Multi-Granularity and Multi-Modal Feature Fusion for Indoor Positioning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Recent Advances and Challenges in Wi-Fi-Based Positioning Systems
2.2. Recent Advances in Image-Based Localization Techniques
2.3. Research Status of Fusion Data Localization
3. Preliminary Aspects
3.1. Description of CSI Data
3.2. Image Data Description
3.3. Scale-Space Extremum Detection
3.4. Key Point Positioning
3.5. Determine the Direction of the Key Point
3.6. Feature Descriptor Construction
4. Multi-Modal Localization
4.1. Proposed Method
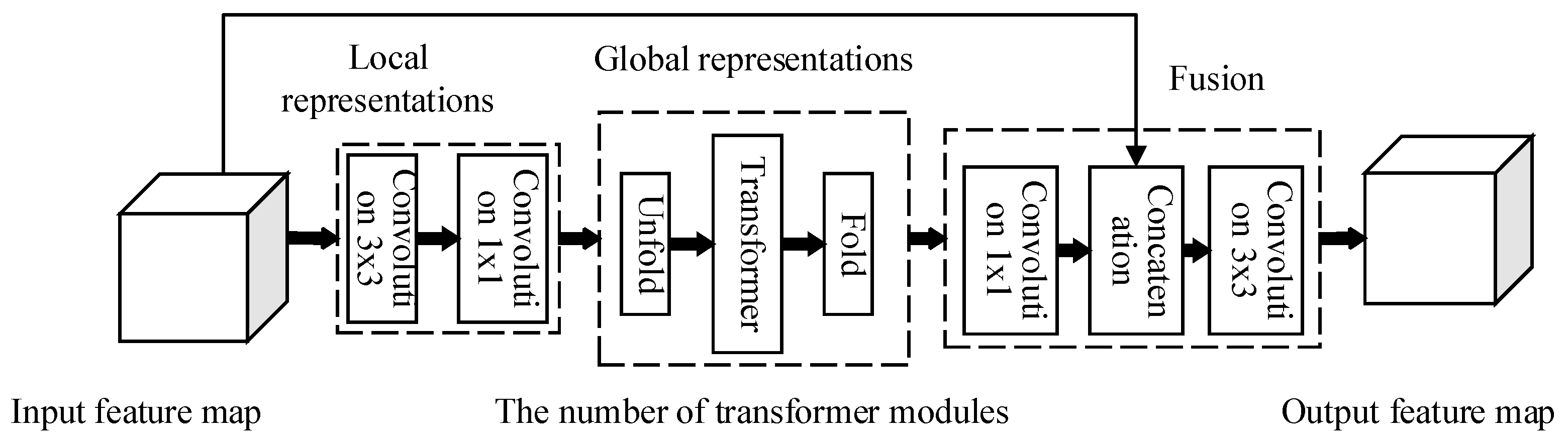
4.2. Coarse-Grained Location Is Conducted by Mobilevit Network
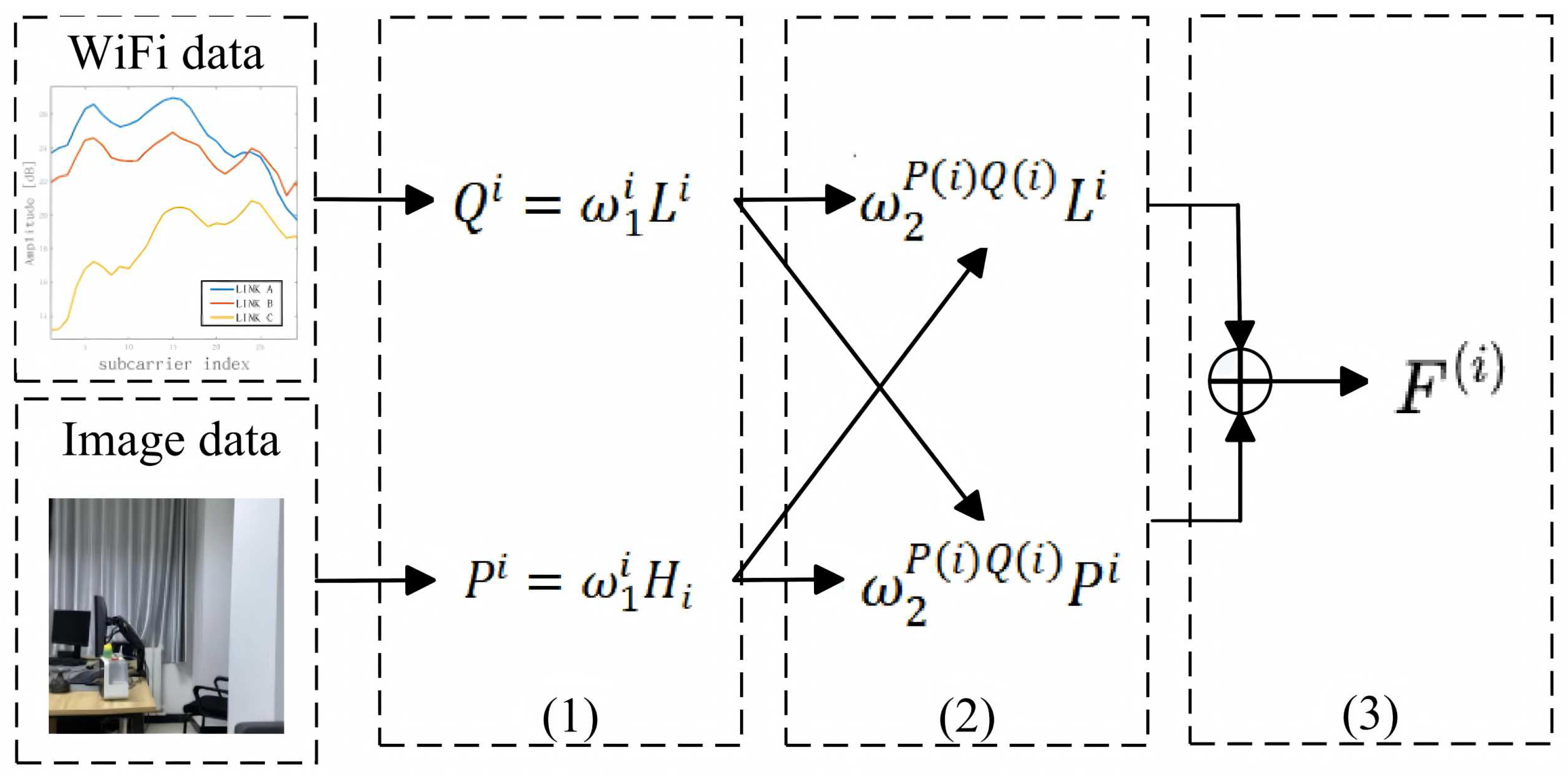
4.3. Improved Feature Fusion Method
4.4. Train the SVM Model for Positioning
| Algorithm 1 Indoor positioning method based on multi-granularity and multi-modal features |
|
5. Experimental Analysis and Verification
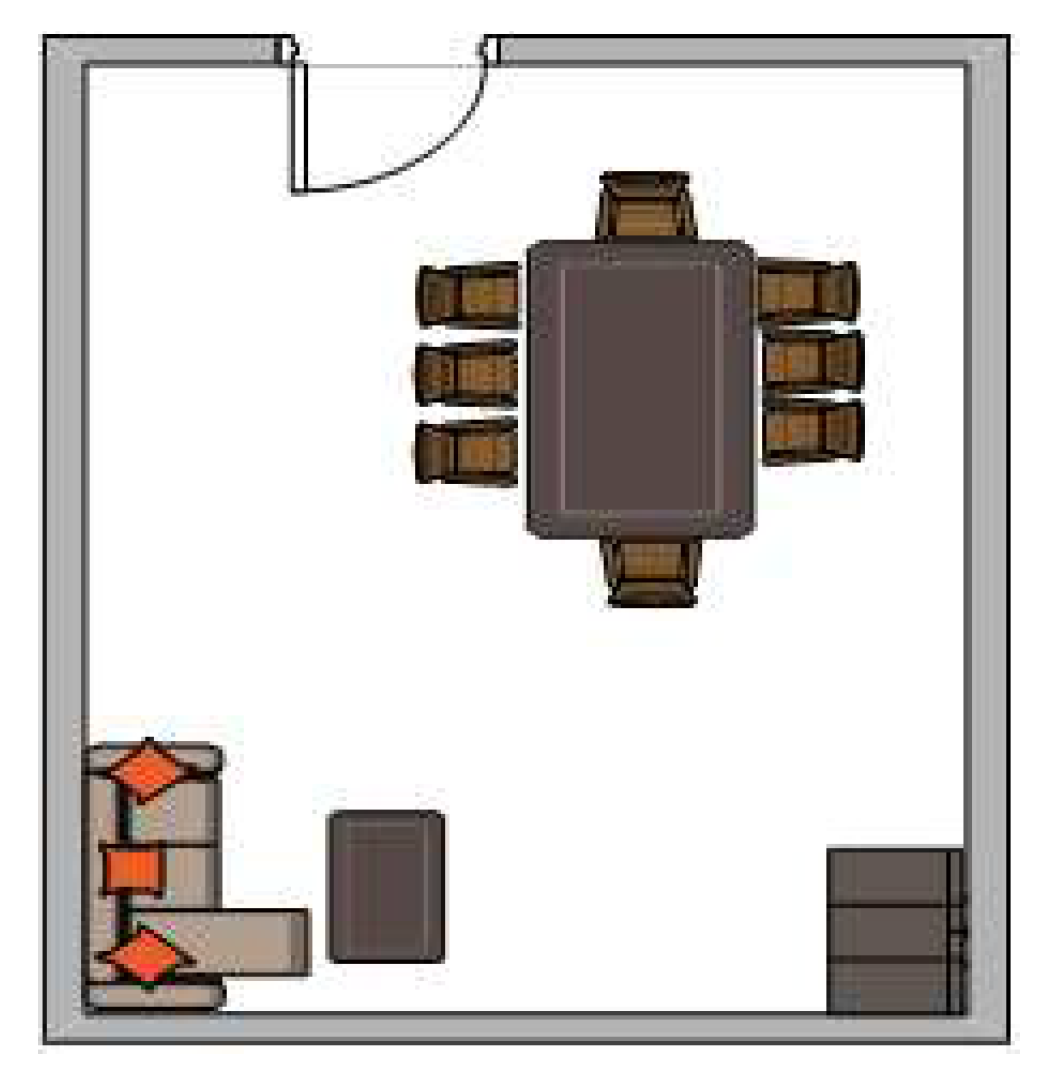
5.1. Experimental Environment Setup
5.2. Comparison of Coarse-Grained Positioning Experiments
5.3. Comparison of Fine-Grained Positioning Experiments
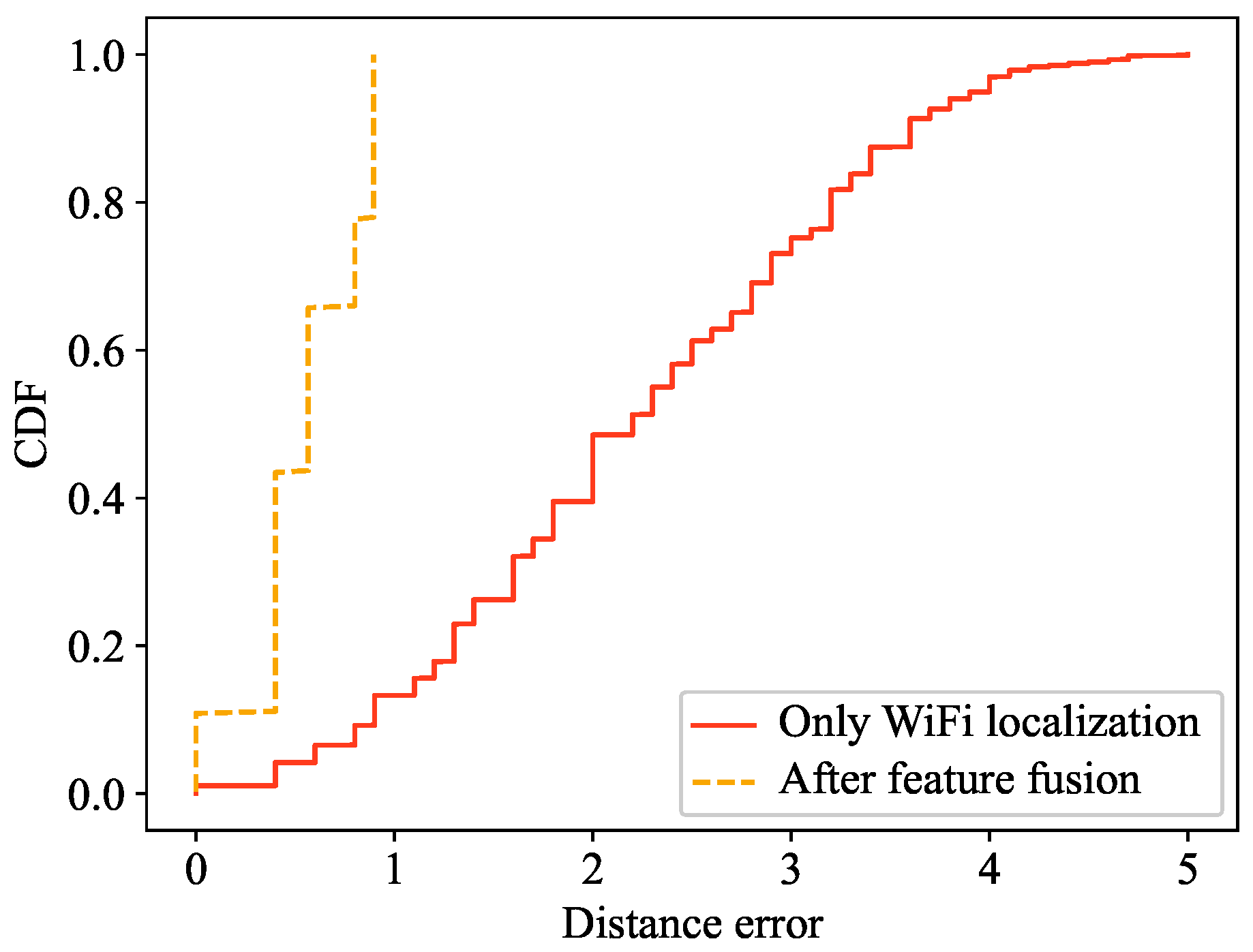
5.4. Comparison with the Method Without Image Data and Only Using Wi-Fi Data for Positioning
5.5. Comparison of Experiments with Different Sample Sizes
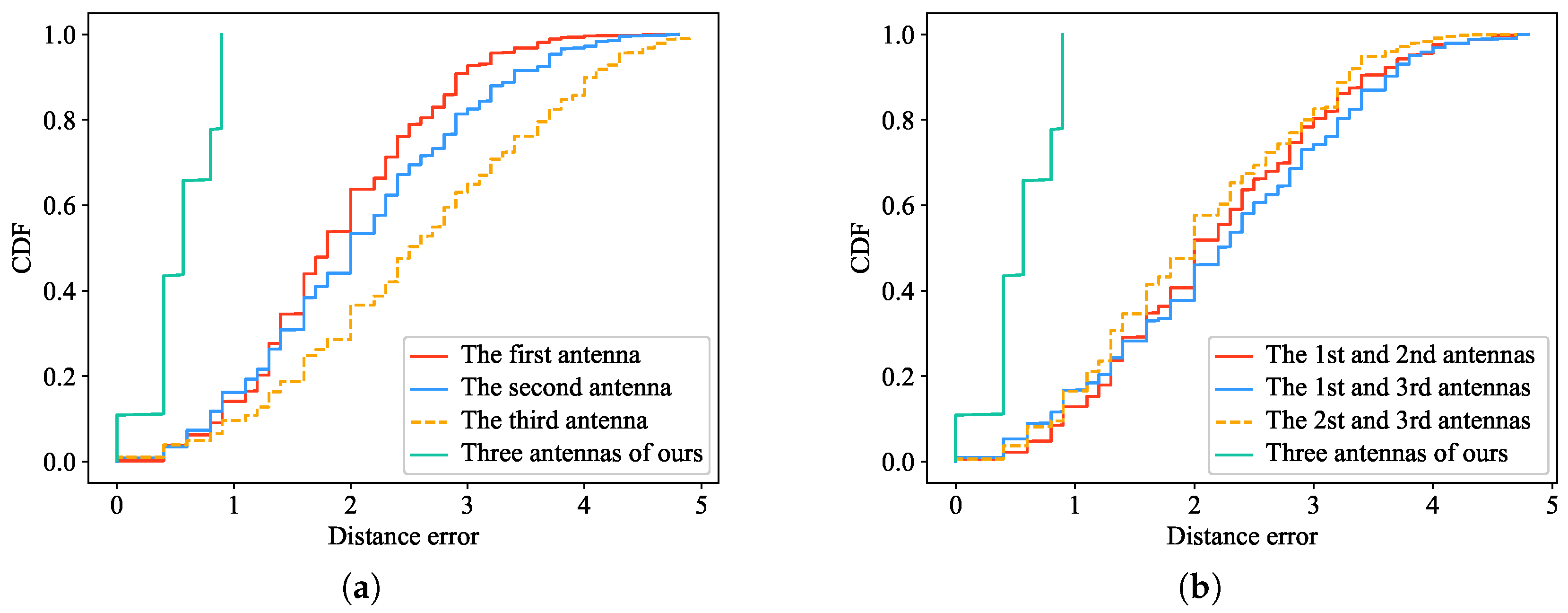
5.6. Comparison with Different Antenna Numbers
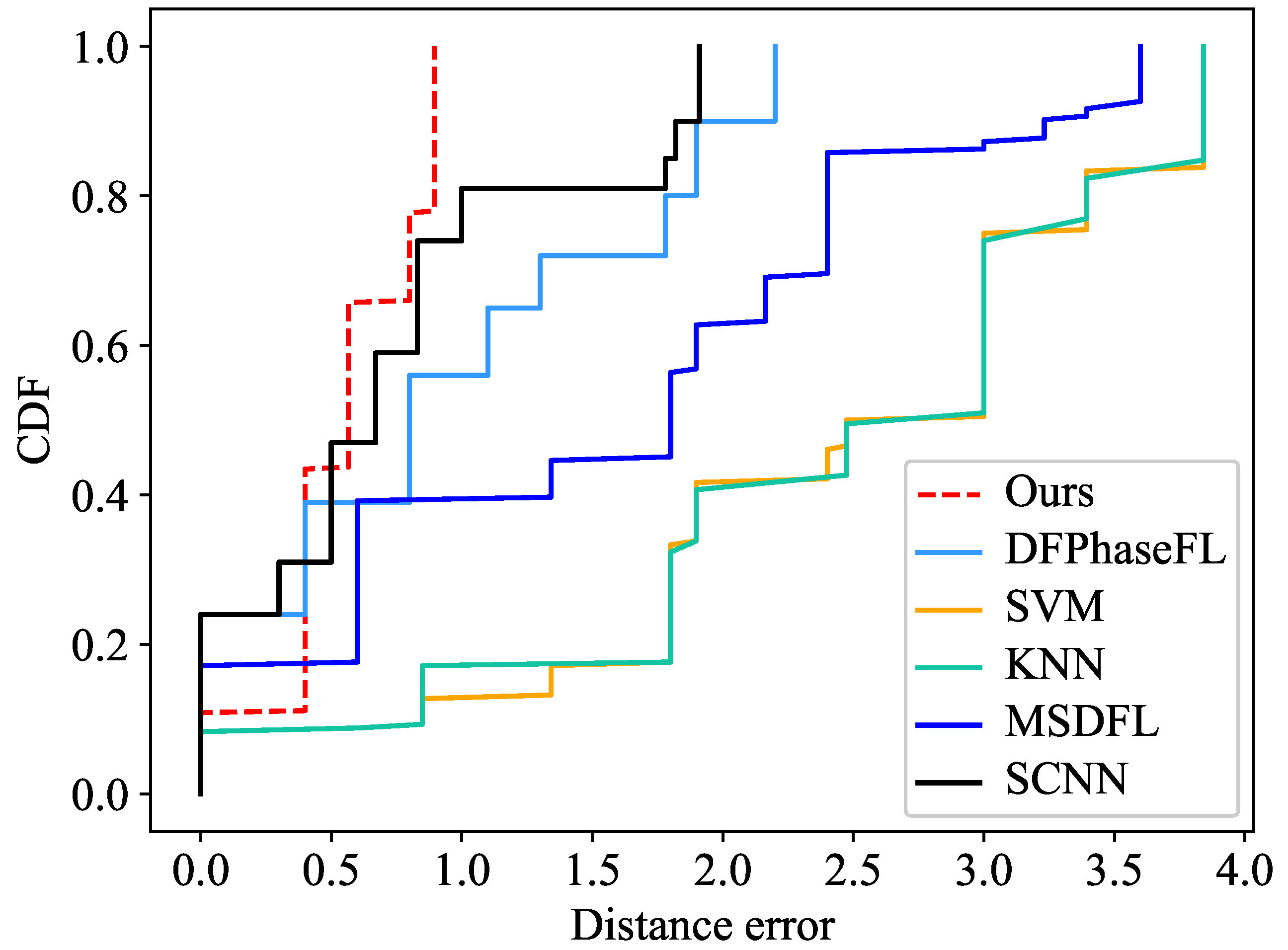
5.7. Comparison with Popular Algorithms
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, C.; Shi, Z.; Wu, F. Intelligent RFID Indoor Localization System Using a Gaussian Filtering Based Extreme Learning Machine. Symmetry 2017, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Seo, J.; Won, Y. Ephemeral ID Beacon-Based Improved Indoor Positioning System. Symmetry 2018, 10, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Guan, L.; Huang, R.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y.; Yin, Y. Sustainable development of animal husbandry in China. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. (Chin. Version) 2019, 34, 135–144. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Xue, B. Development history and trend of beidou satellite navigation system. J. Navig. Position. 2022, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, W.; Guo, C. Review of indoor positioning methods based on machine learning. In Proceedings of the 12th China Satellite Navigation Annual Conference, Nanchang, China, 26–28 May 2021; pp. 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Liu, S.; Hwang, S.H. Local Batch Normalization-Aided CNN Model for RSSI-Based Fingerprint Indoor Positioning. Electronics 2025, 14, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasco, N.; Sidibé, D.; Demonceaux, C.; Gouet-Brunet, V. A survey on visual-based localization: On the benefit of heterogeneous data. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 74, 90–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Zou, J. Fingerprint positioning method of CSI based on PCA-SMO. GNSS World China 2021, 46, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Lee, M.; Choi, S. Deep-Learning-Based Wi-Fi Indoor Positioning System Using Continuous CSI of Trajectories. Sensors 2021, 21, 5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, R.; Chen, H. Channel State Information Based Indoor Fingerprinting Localization. Sensors 2023, 23, 5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, P.; Yang, Y.; Wang, M.; Yan, R. Combination of DNN and Improved KNN for indoor location fingerprinting. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2019, 2019, 4283857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Yu, X. CSI indoor positioning based on Kmeans clustering. Appl. Electron. Tech. 2016, 42, 62–64. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, X.; Ru, C.; Hao, Z. An indoor positioning method based on CSI and SVM regression. Comput. Eng. Sci. 2021, 43, 853–861. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, X.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S. DFPhaseFL: A robust device-free passive fingerprinting wireless localization system using CSI phase information. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 14909–14927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, I.; Zikria, Y.B.; Hur, S. Localizing pedestrians in indoor environments using magnetic field data with term frequency paradigm and deep neural networks. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2021, 12, 3203–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, D.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. WiDir: Walking direction estimation using wireless signals. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, Heidelberg Germany, 12–16 September 2016; pp. 351–362. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Tan, B.; Ding, S.; Li, Y.; Li, G. Device-free indoor localization based on sparse coding with nonconvex regularization and adaptive relaxation localization criteria. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2023, 14, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Tang, Y.; Tian, Z. WLAN indoor positioning algorithm based on manifold interpolation database construction. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2017, 39, 1826–1834. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Jia, W.; Zhang, H.; Mao, Z.; Sun, M. Landmark-based indoor positioning for visually impaired individuals. In Proceedings of the 2014 12th International Conference on Signal Processing (ICSP), Hangzhou, China, 19–23 October 2014; pp. 678–681. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Chen, L.; Liang, W. Monocular vision based robot self-localization. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Tianjin, China, 14–18 December 2010; pp. 1189–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Yao, M.; Gu, Q. Pothole detection using location-aware convolutional neural networks. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2020, 11, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, M.; Kessel, M.; Marouane, C. Indoor positioning using smartphone camera. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation, Guimaraes, Portugal, 21–23 September 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dryanovski, I.; Valenti, R.; Xiao, J. Fast visual odometry and mapping from RGB-D data. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 2305–2310. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Wu, X.; Qi, Y.; Gong, W. Vision-based localization method for indoor mobile robots based on line detection. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2016, 11, 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Buyval, A.; Mustafin, R.; Gavrilenkov, M.; Gabdullin, A.; Shimchik, I. Visual localization for copter based on 3D model of environment with CNN segmentation. In Proceedings of the Information Science and Cloud Computing (ISCC 2017); Guangzhou, China, 16–17 December 2017, pp. 36–41.
- Wu, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Gan, Y.; Fang, M.; Xu, T. OCR-RTPS: An OCR-based real-time positioning system for the valet parking. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 17920–17934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Huang, Y.; Song, X. Convolutional transformer network: Future pedestrian location in first-person videos using depth map and 3D pose. In Proceedings of the 22nd Asia Simulation Conference, Langkawi, Malaysia, 25–26 October 2023; pp. 44–59. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Shi, Y.; Hu, Y.; Ming, Y.; Zou, B. Location optimization of on-campus bicycle-sharing electronic fences. Manag. Syst. Eng. 2023, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacsyürek, M.; Türkdamar, M.U.; Öztürk, C. DSHFS: A new hybrid approach that detects structures with their spatial location from large volume satellite images using CNN, GeoServer and TileCache. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 36, 1237–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keil, J.; Korte, A.; Ratmer, A.; Edler, D.; Dickmann, F. Augmented reality (AR) and spatial cognition: Effects of holographic grids on distance estimation and location memory in a 3D indoor scenario. PFG Photogramm. Remote Sens. Geoinf. Sci. 2020, 88, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Raw, R.S.; Bansal, A. Minimize the routing overhead through 3D cone shaped location-aided routing protocol for FANETs. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 2021, 13, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, T.; Sako, S. 3D human pose estimation model using location-maps for distorted and disconnected images by a wearable omnidirectional camera. IPSJ Trans. Comput. Vis. Appl. 2020, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, K.; Xi, W.; Qu, Y.; He, H.; Guo, Z.; Ma, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, P.; et al. 3D target location based on RFID polarization phase model. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2022, 2022, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Mei, T.; Li, H.; Luo, J. Vision-based fine-grained location estimation. In Multimodal Location Estimation of Videos and Images; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 63–83. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Y.; Xiong, Y.; From, P.J. Three-dimensional location methods for the vision system of strawberry-harvesting robots: Development and comparison. Precis. Agric. 2023, 24, 764–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, J.; Wu, J.; Hao, J.; Qian, H. Enhancing camera-based multi-modal indoor localization with device-free movement measurement using WiFi. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 7, 1024–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, Y.; Noreikis, M.; Ou, Z.; Yl-Jski, A. iMoon: Using smartphones for image-based indoor navigation. In Proceedings of the 13th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 1–4 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.; Chen, J.; Franklin, T.; Zhang, L.; Ruci, A.; Tang, H.; Zhu, Z. Multimodal information integration for indoor navigation using a smartphone. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 21st International Conference on Information Reuse and Integration for Data Science (IRI), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 11–13 August 2020; pp. 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, X.; Li, Z. MSDFL: A robust minimal hardware low-cost device-free WLAN localization system. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 9261–9278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agah, N.; Evans, B.; Meng, X.; Xu, H. A local machine learning approach for fingerprint-based indoor localization. In Proceedings of the SoutheastCon 2023, Orlando, FL, USA, 1–16 April 2023; pp. 240–245. [Google Scholar]



| Area Classification | Location Points Included in Each Category | Sample Quantity in Each Category | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 categories | 1 | 1 × 88 | 38.31% |
| 10 categories | 5 | 5 × 88 | 88.23% |
| Category 6 | 16 | 16 × 88 | 96.48% |
| Category 2 | 50 | 50 × 88 | 99.34% |
| Model | Categories | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 6 | 10 | |
| ResNet | 91.88% | 79.74% | 65.21% |
| MobileNet | 95.60% | 89.86% | 72.83% |
| MobileVit | 99.34% | 96.48% | 88.23% |
| Positioning Algorithm | Cumulative Probability Distribution of Positioning Error/% | Average Positioning Error/m | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Distance Error = 0∼0.4 m | Distance Error = 0∼0.8 m | ||
| Ours | 43 | 64 | 0.67 |
| SCNN | 41 | 59 | 0.77 |
| DFPhaseFL | 37 | 52 | 0.83 |
| MSDFL | 18 | 41 | 1.15 |
| SVM | 10 | 17 | 2.21 |
| KNN | 9 | 19 | 2.38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, L.; Wang, Y.; Pei, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Dong, S. Multi-Granularity and Multi-Modal Feature Fusion for Indoor Positioning. Symmetry 2025, 17, 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17040597
Ye L, Wang Y, Pei S, Wang Y, Zhao H, Dong S. Multi-Granularity and Multi-Modal Feature Fusion for Indoor Positioning. Symmetry. 2025; 17(4):597. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17040597
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Lijuan, Yi Wang, Shenglei Pei, Yu Wang, Hong Zhao, and Shi Dong. 2025. "Multi-Granularity and Multi-Modal Feature Fusion for Indoor Positioning" Symmetry 17, no. 4: 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17040597
APA StyleYe, L., Wang, Y., Pei, S., Wang, Y., Zhao, H., & Dong, S. (2025). Multi-Granularity and Multi-Modal Feature Fusion for Indoor Positioning. Symmetry, 17(4), 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17040597






