Layered Double Hydroxides with Intercalated Permanganate and Peroxydisulphate Anions for Oxidative Removal of Chlorinated Organic Solvents Contaminated Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Samples
2.2. Characterisation Methods
2.3. Chlorinated Organic Solvent Oxidation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Synthesized Materials
3.1.1. ICP-OES
3.1.2. Powder X-Ray Diffraction
3.1.3. Thermal Analysis and Evolved Gas Analysis
3.1.4. FTIR Spectroscopy
3.1.5. Particle Size Distribution
3.2. Reactivity Studies
3.2.1. TCE–Mg,Al-LDHs System
3.2.2. TCE–Ca,Al-LDHs System
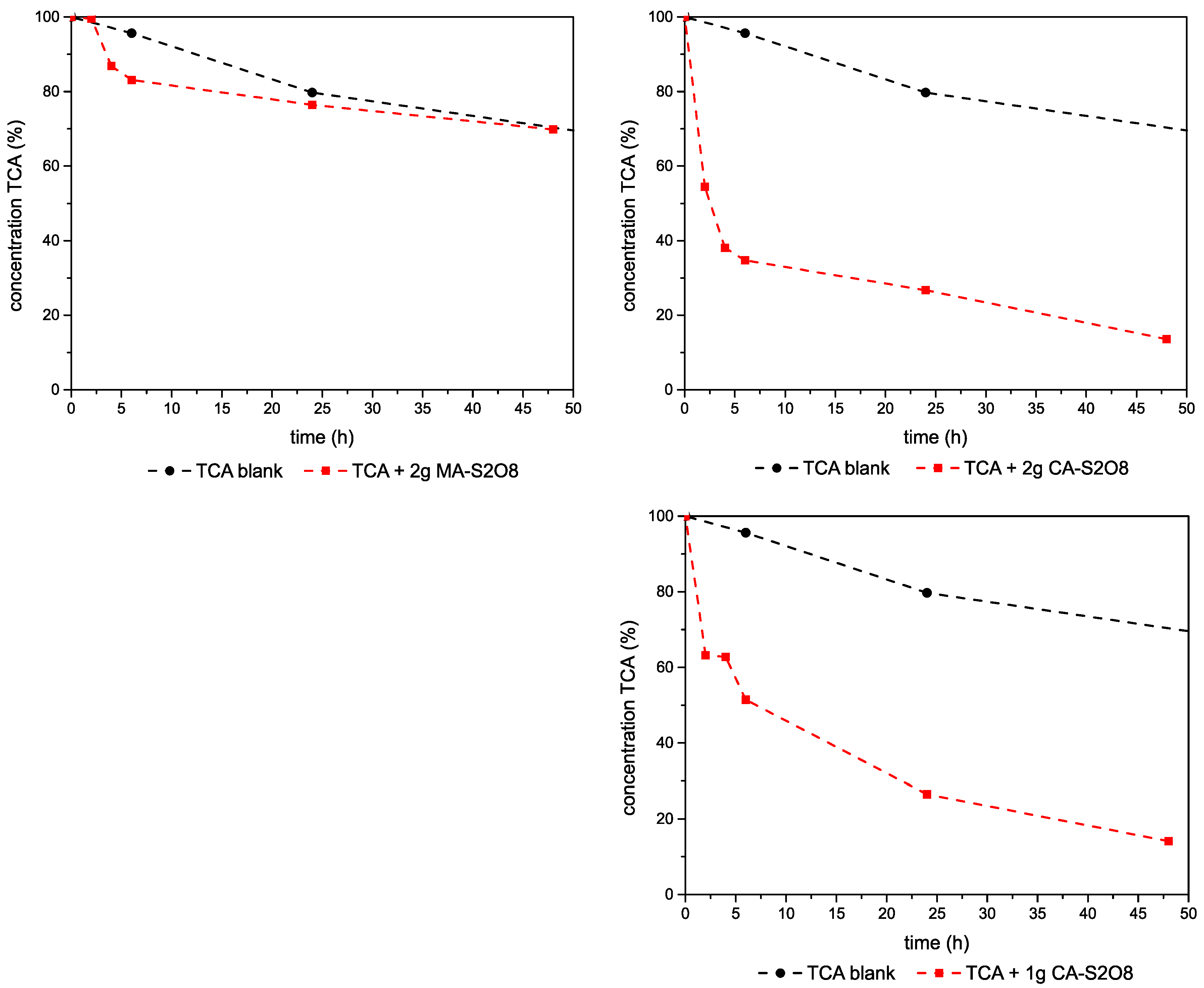
3.2.3. Experiments–1,1,2-TCA-Mg,Al- and Ca,Al-LDHs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huling, S.G.; Weaver, W. Dense Nonaqueous Phase Liquids Ground Water Issue; EPA/540/4-91/002; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1991.
- Sobsey, M.D.; Bartram, S. Water quality and health in the new millennium: The role of the World Health Organization Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. Forum Nutr. 2003, 56, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Technical and Regulatory Guidance for In Situ Chemical Oxidation of Contaminated Soil and Groundwater, 2nd ed.; Interstate Technology & Regulatory Council (ITRC) In Situ Chemical Oxidation: Malvern, UK, 2005.
- O’Connor, D.; Hou, D.; Ok, Y.S.; Song, Y.; Sarmah, A.K.; Li, X.; Tack, F.M. Sustainable in situ remediation of recalcitrant organic pollutants in groundwater with controlled release materials: A review. J. Control. Release 2018, 283, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semkiw, S.E.; Barcelona, M.J. Field Study of Enhanced TCE Reductive Dechlorination by a Full-Scale Whey PRB. Ground Water Monit. Remediat. 2011, 31, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambhu, A.; Comfort, S.; Chokejaroenrat, C.; Sakulthaew, C. Developing slow-release persulfate candles to treat BTEX contaminated groundwater. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheu, Y.; Chen, S.; Chien, C.; Chen, C.; Kao, C. Application of a long-lasting colloidal substrate with pH and hydrogen sulfide control capabilities to remediate TCE-contaminated groundwater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 284, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christenson, M.; Kambhu, A.; Reece, J.; Comfort, S.; Brunner, L. A five-year performance review of field-scale, slow-release permanganate candles with recommendations for second-generation improvements. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christensen, T.H.; Bjerg, P.L.; Banwart, S.A.; Jakobsen, R.; Heron, G.; Albrechtsen, H.-J. Characterization of redox conditions in groundwater contaminant plumes. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2000, 45, 165–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In Situ Remediation of Chlorinated Solvent Plumes. In In Situ Chemical Oxidation for Groundwater Remediation; Springer Science and Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 217–280.
- Engelmann, C.; Händel, F.; Binder, M.; Yadav, P.K.; Dietrich, P.; Liedl, R.; Walther, M. The fate of DNAPL contaminants in non-consolidated subsurface systems—Discussion on the relevance of effective source zone geometries for plume propagation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 375, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennedsen, L.R. In situ Chemical Oxidation—The Mechanisms and Applications of Chemical Oxidants for Remediation Purposes. In Chemistry of Advanced Environmental Purification Processes of Water—Fundamentals and Applications; Sorgaard, E., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 26–87. [Google Scholar]
- Huling, S.G.; Pivetz, B.E. In-Situ Chemical Oxidation Engineering Issue; EPA/600/R-06/072; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2007.
- Watts, R.J.; Teel, A.L. Treatment of Contaminated Soils and Groundwater Using ISCO. Pr. Period. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste Manag. 2006, 10, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegrist, R.L.; Urynowicz, M.A.; Crimi, M.; Lowe, K.S. Genesis and Effects of Particles Produced during In Situ Chemical Oxidation Using Permanganate. J. Environ. Eng. 2002, 128, 1068–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Chen, Y.; Fu, M.-L. Degradation efficiencies and mechanisms of trichloroethylene (TCE) by controlled-release permanganate (CRP) oxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 192, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, P.J.; Dugan, P.J.; Nguyen, D.; Lamar, M.; Crimi, M. Slow-release permanganate versus unactivated persulfate for long-term in situ chemical oxidation of 1,4-dioxane and chlorinated solvents. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietmann, K.M.; Linke, T.; Trujillano, R.; Rives, V. Effect of Chain Length and Functional Group of Organic Anions on the Retention Ability of MgAl- Layered Double Hydroxides for Chlorinated Organic Solvents. ChemEngineering 2019, 3, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alonso-De-Linaje, V.; Mangayayam, M.C.; Tobler, D.J.; Dietmann, K.M.; Espinosa, R.; Rives, V.; Dalby, K.N. Sorption of chlorinated hydrocarbons from synthetic and natural groundwater by organo-hydrotalcites: Towards their applications as remediation nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, S.J.; Christy, A.; Génin, J.-M.R.; Kameda, T.; Colombo, F. Nomenclature of the hydrotalcite supergroup: Natural layered double hydroxides. Miner. Mag. 2012, 76, 1289–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Roy, A.; Forano, C.; Besse, J.P. Layered Double Hydroxides: Synthesis and Post-Synthesis Modification. In Layered Double Hydroxides: Present and Future; Rives, V., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 1–40. ISBN 978-1-61209-289-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bookin, A.S. Polytype Diversity of the Hydrotalcite-Like Minerals, I. Possible Polytypes and their Diffraction Features. Clays Clay Miner. 1993, 41, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allmann, R.; Jepsen, H.P. Die Struktur des Hydrotalkits. Neues Jahrb. Mineral. Mon. 1969, 1969, 544–551. [Google Scholar]
- Miyata, S. Synthesis of Hydrotalcite-Like Compounds and their Physico-Chemical Properties—The Systems Mg2+-Al3+-SO42− and Mg2+-Al3+-CrO42−. Clays Clay Miner. 1977, 25, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, W. Synthesis of anionic clay minerals (mixed metal hydroxides, hydrotalcite). Solid State Ion. 1986, 22, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantino, V.R.; Pinnavaia, T.J. Basic Properties of Mg2+1-xAl3+x Layered Double Hydroxides Intercalated by Carbonate, Hydroxide, Chloride, and Sulfate Anions. Inorg. Chem. 1995, 34, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousselot, I.; Taviot-Gueho, C.; Leroux, F.; Leone, P.; Palvadeau, P.; Besse, J.-P. Insights on the Structural Chemistry of Hydrocalumite and Hydrotalcite-like Materials: Investigation of the Series Ca2M3+(OH)6Cl•2H2O (M3+: Al3+, Ga3+, Fe3+, and Sc3+) by X-Ray Powder Diffraction. J. Solid State Chem. 2002, 167, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebout, R.; Tichit, D.; Layrac, G.; Barama, A.; Coq, B.; Cota, I.; Rangel, E.R.; Medina, F. New basic catalysts obtained from layered double hydroxides nanocomposites. Solid State Sci. 2010, 12, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas, J.C.; Giraldo, O.H.; Laubernds, K.; Suib, S.L. New Layered Double Hydroxides Containing Intercalated Manganese Oxide Species: Synthesis and Characterization. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 42, 5621–5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risch, A.; Göske, J.; Ecker, M.; Pöllmann, H. ICDD Grant-in-Aid Program; ICDD: Newtown Square, PA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Rapin, J.-P.; Renaudin, G.; Elkaïm, E.; François, M. Structural transition of Friedel’s salt 3CaO•Al2O3•CaCl2•10H2O studied by synchrotron powder diffraction. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pöllmann, H.; Witzke, T.; Kohler, H. Ca4Al2 (OH)12. Neues Jahrb. Mineral. Mon. 1997, 1997, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrer, P. Bestimmung der Größe und der inneren Struktur von Kolloidteilchen mittels Röntgenstrahlen Nachrichten von der Gesellschaft der Wissenschaften zu Göttingen. Math. Phys. Kl. 1918, 26, 98–100. [Google Scholar]
- Rives, V. Study of Layered Double Hydroxides by Thermal Methods. In Layered Double Hydroxides: Present and Future; Rives, V., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 127–152. ISBN 978-1-61209-289-8. [Google Scholar]
- Rives, V. Comment on “Direct Observation of a Metastable Solid Phase of Mg/Al/CO3-Layered Double Hydroxide by Means of High-Temperature in Situ Powder XRD and DTA/TG”1. Inorg. Chem. 1999, 38, 406–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbstein, F.H.; Ron, G.; Weissman, A. The thermal decomposition of potassium permanganate and related substances. Part, I. Chemical aspects. J. Chem. Soc. A 1971, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Moreno, M.J.; Ulibarri, M.A.; Rendon, J.L.; Serna, C.J. IR Characteristics of Hydrotalcite-like Compounds. Phys. Chem. Miner. 1985, 12, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labajos, F.M.; Rives, V.; Ulibarri, M.A. Effect of hydrothermal and thermal treatments on the physicochemical properties of Mg-Al hydrotalcite-like materials. J. Mater. Sci. 1992, 27, 1546–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloprogge, T.; Hickey, L.; Frost, R.L. FT-Raman and FT-IR spectroscopic study of synthetic Mg/Zn/Al-hydrotalcites. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2004, 35, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richardson, M.C.; Braterman, P.S. Infrared Spectra of Oriented and Nonoriented Layered Double Hydroxides in the Range from 4000 to 250 cm−1, with Evidence for Regular Short-Range Order in a Synthetic Magnesium−Aluminum LDH with Mg:Al = 2:1 but Not with Mg:Al = 3:1. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 4209–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, K. Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds—Part A: Theory and Applications in Inorganic Chemistry, 6th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-471-74339-2. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Vilchez, F.; Griffith, W.P. Transition-metal tetra-oxo-complexes and their vibrational spectra. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1972, 13, 1416–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Richter, H. RAMAN-und Ultrarotspektroskopische Untersuchungen an Salzen der Peroxodischwefelsäure. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1962, 315, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blott, S.; Croft, D.J.; Pye, K.; Saye, S.E.; Wilson, H.E. Particle size analysis by laser diffraction. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spéc. Publ. 2004, 232, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitonaki, A.; Petri, B.; Crimi, M.; Mosbæk, H.; Siegrist, R.L.; Bjerg, P.L. In Situ Chemical Oxidation of Contaminated Soil and Groundwater Using Persulfate: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 40, 55–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Lee, I.-L.; Hsu, I.-Y.; Liang, C.-P.; Lin, Y.-L. Persulfate oxidation of trichloroethylene with and without iron activation in porous media. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, T.M.; Criddle, C.S.; Mccarty, P.L. ES Critical Reviews: Transformations of halogenated aliphatic compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1987, 21, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobiszewski, M.; Namieśnik, J. Abiotic degradation of chlorinated ethanes and ethenes in water Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2012, 19, 1994–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Sample | Mg | Ca | Al | Mn | S | Mg/Al | Ca/Al | X/Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MA-MnO4 | 21.20 | 8.04 | 15.03 | 2.93 | 0.92 | |||
| MA-S2O8 | 19.03 | 7.36 | 6.36 | 2.87 | 0.36 | |||
| CA-MnO4 | 13.37 | 4.65 | 8.85 | 1.94 | 0.94 | |||
| CA-S2O8 | 8.29 | 2.89 | 2.05 | 1.93 | 0.30 |
| Sample | a | c’ | c | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MA–MnO4 | 3.03 | 8.7 | 26.1 | 50 |
| MA–S2O8 | 3.02 | 8.8 | 26.4 | 60 |
| CA–MnO4 | 5.73 | 8.6 | 25.8 | 350 |
| CA–S2O8 | 5.75 | 8.7 | 52.0 | 420 |
| Sample | Event | Mass Loss (%) | Temperature Range (°C) | Evolved Gases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MA–MnO4 | I | 11.6 | 25–160 | H2O |
| II | 36.4 | 160–527 | NO2, H2O | |
| III | 1.7 | 527–900 | ||
| Total | 49.7 | 25–900 | ||
| MA–S2O8 | I | 11.6 | 25–218 | H2O |
| II | 29 | 218–536 | SO3, CO2, NO2, H2O | |
| III | 2.7 | 536–900 | ||
| Total | 43.3 | 25–900 | ||
| CA–MnO4 | I | 10.8 | 25–130 | H2O |
| II | 13.8 | 130–300 | H2O | |
| III | 15.4 | 300–560 | NO2 | |
| IV | 6 | 560–900 | ||
| Total | 46 | 25–900 | ||
| CA–S2O8 | I | 20.6 | 25–125 | H2O |
| II | 9.4 | 125–330 | H2O | |
| III | 23 | 330–686 | SO3, NO2, H2O | |
| IV | 1.5 | 686–900 | ||
| Total | 54.5 | 25–900 |
| Sample | Chemical Formula |
|---|---|
| MA–MnO4 | [Mg0.75Al0.26(OH)2](MnO4)0.23(NO3)0.02•0.64H2O |
| MA–S2O8 | [Mg0.74Al0.26(OH)2](S2O8)0.09(NO3)0.07•0.56H2O |
| CA–MnO4 | [Ca0.66Al0.34(OH)2](MnO4)0.32(NO3)0.02•0.73H2O |
| CA–S2O8 | [Ca0.66Al0.34(OH)2](S2O8)0.10(NO3)0.147•1.40H2O |
| Sample | Particle Size (µm) | |
|---|---|---|
| d(0.5) Aggregated | d(0.5) De-Aggregated | |
| MA–MnO4 | 220 | 180 |
| MA–S2O8 | 210 | 80 |
| CA–MnO4 | 170 | 5 |
| CA–S2O8 | 70 | 5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dietmann, K.M.; Linke, T.; Nogal Sánchez, M.d.; Pérez Pavón, J.L.; Rives, V. Layered Double Hydroxides with Intercalated Permanganate and Peroxydisulphate Anions for Oxidative Removal of Chlorinated Organic Solvents Contaminated Water. Minerals 2020, 10, 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10050462
Dietmann KM, Linke T, Nogal Sánchez Md, Pérez Pavón JL, Rives V. Layered Double Hydroxides with Intercalated Permanganate and Peroxydisulphate Anions for Oxidative Removal of Chlorinated Organic Solvents Contaminated Water. Minerals. 2020; 10(5):462. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10050462
Chicago/Turabian StyleDietmann, Karen Maria, Tobias Linke, Miguel del Nogal Sánchez, José Luis Pérez Pavón, and Vicente Rives. 2020. "Layered Double Hydroxides with Intercalated Permanganate and Peroxydisulphate Anions for Oxidative Removal of Chlorinated Organic Solvents Contaminated Water" Minerals 10, no. 5: 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10050462
APA StyleDietmann, K. M., Linke, T., Nogal Sánchez, M. d., Pérez Pavón, J. L., & Rives, V. (2020). Layered Double Hydroxides with Intercalated Permanganate and Peroxydisulphate Anions for Oxidative Removal of Chlorinated Organic Solvents Contaminated Water. Minerals, 10(5), 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10050462






