisymmetric self-similar force-free fields. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 359, 725–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gourgouliatos, K.N.; Lynden-Bell, D. Fields from a relativistic magnetic explosion. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 391, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gourgouliatos, K.N. Relativistically expanding cylindrical electromagnetic fields. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 396, 2399–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barkov, M.V.; Sharma, P.; Gourgouliatos, K.N.; Lyutikov, M. Relativistic Magnetic Explosions. Astrophys. J. 2022, 934, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntotsikas, D.; Gourgouliatos, K.N.; Contopoulos, I.; Lander, S.K. Twisted magnetar magnetospheres. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 527, 6691–6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.H. Expanding Force-free Magnetized Plasmoid. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1990, 348, L73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourgouliatos, K.N.; Vlahakis, N. Relativistic expansion of a magnetized fluid. Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn. 2010, 104, 431–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aly, J.J. Asymptotic formation of a current sheet in an indefinitely sheared force-free field: An analytical example. Astron. Astrophys. 1994, 288, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Lynden-Bell, D.; Boily, C. Self-Similar Solutions up to Flashpoint in Highly Wound Magnetostatics. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1994, 267, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boily, C.M.; Lynden-Bell, D. Wound Magnetostatics and Flaring. Astrophys. Space Sci. 1996, 243, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourgouliatos, K.N. Self-similar magnetic arcades. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 385, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegelmann, T. Nonlinear force-free modeling of the solar coronal magnetic field. J. Geophys. Res. (Space Phys.) 2008, 113, A03S02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeates, A.R.; Amari, T.; Contopoulos, I.; Feng, X.; Mackay, D.H.; Mikić, Z.; Wiegelmann, T.; Hutton, J.; Lowder, C.A.; Morgan, H.; et al. Global Non-Potential Magnetic Models of the Solar Corona During the March 2015 Eclipse. Space Sci. Rev. 2018, 214, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourgouliatos, K.N. Relativistic Magnetohydrodynamics. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sturrock, P.A. Plasma Physics, An Introduction to the Theory of Astrophysical, Geophysical and Laboratory Plasmas; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulsrud, R.M. Plasma Physics for Astrophysics; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dombre, T.; Frisch, U.; Henon, M.; Greene, J.M.; Soward, A.M. Chaotic streamlines in the ABC flows. J. Fluid Mech. 1986, 167, 353–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, A.; Peralta-Salas, D. Arnold Diffusion of Charged Particles in ABC Magnetic Fields. J. NonLinear Sci. 2017, 27, 721–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalewajko, K. Three-dimensional kinetic simulations of relativistic magnetostatic equilibria. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 481, 4342–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, B.C. Evolving force-free magnetic fields. I. The development of the preflare stage. Astrophys. J. 1977, 212, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birn, J.; Goldstein, H.; Schindler, K. A theory of the onset of solar eruptive processes. Sol. Phys. 1978, 57, 81–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priest, E.R.; Milne, A.M. Force-Free Magnetic Arcades Relevant to Two-Ribbon Solar Flares. Sol. Phys. 1980, 65, 315–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumeliotis, G. A New Class of Exact, Nonlinear Solutions to the Grad-Shafranov Equation. Astrophys. J. 1993, 404, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourgouliatos, K.N.; Braithwaite, J.; Lyutikov, M. Structure of magnetic fields in intracluster cavities. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 409, 1660–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gourgouliatos, K.N.; Fendt, C.; Clausen-Brown, E.; Lyutikov, M. Magnetic field structure of relativistic jets without current sheets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 419, 3048–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Woltjer, L. A Theorem on Force-Free Magnetic Fields. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1958, 44, 489–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contopoulos, I.; Kazanas, D.; Fendt, C. The Axisymmetric Pulsar Magnetosphere. Astrophys. J. 1999, 511, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynden-Bell, D. On why discs generate magnetic towers and collimate jets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 341, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynden-Bell, D. Magnetic jets from swirling discs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 369, 1167–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabuzda, D.C.; Murray, É.; Cronin, P. Helical magnetic fields associated with the relativistic jets of four BL Lac objects. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 351, L89–L93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Yuan, F. Three-dimensional Magnetohydrodynamical Simulations of the Morphology of Head-Tail Radio Galaxies Based on the Magnetic Tower Jet Model. Astrophys. J. 2017, 839, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki-Vidal, F.; Patankar, S.; Lebedev, S.V.; Bland, S.N.; Doyle, H.; Bigourd, D.; Burdiak, G.; de Grouchy, P.; Hall, G.N.; Harvey-Thompson, A.J.; et al. Observation of energetic protons trapped in laboratory magnetic-tower jets. New J. Phys. 2013, 15, 125008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciardi, A.; Lebedev, S.V.; Frank, A.; Blackman, E.G.; Ampleford, D.J.; Jennings, C.A.; Chittenden, J.P.; Lery, T.; Bland, S.N.; Bott, S.C.; et al. 3D MHD Simulations of Laboratory Plasma Jets. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2007, 307, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gourgouliatos, K.N. Logarithmic Separable Solutions of Force-Free Magnetic Fields in Plane-Parallel and Axial Symmetry. Symmetry 2025, 17, 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17020175
Gourgouliatos KN. Logarithmic Separable Solutions of Force-Free Magnetic Fields in Plane-Parallel and Axial Symmetry. Symmetry. 2025; 17(2):175. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17020175
Chicago/Turabian StyleGourgouliatos, Konstantinos N. 2025. "Logarithmic Separable Solutions of Force-Free Magnetic Fields in Plane-Parallel and Axial Symmetry" Symmetry 17, no. 2: 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17020175
APA StyleGourgouliatos, K. N. (2025). Logarithmic Separable Solutions of Force-Free Magnetic Fields in Plane-Parallel and Axial Symmetry. Symmetry, 17(2), 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17020175




