Silver-Rich Chalcopyrite from the Active Cerro Pabellón Geothermal System, Northern Chile
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geological Overview
3. Samples and Methods
4. Results
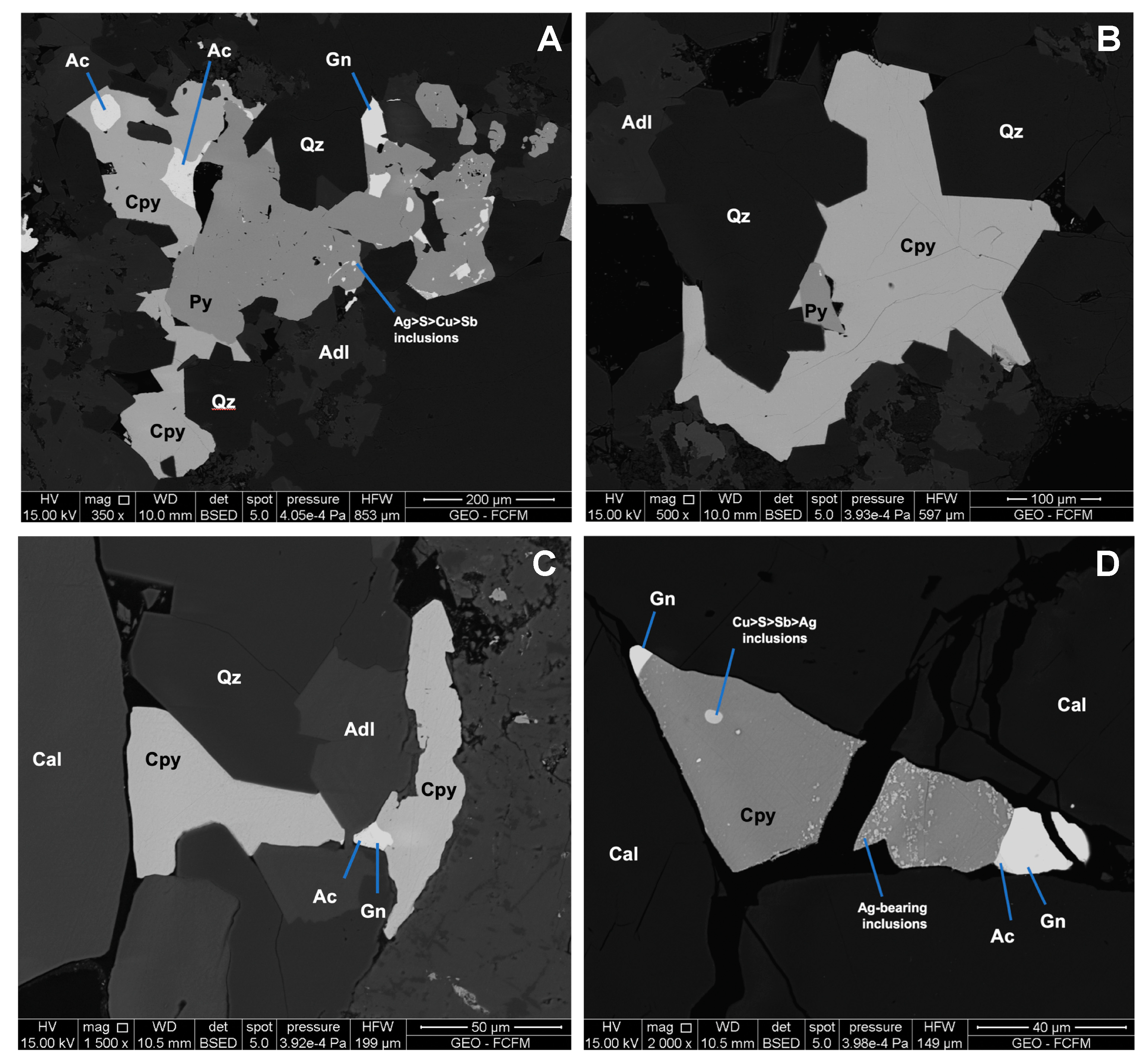
4.1. Micro-Textural Observations
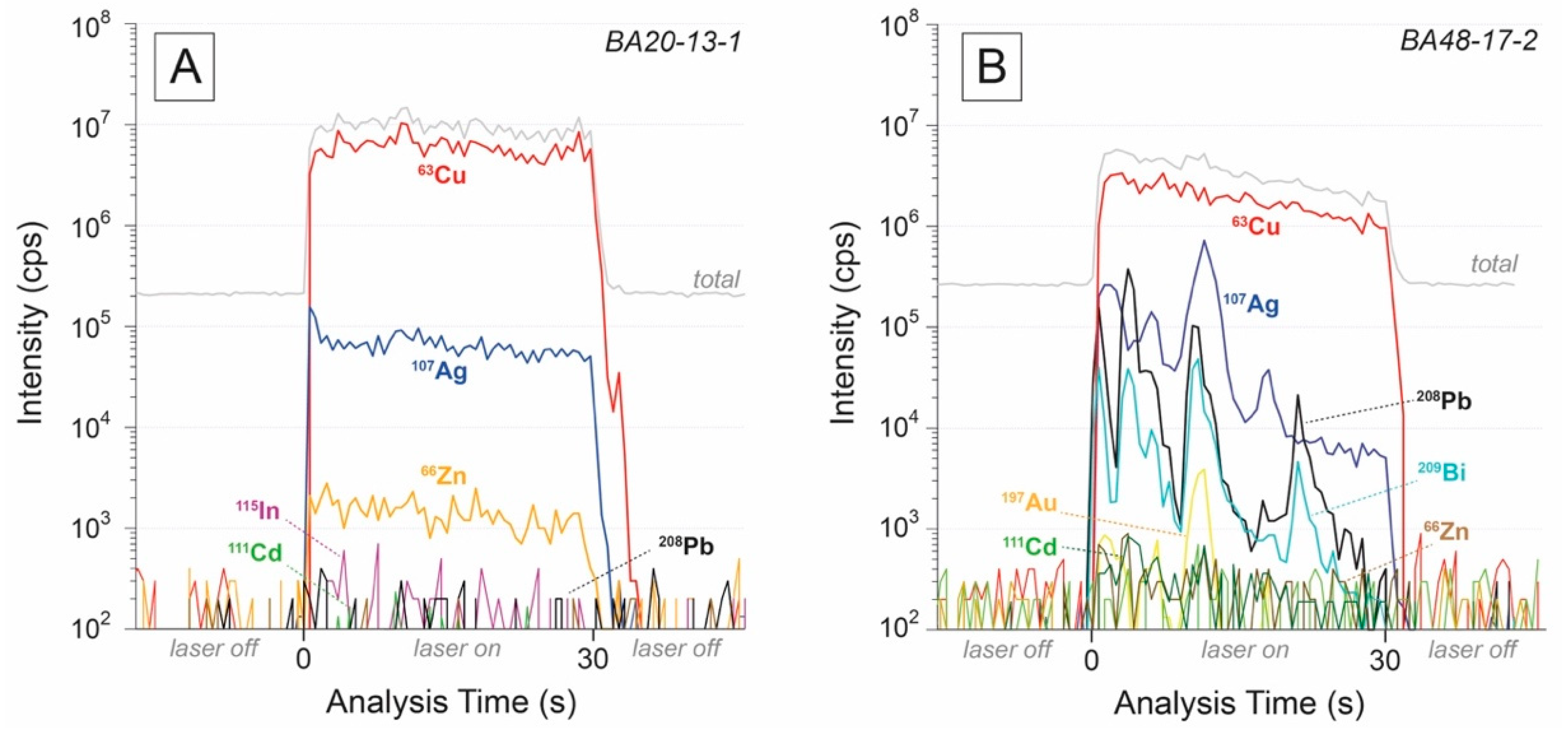
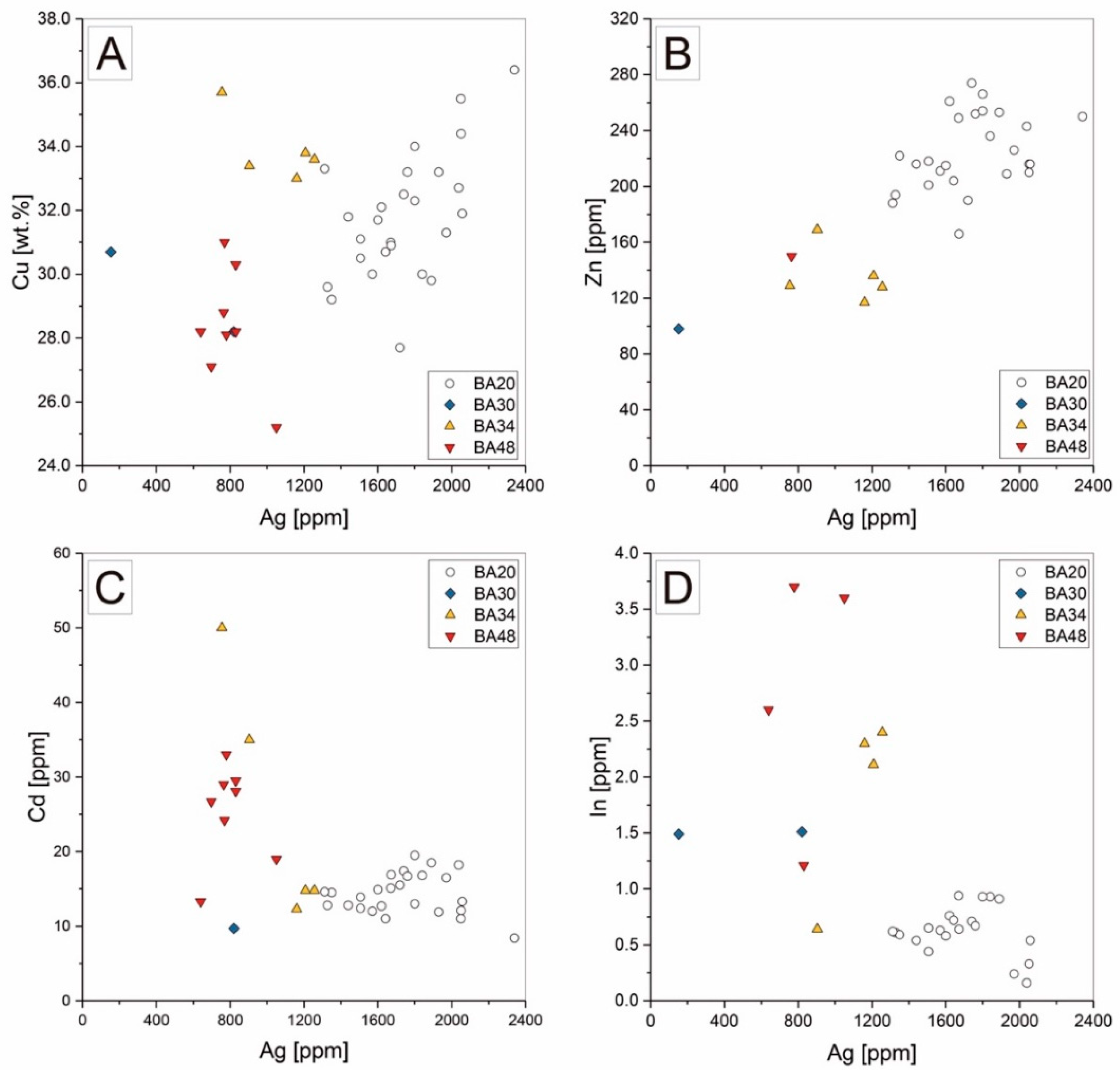
4.2. EMPA and LA-ICP-MS Data
5. Discussion
6. Final Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barnes, S.J.; Lightfoot, P.C. Formation of magmatic nickel-sulfide ore deposits and processes affecting their copper and platinum-group element contents. In Economic Geology 100th Anniversary; Hedenquist, J.W., Thompson, J.F.H., Goldfarb, R.J., Richards, J.P., Eds.; Society of Economic Geologists, Inc.: Littleton, CO, USA, 2005; pp. 179–213. [Google Scholar]
- Sillitoe, R.H. Porphyry copper systems. Econ. Geol. 2010, 105, 3–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barton, M.D. Iron oxide(-Cu-Au-REE-P-Ag-U-Co) systems. Treatise Geochem. 2014, 13, 515–541. [Google Scholar]
- Meinert, L.D.; Dipple, G.M.; Nicolescu, S. World Skarn Deposits. In Economic Geology 100th Anniversary; Hedenquist, J.W., Thompson, J.F.H., Goldfarb, R.J., Richards, J.P., Eds.; Society of Economic Geologists, Inc.: Littleton, CO, USA, 2005; pp. 299–336. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, S.F.; White, N.C.; John, D.A. Geological characteristics of epithermal precious and base metal deposits. In Economic Geology 100th Anniversary; Hedenquist, J.W., Thompson, J.F.H., Goldfarb, R.J., Richards, J.P., Eds.; Society of Economic Geologists, Inc.: Littleton, CO, USA, 2005; pp. 485–522. [Google Scholar]
- Galley, A.G.; Hannington, M.D.; Jonasson, I.R. Volcanogenic massive sulphide deposits. In Mineral Deposits of Canada: A Synthesis of Major Deposit-Types, District Metallogeny, the Evolution of Geological Provinces, and Exploration Methods; Goodfellow, W.D., Ed.; Geological Association of Canada: St. John’s, NL, Canada, 2007; pp. 141–161. [Google Scholar]
- Hitzman, M.W.; Selley, D.; Bull, S. Formation of sedimentary rock-hosted stratiform copper deposits through earth history. Econ Geol. 2010, 105, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, D.C.; Cabri, L.J.; Nobiling, R. Silver-bearing chalcopyrite, a principal source of silver in the Izok Lake massive-sulfide deposit; confirmation by electron- and proton-microprobe analyses. Can. Mineral. 1984, 22, 493–498. [Google Scholar]
- Cabri, L.J.; Campbell, J.L.; Laflamme, J.H.G.; Leigh, R.G.; Maxwell, J.A.; Scott, J.D. Proton-micro- probe analysis of trace elements in sulfides from some massive-sulfide deposits. Can. Mineral. 1985, 23, 133–148. [Google Scholar]
- Larocque, A.C.L.; Jackman, J.A.; Cabri, L.J.; Hodgson, C.J. Calibration of the ion microprobe for the determination of silver in pyrite and chalcopyrite from the Mobrun VMS deposit, Rouyn-Noranda, Quebec. Can. Mineral. 1995, 33, 361–372. [Google Scholar]
- Huston, D.L.; Sie, S.H.; Suter, G.F.; Cooke, D.R.; Both, R.A. Trace elements in sulfide minerals from eastern Australian volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposits: Part I. Proton microprobe analyses of pyrite, chalcopyrite, and sphalerite, and Part II. Selenium levels in pyrite: comparison with δ34S values and implications for the source of sulfur in volcanogenic hydrothermal systems. Econ. Geol. 1995, 90, 1167–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, I.B.; Nesbitt, R.W. Trace element distributions in the chalcopyrite wall of a black smoker chimney: Insights from laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1999, 167, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, R.U.; Ayres, L.W.; Råde, I. The Life Cycle of Copper; its Co-Products and Byproducts. In Eco-Efficiency in Industry and Science; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; 199p. [Google Scholar]
- Arif, J.; Baker, T. Gold paragenesis and chemistry at Batu Hijau, Indonesia: Implications for gold-rich porphyry copper deposits. Miner. Deposita 2004, 39, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Gilbert, S. Minor and trace elements in bornite and associated Cu-(Fe) sulfides: A LA-ICP-MS study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 6473–6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, M.; Palacios, C.; Barra, F.; Chryssoulis, S. “Invisible” silver in chalcopyrite and bornite from the Mantos Blancos copper deposit. Eur. J. Mineral. 2013, 25, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioaca, M.E.; Munteanu, M.; Qi, L.; Costin, G. Trace element concentrations in porphyry copper deposits from Metaliferi Mountains, Romania: A reconnaissance study. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 63, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, L.L.; Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L. Partitioning of trace elements in co-crystallized sphalerite–galena–chalcopyrite hydrothermal ores. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 77, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, L.L.; Cook, N.J.; Crowe, B.B.P.; Ciobanu, C.L. Trace elements in hydrothermal chalcopyrite. Mineral. Mag. 2018, 82, 59–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlgemuth-Ueberwasser, C.C.; Viljoen, F.; Petersen, S.; Vorster, C. Distribution and solubility limits of trace elements in hydrothermal black smoker sulfides: An in situ LA-ICP-MS study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 159, 16–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslennikov, V.V.; Maslennikova, S.P.; Large, R.R.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Herrington, R.J.; Ayupova, N.R.; Zaykov, V.V.; Lein, A.Y.; Tseluyko, A.S.; Melekestseva, I.Y.; et al. Chimneys in Paleozoic massive sulfide mounds of the Urals VMS deposits: mineral and trace element comparison with modern black, grey, white and clear smokers. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 85, 64–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melekestseva, I.Y.; Maslennikov, V.V.; Tret’Yakov, G.A.; Nimis, P.; Beltenev, V.E.; Rozhdestvenskaya, I.I.; Maslennikova, S.P.; Belogub, E.V.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Large, R.R.; et al. Gold- and Silver-Rich Massive Sulfides from the Semenov-2 Hydrothermal Field, 13°31.13′N, Mid-Atlantic Ridge: A Case of Magmatic Contribution? Econ. Geol. 2017, 112, 741–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, P.; Heine, T.; Fayek, M.; Potter, E.; Sharpe, R. Ore mineralogy of the Chisel Lake Zn-Cu-Ag (+Au) VMS deposit in the Flin Flon—Snow Lake Domain, Manitoba, Canada. Can. Mineral. 2019, 57, 925–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, I.M.; Stumpfl, E.; Helmy, H.M.; El Mahallawi, M.M.; Kamel, O.A. Silver and silver-bearing minerals at the Um Samiuki volcanogenic massive sulphide deposit, Eastern Desert, Egypt. Miner. Depos. 2004, 39, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, Q.; Yang, J.; Tang, X. Geochemistry of pyrite and chalcopyrite from an active black smoker in 49.6°E Southwest Indian Ridge. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2018, 39, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallon, E.K.; Frische, M.; Petersen, S.; Brooker, R.A.; Scott, T.B. Geological, Mineralogical and Textural Impacts on the Distribution of Environmentally Toxic Trace Elements in Seafloor Massive Sulfide Occurrences. Minerals 2019, 9, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Libbey, R.B.; Williams-Jones, A.E. Relating sulfide mineral zonation and trace element chemistry to subsurface processes in the Reykjanes geothermal system, Iceland. J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res. 2016, 310, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedenquist, J.W.; Lowenstern, J.B. The Role of Magmas in the Formation of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits. Nature 1994, 370, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.J.; Simmons, S.F.; Stoffell, B. How metalliferous brines line Mexican epithermal veins with silver. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.L. Gold deposition from geothermal discharges in New Zealand. Econ. Geol. 1986, 81, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, P.B., Jr.; Skinner, B.J. Sulfide mineral stabilities. In Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits; Barnes, H.L., Ed.; Wiley Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 278–403. [Google Scholar]
- White, N.C.; Leake, M.J.; McCaughey, S.N.; Parris, B.W. Epithermal deposits of the southwest Pacific. J. Geochem. Explor. 1995, 54, 87–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urzúa, L.; Powell, T.; Cumming, W.; Dobson, P. Apacheta, a new geothermal prospect in Northern Chile. Geotherm. Resour. Council Trans. 2002, 26, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Piscaglia, F. The high temperature geothermal field of the Apacheta-Aguilucho Volcanic Complex (northern Chile): Geo-petrographic surface exploration, crustal heat sources and cap-rocks. Plinius 2012, 38, 148–153. [Google Scholar]
- Mercado, J.L.; Ahumada, S.; Aguilera, F.; Medina, E.; Renzulli, A. Geological and Structural Evolution of Apacheta- Aguilucho Volcanic Complex (AAVC), Northern Chile. Actas XII Congreso Geológico Chileno. 2019. Santiago Chile (S7:002). Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/738e/e1837bd8c577546e7ec3c048e940ffaf423d.pdf (accessed on 23 January 2020).
- Maza, S.N.; Collo, G.; Morata, D.; Lizana, C.; Camus, E.; Taussi, M.; Renzulli, A.; Mattioli, M.; Godoy, B.; Alvear, B.; et al. Clay mineral associations in the clay cap from the Cerro Pabellón blind geothermal system, Andean Cordillera, Northern Chile. Clay Miner. 2018, 53, 117–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, N.; Reich, M.; Leisen, M.; Morata, D.; Barra, F. Geochemical and micro-textural fingerprints of boiling in pyrite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2019, 246, 60–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taussi, M.; Nisi, B.; Pizarro, M.; Morata, D.; Veloso, E.A.; Volpi, G.; Vaselli, O.; Renzulli, A. Sealing capacity of clay-cap units above the Cerro Pabellón hidden geothermal system (northern Chile) derived by soil CO2 flux and temperature measurements. J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res. 2019, 384, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taussi, M.; Godoy, B.; Piscaglia, F.; Morata, D.; Agostini, S.; Le Roux, P.; Gonzalez-Maurel, O.; Gallmeyer, G.; Menzies, A.; Renzulli, A. The upper crustal magma plumbing system of the Pleistocene Apacheta-Aguilucho Volcanic Complex area (Altiplano-Puna, northern Chile) as inferred from the erupted lavas and their enclaves. J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res. 2019, 373, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, C.; Hellstrom, J.; Paul, B.; Woodhead, J.; Hergt, J. Iolite: freeware for the visualisation and processing of mass spectrometric data. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2011, 26, 2508–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, J.F.W.; Howie, R.A.; Vaughan, D.J.; Zussman, J. Non-silicates: Oxides, Hydroxides, and Sulfides. In Rock-Forming Minerals, 2nd ed.; The Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2011; Volume 5A, 920p. [Google Scholar]
- Thole, R.H. The geology of the Shamrocke mine, Rhodesia—A stratiform copper deposit. Econ. Geol. 1976, 71, 202–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajwah, Z.; Seccombe, P.; Offler, R. Trace element distribution, Co:Ni ratios and genesis of the Big Cadia iron-copper deposit, New South Wales, Australia. Miner. Depos. 1987, 22, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zou, F.; Wang, L.; Yu, L.; Hu, M. Mineralogy and trace element geochemistry of the Co-and Cu-bearing sulfides from the Shilu Fe–Co–Cu ore district in Hainan Province of South China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 113, 980–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belissont, R.; Munoz, M.; Boiron, M.C.; Luais, B.; Mathon, O. Germanium Crystal Chemistry in Cu-Bearing Sulfides from Micro-XRF Mapping and Micro-XANES Spectroscopy. Minerals 2019, 9, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reich, M.; Kesler, S.E.; Utsunomiya, S.; Palenik, C.S.; Chryssoulis, S.L.; Ewing, R.C. Solubility of gold in arsenian pyrite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 2781–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, M.; Chryssoulis, S.L.; Deditius, A.; Palacios, C.; Zuniga, A.; Weldt, M.; Alvear, M. ‘‘Invisible’’ silver and gold in supergene digenite (Cu1.8S). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 6157–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobanu, C.L.; Cook, N.J.; Pring, A.; Brugger, J.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Shimizu, M. ‘‘Invisible gold’’ in bismuth chalco- genides. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 1970–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deditius, A.P.; Reich, M.; Kesler, S.E.; Utsunomiya, S.; Chryssoulis, S.L.; Walshe, J.; Ewing, R.C. The coupled geochemistry of Au and As in pyrite from hydrothermal ore deposits. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 140, 644–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becker, U.; Rosso, K.M.; Hochella, M.F. The proximity effect on semiconducting mineral surfaces: A new aspect of mineral surface reactivity and surface complexation theory? Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 2641–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouinard, A.; Paquette, J.; Williams-Jones, A.E. Crystallographic controls on trace-element incorporation in auriferous pyrite from the epithermal high-sulfidation Pascua deposit, Chile–Argentina. Can. Mineral. 2005, 43, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reich, M.; Román, N.; Barra, F.; Morata, D. Silver-Rich Chalcopyrite from the Active Cerro Pabellón Geothermal System, Northern Chile. Minerals 2020, 10, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10020113
Reich M, Román N, Barra F, Morata D. Silver-Rich Chalcopyrite from the Active Cerro Pabellón Geothermal System, Northern Chile. Minerals. 2020; 10(2):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10020113
Chicago/Turabian StyleReich, Martin, Nelson Román, Fernando Barra, and Diego Morata. 2020. "Silver-Rich Chalcopyrite from the Active Cerro Pabellón Geothermal System, Northern Chile" Minerals 10, no. 2: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10020113
APA StyleReich, M., Román, N., Barra, F., & Morata, D. (2020). Silver-Rich Chalcopyrite from the Active Cerro Pabellón Geothermal System, Northern Chile. Minerals, 10(2), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10020113





