Abstract
Fish fossilisation is relatively poorly known, and skeletal element modifications resulting from predation, burial and diagenesis need to be better investigated. In this article, we aim to provide new results about surface, structural and chemical changes in modern and fossil fish bone. Fossil samples come from two distinct localities of roughly the same age in the Pliocene–Pleistocene Chiwondo Beds adjacent to Lake Malawi. Optical and scanning electron microscope (SEM) observations, energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) analyses and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectrometry were carried out on three categories of fish bones: (i) fresh modern samples collected in the lake, (ii) extracted from modern fish eagle regurgitation pellets, and (iii) fossils from Malema and Mwenirondo localities. A comparison of these data allowed us to detect various modifications of bone surfaces and structure as well as composition changes. Some differences are observed between fresh bones and modern pellets, and between pellets and fossils. Moreover, fossil fish bone surface modifications, crystallinity, and chemical composition from Malema and Mwenirondo differ despite their chronological and spatial proximities (2.5–2.4 Ma, 500 m). In both sites, the post-predation modifications are strong and may hide alterations due to the predation by bird of prey such as the fish eagle. The combination of the used methods is relevant to analyses of diagenetic alterations in fish bones.
1. Introduction
During fossilization processes, bones undergo various modifications of their surface, structure, organic and mineral composition. The nature and aspect of these transformations, both studied qualitatively and quantitatively, can contribute to the general understanding of a site formation, and of the palaeoenvironmental conditions that occurred during the burial and post-burial stages. For instance, modifications at the bone surface can be indicative of the climatic environment during pre-burial stages or provide information about the predators that accumulated the bones. Most taphonomic studies deal with the number and type of preserved bones and teeth, and their external aspect for trampling, breakage, etc. Digestion processes and diagenetic changes have been studied on various African small mammals and some predators [1,2,3,4]. Every predator type may have its own signature [5], but also local environmental conditions are important and drive the skeletal element alterations [6].
Nevertheless, comparisons of modern bones, bones extracted from regurgitation pellets or faeces, and fossils in a same locality are still scarce, especially regarding the structure and chemistry. The paucity of data available on the chemical compositions of fish bones, whether they are modern, extracted from regurgitation pellets, or fossils, is even greater. Thus, it is not known whether the diagenetic behaviour of fish bones is similar to that of mammal bones.
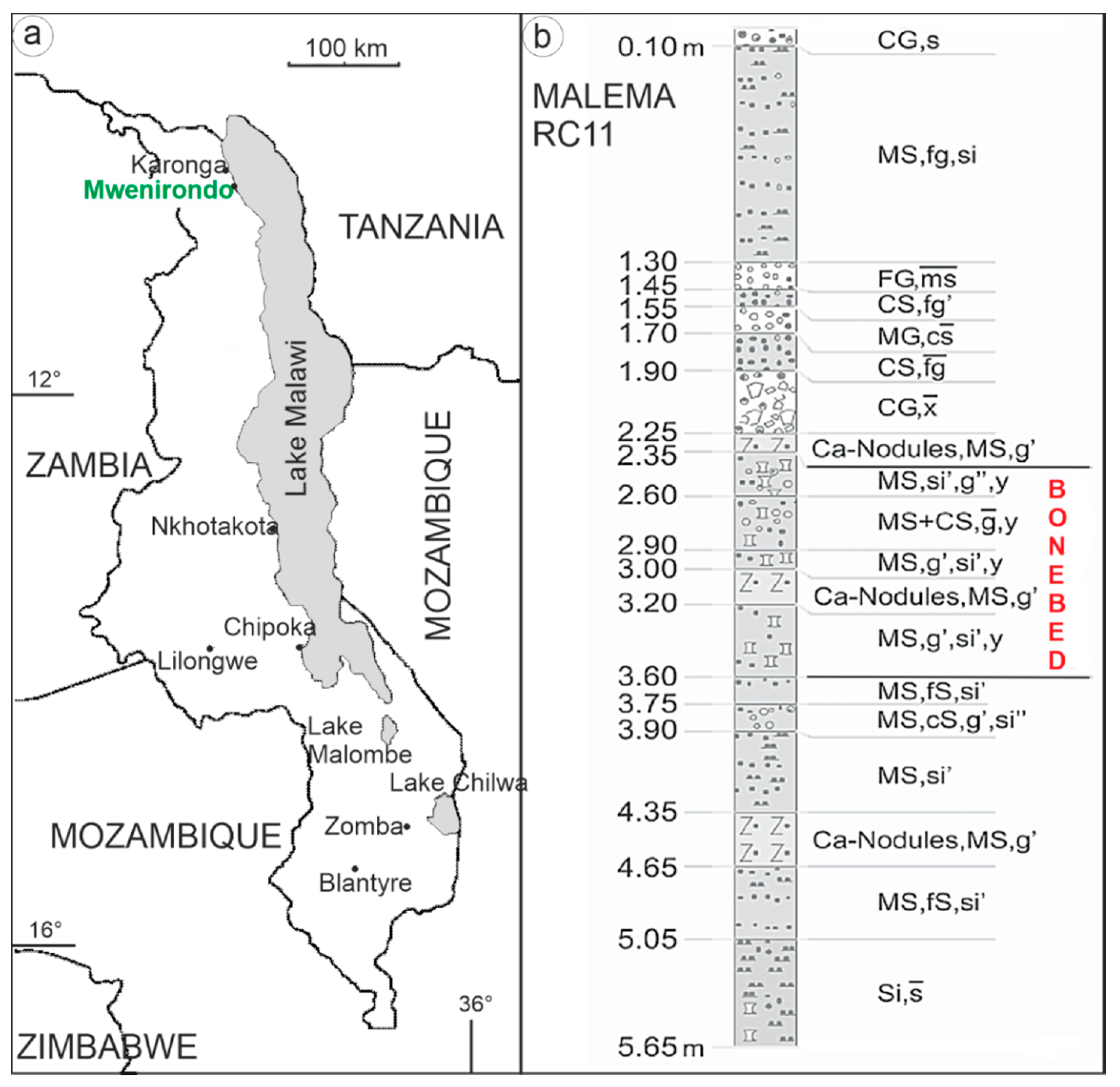
Among the Pliocene and Pleistocene hominid bearing deposits of Africa, lake-margin sites are mainly situated along the Rift Valley in East Africa. Pliocene–Pleistocene Chiwondo Beds in the Karonga District of the Northern Region, Malawi, combine an area of about 70 km North–South and 10 km East–West (Figure 1). At least 145 fossil localities yielded remains of large mammals and other vertebrates. Among them, Malema and Mwenirondo have yielded fishes, crocodiles, and large mammals [7,8]. In 1996, the remains of Paranthropus boisei were recovered, making Malema the southernmost locality in the African Rift Valley yielding a robust australopithecine. Just north of Malema, the locality Mwenirondo yielded another hominin fossil assigned to Homo rudolfensis [9].
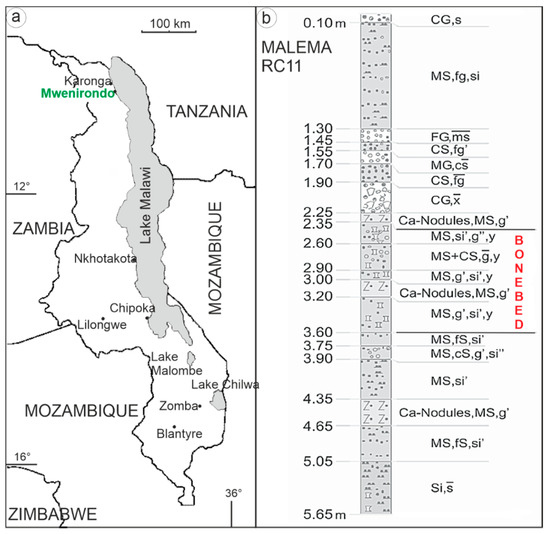
Figure 1.
(a) Map showing the main location in the northern part of Malawi. Note that Malema (not indicated here) is very close from Mwenirondo (500 m). (b) Lithological section, RC11 locality of unit 3A, showing the bone bed layers. Si = silt, si = silty; fs = fine sand; ms = middle sand; cs = coarse sand; s = sandy; fg = fine gravel; mg = middle gravel; cg = coarse gravel; g = gravelly; x = stone; y = boulder; quantity of sediment fraction ‘ = slight, “ = very slight, — = strong. Redrawn from [8].
Despite their equivalent age (between 2.5–2.3 Ma) and a close proximity (500 m), preliminary research has shown that both sites are characterized by different sedimentological and faunal assemblages, suggesting different taphonomic histories [10,11]. Oxygen (δ18O), carbon (δ13C), and clumped (Δ47) isotope data on palaeosoils, hominins, and selected fauna elucidate an unexpected diversity in the Pleistocene hominin diet in the various habitats of the East African rift system. Stable carbon and oxygen isotope data of hominin fossil tooth enamel from the Malawi rift show that ca. 2.4 Ma H. rudolfensis and P. boisei included a large fraction of C3 food resources in their diets, while thriving in relatively cool and wet wooded savanna ecosystems along the western shore of palaeolake Malawi [12].
In previous studies, only mammals and reptiles collected in these two localities were taken into account, despite fish remains representing about 25% of the vertebrate remains [7]. So far, Chiwondo fishes have been studied to reconstruct the origins of the modern Lake Malawi ichthyofauna. Stewart and Murray [13] pointed out that the Chiwondo fish assemblages at Malema and Uraha are very different, and composed mainly of East Coast Africa province rivers, in particular members of the Rufiji River system from South Tanzania. In freshwater sites, fossil fishes may have important palaeoenvironmental implications indicating, for instance, the nature of palaeowater properties, salinity, and depth [14,15,16]. Their preservation shows the presence of alkaline versus acidic water conditions: soft tissues are affected by pH [17], and calcareous otoliths are not preserved in acidic water. Lacustrine fish may be ingested by hominids and their digested remains may have significance for the overall faunal assemblages in fossil sites [18,19,20,21]. They are also common prey of some birds, such as the African fish eagle [22,23]. These accumulations of dejections or regurgitation pellets can be fossilized but potential structural and chemical changes due to digestive processes are still unknown for fish bones. Only some recent works have shown the effect of digestion on the surfaces of fish bones ingested by Lutra or Bubo bubo [24,25], but these studies did not take in account the degradation of bone tissue as well as its chemistry.
In the present work, we compare the structure and composition of fresh fish bones, fish bones extracted from modern regurgitation pellets of the fish eagle, and fossil samples collected in Malema and Mwenirondo sites. The fossil material sorted from sediment specifically collected for taphonomical purposes was not included in the fish fossils collected for paleontological curation [13], which is currently the focus of another study (Otero et al. in prep.).
Due to the paucity of microstructural and chemical data on the three stages occurring in the geological history of fossil fish bones (capture, digestion, diagenesis), several interrelated questions arise about the fossil fishes from Malawi: are the effects of digestion and diagenesis different, allowing them to be assigned to one of these processes? Are traces of digestion destroyed and/or hidden by the fossilisation process or are they still visible in fossil remains? Are the used techniques suitable for such studies? Is the previous hypothesis, established from studies of mammalian remains that Malema and Mwenirondo taphonomic histories differ, confirmed or denied by our study of the fish bones?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Recent fishes were collected in Lake Malawi (580 km long, 30–80 km wide) close to the Ngara village (30 km south of Malema) in shallow waters. Three long bones and three vertebrae from Oreochromis (Cichlidae) and Bagrus (Siluriformes) were analysed.
Fish-eagle (Haliaeetus vocifer) pellets were collected on Namalenje Island close to Salima at Lake Malawi. Their content comprises fish bones and crab elements without small mammals. The bone surfaces were observed by a low-magnification binocular microscope and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Four fish bones (vertebrae and spines) extracted from pellets were analysed for chemical composition.
The fossil fishes were collected by screening using a 0.5 mm sieve in the Malema RC-11 locality and Mwenirondo. Furthermore, 200 fossil elements, including bones and teeth, were collected in the fish assemblage of Malema, and about 300 in the Mwenirondo assemblage.
The Chiwondo and Chitimwe Beds represent transgressive–regressive sedimentary cycles, consisting of five depositional units [26]. Each unit is split by angular and erosional unconformities or paleosols, the latter indicating lake level changes. According to these authors, the main sedimentary facies elements are braided and meandering river systems, delta deposits, lake beds, alluvial fans and aeolian sands. The overall thickness is about 130 m. The age of the Chiwondo Beds still relies on faunal correlation with radiometrically dated biostratigraphic units in Eastern Africa. The age range refers to radiometric well-dated volcanic tuffs within the Koobi Fora and Shungura Formations [27,28]. The age spectrum of significant units 2 and 3 of the Chiwondo Beds lies about >4 Ma to <1.5 Ma [29,30]. The two studied localities yielded important faunal mammal remains, from which relative faunal datings between 2.7–1.8 Ma (biozone 3A-2) have been proposed, and that also suggested they may have been contemporaneous [9,31].
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Sample Preparation
Fresh fishes were air dried. The main part of the flesh was removed with a scalpel, taking care not to contact the surface of the bone. The final stage of cleaning was a bath of commercial bleach for 1 h with intermittent ultrasonication. Bones were then rinsed in tap water and air dried. Flesh is not fully destroyed, so the bone is presumed not to be affected.
Pellet bones were extracted from the pellets by dry dissection with a pair of tweezers, then ultrasonically cleaned in tap water, and dried at room temperature.
Fossil bones were first cleaned using an ultrasonic water bath to remove the sandy particles. They were then cleaned with a solution of dilute formic acid (5%) for 1 min or 1.5 min at room temperature to remove excess sediment. They were rinsed in tap water and air dried at room temperature.
2.2.2. Fish Taxonomic Identifications
In the fish eagle pellets, most material is composed of bony elements. Five morphological types of cichlid spines, three types of cichlid vertebrae and two types of catfish spines were observed together with fragments of cichlid jawbone fragments bearing minute teeth. Altogether, they allow us to identify the presence of at least 3 species of cichlids and 2 species of catfish. The element dimensions vary from 1 mm (some vertebrae) to 20 mm (bigger spine length), which correspond to fishes smaller than 20/25 cm in length; the largest one is a Bagrus sp. catfish.
Most of the fish remains found in the fossil sample are teeth that belong mainly to cyprinid and alestid fish, and some of them to cichlids. Other identified remains are bones, mainly fin spines and vertebrae of siluriform (cf. Bagrus and cf. Clarias/Heterobranchus) and of cichlid fish). The material identified is less abundant in Malema where cichlid vertebrae are absent, and catfish remain undetermined. Skeletal elements measure from less than 5 mm up to 1 cm in Mwenirondo and up to 2 cm and larger in Malema.
2.2.3. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
Scanning electron microscope observations were completed on gold or carbon coated samples with a Philips XL30 SEM (Philips, Eindhoven, Netherlands) at 25 keV, a JEOL JSM25 (Jeol Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), and a HITACHI SU3500 (Hitachi Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) at 10 kV. Untreated natural and broken surfaces were cleaned using a water ultrasonic bath. When the sample was embedded in a sedimentary deposit, the surface was cleaned using a formic acid solution (5%, 10 s). Details of the cleaning procedures are given in the figure captions.
2.2.4. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
All spectra were recorded at 4 cm−1 resolution with 16 scans with a strong Norton–Beer apodization on a Perkin-Elmer Frontier Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR) (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA), from 4000 to 450 cm−1. The spectrometer was equipped with a diffuse reflectance accessory that permits DRIFT (diffuse reflectance Infra Red Fourier-Transform) measurements with high sensitivity on powders. All spectra were corrected by the Kubelka–Munk function.
Powdered bones and potassium bromide (KBr) were mixed (about 5% powdered bone in KBr) and loaded into the sample cup. A thin glass strip was pulled across the top to produce a flat surface. Increasing density by applying pressure to the sample surface increases the response of the spectra, and thus no supplementary handling was necessary. Before a spectrum was run, the height of the sample cup was adjusted by using the alignment routine provided by Perkin-Elmer Spectrum software (for the model PE FTIR 1600), so that a maximal signal throughput was obtained. A background spectrum was measured for pure KBr. Sample spectra were automatically ratioed against the background to minimize CO2 and H2O bands; they were normalized on the v3PO4 band.
Two standards were used to assign the mineral bands (geological apatite) and organic bands (commercial type I collagen).
Several ratios were calculated from the infrared spectra. Crystallinity index (CI), also called splitting factor, can be calculated from height 606 cm−1 band + 565 cm−1 band/595 cm−1 band intensities [32,33]. CO3/PO4 index was based on the band intensity at 1457 cm−1 (CO23−) and 1037 cm−1 (PO34-) [34]. Carbonate ions substitute for PO43 (type B) and OH (type A) in bioapatites [35,36]. The amount of type B carbonate to phosphate (BPI) was calculated using the ν3 carbonate band at 1415 cm−1 and the ν4 phosphate band at 605 cm−1 [37]. The amount of type A carbonate to phosphate (API) was calculated using the ν3 carbonate band at 1540 cm−1 and the ν4 band at 605 cm−1. Fluoridated apatites show two bands close to 718 and 692 cm−1 [38]. Samples enriched in fluorine have a high 605/567 cm−1 ratio and a strong band at 1096 cm−1 [32]. To estimate the changes in organic and mineral composition, the intensity ratio of two amide bands (amide I and amide A) to phosphate and carbonate ions has been calculated [39].
2.2.5. Chemical Analyses
Data were obtained on an analytical scanning electron microscope (Philips 505 SEM, Philips, Eindhoven, The Netherlands) equipped with an energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS). Quantitative analyses were obtained using a Link AN10000 ZAF/PB program that estimates peak-to-background ratios. The ZAF/PB method can be applied to specimens with rough surfaces, essential for the etched surfaces (see below). Small pieces of bones were embedded in an epoxy resin and polished using various grades of diamond paste. The polished surfaces were lightly etched in 5% formic acid for 15 s to reveal microstructural details of the samples. The locations of the analysed points with respect to the structural features were therefore precisely known. Cobalt was used to provide the EDS calibration, and measurements were made using a live time of 100 or 200 s with an accelerating voltage of 15 kV. The electron beam was optimised to achieve a small spot size that was estimated to have a diameter of 100 nm. The elements Na, Mg, P, S, Ca, Mn, Fe and Sr were selected to illustrate aspects of bone composition. Several (>10) microprobe EDS analyses were made at various locations on each sample, and analyses averaged to obtain an “individual” mean. Three fresh bones and four bones extracted from modern pellets were used. Seven bones came from Mwenirondo, fourteen from Malema. All samples were carbon coated.
2.2.6. Statistical Methods
Although several microprobe EDS analyses were made at various locations on individual bone fragments, we have calculated the mean values as being representative of the sample. Thus, the standard deviations are higher than if they had been calculated from punctual analyses. Due to the small size of the analysed individuals, the comparison of chemical contents was estimated using the non-parametric Mann–Whitney test, at α = 5%. Only those elements with concentrations above the detection limit of the microprobe were used. Multivariate analyses (principal component analyses) were based on correlation matrices, so that the statistical weights of elements with high concentrations (i.e., Ca) were moderated within the software (Statgraphics XVI). The concentrations of elements were assigned as the variables, and the bone fragments assigned to individuals.
3. Results
3.1. Bone Surface Preservation and Microstructures
3.1.1. Modern Fresh Bones
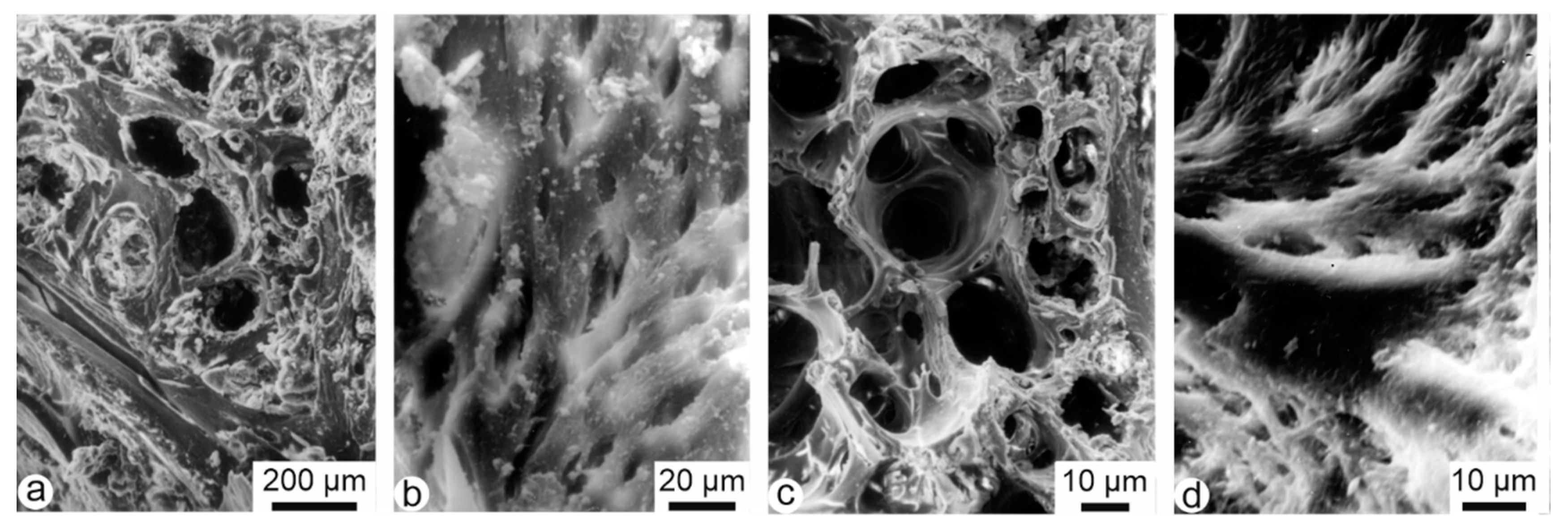
Due to the mild cleaning process, remains of flesh and organic components are present in the holes of the fresh bones of Bagrus and Oreochromis (Figure 2a,c). The mineralized collagen fibres are locally visible (Figure 2b,d). From structural data, Bagrus and Oreochromis are similar.
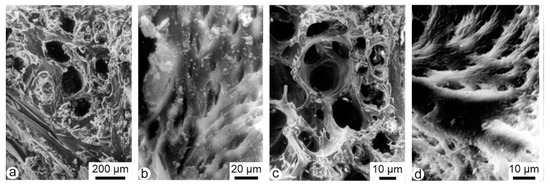
Figure 2.
Structure of fresh fish bones, showing the natural cavities and the mineralized collagen fiber bundles in vertebrae of Bagrus (a,b), and Oreochromis (c,d).
3.1.2. Fish-Eagle Pellets
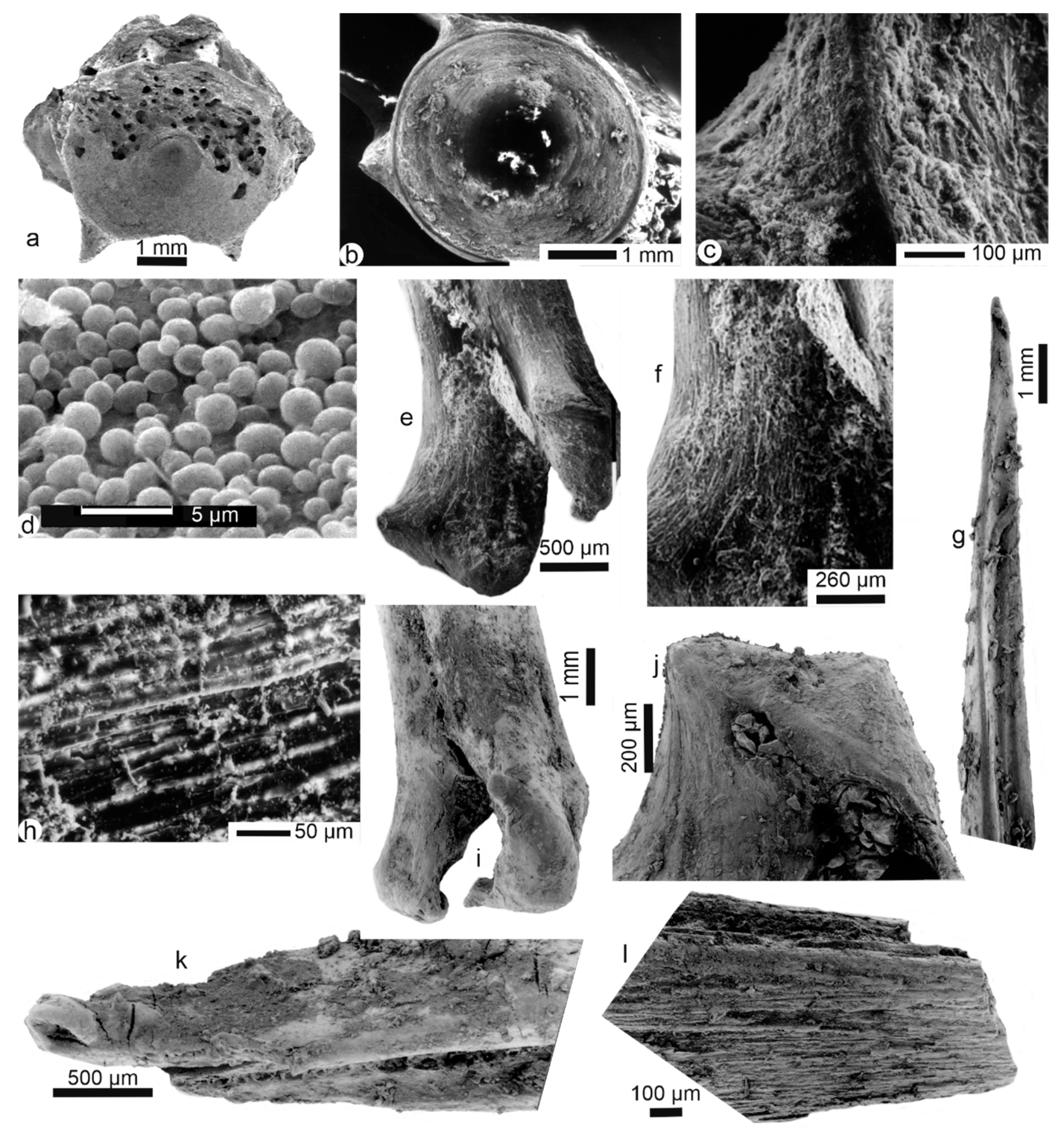
Most bones are fish spines and vertebrae. Vertebrae and fins on their pterygiophores are sometimes found articulated, and fragile elements such as scales and skull bones are preserved together with otoliths (data not shown). Some vertebrae are strongly digested, showing the alveolar structure (Figure 3a), whereas some others seem better preserved (Figure 3b). The central part of the vertebrae does not seem compressed (Figure 3b), contrary to those found in mammalian faeces and rejection pellets of birds of prey [24]. Samples are still embedded in remains of flesh (Figure 3c,h). The outer surfaces of the bones are also coated by secondary deposits, comprising round granules of unknown origin (Figure 3c,d). One digested spine shows the characteristic twisting of its extremity due to digestion and is coated by a secondary deposit (Figure 3k). Bone surfaces do not appear polished (Figure 3e–g,i–l); some longitudinal cracking occurs as if the pellets were subject to slight weathering during exposure on the ground of the island (Figure 3l). Some bones present a rather strong degree of digestion, with destroyed outer layers on the diaphysis (Figure 3h). Globally, bones and teeth are a little weathered.
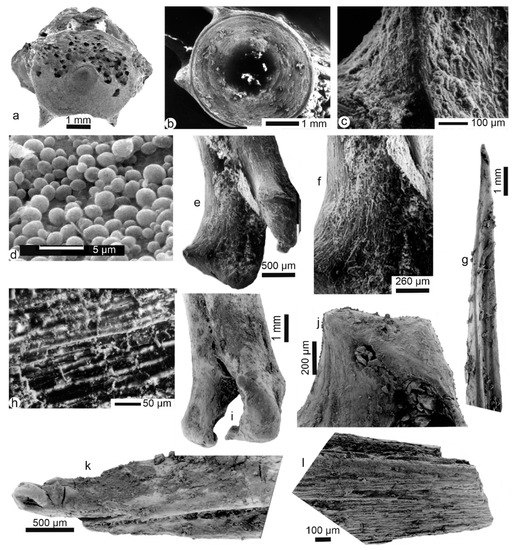
Figure 3.
Fish bones from eagle owl pellets, Namalenje Island, Salima, Malawi Lake border. (a) Vertebra centrum showing digestion holes, and broken apophyses. (b) Outer surface of a light digested vertebra showing the central hole and broken apophyses. (c) Outer surface of a vertebra showing secondary deposits. (d) Detail of the central part of Figure 3b, showing rounded particles. (e), (f) Secondary deposits and remains of flesh on the articular extremity of a spine. (g) Well preserved spine with punctual secondary deposits. (h) Surface of a long bone showing erosion of the external layers. (i) Secondary deposits on the articular extremity of a spine bone with polished epiphyses and tiny holes resulting from very light digestion. (j) Detail of the articular zone of another spine with some small holes filled with secondary deposits. (k) Secondary deposits on a digested spine with twisted extremity. (l) Eroded (weathering) surface of a broken spine.
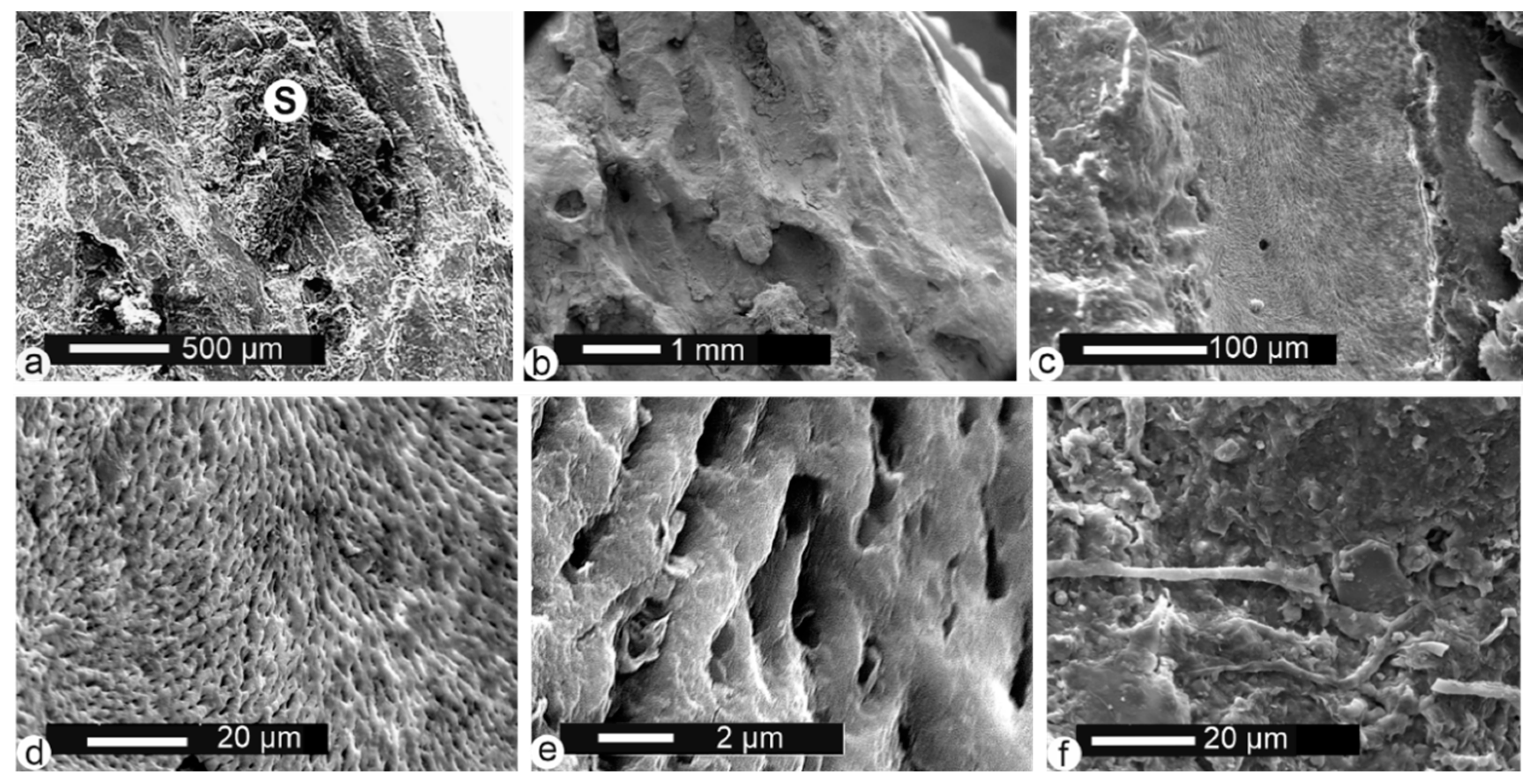
3.1.3. Fossil Bones
Malema fossil fish bones: vertebrae from Malema show a rough surface with no apophyses preserved (Figure 4a). Some spine bones show a smooth surface with rounded extremities and small holes on the articular surfaces, which indicate light stages of digestion and/or transport polishing (Figure 4b,c). All spines are broken but some fractures are rectilinear (Figure 4d,e). On their surface, one can see traces of bone flaking, desquamation (Figure 4f,h) and trampling (Figure 4e). Secondary deposits (sediment) are visible in the holes (Figure 4b,c), and coating is relatively frequent (Figure 4e). The structure of the bone is visible (Figure 4h) but not preserved when the outer layers are destroyed (Figure 4g).
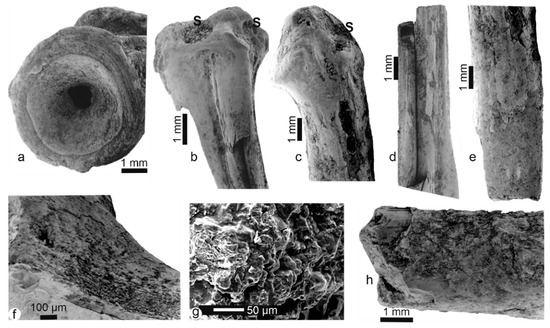
Figure 4.
Malema fossil bones. (a) Centrum of a vertebrae showing rounding and desquamation and perforated centre. (b,d) Spines displaying very light digestion (polishing and small holes) on articular zones accompanied by desquamation. (c) Spine showing polishing and holes of light digestion on the articular extremity. (e) Spine fragment displaying old breakage, rounding and desquamation. (f) Alteration of the bone structure near an articular extremity of the spine, the outer layers being destroyed. (g) Surface of a broken bone showing a strongly modified structure, cleaned using an ultrasonic bath and H2O. (h) Desquamation on a broken bone. S: sediment.
Detailed pictures show large differences in the surface of the samples: the etched surface of some bones is encrusted with sediments (Figure 5a), while some others are better preserved and show only a thin sedimentary coating (Figure 5b). The bone structure is well preserved in blood canals (Figure 5c–e). Filaments (fungi?) are visible (Figure 5f).
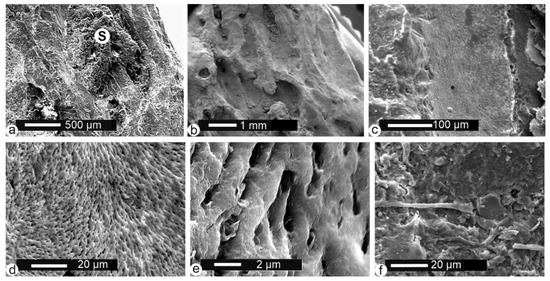
Figure 5.
Fossil bones from Malema. (a) Secondary deposits on an etched surface of a long bone cleaned using an ultrasonic bath and H2O. (b) Alveolar structure of the same long bone. (c) Fracture showing the inner surface of a blood vessel. (d,e) Detail of Figure 5c, showing the preserved structure of the bone. (f) Organic filaments (fungi?) on the outer surface; sample cleaned using an ultrasonic bath and H2O. S: sediment.
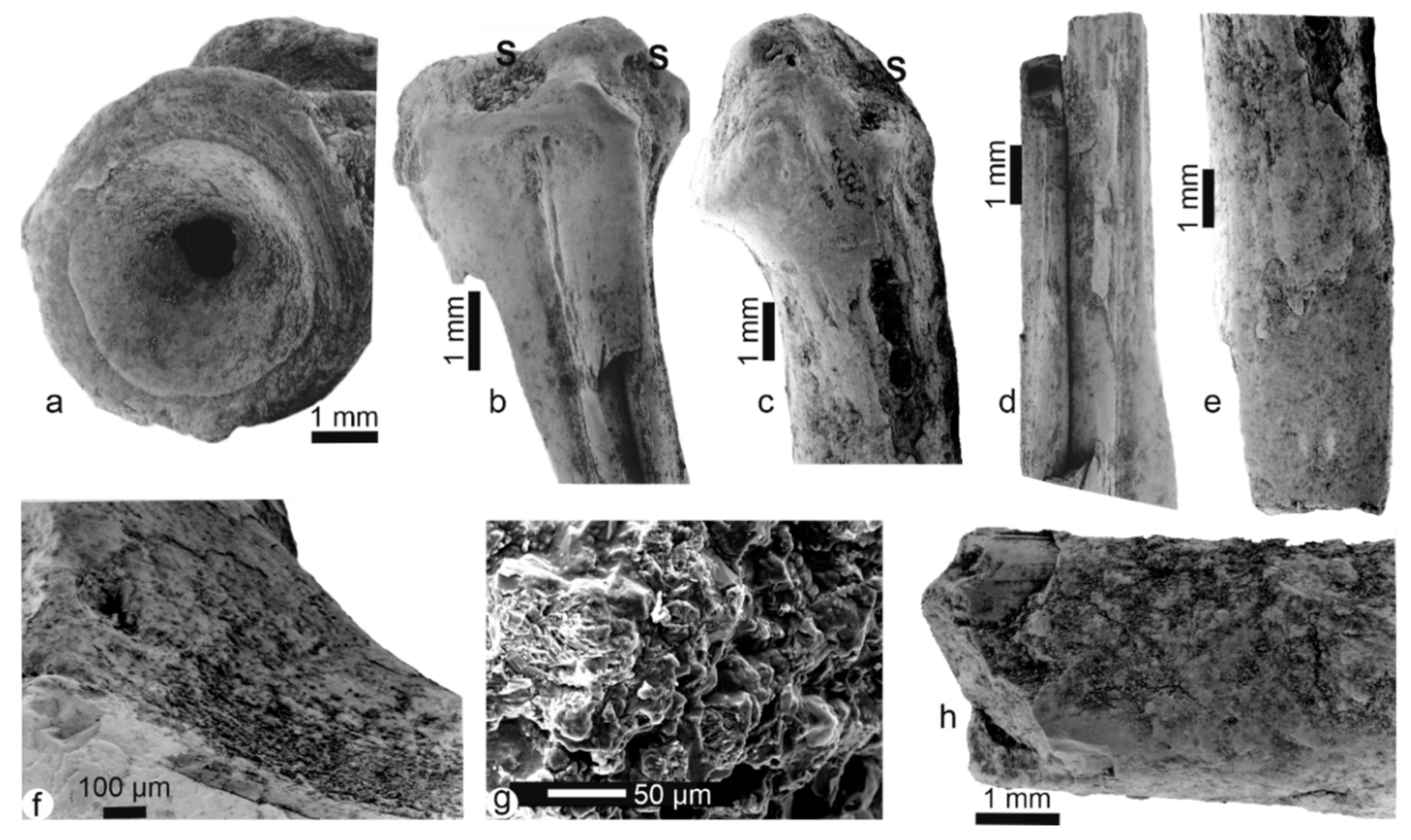
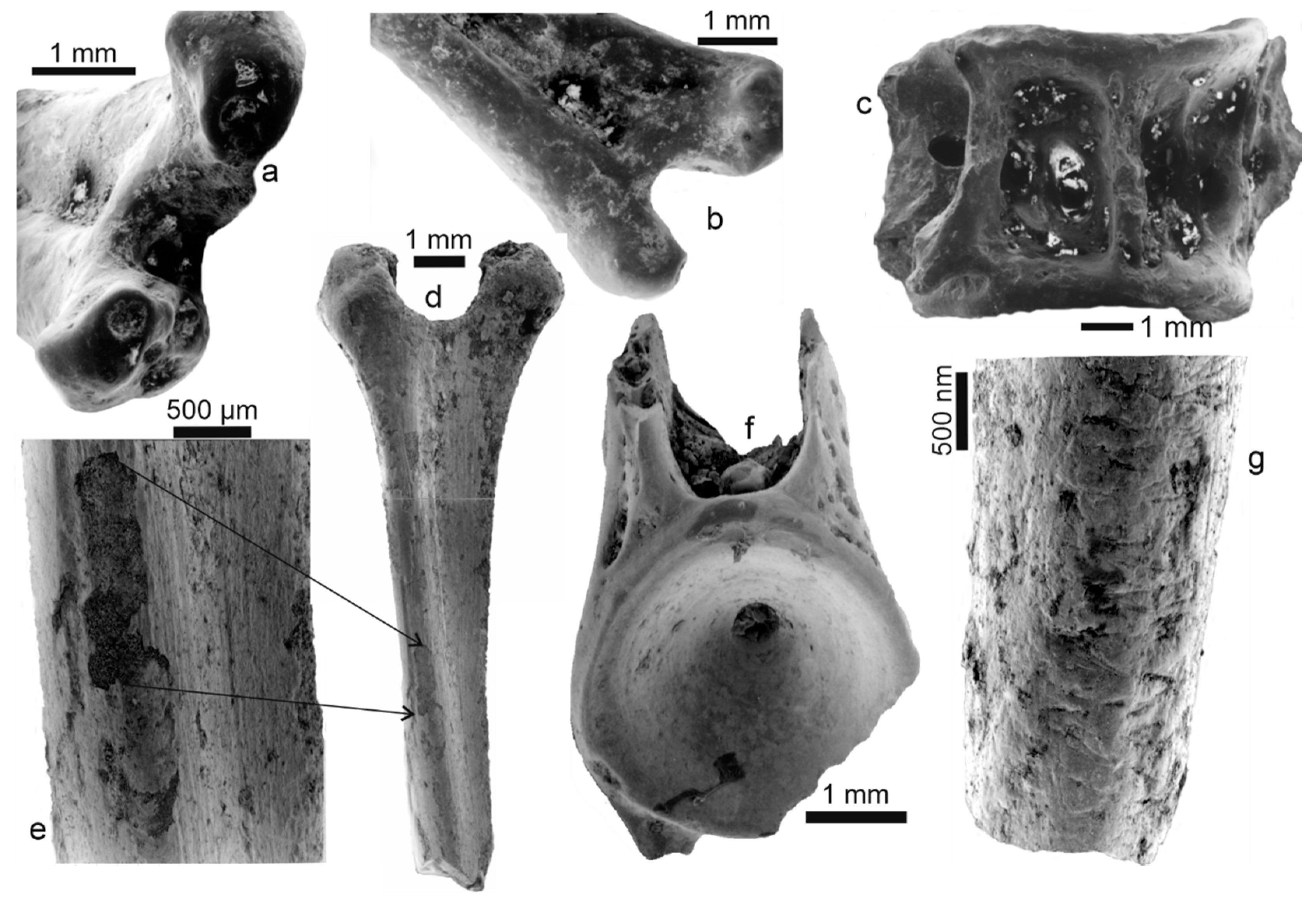
Mwenirondo fossil bones: visually as well as under SEM observations, there is a higher proportion of rounded smooth polished bones associated with more rough specimens displaying various alterations. Some fish bones have a rounded surface with holes in the epiphysis and some very light weathering and desquamation (Figure 6a,b,d,e). Sedimentary deposits are abundant in both spines and vertebrae (Figure 6a–d,f). In the same bone, some zones of the surface are smooth, whereas others are rugose (Figure 6e). The rugose surface of some samples seems generated by desquamation (Figure 6g).
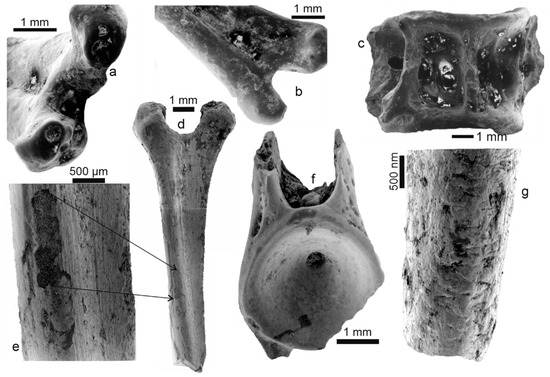
Figure 6.
Fossil bones from Mwenirondo. (a) Fin spine articular head with sedimentary particles on articular zones despite the cleaning process (formic acid 5% for 1 min). (b) Posterior view of the same bone. (c) Lateral view of a vertebra with small sedimentary particles. (d) Spine bone displaying traces of digestion on the articular extremity (holes, polished surfaces) but also a light weathering, light desquamation, and dissolution of the surface. (e) Detail of Figure 6d, showing the rough surface of a spine bone with irregular eroded zones. (f) Vertebra centrum with a polished surface and tiny holes on the apophyses. (g) Spine bone ending with a transvers fracture and showing a rough surface with desquamation.
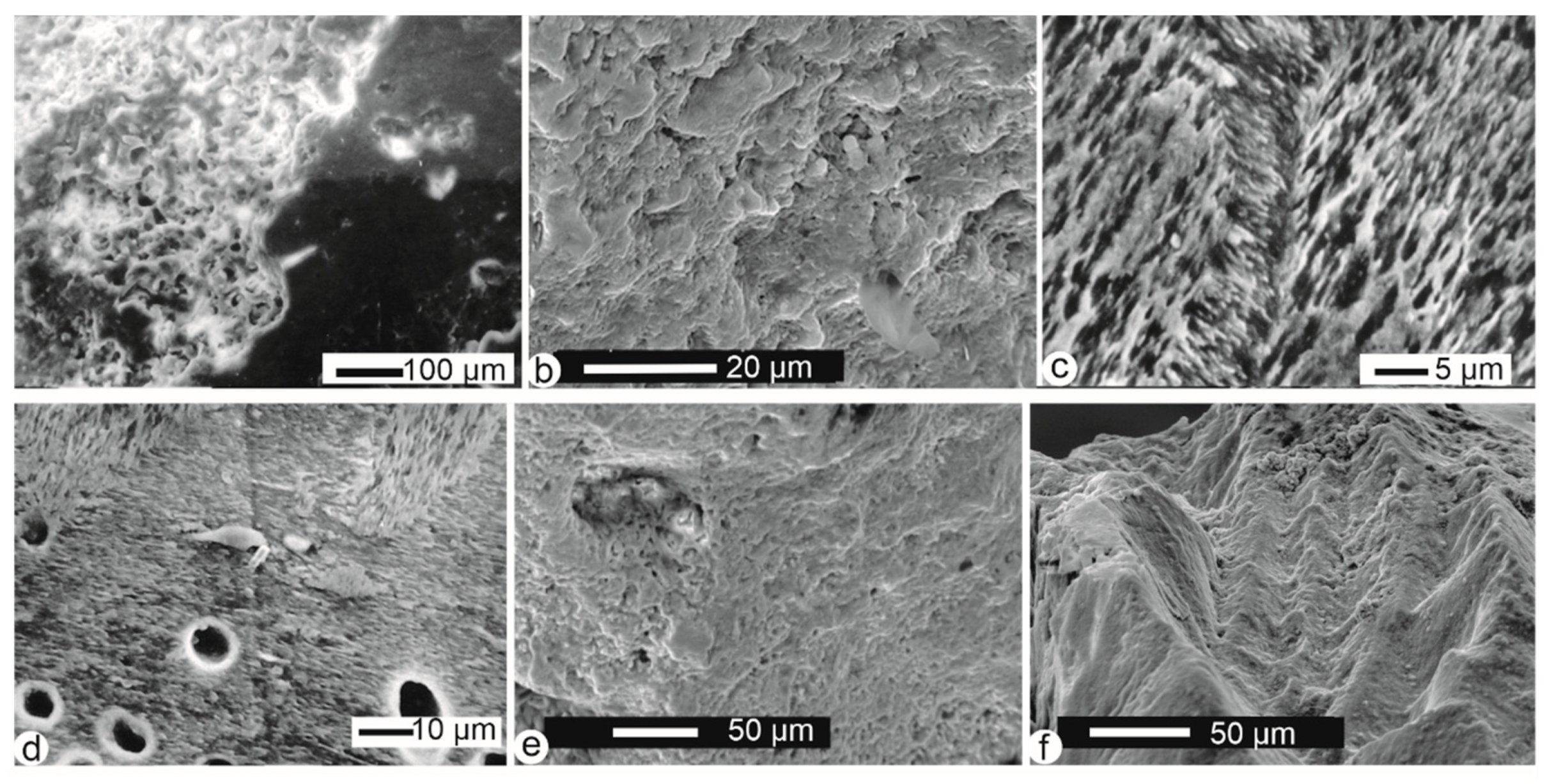
Some bones, vertebrae included, from Mwenirondo show both a smooth surface and a rather polished aspect with pitting that could result from digestion (Figure 6c,d,f), associated with a strong erosion (Figure 7a). The inner structure of the bone is usually not visible in old fractures (Figure 7b), but polished and etched surfaces show the elongated crystallites with different orientations (Figure 7c,d). Nevertheless, holes are abundant, with a diameter consistent with those of boring fungi. The articular zone is rounded, with the bone structure not clearly visible (Figure 7e). In some samples, fractures have a zigzag outline, and display a granular surface due to digestion and/or desquamation (Figure 7f).

Figure 7.
Fossil bones from Mwenirondo. (a) Detail of the surface of vertebra shown in Figure 6c with polished and eroded zones. (b) Fractured long bone: the outer layers have been destroyed and the structure of the bone is not preserved; cleaned using an ultrasonic bath and H2O. (c) Polished and etched surface of a large vertebra showing the preserved inner structure. (d) Holes in the sample shown in Figure 7c. (e) Small holes on the altered articular zone of the sample shown in Figure 7b. (f) Fracture of the sample of Figure 7b, showing the strongly modified bone structure.
The large variability of the morphological and structural preservations of the fossil fish bones suggests a complex surperimposition of predation damages and post-predation alterations, hiding the possible differences in the taphonomic histories of Malema and Mwenirondo sites.
3.2. Chemical Composition
3.2.1. Bulk Composition
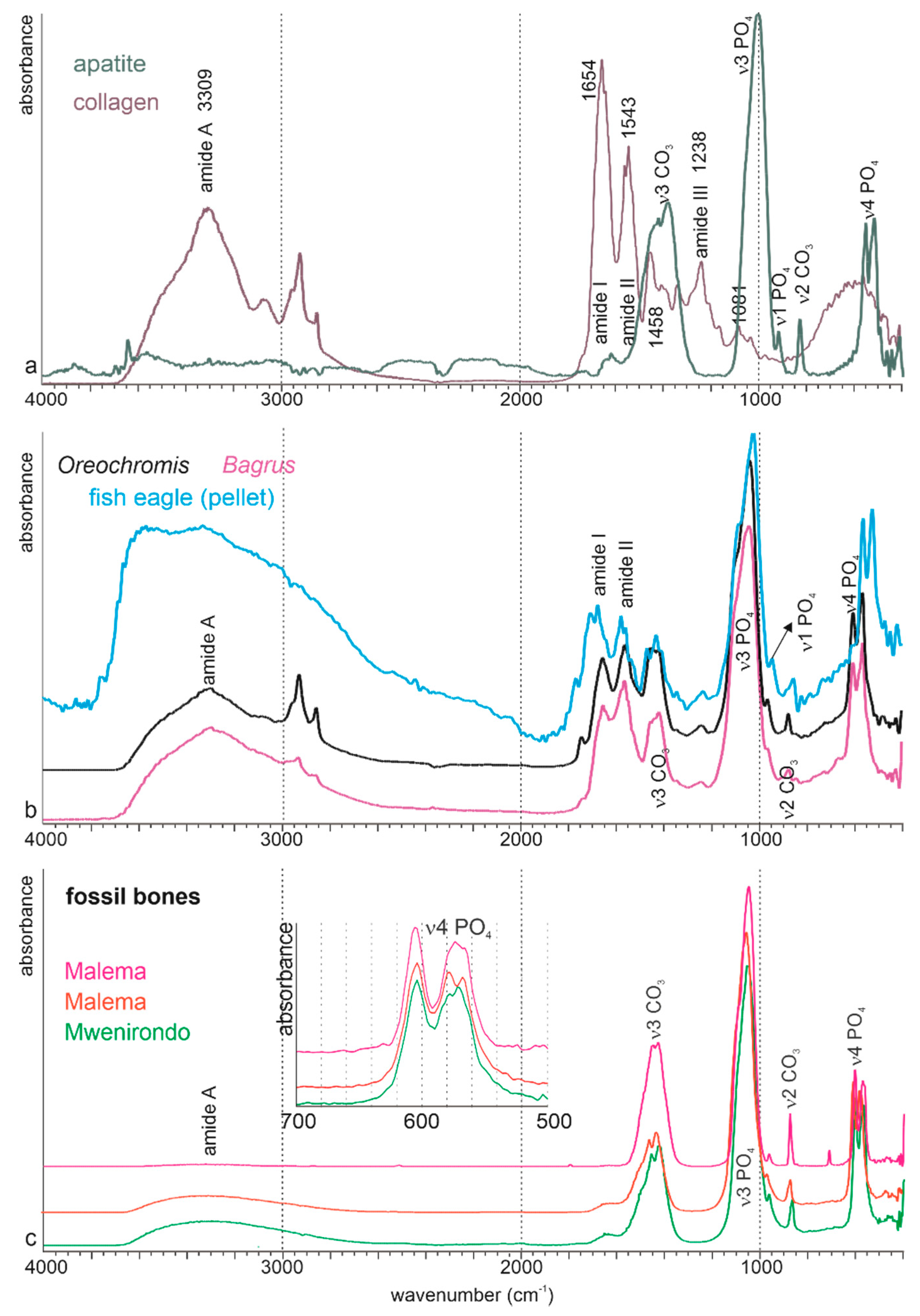
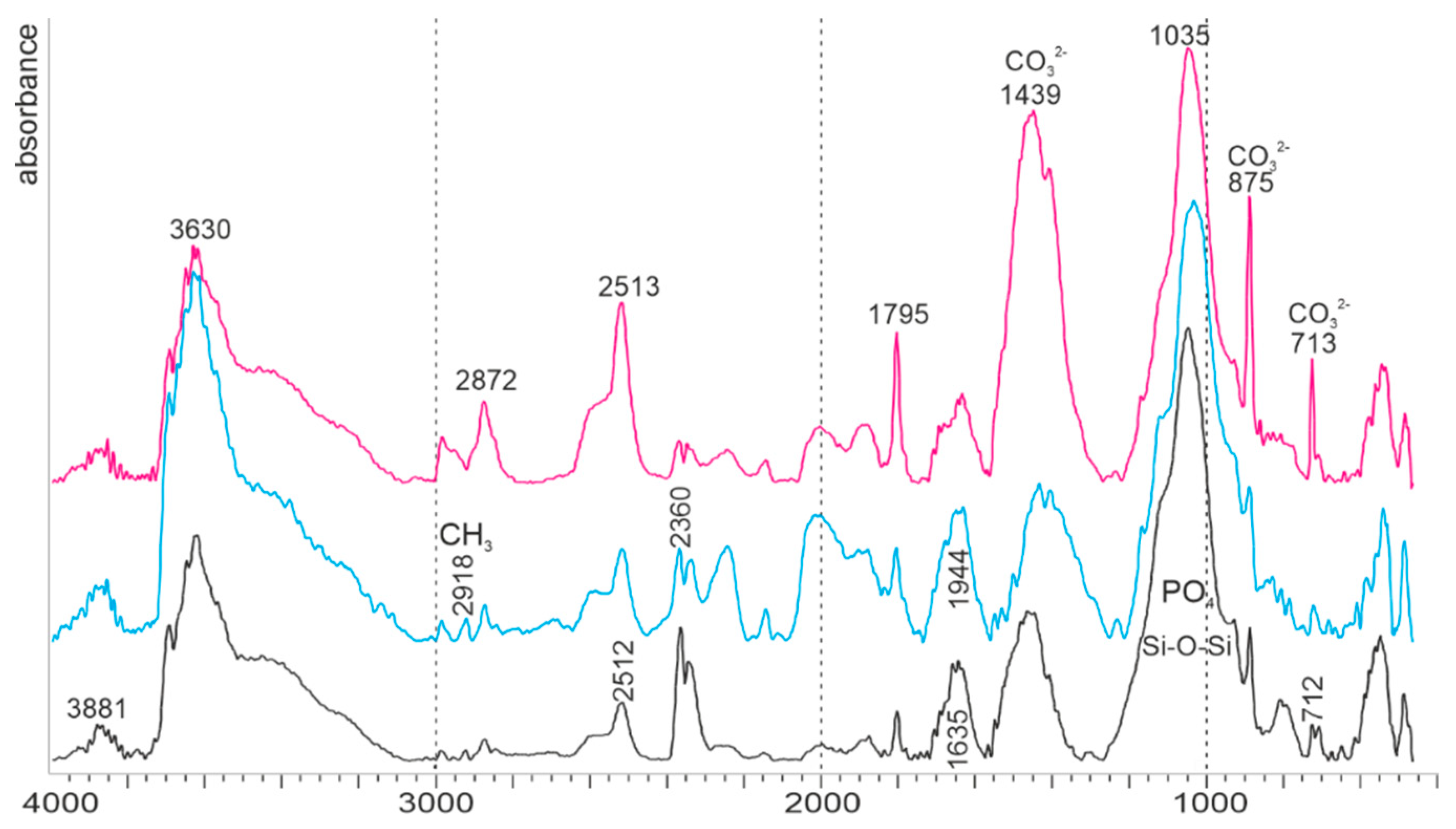
The bulk composition is obtained by infrared analyses. The main components of bones are apatite and collagen. Apatite is a family of phosphate minerals of variable chemical composition. The three common minerals of the apatite family are hydroxylapatite, chloroapatite, fluoroapatite. A typical spectrum of apatite shows weak bands near 3500 cm−1 assigned to OH (stretch), PO43− bands at 1087 cm−1 and 1040 cm−1 (ν3), at 962 cm−1 (ν1 symmetrical stretch), 600 and 570 cm−1 (ν4). Bands assigned to CO32− are at 878–878 cm−1 (ν2), 1410–1460 cm−1 (ν3). These main features are visible in the geological apatite (Figure 8a).
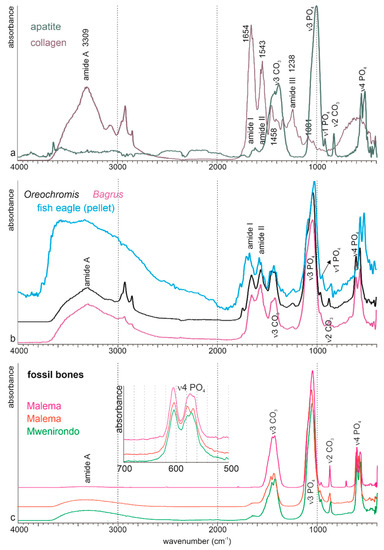
Figure 8.
Fourier transform infrared spectrometry on powdered samples of fish bones. (a) Geological apatite and commercial collagen type B used as standards. (b) Modern bones: two fresh bones (Bagrus and Oreochromis) showing the mixed organic + mineral composition. The composition of a bone extracted from a modern pellet is modified. (c) Examples of fossil bones, showing the loss of organic components. Insert: detailed zone used for calculation of the crystallinity index.
The main bands (amide) of type I collagen are well visible (Figure 9a).
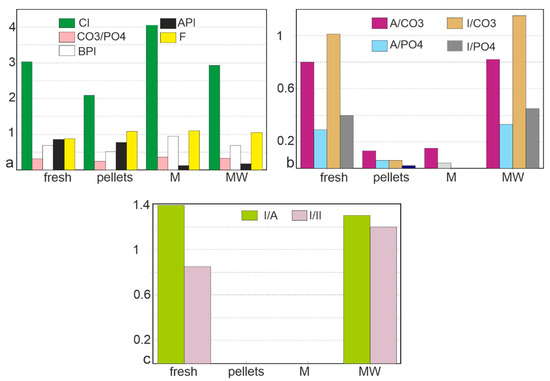
Figure 9.
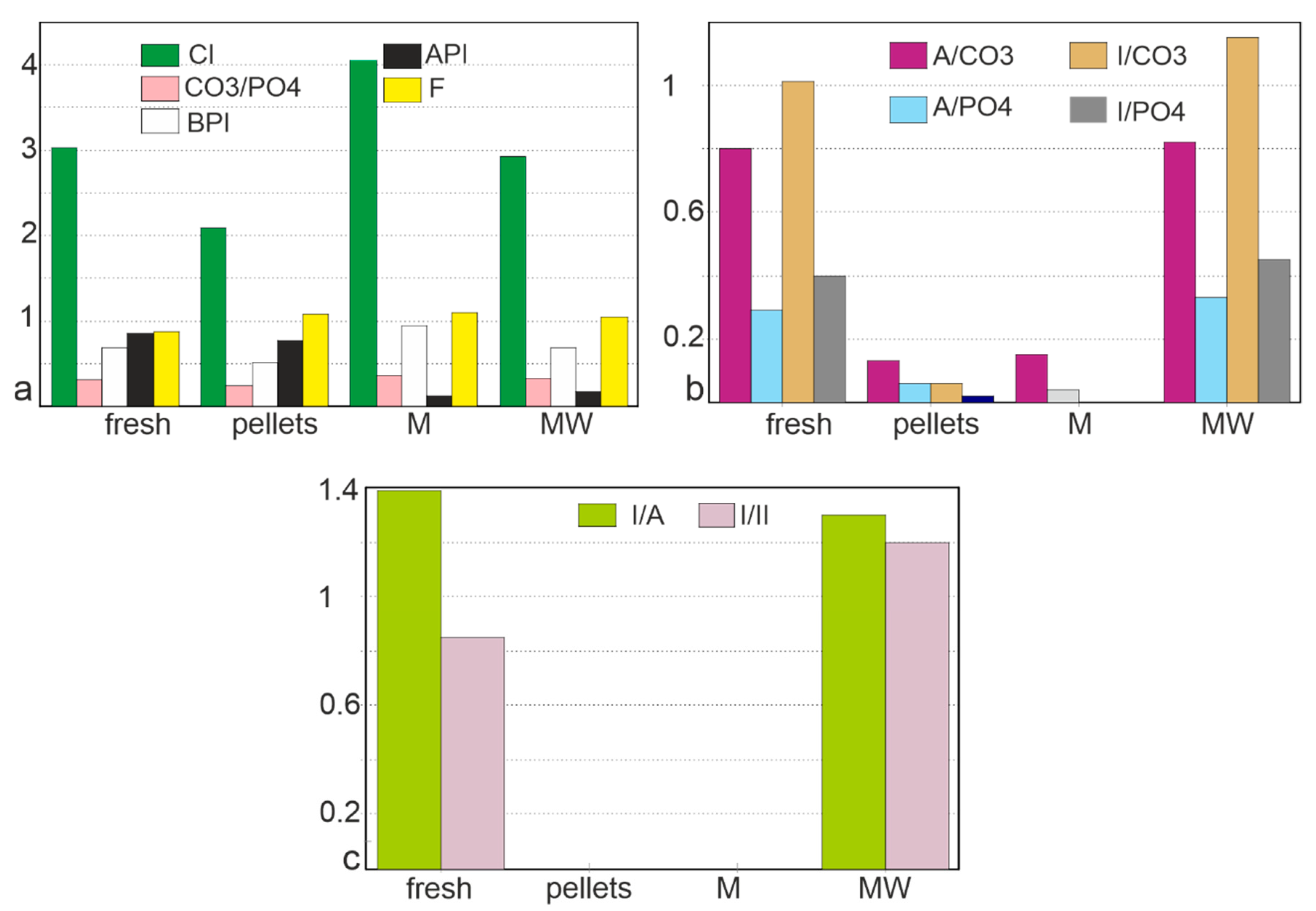
(a) Crystallinity (CI), CO3/PO4 ratios, type B carbonate to phosphate substitution (BPI), type A carbonate to phosphate substitution (API) and F content (F) calculated from FTIR spectra. (b) Organo–mineral ratios based on amide A (A), amide I (I), CO3 and PO4 bands, calculated from FTIR spectra. (c) Amide I/amide A ratio and amide I/amide II ratio from FTIR spectra. M: Malema, MW: Mwenirondo.
The abundance of the organic components in modern bones is clearly shown by the intensity of amide bands (Figure 8b). The mineral and organic components are similar in Bagrus and Oreochromis. The asymmetry of intensity shown by the doublets at 575–605 cm−1 and 1458–1420 cm−1 is due to low F concentrations. The main organic and mineral bands are also present in the bone extracted from the regurgitation pellet of the fish eagle (Figure 8b). Nevertheless, modifications are visible. The amide A band is larger, more intense. The ratio between amide I and II is inverted, the v3 PO4 has a shoulder and the v4 PO4 band is shifted (Figure 8b). Therefore, it can be said that the digestive stage has altered the initial composition of the fish bone.
FTIR spectra of three examples of fossil bones are displayed in Figure 8c. Except for a weak and large shoulder for amide A, all the bands are assigned to mineral components: PO4 or CO3 bands. The main part of the organic content has been removed by the diagenetic alteration.
The crystallinity index (CI) of the two modern bones is similar, and higher than that of the digested bone (Figure 9a). These changes can be assigned to the loss of the smallest bone crystals during the digestion. CI is variable in the fossil samples, but higher than those of bones extracted from pellets. CO3/PO4 index is less variable (Figure 9a), with no clear trend from the modern to the fossil samples. The substitution index of carbonate B to PO4 (BPI) is slightly variable (Figure 9a), and the substitution index of carbonate A to PO4 (API) is very low in fossil samples. F content is slightly higher in pellets and fossils (605/567 cm−1 ratio), but the 1096 cm−1 band assigned to the F enrichment is not detected in the fossils (Figure 9a).
Despite the strong differences in the spectra, the organic/mineral ratios of fresh bones and fossils from Mwenirondo are similar (Figure 9b). These ratios are very low in pellets and Malema fossils, whatever the mineral bands (CO3 and PO4) and organic bands (amide A, amide I) (Figure 9b). The loss of the organic components in bones from pellets and fossils is also demonstrated by the amide ratios (Figure 9c). Again, the differences between the two fossil sites are shown by these ratios.
3.2.2. Elemental Composition
Average concentrations and coefficients of standard errors for both major and minor elements in the modern and fossil bones are shown in Table 1. Some elements are below the detection limit of the EDS microprobe in modern samples, but this information is important because it allows for a direct comparison with modern and fossil samples. For example, high Fe, Mn, or K contents are often indicative of diagenetic alterations.

Table 1.
Elemental composition of bones and sediment (in ppm) obtained from EDS analyses; m = mean; sd: standard deviation; n: number of analysed bones. A minimum of 10 punctual analyses were completed for every bone, ca a total of 320 EDS analyses.
Modern bones (fresh and pellets) have low Ca and P contents, and a similar Ca/P ratio. Their minor element compositions are similar, except for the Na depletion in pellets. S is of special interest because it is mainly related to the organic matrices (sulphated polysaccharides). Fossil bones of both sites, Malema and Mwenirondo, are strongly enriched in P and Ca, with high Ca/P ratios. Both are depleted in Mg and S, and are enriched in Al, Si, Mn, Sr, and Fe. K and Ba contents are low and similar in both modern and fossil bones. The brown colour observed in some bones is probably due to the high Fe and Mn contents of fossil bones. Si, Fe and Mn contents are higher in the fossil bones, whereas S is lower (Table 1), Mwenirondo samples being the richest.
According to the non-significant Mann–Whitney test, the chemical compositions of the fresh bones and those extracted from the regurgitation pellets are similar (Table 2, F/P line). From this test, the main differences are between the fresh bones and the fossil bones from Malema (Table 2, F/M line), and between the bones from pellets and fossil bones from Malema (Table 2, P/M line). Nevertheless, despite the number of significant tests being the same (8), the chemical elements are not the same (Na, Mg). S, Mn, Fe are the most modified elements, Na and Mg being the least modified.

Table 2.
Mann–Whitney test at α = 5% based on the chemical analyses of modern and fossil fish bones; F: fresh bones, P: bones extracted from pellets, M: Malema fossil samples, MW: Mwenirondo fossil samples, S: significant differences, NS: non-significant differences.
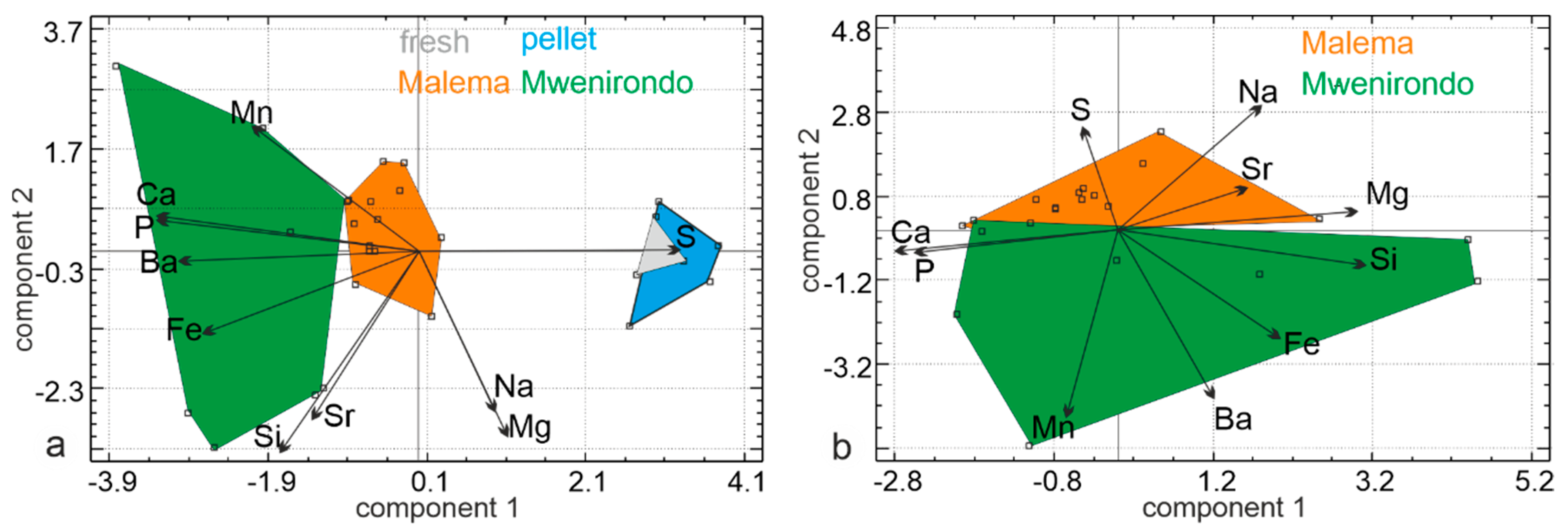
A first principal components analysis (PCA) was performed on chemical elements data on modern (fresh and pellet bones) and fossil bones from both sites. The first principal axis contains 42.9% of the total variance, axis two represents 20.5% and axis three represents 13.2%. The first principal component comprises higher P and Ca opposed to S and Ba values. In the second principal component, the samples are sorted with higher Si, Mg, Sr, and Na. The plot of two first principal components shows that there is a clear discrimination between the modern and fossil samples (Figure 10a). Fresh and pellet bones show high S contents. Fossil bones show high Ca, P, Fe, Mn and Ba contents, and lower S, Mg and Na contents. P and Ca, as well as Si and Sr, and Na and Mg are strongly correlated. The plot shows a large overlap between fresh and pellet samples, whereas the fossil sites do not show overlap (Figure 10a).
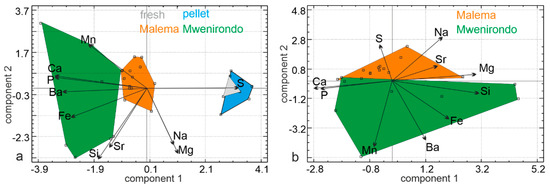
Figure 10.
Principal analysis components of fish bones. (a) Fresh and pellet bones (rich in S) and fossil bones (rich in P, Ca, Fe and Ba). (b) Chemical compositions of fossil bones of Malema and Mwenirondo differ.
A second PCA performed only on fossil bones from both sites revealed that the first principal axis contains 34.7% of the total variance, axis two represents 23% and axis three: 14.7% (Figure 10b). The first principal component comprises higher Si and Mg opposed to Ca values. In the second principal component, the samples are sorted with higher Mn and Ba opposed to Na values. The plot of two first principal components shows that there is some discrimination along axis two between samples from Malema and Mwenirondo (Figure 10b) with a small overlap between both sites. Malema bones show high S, Mg, Na and Sr contents. Mwenirondo bones show high Mn, Ba and Fe contents, and low S, Mg and Na contents. The size of the domains of Malema bones is smaller than those of Mwenirondo, showing that Malema samples have a less variable composition.
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Fresh Bones and Bones Extracted From Regurgitation Pellets
4.1.1. Surface and Microstructure
Bones from the fish eagle regurgitation pellets are disarticulated for most of them and broken for others. However, most types of skeletal elements were recovered in this study, along with fragile scales and otoliths. Compared to fresh bones, they display some surface characteristics of digestion such as polished (smooth) surfaces and typical spongious bone lacunae enlargement (Otero et al. in prep.) and even some twisting. These are comparable to fish bones collected in European Lutra lutra faeces and Bubo bubo pellets [25,26]. Similarly, the apophyses are broken but we could not observe the compaction (deformation) of the vertebrae noticed by these authors. Moreover, some traces of post-predation modification were observed on the extracted bones from the pellets, c.a; splitting and cracking, desquamation of the bone that may correspond to light weathering that could result from a long stay of the pellets at the surface of the soil in a dry tropical climate [40]. A more complete taphonomic study (Denys et al. in prep.) will allow the refining of this analysis.
Thus, it can be said that the digestion marks and the pre-burial alterations differ in the modern fish bones collected in Malema and Mwenirondo.
4.1.2. Mineralogy, Composition
As shown by the Mann–Whitney test, the chemical compositions of the fresh bones and those extracted from the regurgitation pellets are not significantly different (Table 2: digestion by the African fish eagle does not significantly affect the elemental chemical composition of the bone).
Although infrared spectra show that the bones extracted from regurgitation pellets are modified, the main features are preserved. Nevertheless, the size of the crystallites is reduced in pellet bones, as shown by the crystallinity index. It can be suggested that the largest crystals are dissolved or at least reduced to smaller units by the digestive processes. The loss of organic matrices is mainly assigned to amide A. The quality of the organic matrix is also modified by the digestive processes, as shown by the shift of the wave numbers for amide bands.
4.2. Comparison of Modern and Fossil Fish Bones
4.2.1. Surface and Microstructure
Compared to the modern fish bones, the fossils seem modified. Among the main observed changes, one can notice a rougher surface with flaking of the concentric bone and coating of some parts of the surfaces. Some of the bones also display splitting and cracking aligned in the longitudinal axis of the bones and observable on the whole surface, which may correspond to weathering. Important secondary coatings are visible on most of the fossil bones as already observed for large mammals [10,11]. Traces of polishing and rounding have also been observed, especially in Mwenirondo, which may result from water abrasion [41]. In both sites, the fossils display enlarged spongious bone lacunae on the articular surfaces that correspond to relatively light digestion (Denys et al., in prep.). Further taphonomic study will attempt to evaluate the intensity of the digestion and compare it to fish eagle predation and other local potential predators.
Traces of digestion on the surfaces of the fossil bones collected at Malema and Mwenirondo are still preserved, despite the strong post-burial modifications. Further post-predation actions occurred after burial in the lacustrine sediments (weathering, transport by water…). Did these digestion and early diagenetic phases modify the structure and chemistry so that the burial process resulted in more important changes? This is not known, but it is probable.
4.2.2. Mineralogy and Composition
From the chemical and FTIR analyses, modern and fossil bones are clearly different. EDS analyses show that fossil bones are enriched in P and Ca, whereas FTIR data show that they have lost a large part of the organic matrix. The lost organic components are “replaced” by some chemical elements such as Mn and Fe, and also P and Ca. The changes in the crystallinity index (CI), i.e., the size of the bone crystallites, prove difficult to be assigned to a unique phenomenon. The loss (dissolution) of the smallest crystals increases the CI because only the large crystals are preserved, but the reworking (dissolution, then re-precipitation) can increase the size of these smallest crystals. According to Trueman et al. [42], crystal sizes increase during diagenesis, but the studied bones were recent and not buried.
As shown by the Mann–Whitney test, the chemical compositions of the fresh bones and those extracted from the regurgitation pellets are similar (Table 2). The main differences are observed between the fresh bones and the fossil bones from Malema, and between the bones from pellets and those from Malema (both with eight significant Mann–Whitney tests). Si, S, Mn, Fe, P and Ca are the most modified elements. Si, Fe and Mn contents are higher in the fossil bones, whereas S is lower (Table 1).
4.3. Comparison of the Fossil Bones From Malema and Mwenirondo
The digestive damages, such as smoothing, observed in both Malema and Mwenirondo fossils correspond to those observed on the modern ones, which indicates that at least part of the bone accumulations are due to a fish eagle or an equivalent predator. For this point, we were unable to observe differences resulting from the differential digestion intensity categories of predators between both sites. Other processes have certainly played a role in the accumulation, and they performed differently between Malema and Mwenirondo as suggested by the following differences observed in the patterns of bone surface modifications. Globally, in Mwenirondo, polished elements are relatively more frequent when compared with unpolished ones while desquamation, coating and weathering are more abundant in Malema. These differences can be related to different post-predation, burial processes and also palaeoenvironmental local conditions. Higher energy water transport conditions at Mwenirondo may explain these differences between sites according to the sedimentological study of the series [26].
4.4. Fossil Bones and Sediment
Infrared data show strong differences between the bones from the fossil sites. One of the main differences is the crystallinity index (CI), higher in the Malema bones. The loss of organic components is stronger in Malema than in Mwenirondo. PCA shows that both fossil samples are clearly different from the modern ones, but when the PCA is dedicated to the fossil bones only, the overlap is small. Si, Mn, and Fe contents are higher in Mwenirondo bones. Contents of these chemical elements are also high in the sediment.
Infrared spectra of three samples of the sandy sediment show several strong bands (Figure 11). OH-stretching modes lie in the 3400–3750 cm−1 region; clays are very sensitive to H2O, so that these bands are sometimes amplified by the atmospheric composition despite the software correction and background. Several assignments are possible for the 1035 cm−1 band: PO4 or/and Si–O–Si [43]. The PO4 band can be attributed to bone fragments mixed in the sediment. Bands at about 794 cm−1 and 698 cm−1 (Si–O) are known in kaolinite [44]. CO32− bands related to calcite are also present.
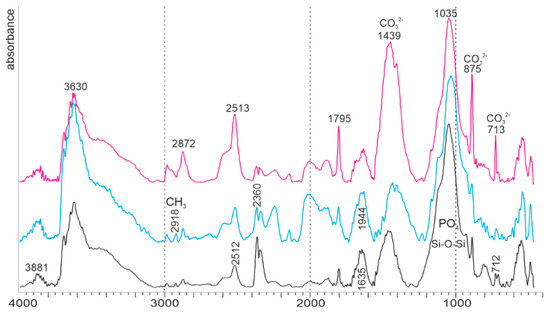
Figure 11.
FTIR spectra of some samples of the sandy sediment, showing the presence of calcite, clays and probably bone fragments.
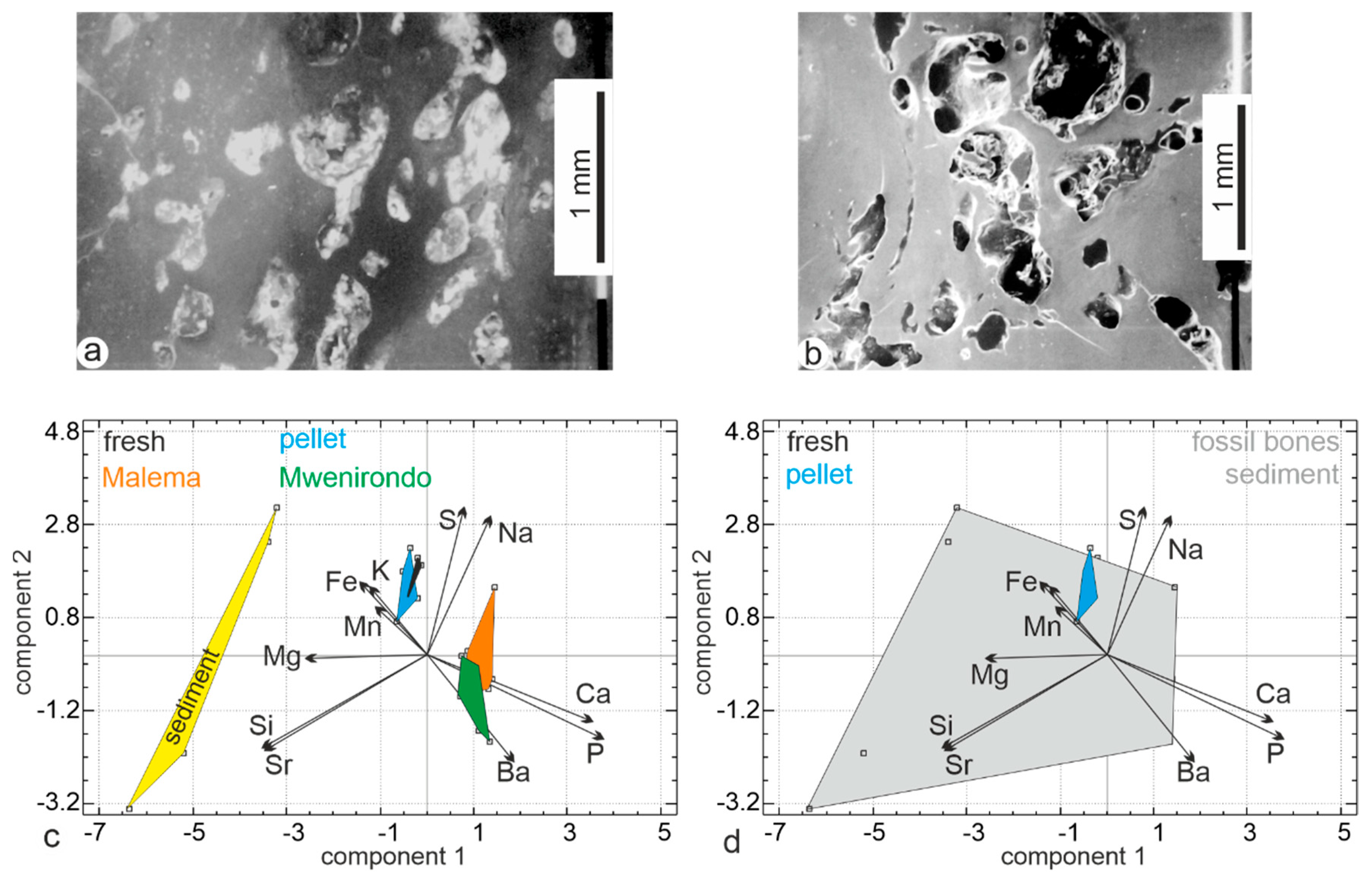
To reveal the possible mineral exchanges between the bones and the sediment, a principal component analysis was performed using the same chemical elements (Figure 12). The first principal axis contains 34.7% of the total variance, axis two represents 19.6% and axis three represents 18.2%. The first principal component comprises higher P and Ca opposed to Si and Sr values. In the second principal component, the samples are sorted with higher S and Na opposed to Ba values. The sediment is clearly different from the fossil bones from both Malema and Mwenirondo sites. Sediment is sandy, so some grains penetrate within broken bones, as shown in the polished samples used for electron microprobe EDS analyses (Figure 12a,b). The fossil fish bones collected at the sites are not large, so only small sandy grains are found within the bones. Using the electron microprobe on polished samples, the location of the analyses (bone or sediment) is known, so that grain sands and bone tissue are easily separated in the PCA analyses (Figure 12c). Fossil bones are enriched in Si (and Al, data not shown), but silty sedimentary particles are too small to be detected by the EDS analyses.
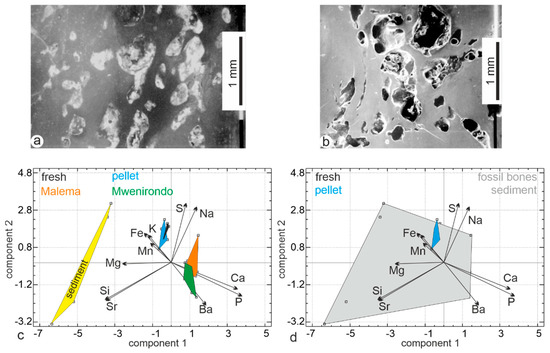
Figure 12.
(a,b) SEM images of polished bones showing that, within a bone, original cavities are filled with sedimentary particles or still empty. (c) Principal component analyses of the modern, fossil bones and sediment. (d) Principal component analyses when fossil bones and sediment are mixed.
It must be noted that the results from the FTIR and EDS analyses of sedimentary particles are concordant. The primary cavities in bone emphasize the role of the analytical techniques. When fossil bones and sediment are identified, the composition of bones from Malema and Mwenirondo on one hand, and sediment on the other hand clearly differ (Figure 12c). To mimic analyses in which the precise locations of chemical analyses are unknown (powdered samples), fossil bones and sediment have been grouped into one area. This set of samples (fossil bones + sediment) represents a large domain in which modern bones are included (Figure 12d). Thus, it is not possible to unravel the diagenetic changes in non-localised analyses, mixing tissue and secondary fillings. Despite it often being said that electron microprobes (EDS or WDS types) may not be sufficiently sensitive, they are the best choice for taphonomic studies. Electron microprobes allow us to see the sample as we do with SEM, so that the bone and the sediment are clearly identified. Thus, it is easy to select specific anatomical or geological locations of the sample for chemical analyses. The sample is not destroyed (neither powdered nor dissolved) and can be studied using Raman or infrared spectrometry, among other techniques. It is also possible to acquire chemical maps, showing the inner variability of a sample.
To obtain the bulk composition of the samples, Fourier transform infrared spectrometry provided data on the mineralogy, presence of organic components and crystallinity, so that the compositional changes between different samples would be visible. For the Malawi fish bones, the comparison of EDS and FTIR analyses confirms some differences. Both analyses show the enrichment in minerals and the related loss of organic components of fossil bones. It must be also noticed that the “high” Si content detected by EDS analyses is confirmed by FTIR analyses, despite the silty particles being too small to be visible.
5. Conclusions
Comparisons of surface alterations show that light diagenetic changes are already visible in the fish bones extracted from modern pellets, whereas traces of digestion are still visible in fossil bones. Diagenetic changes before burial have been also observed in other vertebrate accumulations [45,46]. In the bones extracted from the modern pellets, organic components (mainly collagen) are more or less destroyed by digestion and the mineral phase is more or less dissolved, as shown by the FTIR analyses (Figure 9), so that the remaining bone is more fragile and permeable. If the regurgitation pellets are exposed to bad weather, even for a short time, traces of weathering are visible. Despite their geographical proximity, fossil fish samples from Malema and Mwenirondo are unquestionably chemically different. A similar phenomenon was observed in the fossil bones of rodents from Olduvai Gorge [6]. The Chiwondo Bed sites are located on the same side of a palaeolake, separated by only 200 m. Sediments are lake margin deposits (silty clays). Thus, fluctuations in the position of the lake margin relative to the sites (resulting from differences in drainage or size of the lake) could give rise to the changes in the salinity and/or immersion of the sites.
Iron and manganese crusts on the surface of bones are often said to be significant evidence of sub-aerial surface alterations, or/and the presence of a palaeosoil. The chemical analytical technique used in this study is not based on the outer surface of bones, but on sections. Mn and Fe are not only surficial crusts, they are also within the bones. Increases in the concentrations of Fe, Mn, Si and Ba in fossil vs. fresh and modern pellet bones reflect mixtures of chemically modified apatite and secondary minerals.
Fish bones are less mineralized than mammal bones [47], and more fragile than those of mammals when submitted to experimental burials in soils [48]. Another difference between teleost fish and mammals is the absence of osteocytes in the former, so that these fish bones are described as “acellular” [49,50,51]. Moreover, theoretical and experimental studies have shown that mineral components are less tightly packed among collagen fibres in fish relative to mammals. Young’s modulus measurements show that fish bones are “more elastic” than their mammal counterparts [47]. Therefore, it is not surprising that digestion and incipient weathering modifications are visible on the surfaces of modern samples.
Traces of digestion are still visible on the surfaces of fossils from Malema but are more or less hidden or erased by post digestion alterations in Mwenirondo. All fossil bones are strongly enriched in Ca, P and Fe, and impoverished in S, the latter being mainly in the organic matrix [52]. Thus, from consistent features of the surface, structural and chemical analyses, fish bones from Mwenirondo are more modified than those of Malema. The preliminary results of the chemical elemental compositions performed on a small sample of fossil fish and mammal bones [11] are confirmed. Nevertheless, up to now “Patterns of fish preservation defy description by simple rules based on readily observed environmental gradients” [53].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.D., C.D.; field work, C.D., O.K., O.S., F.S., T.G.B.; data collection and analyses, Y.D., C.D., O.O.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.D., C.D. All authors have read and agreed to the submitted version of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding was obtained via the Hominid Corridor Research Project (HCRP) research project, the Wenner-Grenn foundation and a grant from the Singer-Polignac Foundation attributed to C. Denys and F. Schrenk.
Acknowledgments
Some SEM pictures were taken by C. Chancogne-Weber at the Museum National d’histoire Naturelle (MNHN) and the technical platform of electron microscopy and microanalysis of the MNHN Paris. We also thank A. Denis (Université d’Orsay) who prepared the included and polished samples, and his help with the EDS analyses.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dauphin, Y.; Denys, C.; Denis, A. Les mécanismes de formation des gisements de microvertébrés: Modifications de la composition chimique des os et dents de rongeurs issus de pelotes de régurgitation de rapaces. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 1988, 307, 603–608. [Google Scholar]
- Dauphin, Y.; Denys, C.; Denis, A. Les mécanismes de formation des gisements de microvertébrés. 2- Composition chimique élémentaire des os et dents de rongeurs provenant de pelotes de régurgitation de rapaces. Bull. Muséum Natl. Hist. Nat. 1989, 11, 211–237. [Google Scholar]
- Dauphin, Y.; Andrews, P.J.; Denys, C.; Fernandez-Jalvo, Y.; Williams, C.T. Digestion and bone modification in a modern pellet assemblage of Olduvai gorge, Tanzania. J. Taphon. 2003, 1, 209–232. [Google Scholar]
- Denys, C.; Stoetzel, E.; Andrews, P.; Bailon, S.; Rihane, A.; Huchet, J.B.; Fernandez-Jalvo, Y.; Laroulandie, V. Taphonomy of small predators multi-taxa accumulations: Palaeoecological implications. Histor. Biol. 2018, 30, 868–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauphin, Y.; Castillo-Michel, H.; Farre, B.; Mataame, A.; Rbii, K.; Rihane, A.; Stoetzel, E.; Denys, C. Identifying predation on rodent teeth through structure and composition: A case from Morocco. Micron 2015, 75, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denys, C.; Williams, T.; Dauphin, Y.; Andrews, P.; Fernandez-Jalvo, Y. Diagenetical changes in Pleistocene small mammal bones from Olduvai Bed I. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 1996, 126, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrenk, F.; Bromage, T.G.; Gorthner, A.; Sandrock, O. Paleoecology of the Malawi Rift: Vertebrate and invertebrate faunal context of the Chiwondo Beds, northern Malawi. J. Human Evol. 1995, 29, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandrock, O.; Kullmer, O.; Schrenk, F.; Juwayeyi, Y.M.; Bromage, T. Fauna, taphonomy, and ecology of the Plio-Pleistocene Chiwondo beds, Northern Malawi. In Hominin Environments in the East African Pliocene: An Assessment of the Faunal Evidence; Bobe, R., Alemseged, Z., Behrensmeyer, A.K., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, Germany, 2007; pp. 315–332. [Google Scholar]
- Kullmer, O.; Sandrock, O.; Kupczik, K.; Frost, S.R.; Volpato, V.; Bromage, T.G.; F Schrenk, F. Primate remains from Mwenirondo, Chiwondo Beds in northern Malawi. J. Hum. Evol. 2011, 61, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandrock, O. The Taphonomy and Paleo Ecology of the Malema Hominid Site, Northern Malawi. Ph.D. Thesis, Johannes Gutenberg Universität Mainz, Mainz, Germany, 1999; p. 276. [Google Scholar]
- Sandrock, O.; Dauphin, Y.; Kullmer, O.; Abel, R.; Schrenk, F.; Denys, C. Malema: Preliminary taphonomic analysis of an African hominid locality. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 1999, 328, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüdecke, T.; Kullmer, O.; Wacker, U.; Sandrock, O.; Fiebig, J.; Schrenk, F.; Mulch, M. Dietary versatility of Early Pleistocene hominins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 13330–13335. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, K.M.; Murray, A.M. Earliest fish remains from the Lake Malawi Basin, and biogeographical implications. J. Vert. Paleont. 2013, 33, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, K.M. Fishing sites of North and East Africa in the Late Pleistocene and Holocene: Environmental change and human adaptation. BAR Int. Ser. 1989, 521, 1–292. [Google Scholar]
- Van Neer, W. New Late Tertiary fish fossils from the Sinda Region, Eastern Zaire. Afr. Study Monogr. 1992, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, O.; Pinton, A.; Mackaye, H.T.; Likius, A.; Vignaud, P.; Brunet, M. The fish assemblage associated with the Late Miocene Chadian hominid (site TM266, Toros-Menalla, Western Djurab), and its palaeoenvironmental signification. Palaeontographica 2010, A292, 21–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gäb, F.; Ballhaus, C.; Stinnesback, E.; Kral, A.G.; Janssen, K.; Bierbaum, G. Experimental taphonomy of fish - rôle of elevated pressure, salinity and pH. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, V.L. Natural versus cultural salmonid remains: Origin of the Dalles Roadcut bones, Columbia River, Oregon, USA. J. Archaeol. Sci. 1993, 20, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.K.G. Fish bone survival in the digestive systems of the pig, dogs and man: Some experiments. In Fish and Archaeology: Studies in Osteometry, Taphonomy, Seasonality and Fishing Methods; BAR International series 294; Brinkhuizen, D.C., Clason, A.T., Eds.; BAR International: Oxford, UK, 1986; pp. 53–61. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, R.A. An investigation into the effects on fish bone passage through the human gut: Some experiments and comparisons with archaeological material. Circaea 1992, 10, 38–50. [Google Scholar]
- Van Neer, W.; Alhaique, F.; Wouters, W.; Dierickx, K.; Gala, M.; Goffette, Q.; Mariani, G.S.; Zerboni, A.; di Lernia, S. Aquatic fauna from the Takarkori rock shelter reveals the Holocene central Saharan climate and palaeohydrography. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, K.M.; Matthiesen, D.P.; Leblanc, L.; West, J. Prey diversity and selectivity of the African fish eagle: Data from a roost in northern Kenya. Afr. J. Ecol. 1997, 35, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, K.M.; Leblanc, L.; Matthiesen, D.P.; West, J. Microfaunal remains from a modern east African raptor roost: Patterning and implications for fossil bone scatters. Paleobiology 1999, 25, 483–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaud, E.; Bearez, P.; Denys, C.; Raimond, S. New data on fish diet and bone digestion of the Eurasian otter (Lutra lutra) (Mammalia: Mustelidae) in central France. Europ. Zool. J. 2017, 84, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaud, E.; Lebreton, L.; Béarez, P. Taphonomic signature of Eurasian eagle owl (Bubo bubo) on fish remains. Folia Zool. 2018, 67, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betzler, C.; Ring, U. Sedimentology of the Malawi Rift: Facies and stratigraphy of the Chiwondo Beds, northern Malawi. J. Hum. Evol. 1995, 28, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, F.H.; McDougall, I.; Davies, T.; Maier, R. An integrated Plio-Pleistocene chronology for the Turkana Basin. In Ancestors: The Hard Evidence; Delson, E., Ed.; Alan R. Liss: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, F.H.; Feibel, C.S. Revision of lithostratigraphic nomenclature in the Koobi Fora region, Kenya. J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 1986, 143, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrenk, F.; Bromage, T.G.; Betzler, C.G.; Ring, U.; Juwayeyi, Y.M. Oldest Homo and Pliocene biogeography of the Malawi Rift. Nature 1993, 365, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromage, T.G.; Schrenk, F.; Juwayeyi, Y.M. Palaeobiogeography of the Malawi Rift: Age and vertebrate paleontology of the Chiwondo Beds, northern Malawi. J. Hum. Evol. 1995, 28, 37–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullmer, O. The fossil suidae from the Plio-Pleistocene Chiwondo Beds of northern Malawi, Africa. J. Vert. Paleontol. 2008, 208, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemesh, A. Crystallinity and diagenesis of sedimentary apatite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 545, 2433–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, S.; Bar-Yosef, O. States of preservation of bones from prehistoric sites in the Near East: A survey. J. Archaeol. Sci. 1990, 17, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillen, A. Biogenic and diagenetic Sr/Ca in Plio-Pleistocene fossils of the Omo Shungura formation. Paleobiology 1986, 12, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeGeros, R.; Trautz, O.R.; Klein, E.; LeGeros, J.P. Two types of carbonate substitution in the apatite structure. Experientia 1969, 25, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey, C.; Renugopalakrishnan, V.; Collins, B.; Glimcher, M.J. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic study of the carbonate ions in bone mineral during aging. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1991, 46, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botha, J.; Lee-Thorp, J.; Sponheimer, M. An examination of Triassic cynodont tooth enamel chemistry using Fourier Transform infrared spectroscopy. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2004, 74, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Feki, H.; Rey, C.; Vignoles, M. Carbonate ions in apatites: Infrared investigations in the v4 CO3 domain. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1991, 49, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauphin, Y. Potential of the Diffuse Reflectance Infrared Fourier Transform (DRIFT) method in paleontological studies of bones. Appl. Spectrosc. 1993, 47, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Jalvo, Y.; Andrews, P. Atlas of Taphonomic Identifications: 1001+ Images of Fossil and Recent Mammal Bone Modification; Vertebrate Paleobiology and Paleoanthropology Series; Springer: Dordrecht, Germany, 2016; pp. 1–359. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Jalvo, Y.; Andrews, P. Experimental effects of water abrasion on bone fragments. J. Taphon. 2003, 1, 147–163. [Google Scholar]
- Trueman, C.N.G.; Behrensmayer, A.K.; Tuross, N.; Weiner, S. Mineralogical and compositional changes in bones exposed on soil surfaces in Amboseli National park, Kenya: Diagenetic mechanisms and the role of sediment pore fluids. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2004, 31, 721–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madejova, J.; Gates, W.P.; Petit, S. IR spectra of clay minerals. In Developments in Clay Science, 8; Gates, W., Kloprogge, J.T., Madejova, J., Bergaya, F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; p. 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaculikova, L.; Plevova, E. Identification of clay minerals and micas in sedimentary rocks. Acta Geodyn. Geomater. 2005, 2, 165–175. [Google Scholar]
- Dauphin, Y.; Kowalski, C.; Denys, C. Assemblage data and bone and teeth modifications as an aid to paleoenvironmental interpretations of the open-air pleistocene site of Tighenif (Algeria). Quat. Res. 1994, 42, 340–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denys, C.; Kowalski, K.; Dauphin, Y. Mechanical and chemical alterations of skeletal tissues in a recent Saharian accumulation of faeces from Vulpes rueppelli (Carnivora, Mammalia). Acta Zool. Cracov. 1992, 35, 265–283. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, L.; Dean, M.; Shipov, A.; Atkins, A.; Monsonego-Ornan, E.; Shahar, R. Comparison of structural, architectural and mechanical aspects of cellular and acellular bone in two teleost fish. J. Experim. Biol. 2012, 215, 1983–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, R.A. Fish bone diagenesis in different soils. Archaeofauna 1996, 5, 79–91. [Google Scholar]
- Kölliker, A. On the different types in the microscopic structure of the skeleton of osseous fishes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1857, 9, 656–668. [Google Scholar]
- Meunier, F.J.; Huysseune, A. The concept of bone tissue in Osteichthyes. Neth. J. Zool. 1992, 42, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currey, J.D.; Shahar, R. Cavities in the compact bone in tetrapods and fish and their effect on mechanical properties. J. Struct. Biol. 2013, 183, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohar, I.; Belmaker, M.; Nadel, D.; Gafny, S.; Goren, G.; Hershkovitz, I.; Dayan, T. The living and the dead: How do taphonomic processes modify relative abundance and skeletal completeness of freshwater fish? Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl. Palaeoecol. 2008, 258, 292–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccari, F.; Ferrarini, F.; Volpi, N. Structural characterization of chondroitin sulfate from sturgeon bone. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 145, 1575–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).