Image Region Duplication Forgery Detection Based on Angular Radial Partitioning and Harris Key-Points
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Pixel based techniques are based on detecting the statistical irregularity or pixel level correlations, introduced at the pixel level during the forgery process [1]. Pixel-based approaches are the most popular in image forgery.
- Format based techniques are based on detecting the transformation of image forgery via analysis of JPEG compression artifacts [2].
- Camera based techniques concentrate on detecting the clues of image forgery by exploiting the artifacts introduced by different stages of the image capturing process [3].
- Physics-based techniques are based on estimating the lighting directions and differences in lighting between image regions in the image as a telltale sign of image tampering [4].
- Geometric based techniques are based on estimating principal point of image regions across the image, and the inconsistency between principal points, can be used as evidence of image forgery [5].
- Image retouching manipulates an image by enhancing or reducing certain features of the image without making significant changes on image content [10].
1.1. Block Based Algorithm
1.2. Key Point Based Algorithm
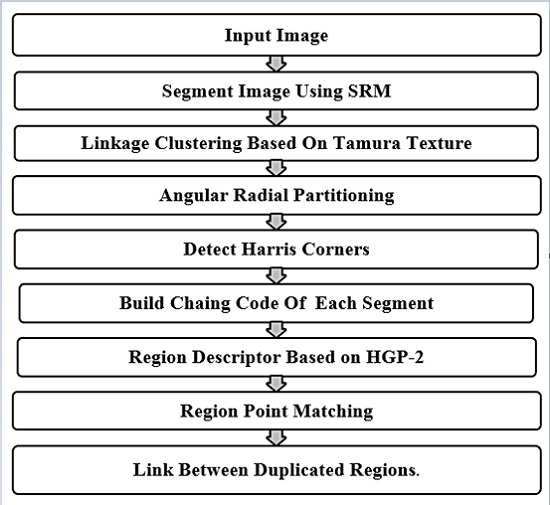
2. Proposed Method
- (1)
- Input the suspicious color image.
- (2)
- Segment the input image of size M × N pixels into image regions using Statistical Region Merging Segmentation (SRM).
- (3)
- Locate centroids of each image region.
- (4)
- Crop each segmented image region to 11 × 11 pixel square image blocks around the centroids of detected regions.
- (5)
- Apply Tamura texture on each square image block.
- (6)
- Cluster similar image regions by texture.
- (7)
- Apply angular radial partitioning (ARP) on each image region indexed by its centroid coordinates in the same cluster.
- (8)
- Convert input image into grayscale and extract key points with Harris detectors.
- (9)
- Calculate the total number of Harris corners in each sector of a circle image region in the same cluster.
- (10)
- Represent the total number of Harris corners by a chain code, and search for closely one-to-one matching between two images regions in the same cluster.
- (11)
- Extract regularity-based features the centroid and around each Harris corners of the image regions that have the same chain code by using an HGP-2 descriptor.
- (12)
- Compute median absolute deviation (MAD) for all HGP-2s of the two matched image regions, and save it in feature vector fv.
- (13)
- Find the Euclidean distance between two corresponding final feature vectors fv and fv’.
- (14)
- Detect and localize the tampered regions.
2.1. Statistical Region Merging Segmentation (SRM)
2.2. Linkage Clustering of Image Regions Based on Tamura
- 1—Locate centroid of each segmented image region.
- 2—Crop each segmented image region to 11 × 11 pixels around its centroid.
- 3—Apply Tamura texture on each square image block.
- 4—Cluster similar image regions by texture.
2.3. Angular Radial Partitioning (ARP)
2.4. Harris Corner Detection
2.5. Region Descriptor Based on Chain Code
2.6. Regularity Based Descriptor
2.7. Region Duplication Localization
2.8. Threshold Selection Value
2.9. The Algorithmic Complexity
3. Experiment Results
- TP (True Positive): forged images detected correctly as forged images.
- FP (False Positive): original images detected wrongly as forged images.
- FN (False Negative): forged images falsely missed as forged images.
3.1. Performance Test
3.2. Robustness Test
3.2.1. JPEG Compression
3.2.2. Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN)
3.2.3. Rotation Copy–Move Forgery
3.2.4. Scaled Copy–Move Forgery
4. Comparison and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silva, E.; Carvalho, T.; Ferreira, A.; Rocha, A. Going deeper into copy-move forgery detection: Exploring image telltales via multi-scale analysis and voting processes. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2015, 29, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-L.; Hsu, C.-T. Detecting recompression of JPEG images via periodicity analysis of compression artifacts for tampering detection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2011, 6, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-T. Source camera identification using enhanced sensor pattern noise. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2010, 5, 280–287. [Google Scholar]
- Kee, E.; O’Brien, J.F.; Farid, H. Exposing photo manipulation with inconsistent shadows. ACM Trans. Graph. 2013, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.K.; Farid, H. Detecting photographic composites of people. In Digital Watermarking; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 19–33. [Google Scholar]
- Moghaddasi, Z.; Jalab, H.A.; Md Noor, R.; Aghabozorgi, S. Improving RLRN image splicing detection with the use of PCA and kernel PCA. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, R.W.; Moghaddasi, Z.; Jalab, H.A.; Noor, R.M. Fractional differential texture descriptors based on the machado entropy for image splicing detection. Entropy 2015, 17, 4775–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddasi, Z.; Jalab, H.A.; Noor, R.M. SVD-Based Image Splicing Detection. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference onInformation Technology and Multimedia (ICIMU), Putrajaya, Malaysia, 18–20 November 2014; pp. 27–30.
- Moghaddasi, Z.; Jalab, H.A.; Noor, R.M. A Comparison Study on Svd-Based Features in Different Transforms for Image Splicing Detection. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Taiwan (ICCE-TW), Taipei, Taiwan, 6–8 June 2015; pp. 13–14.
- Granty, R.E.J.; Aditya, T.; Madhu, S.S. Survey on passive methods of image tampering detection. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Communication and Computational Intelligence (INCOCCI), Erode, India, 27–29 December 2010; pp. 431–436.
- Al-Qershi, O.M.; Khoo, B.E. Passive detection of copy-move forgery in digital images: State-of-the-art. Forensic Sci. Int. 2013, 231, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uliyan, D.M.; Jalab, H.A.; Wahab, A.W.A. Copy move image forgery detection using hessian and center symmetric local binary pattern. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Confernece on Open Systems (ICOS), Melaka, Malaysia, 24–26 August 2015; pp. 7–11.
- Sadeghi, S.H.A.J.; Wong, K.S.; Uliyan, D.; Dadkhah, S. Keypoint based authentication and localization of copy-move forgery in digital image. Malays. J. Comput. Sci. 2016. accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Fridrich, A.J.; Soukal, B.D.; Lukáš, A.J. Detection of Copy-Move Forgery in Digital Images, Proceedings of the Digital Forensic Research Workshop, Cleveland, OH, USA, 5–8 August 2003; pp. 55–61.
- Sheng, G.; Gao, T.; Cao, Y.; Gao, L.; Fan, L. Robust algorithm for detection of copy-move forgery in digital images based on ridgelet transform. In Artificial Intelligence and Computational Intelligence; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 317–323. [Google Scholar]
- Zimba, M.; Xingming, S. DWT-PCA(EVD) based copy-move image forgery detection. Int. J. Dig. Content Technol. Its Appl. 2011, 5, 251–258. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Y. Detection of copy-move forgery in digital images using sift algorithm. In Proceedings of the Pacific-Asia Workshop on Computational Intelligence and Industrial Application, 2008 (PACIIA'08), Wuhan, China, 19–20 December 2008; pp. 272–276.
- Amerini, I.; Ballan, L.; Caldelli, R.; Del Bimbo, A.; Serra, G. A sift-based forensic method for copy–move attack detection and transformation recovery. IEEE Ttans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2011, 6, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battiato, S.; Farinella, G.M.; Messina, E.; Puglisi, G. Robust image alignment for tampering detection. IEEE Ttans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2012, 7, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, J.; Lian, S.; Wang, Z. A passive image authentication scheme for detecting region-duplication forgery with rotation. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2011, 34, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.; Wang, L.; Zou, F.; Yan, W. Fine-search for image copy detection based on local affine-invariant descriptor and spatial dependent matching. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2011, 52, 551–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakar, P.; Sudha, N. Exposing postprocessed copy–paste forgeries through transform-invariant features. IEEE Ttans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2012, 7, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayram, S.; Sencar, H.T.; Memon, N. An efficient and robust method for detecting copy-move forgery. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP 2009), Taipei, Taiwan, 19–24 April 2009; pp. 1053–1056.
- Shao, H.; Yu, T.; Xu, M.; Cui, W. Image region duplication detection based on circular window expansion and phase correlation. Forensic Sci. Int. 2012, 222, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, S.-J.; Kirchner, M.; Lee, M.-J.; Lee, H.-K. Rotation invariant localization of duplicated image regions based on zernike moments. IEEE Ttans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2013, 8, 1355–1370. [Google Scholar]
- Nock, R.; Nielsen, F. Statistical region merging. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2004, 26, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christlein, V.; Riess, C.; Jordan, J.; Riess, C.; Angelopoulou, E. An evaluation of popular copy-move forgery detection approaches. IEEE Ttans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2012, 7, 1841–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Malik, J. Normalized cuts and image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2000, 22, 888–905. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.-W.; Chen, Y.-L.; Chien, S.-Y. Fast image segmentation based on k-means clustering with histograms in HSV color space. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE 10th Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing, Cairns, Australia, 8–10 October 2008; pp. 322–325.
- Sekeh, M.A.; Maarof, M.A.; Rohani, M.F.; Mahdian, B. Efficient image duplicated region detection model using sequential block clustering. Dig. Investig. 2013, 10, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, H.; Mori, S.; Yamawaki, T. Textural features corresponding to visual perception. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1978, 8, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timm, N.H. Applied Multivariate Analysis; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; SPIN 10848751. [Google Scholar]
- Chalechale, A.; Mertins, A.; Naghdy, G. Edge image description using angular radial partitioning. IEE Proc. Vis. Image Signal Process. 2004, 151, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.; Stephens, M. A Combined Corner and Edge Detector. In Proceedings of the Alvey Vision Conference, Manchester, UK, 2 September 1988.
- Trujillo, L.; Legrand, P.; Olague, G.; Lévy-Vehel, J. Evolving estimators of the pointwise hölder exponent with genetic programming. Inf. Sci. 2012, 209, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leys, C.; Ley, C.; Klein, O.; Bernard, P.; Licata, L. Detecting outliers: Do not use standard deviation around the mean, use absolute deviation around the median. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2013, 49, 764–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Mishra, N.; Sharma, S.; Patel, R. Region duplication forgery detection technique based on SURF and HAC. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Lyu, S. Region duplication detection using image feature matching. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2010, 5, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, A.C.; Farid, H. Exposing digital forgeries in color filter array interpolated images. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2005, 53, 3948–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Chain Code (C1) for Region 1 | Chain Code (C2) for Region 2 | Estimated Rotation Angle |
|---|---|---|
| [2 2 1 2 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2] | [2 1 2 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2] | 30° |
| [1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1] | [2 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1] | 60° |
| [1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1] | [0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0] | 90° |
| Threshold Value (θ) | True Positive Rate (TPR) | False Positive Rate (FPR) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.14 | 0.92% | 3% |
| 0.16 | 0.94% | 6% |
| 0.18 | 0.96% | 2.8% |
| 0.20 | 0.96% | 7% |
| 0.22 | 0.96% | 8% |
| 0.25 | 0.96% | 12% |
| Operations | Quality Factors | 90 | 80 | 70 | 60 | 50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal copy move | TPR | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.90 | 0.90 |
| FPR | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 | |
| Rotation | TPR | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.90 | 0.86 | 0.80 |
| FPR | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR)decibel (dB) | 35 | 30 | 25 | 20 | 15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| True Positive Rate (TPR) | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 |
| False Positive Rate (FPR) | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| Title | 64 × 64 | 96 × 96 | 128 × 128 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scale | TPR | FPR | TPR | FPR | TPR | FPR |
| 0.8 | 0.90 | 0.06 | 0.88 | 0.07 | 0.96 | 0.08 |
| 0.9 | 0.94 | 0.08 | 0.96 | 0.08 | 0.96 | 0.08 |
| 1.1 | 0.92 | 0.08 | 0.94 | 0.10 | 0.92 | 0.10 |
| 1.2 | 0.92 | 0.10 | 0.94 | 0.10 | 0.91 | 0.07 |
| Methods | TPR | FPR | Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pan and Lyu’s method [38] | 89.96 | 1.25 | 10 |
| Amerini et al. [18] | 100 | 8 | 4.94 |
| Fridirch et al. [14] | 89 | 84 | 294.96 |
| Popescu and Farid [39] | 87 | 86 | 70.97 |
| Kakar et al. [22] | 90 | 3 | NA |
| Mishra et al. [37] | 73.64 | 3.64 | 2.85 |
| The proposed method | 96 | 2.89 | 4 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uliyan, D.M.; Jalab, H.A.; Abdul Wahab, A.W.; Sadeghi, S. Image Region Duplication Forgery Detection Based on Angular Radial Partitioning and Harris Key-Points. Symmetry 2016, 8, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym8070062
Uliyan DM, Jalab HA, Abdul Wahab AW, Sadeghi S. Image Region Duplication Forgery Detection Based on Angular Radial Partitioning and Harris Key-Points. Symmetry. 2016; 8(7):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym8070062
Chicago/Turabian StyleUliyan, Diaa M., Hamid A. Jalab, Ainuddin W. Abdul Wahab, and Somayeh Sadeghi. 2016. "Image Region Duplication Forgery Detection Based on Angular Radial Partitioning and Harris Key-Points" Symmetry 8, no. 7: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym8070062
APA StyleUliyan, D. M., Jalab, H. A., Abdul Wahab, A. W., & Sadeghi, S. (2016). Image Region Duplication Forgery Detection Based on Angular Radial Partitioning and Harris Key-Points. Symmetry, 8(7), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym8070062